目录
二、自定义BeanFactoryPostProcessor实现类
三、BeanFactoryPostProcessor执行细节
四、BeanFactoryPostProcessor常用子类
一、定义
官网对BeanFactoryPostProcessor的描述如下:
- Spring IoC容器允许我们自定义BeanFactoryPostProcessor在容器实例化任何bean之前读取bean的定义信息(配置元数据),并修改它,如我们可以把某个bean的scope从singleton改为prototype,也可以把bean的属性值给修改掉,还可以往bean工厂中新增加bean定义等等;
- BeanFactoryPostProcessor可以操作BeanDefinition,但是千万不要进行bean实例化操作,这样做可能会导致过早的bean实例化,违反了容器导致意想不到的副作用。如果bean实例交互是必需的,考虑使用BeanPostProcessor后置处理器;
BeanFactoryPostProcessor是一个函数式接口,其定义如下:
@FunctionalInterface
public interface BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
// 此方法在Bean对象实例化之前执行,可以通过beanFactory可以获取bean的定义信息,然后修改bean的定义信息
void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException;
}BeanFactoryPostProcessor是在Spring容器加载了bean的定义信息之后,在bean实例化之前执行的。
二、自定义BeanFactoryPostProcessor实现类
如果需要自定义BeanFactoryPostProcessor的话,我们只需要实现BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口,并重写postProcessorBeanFactory()方法。下面我们通过一个简单的示例说明自定义BeanFactoryPostProcessor的用法,通过beanFactory获取bean的定义信息,并修改bean的定义信息。
- (一)、编写一个简单的bean
public class Student implements Serializable {
private String id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
public Student() {
System.out.println("Student实例化...");
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"id='" + id + '\'' +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
- (二)、编写BeanFactoryPostProcessor实现类
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.MutablePropertyValues;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.core.Ordered;
/**
* @Description: 自定义BeanFactoryPostProcessor
* @Date: 2021/12/23 11:16
* 说明: BeanFactoryPostProcessor在容器实例化任何bean之前读取bean的定义(配置元数据),并可以修改它
* 可以通过实现Ordered接口指定order属性的值,从而设置BeanFactoryPostProcessor的执行顺序,order属性的值越小,优先级越高
*/
public class MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor01 implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor, Ordered {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("执行MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor01的postProcessBeanFactory()方法");
// 获取工厂当前所有注册的beanNames数组
String[] beanDefinitionNames = beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionNames();
// 循环遍历
for (String beanName : beanDefinitionNames) {
if ("student".equals(beanName)) {
// 根据beanName获取对应的bean定义信息
// 当我们拿到BeanDefinition对象后,我们可以手动修改bean标签中所定义的属性值
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition(beanName);
// 获取对应的属性值
MutablePropertyValues propertyValues = beanDefinition.getPropertyValues();
// 更新属性值
if (propertyValues.contains("name")) {
System.out.println("修改name属性...旧值:" + propertyValues.get("name"));
propertyValues.add("name", "李四");
}
}
}
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return 0;
}
}
public class MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor02 implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor, Ordered {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("执行MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor02的postProcessBeanFactory()方法");
// 获取工厂当前所有注册的beanNames数组
String[] beanDefinitionNames = beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionNames();
// 循环遍历
for (String beanName : beanDefinitionNames) {
if ("student".equals(beanName)) {
// 根据beanName获取对应的bean定义信息
// 当我们拿到BeanDefinition对象后,我们可以手动修改bean标签中所定义的属性值
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition(beanName);
// 获取对应的属性值
MutablePropertyValues propertyValues = beanDefinition.getPropertyValues();
// 更新属性值
if (propertyValues.contains("age")) {
System.out.println("修改age属性...旧值:" + propertyValues.get("age"));
propertyValues.add("age", "20");
}
}
}
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return 1;
}
}
可以实现Ordered接口,指定order属性的值,从而改变各个BeanFactoryPostProcessor执行顺序,order的值越小,BeanFactoryPostProcessor执行的优先级越高。
- (三)、编写spring配置文件,注册自定义的BeanFactoryPostProcessor、bean信息?
<!--自定义BeanFactoryPostProcessor-->
<bean id="student" class="com.wsh.beanfactorypostprocessor.Student">
<property name="id" value="1"/>
<property name="name" value="张三"/>
<property name="age" value="10"/>
</bean>
<bean id="myBeanFactoryPostProcessor01" class="com.wsh.beanfactorypostprocessor.MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor01"/>
<bean id="myBeanFactoryPostProcessor02" class="com.wsh.beanfactorypostprocessor.MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor02"/>- (四)、测试类
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:spring-config.xml");
System.out.println(applicationContext.getBean("student"));
}
}- (五)、运行结果
执行MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor01的postProcessBeanFactory()方法
修改name属性...旧值:TypedStringValue: value [张三], target type [null]
执行MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor02的postProcessBeanFactory()方法
修改age属性...旧值:TypedStringValue: value [10], target type [null]
Student实例化...
Student{id='1', name='李四', age=20}从输出结果,我们可以看出postProcessBeanFactory()方法执行的顺序是在Bean实例化之前,并且通过自定义BeanFactoryPostProcessor把bean的属性给覆盖了。
三、BeanFactoryPostProcessor执行细节
- BeanFactoryPostProcessor的执行时机?
熟悉Spring IOC容器刷新流程的话,应该很容易想到,BeanFactoryPostProcessor的执行时机就是在容器刷新核心方法refresh()方法中的第五步:invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory)方法。
从AbstractApplicationContext#refresh()方法开始,找到invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory)方法:
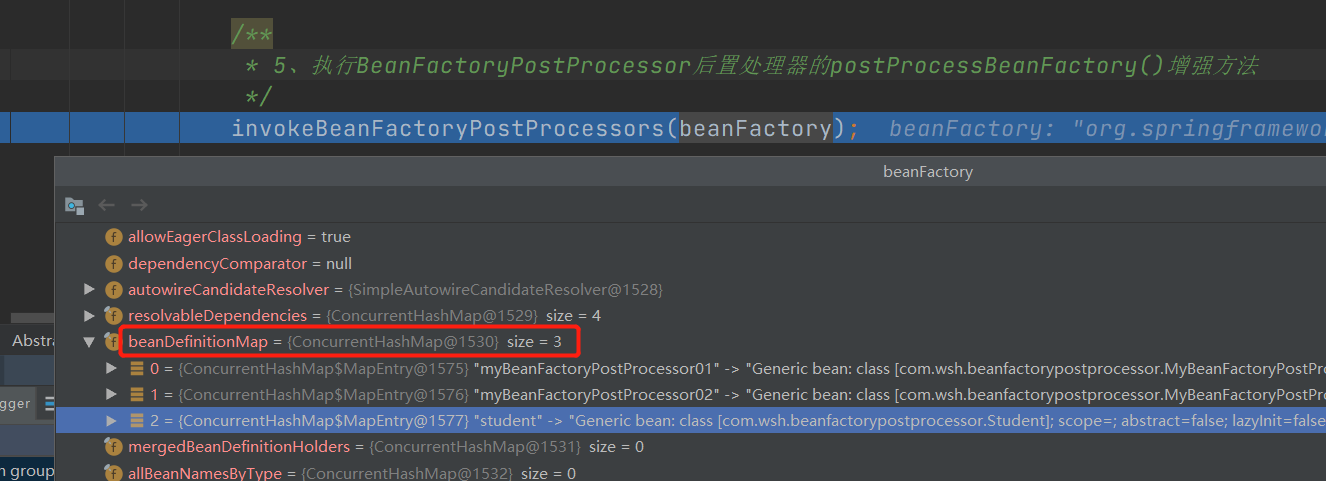
可以看到,执行invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory)方法之前,配置文件中的bean定义信息已经被封装到beanDefinitionMap中了。
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors()方法实现如下:?
// 实例化并调用所有已注册的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// 1.拿到当前应用上下文beanFactoryPostProcessors变量中的值
// 2.实例化并调用所有已注册的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found in the meantime
// (e.g. through an @Bean method registered by ConfigurationClassPostProcessor)
if (beanFactory.getTempClassLoader() == null && beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
}简述一下invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors()的处理流程:
- (1)、首先对BeanFactoryPostProcessor的子类BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor进行处理,从容器找出所有实现BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的Bean,然后按照优先级进行排序后,依次回调BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry()方法;
- (2)、接着处理普通的BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口,同样的,从容器找出所有实现BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的Bean,使用三个不同的集合,分别存放实现了PriorityOrdered接口、实现了Ordered接口、普通的BeanFactoryPostProcessor。接着按照优先级排序后,会执行postProcessBeanFactory()回调;
下面是具体的代码实现:
// org.springframework.context.support.PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate#invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory, java.util.List<org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor>)
public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
// Invoke BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors first, if any.
// 记录已经处理过的BeanFactoryPostProcessor集合,无需重复执行
Set<String> processedBeans = new HashSet<>();
// 对BeanDefinitionRegistry类型的处理
if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) {
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory;
// 存放普通的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> regularPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
// 存放BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor继承了BeanFactoryPostProcessor
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> registryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
// 循环遍历硬编码方式注册的BeanFactoryPostProcessor后置处理器
for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
// 区分普通的BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor,分别放入不同的集合中
if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) {
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor =
(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor;
// 如果是BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的话,直接执行BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法
registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
// BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor);
}
else {
// 普通BeanFactoryPostProcessor
regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor);
}
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
// Separate between BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement
// PriorityOrdered, Ordered, and the rest.
// 记录本次要执行的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
List<BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor> currentRegistryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
// 配置注册的后置处理器
// 1、调用所有实现PriorityOrdered接口的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor实现类
// 找出所有实现BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的Bean
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// 循环遍历,判断是否实现PriorityOrdered接口
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
// 添加到将要执行的集合中,避免重复执行
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
// 按照优先级进行排序
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
// 调用BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry()方法
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// 2、调用所有实现了Ordered接口的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor实现类
// 找出所有实现BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口的类
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// 循环遍历,判断是否实现Ordered接口
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
// 未执行过 && 实现Ordered接口
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
// 添加到将要执行的集合中,避免重复执行
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
// 按照order排序
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
// 调用BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry()方法
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// 3、调用所有剩下的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors
boolean reiterate = true;
while (reiterate) {
reiterate = false;
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
// 未执行过的
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
reiterate = true;
}
}
// 排序
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
// 调用BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry()方法
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
}
// 回调所有BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanFactory方法
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory);
// 回调普通BeanFactoryPostProcessor的postProcessBeanFactory方法
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
else {
// 调用在上下文实例中注册的工厂处理器
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactoryPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
// 从bean工厂中获取到BeanFactoryPostProcessor
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Separate between BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
// 存放实现了PriorityOrdered接口的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
// 存放实现了Ordered接口的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
// 存放其它BeanFactoryPostProcessor
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
// 循环从工厂中获取的BeanFactoryPostProcessor, 分别存入到三个不同的集合中
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
// 针对已经处理过的BeanFactoryPostProcessor,不做任何操作,无需重复执行
if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
// skip - already processed in first phase above
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
// PriorityOrdered接口的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
// Ordered接口的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
// 普通BeanFactoryPostProcessor
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// 1、调用所有实现PriorityOrdered接口的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
// 排序
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// 执行postProcessBeanFactory()回调
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// 2、调用所有实现Ordered接口的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
// 这里会触发BeanFactoryPostProcessor的创建流程
orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
// 排序
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// 执行postProcessBeanFactory()回调
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// 3、调用所有其他BeanFactoryPostProcessor
List<BeanFactoryPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
// 执行postProcessBeanFactory()回调
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Clear cached merged bean definitions since the post-processors might have
// modified the original metadata, e.g. replacing placeholders in values...
// 清除元数据缓存
beanFactory.clearMetadataCache();
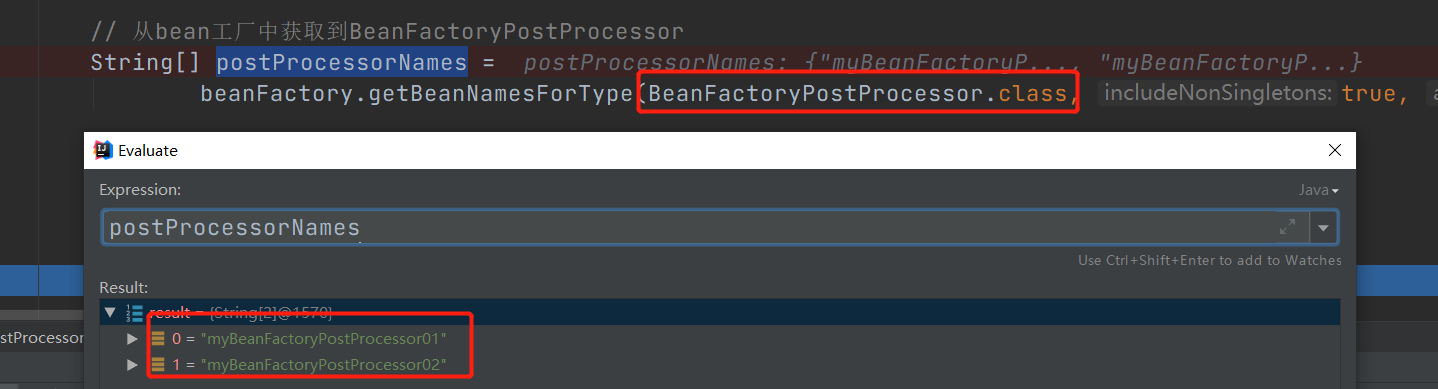
}通过beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false),获取Spring配置文件中定义的所有实现BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口的bean,然后根据优先级进行排序,如下图:
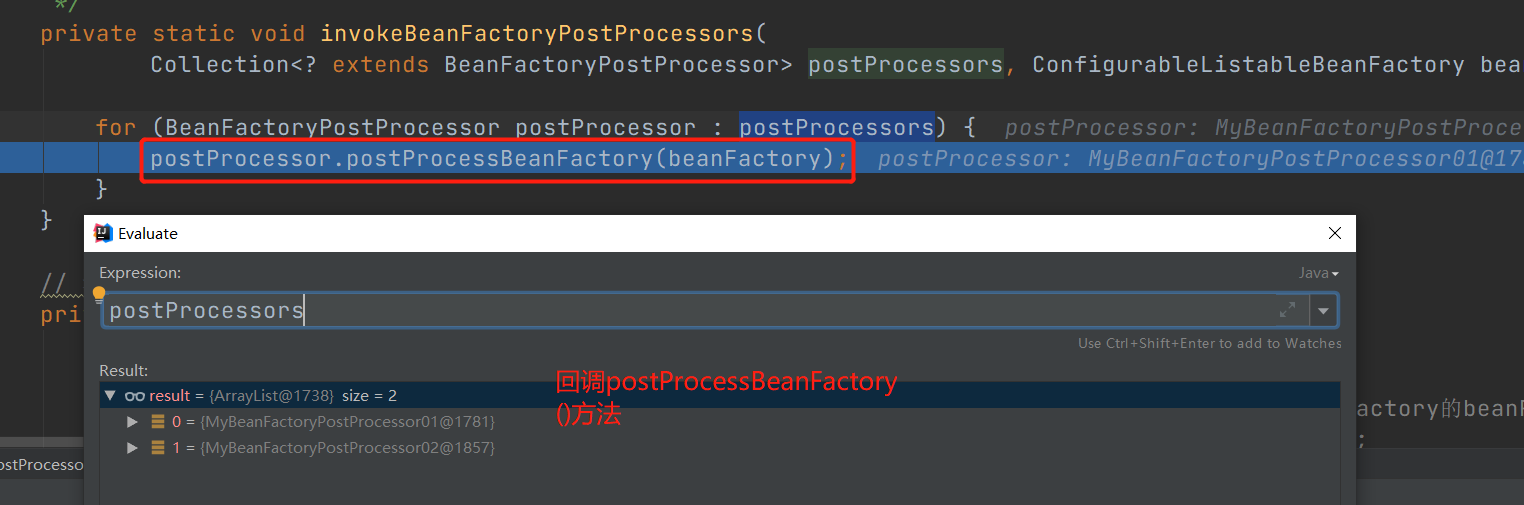
针对每个BeanFactoryPostProcessor,调用postProcessBeanFactory方法:
private static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(
Collection<? extends BeanFactoryPostProcessor> postProcessors, ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {
// 回调postProcessBeanFactory()方法
postProcessor.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
}
}如下图:
以上就是BeanFactoryPostProcessor具体的执行流程。
四、BeanFactoryPostProcessor常用子类
BeanFactoryPostProcessor有几个比较常用的子类,下面简单列举一些:
- BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor:可以注册更多的BeanDefinition,在BeanFactoryPostProcessor调用之前。该接口也只有一个方法postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry()。
- PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer:解析XML配置文件中的${xxx}占位符,将${xxx}替换为指定的properties文件中的值 ;
- ConfigurationClassPostProcessor:解析加了@Configuration的配置类,还会解析@ComponentScan、@ComponentScans注解扫描的包,以及解析@Import等注解;
- .......
BeanFactoryPostProcessor是Spring提供给我们的一个扩展点,通过BeanFactoryPostProcessor,我们可以在bean实例化之前做一些逻辑处理,比如修改一些bean定义里面的属性值等,我们从其作用、自定义实现示例、以及具体的执行流程等方面介绍了BeanFactoryPostProcessor,在实际项目中,我们可以根据具体的场景自定义BeanFactoryPostProcessor。
希望本篇文章对大家有所帮助,也希望大家能指出不对之处。这应该是2021年总结的最后一篇文章啦,最后祝大家2022年新年快乐吧,2022年希望自己能继续坚持学习,每天进步一点点!