老规矩,从新建项目开始
新建一个springboot项目,把该有的都建好,controler,service啥的
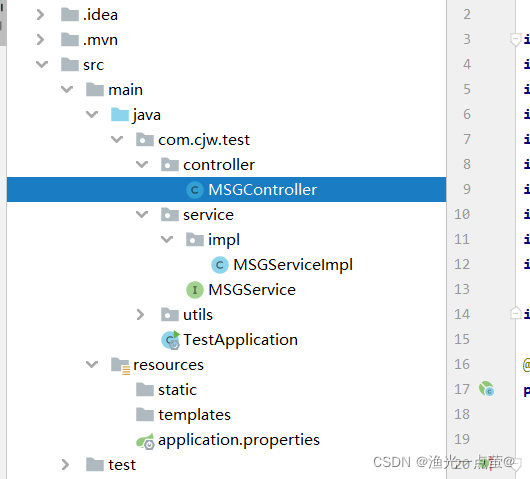
结构如下:
第一步,先来个pom依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.62</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 短信服务 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.aliyun</groupId>
<artifactId>aliyun-java-sdk-core</artifactId>
<version>4.5.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.aliyun</groupId>
<artifactId>dysmsapi20170525</artifactId>
<version>2.0.9</version>
</dependency>
然后可以开干service了,不过在这之前还需要用一个工具类,你觉得手机收到的验证码是自己代码里面生成的还是人家阿里云给你弄好的?
肯定是自己生成啊,这种小事情都要阿里云来做?不可能。
我们就来一个四位数字的验证码,下面是代码,直接copy到你的工具类上去
package com.cjw.test.utils;
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
/**
* 获取随机数
*
*/
public class RandomUtil {
private static final Random random = new Random();
private static final DecimalFormat fourdf = new DecimalFormat("0000");
private static final DecimalFormat sixdf = new DecimalFormat("000000");
public static String getFourBitRandom() {
return fourdf.format(random.nextInt(10000));
}
public static String getSixBitRandom() {
return sixdf.format(random.nextInt(1000000));
}
/**
* 给定数组,抽取n个数据
* @param list
* @param n
* @return
*/
public static ArrayList getRandom(List list, int n) {
Random random = new Random();
HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap = new HashMap<Object, Object>();
// 生成随机数字并存入HashMap
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
int number = random.nextInt(100) + 1;
hashMap.put(number, i);
}
// 从HashMap导入数组
Object[] robjs = hashMap.values().toArray();
ArrayList r = new ArrayList();
// 遍历数组并打印数据
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
r.add(list.get((int) robjs[i]));
System.out.print(list.get((int) robjs[i]) + "\t");
}
System.out.print("\n");
return r;
}
}
现在就开搞service,先接口
package com.cjw.test.service;
import java.util.Map;
public interface MSGService {
boolean send(Map map, String phone);
}
实现
package com.cjw.test.service.impl;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import com.aliyun.dysmsapi20170525.Client;
import com.aliyun.dysmsapi20170525.models.SendSmsRequest;
import com.aliyun.dysmsapi20170525.models.SendSmsResponse;
import com.aliyun.teaopenapi.models.Config;
import com.cjw.test.service.MSGService;
import com.google.gson.Gson;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import java.util.Map;
@Service
public class MSGServiceImpl implements MSGService {
@Override
public boolean send(Map map, String phone) {
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(phone)) return false;
//下面导包看着点,千万别导错了,对着上面我的导包
Config config = new Config()
// 您的AccessKey ID
.setAccessKeyId("LTAI4G7nRizWr6666RfgSys")
// 您的AccessKey Secret (这两个还不知道的去我前两次关于阿里云的有教程哪里找)
.setAccessKeySecret("n9TuOpZP77777kZusepek");
// 访问的域名(这个不用变都是这个)
config.endpoint = "dysmsapi.aliyuncs.com";
Client client = null;
try {
client = new Client(config);
SendSmsRequest request = new SendSmsRequest();
request.setSignName("阿里云短信测试");//签名名称
request.setTemplateCode("SMS_154950000");//模版Code
request.setPhoneNumbers("1991470000");//电话号码
//这里的参数是json格式的字符串
request.setTemplateParam(JSONObject.toJSONString(map));
SendSmsResponse response = client.sendSms(request);
System.out.println("发送成功:"+new Gson().toJson(response));
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
}
控制层
package com.cjw.test.controller;
import com.cjw.test.service.MSGService;
import com.cjw.test.utils.RandomUtil;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("JWTTest")
public class MSGController {
@Autowired
private MSGService jwtService;
@GetMapping("send/{phone}/interAspect")
public void sendMsm(@PathVariable String phone){
//生成随机数
String code = RandomUtil.getFourBitRandom();
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("code",code);
boolean b = jwtService.send(map,phone);
}
}
然后用postman测试,里面是手机号码,然后点击测试,发现手机有验证码,大功告成!!

················································这里说一下小细节·················································
我用的是测试版的,现在阿里云的短信服务改了,注册模板还是可以的,注册签名的时候一般人审核都不通过,除非有什么企事业单位的、已上线APP、公众号或者小程序、已备案网站(也要有实际业务内容不然也不通过,我试过了),所以暂时屈尊用测试的吧,
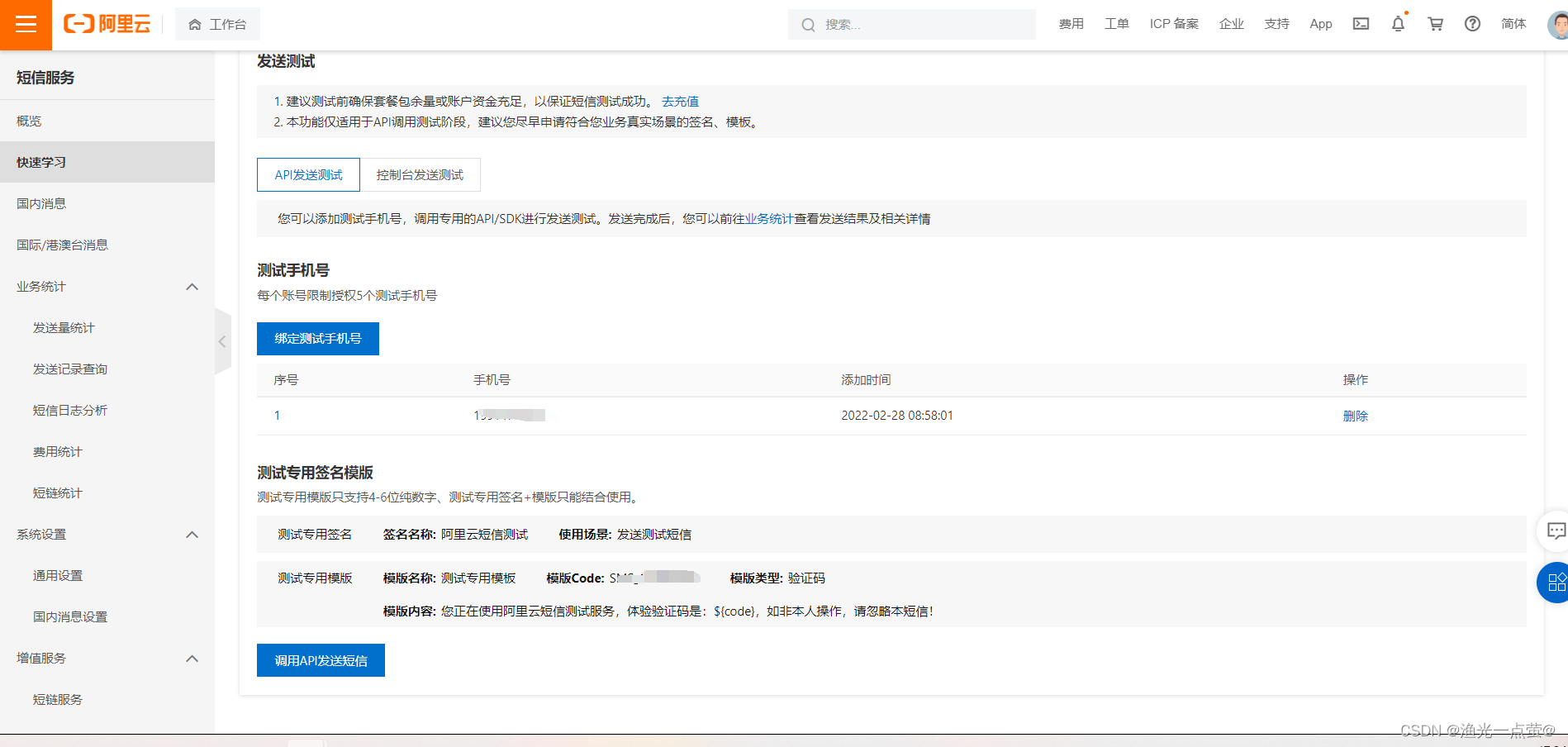
测试版的话要把手机号绑定一下,下图:
·············································································································
看到这里功能确实实现了,但还可以让它稍微完美一点,如果上面觉得已经可以了的话可以不用往下看,如果有兴趣就接着看,或者点个关注点个赞,没兴趣的点个赞就可以走
问题:如果我用postman一直点发送验证码,想象一下,是不是每一秒钟都是一个新的验证码,但是一般验证码都会写多少分钟有效,这怎么搞?还有啊,阿里云的短信服务是要钱的,每发一条多少多少钱,虽然很少,但也遭不住你一直点发验证码的轰炸啊。
解决:可以把一开始获得的验证码跟手机号存起来,来个判断,看看有没有,如果此手机号查不出对应的验证码,就来一次验证码发送,如果有,就还是原先这个返回给他,还要设置一下有效时间。那用什么比较好做呢?用redis
话不多说,上代码,只在控制层上修改一下就可。
pom文件加redis依赖
<!-- redis -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
<version>2.6.4</version>
</dependency>
package com.cjw.test.controller;
import com.cjw.test.service.MSGService;
import com.cjw.test.utils.RandomUtil;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("JWTTest")
public class MSGController {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String,String> redisTemplate;
@Autowired
private MSGService jwtService;
@GetMapping("send/{phone}/interAspect")
public void sendMsm(@PathVariable String phone){
// 从redis获取验证码,如果获取到直接返回
String code = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(phone);
if(!StringUtils.isEmpty(code)) {
return;
}
// 如果redis获取不到,进行阿里云发送
//生成随机数
code = RandomUtil.getFourBitRandom();
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("code",code);
boolean b = jwtService.send(map,phone);
if (b){
//如果发送成功,就把验证码存到redis里,设置5分钟有效时间
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(phone,code,5, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
System.out.println("succeed");
System.out.println("验证码为"+code);
}else {
System.out.println("fail");
}
}
}
测试一下,5分钟内再次点击还是原先那个验证码。成功!!!!