目录
4.1 ThreadLocal的一种实现方式-维护线程与实例的映射(JDK未采用)
4.2 ThreadLocal的另一种实现方式-线程维护ThreadLocal与实例的映射
1.对ThreadLocal不恰当的理解
- ThreadLocal的用途是解决多线程程序的并发(同步)问题
- ThreadLocal的目的是为了解决多线程访问资源时的共享问题
2.ThreadLocal的基本原理
- 同一个ThreadLocal所包含的对象,在不同的Thread中有不同的副本
- 每个线程都有自己的实例副本,线程之间是不可以访问的,那么就不存在共享资源的问题就更不会涉及到同步的问题
- 每个线程需要自己独立的实例且该实例需要在多个方法中被使用(变量在线程间隔离,在方法或者类中共享)
public class Competition {
/** 初始化一个默认的ThreadLocal
* threadLocal.set() : 设置当前线程threadLocal里面的素材
* threadLocal.get() : 返回当前线程threadLocal保存的素材
* ThreadLocal里面没有初始化获取的就是null
*/
public static ThreadLocal<Material> threadLocal = ThreadLocal.withInitial(
() ->new Material("初始化编码","初始化配置")
);
public static class Material{
private String code;
private String config;
public Material() {
}
public Material(String code, String config) {
this.code = code;
this.config = config;
}
public String getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(String code) {
this.code = code;
}
public String getConfig() {
return config;
}
public void setConfig(String config) {
this.config = config;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Material{" +
"code='" + code + '\'' +
", config='" + config + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
}
public class DoCompetition {
public void code(){
Competition.Material material = Competition.threadLocal.get();
material.setCode(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
public void config(){
Competition.Material material = Competition.threadLocal.get();
material.setCode(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
public void print(){
System.out.println(
String.format("Thread name: %s,ThreadLocal Hashcode:%s, Instance Hashcode:%s," +
"Value:%s",
Thread.currentThread().getName(),
Competition.threadLocal.hashCode(),
Competition.threadLocal.get().hashCode(),
Competition.threadLocal.get().toString())
);
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
new Thread(
() ->{
DoCompetition doCompetition =new DoCompetition();
doCompetition.code();
doCompetition.config();
doCompetition.print();
},"Thread-" + (i + 1)
).start();
}
}
}
//打印出的结果
Thread name: Thread-2,ThreadLocal Hashcode:1524369652, Instance Hashcode:243749005,Value:Material{code='Thread-2', config='Thread-2'}
Thread name: Thread-3,ThreadLocal Hashcode:1524369652, Instance Hashcode:253814826,Value:Material{code='Thread-3', config='Thread-3'}
Thread name: Thread-1,ThreadLocal Hashcode:1524369652, Instance Hashcode:1847780726,Value:Material{code='Thread-1', config='Thread-1'}
ThreadLocal的哈希值相同:只有一个
ThreadLocal实例的哈希值三个均不同(也就是一个个Material):ThreadLocal保存的是一个个线程中独立的副本
//下面会以图形化的方式解释3.ThreadLocal常见的使用误区
- ThreadLocal并不支持继承(在子线程中获取不到主线程(父线程)中定义的ThreadLocal)
- 当前线程去new一个新的线程,新的线程就是子线程,执行new操作的线程就是父线程
public class Main {
/**
* ThreadLocal不支持继承
*/
private static void threadLocalCanNotInherit(){
ThreadLocal<String> threadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();
threadLocal.set("天不生我李淳罡");
//当前线程是父线程,定义一个子线程
Thread subThread = new Thread(
() -> {
System.out.println("Name in Sub:"+ threadLocal.get());
}
);
subThread.start();
System.out.println("Name in Main:"+ threadLocal.get());
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main.threadLocalCanNotInherit();
}
}
//打印结果
Name in Main:天不生我李淳罡
Name in Sub:null- ThreadLocal遇到线程池,如果不及时清理线程,会造成数据混乱
- 线程池中的线程会不断复用的,ThreadLocal中的副本属于线程相关的,如果被复用的线程去执行新的任务时,会使用上一个线程操纵过的对象,会造成数据混乱
/**
* 在线程池中使用threadlocal
*/
public class ThreadLocalValueHolder {
//设置初始值为0
private static ThreadLocal<Integer> holder = ThreadLocal.withInitial(
() -> 0
);
public static int getValue() {
return holder.get();
}
public static void removeValue() {
holder.remove();
}
public static void increment() {
holder.set(holder.get() + 1);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService threadpool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
for (int i = 0; i != 15; i++) {
//预期情况下:before为0,after为1
threadpool.execute(
() -> {
int beforeValue = getValue();
increment();
int afterValue = getValue();
System.out.println("before: " + beforeValue + ",after: " + afterValue +
",Thread name: " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
});
}
}
}
//打印出的结果
//线程池中的前三个线程符合预期
before: 0,after: 1,Thread name: pool-1-thread-2
before: 0,after: 1,Thread name: pool-1-thread-1
before: 0,after: 1,Thread name: pool-1-thread-3
//复用pool-1-thread-1,pool-1-thread-3,pool-1-thread-2的时候数据不符合预期
before: 1,after: 2,Thread name: pool-1-thread-1
before: 1,after: 2,Thread name: pool-1-thread-3
before: 1,after: 2,Thread name: pool-1-thread-2
before: 2,after: 3,Thread name: pool-1-thread-3
before: 2,after: 3,Thread name: pool-1-thread-1
before: 3,after: 4,Thread name: pool-1-thread-3
before: 2,after: 3,Thread name: pool-1-thread-2
before: 4,after: 5,Thread name: pool-1-thread-3
before: 3,after: 4,Thread name: pool-1-thread-1
before: 5,after: 6,Thread name: pool-1-thread-3
before: 3,after: 4,Thread name: pool-1-thread-2
before: 4,after: 5,Thread name: pool-1-thread-1
/**
*
* 在线程池中使用threadlocal
*/
public class ThreadLocalValueHolder {
//设置初始值为0
private static ThreadLocal<Integer> holder = ThreadLocal.withInitial(
() -> 0
);
public static int getValue() {
return holder.get();
}
public static void removeValue() {
holder.remove();
}
public static void increment() {
holder.set(holder.get() + 1);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ExecutorService threadpool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);
for (int i = 0; i != 15; i++) {
threadpool.execute(
() -> {
try {
int beforeValue = getValue();
increment();
int afterValue = getValue();
System.out.println("before: " + beforeValue + ",after: " + afterValue +
",Thread name: " + Thread.currentThread().getName());
}finally {
//及时的清理本地的内存变量
removeValue();
}
});
}
}
}
//清除线程中的ThreadLocal后数据完全符合预期
before: 0,after: 1,Thread name: pool-1-thread-3
before: 0,after: 1,Thread name: pool-1-thread-2
before: 0,after: 1,Thread name: pool-1-thread-1
before: 0,after: 1,Thread name: pool-1-thread-2
before: 0,after: 1,Thread name: pool-1-thread-1
before: 0,after: 1,Thread name: pool-1-thread-2
before: 0,after: 1,Thread name: pool-1-thread-2
before: 0,after: 1,Thread name: pool-1-thread-1
before: 0,after: 1,Thread name: pool-1-thread-3
before: 0,after: 1,Thread name: pool-1-thread-2
before: 0,after: 1,Thread name: pool-1-thread-3
before: 0,after: 1,Thread name: pool-1-thread-1
before: 0,after: 1,Thread name: pool-1-thread-1
before: 0,after: 1,Thread name: pool-1-thread-3
before: 0,after: 1,Thread name: pool-1-thread-2
4.ThreadLocal的实现原理
4.1 ThreadLocal的一种实现方式-维护线程与实例的映射(JDK未采用)
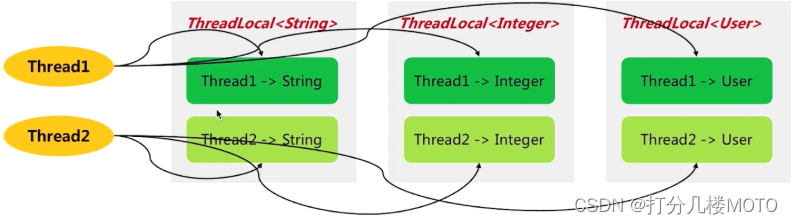
- 每一个threadlocal变量的副本都有一个自己本地的副本
- Threadlocal维护一个个副本(一个个map):key是ThreadId,value是在线程中的一个实例
- 线程以ThreadId为键去map中找到对应的实例.
- 每个线程访问ThreadLocal的时候需要添加一个映射,线程结束的时候应该清除这个映射
- 问题:增加或者删除map中的元素需要在多线程下保证安全,需要锁,效率低
4.2 ThreadLocal的另一种实现方式-线程维护ThreadLocal与实例的映射

- ?map由线程自己维护,每一个线程只访问自己的map,不存在锁的问题;
- 每一个线程访问ThreadLocal变量之后,都会在自己的map中维护ThreadLocal变量与具体实例的一个映射:key是ThreadLocal变量,value:线程维护的一个实例副本;线程使用完之后不及时的清理线程会存在内存泄露的问题
5.ThreadLocal的使用场景:
- 1.每一个线程需要自己单独的实例副本
- 2.实例需要在多个方法中共享,并不希望被多个线程所共享
6.总结
????????多线程访问同一个共享变量尤其是多个线程对一个变量进行写入的时候,为了保证线程安全,一般在访问共享变量的时候需要进行额外的同步措施(通常会使用synchronized来保证同一时刻只有一个线程对共享变量进行操作)才能保证线程安全性。ThreadLocal是除了加锁这种同步方式之外的另一种保证多线程访问变量时的线程安全的方法(将变量放到ThreadLocal类型的对象中,使变量在每个线程中都有独立拷贝,在一个线程中对变量的任何操作都不会影响到其它线程的变量);每个线程对变量的访问都是基于线程自己的变量不会存在线程不安全问题。? ??