前言:
上一篇文章简单记述了关于 springboot 框架的基本使用,本篇文章简单分析一下 springboot 的底层原理、运行机制。
课程视频笔记:https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1PE411i7CV
一、项目结构分析
通过上面步骤完成了基础项目的创建。就会自动生成以下文件。
1、程序的主启动类
2、一个 application.properties 配置文件
3、一个 测试类
4、一个 pom.xml
pom.xml 分析
打开 pom.xml,分析一下 Spring Boot 项目的依赖:
- 父依赖
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.5.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
- web场景启动器
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
- springboot 单元测试
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
<!-- 剔除依赖 -->
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
- 打包插件
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
二、运行原理简单分析
研究一下上一篇文章中的 SpringBoot 项目,到底是怎么运行的呢,首先一个 Maven 项目,我们一般从 pom.xml 文件探究起。
1、父依赖
其中它主要是依赖一个父项目,主要是管理项目的资源过滤及插件!
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.5.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
点进去,发现还有一个父依赖
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>2.2.5.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath>../../spring-boot-dependencies</relativePath>
</parent>
这里才是真正管理 SpringBoot 应用里面所有依赖版本的地方,SpringBoot 的版本控制中心;
以后我们导入依赖默认是不需要写版本;但是如果导入的包没有在依赖中管理着就需要手动配置版本了。
2、启动器 spring-boot-starter
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
springboot-boot-starter-xxx:就是 spring-boot 的场景启动器
spring-boot-starter-web:帮我们导入了 web 模块正常运行所依赖的组件;
SpringBoot 将所有的功能场景都抽取出来,做成一个个的 starter (启动器),只需要在项目中引入这些 starter 即可,所有相关的依赖都会导入进来 , 我们要用什么功能就导入什么样的场景启动器即可 。当然我们也可以自己自定义 starter。
3、主启动类
分析完了 pom.xml 来看看这个启动类
默认的主启动类
//@SpringBootApplication 来标注一个主程序类
//说明这是一个Spring Boot应用
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//以为是启动了一个方法,没想到启动了一个服务
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootApplication.class, args);
}
}
其实一个简单的启动类并不简单,它的这些注解会做许多事情,这里我们就不再进行深入研究了,毕竟深入了解 springboot 的运行机制与原理也不是我们这门课程的主要目的,我们目前的目标还是会使用 springboot 来搭建项目。所以学到这里基本已经够用了。
4、run 方法流程分析
贴上一张狂神课程中讲述的流程分析图
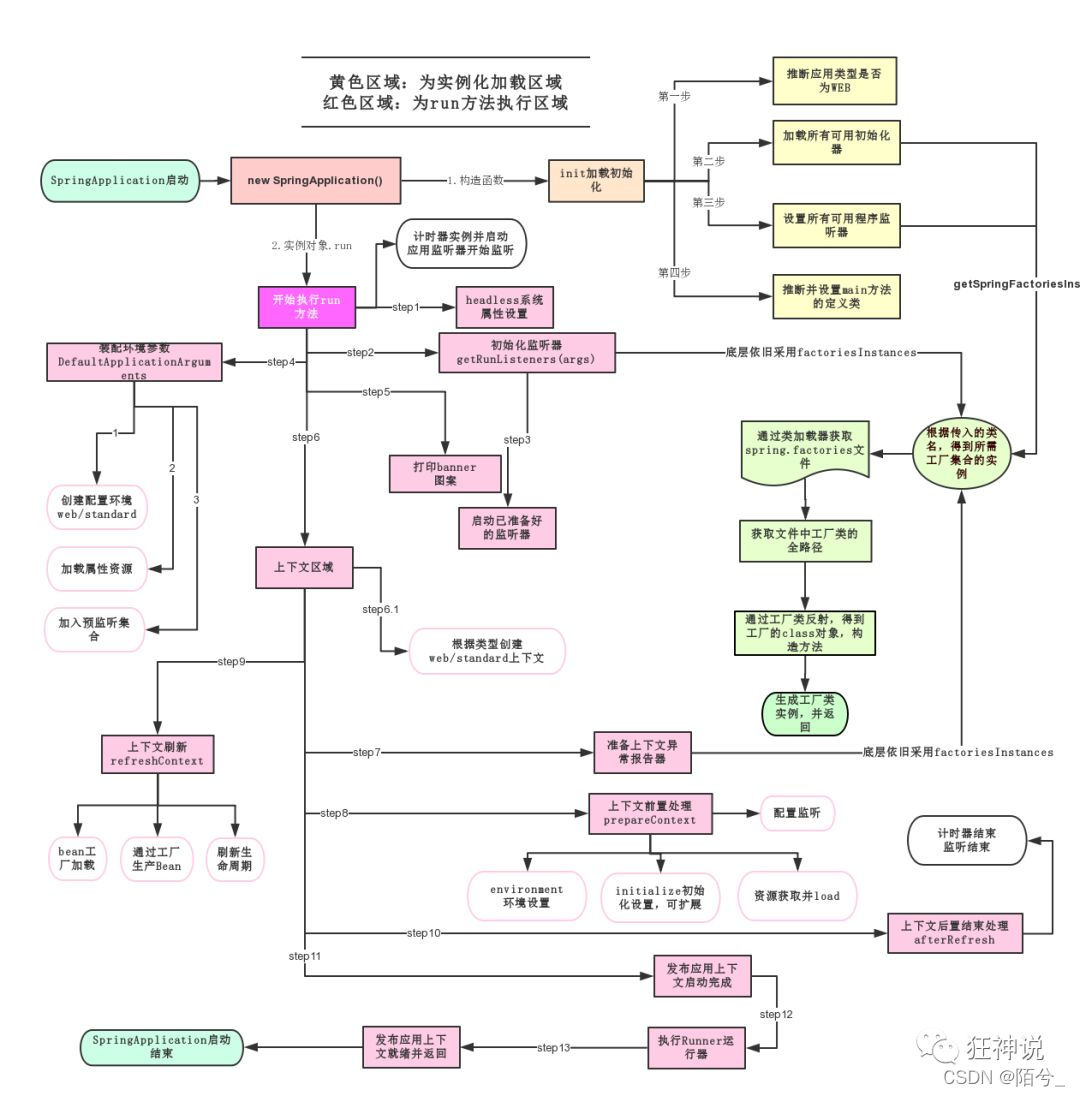
(图片源自公众号:狂神说)
参考资料
参考博客:
https://blog.csdn.net/cowbin2012/article/details/88861160
https://www.cnblogs.com/shamo89/p/8184960.html
https://www.jianshu.com/p/ef6f0c0de38f
https://www.cnblogs.com/jstarseven/p/11087157.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/gslblog/p/7986279.html
参考视频:
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1PE411i7CV
https://www.bilibili.com/video/av838087622/