多线程教程(三十二)ThreadPoolExecutor
1.线程池状态
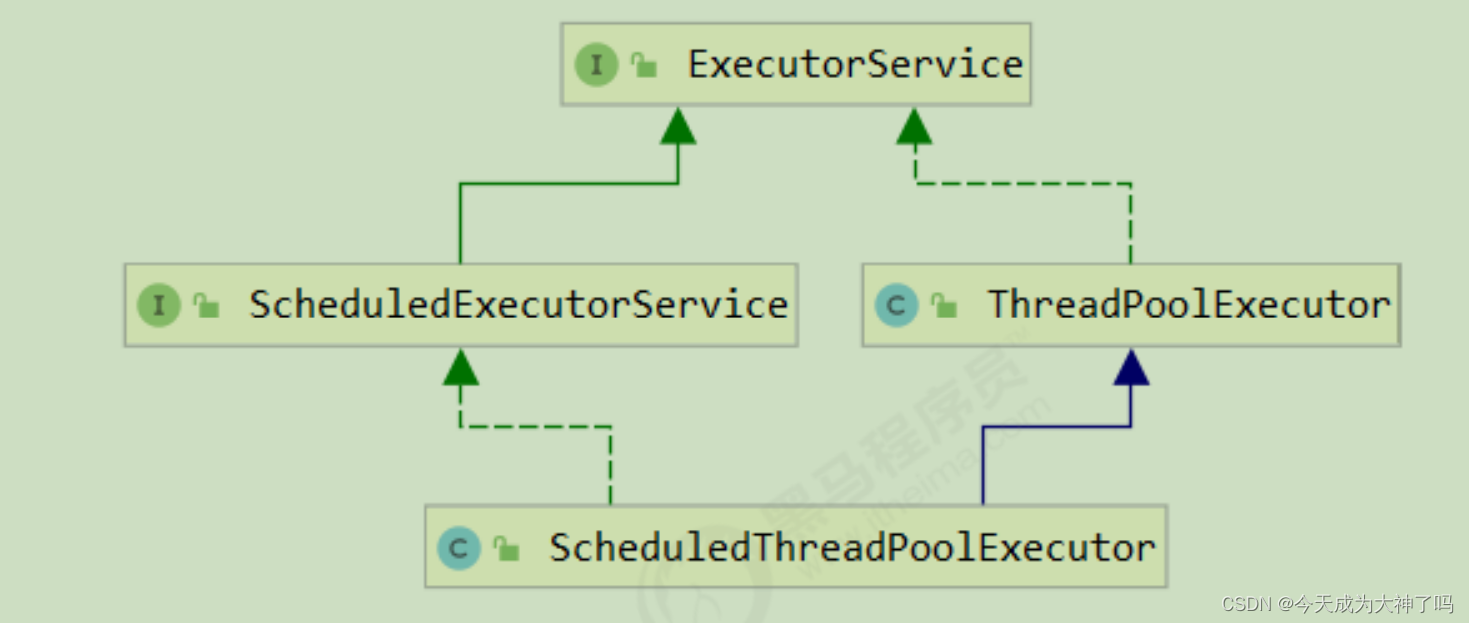
ThreadPoolExecutor 使用 int 的高 3 位来表示线程池状态,低 29 位表示线程数量
| 状态名 | 高 3位 | 接收新任务 | 处理阻塞队列任务 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RUNNING | 111 | Y | Y | |
| SHUTDOWN | 000 | N | Y | 不会接收新任务,但会处理阻塞队列剩余任务 |
| STOP | 001 | N | N | 会中断正在执行的任务,并抛弃阻塞队列任务 |
| TIDYING | 010 | - | - | 任务全执行完毕,活动线程为 0 即将进入终结 |
| TERMINATED | 011 | - | - | 终结状态 |
从数字上比较,TERMINATED > TIDYING > STOP > SHUTDOWN > RUNNING
这些信息存储在一个原子变量 ctl 中,目的是将线程池状态与线程个数合二为一,这样就可以用一次 cas 原子操作进行赋值
// c 为旧值, ctlOf 返回结果为新值
ctl.compareAndSet(c, ctlOf(targetState, workerCountOf(c))));
// rs 为高 3 位代表线程池状态, wc 为低 29 位代表线程个数,ctl 是合并它们
private static int ctlOf(int rs, int wc) { return rs | wc; }
2.构造方法
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit,
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler)
- corePoolSize 核心线程数目 (最多保留的线程数)
- maximumPoolSize 最大线程数目
- keepAliveTime 生存时间 - 针对救急线程
- unit 时间单位 - 针对救急线程
- workQueue 阻塞队列
- threadFactory 线程工厂 - 可以为线程创建时起个好名字
- handler 拒绝策略
工作方式

-
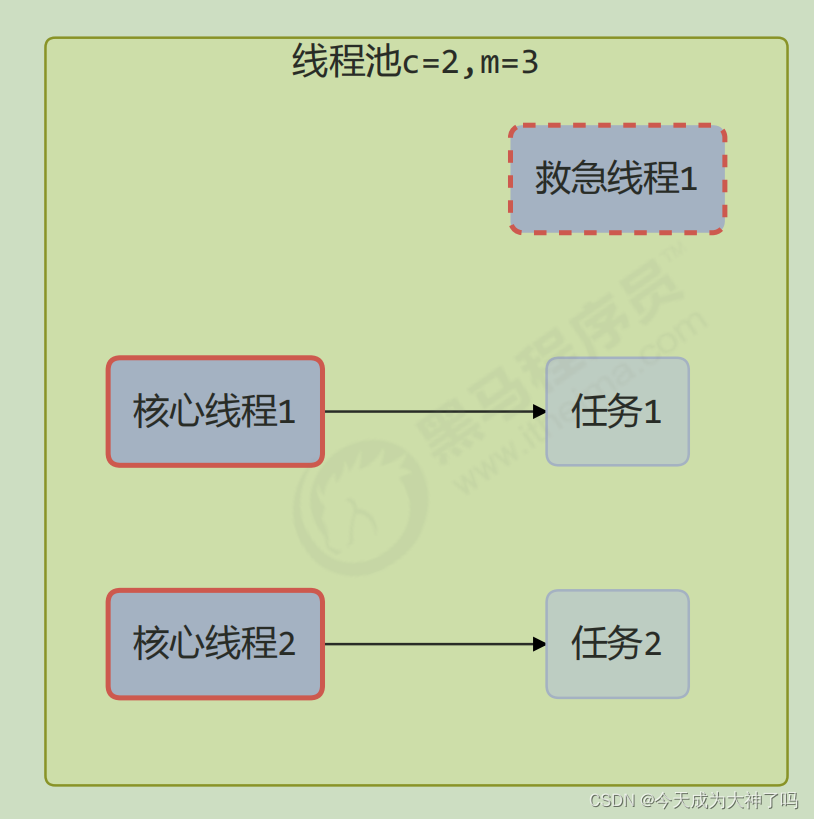
线程池中刚开始没有线程,当一个任务提交给线程池后,线程池会创建一个新线程来执行任务。
-
当线程数达到 corePoolSize 并没有线程空闲,这时再加入任务,新加的任务会被加入workQueue 队列排队,直到有空闲的线程。
-
如果队列选择了有界队列,那么任务超过了队列大小时,会创建 maximumPoolSize - corePoolSize (差值)数目的线程来救急。
-
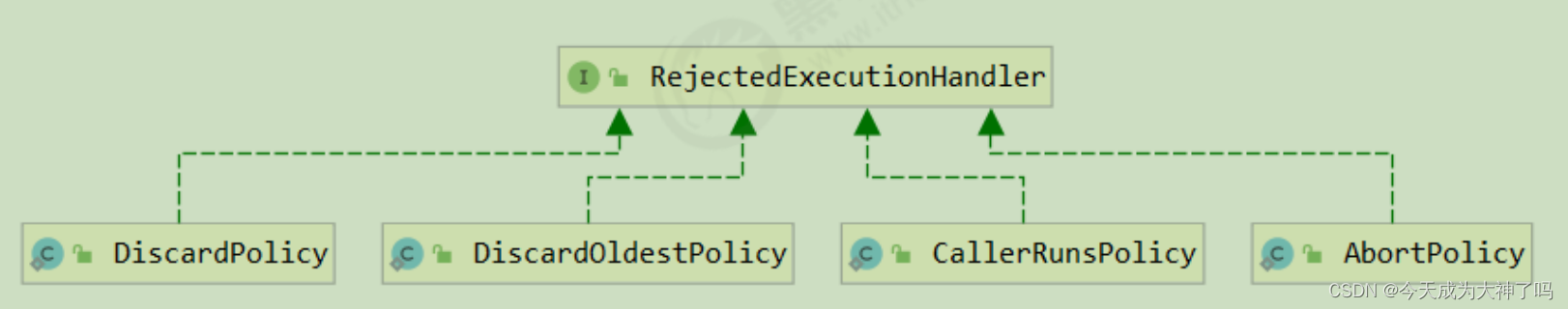
如果线程到达 maximumPoolSize 仍然有新任务这时会执行拒绝策略。拒绝策略 jdk 提供了 4 种实现,其它著名框架也提供了实现。
- AbortPolicy 让调用者抛出 RejectedExecutionException 异常,这是默认策略
- CallerRunsPolicy 让调用者运行任务
- DiscardPolicy 放弃本次任务
- DiscardOldestPolicy 放弃队列中最早的任务,本任务取而代之
- Dubbo 的实现,在抛出 RejectedExecutionException 异常之前会记录日志,并 dump 线程栈信息,方便定位问题
- Netty 的实现,是创建一个新线程来执行任务
- ActiveMQ 的实现,带超时等待(60s)尝试放入队列,类似我们之前自定义的拒绝策略
- PinPoint 的实现,它使用了一个拒绝策略链,会逐一尝试策略链中每种拒绝策略
-
当高峰过去后,超过corePoolSize 的救急线程如果一段时间没有任务做,需要结束节省资源,这个时间由keepAliveTime 和 unit 来控制。
根据这个构造方法,JDK Executors 类中提供了众多工厂方法来创建各种用途的线程池
3.newFixedThreadPool
public static ExecutorService newFixedThreadPool(int nThreads) {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(nThreads, nThreads,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>());
}
特点
-
核心线程数 == 最大线程数(没有救急线程被创建),因此也无需超时时间
-
阻塞队列是无界的,可以放任意数量的任务
评价 适用于任务量已知,相对耗时的任务
4.newCachedThreadPool
public static ExecutorService newCachedThreadPool() {
return new ThreadPoolExecutor(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE,
60L, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new SynchronousQueue<Runnable>());
}
特点
-
核心线程数是 0,
-
最大线程数是 Integer.MAX_VALUE,救急线程的空闲生存时间是 60s,意味着
- 全部都是救急线程(60s 后可以回收)
- 救急线程可以无限创建
-
队列采用了 SynchronousQueue 实现特点是,它没有容量,没有线程来取是放不进去的(一手交钱、一手交货)
SynchronousQueue<Integer> integers = new SynchronousQueue<>();
new Thread(() -> {
try {
log.debug("putting {} ", 1);
integers.put(1);
log.debug("{} putted...", 1);
log.debug("putting...{} ", 2);
integers.put(2);
log.debug("{} putted...", 2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"t1").start();
sleep(1);
new Thread(() -> {
try {
log.debug("taking {}", 1);
integers.take();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"t2").start();
sleep(1);
new Thread(() -> {
try {
log.debug("taking {}", 2);
integers.take();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"t3").start();
输出
11:48:15.500 c.TestSynchronousQueue [t1] - putting 1
11:48:16.500 c.TestSynchronousQueue [t2] - taking 1
11:48:16.500 c.TestSynchronousQueue [t1] - 1 putted...
11:48:16.500 c.TestSynchronousQueue [t1] - putting...2
11:48:17.502 c.TestSynchronousQueue [t3] - taking 2
11:48:17.503 c.TestSynchronousQueue [t1] - 2 putted...
评价 整个线程池表现为线程数会根据任务量不断增长,没有上限,当任务执行完毕,空闲 1分钟后释放线程。 适合任务数比较密集,但每个任务执行时间较短的情况
5. newSingleThreadExecutor
public static ExecutorService newSingleThreadExecutor() {
return new FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService
(new ThreadPoolExecutor(1, 1,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>()));
}
使用场景:
希望多个任务排队执行。线程数固定为 1,任务数多于 1 时,会放入无界队列排队。任务执行完毕,这唯一的线程也不会被释放。
区别:
-
自己创建一个单线程串行执行任务,如果任务执行失败而终止那么没有任何补救措施,而线程池还会新建一个线程,保证池的正常工作
-
Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor() 线程个数始终为1,不能修改
- FinalizableDelegatedExecutorService 应用的是装饰器模式,只对外暴露了 ExecutorService 接口,因此不能调用 ThreadPoolExecutor 中特有的方法
-
Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1) 初始时为1,以后还可以修改
- 对外暴露的是 ThreadPoolExecutor 对象,可以强转后调用 setCorePoolSize 等方法进行修改
6.提交任务
// 执行任务
void execute(Runnable command);
// 提交任务 task,用返回值 Future 获得任务执行结果
<T> Future<T> submit(Callable<T> task);
// 提交 tasks 中所有任务
<T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks)
throws InterruptedException;
// 提交 tasks 中所有任务,带超时时间
<T> List<Future<T>> invokeAll(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks,
long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException;
// 提交 tasks 中所有任务,哪个任务先成功执行完毕,返回此任务执行结果,其它任务取消
<T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException;
// 提交 tasks 中所有任务,哪个任务先成功执行完毕,返回此任务执行结果,其它任务取消,带超时时间
<T> T invokeAny(Collection<? extends Callable<T>> tasks,
long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException;
7.关闭线程池
shutdown
/*
线程池状态变为 SHUTDOWN
- 不会接收新任务
- 但已提交任务会执行完
- 此方法不会阻塞调用线程的执行
*/
void shutdown();
public void shutdown() {
final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock;
mainLock.lock();
try {
checkShutdownAccess();
// 修改线程池状态
advanceRunState(SHUTDOWN);
// 仅会打断空闲线程
interruptIdleWorkers();
onShutdown(); // 扩展点 ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor
} finally {
mainLock.unlock();
}
// 尝试终结(没有运行的线程可以立刻终结,如果还有运行的线程也不会等)
tryTerminate();
}
shutdownNow
/*
线程池状态变为 STOP
- 不会接收新任务
- 会将队列中的任务返回
- 并用 interrupt 的方式中断正在执行的任务
*/
List<Runnable> shutdownNow();
public List<Runnable> shutdownNow() {
List<Runnable> tasks;
final ReentrantLock mainLock = this.mainLock;
mainLock.lock();
try {
checkShutdownAccess();
// 修改线程池状态
advanceRunState(STOP);
// 打断所有线程
interruptWorkers();
// 获取队列中剩余任务
tasks = drainQueue();
} finally {
mainLock.unlock();
}
// 尝试终结
tryTerminate();
return tasks; }
其它方法
// 不在 RUNNING 状态的线程池,此方法就返回 true
boolean isShutdown();
// 线程池状态是否是 TERMINATED
boolean isTerminated();
// 调用 shutdown 后,由于调用线程并不会等待所有任务运行结束,因此如果它想在线程池 TERMINATED 后做些事
情,可以利用此方法等待
boolean awaitTermination(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException;
8. 任务调度线程池
在『任务调度线程池』功能加入之前,可以使用 java.util.Timer 来实现定时功能,Timer 的优点在于简单易用,但由于所有任务都是由同一个线程来调度,因此所有任务都是串行执行的,同一时间只能有一个任务在执行,前一个任务的延迟或异常都将会影响到之后的任务。
public static void main(String[] args) {
Timer timer = new Timer();
TimerTask task1 = new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
log.debug("task 1");
sleep(2);
}
};
TimerTask task2 = new TimerTask() {
@Override
public void run() {
log.debug("task 2");
}
};
// 使用 timer 添加两个任务,希望它们都在 1s 后执行
// 但由于 timer 内只有一个线程来顺序执行队列中的任务,因此『任务1』的延时,影响了『任务2』的执行
timer.schedule(task1, 1000);
timer.schedule(task2, 1000);
}
输出
20:46:09.444 c.TestTimer [main] - start...
20:46:10.447 c.TestTimer [Timer-0] - task 1
20:46:12.448 c.TestTimer [Timer-0] - task 2
使用 ScheduledExecutorService 改写:
ScheduledExecutorService executor = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(2);
// 添加两个任务,希望它们都在 1s 后执行
executor.schedule(() -> {
System.out.println("任务1,执行时间:" + new Date());
try { Thread.sleep(2000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { }
}, 1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
executor.schedule(() -> {
System.out.println("任务2,执行时间:" + new Date());
}, 1000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
输出
任务1,执行时间:Thu Jan 03 12:45:17 CST 2019
任务2,执行时间:Thu Jan 03 12:45:17 CST 2019
scheduleAtFixedRate 例子:
ScheduledExecutorService pool = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);
log.debug("start...");
pool.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {
log.debug("running...");
}, 1, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
输出:
21:45:43.167 c.TestTimer [main] - start...
21:45:44.215 c.TestTimer [pool-1-thread-1] - running...
21:45:45.215 c.TestTimer [pool-1-thread-1] - running...
21:45:46.215 c.TestTimer [pool-1-thread-1] - running...
21:45:47.215 c.TestTimer [pool-1-thread-1] - running...
scheduleAtFixedRate 例子(任务执行时间超过了间隔时间):
ScheduledExecutorService pool = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);
log.debug("start...");
pool.scheduleAtFixedRate(() -> {
log.debug("running...");
sleep(2);
}, 1, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
输出分析:一开始,延时 1s,接下来,由于任务执行时间 > 间隔时间,间隔被『撑』到了 2s
21:44:30.311 c.TestTimer [main] - start...
21:44:31.360 c.TestTimer [pool-1-thread-1] - running...
21:44:33.361 c.TestTimer [pool-1-thread-1] - running...
21:44:35.362 c.TestTimer [pool-1-thread-1] - running...
21:44:37.362 c.TestTimer [pool-1-thread-1] - running...
scheduleWithFixedDelay 例子:
ScheduledExecutorService pool = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);
log.debug("start...");
pool.scheduleWithFixedDelay(()-> {
log.debug("running...");
sleep(2);
}, 1, 1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
输出分析:一开始,延时 1s,scheduleWithFixedDelay 的间隔是 上一个任务结束 <-> 延时 <-> 下一个任务开始 所以间隔都是 3s
21:40:55.078 c.TestTimer [main] - start...
21:40:56.140 c.TestTimer [pool-1-thread-1] - running...
21:40:59.143 c.TestTimer [pool-1-thread-1] - running...
21:41:02.145 c.TestTimer [pool-1-thread-1] - running...
21:41:05.147 c.TestTimer [pool-1-thread-1] - running...
评价 整个线程池表现为:线程数固定,任务数多于线程数时,会放入无界队列排队。任务执行完毕,这些线程也不会被释放。用来执行延迟或反复执行的任务
9.正确处理执行任务异常
方法1:主动捉异常
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
pool.submit(() -> {
try {
log.debug("task1");
int i = 1 / 0;
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("error:", e);
}
});
输出
21:59:04.558 c.TestTimer [pool-1-thread-1] - task1
21:59:04.562 c.TestTimer [pool-1-thread-1] - error:
java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
at cn.itcast.n8.TestTimer.lambda$main$0(TestTimer.java:28)
at java.util.concurrent.Executors$RunnableAdapter.call(Executors.java:511)
at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.run(FutureTask.java:266)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1149)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:624)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748)
方法2:使用 Future
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
Future<Boolean> f = pool.submit(() -> {
log.debug("task1");
int i = 1 / 0;
return true;
});
log.debug("result:{}", f.get());
输出
21:54:58.208 c.TestTimer [pool-1-thread-1] - task1
Exception in thread "main" java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException:
java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.report(FutureTask.java:122)
at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.get(FutureTask.java:192)
at cn.itcast.n8.TestTimer.main(TestTimer.java:31)
Caused by: java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
at cn.itcast.n8.TestTimer.lambda$main$0(TestTimer.java:28)
at java.util.concurrent.FutureTask.run(FutureTask.java:266)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor.runWorker(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:1149)
at java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor$Worker.run(ThreadPoolExecutor.java:624)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748)