第八章 - 共享模型之JUC
AQS 原理
概述
全称是 AbstractQueuedSynchronizer,是阻塞式锁和相关的同步器工具的框架
特点:
- 用
state属性来表示资源的状态(分独占模式和共享模式),子类需要定义如何维护这个状态,控制如何获取锁和释放锁getState- 获取 state 状态setState- 设置 state 状态compareAndSetState- CAS 机制设置 state 状态独占模式是只有一个线程能够访问资源,而共享模式可以允许多个线程访问资源
- 提供了基于 FIFO (先进先出) 的等待队列,类似于 Monitor 的
EntryList - 条件变量来实现
等待、唤醒机制,支持多个条件变量,类似于 Monitor 的WaitSet
子类主要实现这样一些方法(默认抛出
UnsupportedOperationException)
tryAcquiretryReleasetryAcquireSharedtryReleaseSharedisHeldExclusively
获取锁的姿势
// 如果获取锁失败
if (!tryAcquire(arg)) {
// 入队, 可以选择阻塞当前线程 park unpark
}
获取锁的姿势
// 如果释放锁成功
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
// 让阻塞线程恢复运行
}
实现不可重入锁
下面实现一个不可重入的阻塞式锁:使用
AbstractQueuedSynchronizer自定义一个同步器来实现自定义锁!
/**
* @author xiexu
* @date 2022/2/14 10:52
*/
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestAQS")
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class TestAqs {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLock lock = new MyLock();
new Thread(() -> {
lock.lock();
try {
log.debug("locking...");
Sleeper.sleep(2);
} finally {
log.debug("unlocking...");
lock.unlock();
}
}, "t1").start();
new Thread(() -> {
lock.lock();
try {
log.debug("locking...");
} finally {
log.debug("unlocking...");
lock.unlock();
}
}, "t2").start();
}
}
// 自定义锁(不可重入锁)
class MyLock implements Lock {
// 独占锁 同步器类
class MySync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
@Override // 尝试获取锁
protected boolean tryAcquire(int arg) {
// 确保原子性,如果当前State是0,就将其设置为1,表示获得了锁
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1)) {
// 加上了锁,并设置 owner 为当前线程
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
return true; // 成功获取到锁返回true
}
// 返回false表示加锁失败
return false;
}
@Override // 尝试释放锁
protected boolean tryRelease(int arg) {
// 这里不需要确定原子性, 因为是持锁者进行释放
// 把setExclusiveOwnerThread(null)放在setState(0)前面, 是为了防止指令重排序带来的问题
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null); // 表示没有线程占用
setState(0); // state是volatile修饰的, 在setState(0)前面的属性修改, 对于其他线程也是可见的, 具体见volatile原理(写屏障)
return true;
}
@Override // 是否持有独占锁
protected boolean isHeldExclusively() {
return getState() == 1;
}
// 创建条件变量
public Condition newCondition() {
return new ConditionObject();
}
}
// 同步器类对象
private MySync sync = new MySync();
@Override // 加锁(不成功会进入等待队列)
public void lock() {
sync.acquire(1);
}
@Override // 加锁,可打断
public void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException {
sync.acquireInterruptibly(1);
}
@Override // 尝试加锁(尝试一次)
public boolean tryLock() {
return sync.tryAcquire(1);
}
@Override // 尝试加锁(带超时)
public boolean tryLock(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
return sync.tryAcquireNanos(1, unit.toNanos(time));
}
@Override // 解锁
public void unlock() {
sync.release(1);
}
@Override // 创建条件变量
public Condition newCondition() {
return sync.newCondition();
}
}
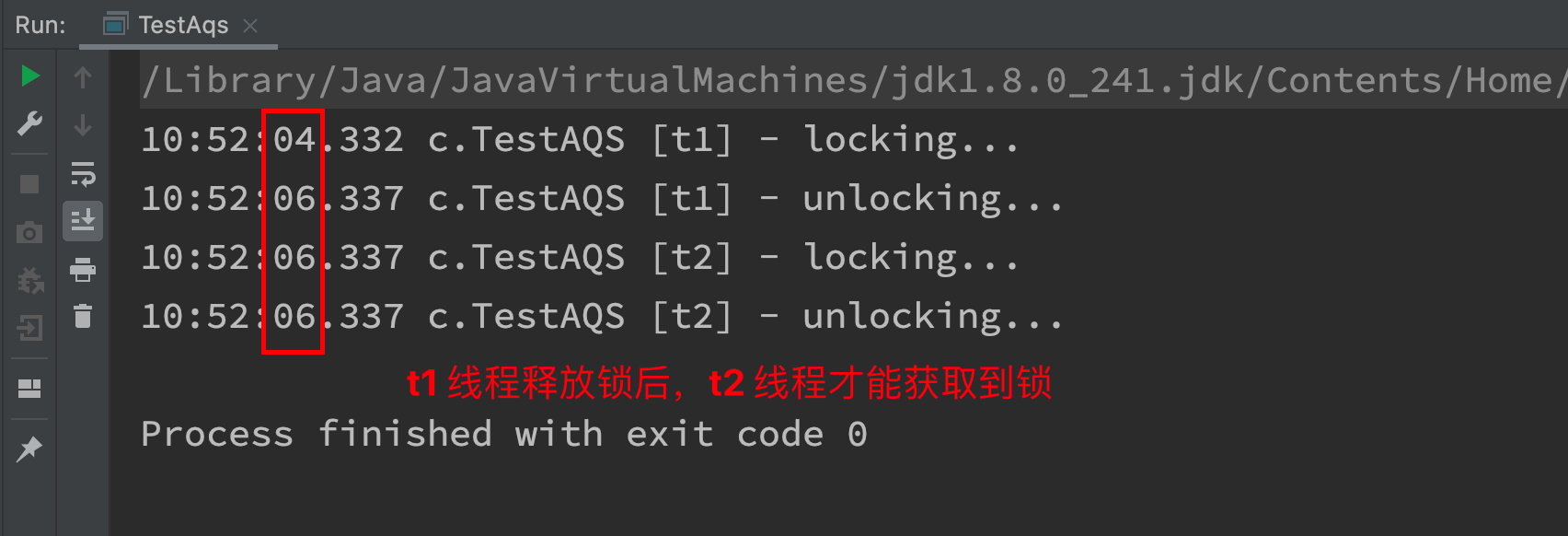
不可重入测试
- 如果改为下面代码,会发现自己也会被挡住(只会打印一次 locking)
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyLock lock = new MyLock();
new Thread(() -> {
lock.lock();
log.debug("locking...");
// 不可重入锁, 同一线程在锁释放前, 只能加一次锁
lock.lock();
log.debug("locking...");
try {
log.debug("locking...");
Sleeper.sleep(2);
} finally {
log.debug("unlocking...");
lock.unlock();
}
}, "t1").start();
}
ReentrantLock 原理
- ReentrantLock提供了两个同步器,实现
公平锁和非公平锁,默认是非公平锁!
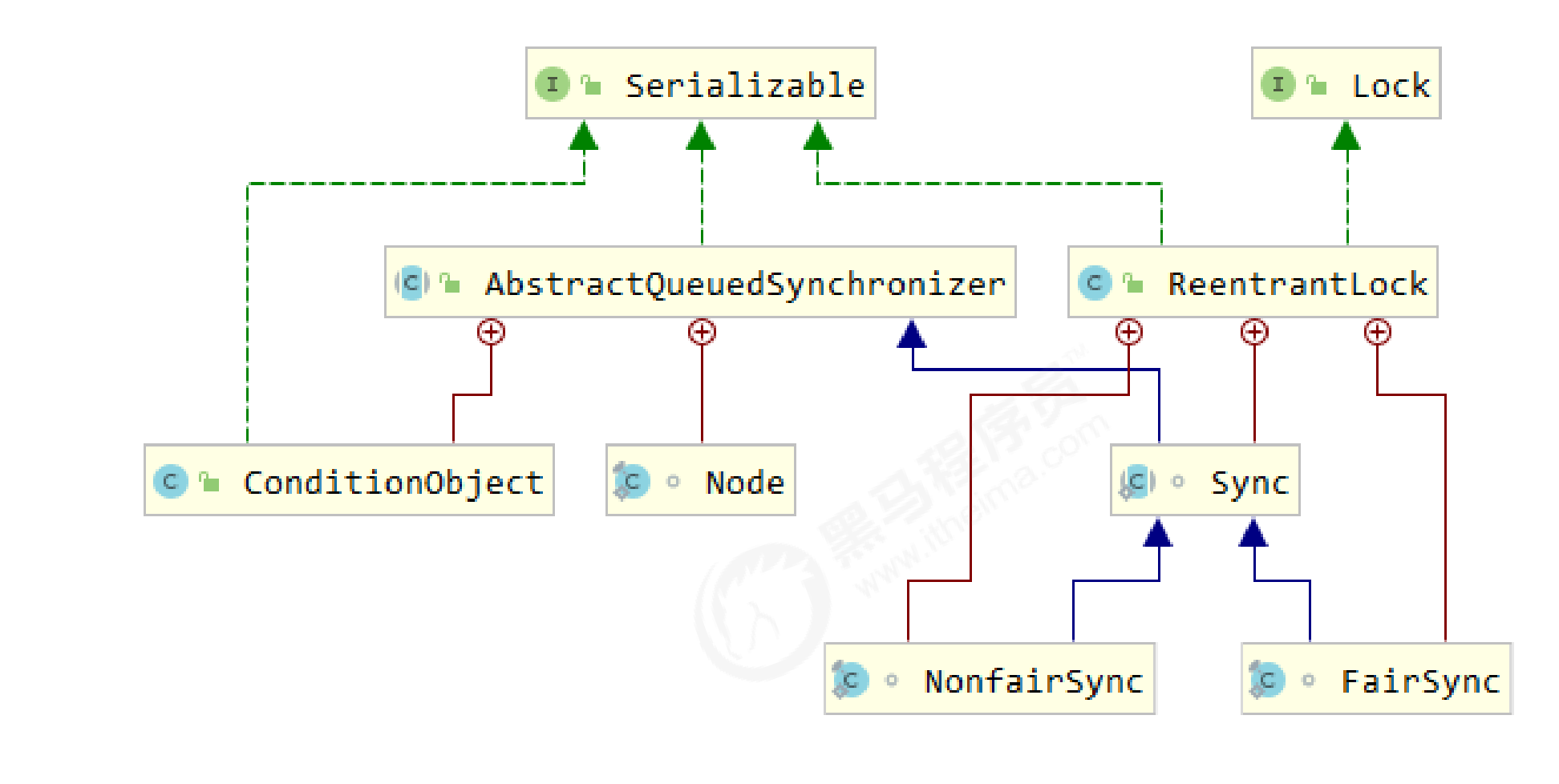
非公平锁实现原理
加锁解锁流程
先从构造器开始看,默认为
非公平锁实现
public ReentrantLock() {
sync = new NonfairSync();
}
NonfairSync 继承自 AQS
- 没有竞争时
- Thread-0成为锁的持有者
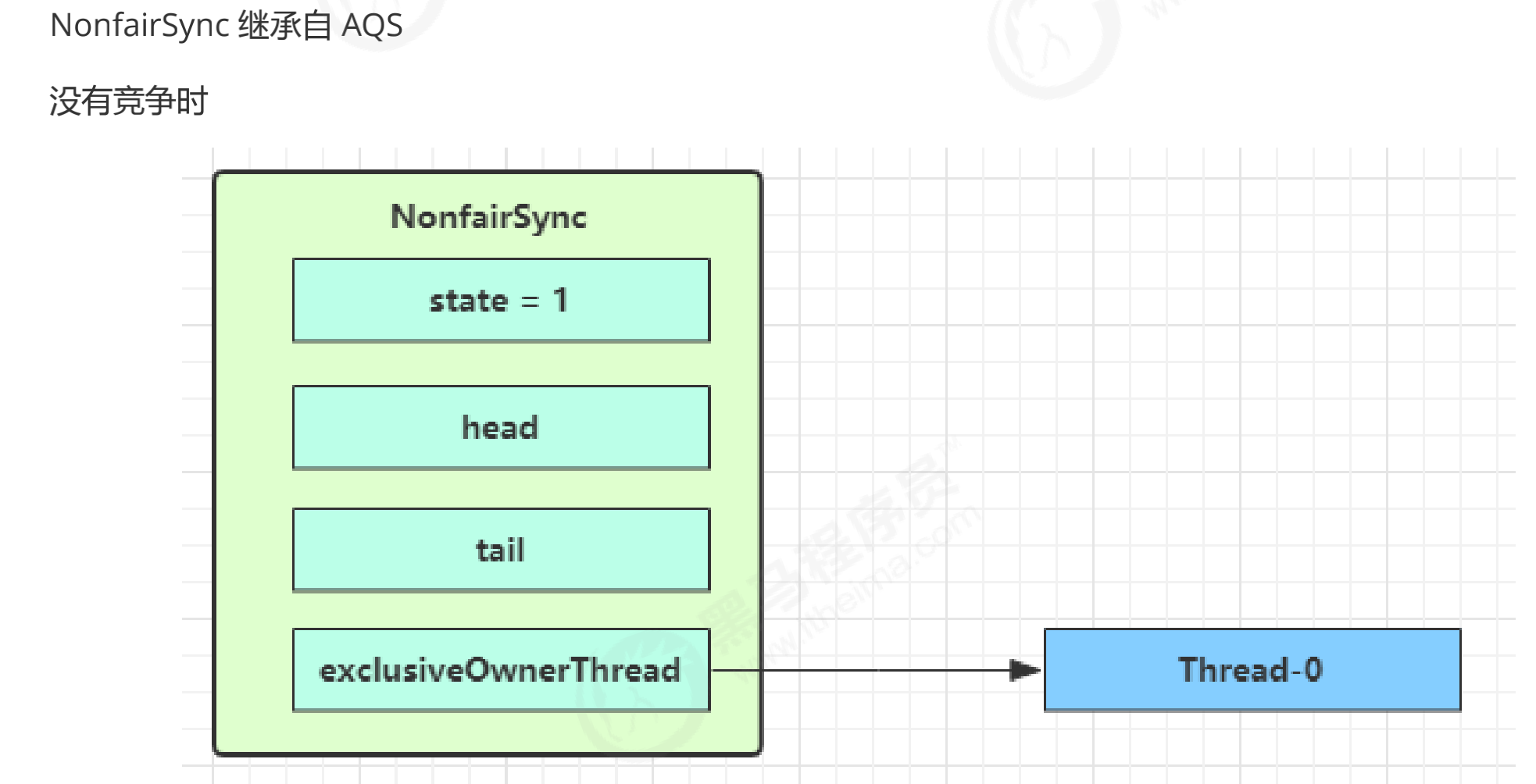
- 第一个竞争出现时,查看源码的
NonfairSync的lock方法
**
new NonfairSync( );源码
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7316153563782823691L;
/**
* Performs lock. Try immediate barge, backing up to normal
* acquire on failure.
*/
final void lock() {
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
else
acquire(1);
}
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires);
}
}
**
acquire( )源码
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
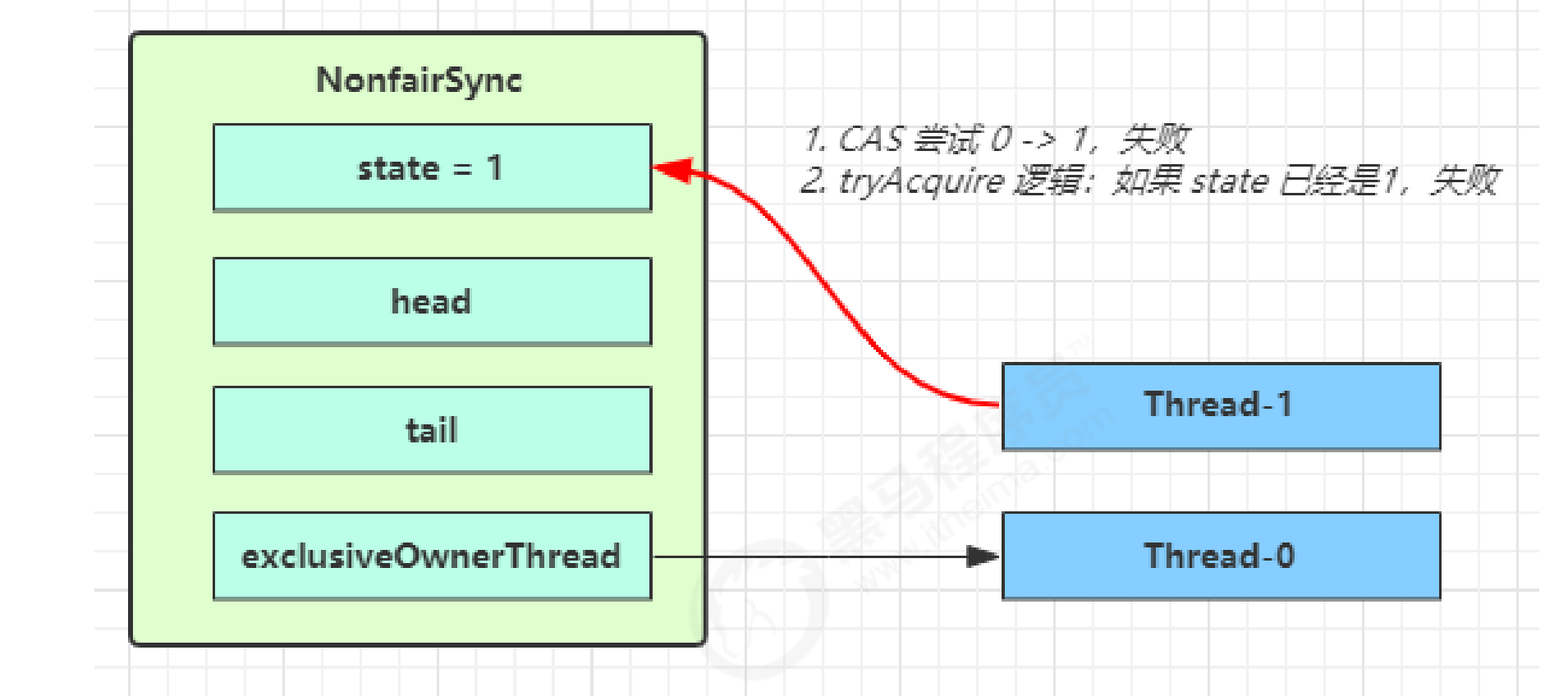
Thread-1 执行了
- lock方法中 CAS 尝试将 state 由 0 改为 1,结果失败 (因为此时CAS操作, 已经state已经为1了)
- lock方法中进一步调用acquire方法,进入 tryAcquire 逻辑,这里我们认为这时 state 已经是1,结果仍然失败
- 接下来进入 acquire方法的addWaiter 逻辑,构造 Node 队列 (双向链表实现)
- 下图中黄色三角表示该 Node 的waitStatus状态,其中 0 为默认正常状态
- Node 的创建是懒惰的
- 其中第一个 Node 称为 Dummy(虚拟头结点)或哨兵,用来占位,并不关联线程
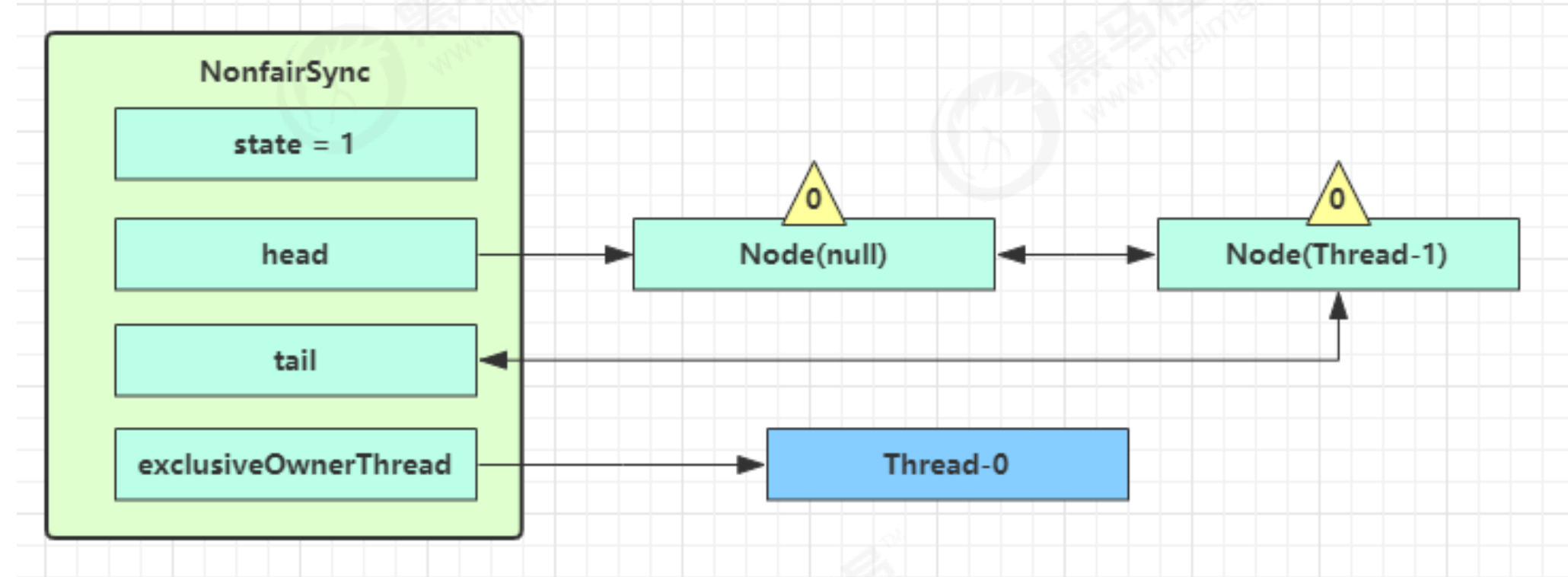
当前线程进入 acquire方法的 acquireQueued 逻辑
- acquireQueued 会在一个死循环中不断尝试获得锁,失败后进入 park 阻塞
- 如果自己是紧邻着 head(
排第二位,第一位是虚拟头结点),那么再次 tryAcquire尝试获取锁,我们这里设置这时 state 仍为 1,失败 - 进入
shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire逻辑,将前驱 node,即 head (dummy) 的 waitStatus 改为 -1,这次返回 false
**
acquireQueued( )源码
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
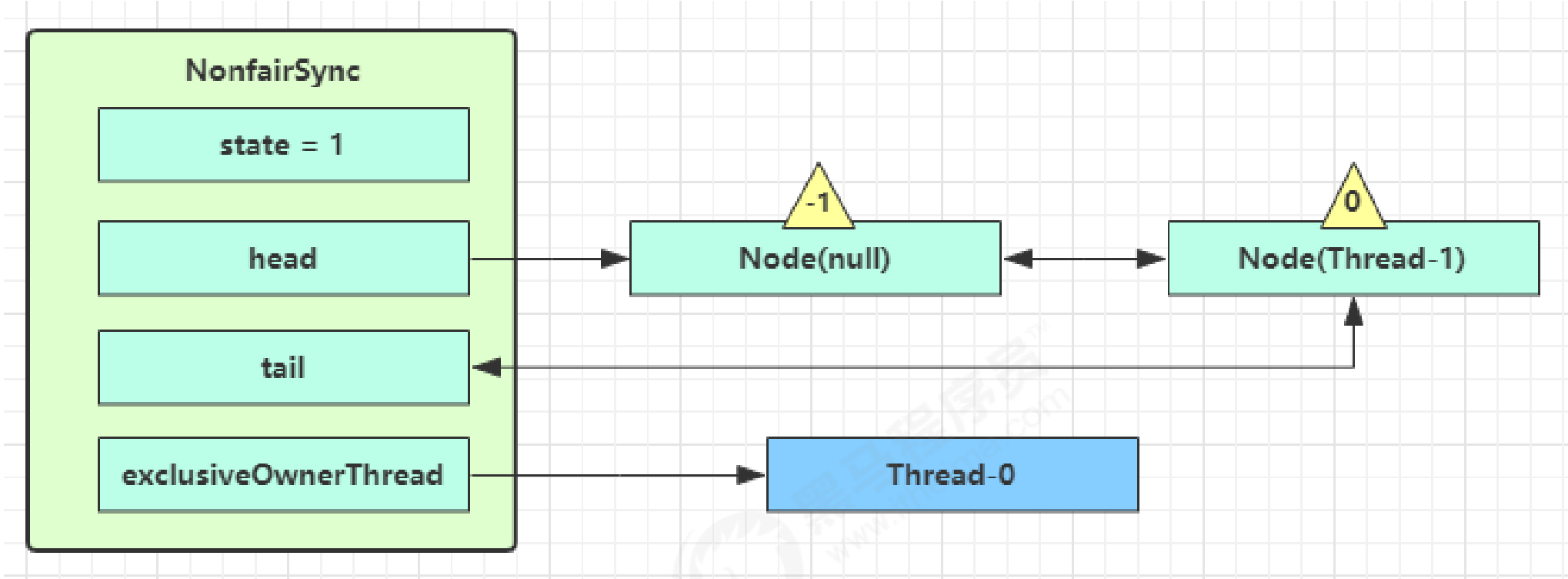
- shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire 执行完毕回到 acquireQueued ,再次 tryAcquire 尝试获取锁,当然这时 state 仍为 1,失败
- 当再次进入 shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire 时,这时因为其前驱 node(dummy) 的 waitStatus 已经是 -1,这次返回 true
- 进入parkAndCheckInterrupt, Thread-1 park(灰色表示已经阻塞)
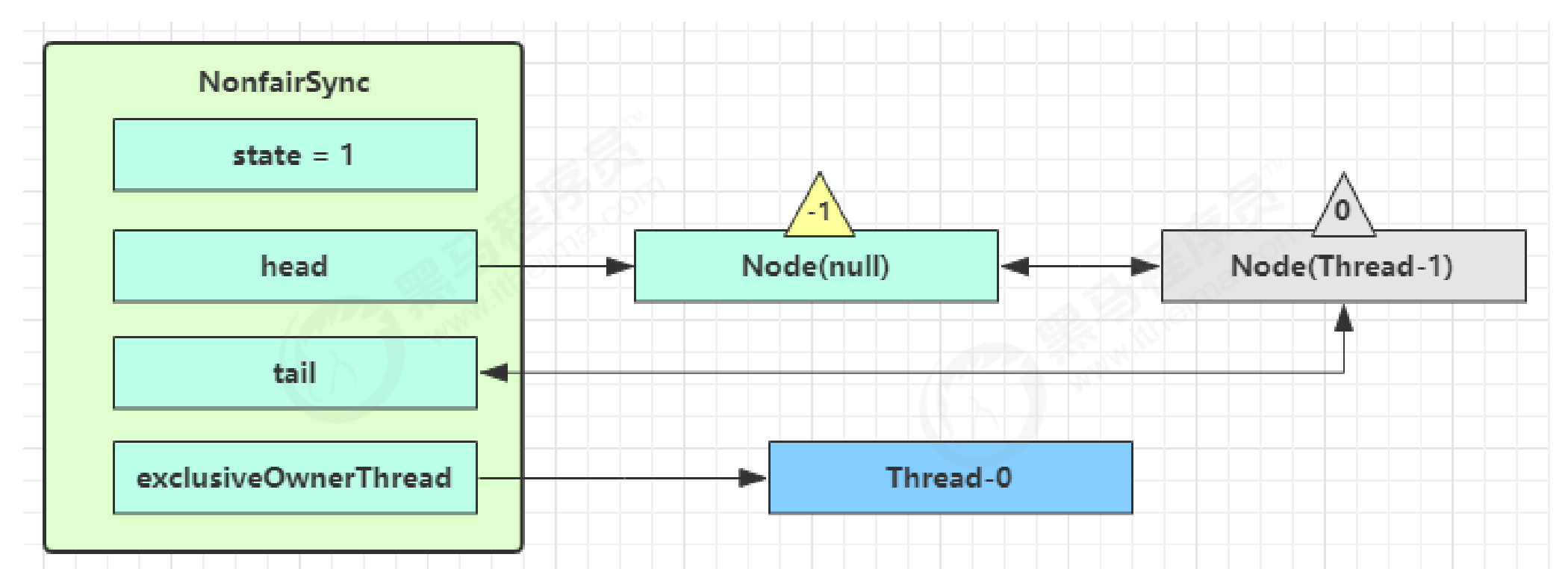
- 再次有多个线程经历上述过程竞争失败,变成这个样子
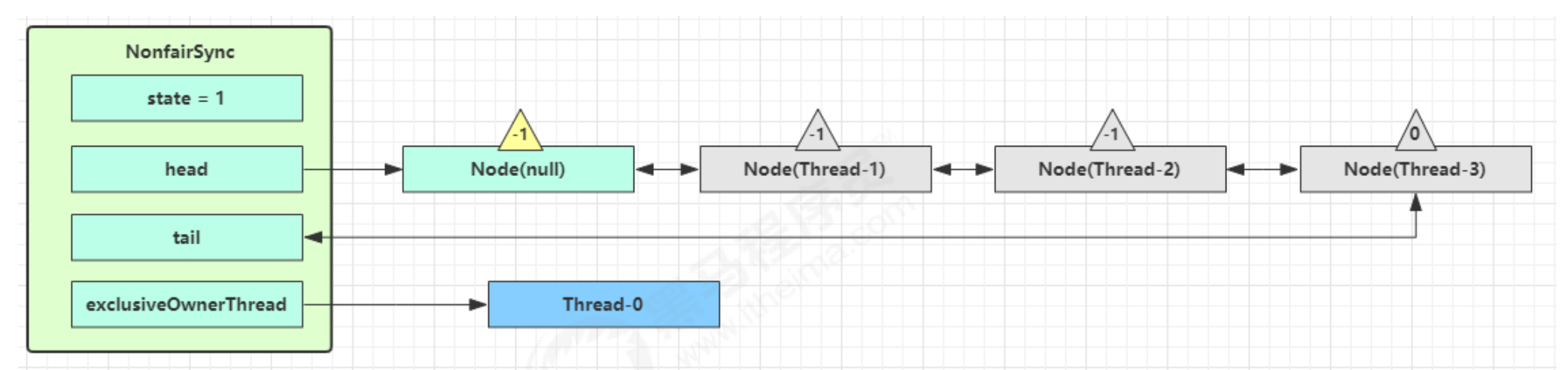
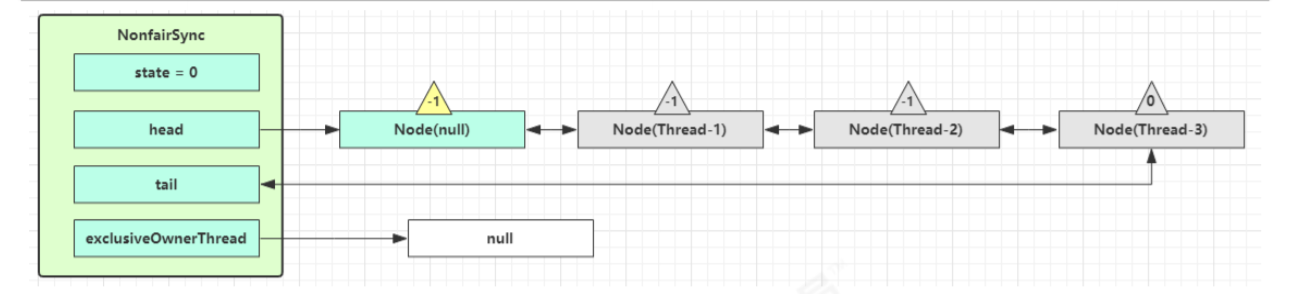
- Thread-0 调用
unlock方法(在ReentrantLock里面)里的release方法释放锁,进入tryRelease流程,如果成功,设置exclusiveOwnerThread 为 null,state = 0
unlock、release源码
public void unlock() {
sync.release(1);
}
public final boolean release(int arg) {
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}
tryRelease( )源码
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
int c = getState() - releases;
if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
boolean free = false;
if (c == 0) {
free = true;
// 锁的拥有者置空
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
}
// 此时state 设置为0
setState(c);
return free;
}
- unlock方法里的release方法方法中,
如果当前队列不为 null,并且 head 的 waitStatus = -1,进入unparkSuccessor流程:unparkSuccessor中会找到队列中离 head 最近的一个 Node(没取消的,也就是Thread-1),unpark 唤醒Thread-1 恢复其运行,本例中即为 Thread-1 回到 Thread-1 阻塞的位置继续执行, 会继续执行 acquireQueued 流程
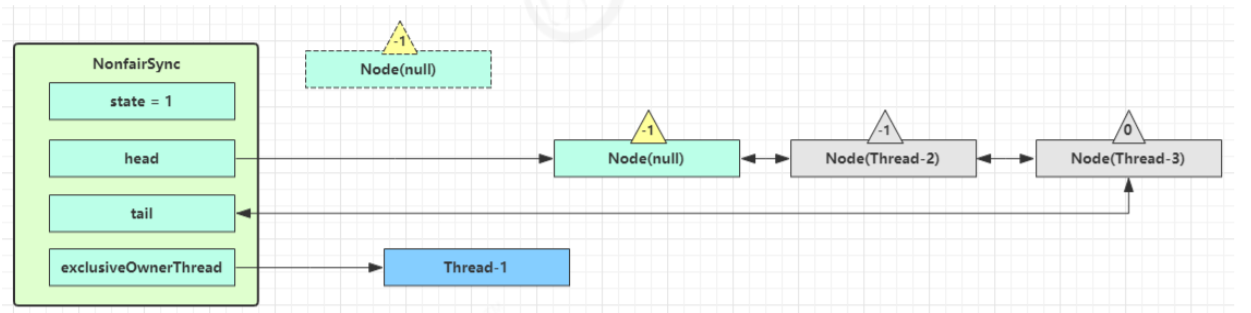
- 如果加锁成功(没有竞争),会设置 (acquireQueued 方法中)
- exclusiveOwnerThread 为 Thread-1,state = 1
- head 指向刚刚 Thread-1 所在的 Node,该 Node 清空 Thread
- 原本的 head 因为从链表断开,而可被垃圾回收
- 如果这时候有其它线程来竞争(非公平的体现),例如这时有 Thread-4 来了
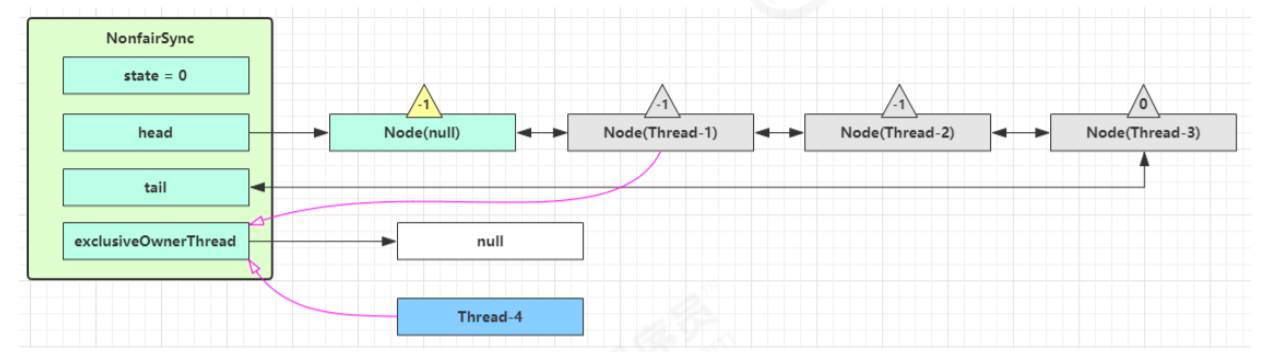
- 如果不巧又被 Thread-4 占了先
- Thread-4 被设置为 exclusiveOwnerThread,state = 1
Thread-1 再次进入 acquireQueued 流程,获取锁失败,重新进入 park 阻塞
加锁源码
// Sync 继承自 AQS
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7316153563782823691L;
// 加锁实现
final void lock() {
// 首先用 cas 尝试(仅尝试一次)将 state 从 0 改为 1, 如果成功表示获得了独占锁
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
else
// 如果尝试失败,进入 ㈠
acquire(1);
}
// ㈠ AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
public final void acquire(int arg) {
// ㈡ tryAcquire
if (
!tryAcquire(arg) &&
// 当 tryAcquire 返回为 false 时, 先调用 addWaiter ㈣, 接着 acquireQueued ㈤
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg)
) {
selfInterrupt();
}
}
// ㈡ 进入 ㈢
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires);
}
// ㈢ Sync 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
// 如果还没有获得锁
if (c == 0) {
// 尝试用 cas 获得, 这里体现了非公平性: 不去检查 AQS 队列
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
// 如果已经获得了锁, 线程还是当前线程, 表示发生了锁重入
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
// state++
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
// 获取失败, 回到调用处
return false;
}
// ㈣ AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
// 将当前线程关联到一个 Node 对象上, 模式为独占模式,新建的Node的waitstatus默认为0,因为waitstatus是成员变量,默认被初始化为0
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
// 如果 tail 不为 null, cas 尝试将 Node 对象加入 AQS 队列尾部
Node pred = tail;
if (pred != null) {
node.prev = pred;
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {
// 双向链表
pred.next = node;
return node;
}
}
//如果tail为null,尝试将 Node 加入 AQS, 进入 ㈥
enq(node);
return node;
}
// ㈥ AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
private Node enq(final Node node) {
for (;;) {
Node t = tail;
if (t == null) {
// 还没有, 设置 head 为哨兵节点(不对应线程,状态为 0)
if (compareAndSetHead(new Node())) {
tail = head;
}
} else {
// cas 尝试将 Node 对象加入 AQS 队列尾部
node.prev = t;
if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {
t.next = node;
return t;
}
}
}
}
// ㈤ AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
// 上一个节点是 head, 表示轮到自己(当前线程对应的 node)了, 尝试获取
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
// 获取成功, 设置自己(当前线程对应的 node)为 head
setHead(node);
// 上一个节点 help GC
p.next = null;
failed = false;
// 返回中断标记 false
return interrupted;
}
if (
// 判断是否应当 park, 进入 ㈦
shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
// park 等待, 此时 Node 的状态被置为 Node.SIGNAL ㈧
parkAndCheckInterrupt()
) {
interrupted = true;
}
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
// ㈦ AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) {
// 获取上一个节点的状态
int ws = pred.waitStatus;
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) {
// 上一个节点都在阻塞, 那么自己也阻塞好了
return true;
}
// > 0 表示取消状态
if (ws > 0) {
// 上一个节点取消, 那么重构删除前面所有取消的节点, 返回到外层循环重试
do {
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
} while (pred.waitStatus > 0);
pred.next = node;
} else {
// 这次还没有阻塞
// 但下次如果重试不成功, 则需要阻塞,这时需要设置上一个节点状态为 Node.SIGNAL
compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL);
}
return false;
}
// ㈧ 阻塞当前线程
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {
LockSupport.park(this);
return Thread.interrupted();
}
}
解锁源码
// Sync 继承自 AQS
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
// 解锁实现
public void unlock() {
sync.release(1);
}
// AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
public final boolean release(int arg) {
// 尝试释放锁, 进入 ㈠
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
// 队列头节点 unpark
Node h = head;
if (
// 队列不为 null
h != null &&
// waitStatus == Node.SIGNAL 才需要 unpark
h.waitStatus != 0
) {
// unpark AQS 中等待的线程, 进入 ㈡
unparkSuccessor(h);
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
// ㈠ Sync 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
// state--
int c = getState() - releases;
if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
boolean free = false;
// 支持锁重入, 只有 state 减为 0, 才释放成功
if (c == 0) {
free = true;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
}
setState(c);
return free;
}
// ㈡ AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {
// 如果状态为 Node.SIGNAL 尝试重置状态为 0, 如果线程获取到了锁那么后来头结点会被抛弃掉
// 不成功也可以
int ws = node.waitStatus;
if (ws < 0) {
compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);
}
// 找到需要 unpark 的节点, 但本节点从 AQS 队列中脱离, 是由唤醒节点完成的
Node s = node.next;
// 不考虑已取消的节点, 从 AQS 队列从后至前找到队列最前面需要 unpark 的节点
if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {
s = null;
for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)
if (t.waitStatus <= 0)
s = t;
}
if (s != null)
LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);
}
}
可重入原理
同一个线程, 锁重入, 会对
state进行自增. 释放锁的时候, state进行自减; 当state自减为0的时候. 此时线程才会将锁释放成功, 才会进一步去唤醒其他线程来竞争锁
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
// ...
// Sync 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
// 如果已经获得了锁, 线程还是当前线程, 表示发生了锁重入
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
// state++
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
// Sync 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
// state--
int c = getState() - releases;
if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
boolean free = false;
// 支持锁重入, 只有 state 减为 0, 才释放成功
if (c == 0) {
free = true;
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
}
setState(c);
return free;
}
}
可打断原理
不可打断模式
在此模式下,即使它被打断,仍会驻留在 AQS 队列中,一直要等到获得锁后方能得知自己被打断了
// Sync 继承自 AQS
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
// ...
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {
// 如果打断标记已经是 true, 则 park 会失效
// 被park阻塞的线程, 可以被别的线程调用它的interrupt方法打断该park阻塞
LockSupport.park(this);
// interrupted 会清除打断标记; 下次park仍然可以阻塞
return Thread.interrupted();
}
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null;
failed = false;
// 还是需要获得锁后, 才能返回打断状态
return interrupted;
}
if (
shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt()
) {
// 如果是因为 interrupt 被唤醒, 返回打断状态为 true
interrupted = true;
}
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (
!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg)
) {
// 如果打断状态为 true
selfInterrupt();
}
}
static void selfInterrupt() {
// 重新产生一次中断,这时候线程是如果正常运行的状态,那么不是出于sleep等状态,interrupt方法就不会报错
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
}
可打断模式
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
public final void acquireInterruptibly(int arg) throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
// 如果没有获得到锁, 进入 ㈠
if (!tryAcquire(arg))
doAcquireInterruptibly(arg);
}
// ㈠ 可打断的获取锁流程
private void doAcquireInterruptibly(int arg) throws InterruptedException {
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE);
boolean failed = true;
try {
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return;
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt()) {
// 在 park 过程中如果被 interrupt 会进入此
// 这时候抛出异常, 而不会再次进入 for (;;)
throw new InterruptedException();
}
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
}
公平锁实现原理
看AQS队列中, 自己(线程) 有没有前驱节点(这个节点是指线程,而不是占位的哨兵节点); 如果有就不去竞争锁;如果没有, 才会去CAS操作
if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() &&
compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
static final class FairSync extends Sync {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -3000897897090466540L;
final void lock() {
acquire(1);
}
// AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (
!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg)
) {
selfInterrupt();
}
}
// 与非公平锁主要区别在于 tryAcquire 方法的实现
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
// 先检查 AQS 队列中是否有前驱节点, 没有才去竞争
if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() &&
compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
// ㈠ AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
public final boolean hasQueuedPredecessors() {
Node t = tail;
Node h = head;
Node s;
// h != t 时表示队列中有 Node
return h != t &&
(
// (s = h.next) == null 表示队列中还有没有老二
(s = h.next) == null || // 或者队列中老二线程不是此线程
s.thread != Thread.currentThread()
);
}
}
条件变量实现原理
每个条件变量其实就对应着一个等待队列,其实现类是 ConditionObject
await 流程
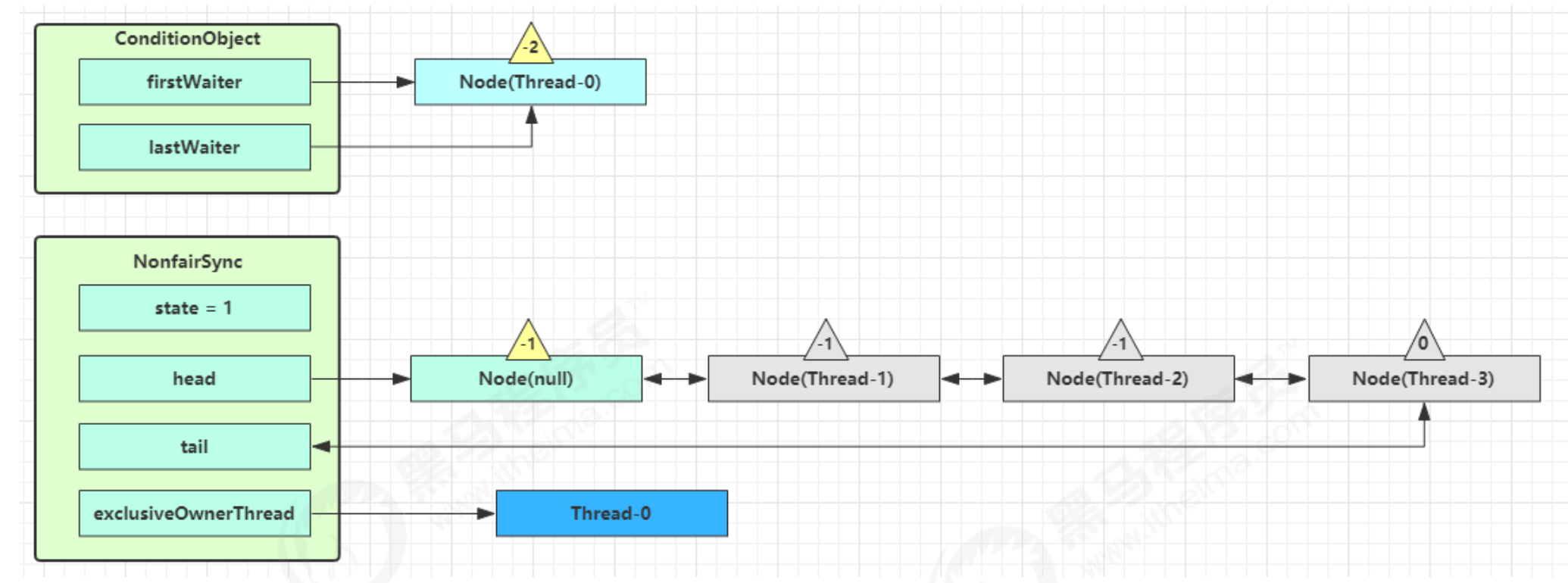
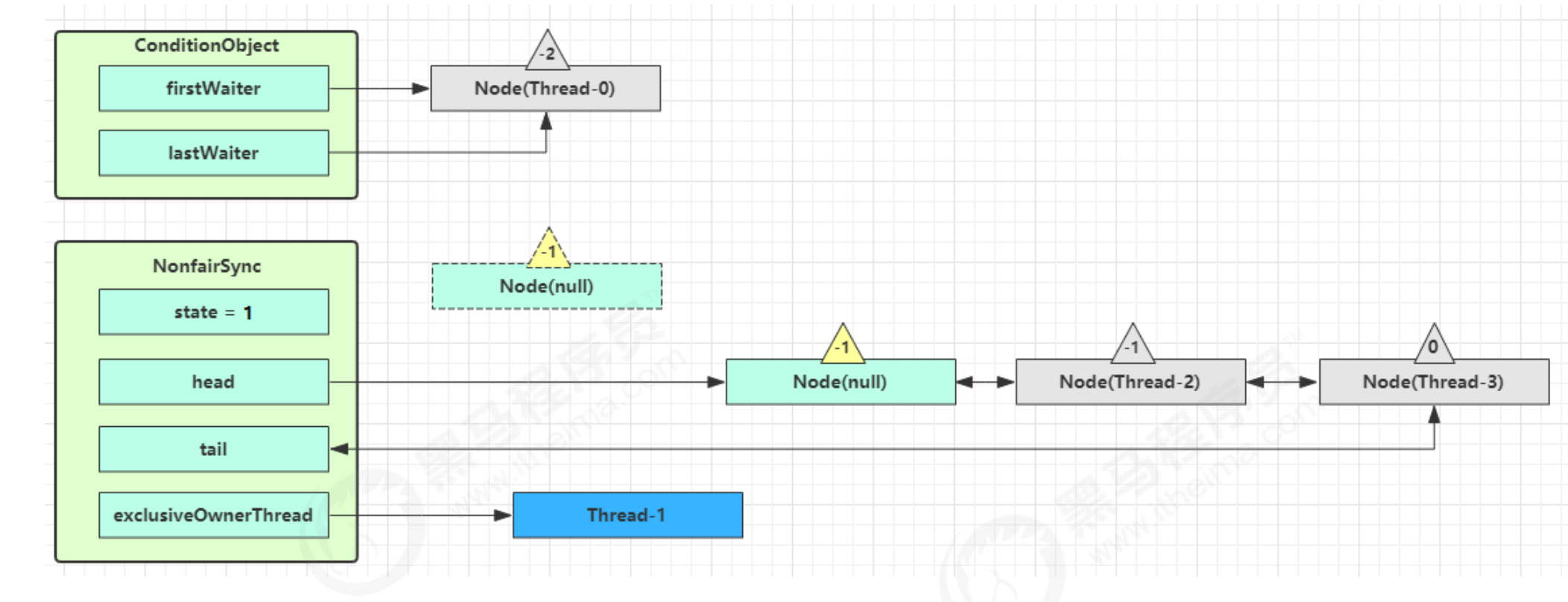
- 开始 Thread-0 持有锁,conditionObject 对象调用?
await,进入 ConditionObject的?addConditionWaiter流程 - 创建新的 Node 状态为?
-2(Node.CONDITION),关联 Thread-0,加入等待队列尾部
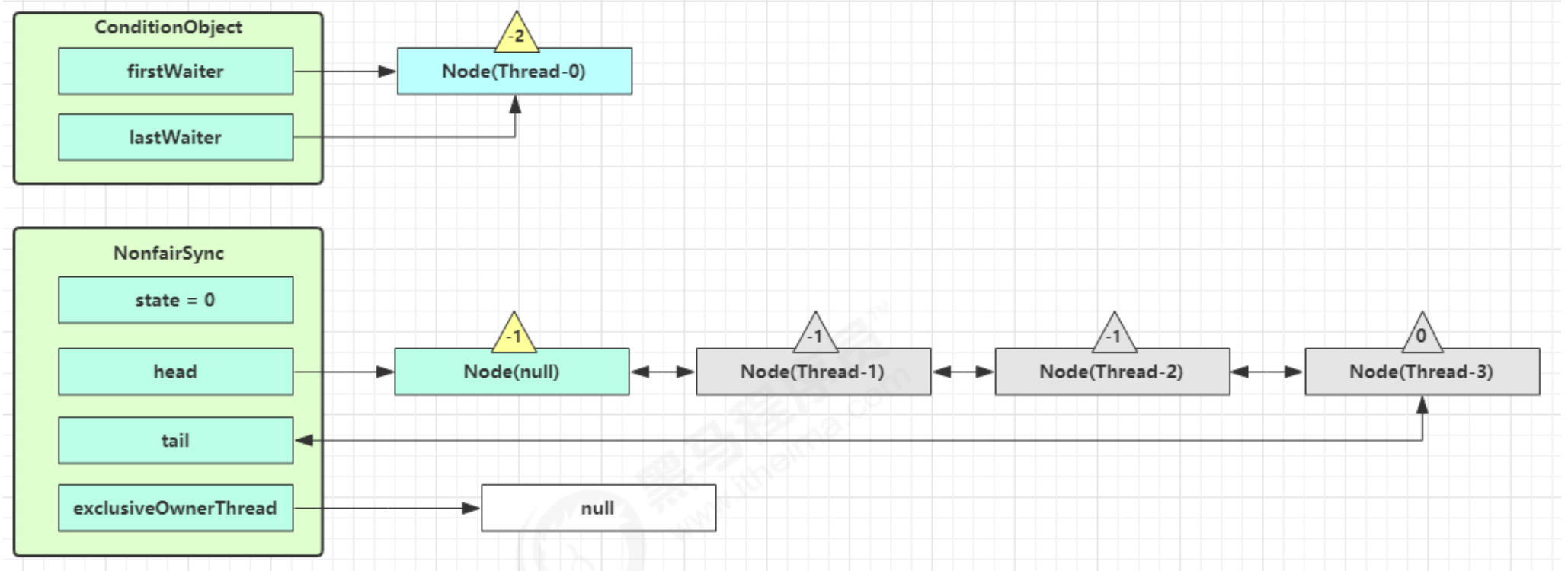
- 接下来进入 AQS 的?
fullyRelease流程,释放同步器上的所有的锁 (因为线程可能发生可重入, 锁有很多层)
unparkSuccessor(h);?—> unpark唤醒 AQS 队列中的下一个节点,竞争锁,假设没有其他竞争线程,那么?Thread-1竞争成功
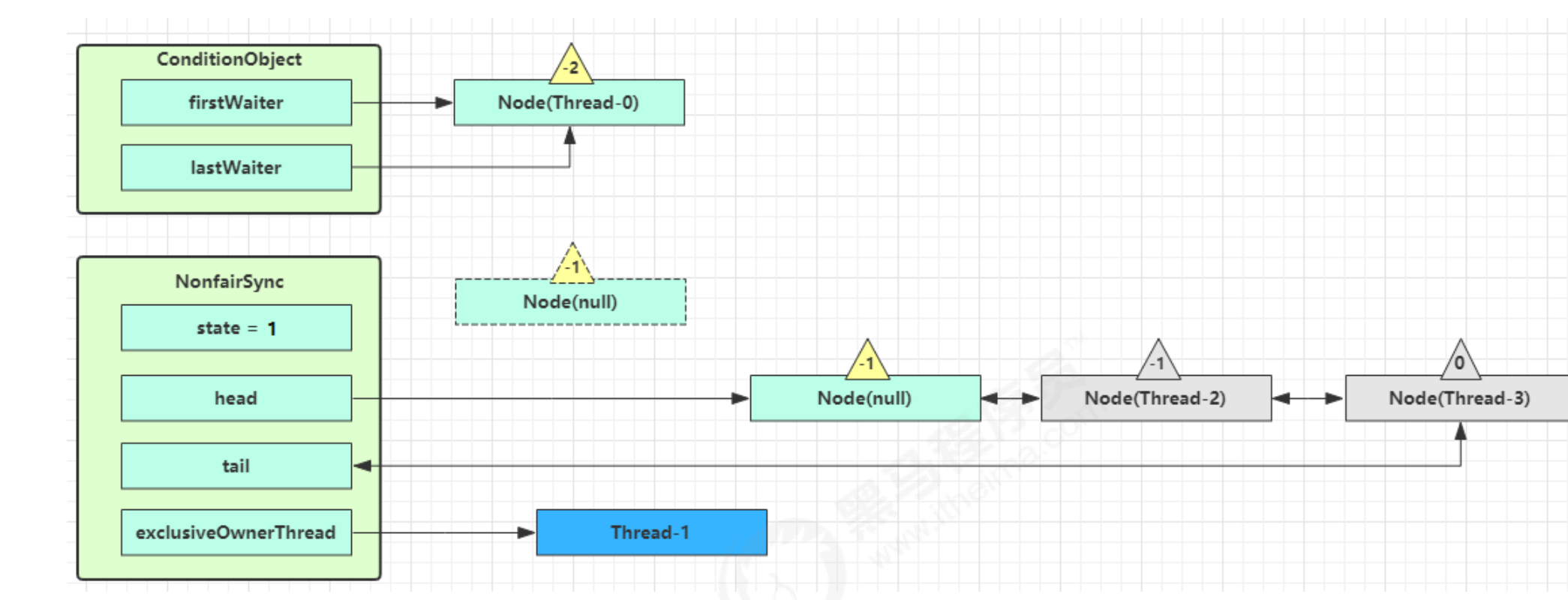
LockSupport.park(this);—> park 阻塞 Thread-0
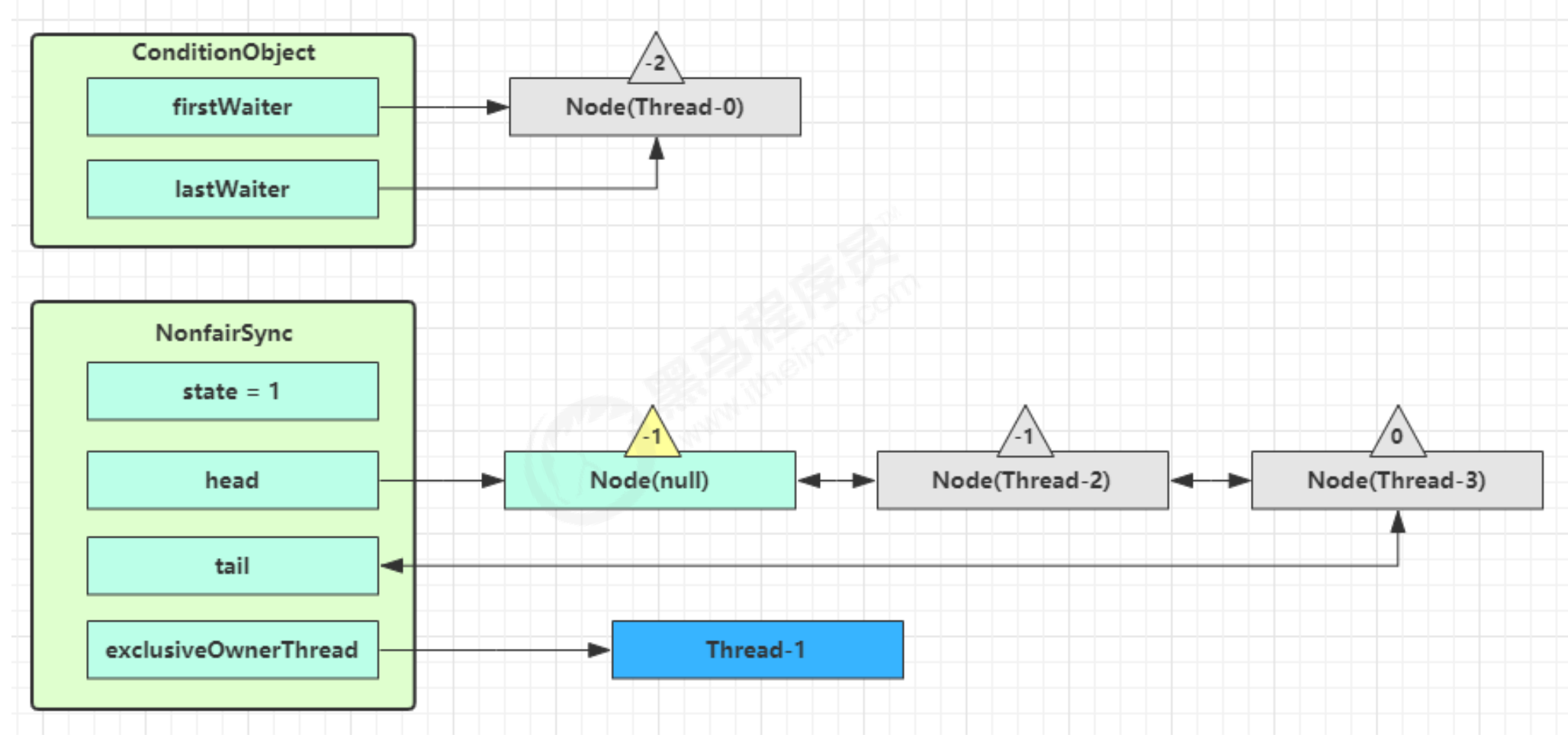
signal 流程
- 假设 Thread-1 要来唤醒 Thread-0
// 如果没有持有锁,会抛出异常 --> 这里表示Thread-1要持有锁, 才可以去条件变量中去唤醒等待的线程
if (!isHeldExclusively())
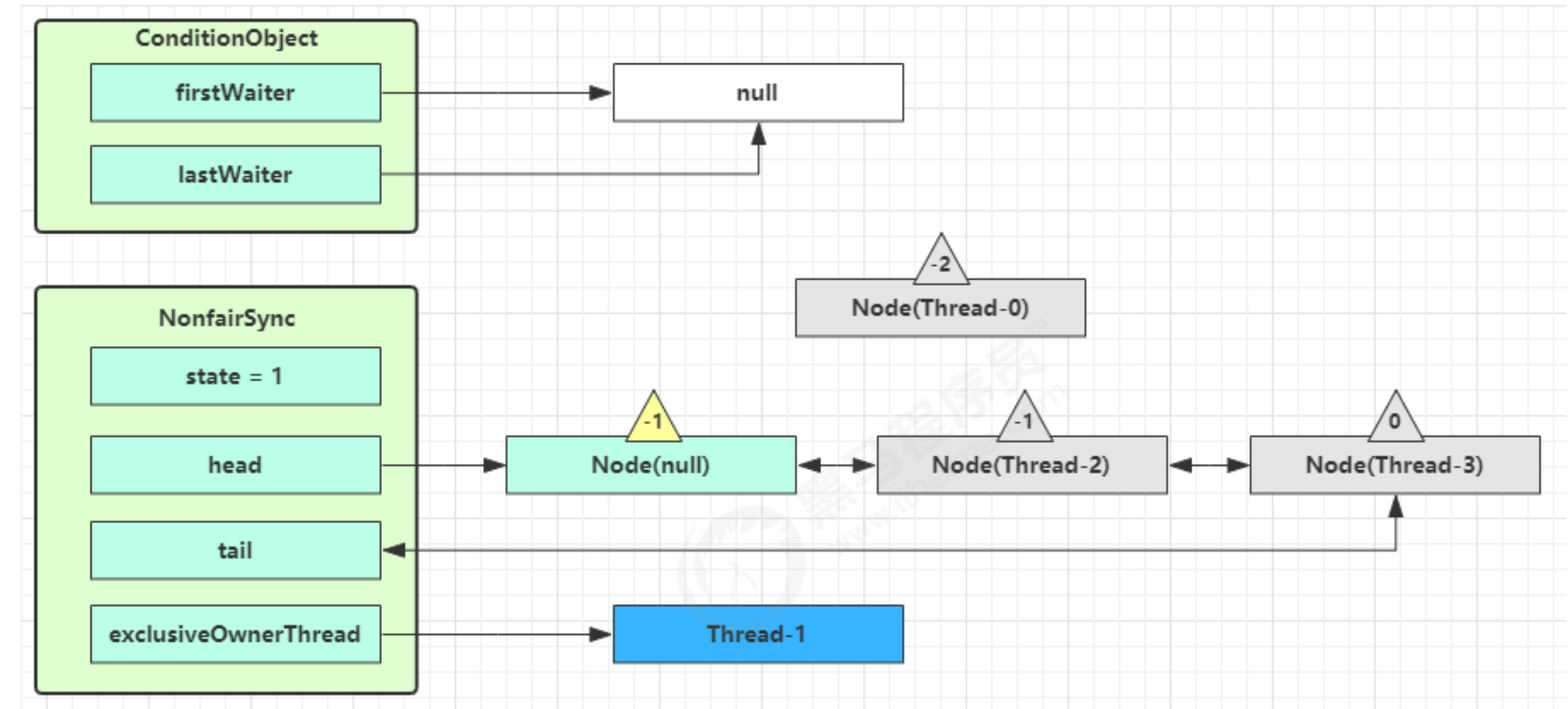
- 进入 ConditionObject 的 doSignal 流程,取得等待队列中第一个 Node,即 Thread-0 所在 Node
private void doSignal(Node first) {
do {
// 去firstWaiter条件变量中将等待的线程拿出来.
if ( (firstWaiter = first.nextWaiter) == null)
lastWaiter = null;
first.nextWaiter = null;
// 转移到AQS的队列中, 等待竞争锁
} while (!transferForSignal(first) &&
(first = firstWaiter) != null);
}
- 执行?
transferForSignal流程,将该 Node 加入 AQS 队列尾部,将 Thread-0 waitStatus 改为 0,Thread-3 的waitStatus 改为 -1, 改为-1就有责任去唤醒自己的后继节点
final boolean transferForSignal(Node node) {
/*
* If cannot change waitStatus, the node has been cancelled.
*/
// 先把状态码从等待状态-2改为队列状态0
if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, Node.CONDITION, 0))
return false;
/*
* Splice onto queue and try to set waitStatus of predecessor to
* indicate that thread is (probably) waiting. If cancelled or
* attempt to set waitStatus fails, wake up to resync (in which
* case the waitStatus can be transiently and harmlessly wrong).
*/
// 进入队列的尾部
Node p = enq(node);
// 返回它前驱节点的状态码
int ws = p.waitStatus;
// 试图把前驱节点的状态码修改为-1,因为要让他之后去唤醒node
if (ws > 0 || !compareAndSetWaitStatus(p, ws, Node.SIGNAL))
LockSupport.unpark(node.thread);
return true;
}
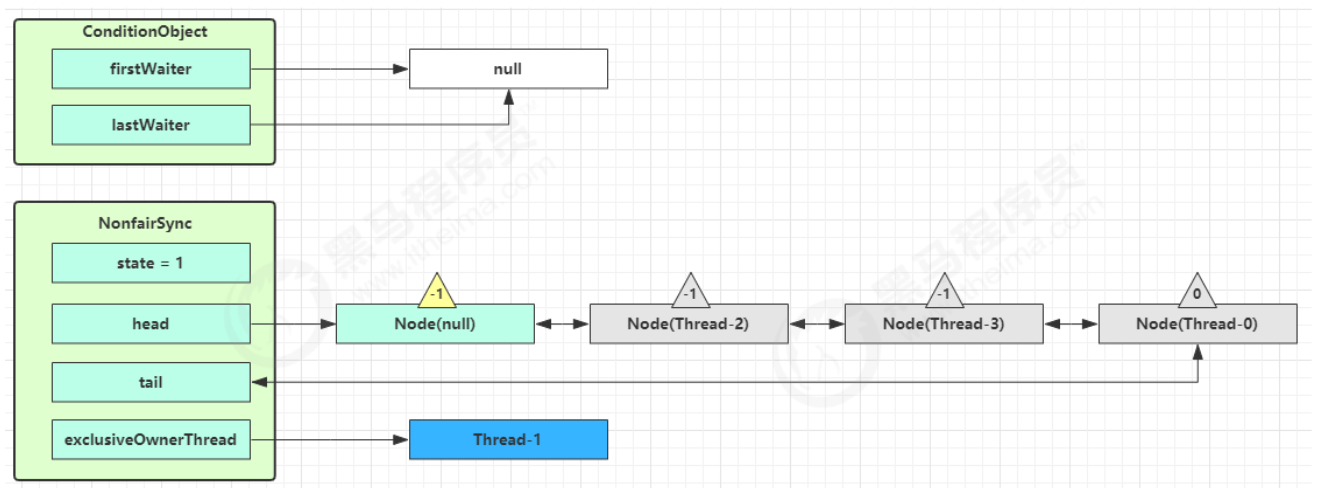
- Thread-1 释放锁,进入 unlock 流程,略
源码分析
public class ConditionObject implements Condition, java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1173984872572414699L;
// 第一个等待节点
private transient Node firstWaiter;
// 最后一个等待节点
private transient Node lastWaiter;
public ConditionObject() { }
// ㈠ 添加一个 Node 至等待队列
private Node addConditionWaiter() {
Node t = lastWaiter;
// 所有已取消的 Node 从队列链表删除, 见 ㈡
if (t != null && t.waitStatus != Node.CONDITION) {
unlinkCancelledWaiters();
t = lastWaiter;
}
// 创建一个关联当前线程的新 Node, 添加至队列尾部
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), Node.CONDITION);
if (t == null)
firstWaiter = node;
else
t.nextWaiter = node;
lastWaiter = node;
return node;
}
// 唤醒 - 将没取消的第一个节点转移至 AQS 队列
private void doSignal(Node first) {
do {
// 已经是尾节点了
if ( (firstWaiter = first.nextWaiter) == null) {
lastWaiter = null;
}
first.nextWaiter = null;
} while (
// 将等待队列中的 Node 转移至 AQS 队列, 不成功且还有节点则继续循环 ㈢
!transferForSignal(first) &&
// 队列还有节点
(first = firstWaiter) != null
);
}
// 外部类方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
// ㈢ 如果节点状态是取消, 返回 false 表示转移失败, 否则转移成功
final boolean transferForSignal(Node node) {
// 设置当前node状态为0(因为处在队列末尾),如果状态已经不是 Node.CONDITION, 说明被取消了
if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, Node.CONDITION, 0))
return false;
// 加入 AQS 队列尾部
Node p = enq(node);
int ws = p.waitStatus;
if (
// 插入节点的上一个节点被取消
ws > 0 ||
// 插入节点的上一个节点不能设置状态为 Node.SIGNAL
!compareAndSetWaitStatus(p, ws, Node.SIGNAL)
) {
// unpark 取消阻塞, 让线程重新同步状态
LockSupport.unpark(node.thread);
}
return true;
}
// 全部唤醒 - 等待队列的所有节点转移至 AQS 队列
private void doSignalAll(Node first) {
lastWaiter = firstWaiter = null;
do {
Node next = first.nextWaiter;
first.nextWaiter = null;
transferForSignal(first);
first = next;
} while (first != null);
}
// ㈡
private void unlinkCancelledWaiters() {
// ...
}
// 唤醒 - 必须持有锁才能唤醒, 因此 doSignal 内无需考虑加锁
public final void signal() {
// 如果没有持有锁,会抛出异常
if (!isHeldExclusively())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
Node first = firstWaiter;
if (first != null)
doSignal(first);
}
// 全部唤醒 - 必须持有锁才能唤醒, 因此 doSignalAll 内无需考虑加锁
public final void signalAll() {
if (!isHeldExclusively())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
Node first = firstWaiter;
if (first != null)
doSignalAll(first);
}
// 不可打断等待 - 直到被唤醒
public final void awaitUninterruptibly() {
// 添加一个 Node 至等待队列, 见 ㈠
Node node = addConditionWaiter();
// 释放节点持有的锁, 见 ㈣
int savedState = fullyRelease(node);
boolean interrupted = false;
// 如果该节点还没有转移至 AQS 队列, 阻塞
while (!isOnSyncQueue(node)) {
// park 阻塞
LockSupport.park(this);
// 如果被打断, 仅设置打断状态
if (Thread.interrupted())
interrupted = true;
}
// 唤醒后, 尝试竞争锁, 如果失败进入 AQS 队列
if (acquireQueued(node, savedState) || interrupted)
selfInterrupt();
}
// 外部类方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
// ㈣ 因为某线程可能重入,需要将 state 全部释放,获取state,然后把它全部减掉,以全部释放
final int fullyRelease(Node node) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
int savedState = getState();
// 唤醒等待队列队列中的下一个节点
if (release(savedState)) {
failed = false;
return savedState;
} else {
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
}
} finally {
if (failed)
node.waitStatus = Node.CANCELLED;
}
}
// 打断模式 - 在退出等待时重新设置打断状态
private static final int REINTERRUPT = 1;
// 打断模式 - 在退出等待时抛出异常
private static final int THROW_IE = -1;
// 判断打断模式
private int checkInterruptWhileWaiting(Node node) {
return Thread.interrupted() ?
(transferAfterCancelledWait(node) ? THROW_IE : REINTERRUPT) :
0;
}
// ㈤ 应用打断模式
private void reportInterruptAfterWait(int interruptMode)
throws InterruptedException {
if (interruptMode == THROW_IE)
throw new InterruptedException();
else if (interruptMode == REINTERRUPT)
selfInterrupt();
}
// 等待 - 直到被唤醒或打断
public final void await() throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
throw new InterruptedException();
}
// 添加一个 Node 至等待队列, 见 ㈠
Node node = addConditionWaiter();
// 释放节点持有的锁
int savedState = fullyRelease(node);
int interruptMode = 0;
// 如果该节点还没有转移至 AQS 队列, 阻塞
while (!isOnSyncQueue(node)) {
// park 阻塞
LockSupport.park(this);
// 如果被打断, 退出等待队列
if ((interruptMode = checkInterruptWhileWaiting(node)) != 0)
break;
}
// 退出等待队列后, 还需要获得 AQS 队列的锁
if (acquireQueued(node, savedState) && interruptMode != THROW_IE)
interruptMode = REINTERRUPT;
// 所有已取消的 Node 从队列链表删除, 见 ㈡
if (node.nextWaiter != null)
unlinkCancelledWaiters();
// 应用打断模式, 见 ㈤
if (interruptMode != 0)
reportInterruptAfterWait(interruptMode);
}
// 等待 - 直到被唤醒或打断或超时
public final long awaitNanos(long nanosTimeout) throws InterruptedException {
if (Thread.interrupted()) {
throw new InterruptedException();
}
// 添加一个 Node 至等待队列, 见 ㈠
Node node = addConditionWaiter();
// 释放节点持有的锁
int savedState = fullyRelease(node);
// 获得最后期限
final long deadline = System.nanoTime() + nanosTimeout;
int interruptMode = 0;
// 如果该节点还没有转移至 AQS 队列, 阻塞
while (!isOnSyncQueue(node)) {
// 已超时, 退出等待队列
if (nanosTimeout <= 0L) {
transferAfterCancelledWait(node);
break;
}
// park 阻塞一定时间, spinForTimeoutThreshold 为 1000 ns
if (nanosTimeout >= spinForTimeoutThreshold)
LockSupport.parkNanos(this, nanosTimeout);
// 如果被打断, 退出等待队列
if ((interruptMode = checkInterruptWhileWaiting(node)) != 0)
break;
nanosTimeout = deadline - System.nanoTime();
}
// 退出等待队列后, 还需要获得 AQS 队列的锁
if (acquireQueued(node, savedState) && interruptMode != THROW_IE)
interruptMode = REINTERRUPT;
// 所有已取消的 Node 从队列链表删除, 见 ㈡
if (node.nextWaiter != null)
unlinkCancelledWaiters();
// 应用打断模式, 见 ㈤
if (interruptMode != 0)
reportInterruptAfterWait(interruptMode);
return deadline - System.nanoTime();
}
// 等待 - 直到被唤醒或打断或超时, 逻辑类似于 awaitNanos
public final boolean awaitUntil(Date deadline) throws InterruptedException {
// ...
}
// 等待 - 直到被唤醒或打断或超时, 逻辑类似于 awaitNanos
public final boolean await(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
// ...
}
// 工具方法 省略 ...
}
读写锁
ReentrantReadWriteLock
- 当读操作远远高于写操作时,这时候使用
读写锁让读-读可以并发,提高性能。 类似于数据库中的select …from … lock in share mode - 提供一个
数据容器类内部分别使用读锁保护数据的read( )方法,写锁保护数据的write( )方法
@Slf4j(topic = "c.DataContainer")
class DataContainer {
private Object data;
private ReentrantReadWriteLock rw = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
// 读锁
private ReentrantReadWriteLock.ReadLock r = rw.readLock();
// 写锁
private ReentrantReadWriteLock.WriteLock w = rw.writeLock();
public Object read() {
log.debug("获取读锁...");
r.lock();
try {
log.debug("读取");
sleep(1);
return data;
} finally {
log.debug("释放读锁...");
r.unlock();
}
}
public void write() {
log.debug("获取写锁...");
w.lock();
try {
log.debug("写入");
sleep(1);
} finally {
log.debug("释放写锁...");
w.unlock();
}
}
}
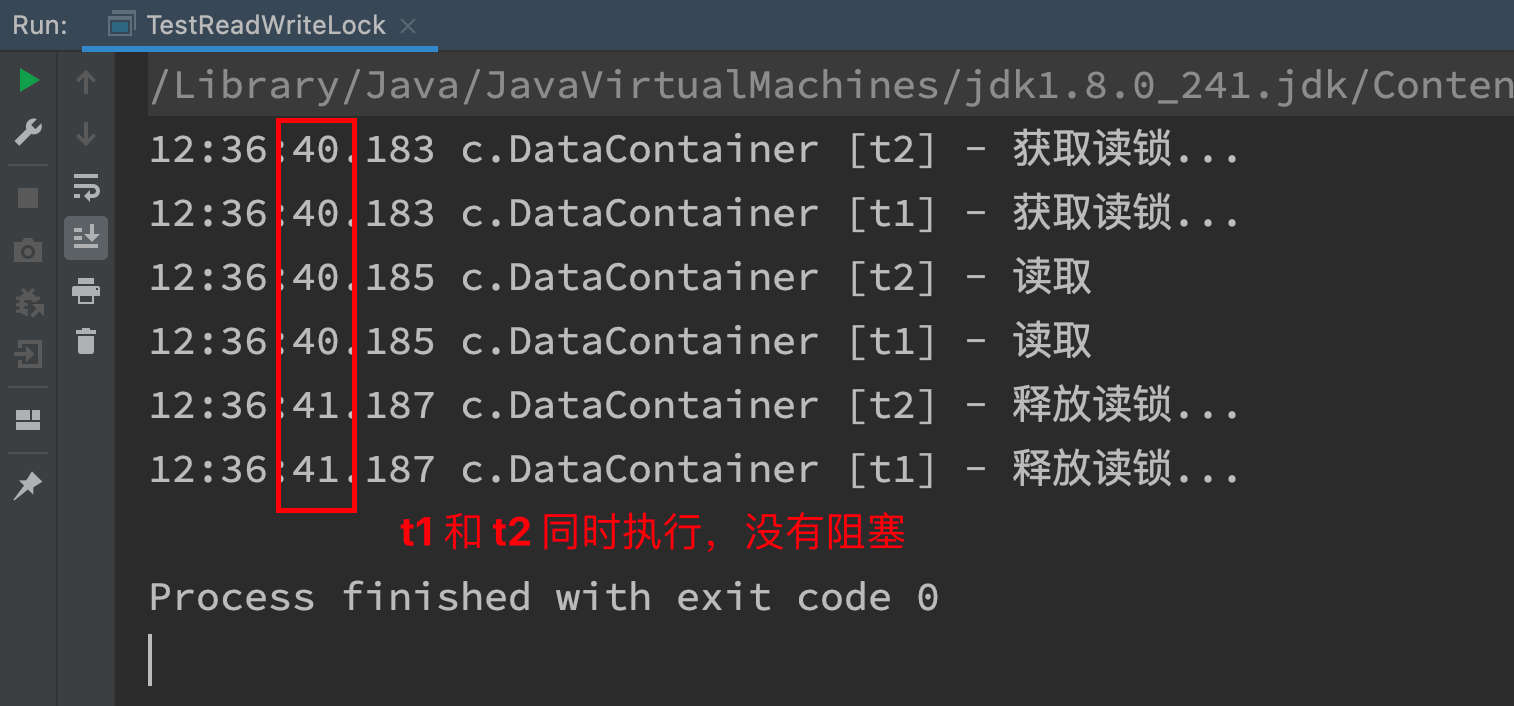
测试 读锁-读锁 可以并发
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestReadWriteLock")
public class TestReadWriteLock {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
DataContainer dataContainer = new DataContainer();
new Thread(() -> {
dataContainer.read();
}, "t1").start();
new Thread(() -> {
dataContainer.read();
}, "t2").start();
}
}
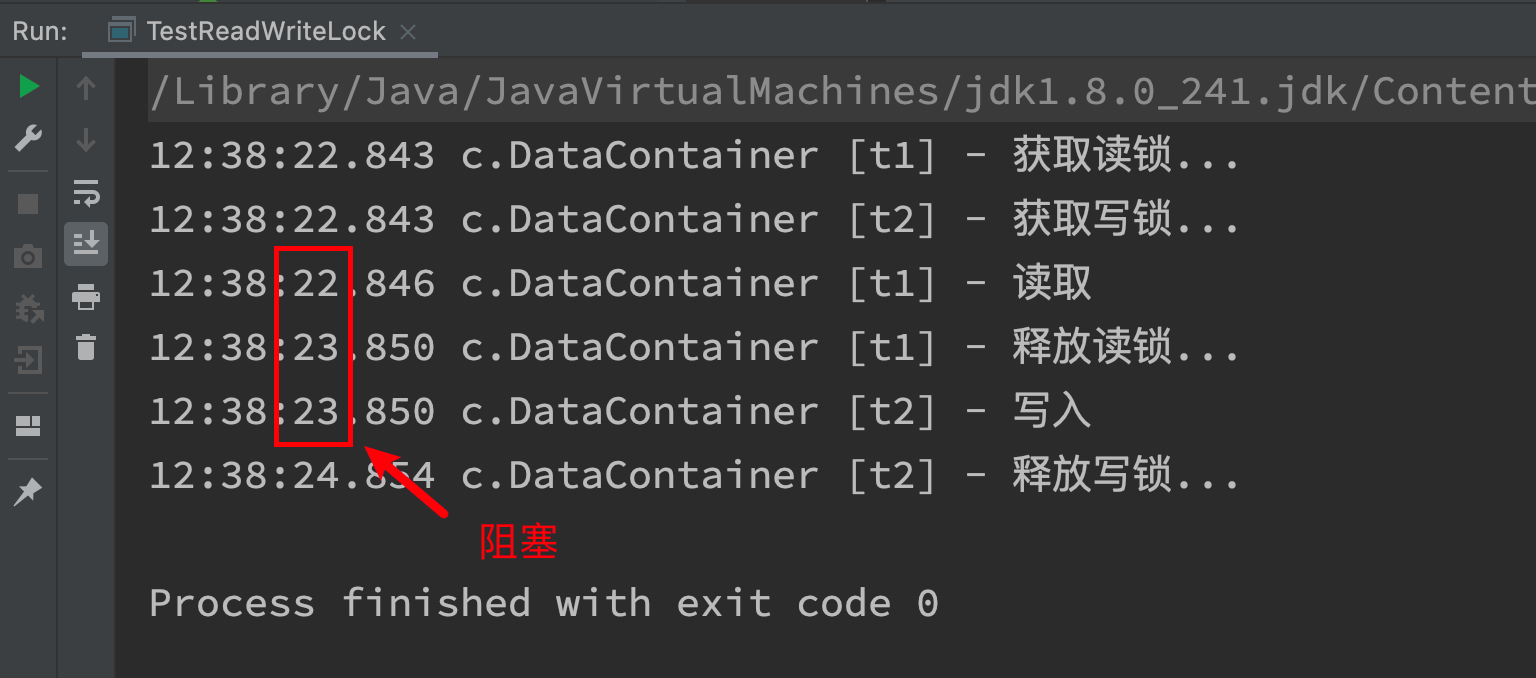
测试 读锁-写锁 相互阻塞
@Slf4j(topic = "c.TestReadWriteLock")
public class TestReadWriteLock {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
DataContainer dataContainer = new DataContainer();
new Thread(() -> {
dataContainer.read();
}, "t1").start();
new Thread(() -> {
dataContainer.write();
}, "t2").start();
}
}
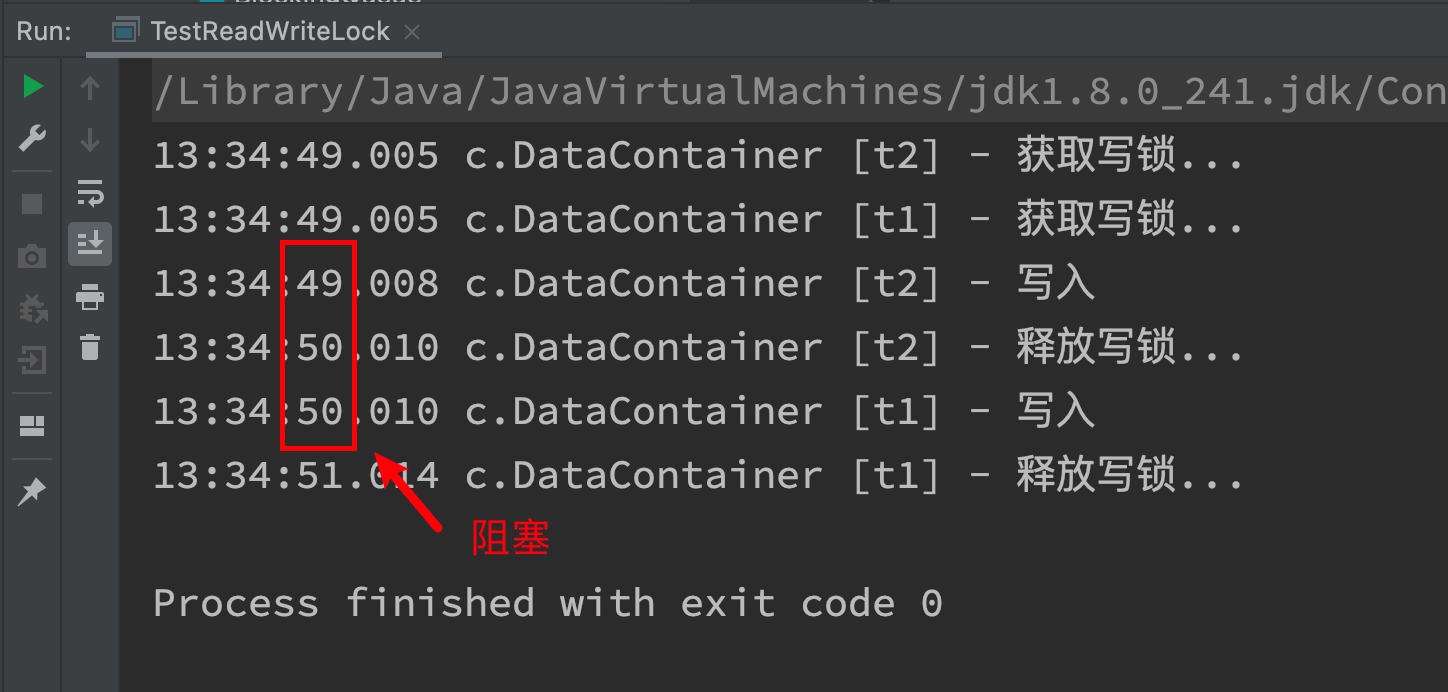
测试 写锁-写锁 相互阻塞
注意事项
- 读锁不支持条件变量,写锁支持条件变量
- 重入时升级不支持:即持有读锁的情况下去获取写锁,会导致获取写锁永久等待
r.lock();
try {
// ...
w.lock();
try {
// ...
} finally{
w.unlock();
}
} finally{
r.unlock();
}
- 重入时降级支持:即持有写锁的情况下可以去获取读锁
class CachedData {
Object data;
// 是否有效,如果失效,需要重新计算 data
volatile boolean cacheValid;
final ReentrantReadWriteLock rwl = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
void processCachedData() {
rwl.readLock().lock();
// 判断数据是否有效
if (!cacheValid) {
// 获取写锁前必须先释放读锁
rwl.readLock().unlock();
rwl.writeLock().lock();
try {
// 判断是否有其它线程已经获取了写锁、更新了缓存, 避免重复更新(双重检查)
if (!cacheValid) {
data = ...
cacheValid = true;
}
// 写锁释放开之前获取读锁
// 降级为读锁, 释放写锁, 这样能够让其它线程读取缓存
rwl.readLock().lock();
} finally {
rwl.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
// 拿到读锁,自己用完数据, 释放读锁(防止自己读的时候别人写)
// ①数据没失效,拿到读锁,可以直接读
// ②数据失效后,那就重新计算data,然后释放写锁前拿到读锁,继续读
try {
use(data);
} finally {
rwl.readLock().unlock();
}
}
}
StampedLock
概念
该类自 JDK 8 加入,是为了进一步优化读性能,它的特点是在使用读锁、写锁时都必须配合【戳】使用
加解读锁
long stamp = lock.readLock();
lock.unlockRead(stamp);
加解写锁
long stamp = lock.writeLock();
lock.unlockWrite(stamp);
乐观读,StampedLock 支持 tryOptimisticRead() 方法(乐观读),读取完毕后需要做一次 戳校验 如果校验通过,表示这期间确实没有写操作,数据可以安全使用,如果校验没通过,需要重新获取读锁,保证数据安全。
long stamp = lock.tryOptimisticRead();
// 验戳
if(!lock.validate(stamp)){
// 锁升级
}
示例
提供一个 数据容器类 内部分别使用读锁保护数据的 read( ) 方法,写锁保护数据的 write( ) 方法
@Slf4j(topic = "c.DataContainerStamped")
class DataContainerStamped {
private int data;
private final StampedLock lock = new StampedLock();
public DataContainerStamped(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
public int read(int readTime) {
long stamp = lock.tryOptimisticRead();
log.debug("optimistic read locking...{}", stamp);
sleep(readTime);
if (lock.validate(stamp)) {
log.debug("read finish...{}, data:{}", stamp, data);
return data;
}
// 锁升级 - 读锁
log.debug("updating to read lock... {}", stamp);
try {
stamp = lock.readLock();
log.debug("read lock {}", stamp);
sleep(readTime);
log.debug("read finish...{}, data:{}", stamp, data);
return data;
} finally {
log.debug("read unlock {}", stamp);
lock.unlockRead(stamp);
}
}
public void write(int newData) {
long stamp = lock.writeLock();
log.debug("write lock {}", stamp);
try {
sleep(2);
this.data = newData;
} finally {
log.debug("write unlock {}", stamp);
lock.unlockWrite(stamp);
}
}
}
应用之缓存
缓存更新策略
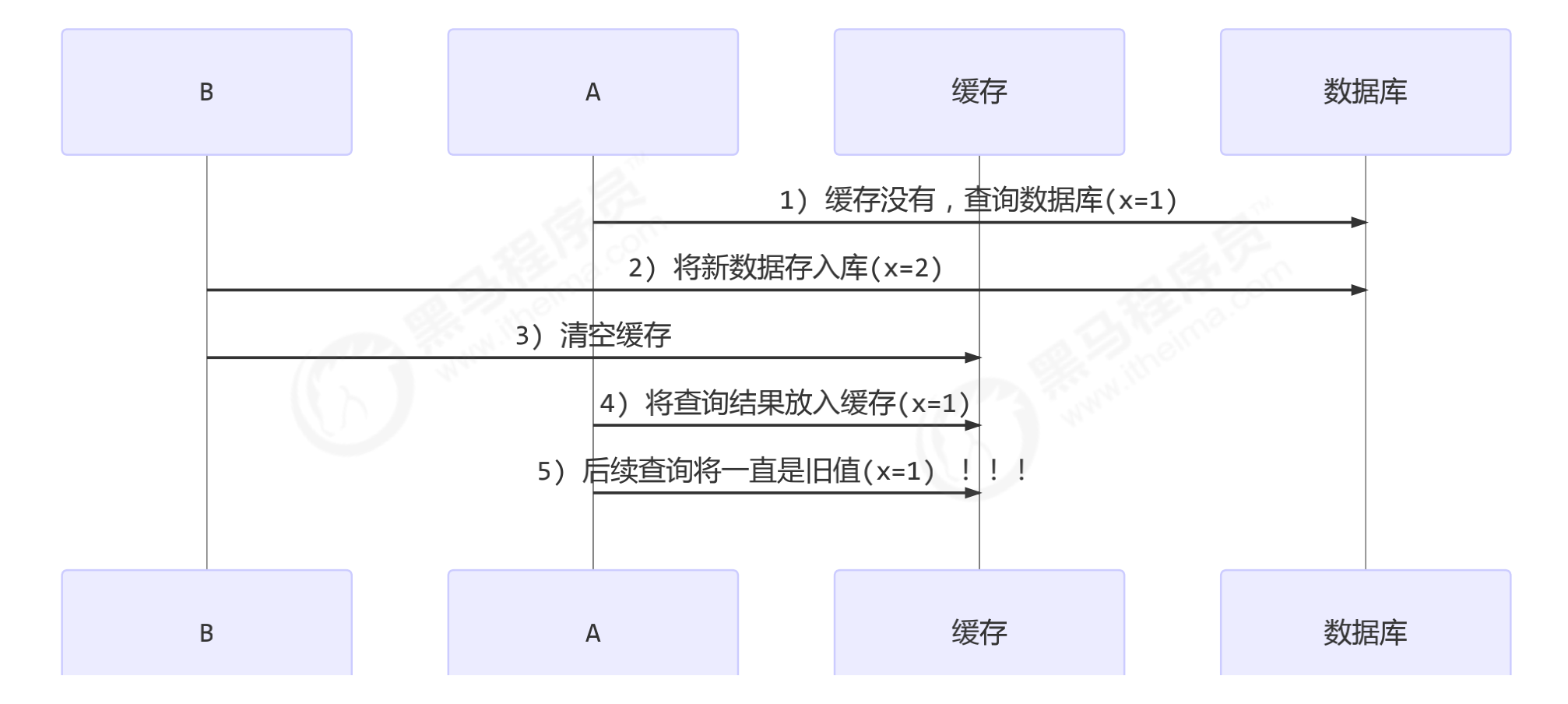
更新时,是先清缓存还是先更新数据库
- 先清缓存
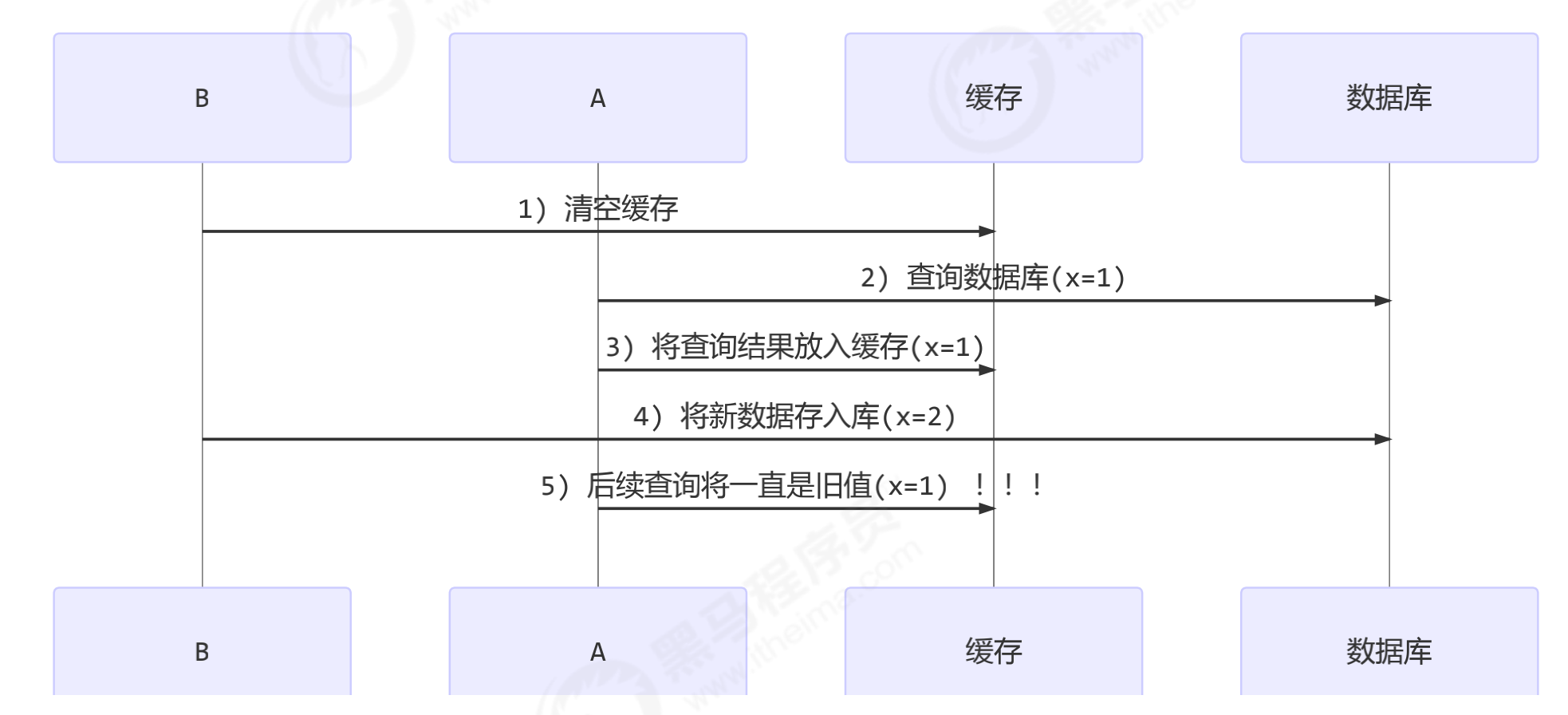
- 先更新数据库(推荐)
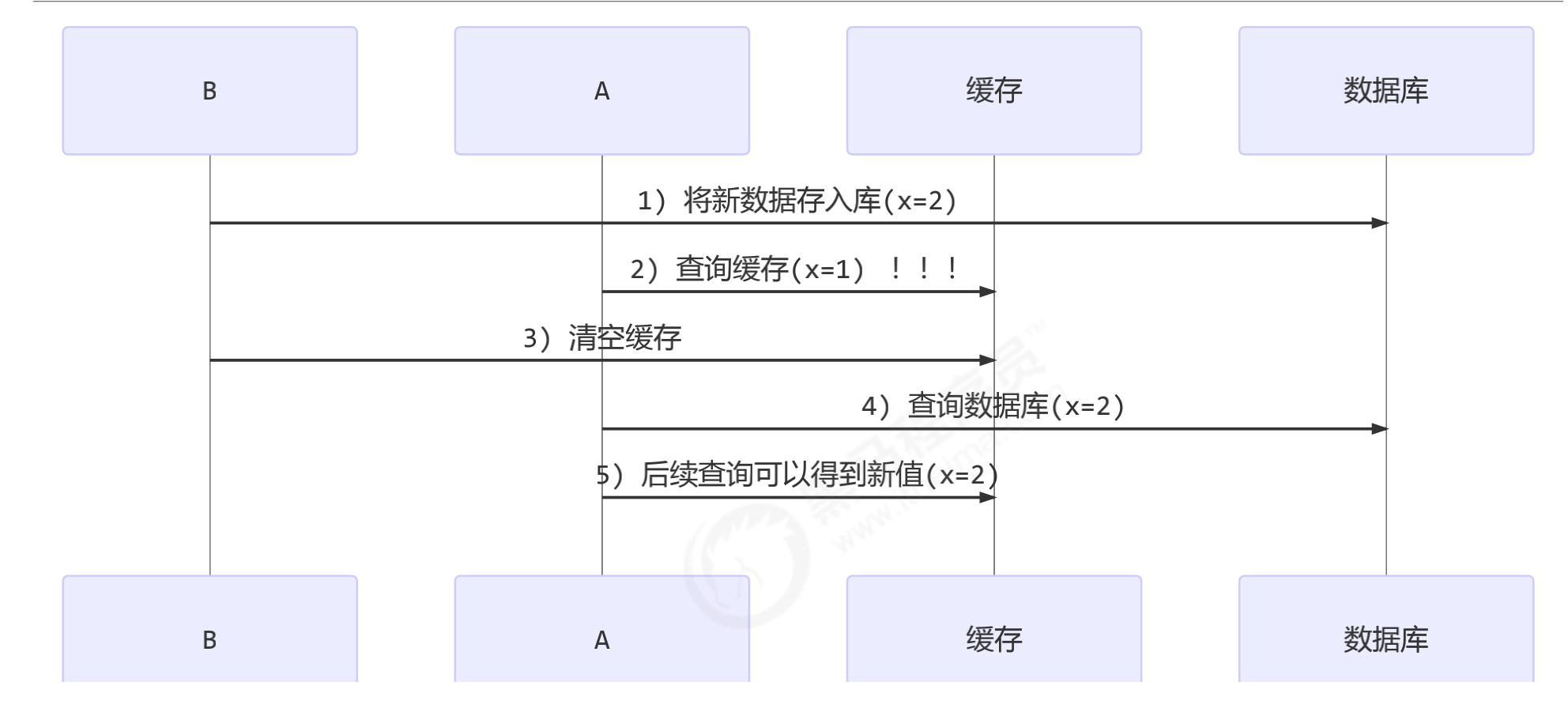
- 补充一种情况,假设查询线程 A 查询数据时恰好缓存数据由于时间到期失效,或是第一次查询
- 这种情况的出现几率非常小
- 由此可见,要保证这里的数据的一致性,就要保证更新数据库和清除缓存的原子性。
读写锁实现一致性缓存
使用读写锁实现一个简单的按需加载缓存
public class TestGenericDao {
public static void main(String[] args) {
GenericDao dao = new GenericDaoCached();
System.out.println("============> 查询");
String sql = "select * from emp where empno = ?";
int empno = 7369;
Emp emp = dao.queryOne(Emp.class, sql, empno);
System.out.println(emp);
emp = dao.queryOne(Emp.class, sql, empno);
System.out.println(emp);
emp = dao.queryOne(Emp.class, sql, empno);
System.out.println(emp);
System.out.println("============> 更新");
dao.update("update emp set sal = ? where empno = ?", 800, empno);
emp = dao.queryOne(Emp.class, sql, empno);
System.out.println(emp);
}
}
class GenericDaoCached extends GenericDao {
private GenericDao dao = new GenericDao();
private Map<SqlPair, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
// 读写锁
private ReentrantReadWriteLock rw = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
@Override
public <T> List<T> queryList(Class<T> beanClass, String sql, Object... args) {
return dao.queryList(beanClass, sql, args);
}
@Override
public <T> T queryOne(Class<T> beanClass, String sql, Object... args) {
// 先从缓存中找,找到直接返回
SqlPair key = new SqlPair(sql, args);;
rw.readLock().lock();
try {
T value = (T) map.get(key);
if(value != null) {
return value;
}
} finally {
rw.readLock().unlock();
}
rw.writeLock().lock();
try {
// 多个线程
T value = (T) map.get(key);
if(value == null) {
// 缓存中没有,查询数据库
value = dao.queryOne(beanClass, sql, args);
map.put(key, value);
}
return value;
} finally {
rw.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
@Override
public int update(String sql, Object... args) {
rw.writeLock().lock();
try {
// 先更新库
int update = dao.update(sql, args);
// 清空缓存
map.clear();
return update;
} finally {
rw.writeLock().unlock();
}
}
class SqlPair {
private String sql;
private Object[] args;
public SqlPair(String sql, Object[] args) {
this.sql = sql;
this.args = args;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) {
return true;
}
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) {
return false;
}
SqlPair sqlPair = (SqlPair) o;
return Objects.equals(sql, sqlPair.sql) &&
Arrays.equals(args, sqlPair.args);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
int result = Objects.hash(sql);
result = 31 * result + Arrays.hashCode(args);
return result;
}
}
}
注意
以上实现体现的是读写锁的应用,保证缓存和数据库的一致性,但有下面的问题没有考虑
- 适合读多写少,如果写操作比较频繁,以上实现性能低
- 没有考虑缓存容量,只存不删
- 没有考虑缓存过期,长期不用的数据没有清理
- 只适合单机,这里是在一个java进程实现的,不适合分布式的
- 并发性还是低,目前只会用一把锁。
- 如果查询多个表,表1、表2的读写操作不相关,但是由于用的是同一把锁,表1操作时,表2动不了。
- 更新方法太过简单粗暴,清空了所有 key(考虑按类型分区或重新设计 key)
- 表1的key清空,表2不应该受影响
读写锁原理
图解流程
读写锁用的是同一个 Sycn 同步器,因此等待队列、state 等也是同一个
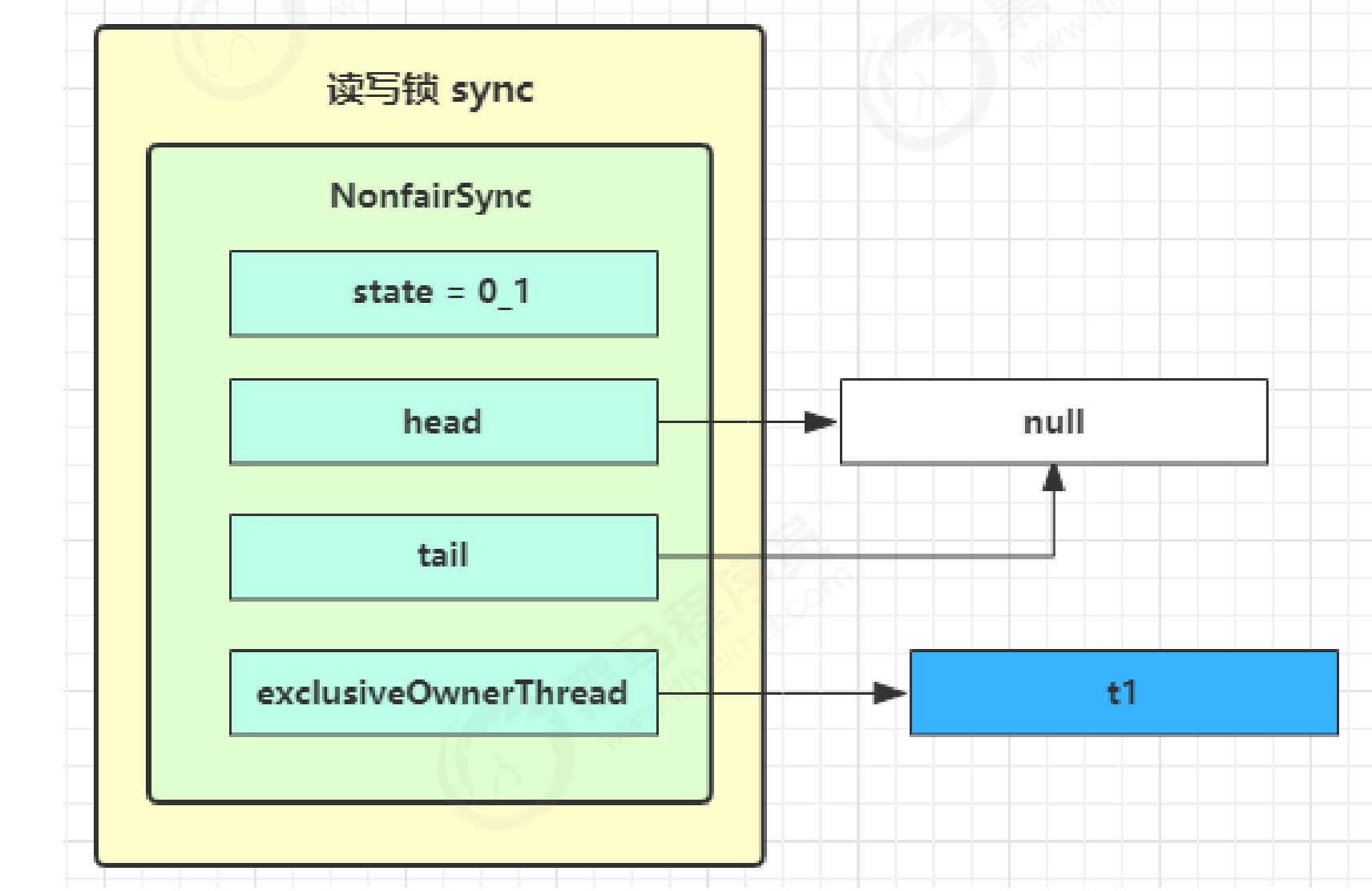
t1 w.lock,t2 r.lock
- t1 成功上锁,流程与 ReentrantLock 加锁相比没有特殊之处,不同是
写锁状态占了 state 的低 16 位,而读锁使用的是 state 的高 16 位
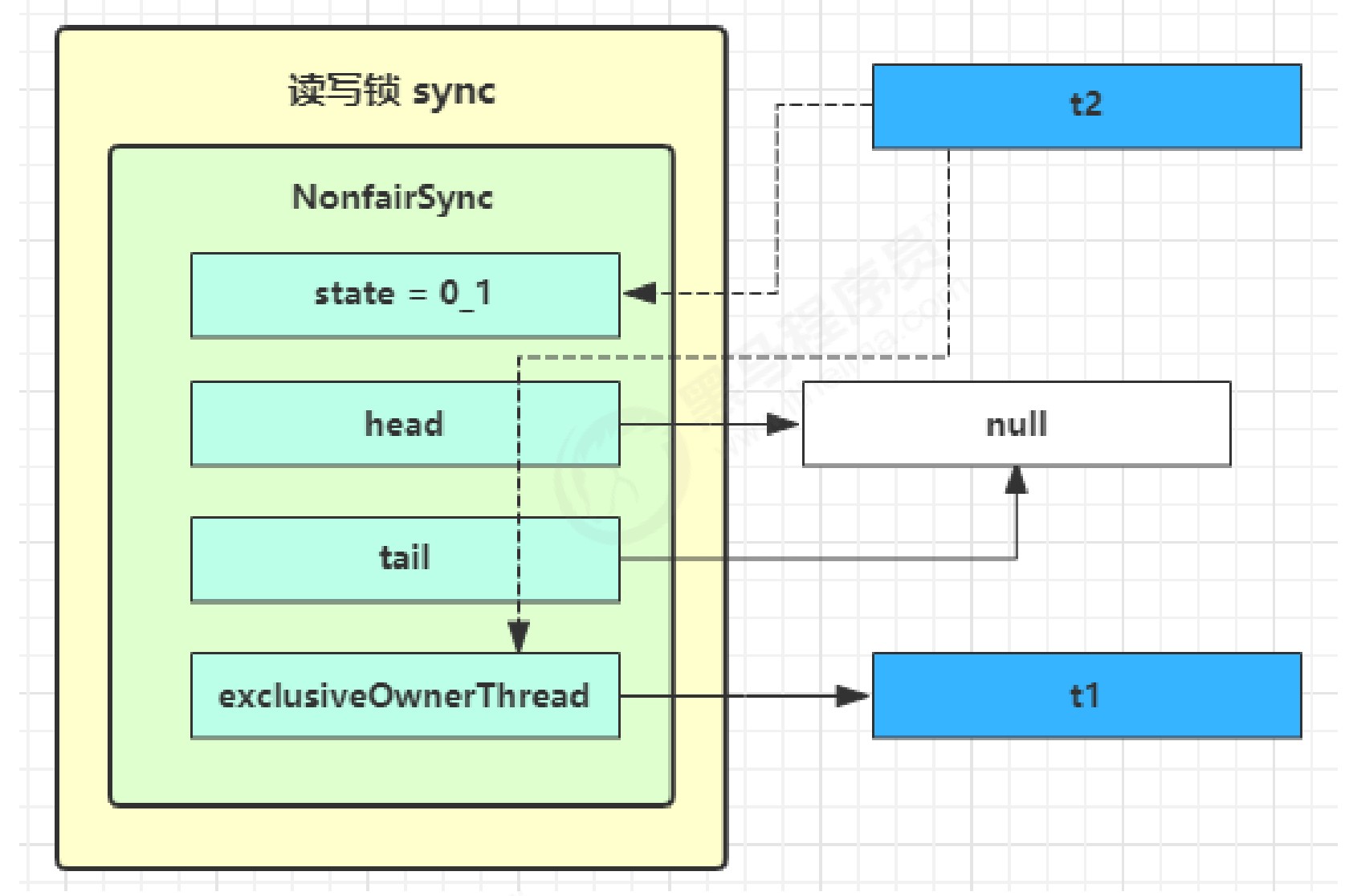
- t2 执行 r.lock,这时进入读锁的 sync.acquireShared(1) 流程,首先会进入 tryAcquireShared 流程。如果有写锁占据,那么 tryAcquireShared 返回 -1 表示失败
tryAcquireShared 返回值表示
- 1 表示失败
- 0 表示成功,但后继节点不会继续唤醒
- 正数表示成功,而且数值是还有几个后继节点需要唤醒,读写锁返回 1
- 这时会进入 sync.doAcquireShared(1) 流程,首先也是调用 addWaiter 添加节点,不同之处在于节点被设置为Node.SHARED 模式而非 Node.EXCLUSIVE 模式,注意此时 t2 仍处于活跃状态
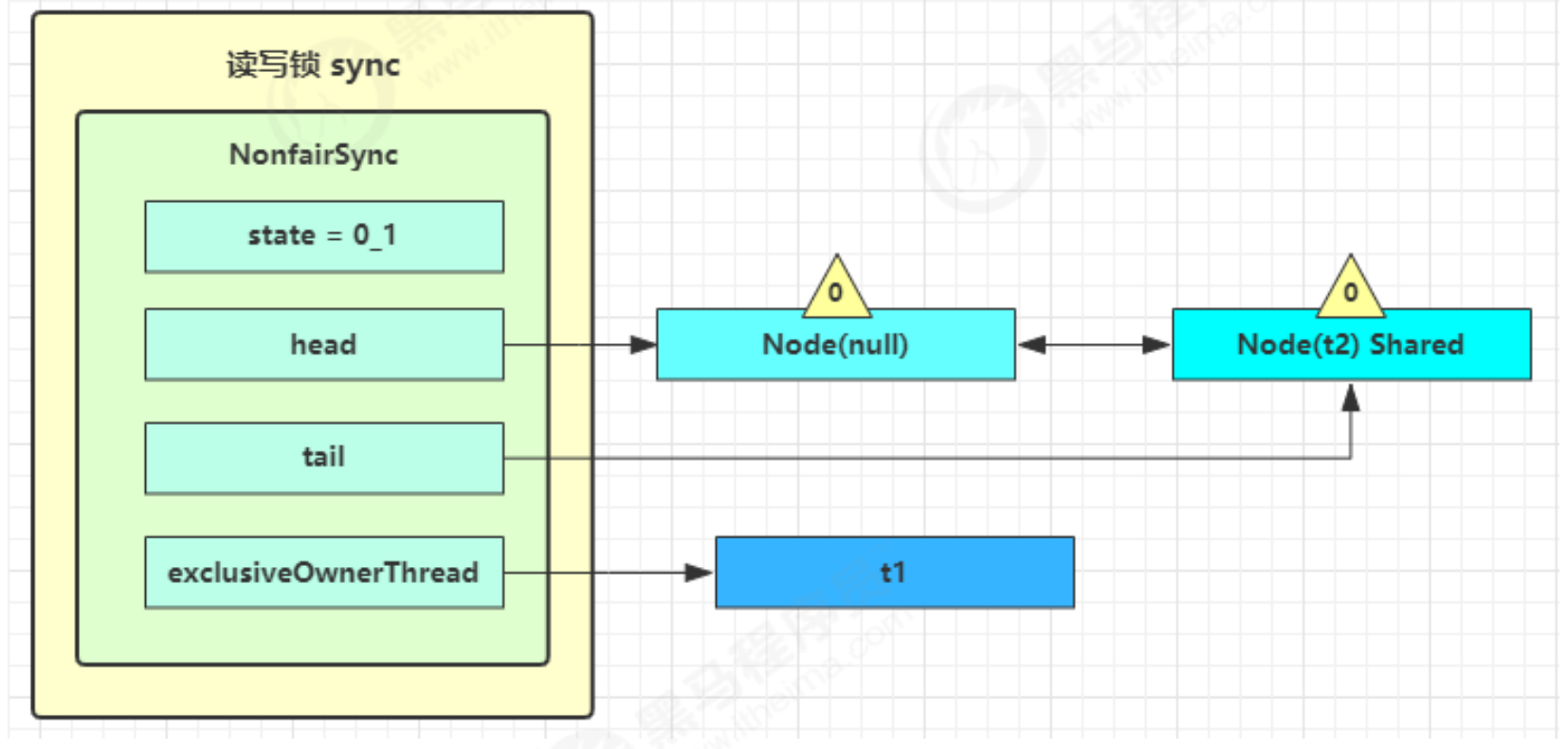
- t2 会看看自己的节点是不是老二,如果是,还会再次调用
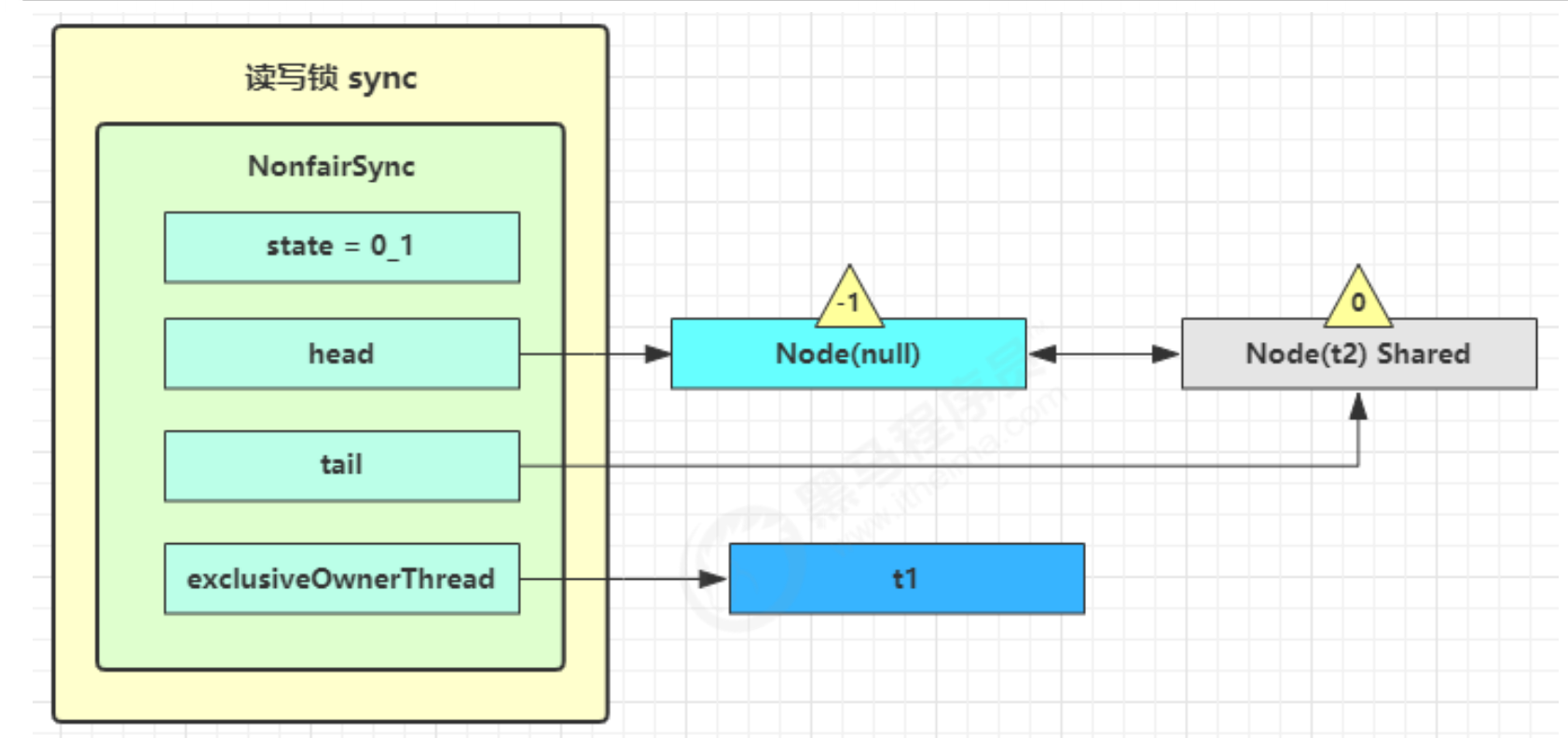
tryAcquireShared(1)来尝试获取锁 - 如果没有成功,在 doAcquireShared 内 for ( ; ; ) 循环一次,把前驱节点的 waitStatus 改为 -1,再 for ( ; ; ) 循环一次尝试 tryAcquireShared(1) 如果还不成功,那么在
parkAndCheckInterrupt( ) 处 park
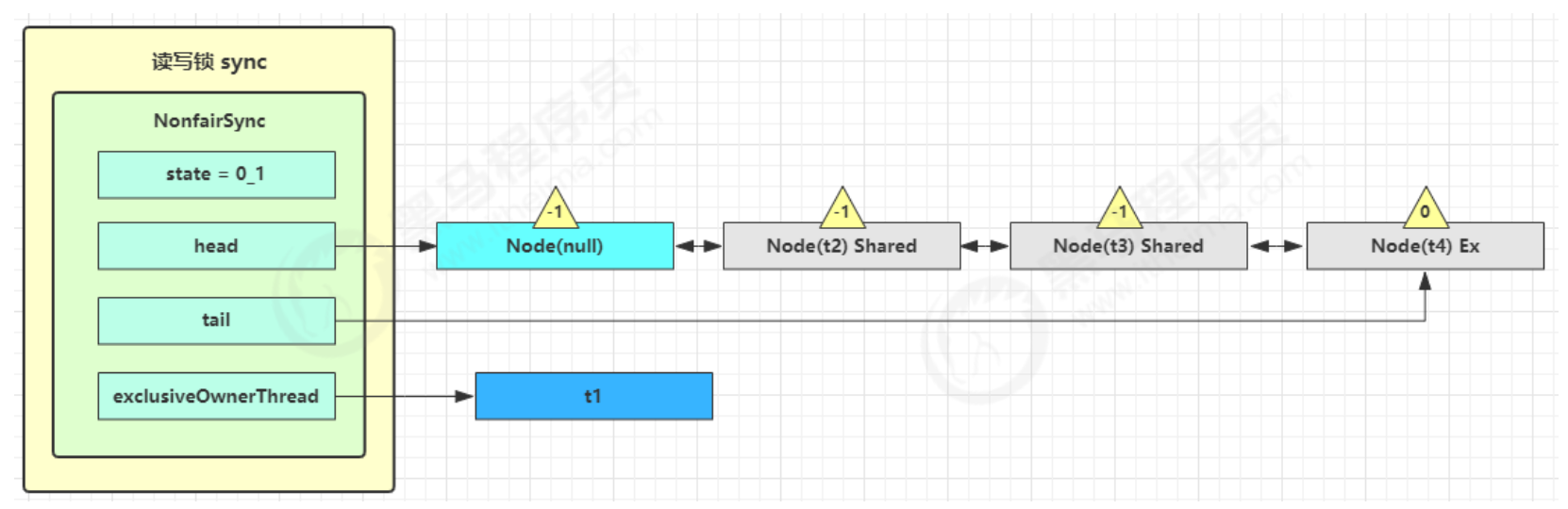
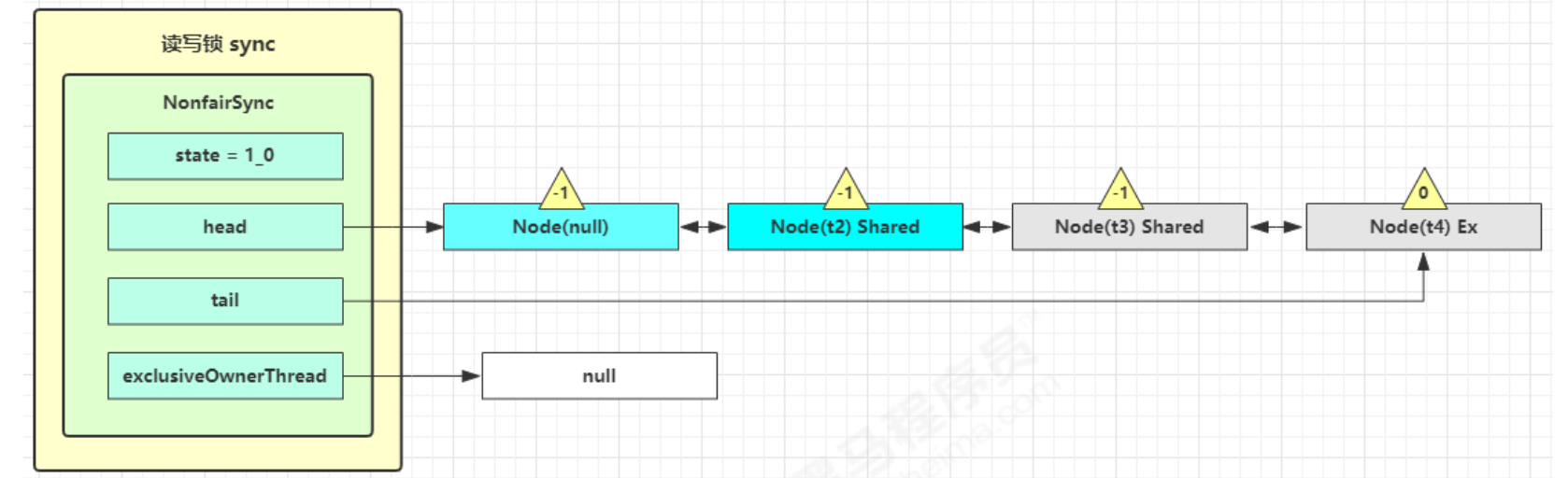
t3 r.lock,t4 w.lock
这种状态下,假设又有 t3 加读锁和 t4 加写锁,这期间 t1 仍然持有锁,就变成了下面的样子
- 读锁 Share 共享模式
- 写锁 Ex 独占模式
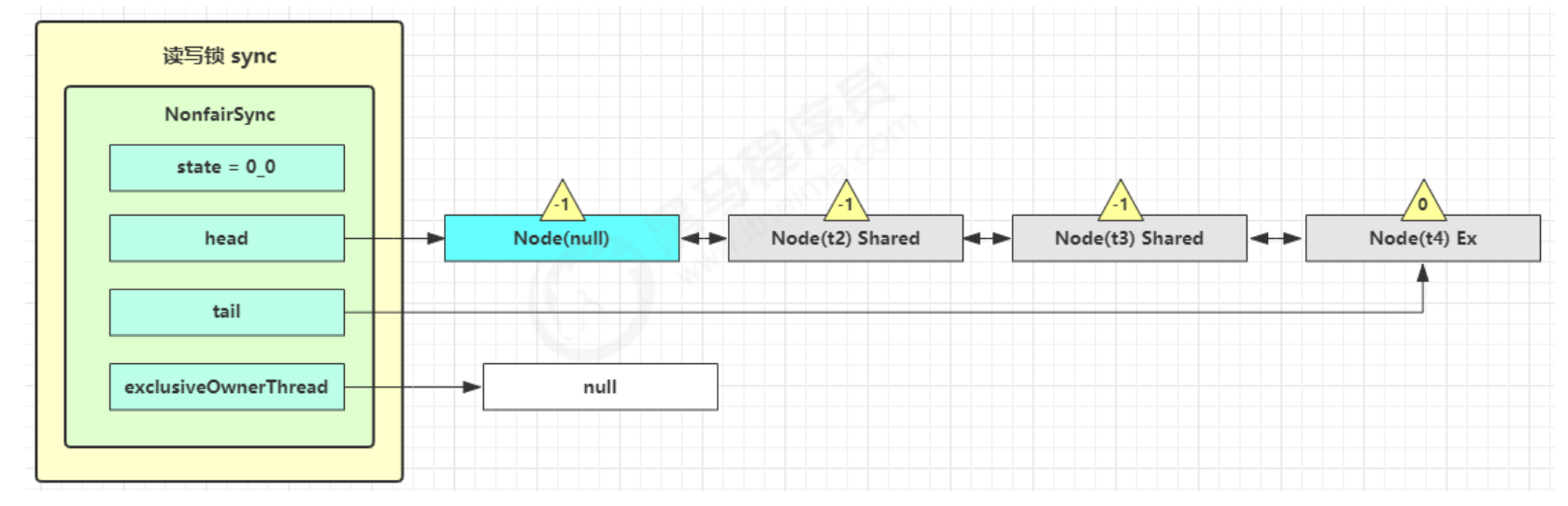
t1 w.unlock
- 这时会走到写锁的 sync.release(1) 流程,调用 sync.tryRelease(1) 成功,变成下面的样子
- 接下来执行唤醒流程 sync.unparkSuccessor,即让老二恢复运行,这时 t2 在 doAcquireShared 内parkAndCheckInterrupt() 处恢复运行
- 这回再来一次 for (; ; ) 执行 tryAcquireShared 成功则让读锁计数加一(即下图代码位置)
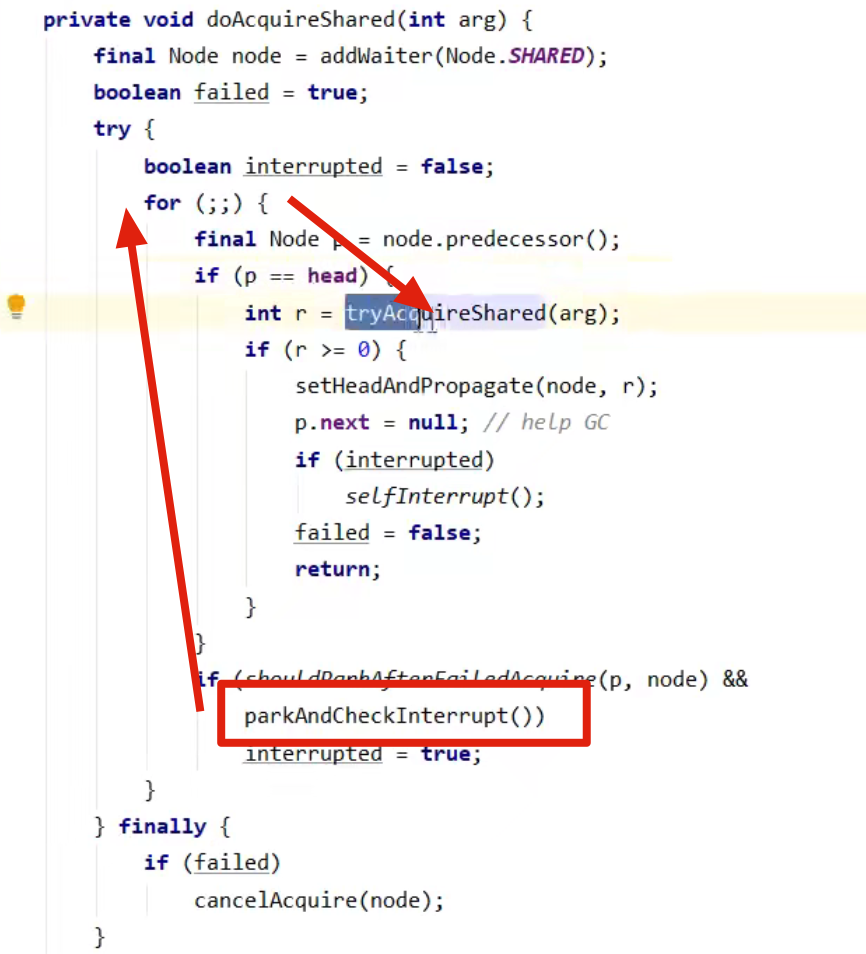
- 这时 t2 已经从节点取出来恢复运行,接下来 t2 调用 setHeadAndPropagate(node, 1),它原本所在节点被置为头节点
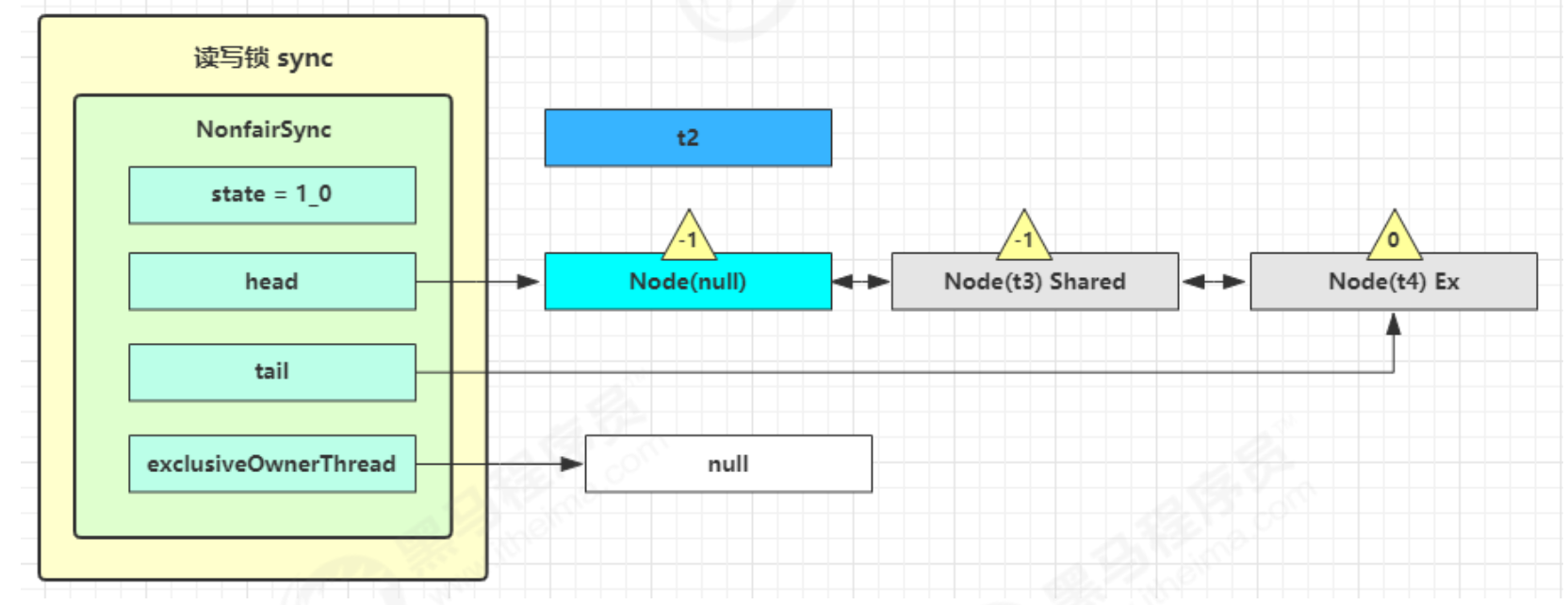
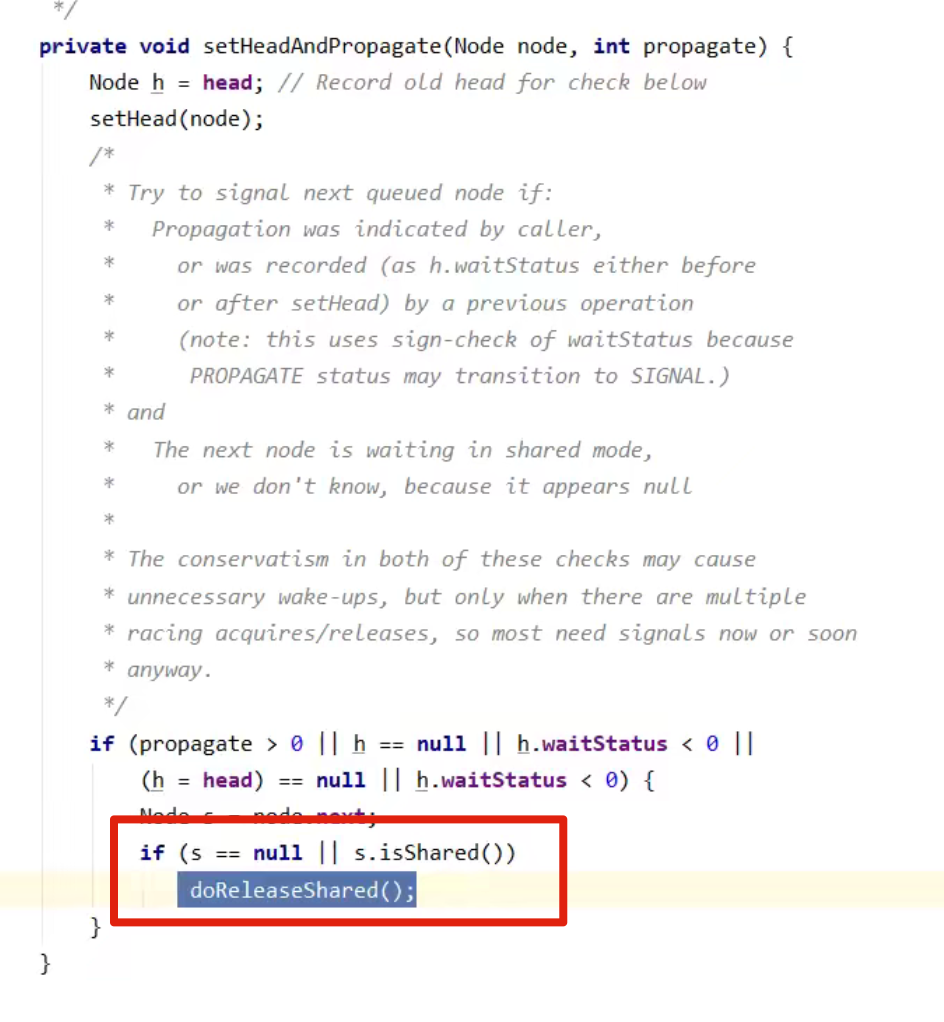
- 事情还没完,在 setHeadAndPropagate 方法内还会检查下一个节点是否是 shared,如果是则调用
doReleaseShared( )将 head 的状态从 -1 改为 0 并唤醒老二,这时 t3 在 doAcquireShared 内parkAndCheckInterrupt( ) 处恢复运行
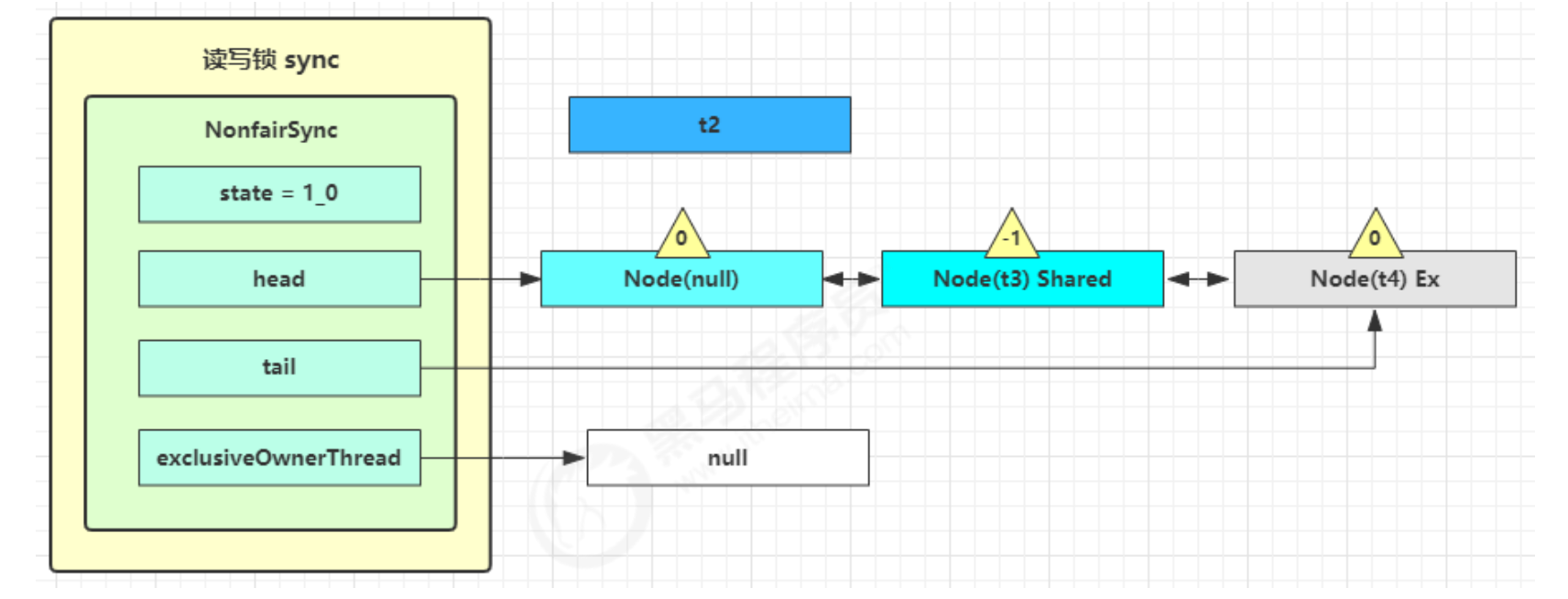
- 这回再来一次 for ( ; ; ) 执行 tryAcquireShared 成功则让读锁计数加一
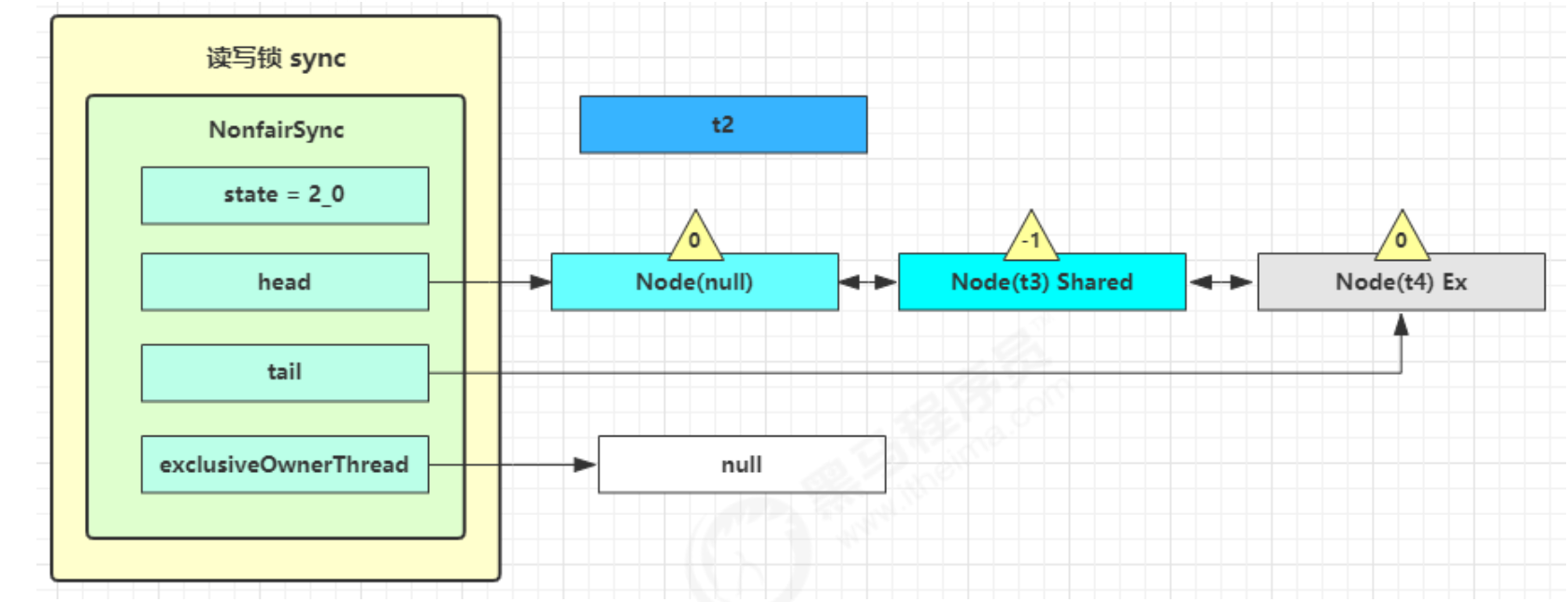
- 这时 t3 已经恢复运行,接下来 t3 调用 setHeadAndPropagate(node, 1),它原本所在节点被置为头节点
- 下一个节点不是 shared 了,因此不会继续唤醒 t4 所在节点
- 可以看到,当下一个节点是share类型的,就会继续执行释放,直到遇到Ex独占型的。这也是读-读可以并发的原因,遇到读锁shared线程就让他执行,然后只是让
state++来计数。
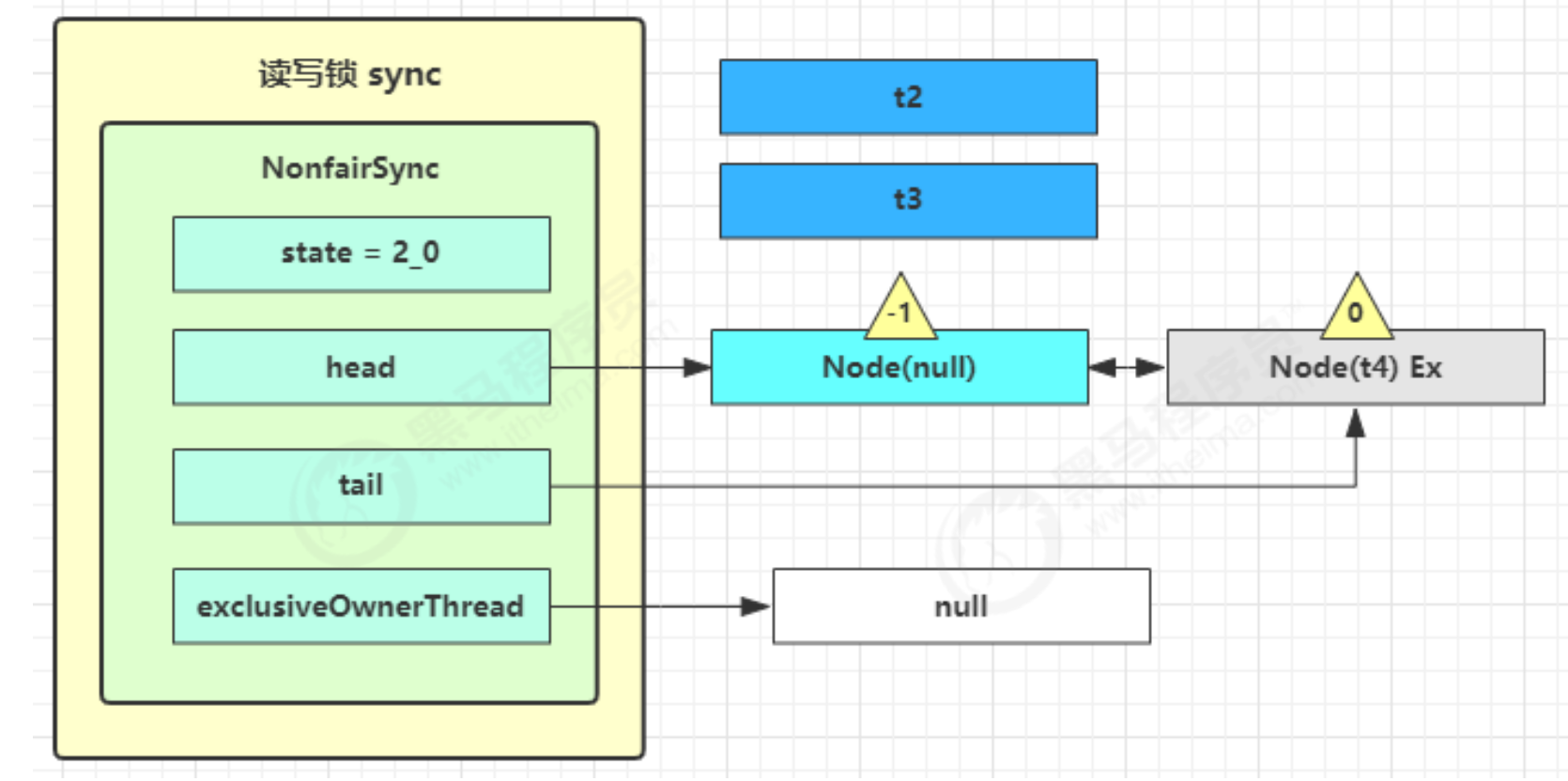
t2 r.unlock,t3 r.unlock
- t2 进入 sync.releaseShared(1) 中,调用 tryReleaseShared(1) 让计数减一,但由于计数还不为零
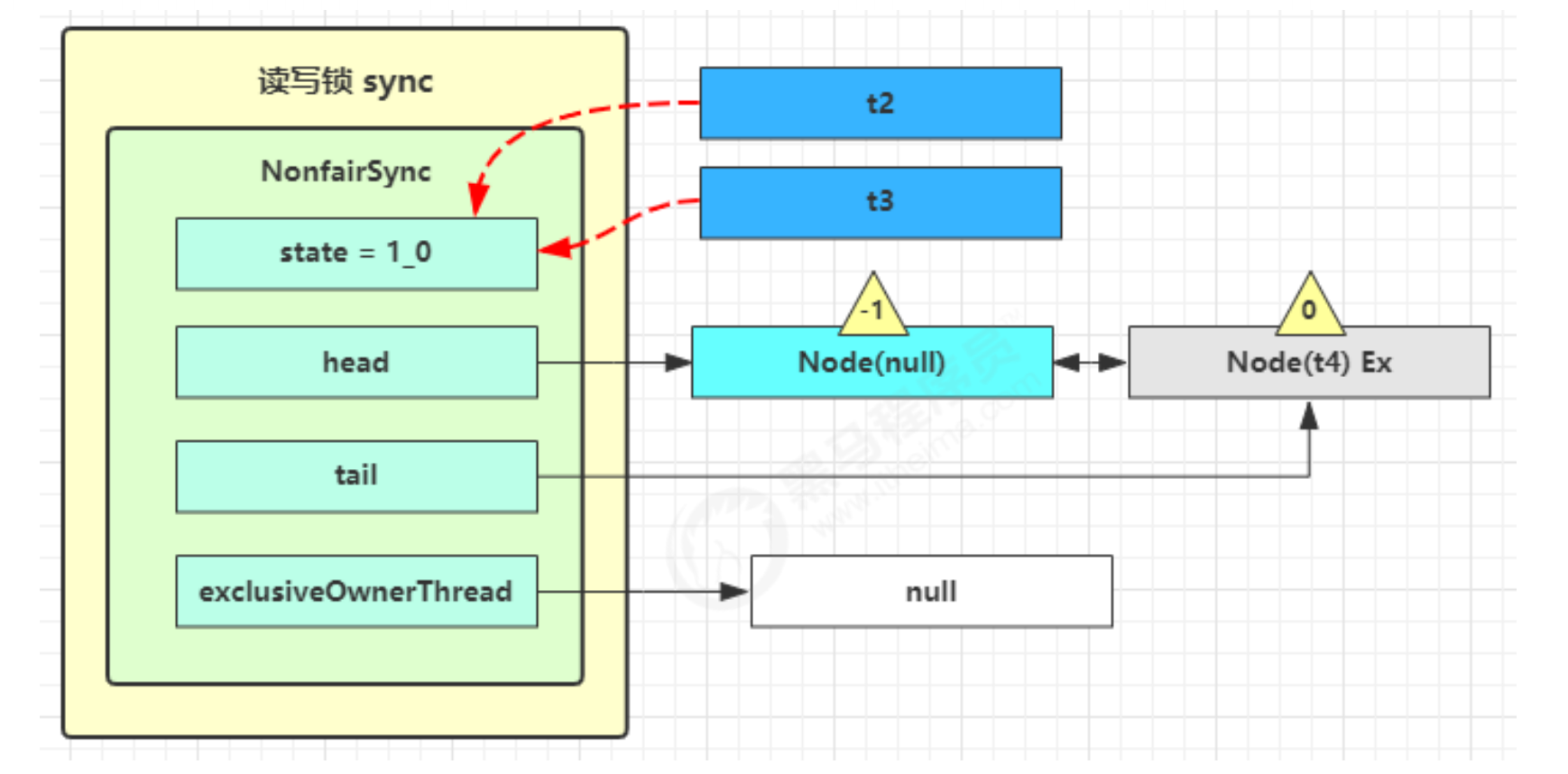
- t3 进入 sync.releaseShared(1) 中,调用 tryReleaseShared(1) 让计数减一,这回计数为零了,进入doReleaseShared( ) 将头节点从 -1 改为 0 并唤醒老二(t4),即
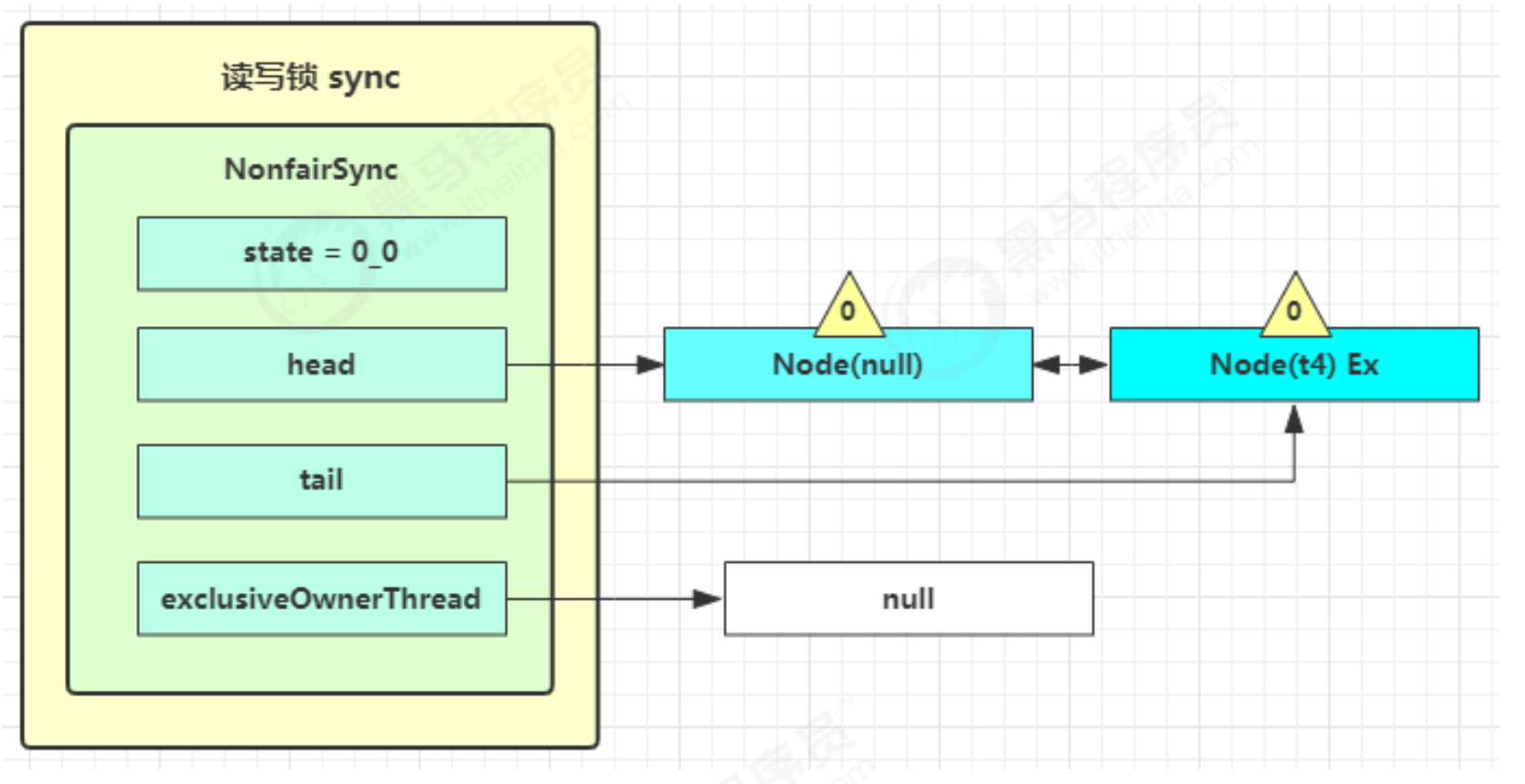
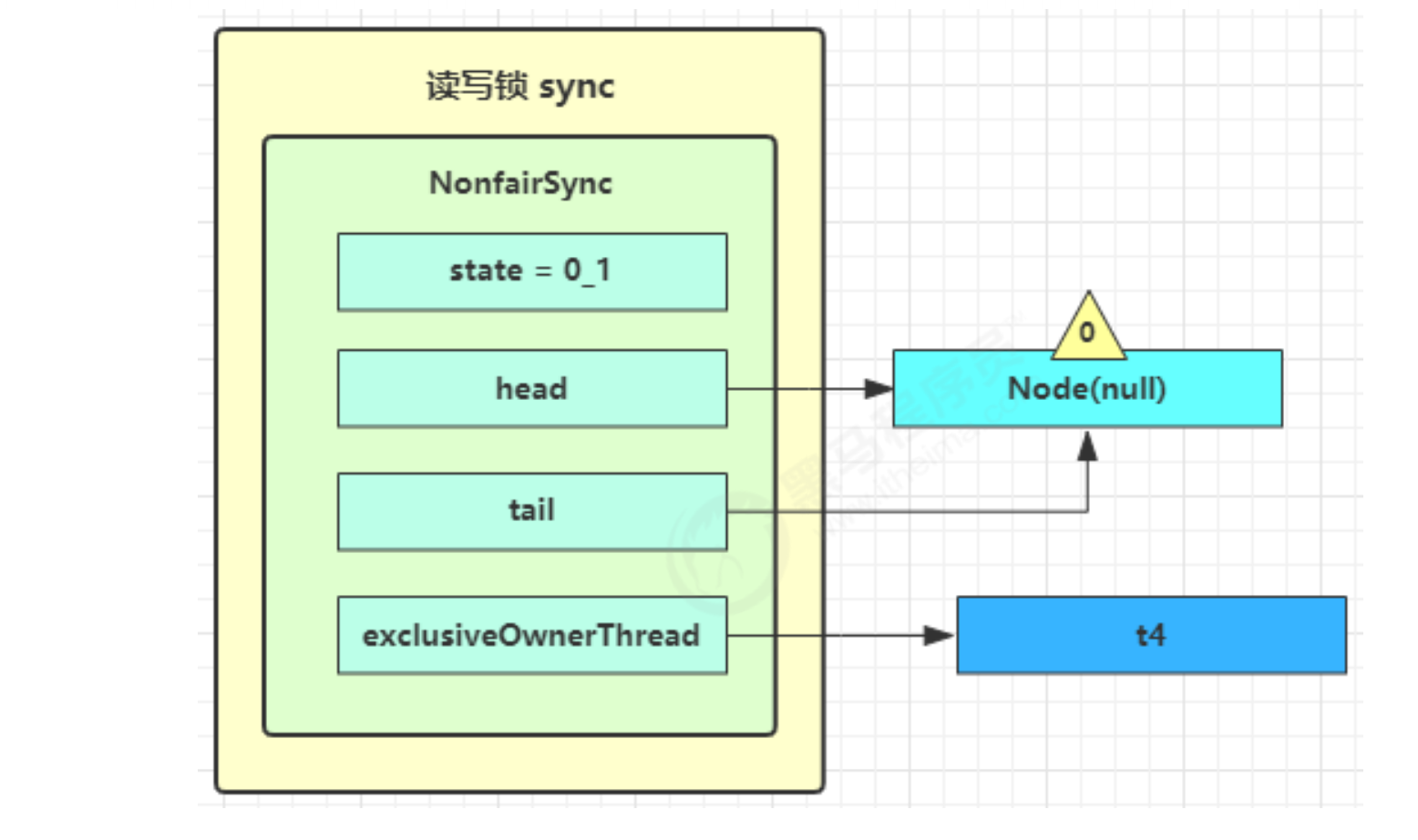
- 之后 t4 在 acquireQueued 中 parkAndCheckInterrupt 处恢复运行,再次 for ( ; ; ) 这次自己是老二,并且没有其他竞争,tryAcquire(1) 成功,修改头结点,流程结束
源码分析
写锁上锁流程
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
// ... 省略无关代码
// 外部类 WriteLock 方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
public void lock() {
sync.acquire(1);
}
// AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (
// 尝试获得写锁失败
!tryAcquire(arg) &&
// 将当前线程关联到一个 Node 对象上, 模式为独占模式
// 进入 AQS 队列阻塞
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg)
) {
selfInterrupt();
}
}
// Sync 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
// 获得低 16 位, 代表写锁的 state 计数
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
int w = exclusiveCount(c);
if (c != 0) {
if (
// c != 0 and w == 0 表示有读锁, 或者
w == 0 ||
// 如果 exclusiveOwnerThread 不是自己
current != getExclusiveOwnerThread()
) {
// 获得写锁失败
return false;
}
// 写锁计数超过低 16 位, 报异常
if (w + exclusiveCount(acquires) > MAX_COUNT)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
// 写锁重入, 获得锁成功
// 此时state高位(读锁)为0,直接加1即整体加1
setState(c + acquires);
return true;
}
if (
// 判断写锁是否该阻塞, 或者
writerShouldBlock() ||
// 尝试更改计数失败
!compareAndSetState(c, c + acquires)
) {
// 获得写锁失败
return false;
}
// 获得写锁成功
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
// 非公平锁 writerShouldBlock 总是返回 false, 无需阻塞
final boolean writerShouldBlock() {
return false;
}
}
写锁释放流程
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
// ... 省略无关代码
// WriteLock 方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
public void unlock() {
sync.release(1);
}
// AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
public final boolean release(int arg) {
// 尝试释放写锁成功
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
// unpark AQS 中等待的线程
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}
// Sync 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
if (!isHeldExclusively())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
int nextc = getState() - releases;
// 因为可重入的原因, 写锁计数为 0, 才算释放成功
boolean free = exclusiveCount(nextc) == 0;
if (free) {
// 把当前锁的持有者设置为 null
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
}
setState(nextc);
return free;
}
}
读锁上锁流程
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
// ReadLock 方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
public void lock() {
sync.acquireShared(1);
}
// AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
public final void acquireShared(int arg) {
// tryAcquireShared 返回负数, 表示获取读锁失败
if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0) {
doAcquireShared(arg);
}
}
// Sync 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
protected final int tryAcquireShared(int unused) {
// 获取当前线程
Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
// 如果是其它线程持有写锁, 获取读锁失败
if (
exclusiveCount(c) != 0 &&
// 或者加写锁的是不是自己
getExclusiveOwnerThread() != current
) {
return -1;
}
int r = sharedCount(c);
if (
// 读锁不该被阻塞(如果老二是写锁,读锁该阻塞), 并且
!readerShouldBlock() &&
// 小于读锁计数, 并且
r < MAX_COUNT &&
// 尝试增加计数成功
// 只让state的高位(读锁)加1
compareAndSetState(c, c + SHARED_UNIT)
) {
// ... 省略不重要的代码
return 1;
}
return fullTryAcquireShared(current);
}
// 非公平锁 readerShouldBlock 看 AQS 队列中第一个节点是否是写锁
// true 则该阻塞, false 则不阻塞
final boolean readerShouldBlock() {
return apparentlyFirstQueuedIsExclusive();
}
// AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
// 与 tryAcquireShared 功能类似, 但会不断尝试 for (;;) 获取读锁, 执行过程中无阻塞
final int fullTryAcquireShared(Thread current) {
HoldCounter rh = null;
for (;;) {
int c = getState();
if (exclusiveCount(c) != 0) {
if (getExclusiveOwnerThread() != current)
return -1;
} else if (readerShouldBlock()) {
// ... 省略不重要的代码
}
if (sharedCount(c) == MAX_COUNT)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
if (compareAndSetState(c, c + SHARED_UNIT)) {
// ... 省略不重要的代码
return 1;
}
}
}
// AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
private void doAcquireShared(int arg) {
// 将当前线程关联到一个 Node 对象上, 模式为共享模式
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED);
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
// 看看自己是不是第二个节点
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head) {
// 再一次尝试获取读锁
int r = tryAcquireShared(arg);
// 成功
if (r >= 0) {
// ㈠
// r 表示可用资源数, 在这里总是 1 允许传播
//(唤醒 AQS 中下一个 Share 节点)
setHeadAndPropagate(node, r);
p.next = null; // help GC
if (interrupted)
selfInterrupt();
failed = false;
return;
}
}
if (
// 是否在获取读锁失败时阻塞(前一个阶段 waitStatus == Node.SIGNAL)
shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
// park 当前线程
parkAndCheckInterrupt()
) {
interrupted = true;
}
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
// ㈠ AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
private void setHeadAndPropagate(Node node, int propagate) {
Node h = head; // Record old head for check below
// 设置自己为 head
setHead(node);
// propagate 表示有共享资源(例如共享读锁或信号量)
// 原 head waitStatus == Node.SIGNAL 或 Node.PROPAGATE
// 现在 head waitStatus == Node.SIGNAL 或 Node.PROPAGATE
if (propagate > 0 || h == null || h.waitStatus < 0 ||
(h = head) == null || h.waitStatus < 0) {
Node s = node.next;
// 如果是最后一个节点或者是等待共享读锁的节点
if (s == null || s.isShared()) {
// 进入 ㈡
doReleaseShared();
}
}
}
// ㈡ AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
private void doReleaseShared() {
// 如果 head.waitStatus == Node.SIGNAL ==> 0 成功, 下一个节点 unpark
// 如果 head.waitStatus == 0 ==> Node.PROPAGATE, 为了解决 bug, 见后面分析
for (;;) {
Node h = head;
// 队列还有节点
if (h != null && h != tail) {
int ws = h.waitStatus;
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) {
if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, Node.SIGNAL, 0))
continue; // loop to recheck cases
// 下一个节点 unpark 如果成功获取读锁
// 并且下下个节点还是 shared, 继续 doReleaseShared
unparkSuccessor(h);
}
else if (ws == 0 &&
!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, 0, Node.PROPAGATE))
continue; // loop on failed CAS
}
if (h == head) // loop if head changed
break;
}
}
}
读锁释放流程
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
// ReadLock 方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
public void unlock() {
sync.releaseShared(1);
}
// AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
public final boolean releaseShared(int arg) {
if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) {
doReleaseShared();
return true;
}
return false;
}
// Sync 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
protected final boolean tryReleaseShared(int unused) {
// ... 省略不重要的代码
for (;;) {
int c = getState();
int nextc = c - SHARED_UNIT;
if (compareAndSetState(c, nextc)) {
// 读锁的计数不会影响其它获取读锁线程, 但会影响其它获取写锁线程
// 计数为 0 才是真正释放
return nextc == 0;
}
}
}
// AQS 继承过来的方法, 方便阅读, 放在此处
private void doReleaseShared() {
// 如果 head.waitStatus == Node.SIGNAL ==> 0 成功, 下一个节点 unpark
// 如果 head.waitStatus == 0 ==> Node.PROPAGATE
for (;;) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h != tail) {
int ws = h.waitStatus;
// 如果有其它线程也在释放读锁,那么需要将 waitStatus 先改为 0
// 防止 unparkSuccessor 被多次执行
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) {
if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, Node.SIGNAL, 0))
continue; // loop to recheck cases
unparkSuccessor(h);
}
// 如果已经是 0 了,改为 -3,用来解决传播性,见后文信号量 bug 分析
else if (ws == 0 &&
!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, 0, Node.PROPAGATE))
continue; // loop on failed CAS
}
if (h == head) // loop if head changed
break;
}
}
}