
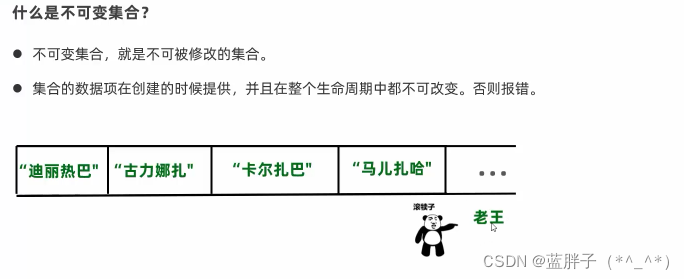
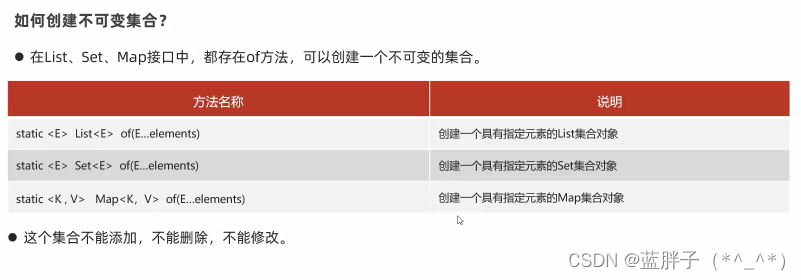
创建不可变集合

?
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 不可变的List集合
List<Double> lists = List.of(569.5 ,700.5 ,523.0 ,570.4);
// lists.add(689.5); // 异常
// lists.set(2, 100.2); // 异常
System.out.println(lists);
// 不可变的Set集合
Set<String> names = Set.of("张三" ,"李四");
// names.add("王麻子"); // 异常
System.out.println(names);
// 不可变的Map集合
Map<String, Integer> maps = Map.of("华为",2 ,"Java" ,1);
// maps.put("苹果",3); // 异常
System.out.println(maps);
}
}Stream流
Stream流的概述

public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> names = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(names, "张三", "李四", "张麻子");
System.out.println(names);
// 找出姓张的放到新集合
List<String> zhang = new ArrayList<>();
for (String name : names) {
if (name.startsWith("张")) {
zhang.add(name);
}
}
System.out.println(zhang);
// 找名称长度为3的姓名
List<String> three = new ArrayList<>();
for (String name : names) {
if (name.length() == 3) {
three.add(name);
}
}
System.out.println(three);
}
}/**
* 使用Stream实现
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> names = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(names, "张三", "李四", "张麻子");
System.out.println(names);
names.stream().filter(s -> s.startsWith("张") && s.length() == 3).forEach(s -> System.out.println(s));
}
}

Stream流的获取

?
/**
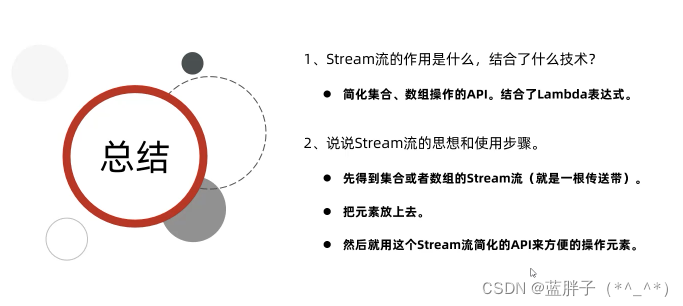
目标:Stream流的获取
Stream流式思想的核心:
是先得到集合或者数组的Stream流(就是一根传送带)
然后就用这个Stream流操作集合或者数组的元素。
然后用Stream流简化替代集合操作的API.
集合获取流的API:
(1) default Stream<E> stream();
小结:
集合获取Stream流用: stream();
数组:Arrays.stream(数组) / Stream.of(数组);
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/** --------------------Collection集合获取流------------------------------- */
Collection<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
Stream<String> s = list.stream();
/** --------------------Map集合获取流------------------------------- */
Map<String ,Integer> maps = new HashMap<>();
// 键流
Stream<String> keyStream = maps.keySet().stream();
// 值流
Stream<Integer> valueStream = maps.values().stream();
// 键值对(拿整体)
Stream<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> keyValueStream = maps.entrySet().stream();
/** ---------------------数组获取流------------------------------ */
String[] names = {"赵敏","小昭","灭绝","周芷若"};
Stream<String> nameStream = Arrays.stream(names);
Stream<String> nameStream2 = Stream.of(names);
}
}?
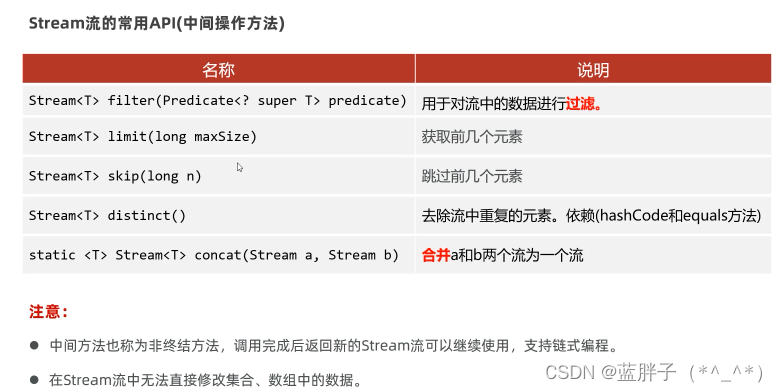
Stream流的常用API(中间操作方法)
?
/**
目标:Stream流的常用API
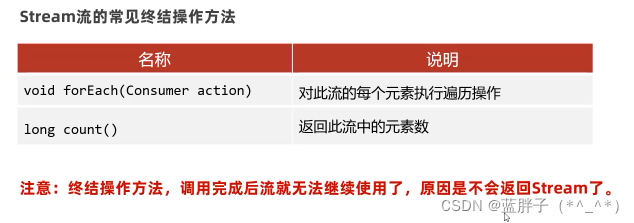
forEach : 逐一处理(遍历)
count:统计个数
-- long count();
filter : 过滤元素
-- Stream<T> filter(Predicate<? super T> predicate)
limit : 取前几个元素
skip : 跳过前几个
map : 加工方法
concat : 合并流。
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list,"张无忌" ,"周芷若" ,"赵敏" ,"张强" ,"张三丰" ,"张三丰");
// Stream<T> filter(Predicate<? super T> predicate)
list.stream().filter( s -> s.startsWith("张")).forEach(s -> System.out.println(s));
long size = list.stream().filter(s -> s.length() == 3).count();
System.err.println(size);
list.stream().filter( s -> s.startsWith("张")).limit(2).forEach(s -> System.out.println(s));
list.stream().filter( s -> s.startsWith("张")).skip(2).forEach(s -> System.out.println(s));
// map加工方法: 第一个参数原材料 -> 第二个参数是加工后的结果。
// 给集合元素的前面都加上一个:隔壁老王的:
list.stream().map(s -> "隔壁老王的" + s).forEach(s -> System.out.println(s));
// 需求:把所有的名称 都加工成一个学生对象。
list.stream().map(s -> new Student(s)).forEach(s -> System.out.println(s));
// 合并流。
Stream<String> s1 = list.stream().filter(s -> s.startsWith("张"));
Stream<String> s2 = Stream.of("Java1" ,"Java2");
Stream<String> s3 = Stream.concat(s1, s2);
s3.forEach(s -> System.out.println(s));
}
}
Stream流的综合应用

public class Topperformer {
private String name;
private double money; // 月薪
public Topperformer() {
}
public Topperformer(String name, double money) {
this.name = name;
this.money = money;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getMoney() {
return money;
}
public void setMoney(double money) {
this.money = money;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Topperformer{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", money=" + money +
'}';
}
}public class Employee {
private String name;
private char sex;
private double salary;
private double bonus;
private String punish; // 处罚信息
public Employee(){
}
public Employee(String name, char sex, double salary, double bonus, String punish) {
this.name = name;
this.sex = sex;
this.salary = salary;
this.bonus = bonus;
this.punish = punish;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public char getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(char sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
public double getSalary() {
return salary;
}
public void setSalary(double salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
public double getBonus() {
return bonus;
}
public void setBonus(double bonus) {
this.bonus = bonus;
}
public String getPunish() {
return punish;
}
public void setPunish(String punish) {
this.punish = punish;
}
public double getTotalSalay(){
return salary * 12 + bonus;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Employee{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", sex=" + sex +
", salary=" + salary +
", bonus=" + bonus +
", punish='" + punish + '\'' +
'}'+"\n";
}
}public class Test {
public static double allMoneyone = 0;
public static double allMoneytwo = 0;
public static double allMoneythree = 0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Employee> one = new ArrayList<>();
one.add(new Employee("猪八戒",'男',30000 , 25000, null));
one.add(new Employee("孙悟空",'男',25000 , 1000, "顶撞上司"));
one.add(new Employee("沙僧",'男',20000 , 20000, null));
one.add(new Employee("小白龙",'男',20000 , 25000, null));
List<Employee> two = new ArrayList<>();
two.add(new Employee("武松",'男',15000 , 9000, null));
two.add(new Employee("李逵",'男',20000 , 10000, null));
two.add(new Employee("西门庆",'男',50000 , 100000, "被打"));
two.add(new Employee("潘金莲",'女',3500 , 1000, "被打"));
two.add(new Employee("武大郎",'女',20000 , 0, "下毒"));
// 1. 开发一部的最高工资的员工
// 指定大小规则了
// Employee e = one.stream().max(( o1, o2) -> Double.compare((o1.getSalary() + o1.getBonus()), (o2.getSalary() + o2.getBonus())))
// .get();
// System.out.println(e);
Topperformer t = one.stream().max(( o1, o2) -> Double.compare((o1.getSalary() + o1.getBonus()), (o2.getSalary() + o2.getBonus())))
.map(e -> new Topperformer(e.getName(),e.getSalary() + e.getBonus())).get();
System.out.println(t);
// 2. 分别统计2个部门的平均月收入,去掉最高最低工资
one.stream().sorted(( e1, e2) -> Double.compare((e1.getSalary() + e1.getBonus()),(e2.getSalary() + e2.getBonus())))
.skip(1).limit(one.size() - 2).forEach(e -> {
// 求出总和,剩余员工的工资总和
allMoneyone += (e.getBonus() + e.getSalary());
});
two.stream().sorted(( e1, e2) -> Double.compare((e1.getSalary() + e1.getBonus()),(e2.getSalary() + e2.getBonus())))
.skip(1).limit(one.size() - 2).forEach(e -> {
// 求出总和,剩余员工的工资总和
allMoneytwo += (e.getBonus() + e.getSalary());
});
System.out.println("开发第一部的平均工资是:" + allMoneyone / (one.size() - 2));
System.out.println("开发第二部的平均工资是:" + allMoneytwo / (one.size() - 2));
// 合并两个集合,再统计
Stream<Employee> s1 = one.stream();
Stream<Employee> s2 = two.stream();
Stream<Employee> s3 = Stream.concat(s1, s2);
s3.sorted(( e1, e2) -> Double.compare((e1.getSalary() + e1.getBonus()),(e2.getSalary() + e2.getBonus())))
.skip(1).limit(one.size() + two.size() - 2).forEach(e -> {
// 求出总和,剩余员工的工资总和
allMoneythree += (e.getBonus() + e.getSalary());
});
BigDecimal a = BigDecimal.valueOf(allMoneythree);
BigDecimal b = BigDecimal.valueOf((one.size() + two.size()) - 2);
System.out.println("开发部的平均工资是:" + (a.divide(b,2, RoundingMode.HALF_UP)));
}
}收集Stream流


public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list,"张无忌" ,"周芷若" ,"赵敏" ,"张强" ,"张三丰" ,"张三丰");
Stream<String> s1 = list.stream().filter(s -> s.startsWith("张"));
// List<String> zhang = s1.collect(Collectors.toList());
// System.out.println(zhang);
// 注意:流只能使用一次
// Set<String> zhang2 = s1.collect(Collectors.toSet());
// System.out.println(zhang2);
// Object[] arrs = s1.toArray();
// String[] arrs = s1.toArray((value) -> new String[value]);
String[] arrs = s1.toArray(String[] :: new);
System.out.println("Arrays数组内容:" + Arrays.toString(arrs));
}
}?
异常处理
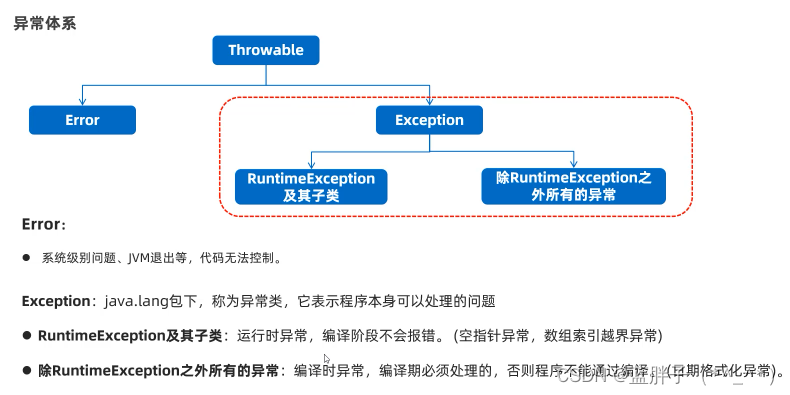
异常概述、体系

?
?

常见运行时异常

public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("程序开始。。。。。。");
/** 1.数组索引越界异常: ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException。*/
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3};
System.out.println(arr[2]);
// System.out.println(arr[3]); // 运行出错,程序终止
/** 2.空指针异常 : NullPointerException。直接输出没有问题。但是调用空指针的变量的功能就会报错!! */
String name = null;
System.out.println(name); // null
// System.out.println(name.length()); // 运行出错,程序终止
/** 3.类型转换异常:ClassCastException。 */
Object o = 23;
// String s = (String) o; // 运行出错,程序终止
/** 5.数学操作异常:ArithmeticException。 */
//int c = 10 / 0;
/** 6.数字转换异常: NumberFormatException。 */
//String number = "23";
String number = "23aabbc";
Integer it = Integer.valueOf(number); // 运行出错,程序终止
System.out.println(it + 1);
System.out.println("程序结束。。。。。");
}
}常见编译时异常
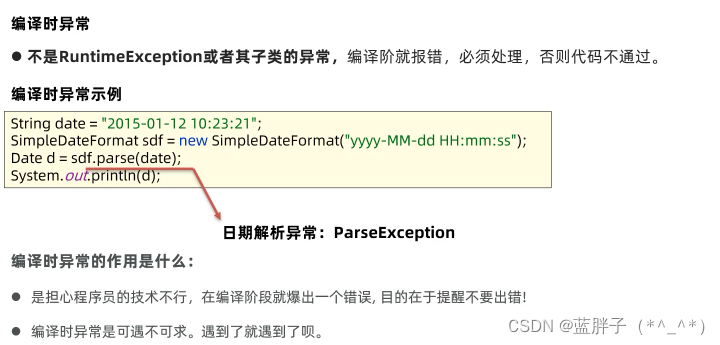
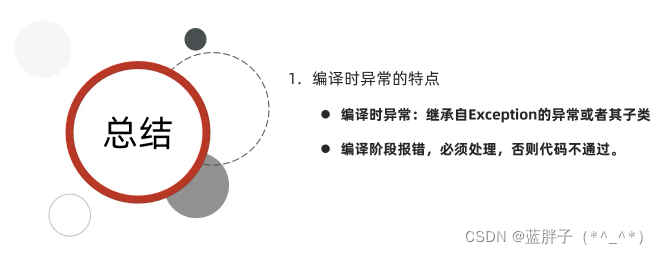
异常的默认处理流程


编译时异常的处理机制


public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("程序开始。。。。。");
parseTime("2011-11-11 11:11:11");
System.out.println("程序结束。。。。。");
}
public static void parseTime(String date) throws Exception {
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
Date d = sdf.parse(date);
System.out.println(d);
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("程序开始。。。。。");
parseTime("2011-11-11 11:11:11");
System.out.println("程序结束。。。。。");
}
public static void parseTime(String date) {
// ctrl + alt + t
try {
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy/MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
Date d = sdf.parse(date);
System.out.println(d);
} catch (Exception e) {
// 解析出现问题
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}?
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
System.out.println("程序开始。。。。。");
// ctrl + alt + t
try {
parseTime("2011-11-11 11:11:11");
System.out.println("成功");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("程序结束。。。。。");
}
public static void parseTime(String date) throws Exception{
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
Date d = sdf.parse(date);
System.out.println(d);
}
}
运行时异常的处理机制

public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("开始");
try {
chu(10 ,0);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("结束");
}
public static void chu(int a ,int b) {
int c = a / b;
System.out.println(c);
}
}异常处理使代码更稳健的案例

public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while (true) {
try {
System.out.println("输入价格");
String priceStr = sc.nextLine();
// 装换成Double类型
double price = Double.valueOf(priceStr);
// 判断价格是否大于0
if (price > 0) {
System.out.println("定价" + price);
break;
} else {
System.out.println("价格必须为正数");
}
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("输入数据有误");
}
}
}
}自定义异常
?
?
 ??
??
/**
* 自定义的编译时异常
* 1. 继承Exception
* 2. 重写构造器
*/
public class myException extends Exception {
public myException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
checkAge(-2);
} catch (myException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void checkAge(int age) throws myException {
if (age <= 0) {
// 抛出去一个异常对象给调用者
// throw :在方法内部直接创建一个异常对象,并从此点抛出
// throws : 用在方法申明上的,抛出方法内部的异常
throw new myException(age + "的年龄非法");
}else {
System.out.println("年龄正确");
}
}
}/**
* 自定义的运行时异常
* 1. RuntimeException
* 2. 重写构造器
*/
public class myException extends RuntimeException {
public myException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
checkAge(-2);
}
public static void checkAge(int age) {
if (age <= 0) {
// 抛出去一个异常对象给调用者
// throw :在方法内部直接创建一个异常对象,并从此点抛出
// throws : 用在方法申明上的,抛出方法内部的异常
throw new myException(age + "的年龄非法");
} else {
System.out.println("年龄正确");
}
}
}