JDK1.7 ConcurrentHashMap 源码分析
Unsafe
Unsafe简介
Unsafe类相当于是一个java语言中的后门类,提供了硬件级别的原子操作,所以在一些并发编程中被大量使用。jdk已经作出说明,该类对程序员而言不是一个安全操作,在后续的jdk升级过程中,可能会禁用该类。所以这个类的使用是一把双刃剑,实际项目中谨慎使用,以免造成jdk升级不兼容问题。
Unsafe Api
这里并不系统讲解Unsafe的所有功能,只介绍和接下来内容相关的操作
arrayBaseOffset:获取数组的基础偏移量

arrayIndexScale:获取数组中元素的偏移间隔,要获取对应所以的元素,将索引号和该值相乘,获得数组中指定角标元素的偏移量getObjectVolatile:获取对象上的属性值或者数组中的元素getObject:获取对象上的属性值或者数组中的元素,已过时putOrderedObject:设置对象的属性值或者数组中某个角标的元素,更高效 (不保证可见性)putObjectVolatile:设置对象的属性值或者数组中某个角标的元素 (保证可见性)putObject:设置对象的属性值或者数组中某个角标的元素,已过时
代码演示
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Integer[] arr = {2,5,1,8,10};
// 获取Unsafe对象
Unsafe unsafe = getUnsafe();
// 获取Integer[]的基础偏移量
int baseOffset = unsafe.arrayBaseOffset(Integer[].class);
// 获取Integer[]中元素的偏移间隔
int indexScale = unsafe.arrayIndexScale(Integer[].class);
// 获取数组中索引为2的元素对象
Object o = unsafe.getObjectVolatile(arr, (2 * indexScale) + baseOffset);
System.out.println(o); // 1
// 设置数组中索引为2的元素值为100
unsafe.putOrderedObject(arr,(2 * indexScale) + baseOffset,100);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); // [2, 5, 100, 8, 10]
// cas操作 -- 拿着2号角标的值,判断是否是1,如果是设置为101,并且返回true
boolean b = unsafe.compareAndSwapObject(arr, (2 * indexScale) + baseOffset, 1, 101);
System.out.println(b); // false
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr)); // [2, 5, 100, 8, 10]
}
// 反射获取Unsafe对象
public static Unsafe getUnsafe() throws Exception {
Field theUnsafe = Unsafe.class.getDeclaredField("theUnsafe");
theUnsafe.setAccessible(true);
return (Unsafe) theUnsafe.get(null);
}
}
jdk1.7 容器初始化
源码解析
无参构造
//空参构造
public ConcurrentHashMap() {
// 调用本类的带参构造
// DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16
// DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f
// int DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL = 16
this(DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY, DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR, DEFAULT_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL);
}
三个参数的构造:一些非核心逻辑的代码已经省略
// 构造方法是没有安全问题的
// initialCapacity 定义ConcurrentHashMap存放元素的容量
// concurrencyLevel 定义ConcurrentHashMap中Segment[]的大小
public ConcurrentHashMap(int initialCapacity,
float loadFactor, int concurrencyLevel) {
int sshift = 0;
int ssize = 1;
// 计算Segment[]数组的大小,保证是2的幂次方数
while (ssize < concurrencyLevel) {
++sshift;
ssize <<= 1;
}
// 这两个值用于后面计算Segment[]的角标
this.segmentShift = 32 - sshift;
this.segmentMask = ssize - 1;
// 计算每个Segment中存储元素的个数
int c = initialCapacity / ssize;
if (c * ssize < initialCapacity)
++c;
// 最小Segment中存储元素的个数为2
int cap = MIN_SEGMENT_TABLE_CAPACITY;
// 矫正每个Segment中存储元素的个数,保证是2的幂次方,最小为2
while (cap < c) {
cap <<= 1;
}
// 创建一个Segment对象,作为其他Segment对象的模板
Segment<K,V> s0 =
new Segment<K,V>(loadFactor, (int)(cap * loadFactor),
(HashEntry<K,V>[])new HashEntry[cap]); // 2
// 创建一个Segment[]数组
Segment<K,V>[] ss = (Segment<K,V>[])new Segment[ssize]; // 16
// 利用Unsafe类,将创建的Segment对象存入0号角标位置
// SBASE:表示基础偏移量
// 等价于:UNSAFE.putOrderedObject(ss, SBASE + (0 * scale), s0);
UNSAFE.putOrderedObject(ss, SBASE, s0);
// 赋值给成员变量数组
this.segments = ss;
}
注意:ConcurrentHashMap中保存了一个默认长度为16的Segment[ ],每个Segment元素中保存了一个默认长度为2的HashEntry[ ],我们添加的元素,是存入对应的Segment中的HashEntry[ ]中。
所以ConcurrentHashMap中默认元素的长度是32个,而不是16个
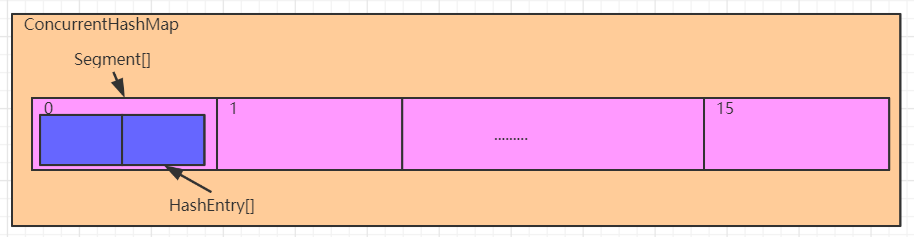
Segment是什么?
我们发现Segment是继承自
ReentrantLock的,学过线程的兄弟都知道,它可以实现同步操作,从而保证多线程下的安全。因为每个Segment之间的锁互不影响,所以我们也将ConcurrentHashMap中的这种锁机制称之为**分段锁**,这比HashTable的线程安全操作高效的多。
static final class Segment<K,V> extends ReentrantLock implements Serializable {
...
}
HashEntry是什么?
// ConcurrentHashMap中真正存储数据的对象
static final class HashEntry<K,V> {
final int hash; // 通过运算,得到的键的hash值
final K key; // 存入的键
volatile V value; // 存入的值
volatile HashEntry<K,V> next; // 记录下一个元素,形成单向链表
HashEntry(int hash, K key, V value, HashEntry<K,V> next) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
this.next = next;
}
}
jdk1.7 添加安全
源码分析
ConcurrentHashMap的put方法
public V put(K key, V value) {
Segment<K,V> s;
// ConcurrentHashMap不允许空键和空值
if (value == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
// 基于key,计算hash值
int hash = hash(key);
// 因为一个键要计算两个数组的索引,为了避免冲突,这里取key的高位计算Segment[]的索引
// 取key的低位计算HashEntry[]的索引
int j = (hash >>> segmentShift) & segmentMask;
// 判断该索引位的Segment对象是否已经创建,没有就创建
// (j << SSHIFT) + SBASE 等价于 (j * scale) + SBASE
if ((s = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObject
(segments, (j << SSHIFT) + SBASE)) == null)
s = ensureSegment(j);
// 调用Segmetn的put方法实现元素添加
return s.put(key, hash, value, false);
}
ConcurrentHashMap的ensureSegment方法
//创建对应索引位的Segment对象,并返回
private Segment<K,V> ensureSegment(int k) {
final Segment<K,V>[] ss = this.segments;
// (k << SSHIFT) + SBASE 等价于 (k * scale) + SBASE
long u = (k << SSHIFT) + SBASE;
Segment<K,V> seg;
// 获取,如果为null,即创建
if ((seg = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(ss, u)) == null) {
// 以0角标位的Segment为模板
Segment<K,V> proto = ss[0];
int cap = proto.table.length;
float lf = proto.loadFactor;
int threshold = (int)(cap * lf);
HashEntry<K,V>[] tab = (HashEntry<K,V>[])new HashEntry[cap];
// 获取,如果为null,即创建
if ((seg = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(ss, u))
== null) {
// 创建
Segment<K,V> s = new Segment<K,V>(lf, threshold, tab);
// 自旋方式,将创建的Segment对象放到Segment[]中,确保线程安全
while ((seg = (Segment<K,V>)UNSAFE.getObjectVolatile(ss, u))
== null) {
// cas操作
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(ss, u, null, seg = s))
break;
}
}
}
// 返回
return seg;
}
Segment的put方法
final V put(K key, int hash, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent) {
// lock.tryLock() 尝试加锁,成功返回true,失败返回false
// 尝试获取锁,获取成功,node为null,代码向下执行
// 如果有其他线程占据锁对象,那么去做别的事情,而不是一直等待,提升效率
// scanAndLockForPut 稍后分析
HashEntry<K,V> node = tryLock() ? null : scanAndLockForPut(key, hash, value);
V oldValue;
try {
HashEntry<K,V>[] tab = table;
// 取hash的低位,计算HashEntry[]的索引
int index = (tab.length - 1) & hash;
// 获取索引位的元素对象
HashEntry<K,V> first = entryAt(tab, index);
for (HashEntry<K,V> e = first;;) {
// 获取的元素对象不为空
if (e != null) {
K k;
// 如果是重复元素,覆盖原值
if ((k = e.key) == key ||
(e.hash == hash && key.equals(k))) {
oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent) {
e.value = value;
++modCount;
}
break;
}
// 如果不是重复元素,获取链表的下一个元素,继续循环遍历链表
e = e.next;
}
// 如果获取到的元素为空
else {
// 当前添加的键值对的HashEntry对象已经创建
if (node != null)
node.setNext(first); //头插法关联即可
// 当前添加的键值对的HashEntry对象没有被创建
else
// 创建当前添加的键值对的HashEntry对象
node = new HashEntry<K,V>(hash, key, value, first);
// 添加的元素数量递增
int c = count + 1;
// 判断是否需要扩容
if (c > threshold && tab.length < MAXIMUM_CAPACITY)
// 需要扩容
rehash(node);
else
// 不需要扩容
// 将当前添加的元素对象,存入数组角标位,完成头插法添加元素
setEntryAt(tab, index, node);
++modCount;
count = c;
oldValue = null;
break;
}
}
} finally {
//释放锁
unlock();
}
return oldValue;
}
Segment的scanAndLockForPut方法
该方法在线程没有获取到锁的情况下,去完成HashEntry对象的创建,提升效率
但是这个操作个人感觉有点累赘了
private HashEntry<K,V> scanAndLockForPut(K key, int hash, V value) {
// 获取头部元素
HashEntry<K,V> first = entryForHash(this, hash);
HashEntry<K,V> e = first;
HashEntry<K,V> node = null;
int retries = -1;
while (!tryLock()) {
// 获取锁失败
HashEntry<K,V> f;
if (retries < 0) {
// 没有下一个节点,并且也不是重复元素,创建HashEntry对象,不再遍历
if (e == null) {
if (node == null)
node = new HashEntry<K,V>(hash, key, value, null);
retries = 0;
}
// 重复元素,不创建HashEntry对象,不再遍历
else if (key.equals(e.key))
retries = 0;
// 继续遍历下一个节点
else
e = e.next;
}
else if (++retries > MAX_SCAN_RETRIES) {
// 如果尝试获取锁的次数过多,直接阻塞
// MAX_SCAN_RETRIES会根据可用cpu核数来确定
lock();
break;
}
else if ((retries & 1) == 0 &&
(f = entryForHash(this, hash)) != first) {
// 如果期间有别的线程获取锁,重新遍历
e = first = f;
retries = -1;
}
}
return node;
}
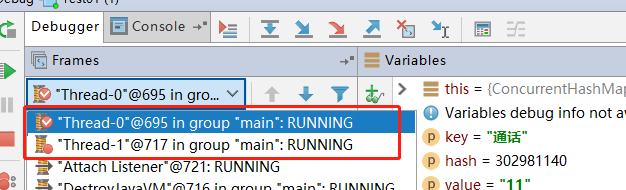
模拟多线程的代码流程
这里“通话”和“重地”的哈希值是一样的,那么他们添加时,会存入同一个Segment对象,必然会存在锁竞争
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
final ConcurrentHashMap chm = new ConcurrentHashMap();
new Thread(){
@Override
public void run() {
chm.put("通话","11");
System.out.println("-----------");
}
}.start();
//让第一个线程先启动,进入put方法
Thread.sleep(1000);
new Thread(){
@Override
public void run() {
chm.put("重地","22");
System.out.println("===========");
}
}.start();
}
多线程环境下的条件断点设置

key.equals("通话")

key.equals("重地")
运行结果
会发现两个线程,分别停在不同的断点位置,这就是多线程锁互斥产生的结果
然后就可以分别让不同的线程向下执行,查看代码走向了。
jdk1.7 扩容安全
源码分析
private void rehash(HashEntry<K,V> node) {
// 获取旧数组
HashEntry<K,V>[] oldTable = table;
// 获取旧数组的容量
int oldCapacity = oldTable.length;
// 两倍容量
int newCapacity = oldCapacity << 1;
threshold = (int)(newCapacity * loadFactor);
// 基于新容量,创建新的HashEntry数组
HashEntry<K,V>[] newTable =
(HashEntry<K,V>[]) new HashEntry[newCapacity];
int sizeMask = newCapacity - 1;
// 实现数据迁移
for (int i = 0; i < oldCapacity ; i++) {
HashEntry<K,V> e = oldTable[i];
if (e != null) {
HashEntry<K,V> next = e.next;
// 应该放在新数组的哪个角标位置
int idx = e.hash & sizeMask;
if (next == null)
//原位置只有一个元素,直接放到新数组即可
newTable[idx] = e;
else {
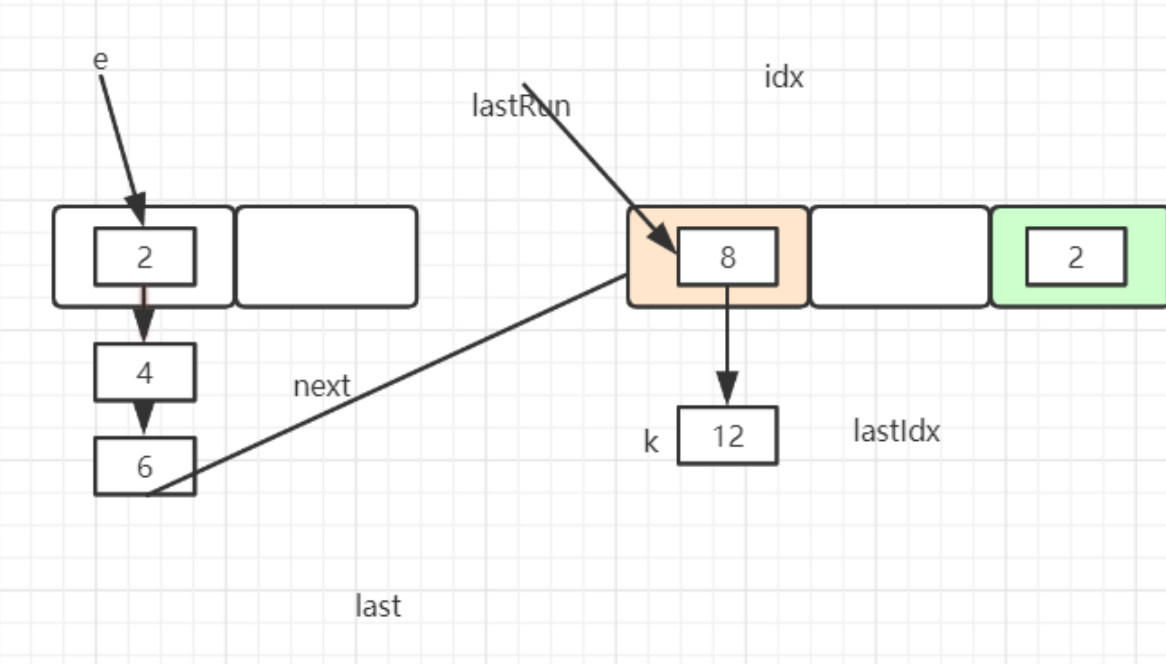
//=========图一=====================
HashEntry<K,V> lastRun = e;
int lastIdx = idx;
for (HashEntry<K,V> last = next;
last != null;
last = last.next) {
int k = last.hash & sizeMask;
if (k != lastIdx) {
lastIdx = k;
lastRun = last;
}
}
//=========图一=====================
//=========图二=====================
newTable[lastIdx] = lastRun;
//=========图二=====================
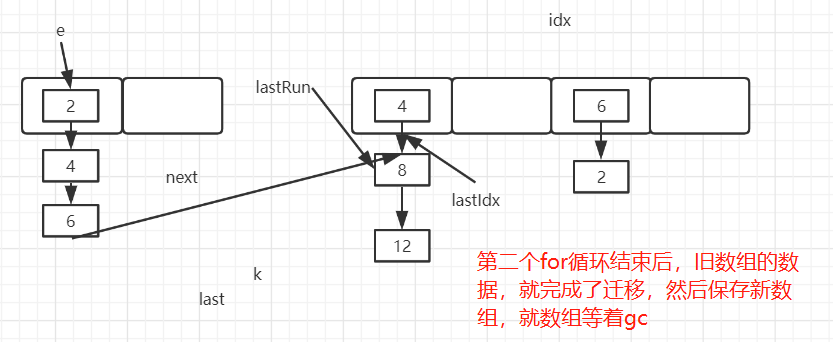
//=========图三=====================
for (HashEntry<K,V> p = e; p != lastRun; p = p.next) {
V v = p.value;
int h = p.hash;
int k = h & sizeMask;
HashEntry<K,V> n = newTable[k];
// 这里旧的HashEntry不会放到新数组
// 而是基于原来的数据创建了一个新的HashEntry对象,放入新数组
newTable[k] = new HashEntry<K,V>(h, p.key, v, n);
}
//=========图三=====================
}
}
}
//采用头插法,将新元素加入到数组中
int nodeIndex = node.hash & sizeMask;
node.setNext(newTable[nodeIndex]);
newTable[nodeIndex] = node;
table = newTable;
}
图解
图一





图二

图三


jdk1.7 集合长度获取
源码分析
public int size() {
final Segment<K,V>[] segments = this.segments;
int size;
boolean overflow;
long sum;
long last = 0L;
int retries = -1;
try {
for (;;) {
// 当第4次走到这个地方时,会将整个Segment[]的所有Segment对象锁住
if (retries++ == RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK) {
for (int j = 0; j < segments.length; ++j)
ensureSegment(j).lock();
}
sum = 0L;
size = 0;
overflow = false;
for (int j = 0; j < segments.length; ++j) {
Segment<K,V> seg = segmentAt(segments, j);
if (seg != null) {
// 累加所有segment的操作次数
sum += seg.modCount;
// 累加所有segment的数量
int c = seg.count;
// 累加所有segment中的元素个数 size+=c
if (c < 0 || (size += c) < 0)
overflow = true;
}
}
// 当这次累加值和上一次累加值一样,证明没有进行新的增删改操作,返回sum
// 第一次last为0,如果有元素的话,这个for循环最少循环两次
if (sum == last)
break;
// 记录累加的值
last = sum;
}
} finally {
// 如果之前有加锁,这里就是释放锁了
if (retries > RETRIES_BEFORE_LOCK) {
for (int j = 0; j < segments.length; ++j)
segmentAt(segments, j).unlock();
}
}
// 溢出,返回int的最大值,否则返回累加的size
return overflow ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : size;
}