前序:十几天前刚学完学Springboot实现了简单的登录验证,以及crud操作,作为回忆总结。因为学前只具有javaWeb基础阶段的知识,并未深入学过spring,springMVC等知识,只了解一下基本的AOP,IoC概念,因此在学习过程中不懂的注解名字功能很多,但学完后对spring体系也算有了一个基本的了解。
已经实现成果:springboot实现的员工管理系统-Java文档类资源
用到的技术
模板引擎Thymeleaf 用于在前端渲染后端数据
数据库 mysql
持久层框架 myBaties
meaven管理jar包
用到的jar包版本
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.6.3</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>StaffingSystem</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>StaffingSystem</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.mybatis.spring.boot/mybatis-spring-boot-starter -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.2.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
项目资源列表
后端代码实现过程
拿到前端页面,首先实现登录验证的功能,登录的账号密码采用的写死的形式,没有从数据库中获取。之后完成管理系统数据库部分的增删改查并展示在界面。
登录验证部分
首先书写Login控制器
表单账号密码提交后会请求? /user/login? 映射的方法login,方法中判断账号是否为空,密码是否为123456,登录成功会将用户名保存到session用于拦截器登录过程中的表单验证。登录成功跳转到管理主页面,失败返回首页登录窗口。
@Controller
public class LoginControler {
@RequestMapping("/user/login")
//@RequestParam:将请求参数绑定到你控制器的方法参数上(是springmvc中接收普通参数的注解)
public String login(@RequestParam("username") String username, @RequestParam("password") String password, Model model, HttpSession session){
//具体业务:
if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(username)&&"123456".equals(password)){
session.setAttribute("loginUser",username);
return "/dashboard.html";
}else {
//告诉用户登录失败
model.addAttribute("msg", "账号或密码错误");
return "/index.html";
}
}
}之后配置拦截器,防止在不登录的情况下访问主页。
//拦截器
public class LoginHandlerInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Override /* 在业务处理器处理请求之前被调用。预处理,可以进行编码、安全控制、权限校验等处理;*/
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
//登录成功有用户的session
Object loginUser = request.getSession().getAttribute("loginUser");
if(loginUser==null){//用户没有登录
request.setAttribute("msg","用户没有登录");
request.getRequestDispatcher("/index.html").forward(request,response);
return false;
}
return true;
}
}
并在MyConfig中将自己定义的拦截器加入到springboot中管理,其中也包含基本的自定义页面跳转。
@Configuration
public class MyConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
//基本页面跳转控制器
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
registry.addViewController("/").setViewName("index");
registry.addViewController("/index.html").setViewName("index");
registry.addViewController("/main.html").setViewName("dashboard");
}
//自定义的国际化组件
@Bean
public LocaleResolver localeResolver(){
return new MyLocaleResolver();
}
//自定义的登录拦截器
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(new LoginHandlerInterceptor()).addPathPatterns("/**")
.excludePathPatterns("/index.html","/user/login","/","/css/*","/js/*","/img/*");
}
}至此登录功能基本实现,接下来实现数据库增删改查部分。
员工数据管理部分
零,配置application.yml文件
spring:
datasource:
username: root
password: 123456
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/staffingsystem?serverTimezone=UTC&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
#整合mybaties
mybatis:
type-aliases-package: com/example/staffingsystem/pojo
mapper-locations: classpath:mybaties/mapper/*.xml
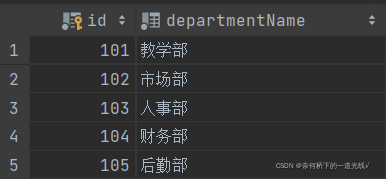
一,新建数据库表
employee员工表结构

department 部门表结构
?二,根据表的结构建立pojo对象
//部门表
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Department {
private Integer id;
private String departmentName;
}
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class Employee {
private Integer id;
private String lastName;
private String email;
private Integer gender;//0:女 1:男
private Integer departmentId;
private Date birth;
public Employee(Integer id, String lastName, String email, Integer gender, int departmentId) {
this.id = id;
this.lastName = lastName;
this.email = email;
this.gender = gender;
this.departmentId = departmentId;
this.birth = new Date();
}
}三,利用mybaties实现对持久层dao数据库的处理
PS :其实可以利用mybatiesPlus自动实现基本的sql功能
@Mapper
@Repository
public interface DepartmentMapper {
// 获取公司部门信息
List<Department> getDepartments();
Department getDepartmentById(Integer id);
}@Mapper
@Repository
public interface EmployeeMapper {
List<Employee> list();
Employee listOneById(Integer id);
int addEmplyee(Employee employee);
int updateEmp(Employee employee);
int delete(Integer id);
}
在resourse表下的mybaties.mapper中利用xml实现sql语句完成
![]()
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.example.staffingsystem.mapper.DepartmentMapper">
<select id="getDepartments" resultType="Department">
select * from staffingsystem.department
</select>
<select id="getDepartmentById" resultType="Department">
select * from staffingsystem.department where id=#{id}
</select>
</mapper>?![]()
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.example.staffingsystem.mapper.EmployeeMapper">
<select id="list" resultType="Employee">
select * from employee
</select>
<select id="listOneById" resultType="Employee">
select * from employee where id=#{id}
</select>
<insert id="addEmplyee" parameterType="Employee">
insert into employee(id, lastName, email, gender,departmentId,birth) VALUES (#{id},#{lastName},#{email},#{gender},#{departmentId},#{birth});
</insert>
<update id="updateEmp" parameterType="Employee">
update employee set lastName=#{lastName},email=#{email},gender=#{gender},departmentId=#{departmentId},birth=#{birth} where id=#{id}
</update>
<delete id="delete" parameterType="int">
delete from employee where id=#{id}
</delete>
</mapper>?四,实现service层和Controller层
由于都是些简单的逻辑服务,就将两层合并了
@Controller
public class EmployeeController {
@Autowired
DepartmentMapper departmentMapper;
@Autowired
EmployeeMapper employeesMapper;
//查所有员工
@RequestMapping("/emps")
public String list(Model model){
List<Employee> listEmployees = employeesMapper.list();
System.out.println(listEmployees);
model.addAttribute("emps",listEmployees);
return "/list.html";
}
@RequestMapping("/emp/add")
public String toAddEmplyee(Model model){
//获得公司信息
Collection<Department> departments = departmentMapper.getDepartments();
model.addAttribute("departments",departments);
return "/employee/add.html";
}
//增加员工
@PostMapping("/emp/addSuccess")
public String addEmplyee(Employee employee){
System.out.println(employee);
employeesMapper.addEmplyee(employee);
return "redirect:/emps";
}
//去员工的修改页面
@RequestMapping("/emp/update") //通过@PathVariable 可以将URL中占位符参数{xxx}绑定到处理器类的方法形参中@PathVariable(“xxx)
public String toUpdateEmp(@RequestParam("id") Integer id,Model model){
//查出原来的数据
Employee employee = employeesMapper.listOneById(id);
model.addAttribute("employee",employee);
//获得公司信息
Collection<Department> departments = departmentMapper.getDepartments();
model.addAttribute("departments",departments);
return "/employee/update.html";
}
@PostMapping("/emp/updateSuccess")
public String updateEmp(Employee employee){
employeesMapper.updateEmp(employee);
return "redirect:/emps";
}
@RequestMapping("/emp/delete")
public String delete(@RequestParam("id") Integer id){
employeesMapper.delete(id);
return "redirect:/emps";
}
@RequestMapping("/emp/logout")
public String logout(HttpSession session){
session.invalidate();
return "redirect:/index.html";
}
}五,前端数据渲染
该部分采用Thymeleaf模板引擎,将后端model保存的数据信息渲染到前端页面即可。
总结:该系统最先接触springboot所实现的第一个简单系统,让我初步了解的springboot功能的强大,从基础的JAVAWeb对比来说以前采用Tomcat作为服务器每一次重启都要耗费很长时间,而由于springboot集成了Tomcat启动速度大大降低。在该过程中Thymleaf语法的强大相较于以前的jsp文件,语法简单,而且运行更快,而且可以直接在html文件中运行。所使用的的mybaties框架,不再需要手动连接数据库,书写基础的JDBC数据库增删改查代码,值=只需要配置简单的接口即可使用。最简单好用的还是springboot的配置注解使用,不再需要配置很多跳转配置,至于要一个注解就能简单实现。