Queue与队列(Java语言)
前言
上篇博客中我们介绍了栈Stack的相关知识,我们知道栈的特点是先进后出的,而这篇博客将介绍队列Queue的相关知识。希望能够对你有所帮助!
Java内置队列
队列对象
在Java中Queue类是一个接口,因此我们不能通过new直接创建对象,而是要通过子类创建。
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<Integer> queue =new LinkedList<>();
}
队列方法
队列常用的基本有6种,其中3个为一组。
| 错误处理 | 抛出异常 | 返回特殊值 |
|---|---|---|
| 入队列 | add(e) | offer(e) |
| 出队列 | remove() | poll() |
| 队首元素 | element() | peek() |
我们以方法offer(e),poll(),peek()为例
offer(e)方法
形式:boolean offer(E e);
解释:在队列中插入一个元素e
例子:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<Integer> queue =new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(1);
queue.offer(2);
queue.offer(3);
queue.offer(4);
}
poll()方法
形式:E poll();
解释:移除队首的元素。
例子:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<Integer> queue =new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(1);
queue.offer(2);
queue.offer(3);
queue.offer(4);
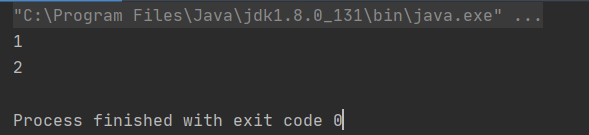
System.out.println(queue.poll());
System.out.println(queue.poll());
}
结果:
peek()方法
形式:E peek();
解释:返回队首元素,但不移除。
例子:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<Integer> queue =new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(1);
queue.offer(2);
queue.offer(3);
queue.offer(4);
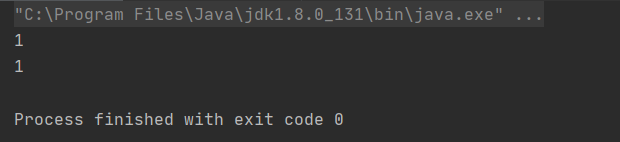
System.out.println(queue.peek());
System.out.println(queue.peek());
}
结果:
相对应的方法add(),remove()方法,element()方法也是类似的效果。那么有什么区别呢?
方法的区别
相对应方法的区别只是在错误的处理上不一样。
offer()方法和add()方法
一些队列有大小的限制,因此如果想在一个满的队列中加入一个新的元素,多出的元素就会被拒绝。add()方法的处理是抛出一个uncheked的异常,而offer()方法不会抛出异常,只是得到offer()方法返回的false
poll()方法和remove()方法
remove()方法和poll()方法都是从队列中删除第一个元素。同样的,remove()方法在遇到队列为null时,会抛出异常,而poll()方法只会返回null。
peek()方法和element()方法
element()和peek()用于在队列的头部查询元素。与remove()方法类似,在队列为空时,element()抛出一个异常,而peek()返回null。
Java内置双端队列
在Java中除了普通的队列还有双端队列,和普通的队列的区别就在于双端队列能够两端进两端出,因此简单介绍一下。
双端队列对象
在Java中Deque类是一个接口,因此我们同样不能通过new直接创建对象,而是要通过子类创建。
public static void main(String[] args) {
Deque<Integer> deque =new LinkedList<>();
}
双端队列方法
双端队列常用方法和普通队列方法类似,我们就简单介绍一下,不作为重点。
| 头部/尾部 | 队首 | 队首 | 队尾 | 队尾 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 错误处理 | 抛出异常 | 返回特殊值 | 抛出异常 | 返回特殊值 |
| 入队列 | addFirst(e) | offerFirst(e) | addLast(e) | offerLast(e) |
| 出队列 | removeFirst() | pollFirst() | removeLast() | pollLast() |
| 获取元素 | getFirst() | peekFirst() | getLast() | peekLast() |
实现队列
为了能够更好的学习队列,我们通过代码自己实现队列。
节点
与栈不同,栈我们可以通过数组头插法就可以实现栈的增删(时间复杂度为O(1)),但是队列是先进先出,我们通过链表的首尾节点才可以完成增删(时间复杂度为O(1))。
class Node {
public int val;
public Node next;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
成员变量和构造方法
public class MyQueue {
public Node head;
public Node last;
public MyQueue(){
}
}
队列可以用单链表实现,但是为了时间复杂度为O(1)需要用到首尾节点,构造方法可以省略不写。
offer()方法
public void offer(int val) {
Node node = new Node(val);
if (head == null) {
head = node;
last = node;
} else {
last.next = node;
last = last.next;
}
}
采用尾插法的方法,如果head节点为null,那么让head和last都为node节点,否则,node节点接到last节点后,并且last往后移动。
isEmpty()方法
public boolean isEmpty() {
return this.head == null;
}
如果head为null返回true,如果head不为null,返回false。
poll()方法
public int poll() {
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列为null");
}
int oldVal = head.val;
this.head = head.next;
return oldVal;
}
如果队列为null,则抛出异常,否则用oldVal存储head的val值,head往后移动,并返回oldVal。
peek()方法
public int peek(){
if (isEmpty()) {
throw new RuntimeException("队列为null");
}
return head.val;
}
与poll()方法类似,不同在于不要移动head节点。
好了,队列的相关知识就介绍到这里,数据结构这方面的知识注重理解,死记硬背的效果不明显,多刷题,勤动手是提高水平的不二选择,希望这篇博客能够对你有所帮助,如果有问题或者建议,欢迎私信和评论!谢谢各位。