🏠:博客首页: 进击的波吉
📕:今日分享的文章:【JAVASE】IO流基础
💝:希望自己对源码的解读的可以帮助到大家🎈
🌱:Boji 还在努力学JavaSE ,如有疑问、疏漏之处,请多多指点🙏
??:自学成长的路上,感谢大家相伴!No hurry , No Pause !💝
文章目录
1、 文件
文件,对于我们并不陌生,文件是保存数据的地方,比如经常使用的word文档,txt文件,excel文件…都是文件。它既可以保存一张图片,也可以保存视频,声音…
1.2 文件流
文件在程序中是以流的形式来操作的
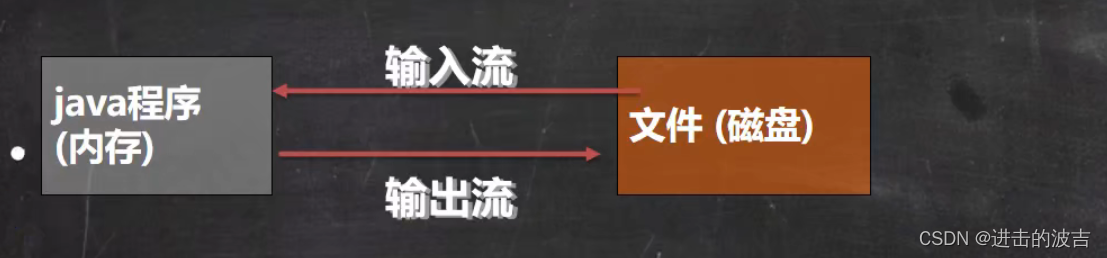
流:数据在数据源(文件)和程序(内存)之间经历的路径 ;
输入流:数据从数据源(文件)到程序(内存)的路径;
输出流:数据从程序(内存)到数据源(文件)的路径 ;
1.3 常用的文件操作
创建文件对象相关构造器和方法
- new File(String pathname)//根据路径处理一个File对象
- new File (String parent,String child)//根据父目录文件 + 子路径构建
- new File (String parent, String child) // 根据父目录 + 子路径构建
目录的操作和文件的删除
mkdir创建一级目录,mkdirs创建多级目录,delete删除空目录或文件
代码示例:
// 方式1 new File(String pathname)
@Test
public void create01() {
String filepath = "e:\\new1.txt" ;
File file = new File(filepath);
try {
file.createNewFile();
System.out.println("文件创建成功");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//方式2 new File(File parent ,String child ) 根据父目录文件 + 子路径构建
// e:\\news2.txt
@Test
public void create02() {
File parentFile = new File("e:\\") ;
String fileName = "news2.txt" ;
//这里的file对象,在java程序中,只是一个java对象而已
//只有执行了createFile 方法,才会真正的,在磁盘创建该文件
File file = new File(parentFile, fileName);
try {
file.createNewFile() ;
System.out.println("创建成功");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// new File (String parent, String child) // 根据父目录 + 子路径构建
@Test
public void create03() {
String parentPath = "e:\\" ;
String filePath = "news3.txt";
File file = new File(parentPath, filePath);
try {
file.createNewFile() ;
System.out.println("创建成功 01");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
2、IO流原理
2.1 I/O基本介绍
I/O是input/Output的缩写,I/O技术是非常实用的技术,用于处理数据传输。如读/写文件,网络通讯等:- Java程序中,对于数据的输入和输出操作以“
流(stream)”的方式进行; - java.io包下提供了各种“流"类和接口,用以获取不同种类的数据,并通过方法输入和输出数据 ;
输入Input:读取外部数据(磁盘、光盘等存储设备数据)到程序(内存)中 ;输出output:将程序(内存)数据输出到磁盘、光盘等存储设备中;
2.2 流的分类

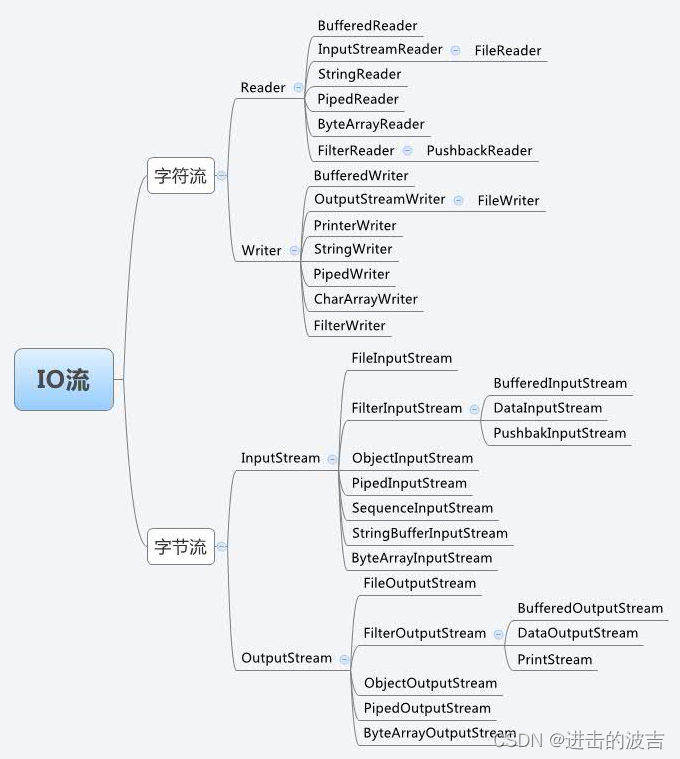
2.3 InputStream:字节输入流

2.3.1 FileInputStream:文件输入流
示例代码:
//单个字节的读取效率低
//使用 read(byte[] b)
@Test
public void readFile01() {
String filePath = "e:\\news2.txt" ;
int readData = 0 ;
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null ;
try {
//创建 FileInputStream 对象,用于读取 文件
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(filePath);
//从该输入流读取一个字节的数据。如果没有输入可用,从方法将阻止
//如果返回-1,表示读取完毕
while ((readData = fileInputStream.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char)readData);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 关闭文件流,释放资源
try {
fileInputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
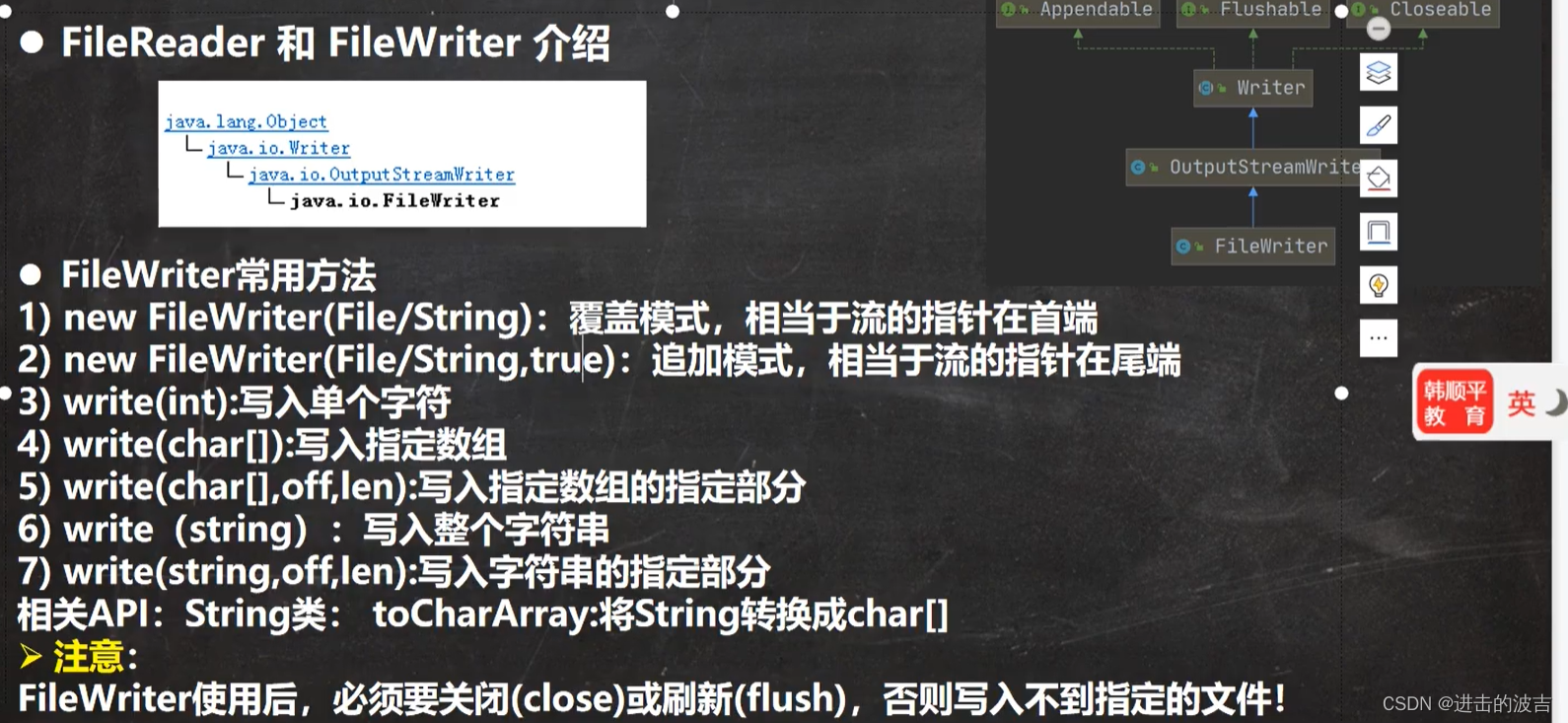
2.4 FileReader 和 FileWriter

2.5 节点流和处理流
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-vL5VeKkp-1645089241772)(C:\Users\阿桂\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20220208195512691.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/2688a2cc3afb42b29ec6454038dfdad8.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_d3F5LXplbmhlaQ,shadow_50,text_Q1NETiBA6L-b5Ye755qE5rOi5ZCJ,size_20,color_FFFFFF,t_70,g_se,x_16)
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-jk4dHYWr-1645089241773)(C:\Users\阿桂\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20220208195436996.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/71b7941e89534924bf366fdcbc9c674c.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_d3F5LXplbmhlaQ,shadow_50,text_Q1NETiBA6L-b5Ye755qE5rOi5ZCJ,size_20,color_FFFFFF,t_70,g_se,x_16)
节点流和处理流的区别和联系
- 节点流是
底层流/低级流,直接跟数据源相接; 处理流(包装流)包装节点流,既可以消除不同节点流的实现差异,也可以提供更方便的方法来完成输入输出;- 处理流(包装流)对节点流进行包装,使用了
修饰器设计模式,不会直接与数据源相连
处理流功能主要体现在以下两个方面:
1.性能的提高:主要以增加缓冲的方式来提高输入输出的效率 ;
2. 操作的便捷:处理流可能提供了一系列便捷的方法来一次输入输出大批量的数据,使用更加灵活便捷;
2.6 处理流
BufferedReader和BufferedWriter 属于字符流,是按照字符来读取数据的
public class BufferedReader_ {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//创建缓冲流对象,套接在指定的节点流基础上
//注意:因为 Reader 和 Writer 是按字符读取,因此不能操作二进制文件(字节文件),比如
//图片,音乐,造成读取错误
String filePath = "e:\\threadUse_.java" ;
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filePath));
//读取
String line ; //按行读取,效率高
//说明:
//1.bufferedReader.readLine() 是按行读取
//2.当返回null时,表示文件读取完毕
while((line = bufferedReader.readLine())!= null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
//关闭流,只需要关闭 BufferedReader,因为底层会自动去关闭 节点流
//FileReader
bufferedReader.close();
}
}
关闭处理流,只需要关闭外层流即可;
BufferedInputStream和BufferedOutputStream
BufferedInputStream是字节流,在创建 BufferedInputStream时,会创建一个内部缓冲区数组
BufferedOutputStream是字节流,实现缓冲的输出流,可以将多个字节写入底层的输出流中,而不必对每次字节写入调用底层系统
public class BufferedScreamCopy_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String src1FilePath = "e:\\boji.jpg" ;
String des1FilePath = "d:\\boji.jpg" ;
// 创建对象
BufferedInputStream bis = null ;
BufferedOutputStream bos = null ;
try {
// FileInputStream 是 InputStream 的子类
bis = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(src1FilePath)) ;
bos = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(des1FilePath)) ;
//循环读取文件,并写入到 des1FilePath
byte[] buff = new byte[1024] ;
int readLen = 0 ;
while ((readLen = bis.read(buff)) != -1) {
bos.write(buff, 0, readLen);
}
System.out.println("文件拷贝完毕..");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//关闭流,关闭外层处理流,底层会去关闭节点流{
try {
if( bis != null)
bis.close();
if (bos != null) {
bos.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
2.7 对象流
对象流 – ObjectInputStream 和 ObjectOutputStream
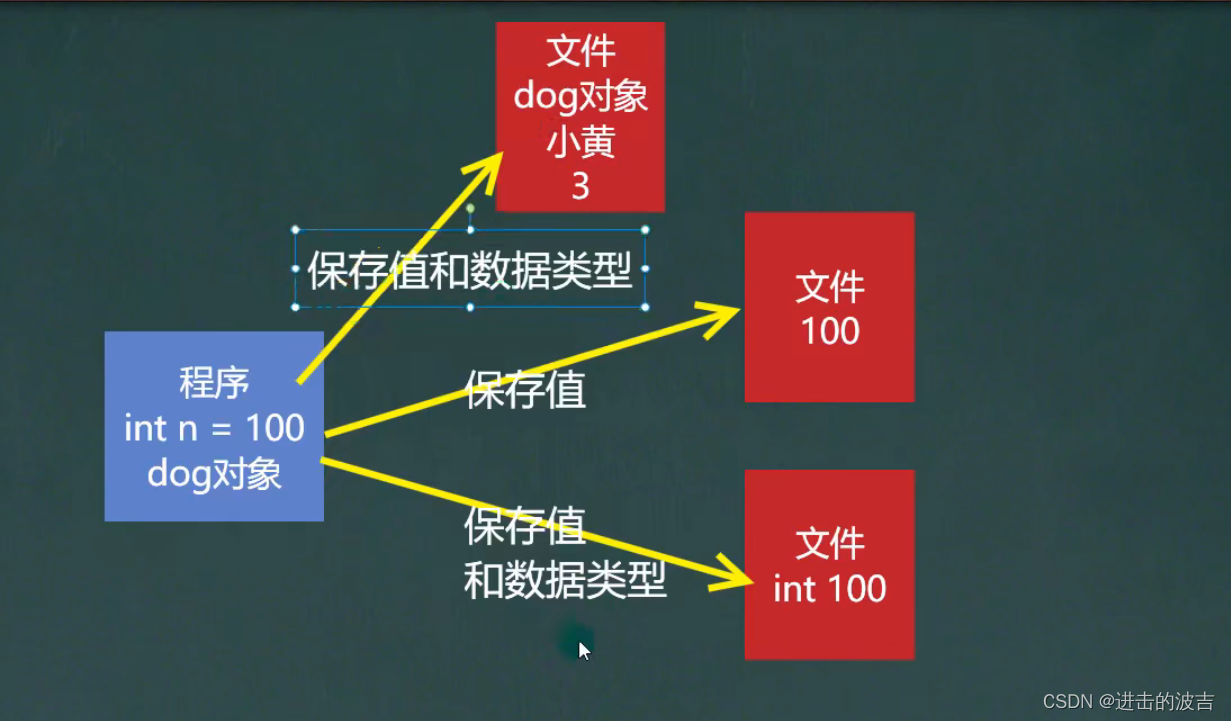
看一个需求
- 将 int num =100 这个int 数据类型保存到文件中,注意不是100数字,而是 int 100 ,并且,能够从文件直接恢复 int 100 ;
- 将 Dog dog = new Dog(“小黄”, 3)这个dog对象保存到文件中,并且能够从从文件中恢复;
- 上面的要求,就是 能够将 基本数据类型 或者对象 进行 序列化 或反序列操作;
2.7.1 序列化 和 反序列化
-
序列化就是保存数据时,保存数据的值和数据类型 ;
-
反序列化就是在恢复数据时,恢复数据的值和类型;
-
需要让某个对象支持序列化机制,则必须让其类是可序列化的,为了让某个类是可序列化的,该类必须实现两个接口之一:
- Serializable // 这是一个标记接口,没有方法
- Exeternalizable //该接口有方法需要实现,因此一般实现上面的 Serializable 接口
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-tMD4Yl8p-1645089741679)(C:\Users\阿桂\AppData\Roaming\Typora\typora-user-images\image-20220209161232527.png)]](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/8e36fdea52cb49f3b2bdd3d7acdf39a9.png?x-oss-process=image/watermark,type_d3F5LXplbmhlaQ,shadow_50,text_Q1NETiBA6L-b5Ye755qE5rOi5ZCJ,size_20,color_FFFFFF,t_70,g_se,x_16)
注意事项
- 读写顺序要一致
- 要求实现序列化和反序列话对象,
需要实现Serialiable - 序列化的类中建议添加 SerialVersionUID,为了提高版本的兼容性;
- 序列化对象时,默认将里面所有的序列化属性进行序列化,但除了static或transient修饰的成员
- 序列化对象时,要求里面属性的类型也需要实现序列化接口
- 序列化具备可继承性,也就是如果某类已经实现了序列化,则他的所有子类也已经默认实现了序列化
public class ObjectInputStream {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//序列化后,保存的文件格式,不是存文本,而是按照他的格式来保存
String filePath = "e:\\data.dat" ;
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(filePath)) ;
//序列化数据到 e:\\data.dat
oos.writeInt(100); ; // int -> Integer (实现了 Serializable)
oos.writeBoolean(true); // boolean -> Boolean
oos.writeChar('a'); // char -> Character
oos.writeDouble(8.5); // double -> Double
oos.writeUTF("niHao"); //String
oos.writeObject(new Dog1("jack", 10));
oos.close();
System.out.println("数据保存完毕(序列化形式)");
}
}
public class ObjectOutputStream {
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception {
//序列化后,保存的文件格式,不是存文本,而是按照他的格式来保存
String filePath = "e:\\data.dat" ;
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(filePath)) ;
//读取
//1.读取(反序列化)的顺序需要和你保存数据(序列化)的顺序一致
//2.否则会出现异常
System.out.println(ois.readInt());
System.out.println(ois.readBoolean());
System.out.println(ois.readChar());
System.out.println(ois.readDouble());
System.out.println(ois.readUTF());
//dog 的编译类型是 Object ,dog 的运行类型是 Dog
Object dog = ois.readObject() ;
System.out.println("运行类型=" + dog.getClass());
System.out.println("dog信息=" + dog); // 底层 Object -> Dog
// 如果需要调用Dog的方法,需要向下转型
//需要我们将Dog类定义,拷贝到引用位置
Dog dog2 = (Dog)dog ;
System.out.println(dog2.getName());
//关闭流,关闭外层流即可,底层会关闭 FIleInputStream 流
ois.close();
}
}