一、Java语言本身也是多线程,回顾Java创建线程方式如下:
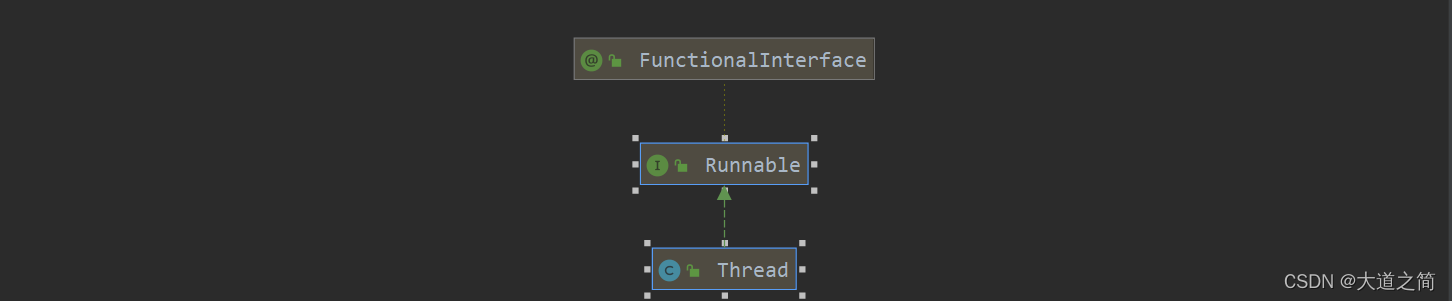
1、继承Thread类,(Thread类实现Runnable接口),来个类图加深印象。
2、实现Runnable接口实现无返回值、实现run()方法,啥时候run,黑话了。
3、实现Callable接口重写call()+FutureTask获取.
public class CustomThread {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 自定义线程
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("Custom Run");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
},"custom-thread-1").start();
}
}
4、基于线程池集中管理创建线程系列周期.【本篇文章重点介绍】
二、JDK线程池工具类.
1、Executors工具类,是JDK中Doug Lea大佬实现供开发者使用。
随着JDK版本迭代逐渐加入了基于工作窃取算法的线程池了,阿里编码规范也推荐开发者自定义线程池,禁止生产直接使用Executos线程池工具类,因此很有可能造成OOM异常。同时在某些类型的线程池里面,使用无界队列还会导致maxinumPoolSize、keepAliveTime、handler等参数失效。因此目前在大厂的开发规范中会强调禁止使用Executors来创建线程池。这里说道阻塞队列。LinkedBlockingQueue。
2、自定义线程池工具类基于ThreadPoolExecutor实现,那个JDK封装的线程池工具类也是基于这个ThreadPoolExecutor实现的。
public class ConstomThreadPool extends ThreadPoolExecutor{
/**
*
* @param corePoolSize 核心线程池
* @param maximumPoolSize 线程池最大数量
* @param keepAliveTime 线程存活时间
* @param unit TimeUnit
* @param workQueue 工作队列,自定义大小
* @param poolName 线程工厂自定义线程名称
*/
public ConstomThreadPool(int corePoolSize, int maximumPoolSize, long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit unit, BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, String poolName) {
super(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue);
setThreadFactory(new CustomThreadFactory(poolName, false));
}
}?自定义线程工厂类,这样线程命名有开发者控制实现了,这样参数可以做到可配置化,生产环境可以供不同业务模块使用,如果系统配置值不生效,就给一个默认值,更加满足业务需要.
/**
* 自定义线程工厂
*/
public class CustomThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory {
/**
* 线程前缀,采用AtomicInteger实现线程编号线程安全自增
*/
private final AtomicInteger atomicInteger = new AtomicInteger(1);
/**
* 线程命名前缀
*/
private final String namePrefix;
/**
* 线程工厂创建的线程是否是守护线程
*/
private final boolean isDaemon;
public CustomThreadFactory(String prefix, boolean daemin) {
if (StringUtils.isNoneBlank(prefix)) {
this.namePrefix = prefix;
} else {
this.namePrefix = "thread_pool";
}
// 是否是守护线程
isDaemon = daemin;
}
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
Thread thread = new Thread(r, namePrefix + "-" + atomicInteger.getAndIncrement());
thread.setDaemon(isDaemon);
// 设置线程优先级
if (thread.getPriority() != Thread.NORM_PRIORITY) {
thread.setPriority(Thread.NORM_PRIORITY);
}
return thread;
}
}?这里Spring框架提供的自定义线程池工厂类,当然了一些开源包也会提供这样的轮子,这个比较简单了.
@SuppressWarnings("serial")
public class CustomizableThreadFactory extends CustomizableThreadCreator implements ThreadFactory {
/**
* Create a new CustomizableThreadFactory with default thread name prefix.
*/
public CustomizableThreadFactory() {
super();
}
/**
* Create a new CustomizableThreadFactory with the given thread name prefix.
* @param threadNamePrefix the prefix to use for the names of newly created threads
*/
public CustomizableThreadFactory(String threadNamePrefix) {
super(threadNamePrefix);
}
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable runnable) {
return createThread(runnable);
}
}?3、SpringBoot框架提供的自定义线程池,基于异步注解@Async名称和一些业务自定义配置项,很好的实现了业务间线程池的隔离。
@Configuration
public class ThreadPoolConfig {
/**
*
* @return ThreadPoolTaskExecutor
*/
@Bean("serviceTaskA")
public ThreadPoolTaskExecutor serviceTaskA() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
executor.setCorePoolSize(2);
executor.setMaxPoolSize(2);
executor.setQueueCapacity(10);
executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(60);
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("service-a");
executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
return executor;
}
/**
*
* @return ThreadPoolTaskExecutor
*/
@Bean("serviceTaskB")
public ThreadPoolTaskExecutor serviceTaskB() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
executor.setCorePoolSize(2);
executor.setMaxPoolSize(2);
executor.setQueueCapacity(10);
executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(60);
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("service-b");
executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
return executor;
}
}整体来看是Spring框架对JDK的线程池做了封装,公开发者使用,毕竟框架嘛,肯定是把方便留给开发者。
4、并发流线程池。
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(4);
list.add("A");
list.add("B");
list.add("C");
list.add("D");
list.parallelStream().forEach(string -> {
string = string + "paralleStream";
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+":-> "+string);
});运行实例:
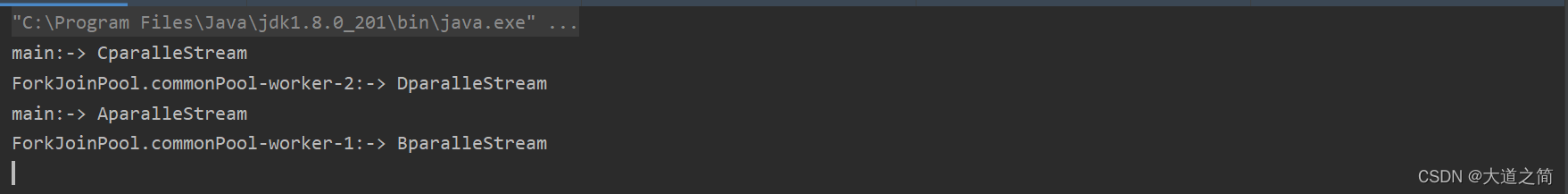
说明:并发流默认使用系统公共的线程池ForkJoinWorkerThread,供整个程序使用。
?类图如下,基于分治法,双端窃取算法实现的一种线程池。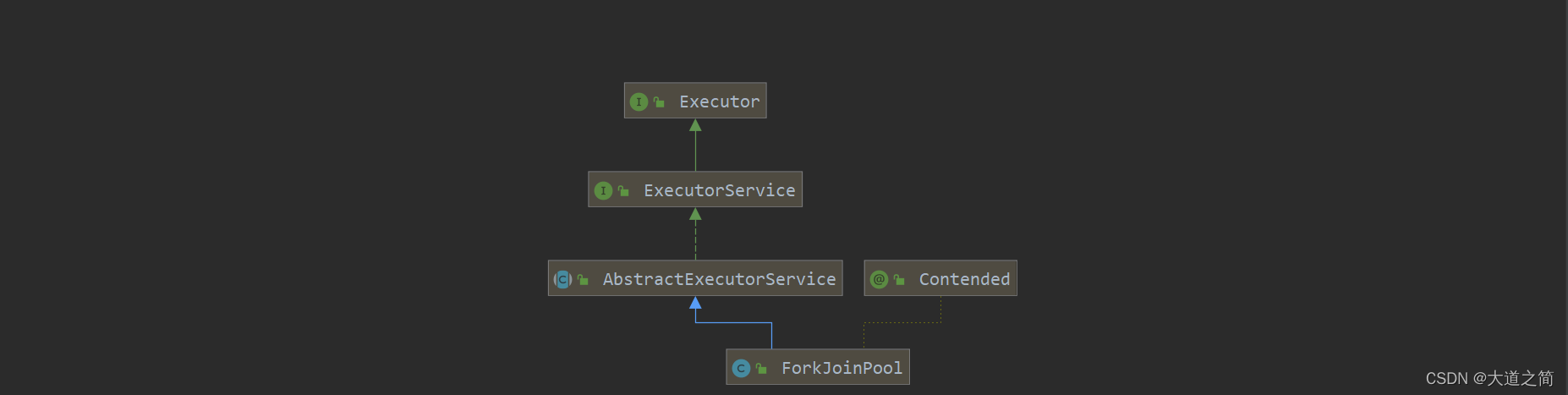
?ForkJoin实现的了自己的线程工厂命名。
 ?也可以自定义并发流线程,然后提交任务,一般并发流适用于短暂耗时业务,避免拖垮整个线程池业务.
?也可以自定义并发流线程,然后提交任务,一般并发流适用于短暂耗时业务,避免拖垮整个线程池业务.
5、实现一个基于系统公用线程池工具类,运行这个系统中的异步业务.
public final class CustomExecutors {
/**
* 核心线程数大小
*/
private static final int CORE_POOL_SIZE=5;
/**
* 核心线程池大小
*/
private static final int MAX_POOL_SIZE=10;
/**
* 线程存活时间
*/
private static final int KEEP_ALIVE_TIME=60;
/**
* 工作队列大小
*/
private static final LinkedBlockingQueue queue=new LinkedBlockingQueue(100);
/**
* 自定义线程池名前缀
*/
private static final String POOL_PREFIX_NAME="Custom-Common-Pool";
private CustomExecutors(){
//throw new XXXXException("un support create pool!");
}
private static ConstomThreadPool constomThreadPool;
/**
* 静态块初始化只执行一次,不关闭,整个系统公用一个线程池
*/
static {
constomThreadPool=new ConstomThreadPool(CORE_POOL_SIZE,MAX_POOL_SIZE,KEEP_ALIVE_TIME,TimeUnit.SECONDS,queue,POOL_PREFIX_NAME);
}
/**
* 单例模式获取线程池
* @return ExecutorService
*/
private static ExecutorService getInstance(){
return constomThreadPool;
}
private static Future<?> submit(Runnable task){
return constomThreadPool.submit(task);
}
private static <T> Future<T> submit(Runnable task, T result){
return constomThreadPool.submit(task,result);
}
private static <T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task){
return constomThreadPool.submit(task);
}
private static void execute(Runnable task){
constomThreadPool.execute(task);
}
}三、业界知名自定义线程池扩展使用.
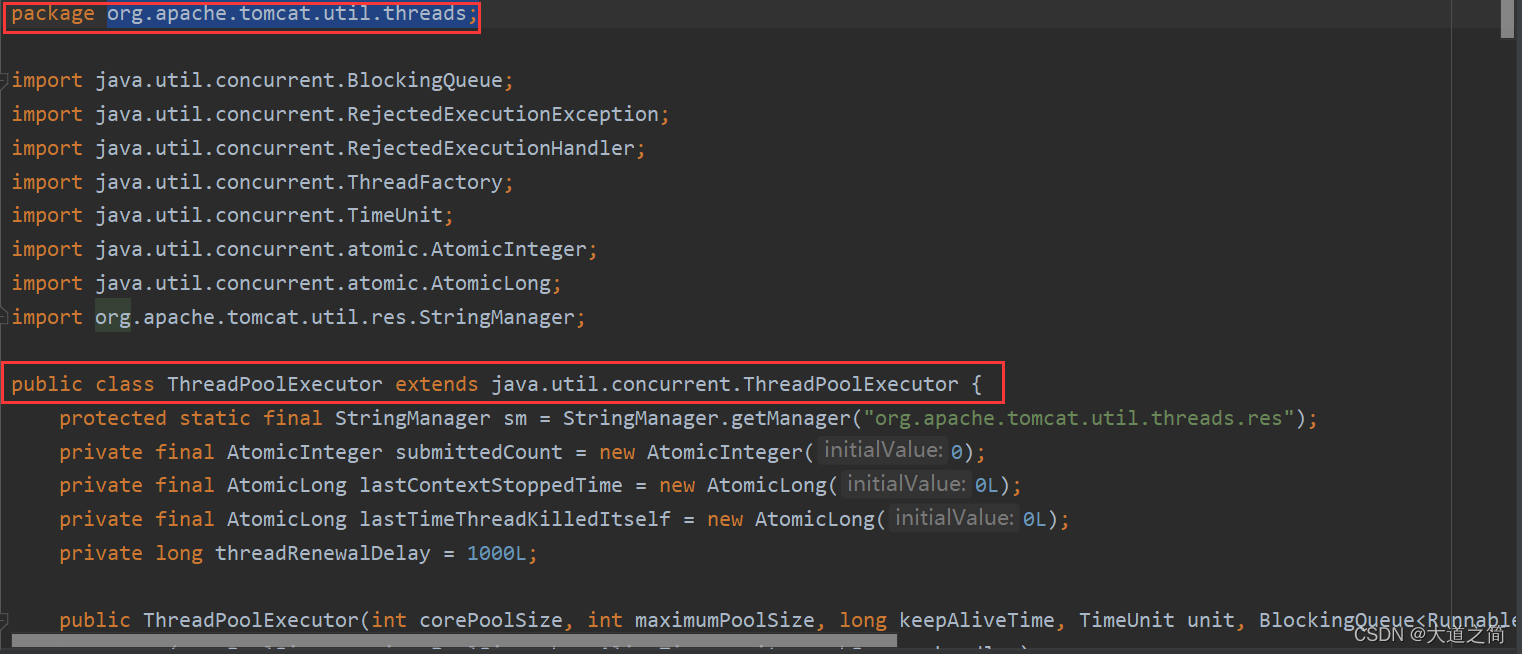
1、org.apache.tomcat.util.threads;【Tomcat线程池】
?2、XXL-JOB分布式任务调度框架的快慢线程池,线程池任务隔离.
public class JobTriggerPoolHelper {
private static Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(JobTriggerPoolHelper.class);
// ---------------------- trigger pool ----------------------
// fast/slow thread pool
private ThreadPoolExecutor fastTriggerPool = null;
private ThreadPoolExecutor slowTriggerPool = null;
public void start(){
fastTriggerPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
10,
XxlJobAdminConfig.getAdminConfig().getTriggerPoolFastMax(),
60L,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(1000),
new ThreadFactory() {
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
return new Thread(r, "xxl-job, admin JobTriggerPoolHelper-fastTriggerPool-" + r.hashCode());
}
});
slowTriggerPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
10,
XxlJobAdminConfig.getAdminConfig().getTriggerPoolSlowMax(),
60L,
TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>(2000),
new ThreadFactory() {
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r) {
return new Thread(r, "xxl-job, admin JobTriggerPoolHelper-slowTriggerPool-" + r.hashCode());
}
});
}
public void stop() {
//triggerPool.shutdown();
fastTriggerPool.shutdownNow();
slowTriggerPool.shutdownNow();
logger.info(">>>>>>>>> xxl-job trigger thread pool shutdown success.");
}
// job timeout count
private volatile long minTim = System.currentTimeMillis()/60000; // ms > min
private volatile ConcurrentMap<Integer, AtomicInteger> jobTimeoutCountMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**
* add trigger
*/
public void addTrigger(final int jobId,
final TriggerTypeEnum triggerType,
final int failRetryCount,
final String executorShardingParam,
final String executorParam,
final String addressList) {
// choose thread pool
ThreadPoolExecutor triggerPool_ = fastTriggerPool;
AtomicInteger jobTimeoutCount = jobTimeoutCountMap.get(jobId);
if (jobTimeoutCount!=null && jobTimeoutCount.get() > 10) { // job-timeout 10 times in 1 min
triggerPool_ = slowTriggerPool;
}
// trigger
triggerPool_.execute(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// do trigger
XxlJobTrigger.trigger(jobId, triggerType, failRetryCount, executorShardingParam, executorParam, addressList);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error(e.getMessage(), e);
} finally {
// check timeout-count-map
long minTim_now = System.currentTimeMillis()/60000;
if (minTim != minTim_now) {
minTim = minTim_now;
jobTimeoutCountMap.clear();
}
// incr timeout-count-map
long cost = System.currentTimeMillis()-start;
if (cost > 500) { // ob-timeout threshold 500ms
AtomicInteger timeoutCount = jobTimeoutCountMap.putIfAbsent(jobId, new AtomicInteger(1));
if (timeoutCount != null) {
timeoutCount.incrementAndGet();
}
}
}
}
});
}
// ---------------------- helper ----------------------
private static JobTriggerPoolHelper helper = new JobTriggerPoolHelper();
public static void toStart() {
helper.start();
}
public static void toStop() {
helper.stop();
}
/**
* @param jobId
* @param triggerType
* @param failRetryCount
* >=0: use this param
* <0: use param from job info config
* @param executorShardingParam
* @param executorParam
* null: use job param
* not null: cover job param
*/
public static void trigger(int jobId, TriggerTypeEnum triggerType, int failRetryCount, String executorShardingParam, String executorParam, String addressList) {
helper.addTrigger(jobId, triggerType, failRetryCount, executorShardingParam, executorParam, addressList);
}
}①、定义两个线程池,一个是fastTriggerPool,另一个是slowTriggerPool。
②、定义一个容器ConcurrentMap,存放每个任务的执行慢次数,60秒后自动清空该容器。
③、在线程的run()方法中计算每个任务的耗时,如果大于500ms,则任务的慢执行次数+1。
?3、基于线程池动态监控动态线程池?
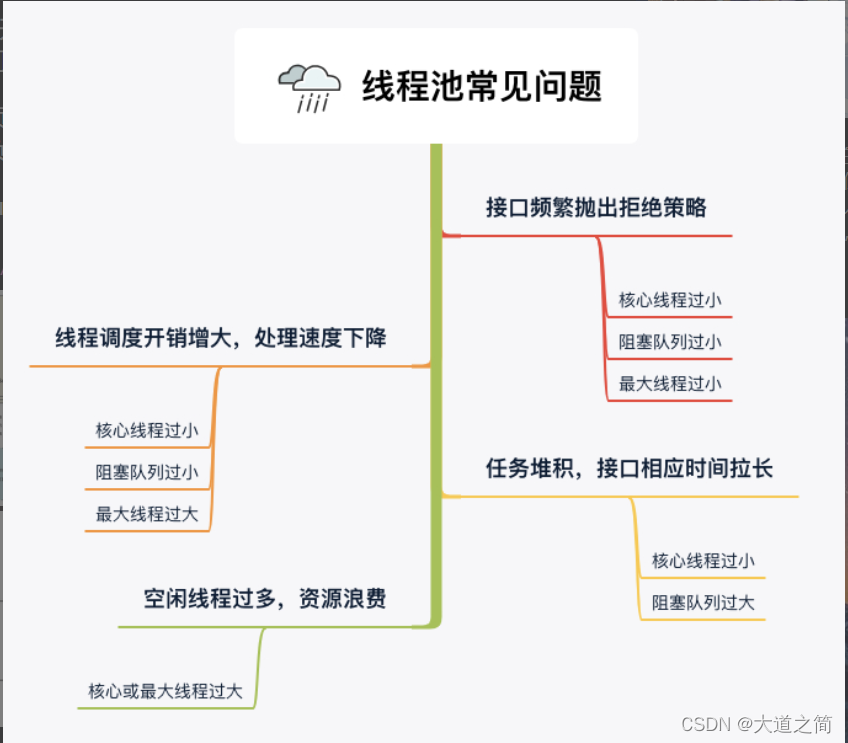
引用图片,线程池常见问题
?4、ES线程池.
ES的并发工具包,org.elasticsearch.common.util.concurrent,es的线程池配置在elasticsearch.yml中配置.
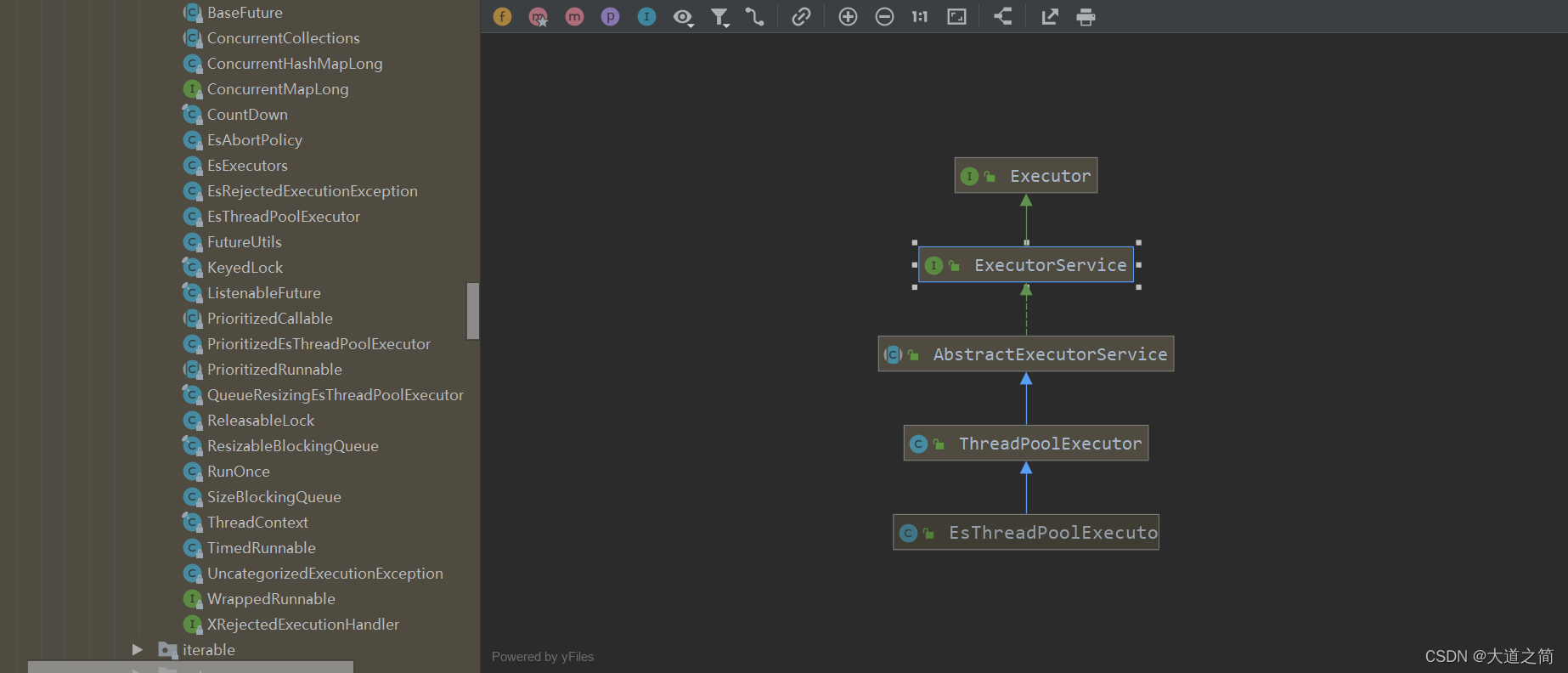
?ES中的线程池类型,ThreadPoolType:?
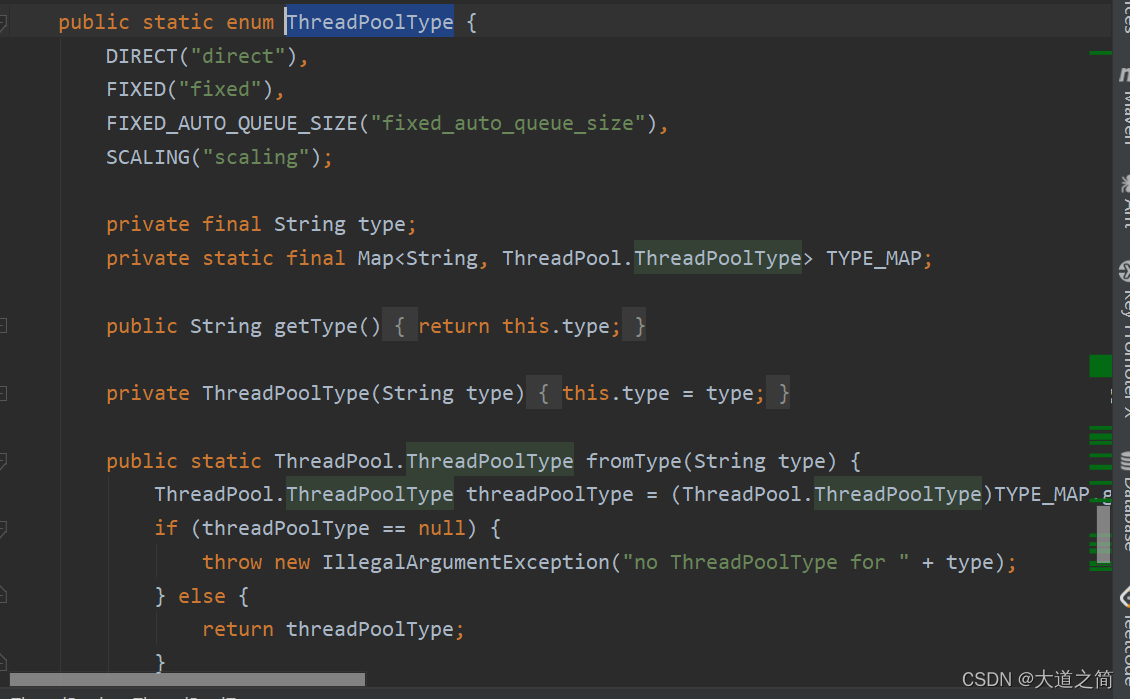
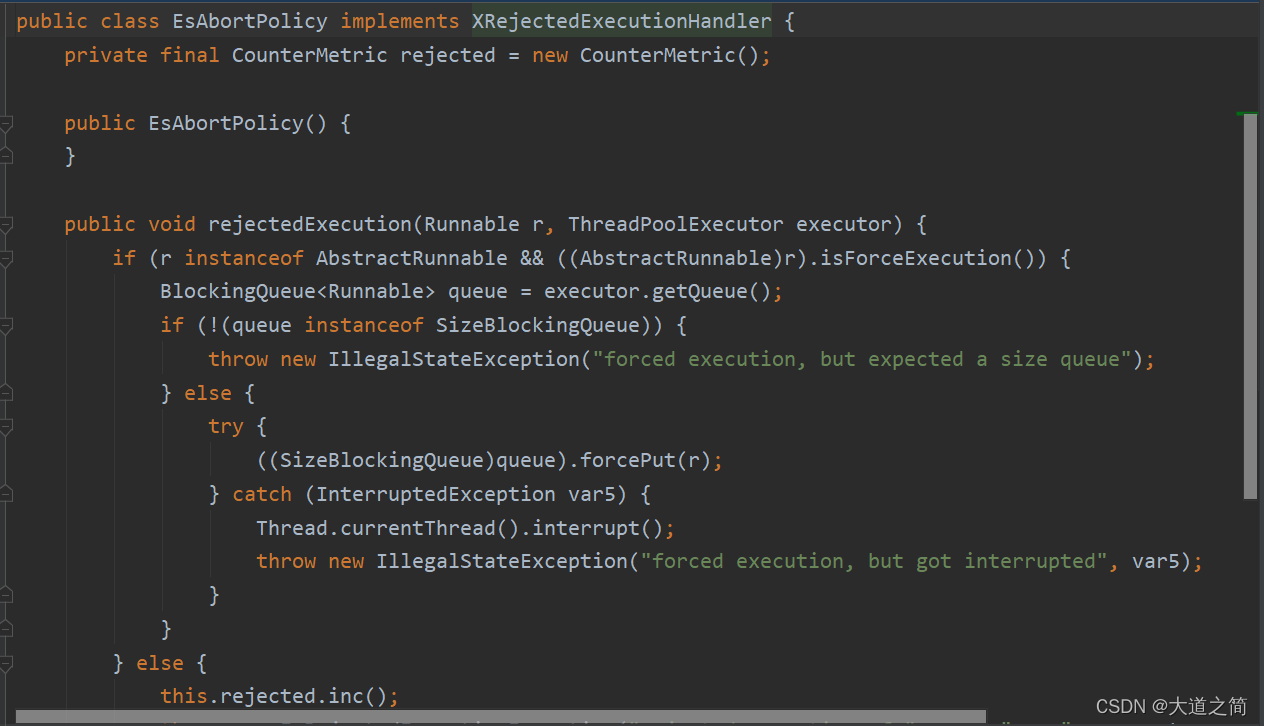
ES自定义线程池拒绝策略:
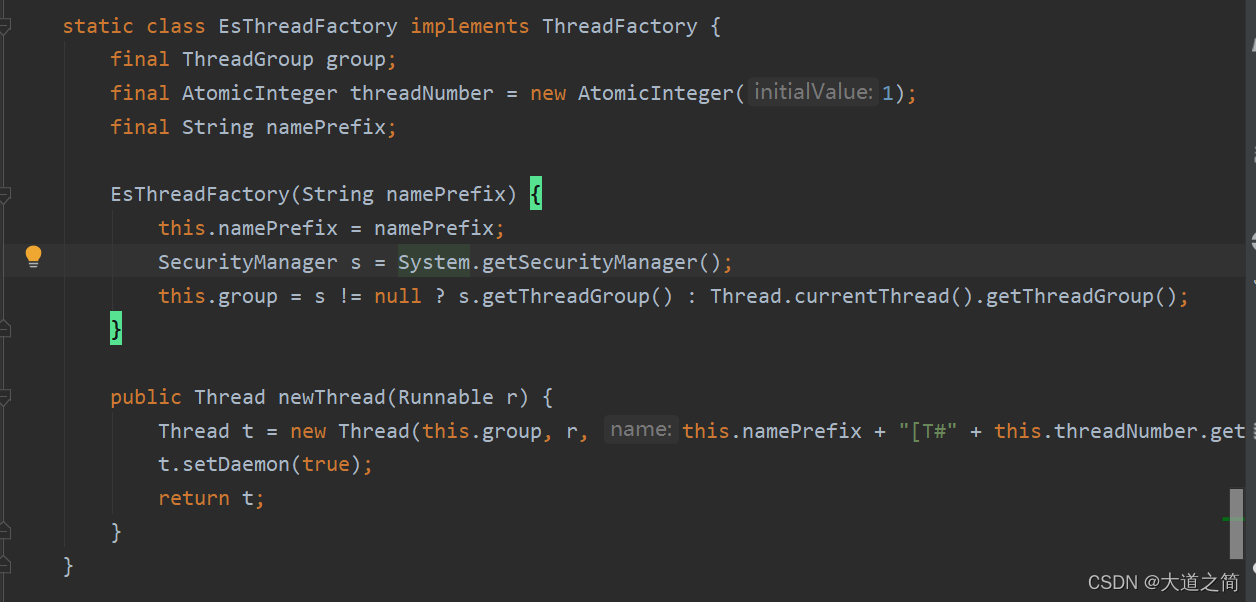
?ES自定义线程池命名:
?如创建索引、查询、bulk写入等都有指定的默认线程池大小的,如果使用云服务可以在租户concole配置,生产可以配置search队列和write对列值告警,方便监控ES。
本文主要介绍Java如何自定义线程池,并介绍了一些知名中间件是如何自定义线程池使用的,方便扩展我们的视野,加深我们对线程池的理解,更好的应用到实战项目中。