一、Spring框架概述
Spring是轻量级的开源的Java EE框架,可以解决企业应用开发的复杂性。
Spring有两个核心部分
- IOC:控制反转,把创建对象过程交给Spring进行管理。
- Aop:面向切面,不修改源代码进行功能增强。
Spring的特点如下:
- 方便解耦。简化开发
- Aop编程支持
- 方便程序测试
- 方便和其他框架进行整合
- 方便进行事务操作
- 降低API开发难度
二、入门案例
第一步,下载Spring5
- 浏览器键入spring.io进入spring官网

- GA表示是稳定版本,SNAPSHOT表示快照

- 点击Github图标,进去后下翻找到Access to Binaries,点击链接进入

- 进入后下翻找到DownLoading a Distribution,进入链接




第二步 导入Spring5相关jar包
Spring5的核心容器如下,因此需要导入这四个包
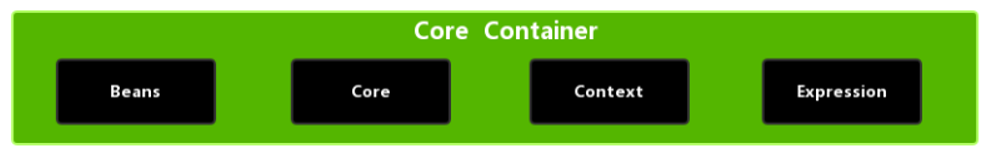
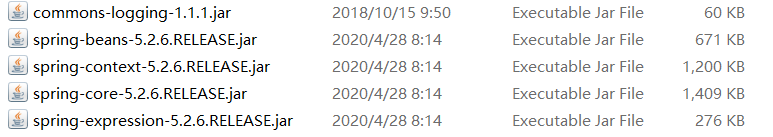
commons-logging是日志包,不添加会报错。
在Java工程下建一个目录lib,将这些jar包复制进去。
左上角File —> Project structure—>Moudle


第三步,创建普通类
package com.atguigu.spring5;
public class User {
public void add(){
System.out.println("添加项");
}
}
第四步,创建Spring配置文件,在配置文件中配置创建的对象
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="user" class="com.atguigu.spring5.User"></bean>
</beans>
第五步,编写测试案例
package com.atguigu.test;
import com.atguigu.spring5.User;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class TestSpring5 {
@Test
public void test(){
// 1.加载Spring配置文件
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean1.xml");
// 2.获取配置创建的对象
User user = context.getBean("user", User.class);
System.out.println(user);
user.add();
}
}
三、IOC容器
3.1 IOC底层原理
IOC(Inversion of Control),即控制反转,将对象创建和对象之间的调用过程,交由Spring进行管理,目的是使代码耦合度降低。
IOC底层原理由三部分实现:
- xml解析
- 工厂模式
- 反射
IOC如何降低耦合度示例:
通常,若一个类要使用另一个类的方法,需要通过new来创建该类的对象,然后通过该对象来调用方法:

但这样做代码耦合度太高了,我们考虑用工厂模式来降低耦合度,即创建一个工厂类,将创建对象通过工厂类的一个方法来实现:

工厂模式虽然能降低一定的耦合,但并不是最优的方式,我们考虑用IOC来做:

这样就通过修改配置文件的内容,即可达到想要的效果,大大降低了代码之间的耦合。
IOC思想基于IOC容器完成,IOC容器底层就是对象工厂。
Spring提供IOC容器有两种实现方式(实际是两个接口):
- BeanFactory接口:IOC容器基本实现,是Spring内部的使用接口,不提供开发人员进行使用。
- ApplicationContext接口:是BeanFactory接口的子接口,提供了更多更强大的功能,一般由开发人员进行使用。
两个接口使用的不同:
- BeanFactory接口在加载配置文件时候不会创建对象,在获取对象使用的时候才去创建对象。
- ApplicationContext接口在加载配置文件时就会将配置文件对象进行创建。
看起来使用BeanFactory接口更为合理,因为在获取对象时候才会创建对象,因此节省了一部分空间。但实际开发时,当服务器启动时就会加载配置文件,此时用ApplicationContext接口会一并创建配置文件中的对象,节省时间。
3.2 IOC操作Bean管理
什么是Bean管理?
Bean管理指的是两个操作
- Spring创建对象
- Spring注入属性
Bean管理操作有两种方式:
- 基于xml配置文件方式实现
- 基于注解方式实现
3.2.1 基于xml配置文件方式实现
1.1 基于xml方式创建对象
在spring配置文件中,使用bean标签,标签里面添加对应属性,就可以实现对象的创建。
在bean标签中常用的属性:
- id属性:唯一标识。
- class属性:类全路径(包类路径)
需要注意的是,创建对象的时候,默认执行无参构造方法来完成对象创建。
<bean id="book" class="com.atguigu.bean.Book">
1.2 基于xml方式注入属性
DI:依赖注入,就是注入属性。
set方法注入
第一步 创建类,定义属性和对应的set方法
package com.atguigu.spring5;
public class Book {
private String bname;
private String bauthor;
public void setBname(String bname) {
this.bname = bname;
}
public void setBauthor(String bauthor) {
this.bauthor = bauthor;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Book{" +
"bname='" + bname + '\'' +
", bauthor='" + bauthor + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
第二步 在spring配置文件配置对象创建,配置属性注入:
<bean id="book" class="com.atguigu.spring5.Book">
<!-- 使用property完成属性注入
name:类里面属性名称
value:向属性注入的值
-->
<property name="bname" value="代码随想录"></property>
<property name="bauthor" value="孙秀洋"></property>
</bean>
使用有参构造进行注入
第一步 创建类,定义属性,创建属性对应的有参构造方法
package com.atguigu.spring5;
public class Book {
private String bname;
private String bauthor;
public Book(String bname, String bauthor) {
this.bname = bname;
this.bauthor = bauthor;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Book{" +
"bname='" + bname + '\'' +
", bauthor='" + bauthor + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
第二步 在spring配置文件中进行配置
<!-- 有参构造器 -->
<bean id="book1" class="com.atguigu.spring5.Book">
<constructor-arg name="bname" value="计算机网络"></constructor-arg>
<constructor-arg name="bauthor" value="自顶向下"></constructor-arg>
<!-- 索引 不推荐使用 可读性不高 -->
<!-- <constructor-arg index="0" value="计算机网络"></constructor-arg> -->
</bean>
p名称空间注入
使用p名称空间注入,可以简化基于xml配置方式。
第一步 添加p名称空间在配置文件中(xmlns:p)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
第二步 进行属性注入,在bean标签中进行操作
<!-- p 名称空间引入 要在beans中加入 xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p" -->
<bean id="book2" class="com.atguigu.spring5.Book" p:bauthor="Kevin Wayne" p:bname="算法第四版"></bean>
1.3 xml注入其他属性
字面量
(1)null值
<property name="bauthor">
<null/>
</property>
(2)属性值包含特殊符号
<!-- 属性值包含特殊符号
1.使用CDATA进行环绕 <![CDATA[]]>
2.对<>进行转义:< >
-->
<property name="bname">
<value><![CDATA[<<南京>>]]></value>
</property>
注入属性-外部bean
(1)创建两个类service类和dao类
(2)在service中调用dao的方法
package com.atguigu.dao;
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao{
@Override
public void update() {
System.out.println("UserDao里的方法");
}
}
package com.atguigu.service;
import com.atguigu.dao.UserDao;
public class UserService {
private UserDao userDao;
public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
public void add(){
System.out.println("Service的add方法");
userDao.update();
}
}
(3)在spring配置文件中进行配置
<bean id="userService" class="com.atguigu.service.UserService">
<!-- 注入UserDao对象
name属性:类里面的属性名称
ref属性:创建userDao对象bean标签的id值
-->
<property name="userDao" ref="userDaoImpl"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="userDaoImpl" class="com.atguigu.dao.UserDaoImpl"></bean>
注入属性-内部bean
(1)一对多关系:部门和员工
一个部门对应多个员工,而一个员工属于一个部门
(2)在实体类之间表示一对多关系,员工表示所属部门,使用对象类型属性进行表示
package com.atguigu.spring5;
public class Employee {
private String ename;
private String gender;
private Department department;
public void setDepartment(Department department) {
this.department = department;
}
public void setEname(String ename) {
this.ename = ename;
}
public void setGender(String gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee{" +
"ename='" + ename + '\'' +
", gender='" + gender + '\'' +
", department=" + department +
'}';
}
}
package com.atguigu.spring5;
public class Department {
private String dname;
public void setDname(String dname) {
this.dname = dname;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Department{" +
"dname='" + dname + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
(3)在 spring 配置文件中进行配置
<bean id="employee" class="com.atguigu.spring5.Employee">
<!-- 设置两个普通属性 -->
<property name="ename">
<value>lucy</value>
</property>
<property name="gender">
<value>女</value>
</property>
<!-- 设置对象类型属性 -->
<property name="department">
<bean id="department" class="com.atguigu.spring5.Department">
<property name="dname" value="财务部"></property>
</bean>
</property>
</bean>
注入属性-级联赋值
(1)第一种写法
<bean id="emp" class="com.atguigu.spring5.Employee">
<property name="ename" value="Tim"></property>
<property name="gender" value="男"></property>
<!-- 级联赋值 -->
<property name="department" ref="dept"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="dept" class="com.atguigu.spring5.Department">
<property name="dname" value="安保部"></property>
</bean>
(2)第二种写法
package com.atguigu.spring5;
public class Employee {
private String ename;
private String gender;
private Department department;
public void setDepartment(Department department) {
this.department = department;
}
public Department getDepartment() {
return department;
}
public void setEname(String ename) {
this.ename = ename;
}
public void setGender(String gender) {
this.gender = gender;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee{" +
"ename='" + ename + '\'' +
", gender='" + gender + '\'' +
", department=" + department +
'}';
}
}
<bean id="dept" class="com.atguigu.spring5.Department">
<property name="dname" value="安保部"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="emp1" class="com.atguigu.spring5.Employee">
<property name="ename" value="James"></property>
<property name="gender" value="男"></property>
<property name="department" ref="dept"></property>
<!-- 必须在Employee类中写getDepartment方法-->
<property name="department.dname" value="技术部"></property>
</bean>
需要注意的是,在第二种级联方式里,最后一个property属性中,name属性的值是department.dname,而dname是Department对象的属性,想要对该属性进行修改,就必须得到Department对象的一个引用,因此要在Employee类中设置getDepartment()方法。
xml注入集合属性
(1)注入数组类型属性
(2)注入List集合类型属性
(3)注入Map集合类型属性
(4)注入Set集合类型属性
package com.atguigu.spring5;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
public class Student {
private String[] course;
private List<String> list;
private Map<String,String> maps;
private Set<String> set;
public void setCourse(String[] course) {
this.course = course;
}
public void setList(List<String> list) {
this.list = list;
}
public void setMaps(Map<String, String> maps) {
this.maps = maps;
}
public void setSet(Set<String> set) {
this.set = set;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"course=" + Arrays.toString(course) +
", list=" + list +
", maps=" + maps +
", set=" + set +
'}';
}
}
<bean id="student" class="com.atguigu.spring5.Student">
<!-- 数组类型引入 -->
<property name="course">
<array>
<value>Java SE</value>
<value>计算机网络</value>
<value>Java EE</value>
</array>
</property>
<!-- list类型引入 -->
<property name="list">
<list>
<value>安东尼·戴维斯</value>
<value>勒布朗·詹姆斯</value>
</list>
</property>
<!-- map类型引入 -->
<property name="maps">
<map>
<entry key="死神" value="杜兰特"></entry>
<entry key="萌神" value="库里"></entry>
</map>
</property>
<!-- set类型引入 -->
<property name="set">
<set>
<value>恩比德</value>
<value>唐斯</value>
</set>
</property>
</bean>
在集合里面设置对象类型值
第一步 新建Course类,在Student类中新增Course类的List集合:courseList属性。
package com.atguigu.spring5;
public class Course {
private String cname;
public void setCname(String cname) {
this.cname = cname;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Course{" +
"cname='" + cname + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
public class Student{
private List<Course> courseList;
public void setCourseList(List<Course> courseList) {
this.courseList = courseList;
}
}
第二步 在spring配置文件进行配置
<bean id="student" class="com.atguigu.spring5.Student">
<property name="courseList">
<list>
<ref bean="course1"></ref>
<ref bean="course2"></ref>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="course1" class="com.atguigu.spring5.Course">
<property name="cname" value="Spring5框架"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="course2" class="com.atguigu.spring5.Course">
<property name="cname" value="SpringMVC"></property>
</bean>
将集合注入部分提取出来
第一步 在spring配置文件中引入名称空间util
xmlns:util=“http://www.springframework.org/schema/util”
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd">
第二步 使用util标签完成list集合注入提取
<!--提取list集合类型属性注入-->
<util:list id="bookList">
<value>Spring</value>
<value>SpringMVC</value>
<value>MyBatis</value>
</util:list>
<!-- 提取list集合类型属性注入使用 -->
<bean id="book" class="com.atguigu.spring5.Book">
<property name="bookList" ref="bookList"></property>
</bean>
1.4 FactoryBean
Spring有两种类型bean,一种普通bean,另一种就是工厂bean(Factory Bean)。
普通Bean:在配置文件中定义的bean类型就是返回类型。
工厂Bean:在配置文件定义的bean类型可以和返回类型不一样。
(1)第一步,创建类,让该类作为工厂bean,实现接口FactoryBean
(2)第二步,实现接口里面的方法,在实现的方法中定义返回的bean类型
package com.atguigu.spring5;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.FactoryBean;
/**
* @Description: TestFactoryBean
* @Author 月上叁竿
* @Date: 2022/1/21 22:37
* @Version: 1.0
*/
public class TestFactoryBean implements FactoryBean<Course> {
@Override
public Course getObject() throws Exception {
Course course = new Course();
course.setCname("数据结构");
return course;
}
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
return null;
}
@Override
public boolean isSingleton() {
return FactoryBean.super.isSingleton();
}
}
<bean id="test" class="com.atguigu.spring5.TestFactoryBean"></bean>
@Test
public void testFactoryBean(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean2.xml");
Course course = context.getBean("test", Course.class);
System.out.println(course);
}
1.5 bean的作用域
在Spring中,默认情况下,bean是单实例对象:
@Test
public void testFactoryBean(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean2.xml");
Course course1 = context.getBean("test", Course.class);
Course course2 = context.getBean("test", Course.class);
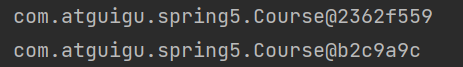
System.out.println(course1); // com.atguigu.spring5.Course@2362f559
System.out.println(course2); // com.atguigu.spring5.Course@2362f559
}
观察输出结果,发现两个对象地址相同。
那么如何设置单实例还是多实例呢?
(1)在spring配置文件的bean标签里有属性(scope)用于设置单实例还是多实例
<!-- bean中的scope属性用于设置多实例或单实例
prototype 多实例
singleton 单实例(不写scope属性默认是单实例)
-->
<bean id="course" class="com.atguigu.spring5.Course" scope="prototype"></bean>
(2)singleton和prototype区别
- singleton单实例,prototype多实例
- 设置scope是singleton时候,加载spring配置文件时就会创建单实例对象。
- 设置scope是prototype时候,不是在加载spring配置文件时创建对象,而是在调用getBean方法时候创建多实例对象。
需要注意的是,Spring bean的作用域还有request和session以及Global Session。
1.6 生命周期
生命周期:指对象创建到销毁的过程。
bean的生命周期:
- 通过构造器创建bean实例(无参构造)
- 为bean的属性设置值和对其他bean的引用(调用set方法)
- 调用bean的初始化方法(需要进行配置初始化的方法)
- bean的使用(获取到对象)
- 当容器关闭的时候,调用bean的销毁的方法(需要进行配置销毁的方法)
演示示例:
package com.atguigu.spring5;
public class Orders {
private String oname;
public Orders() {
System.out.println("无参构造");
}
public void setOname(String oname) {
this.oname = oname;
System.out.println("set方法");
}
public void initMethod(){
System.out.println("初始化方法");
}
public void destroyMethod(){
System.out.println("销毁方法");
}
}
<bean id="orders" class="com.atguigu.spring5.Orders" init-method="initMethod"
destroy-method="destroyMethod">
<property name="oname" value="ANTA KT7"></property>
</bean>
@Test
public void testLiveBean(){
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean2.xml");
Orders orders = context.getBean("orders", Orders.class);
System.out.println("获取对象创建实例");
System.out.println(orders);
context.close();
}

如果添加了bean的后置处理器,则Bean的生命周期有七步:
- 通过构造器创建bean实例(无参构造)
- 为bean的属性设置值和对其他bean的引用(调用set方法)
- 把bean实例传递给bean后置处理器的方法postProcessBeforeInitialization()
- 调用bean的初始化的方法(需要进行配置初始化的方法)
- 把bean实例传递给bean后置处理器的方法postProcessAfterInitialization
- bean的使用(获取到对象)
- 当容器关闭的时候,调用bean的销毁的方法(需要进行配置销毁的方法)
package com.atguigu.spring5;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanPostProcessor;
public class BeanPost implements BeanPostProcessor {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("在初始化之前执行的方法");
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("在初始化之后执行的方法");
return bean;
}
}
<bean id="beanPost" class="com.atguigu.spring5.BeanPost"></bean>

1.7 xml自动装配
自动装配:根据指定的装配规则(属性名称或者属性类型),Spring自动将匹配的属性值进行注入
<!-- 实现自动装配
bean标签属性autowire,配置自动装配
autowire属性常用两个值:
byName 根据属性名称注入,注入值bean的id值和类属性名称一样
byType 根据属性类型注入
-->
<bean id="employee" class="com.atguigu.spring5.Employee" autowire="byType">
<property name="ename" value="Paul"></property>
<property name="gender" value="男"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="employee2" class="com.atguigu.spring5.Employee" autowire="byName">
<property name="ename" value="Carl"></property>
<property name="gender" value="男"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="department" class="com.atguigu.spring5.Department">
<property name="dname" value="技术部"></property>
</bean>
1.8 外部属性文件
1.直接配置数据库信息,引入德鲁伊连接池依赖jar包
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="root"></property>
</bean>
2.引入外部属性文件配置数据库连接池
(1)创建外部属性文件:jdbc.properties
prop.driverClass=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
prop.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test
prop.userName=root
prop.password=root
(2)把外部properties属性文件引入到spring配置文件中
先引入contenxt外部空间:
xmlns:context=“http://www.springframework.org/schema/context”
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:util="http://www.springframework.org/schema/util"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/util http://www.springframework.org/schema/util/spring-util.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
再在spring配置文件使用标签引入外部属性文件
<!--引入外部属性文件-->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
<!--配置连接池 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${prop.driverClass}"></property>
<property name="url" value="${prop.url}"></property>
<property name="username" value="${prop.userName}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${prop.password}"></property>
</bean>
3.2.2 基于注解方式实现
注解是代码特殊标记,格式:@注解名称(属性名字=属性值,属性名称=属性值…)
使用注解,注解作用在类上面,方法上面,属性上面
目的是简化xml的配置
Spring针对Bean管理中创建对象提供注解:
- @Component:Spring中提供的普通的组件,使用它都可以创建对象。
- @Service:用于业务逻辑层,即Service层。
- @Controller:用于Web层。
- @Repository:用于Dao持久层。
上面四个注解功能是一样的,都可以用来创建bean实例。
2.1 基于注解方式创建对象
第一步 引入依赖
引入spring-aop-x.x.x.RELEASE.jar
第二步 开启组件扫描
<!-- 开启组件扫描
1 如果要扫描多个包,多个包使用逗号隔开
2 扫描包的上层目录
-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu.spring5"></context:component-scan>
第三步 创建类,在类上面添加创建对象注解
package com.atguigu.spring5.service;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service(value = "userService")
public class UserService {
public void add(){
System.out.println("Service add");
userDao.add();
}
}
需要注意的是,注解里的value属性值可以省略不写,默认是类名称首字母小写。
此处value的值,对应xml配置中bean标签的id属性值。
第四步 开启组件扫描细节配置
<!-- use-default-filters="false" 表示现在不使用默认filter,自己配置filter -->
<!-- context:include-filter,设置扫描哪些内容 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu.spring5" use-default-filters="false">
<context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
</context:component-scan>
<!-- 扫描包内所有内容 -->
<!-- context:exclude-filter 设置哪些内容不进行扫描 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu.spring5">
<context:exclude-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Service"/>
</context:component-scan>
2.2 基于注解实现属性注入
@Autowired:根据属性类型进行自动装配
在UserService中注入UserDao对象,在UserService中添加dao类型属性,在属性上使用注解。
无需提供set方法,因为在注解中已经封装了。
@Service(value = "userService")
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
public void add(){
System.out.println("Service add");
userDao.add();
}
}
@Qualifier:根据名称进行注入
@Qualifier的使用,要和@Autowired一起使用
@Service(value = "userService")
public class UserService {
@Autowired
@Qualifier(value = "userDao")
private UserDao userDao;
public void add(){
System.out.println("Service add");
userDao.add();
}
}
需要注意的是,@Qualifier注解中的value值应与要匹配的实现类的对象创建注解中的value值一致。
@Resouce:可以根据类型注入,也可以根据名称注入
@Resource是javax.annotation包中的注解,并非是spring提供的,在jdk11中被移除。
@Resource(name="UserDaoImpl1") // 根据名称进行注入
private UserDao userDao;
@Value:注入普通类型属性
@Value(value = "abc")
private String name;
2.3 完全注解开发
(1) 创建配置类,代替xml文件
package com.atguigu.spring5.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.atguigu"})
public class SpringConfig {
}
(2) 编写测试类
@Test
public void testSpringConfig(){
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(SpringConfig.class);
UserService userService = context.getBean("userService", UserService.class);
userService.add();
}
四、AOP
AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming),即面向切面编程,利用AOP可以对业务逻辑的各个部分进行隔离,从而使得业务逻辑各个部分之间的耦合度降低,提高程序的可重用性,同时也提高了开发的效率。
也就是说,不通过修改源代码方式,就可以在主干功能里面添加新的功能。

4.1 AOP底层原理
AOP底层使用动态代理,且有两种情况下的动态代理。
第一种 有接口情况 使用JDK的动态代理
创建接口实现类代理对象,增强类的方法

第二种 没有接口情况 使用CGLIB动态代理
创建子类的代理对象,增强类的方法。

JDK 动态代理的使用
第一步 使用Proxy类的静态方法创建代理对象
static Object newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader,Class<?>[] interfaces, InvocationHandler h)
该方法返回指定接口的代理类的实例,该接口将方法调用分派给指定的调用处理程序。
该方法的三个参数:
- 第一个参数:类加载器
- 第二个参数:增强方法所在的类实现的接口,支持多个接口
- 第三个参数:实现这个接口InvocationHandler,是代理对象的调用处理程序,在代理实例调用方法时,方法调用被编码分派到调用处理程序的invoke方法。
第二步 编写JDK动态代理代码
(1)创建UserDao接口
package com.atguigu.spring5.dao;
public interface UserDao {
int add(int a,int b);
String update(String id);
}
(2)创建接口实现类
package com.atguigu.spring5.dao;
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao{
@Override
public int add(int a, int b) {
System.out.println("add方法执行");
return a + b;
}
@Override
public String update(String id) {
System.out.println("update方法执行");
return id;
}
}
(3)使用Proxy类创建接口代理对象
package com.atguigu.spring5.pojo;
import com.atguigu.spring5.dao.UserDao;
import com.atguigu.spring5.dao.UserDaoImpl;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationHandler;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.lang.reflect.Proxy;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class JDKProxy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
UserDaoImpl userDaoImpl = new UserDaoImpl();
// 创建接口实现类代理对象
// api中对于该方法的解释:
// 返回指定接口的代理类的实例,该接口将方法调用分派给指定的调用处理程序
UserDao userDao = (UserDao) Proxy.newProxyInstance(userDaoImpl.getClass().getClassLoader(), userDaoImpl.getClass().getInterfaces(), new MyHandler(userDaoImpl));
int result = userDao.add(4, 5);
System.out.println("add之后的结果:" + result);
String updateValue = userDao.update("B1");
System.out.println("update之后的结果" + updateValue);
}
}
class MyHandler implements InvocationHandler{
private Object obj;
public MyHandler(Object obj){
this.obj = obj;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// 方法之前
System.out.println("方法之前的执行" + method.getName() + "参数:" + Arrays.toString(args));
// 被增强的方法执行
Object returnValue = method.invoke(obj, args);
// 方法之后
System.out.println("方法之后的执行" + obj);
return returnValue;
}
}
4.2 AOP术语
连接点:类里面哪些方法可以被增强,这些方法被称为连接点。
切入点:实际被真正增强的方法,称为切入点。
通知(增强):实际增强的逻辑部分称为通知(增强)
通知有多种类型:
前置通知
后置通知
环绕通知
异常通知
最终通知
切面:是动作,是把通知应用到切入点的过程。
4.3 AOP操作
Spring框架一般基于AspectJ来实现AOP操作。
AspectJ不是Spring的组成部分,是独立AOP框架,一般把AspectJ和Spring框架一起使用,进行AOP操作。
基于AspectJ实现AOP操作有两种方式:
- 基于xml配置文件实现
- 基于注解方式实现
在项目工程里需要引入的AOP相关依赖:
切入点表达式
切入点表达式的作用:知道对哪个类里面的哪个方法进行增强。
语法结构:execution( [权限修饰符] [返回类型] [类全路径].[方法名称](参数列表) )
标准的表达式写法
public void com.atguigu.dao.BookDao.add(..)
全通配写法
*..*.*(..)
1.访问控制符可省略
void com.atguigu.dao.BookDao.add(..)
2.返回值类型可使用通配符*
* com.atguigu.dao.BookDao.add(..)
3.包名可使用通配符*:表示任意包
有几级包就写几个*
* *.*.*.BookDao.add(..)
表示当前包及其子包*…
* *..BookDao.add(..)
4.类名和方法名都可以使用通配符*
* *..*.*() // 无参方法被增强
5.参数列表
基本数据类型直接写名称
* *..*.*(int)
引用类型写包名
* *..*.*(java.lang.String)
6.参数类型
可以用通配符*表示:前提是必须有参数
* *..*.*(*)
..表示有无参数均可,有参数时可以是任意类型
* *..*.*(..)
7.实际开发中切入点表达式通常写法
切到业务层实现类下的所有方法
* com.atguigu.service.impl.*.*(..)
4.3.1 基于AspectJ注解实现
(1)修改Spring配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--开启注解扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu.spring5"></context:component-scan>
<!--开启Aspect生成代理对象-->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy proxy-target-class="true">
</aop:aspectj-autoproxy>
</beans>
(2)使用注解创建User对象和UserProxy对象
package com.atguigu.spring5.pojo;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class User {
public void add(){
System.out.println("User类的add方法");
}
}
package com.atguigu.spring5.pojo;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Aspect
public class UserProxy {
// 相同切入点抽取
@Pointcut(value = "execution(* com.atguigu.spring5.pojo.User.add(..))")
public void pointDemo(){
}
// 前置通知
@Before(value = "pointDemo()")
public void before(){
System.out.println();
}
// 后置通知
@AfterReturning(value = "pointDemo()")
public void afterReturning(){
System.out.println("afterReturning..");
}
// 最终通知
@After(value = "pointDemo()")
public void after(){
System.out.println("after...");
}
// 异常通知
@AfterThrowing(value = "pointDemo()")
public void afterThrowing(){
System.out.println("afterThrowing..");
}
// 环绕通知
@Around(value = "pointDemo()")
public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint proceedingJoinPoint) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("环绕之前");
// 被增强的方法执行
proceedingJoinPoint.proceed();
System.out.println("环绕之后");
}
}
如果有多个增强类对同一个方法进行增强,可以设置增强类优先级:
在增强类上面添加注解@Order(数字类型值),数字类型值越小优先级越高。
@Component
@Aspect
@Order(1)
public class PersonProxy{
}
完全注解开发:
@Component
@Aspect
@EnableAspectJAutoProxy(proxyTargetClass = true)
public class ConfigAop {
}
4.3.2 基于xml方式实现
创建两个类,增强类和被增强类,在里面写入方法:
package com.atguigu.spring5.pojo;
public class Book {
public void buy(){
System.out.println("Buy book");
}
}
package com.atguigu.spring5.pojo;
public class BookProxy {
public void before(){
System.out.println("before....");
}
}
在xml文件中进行配置:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--创建对象-->
<bean id="book" class="com.atguigu.spring5.pojo.Book"></bean>
<bean id="bookProxy" class="com.atguigu.spring5.pojo.BookProxy"></bean>
<!--配置aop增强-->
<aop:config>
<!--切入点-->
<aop:pointcut id="b" expression="execution(* com.atguigu.spring5.pojo.Book.buy(..))"/>
<!--配置切面-->
<aop:aspect ref="bookProxy">
<!--增强作用在具体的方法上-->
<aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="b"></aop:before>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
</beans>
五、JDBCTemplate
JdbcTemplate是Spring框架对JDBC的封装,使用JdbcTemplate能方便实现对数据库的操作。
要引入的jar包:

对Spring配置文件进行配置
第一步 配置数据库连接池
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" destroy-method="close">
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/book"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="123456"></property>
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"></property>
</bean>
第二步 配置JdbcTemplate的对象,注入DataSource
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
5.1 对数据库的增删改操作
创建Service类和Dao类,并在Dao中注入JdbcTemplate对象
- BookDao Interface
package com.atguigu.jdbcTemplate.dao;
import com.atguigu.jdbcTemplate.pojo.Book;
public interface BookDao {
/**
* 增加记录
* @param book
*/
void add(Book book);
/**
* 修改图书价格
* @param price
* @param id
* @return 返回修改记录的行数
*/
int update(Double price, int id);
/**
* 删除记录
* @param id
* @return 返回删除记录的行数
*/
int delete(int id);
}
- BookDaoImpl class
package com.atguigu.jdbcTemplate.dao;
import com.atguigu.jdbcTemplate.pojo.Book;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class BookDaoImpl implements BookDao{
// 注入JdbcTemplate
@Autowired
public JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Override
public void add(Book book) {
String sql = "insert into t_book(bname,bauthor,bprice) values(?,?,?)";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql,book.getBname(),book.getBauthor(),book.getBprice());
}
@Override
public int update(Double price, int id) {
String sql = "update t_book set bprice = ? where bid = ?";
return jdbcTemplate.update(sql,price,id);
}
@Override
public int delete(int id) {
String sql = "delete from t_book where bid = ?";
return jdbcTemplate.update(sql,id);
}
}
- BookService class
package com.atguigu.jdbcTemplate.service;
import com.atguigu.jdbcTemplate.dao.BookDao;
import com.atguigu.jdbcTemplate.pojo.Book;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class BookService {
// 注入bookDao
@Autowired
private BookDao bookDao;
public void addBook(Book book){
bookDao.add(book);
}
public int updatePrice(Double price,int id){
return bookDao.update(price,id);
}
public int deleteBook(int id){
return bookDao.delete(id);
}
}
- Test example
@Test
public void testAdd(){
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean1.xml");
BookService bookService = context.getBean("bookService", BookService.class);
bookService.addBook(new Book("Introduction to Algorithms","Thomas H. Cormen",128.0));
bookService.updatePrice(79.8, 1);
bookService.deleteBook(1);
}
5.2 对数据库的查询操作
实现查询返回某个特殊值
@Override
public int queryCount() {
String sql = "select count(*) from t_book";
return jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql,Integer.class);
}
实现查询返回对象
@Override
public Book queryBookInfo(int id) {
String sql = "select * from t_book where bid = ?";
return jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql,new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Book>(Book.class),id);
}
实现查询返回集合
@Override
public List queryBookList() {
String sql = "select * from t_book";
List<Book> bookList = jdbcTemplate.query(sql, new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Book>(Book.class));
return bookList;
}
其中,BeanPropertyRowMapper是RowMapper接口的实现类,针对返回不同的类型数据,完成数据的封装操作。
5.3 批量操作
批量操作是指操作表里多条记录。
实现批量添加操作
- BookDaoImpl class
@Override
public void batchAddBook(List<Object[]> args) {
String sql = "insert into t_book(bname,bauthor,bprice) values(?,?,?)";
int[] ints = jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql, args);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ints));
}
- Test example
List<Object[]> batchArgs = new ArrayList<>();
Object[] b1 = {"三国演义","罗贯中",27.6};
Object[] b2 = {"小逻辑","黑格尔",16.8};
batchArgs.add(b1);
batchArgs.add(b2);
bookService.batchAdd(batchArgs);
实现批量修改操作
- BookDaoImpl class
@Override
public void batchUpdateBook(List<Object[]> args) {
String sql = "update t_book set bprice = ? where bid = ?";
int[] ints = jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql, args);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ints));
}
- Test example
List<Object[]> batchArgs = new ArrayList<>();
Object[] b1 = {47.8, 4};
Object[] b2 = {35.5, 5};
batchArgs.add(b1);
batchArgs.add(b2);
bookService.batchUpdate(batchArgs);
实现批量删除操作
- BookDaoImpl class
@Override
public void batchDeleteBook(List<Object[]> args) {
String sql = "delete from t_book where bid = ?";
int[] ints = jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql, args);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(ints));
}
- Test example
List<Object[]> batchArgs = new ArrayList<>();
Object[] b1 = {4};
Object[] b2 = {5};
batchArgs.add(b1);
batchArgs.add(b2);
bookService.batchDelete(batchArgs);
六、事务
事务是数据库操作的最基本单元,是逻辑上的一组操作,要么都成功,如果有一个失败则所有操作都失败。
事务的四个特性(ACID)
- 原子性
- 一致性
- 隔离性
- 持久性
6.1 引入(搭建事务操作环境)
经典案例:银行转账。
环境准备
- AccountDao interface
package com.atguigu.jdbcTemplate.dao;
import com.atguigu.jdbcTemplate.pojo.Account;
public interface AccountDao {
void addAccount(Account account);
void transferMoney();
void receiveMoney();
}
- AccountDaoImpl class
package com.atguigu.jdbcTemplate.dao;
import com.atguigu.jdbcTemplate.pojo.Account;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao{
@Autowired
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Override
public void addAccount(Account account) {
String sql = "insert into t_account values(?,?,?)";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql,account.getId(),account.getUsername(),account.getMoney());
}
@Override
public void transferMoney() {
String sql = "update t_account set money = money - ? where username = ?";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql,10000,"Michel Jordan");
}
@Override
public void receiveMoney() {
String sql = "update t_account set money = money + ? where username = ?";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql,10000,"Larry Brid");
}
}
- AccountService class
package com.atguigu.jdbcTemplate.service;
import com.atguigu.jdbcTemplate.dao.AccountDao;
import com.atguigu.jdbcTemplate.pojo.Account;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class AccountService {
@Autowired
private AccountDao accountDao;
public void addAccount(Account account){
accountDao.addAccount(account);
}
public void modest(){
accountDao.transferMoney();
accountDao.receiveMoney();
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd">
<!--开启组件扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu.jdbcTemplate"></context:component-scan>
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource" destroy-method="close">
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/book"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="123456"></property>
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver"></property>
</bean>
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
上述操作正常执行是没有问题的,但如果代码执行过程中出现异常,就会产生问题:
public void modest(){
accountDao.transferMoney();
int test = 10 / 0;
accountDao.receiveMoney();
}
此时再执行,就会发现用户的钱转出去了,但是收款方并未收到钱。
这就需要用的事务来解决了。
6.2 事务管理
事务一般添加在Java EE三层结构中的Service层中。
在Spring进行事务管理操作有两种方式:
- 编程式事务管理
- 声明式事务管理
编程式事务管理,顾名思义就是通过编程来进行事务的管理操作
public void modest(){
try{
// 第一步 开启事务
// 第二步 进行业务逻辑操作
accountDao.transferMoney();
int test = 10 / 0;
accountDao.receiveMoney();
// 第三步 没有发生异常,则提交事务
} catch (Exception e){
// 第四步 出现异常,事务进行回滚
}
}
这种方式写事务管理,要在每个待开启事务的代码中如法炮制这些步骤,显得十分的臃肿,一般使用声明式事务管理。
声明式事务管理的两种实现方式:
- 基于注解方式
- 基于xml配置文件方式
需要注意的是,在Spring中进行声明式事务管理,底层使用AOP原理。
Spring事务管理中提供一个接口,代表事务管理器,这个接口针对于不同的框架提供不同的实现类:

6.2.1 基于注解方式实现声明式事务管理
第一步 在Spring配置文件中配置事务管理器
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
第二步 在Spring配置文件中开启事务注解
- 引入名称空间tx
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"
xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
- 开始事务注解
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"></tx:annotation-driven>
第三步 在service类上面,或者在service类中要开启事务操作的方法上面添加事务注解
@Service
@Transactional
public class AccountService {
}
6.2.2 基于xml方式实现声明式事务管理
在Spring文件中进行配置
配置事务管理器
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
配置通知
<!--配置通知-->
<tx:advice id="tx_advice">
<!--配置事务参数-->
<tx:attributes>
<!--指定哪种规则的方法上面添加事务-->
<tx:method name="modest" propagation="REQUIRED"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
配置切入点和切面
<aop:config>
<!--配置切入点-->
<aop:pointcut id="pt" expression="execution(* com.atguigu.jdbcTemplate.service.AccountService.modest(..))"/>
<!--配置切面-->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="tx_advice" pointcut-ref="pt"></aop:advisor>
</aop:config>
6.2.3 声明式事务管理参数配置
注解@Transactional里面可以配置事务相关参数。

propagation:事务传播行为
事务传播行为指当一个事务方法被另一个事务方法调用时,这个事务方法应该如何进行。
例如:methodA事务方法调用methodB事务方法时,methodB是继续在调用者methodA的事务中运行,还是为自己开启一个新事物运行,由methodB的事务传播行为决定。

- REQUIRED
如果存在一个事务,则支持当前事务。如果没有事务则开启一个新的事务。
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void method A(){
method B();
//do something
}
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void methodB(){
// do something
}
单独调用methodB方法时,因为当前不存在事务,所以会开启一个新的事务。
调用methodA方法时,因为当前不存在事务,所以开启一个新的事务。当执行到methodB时,methodB发现当前有事务,因此就加入到当前事务中来。
- SUPPORTS
如果存在一个事务,则支持当前事务;如果没有事务,则做非事务的执行。但是对于事务同步的事务管理器,PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS与不使用事务有少许不同。
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void methodA(){
methodB();
// do something
}
// 事务属性为SUPPORTS
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.SUPPORTS)
public void methodB(){
// do something
}
单纯的调用methodB时,methodB方法是非事务的执行。当调用methodA时,methodB则加入了methodA的事务中,事务的执行。
- MANDATORY
如果已经存在一个事务,支持当前事务。如果没有一个活动的事务,则抛出异常。
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void methodA(){
methodB();
// do something
}
// 事务属性为MANDATORY
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.MANDATORY)
public void methodB(){
// do something
}
当单独调用methodB时,因为当前没有一个活动的事务,会抛出异常throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(“Transaction propagation ‘mandatory’ but no existing transaction found”);当调用methodA时,methodB则加入到methodA的事务中,事务的去执行。
- REQUIRES_NEW
使用PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW,需要使用JtaTransactionManager作为事务管理器。
它会开启一个新的事务。如果一个事务已经存在,则先将这个存在的事务挂起。
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public void methodA(){
doSomeThingA();
methodB();
doSomeThingB();
// do else
}
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
public void methodB(){
// do something
}
当调用methodA时,相当于调用
TransactionManager tm = null;
try{
// 获得一个JTA事务管理器
tm = getTransactionManager();
// 开启一个新的事务
tm.begin();
Transaction ts1 = tm.getTransaction();
doSomeThingA();
// 挂起当前事务
tm.suspend();
try{
// 重新开启第二个事务
tm.begin();
Transaction ts2 = tm.getTransaction();
methodB();
// 提交第二个事务
ts2.commit();
}catch(RunTimeException ex){
// 回滚第二个事务
ts2.rollback();
}finally {
//释放资源
}
// methodB执行完毕后,恢复第一个事务
tm.resume(ts1);
doSomeThingB();
// 提交第一个事务
ts1.commit();
}catch(RuntimeException ex){
// 回滚第一个事务
ts1.rollback();
}finally {
// 释放资源
}
其中,ts1称为外层事务,ts2称为内层事务。ts1和ts2是两个独立的事务,互不相干,ts2是否成功并不依赖于ts1,如果methodA方法在调用methodB方法后的doSomeThingB方法失败了,methodB方法所做的结果依然被提交,而除了methodB之外的结果却被回滚了。
- NOT_SUPPORTED
PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED总是非事务的执行,并挂起任何存在的事务。使用PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED,也需要使用JtaTransactionManager作为事务管理器。
@Transactional()
public void methodA(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED){
methodB();
}
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.NOT_SUPPORTED)
public void methodB(){
}
单独执行methodB,做非事务的执行。
执行methodA,当执行到methodB时,会挂起事务A,然后以非事务的方式执行方法B。
- NEVER
总是非事务地执行,如果存在一个活动事务,就抛出异常。
- NESTED
如果一个活动的事务存在,则运行在一个嵌套的事务中。如果没有活动事务,则按照TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED属性执行。
这是一个嵌套事务,使用JDBC3.0驱动时,仅仅支持DataSourceTransactionManager作为事务管理器。
需要JDBC驱动的java.sql.Savepoint类。使用PROPAGATION_NESTED,还需要把PlatformTransactionManager的nestedTransactionAllowed属性设为true(默认为false)。
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
methodA(){
doSomeThingA();
methodB();
doSomeThingB();
}
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.NEWSTED)
methodB(){
// do something
}
如果单独调用methodB方法,则按PROPAGATION.REQUIRED属性执行。
如果调用methodA,相当于如下的效果:
Connection conn = null;
SavePoint sp = null;
try{
conn = getConnection();
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
doSomeThingA();
sp = conn.setSaveponit();
try{
methodB();
}catch(RuntimeException ex) {
conn.rollback(sp);
} finally {
// 释放资源
}
doSomeThingB();
conn.commit();
} catch(RuntimeException ex){
conn.rollback();
} finally {
// 释放资源
}
当methodB方法调用之前,调用setSavepoint方法,保存当前的状态到sp。如果methodB方法调用失败,恢复到之前保存的状态。但这时的事务并没有提交,如果后续的doSomeThingB()调用失败,则回滚包括methodB方法在内的所有操作。
嵌套事务一个非常重要的概念就是内层事务依赖于外层事务。当外层事务失败时,会回滚内层事务所做的动作;而内层事务操作失败并不会引起外层事务的回滚。
isolation:隔离级别
隔离性是针对数据资源的并发访问,规定了各个事务之间相互影响的程度。
数据资源在并发访问时可能出现的问题:
- 脏读:如果一个事务A对数据进行了更改,但是并未提交,另一个事务B可以读到事务A尚未提交的更新结果。这样。当事务A进行回滚时,事务B读到的数据就是脏数据。
- 不可重复读:同一个事务在事务过程中,对同一个数据进行读取操作,读取到的结果不同。例如:事务B在事务A的更新操作之前读到的数据,和在事务A提交更新操作后读到的数据,可能不同。要避免不可重复读,需要将事务操作的记录都加上锁,不允许其他事务对此记录进行写操作。
- 幻读:同样一个查询在整个事务中多次执行,查询得到的结果不同。例如:事务A对全部记录做了更新操作,尚未提交前,事务B又插入了一条记录,那么当事务A再次读取数据库时,会发现还有一条记录(即事务B新插入的记录)没有做更新。
可以通过设置事务隔离级别解决上述问题:

timeout:事务超时时间
默认值为-1。如果超过该时间限制(秒)但事务还没有完成,则自动回滚事务。
readOnly:指定事务是否为只读事务
默认值为false。忽略那些不需要事务的方法,比如查询,可以设置readOnly为true。
rollbackFor:用于指定能够触发事务回滚的异常类型,可以指定多个。
noRollbackFor:抛出指定的异常类型不回滚事务,可以指定多个。
七、Spring5新功能
后续一段时间再看吧,先跳过了。暂时完结撒花~