?当一个类运行需要调用一个成员对象,成员对象也是被容器类托管的类对象时,则可以用依赖注入创建成员对象。让容器类来帮你创建成员对象。
?官网链接:Annotation-based Container Configuration
?前置:
?容器类AppConfig
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan
public class AppConfig {
}
?创建一个接口Hello
public interface Hello {
void HelloWorld();
}
?创建一个类HelloImpl1实现接口Hello。并且被容器托管
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class HelloImpl1 implements Hello{
@Override
public void HelloWorld() {
System.out.println("HelloWorld1");
}
}
一、@Autowired注解
?在声明成员变量上加上@Autowires注解。让容器来帮忙创建对象。该成员变量也必须被容器类托管。
?创建MyHello类,里面有Hello成员对象。如下所示:
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MyHello {
@Autowired
Hello h;
void say(){
h.HelloWorld();
}
}
?如果不加@Autowired运行say()会报错。
?进行测试:
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ac = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
MyHello mh = ac.getBean("myHello",MyHello.class);
mh.say();
}
}
?运行结果:
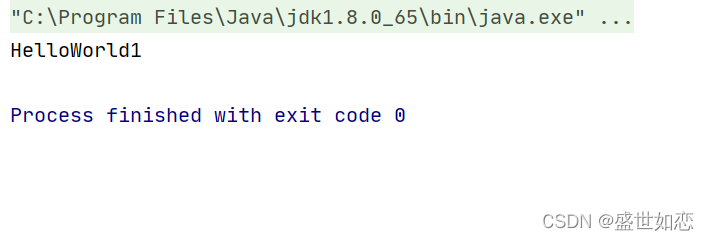
?如果成员对象是接口,并且有多个实现类。则需要使用@Qualifier或者@Primary注解。
?在创建一个类实现Hello接口。
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class HelloImol2 implements Hello{
@Override
public void HelloWorld() {
System.out.println("HelloWorld2");
}
}
?这时,Hello接口有两个实现类。
?再次运行Test类,报错。因为调用类有冲突。

?解决方案有两种。
@Qualifier
?在@Autowired下加入@Qualifier(value="id名") 。id名默认是类名且首字母小写。要指定是调用实现接口中的哪个类。
?如上述解决:
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class MyHello {
@Autowired
@Qualifier(value="helloImpl1") //添加此注解
Hello h;
void say(){
h.HelloWorld();
}
}
@Primary
?在想要用到的多个实现接口对象中的其中一个类,加上@Primary注解
?如: 我想通过Hello运行HelloImpl1。则在HelloImpl加上@Primary注解:
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Primary;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
@Primary
public class HelloImpl1 implements Hello{
@Override
public void HelloWorld() {
System.out.println("HelloWorld1");
}
}
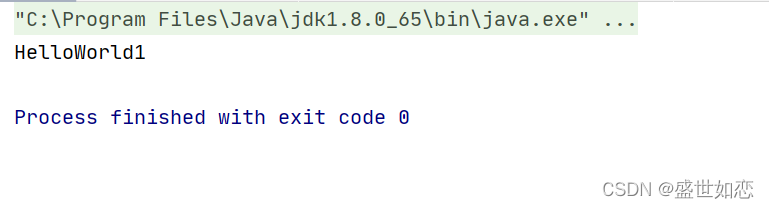
?Test类运行成功

二、@Resource注解
?在成员对象上加入@Resource(name="id名") id名为你想要调用这个接口中实现的哪个类的类名且首字母小写。
?则上述的MyHello类可写成:
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@Component
public class MyHello {
@Resource(name="helloImpl1")
Hello h;
void say(){
h.HelloWorld();
}
}
?运行Test类

三、@Inject 和 @Named注解
?使用这两个注解需要导入坐标。在pom.xml加入
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.inject</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.inject</artifactId>
<version>1</version>
</dependency>
?两个注解一起用在需要创建成员对象上。其中@Named("id名")id名为你想要调用这个接口中实现的哪个类的类名且首字母小写。
?则上述的MyHello类可以修改为:
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import javax.inject.Inject;
import javax.inject.Named;
@Component
public class MyHello {
@Inject
@Named("helloImpl1")
Hello h;
void say(){
h.HelloWorld();
}
}
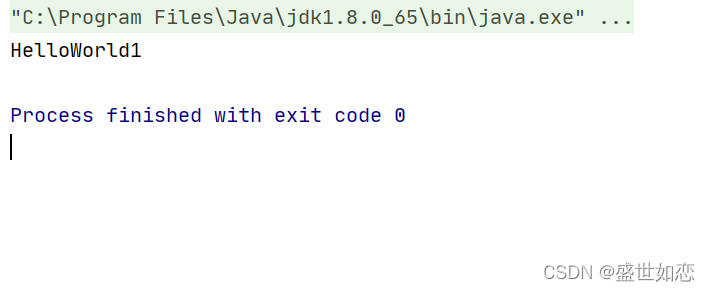
?继续运行Test类,仍然可以运行成功
?上述也可以实现set方法的依赖注入,需要保证传入的参数被容器托管。