(1)分析
【1】在某些场景下我们希望在Service业务逻辑层获取到当前的HttpServletRequest对象,一个简单直接的处理办法是HttpServletRequest对象通过方法参数传递到下一层,但是这种办法并不灵活,我们需要一种更为通用和灵活的方式。
【2】对于这种需要在整个线程内使用的对象,我们很容易想到借助于ThreadLocal对象,是的我们可以使用该组件。然后再借助于RequestListener监听器,通过实现该接口在请求进入时将当前的HttpServletRequest添加到特定的ThreadLocal容器中,然后再后面的业务层中就可以直接在当前特定的ThreadLocal容器中获取HttpServletRequest对象。
【3】上面所描述的功能我们可以通过以下几种方式去实现
利用ServletRequestListener实现
利用Filter实现
利用拦截器实现
【4】对于上面所描述的功能,需要特别注意的一点是只能在一个线程中去实现该功能。在很多的场景下,在接收到请求之后,我们会通过异步子线程的方式去分担任务处理以此提高处理效率。那么如果在异步子线程中去获取ThreadLocal中的对象又会存在问题了,需要我们特别注意。
(2)常见的实现方式
下面几种实现原理都是一样的,使用一个ThreadLocal存储当前HttpServletRequest请求对象,然后后面在service或者dao层直接通过该静态ThreadLocal对象get()获取即可。
【1】利用ServletRequestListener实现
public class RequestHolder implements ServletRequestListener {
//存储HttpServletRequest的线程容器
private static ThreadLocal<HttpServletRequest> httpServletRequestHolder =
new ThreadLocal<HttpServletRequest>();
@Override
public void requestInitialized(ServletRequestEvent requestEvent) {
// 绑定到当前线程
HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest) requestEvent.getServletRequest();
httpServletRequestHolder.set(request);
}
@Override
public void requestDestroyed(ServletRequestEvent requestEvent) {
//移除本次请求对象
httpServletRequestHolder.remove();
}
public static HttpServletRequest getHttpServletRequest() {
return httpServletRequestHolder.get();
}
}
【2】利用Filter实现
public class RequestHolder implements Filter {
//存储HttpServletRequest的线程容器
private static ThreadLocal<HttpServletRequest> httpServletRequestHolder =
new ThreadLocal<HttpServletRequest>();
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
}
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest request, ServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException {
// 绑定到当前线程
httpServletRequestHolder.set((HttpServletRequest) request);
try {
chain.doFilter(request, response);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw e;
} finally {
//移除本次请求对象
httpServletRequestHolder.remove();
}
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
}
public static HttpServletRequest getHttpServletRequest() {
return httpServletRequestHolder.get();
}
}
【3】利用拦截器实现
public class RequestHolder extends HandlerInterceptorAdapter {
//存储HttpServletRequest的线程容器
private static ThreadLocal<HttpServletRequest> httpServletRequestHolder =
new ThreadLocal<HttpServletRequest>();
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler)
throws Exception {
// 绑定到当前线程
httpServletRequestHolder.set(request);
return true;
}
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
Object handler, Exception ex)
throws Exception {
//移除本次请求对象
httpServletRequestHolder.remove();
}
public static HttpServletRequest getHttpServletRequest() {
return httpServletRequestHolder.get();
}
}
(3)RequestContextHolder原理分析
【1】RequestContextHolder类分析
public abstract class RequestContextHolder {
//存储了当前线程的RequestAttributes对象容器
private static final ThreadLocal<RequestAttributes> requestAttributesHolder = new NamedThreadLocal("Request attributes");
//存储科可继承父线程的RequestAttributes对象容器
private static final ThreadLocal<RequestAttributes> inheritableRequestAttributesHolder = new NamedInheritableThreadLocal("Request context");
//清理上次线程资源
public static void resetRequestAttributes() {
requestAttributesHolder.remove();
inheritableRequestAttributesHolder.remove();
}
//处理当前请求对象,赋值到容器存储中
public static void setRequestAttributes(@Nullable RequestAttributes attributes, boolean inheritable) {
if (attributes == null) {
resetRequestAttributes();
} else if (inheritable) {
//是否可继承父线程请求对象
inheritableRequestAttributesHolder.set(attributes);
requestAttributesHolder.remove();
} else {
requestAttributesHolder.set(attributes);
inheritableRequestAttributesHolder.remove();
}
}
//尝试获取当前请求对象属性
@Nullable
public static RequestAttributes getRequestAttributes() {
RequestAttributes attributes = (RequestAttributes)requestAttributesHolder.get();
if (attributes == null) {
attributes = (RequestAttributes)inheritableRequestAttributesHolder.get();
}
return attributes;
}
//获取当前请求对象属性
public static RequestAttributes currentRequestAttributes() throws IllegalStateException {
RequestAttributes attributes = getRequestAttributes();
if (attributes == null) {
if (jsfPresent) {
attributes = RequestContextHolder.FacesRequestAttributesFactory.getFacesRequestAttributes();
}
//如果不是HTTP请求则可能抛出以下错误
if (attributes == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No thread-bound request found: Are you referring to request attributes outside of an actual web request, or processing a request outside of the originally receiving thread? If you are actually operating within a web request and still receive this message, your code is probably running outside of DispatcherServlet: In this case, use RequestContextListener or RequestContextFilter to expose the current request.");
}
}
return attributes;
}
}
【2】org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet#processRequest核心处理类分析。
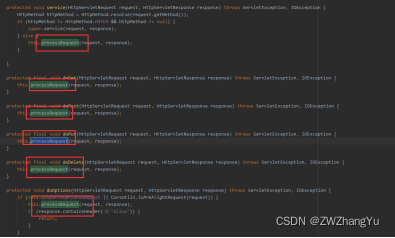
processRequest方法在每次请求时都会被调用执行。如上图所示各个请求类型都会去调用该方法。
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException {
//获取RequestContextHolder当前请求对象,可能为空
RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
//对HttpServletRequest进行包装,包装成ServletRequestAttributes对象
ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = this.buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes);
WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request);
asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new FrameworkServlet.RequestBindingInterceptor());
//初始化本次请求对象,这里主要就是更新当前RequestContextHolder存储的线程请求对象
this.initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes);
try {
this.doService(request, response);
}
}
【3】org.springframework.web.servlet.FrameworkServlet#initContextHolders。调用RequestContextHolder.setRequestAttributes()方法,把requestAttributes对象放入。this.threadContextInheritable默认是false。
即把HttpServletRequest的封装对象ServletRequestAttributes与当前线程绑定。
private void initContextHolders(HttpServletRequest request, @Nullable LocaleContext localeContext, @Nullable RequestAttributes requestAttributes) {
if (localeContext != null) {
LocaleContextHolder.setLocaleContext(localeContext, this.threadContextInheritable);
}
if (requestAttributes != null) {
RequestContextHolder.setRequestAttributes(requestAttributes, this.threadContextInheritable);
}
}
(4)异步子线程应用,继承父线程请求对象
如果此时我们在Service层方法中添加了 @Async注解,进行异步处理。结果如下图所示,无法获取请求对象抛出空指针异常
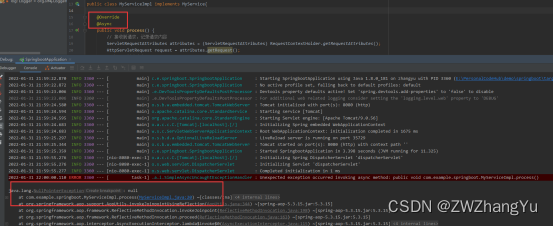
【1】方式一:手动在父线程设置可继承属性,子线程复用父线程请求对象。 RequestContextHolder.setRequestAttributes(RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes(),true);
设置可继承父请求属性。
@Autowired
private MyService myService;
@GetMapping("/get")
public String get(){
RequestContextHolder.setRequestAttributes(RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes(),true);
myService.process();
return "OK";
}
【2】上述方式相对来说需要在每次异步操作时进行手动设置不是很方便,而对于一般的异步处理都是通过线程池分配子线程进行处理的,所以我们也可以通过配置线程池的方式来完成该功能需求。
/**
* 线程处理器,在分配线程时将父线程的RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes();
* 传递给子线程,注意这里的可能会出现一个异常,比如当前请求不是HTTP请求,即分配一个无HTTP参与的任务,
* 比如MQ任务,一般的计算任务等等,但是不会影响任务的执行
* @author zhangyu
* @date 2022/1/27 14:48
**/
public class ContextAwarePoolExecutor extends ThreadPoolTaskExecutor {
@Override
public <T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task) {
RequestAttributes requestAttributes=null;
try{
requestAttributes = RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes();
}catch (IllegalStateException e){
}
return super.submit(new ContextAwareCallable(task,requestAttributes ));
}
@Override
public <T> ListenableFuture<T> submitListenable(Callable<T> task) {
RequestAttributes requestAttributes=null;
try{
requestAttributes = RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes();
}catch (IllegalStateException e) {
}
return super.submitListenable(new ContextAwareCallable(task,requestAttributes));
}
}
/**
* 线程处理
* @author zhangyu
* @date 2022/1/27 14:48
**/
public class ContextAwareCallable<T> implements Callable<T> {
private Callable<T> task;
private RequestAttributes context;
public ContextAwareCallable(Callable<T> task, RequestAttributes context) {
this.task = task;
this.context = context;
}
@Override
public T call() throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
RequestContextHolder.setRequestAttributes(context);
}
try {
return task.call();
} finally {
RequestContextHolder.resetRequestAttributes();
}
}
}
配置线程池
/**
* 线程池配置、启用异步
*
*
*/
@EnableAsync(proxyTargetClass = true)
@Configuration
public class AsycTaskExecutorConfig {
@Bean
public TaskExecutor taskExecutor() {
//自定义线程池对象
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor taskExecutor = new ContextAwarePoolExecutor();
taskExecutor.setCorePoolSize(50);
taskExecutor.setMaxPoolSize(100);
return taskExecutor;
}
}
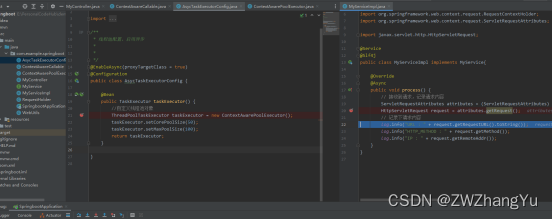
经过测试可以发现可以在子线程中正常获取HTTP请求信息