?
?
在mybatis中sql的来源一般分位两种方式:
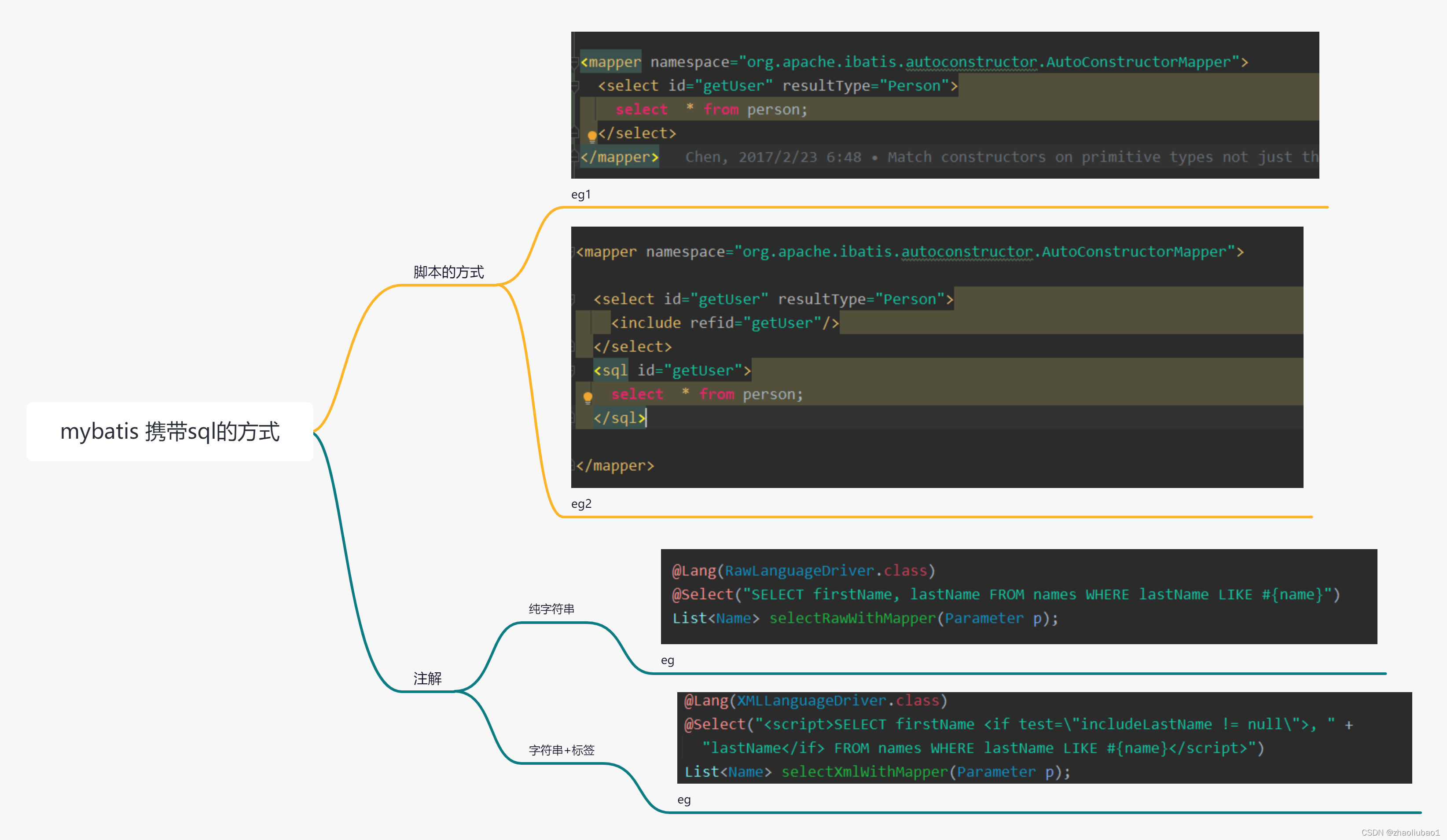
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ?详细总结图
1.写在xml文件中,如:
2.通过注解写入sql,如:

在此文中我们将研究mybatis是如何获取他们,并把他们放在哪。
从上一篇博客(maybatis源码分析(二)——mybatis mapper的注册流程_zhaoliubao1的博客-CSDN博客)我们可以知道,mybatis首先会读取配置文件,并最终构建出mapper接口的代理工厂类,此时我们的mapper接口的相关信息已经被获取,那么接下来我们就要具体去寻找mapper接口对应的方法的sql。有两种情况,一种是写在xml文件中,另一种写通过注解的方式去记录将要执行的sql。
我们先研究mybatis是如何解析注解中携带的sql语句:
源码如下:
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
if (type.isInterface()) {
if (hasMapper(type)) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
//注入该接口对应的代理工厂类
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<>(type));
// It's important that the type is added before the parser is run
// otherwise the binding may automatically be attempted by the
// mapper parser. If the type is already known, it won't try.
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
//------解析sql----//
parser.parse();
? //------解析sql----//
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
?其实我们可以看到,解析sql的时候我们需要传入该类的信息(文件路径)其实就是mapper注册的key值。
接下来便是真正解析sql了:
public void parse() {
String resource = type.toString();
//防止重复解析
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
? //通过xml去解析sql
loadXmlResource();
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
assistant.setCurrentNamespace(type.getName());
parseCache();
parseCacheRef();
//获取改接口的所有方法 遍历解析sql 组装ResultMap
for (Method method : type.getMethods()) {
if (!canHaveStatement(method)) {
continue;
}
if (getAnnotationWrapper(method, false, Select.class, SelectProvider.class).isPresent()
&& method.getAnnotation(ResultMap.class) == null) {
parseResultMap(method);
}
try {
//解析sql的入口
parseStatement(method);
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteMethod(new MethodResolver(this, method));
}
}
}
parsePendingMethods();
}
先看注解解析入口代码:
//注解解析sql的入口 parseStatement(method);
拨开云雾我们终于看到了SqlSource 这便是sql源了
void parseStatement(Method method) {
//获取该方法的返回值
final Class<?> parameterTypeClass = getParameterType(method);
final LanguageDriver languageDriver = getLanguageDriver(method);
getAnnotationWrapper(method, true, statementAnnotationTypes).ifPresent(statementAnnotation -> {
? //这里便是最终得到的sql源代码了
final SqlSource sqlSource = buildSqlSource(statementAnnotation.getAnnotation(), parameterTypeClass, languageDriver, method);
final SqlCommandType sqlCommandType = statementAnnotation.getSqlCommandType();
final Options options = getAnnotationWrapper(method, false, Options.class).map(x -> (Options)x.getAnnotation()).orElse(null);
final String mappedStatementId = type.getName() + "." + method.getName();
final KeyGenerator keyGenerator;
String keyProperty = null;
String keyColumn = null;
.....
}
首先我们需要先了解一下这个方法:
private Optional<AnnotationWrapper> getAnnotationWrapper(Method method, boolean errorIfNoMatch,
Collection<Class<? extends Annotation>> targetTypes) {
String databaseId = configuration.getDatabaseId();
Map<String, AnnotationWrapper> statementAnnotations = targetTypes.stream()
.flatMap(x -> Arrays.stream(method.getAnnotationsByType(x))).map(AnnotationWrapper::new)
.collect(Collectors.toMap(AnnotationWrapper::getDatabaseId, x -> x, (existing, duplicate) -> {
throw new BuilderException(String.format("Detected conflicting annotations '%s' and '%s' on '%s'.",
existing.getAnnotation(), duplicate.getAnnotation(),
method.getDeclaringClass().getName() + "." + method.getName()));
}));
......
}
这段代码的意思就是:将某个方法的注解何预定的注解进行匹配,并返回。?
接下来我们将研究他是如何获取并赋值给?SqlSource对象的,也就是:
final SqlSource sqlSource = buildSqlSource(statementAnnotation.getAnnotation(), parameterTypeClass, languageDriver, method);
我们继续深入可以发现:
private SqlSource buildSqlSource(Annotation annotation, Class<?> parameterType, LanguageDriver languageDriver,
Method method) {
if (annotation instanceof Select) {
return buildSqlSourceFromStrings(((Select) annotation).value(), parameterType, languageDriver);
} else if (annotation instanceof Update) {
return buildSqlSourceFromStrings(((Update) annotation).value(), parameterType, languageDriver);
} else if (annotation instanceof Insert) {
return buildSqlSourceFromStrings(((Insert) annotation).value(), parameterType, languageDriver);
} else if (annotation instanceof Delete) {
return buildSqlSourceFromStrings(((Delete) annotation).value(), parameterType, languageDriver);
} else if (annotation instanceof SelectKey) {
return buildSqlSourceFromStrings(((SelectKey) annotation).statement(), parameterType, languageDriver);
}
return new ProviderSqlSource(assistant.getConfiguration(), annotation, type, method);
}
通过先前getAnnotationWrapper我们已经得到了某个方法对应的注解,那在此处我们就可以知道这个注解的具体信息
我们看其中一段代码:
private SqlSource buildSqlSourceFromStrings(String[] strings, Class<?> parameterTypeClass,
LanguageDriver languageDriver) {
return languageDriver.createSqlSource(configuration, String.join(" ", strings).trim(), parameterTypeClass);
}
继续进入:
@Override
public SqlSource createSqlSource(Configuration configuration, String script, Class<?> parameterType) {
// issue #3
if (script.startsWith("<script>")) {
XPathParser parser = new XPathParser(script, false, configuration.getVariables(), new XMLMapperEntityResolver());
return createSqlSource(configuration, parser.evalNode("/script"), parameterType);
} else {
// issue #127
script = PropertyParser.parse(script, configuration.getVariables());
TextSqlNode textSqlNode = new TextSqlNode(script);
if (textSqlNode.isDynamic()) {
return new DynamicSqlSource(configuration, textSqlNode);
} else {
return new RawSqlSource(configuration, script, parameterType);
}
}
}
通过我们前面的讲解 我们已经知道了 sql来源 ,所以如果我么的来源是注解并且没有<script>标签那么他将会走else逻辑,比如我们现在拿到了一条这样的sql:
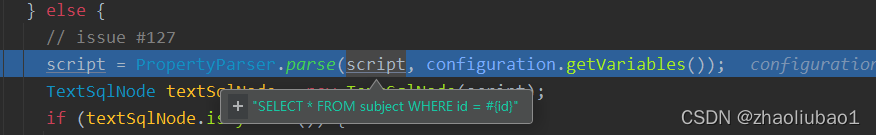
?他究竟会怎么做呢?
我们进入他的解析器一探究竟:
public static String parse(String string, Properties variables) {
VariableTokenHandler handler = new VariableTokenHandler(variables);
GenericTokenParser parser = new GenericTokenParser("${", "}", handler);
return parser.parse(string);
}
我们可以看到 这个解析器主要是用于处理含有$符号的sql,含有#号的sql是通RawSqlSource
类来处理,所以我们将会看到:
public RawSqlSource(Configuration configuration, String sql, Class<?> parameterType) {
SqlSourceBuilder sqlSourceParser = new SqlSourceBuilder(configuration);
Class<?> clazz = parameterType == null ? Object.class : parameterType;
sqlSource = sqlSourceParser.parse(sql, clazz, new HashMap<>());
}
继续进入将会看到:
public SqlSource parse(String originalSql, Class<?> parameterType, Map<String, Object> additionalParameters) { ParameterMappingTokenHandler handler = new ParameterMappingTokenHandler(configuration, parameterType, additionalParameters); GenericTokenParser parser = new GenericTokenParser("#{", "}", handler); String sql; if (configuration.isShrinkWhitespacesInSql()) { sql = parser.parse(removeExtraWhitespaces(originalSql)); } else { sql = parser.parse(originalSql); } return new StaticSqlSource(configuration, sql, handler.getParameterMappings()); }?
通过我们的通用解析器,最终我们将会得到:
 ?
?
?自此我们将得到了每个statement的目标sql