文章目录
一、Thymeleaf模板引擎介绍
1、官方定义
Thymeleaf是一个现代的服务器端 Java 模板引擎,适用于 Web 和独立环境。
Thymeleaf 的主要目标是为您的开发工作流程带来优雅的自然模板— HTML 可以在浏览器中正确显示,也可以作为静态原型工作,从而在开发团队中实现更强的协作。
Thymeleaf 具有 Spring Framework 模块、大量与您最喜爱的工具集成,以及插入您自己的功能的能力,是现代 HTML5 JVM Web 开发的理想选择 — 尽管它可以做的还有很多。
2、特点
(1)语法简单且功能强大
(2)学习成本低
(3)SpringMVC集成Thymeleaf模板引擎,非常方便
二、Springboot整合Thymeleaf(以IDEA为例)
(一)添加依赖
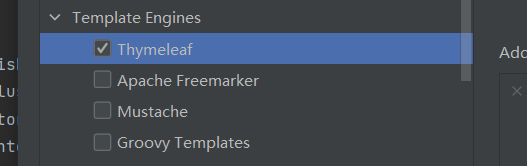
1、使用Spring Initializr 创建Springboot项目 可直接勾选依赖
或者 手动在pom.xml中添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
(二)创建模板文件
1、导入Thymeleaf命名空间
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
2、编写页面代码
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Thymeleaf使用</title>
</head>
<body>
<p>Hello World!</p>
<p th:text="${mess}">Hello World!</p>
</body>
</html>
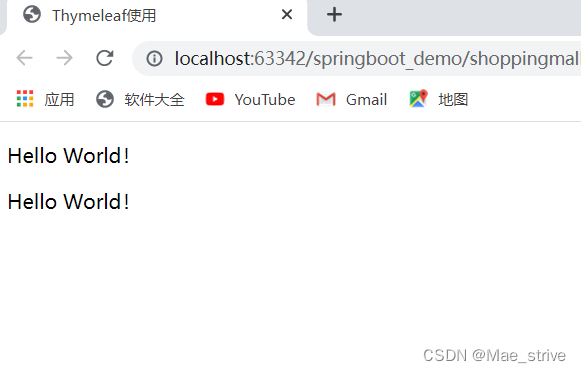
显示内容
3、编写Controller
注意:一定要添加Controller注解
package com.atmae.shoppingmall.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
/**
* @author Mae
*/
@Controller
public class IndexController {
@GetMapping("/test")
public String index(Model model){
model.addAttribute("mess","Mae");
return "index";
}
}
访问 /test
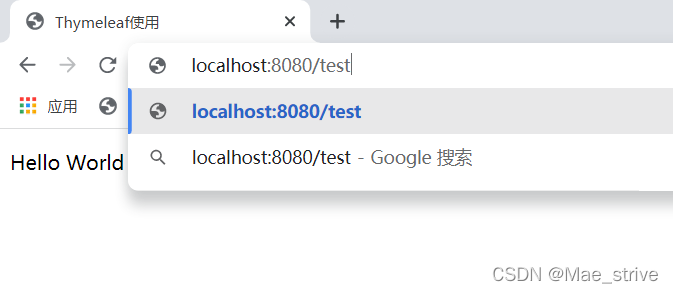
结果:
Mae替换了Hello world
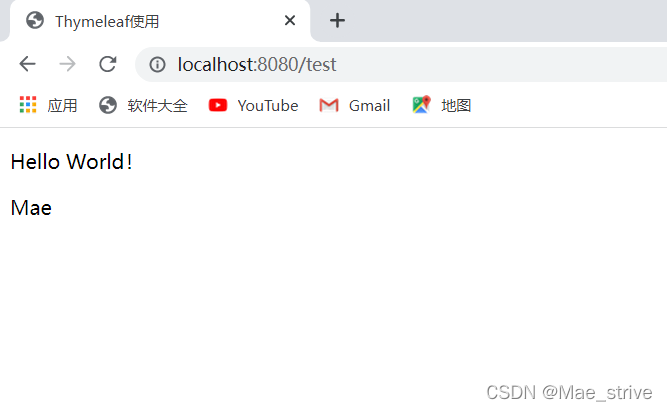
查看网页源代码:p标签中的Mae替换了HelloWorld

三、Thymeleaf属性值的设置
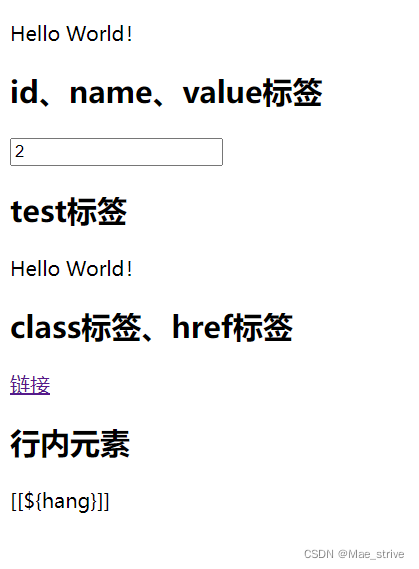
Thymeleaf模板引擎提供了许多标签属性替换HTML5原生属性的值
下面介绍几个常用的:
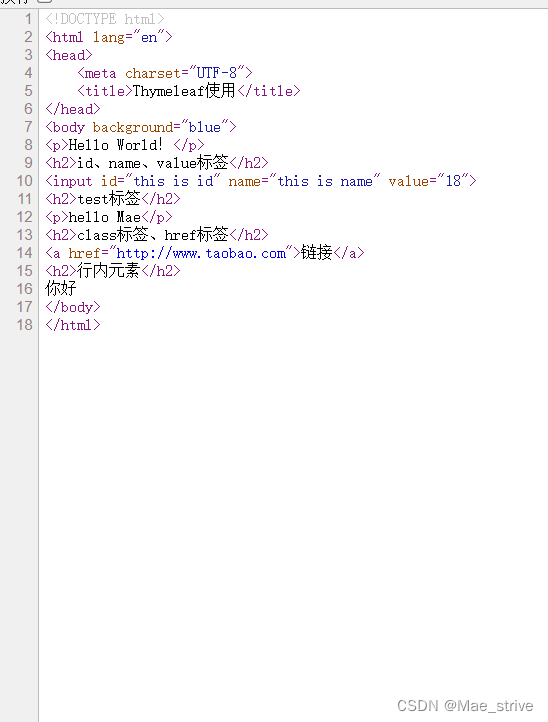
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Thymeleaf使用</title>
</head>
<body th:background="${background}">
<p>Hello World!</p>
<h2>id、name、value标签</h2>
<input id="input" name="input" value="2" th:id="${id}" th:name="${name}" th:value="${value}">
<h2>test标签</h2>
<p th:text="${mess}">Hello World!</p>
<h2>class标签、href标签</h2>
<a th:class="${class0}" th:href="${href}" href="http://www.baidu.com" class="module-label-in-package">链接</a>
<h2>行内元素</h2>
[[${hang}]]
</body>
</html>
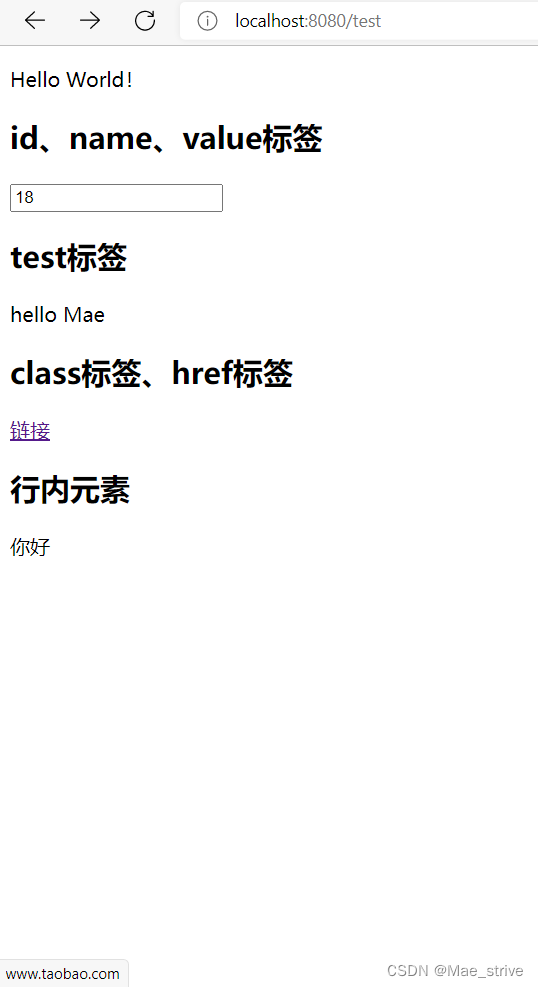
编写Controller测试
package com.atmae.shoppingmall.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.ui.ModelMap;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
/**
* @author Mae
*/
@Controller
public class IndexController {
@GetMapping("/test")
public String index(ModelMap model){
model.put("id","this is id");
model.put("name","this is name");
model.put("value",18);
model.put("class","my_class");
model.put("href","http://www.taobao.com");
return "index";
}
}
结果:
四、thymeleaf语法
(一) 表达式语法
1、变量表达式: ${}
2、选择变量表达式:*{}
3、信息表达式:#{}
4、连接URL表达式:@{}
5、分段表达式:~{}
(二) 字面量
1、字符串:'test'、‘oooo’
2、数组:1.0、1
3、布尔值:true、false
4、NULL值:null
5、字面量标记:sometext、main
(三) 文本运算
1、字符串拼接:+
2、字面量置换:|the name is ${name}|
(四) 算数运算
1、二元运算符:+ 、- 、* 、/ 、%
2、负号:-
(五) 布尔运算
1、二元运算符:and、or
2、非:!、not
(六) 比较运算
1、>、<、>=、<=、==、!=
(七) 条件运算符
1、IF-THEN: (if)?(then)
2、IF-THEN-ELSE: (if)?(then):(else)
3、DEFALUT: (value)?:(defalutvalue)
(八) 无操作
1、_
五、thymeleaf表达式
1、变量表达式: ${}
2、选择变量表达式:*{}
3、信息表达式:#{}
4、连接URL表达式:@{}
5、分段表达式:~{}
注意:这些表达式一般只写在th标签中 否则不会生效
(一) 变量表达式:
变量表达式可以使用内置对象
内置对象:
1、ctx:上下文对象
2、vars:上下文变量
3、locale:上下文语言环境
4、request:Web环境下的HttpServletRequest对象
5、response:Web环境下的HttpServletResponse对象
6、session:Web环境下的HttpSession对象
7、servletContext:Web环境下的HttpContext对象
例:
package com.atmae.shoppingmall.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.ui.ModelMap;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
/**
* @author Mae
*/
@Controller
public class IndexController {
@GetMapping("/test")
public String index(Model model, HttpSession session, HttpServletRequest request){
session.setAttribute("session0","Mae");
request.setAttribute("request0","Strive");
return "index";
}
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Thymeleaf使用</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>内置对象</h2>
<p th:text="${#request.getAttribute('request0')}"></p>
<p th:text="${#session.getAttribute('session0')}"></p>
</body>
</html>

(二)遍历
/**
* @author Mae
*/
@Controller
public class IndexController {
@GetMapping("/test")
public String index(Model model){
List<String> list=new ArrayList<>();
list.add("cooker");
list.add("maoo");
list.add("helo");
list.add("byye");
model.addAttribute("goods",list);
return "index";
}
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Thymeleaf使用</title>
</head>
<body>
<h2>遍历</h2>
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>num</th>
<th>name</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<!--stat.count 用来表示当前数量-->
<tr th:each="good,stat:${goods}">
<td th:text="${stat.count}">+ +</td>
<td th:text="${good}"></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</body>
</html>

(三) URL表达式
/**
* @author Mae
*/
@Controller
public class LoginController {
@GetMapping("/login")
public String login(Model model){
List<String> list=new ArrayList<>();
list.add("cooker");
list.add("maoo");
list.add("helo");
list.add("byye");
model.addAttribute("goods",list);
return "login";
}
}
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Thymeleaf使用</title>
</head>
<body>
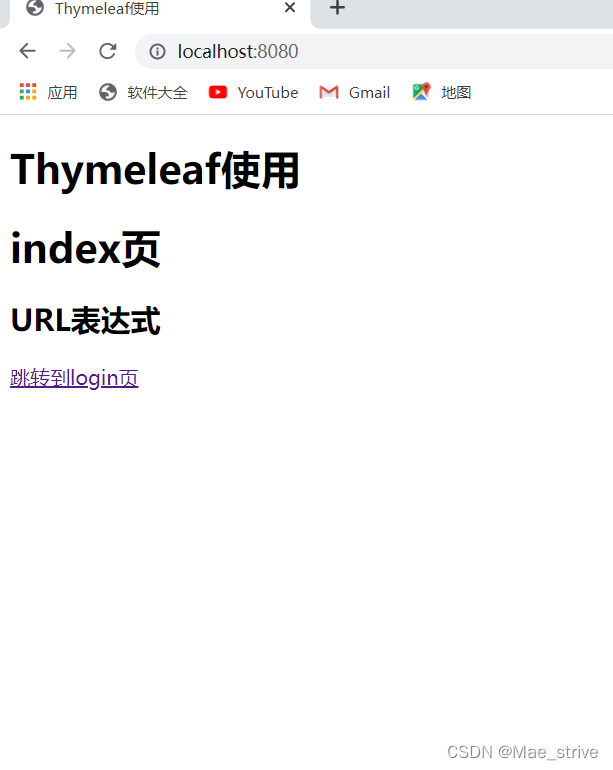
<h1>index页</h1>
<h2>URL表达式</h2>
<a th:href="@{/login}">跳转到login页</a>
</body>
</html>
结果:

六、片段引用
每个页面都有此标题 我们可以将他封装
<h1>Thymeleaf使用</h1>
在common.html中封装此公共代码
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Common</title>
</head>
<body>
<div th:fragment="ttt0">
<h1>Thymeleaf使用</h1>
</div>
</body>
</html>
login 和 index 页面都引用
<div th:replace="common::ttt0"></div>
<div th:include="common::ttt0"></div>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Thymeleaf使用</title>
</head>
<body>
<div th:replace="common::ttt0"></div>
<h1>index页</h1>
<h2>URL表达式</h2>
<a th:href="@{/login}">跳转到login页</a>
</body>
</html>
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Thymeleaf模板使用</title>
</head>
<body>
<div th:include="common::ttt0"></div>
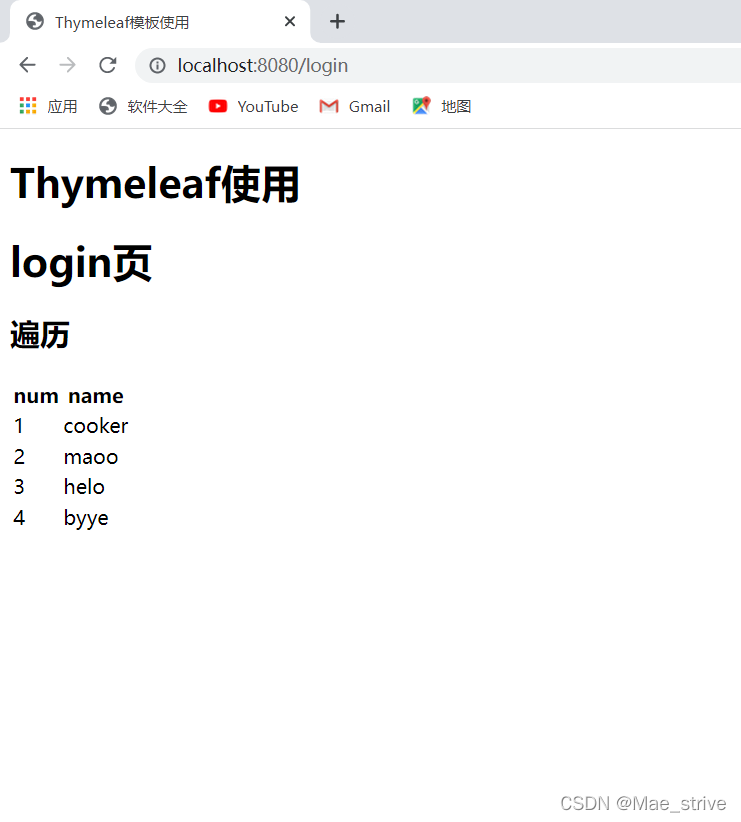
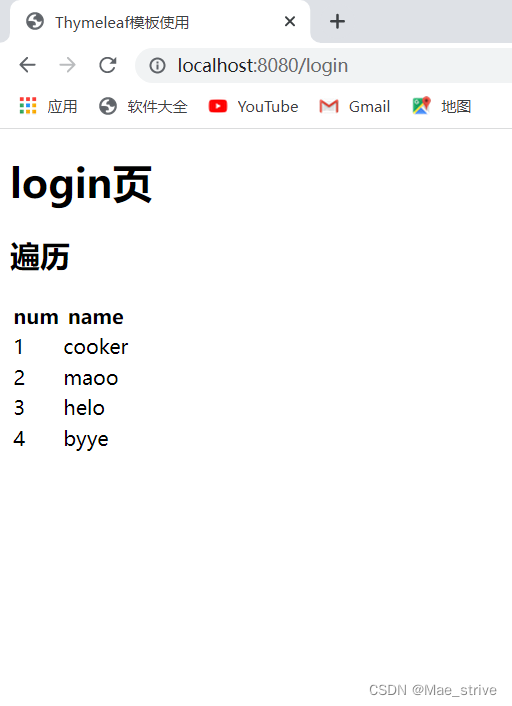
<h1>login页</h1>
<h2>遍历</h2>
<table>
<thead>
<tr>
<th>num</th>
<th>name</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
<tr th:each="good,stat:${goods}">
<td th:text="${stat.count}">+ +</td>
<td th:text="${good}"></td>
</tr>
</tbody>
</table>
</body>
</html>