测试人员与开发人员可能使用的不是同一套环境,Spring支持在不同的环境中进行切换的需求。通过@Profile注解实现。
@Profile的使用案例
在注解装配Bean(五)中的案例中进行修改,配置两个数据库连接池,代码修改如下:
package com.ssm.spring.annotation.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Profile;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.apache.commons.dbcp2.BasicDataSourceFactory;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.util.Properties;
@Component
public class DataSourceBean {
@Bean(name="devDataSource")
@Profile("dev") //使用@Profile注解表明该Bean用于开发
public DataSource getDevDataSource()
{
Properties props = new Properties();
props.setProperty("driver","com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
props.setProperty("url","jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ssm");
props.setProperty("username","root");
props.setProperty("password","123456");
DataSource dataSource = null;
try {
dataSource = BasicDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(props);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return dataSource;
}
@Bean(name="testDataSource")
@Profile("test")//使用@Profile注解表明该Bean用于测试
public DataSource getTestDataSource()
{
Properties props = new Properties();
props.setProperty("driver","com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
props.setProperty("url","jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/profile");
props.setProperty("username","root");
props.setProperty("password","123456");
DataSource dataSource = null;
try {
dataSource = BasicDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(props);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return dataSource;
}
}
其中@Profile("dev")表明该bean用于开发环境(引号内的字段任意取,我这边以开发dev,测试test为例)@Profile("test")表明该bean用于测试环境,开发的数据库名为ssm,测试的数据库名为profile。查询的数据表在创建上是一样的,只是所在的数据库不同。
数据表如下:
ssm中的t_role表:
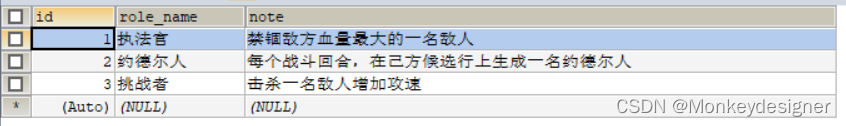
?profile数据库中的t_role表:
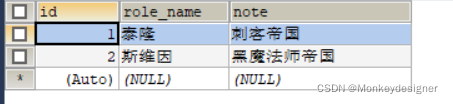
?修改java config代码,代码如下:
package com.ssm.spring.annotation.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.ssm.spring.annotation"})
public class ApplicationConfig {
}由于在配置数据池时没有使用加载properties文件的形式,因此该代码只用于Spring 扫描Bean。
修改测试代码,测试代码如下:
import com.ssm.spring.annotation.config.ApplicationConfig;
import com.ssm.spring.annotation.pojo.Role;
import com.ssm.spring.annotation.service.RoleDataSourceService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.test.context.ActiveProfiles;
import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner;
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = ApplicationConfig.class)
@ActiveProfiles("test")
public class test {
@Autowired
private RoleDataSourceService service = null;
@Test
public void test1()
{
Role role = service.getRole(1L);
System.out.println(role);
}
}该代码使用的spring-test进行测试的,该方式比junit测试更简单。与@Profile注解对应的一个注解是@ActiveProfiles,该注解的配置项表明使用哪种环境进行运行。
注意:如果使用了@Profile注解,而没有使用@ActiveProfiles注解来表明使用哪种环境,不会把对应的Bean加入Ioc容器中,测试代码会报错。
当使用test环境时,上述代码正确查询到profile数据库中id为1的数据:

?当使用dev环境时,上述代码正确查询到ssm数据库中id为1的数据:

?使用Spring的测试方式需要在maven配置环境中导入相应的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>5.3.13</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>