文章链接:日撸 Java 三百行(总述)_minfanphd的博客-CSDN博客
Day33 图的广度优先遍历
33.1 思路:
结合下图,广度优先遍历假设从a节点出发,a访问后,访问领接点b/c,b访问了再访问c,又接着访问b的领接点,c的领接点,这样一层一层的访问,这就好比树的层次遍历一样。在访问图时要借助一个队列来实现
如图广度优先遍历的一种顺序是:a->b->c->d->e
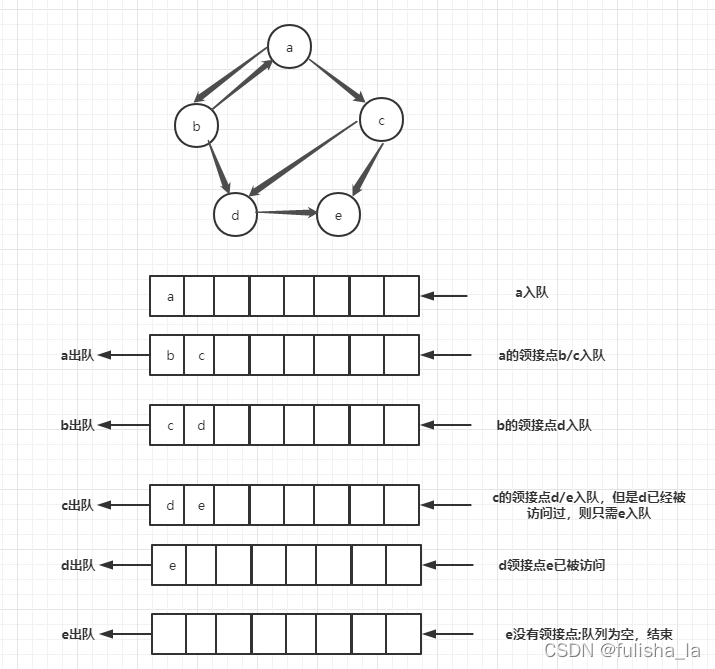
33.2 代码实现
结合上面的思路和文章来敲代码,在这段代码中,正如文章所说矩阵只要准备好了,写这些代码真的很方便。我感受最深的是:找节点的邻接点,这一行代码就可以去判断节点的领接点。
connectivityMatrix.getData()[tempIndex][i] == 0 /**
* Breadth first traversal. paraStartIndex The start index.
* @param paraStartIndex
* @return
*/
public String breadthFirstTraversal(int paraStartIndex) {
CircleQueue tempQueue = new CircleQueue();
String resultString = "";
int tempNumNodes = connectivityMatrix.getRows();
boolean[] tempVisitedArray = new boolean[tempNumNodes];
//Initialize the queue
tempVisitedArray[paraStartIndex] = true;
resultString += paraStartIndex;
tempQueue.enqueue(new Integer(paraStartIndex));
//Now visit the rest of the graph
int tempIndex;
Integer tempInteger = (Integer) tempQueue.dequeue();
while (tempInteger != null) {
tempIndex = tempInteger.intValue();
//Enqueue all its unvisited neighbors.
for (int i = 0; i < tempNumNodes; i++) {
if (tempVisitedArray[i]) {
continue;
}
//Not directly connected
if (connectivityMatrix.getData()[tempIndex][i] == 0) {
continue;
}
//Visit before enqueue.
tempVisitedArray[i] = true;
resultString += i;
tempQueue.enqueue(new Integer(i));
}
//Take out one from the head.
tempInteger = (Integer)tempQueue.dequeue();
}
return resultString;
}结合单元测试的例子画的图如下: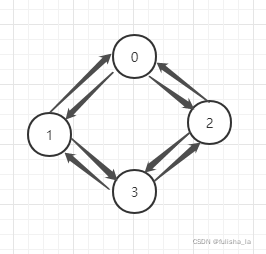
This is the connectivity matrix of the graph.
[[0, 1, 1, 0], [1, 0, 0, 1], [1, 0, 0, 1], [0, 1, 1, 0]]
No element in the queue
The breadth first order of visit: 203133.3 判断联通性
在今天的文章中,这个遍历只能遍历连通图(有向图),若是非连通图,则会漏一些节点数据(需要加一个循环来验证节点是否访问完)。在代码中有一个布尔类型数组:boolean[] tempVisitedArray = new boolean[tempNumNodes];若我们在一次广度遍历完遍历这个tempVisitedArray数组,再循环遍历是否有false,若有则说明图是非连通图,这是我们还需要把未遍历的节点再遍历完。我自己写了一个判断连通,这里传了一个参数,为了方便,没有将这个数组设置为成员变量,仅仅只是做了一个测试。
/**
* Judge connectivity
* @param tempVisitedArray bool类型 数组
* @return
*/
public boolean isConectivity(boolean[] tempVisitedArray) {
int tempNumNodes = connectivityMatrix.getRows();
for (int i = 0; i < tempNumNodes; i++){
if (!tempVisitedArray[i]){
System.out.println("The graph is not connectivity, The node is " + i);
return false;
}
}
return true;
}测试 1:?将测试的领接矩阵改为如下图所示的非连通图,则会发现打印的遍历会少打印
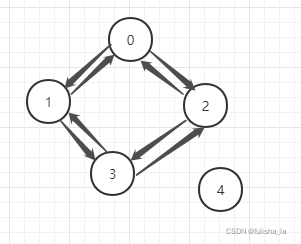
This is the connectivity matrix of the graph.
[[0, 1, 1, 0, 0], [1, 0, 0, 1, 0], [1, 0, 0, 1, 0], [0, 1, 1, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0, 0]]
No element in the queue
The graph is not connectivity, The node is 4 //则是未被访问的节点 则图为非连通
The breadth first order of visit: 2031测试2: (这里考虑的是无向图)
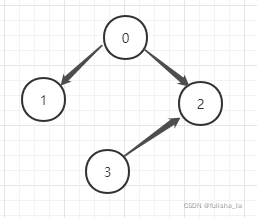
This is the connectivity matrix of the graph.
[[0, 1, 1, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 0, 0, 0], [0, 1, 1, 0]]
No element in the queue
The graph is not connectivity, The node is 3
The breadth first order of visit: 012总结:
今天主要学习了图的遍历之广度优先遍历算法,结合day32利用矩阵运算可以判断图的连通性,则今天的广度优先遍历算法也可以判断图的连通性,我们只需要再借助一个bool类型的数组即可