一、版本差异
Spring Boot 2.2.0 版本开始引入 JUnit 5 作为单元测试默认库,在 Spring Boot 2.2.0 版本之前,spring-boot-starter-test 包含了 JUnit 4 的依赖,Spring Boot 2.2.0 版本之后替换成了 Junit Jupiter。
- pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
导入的依赖如下:
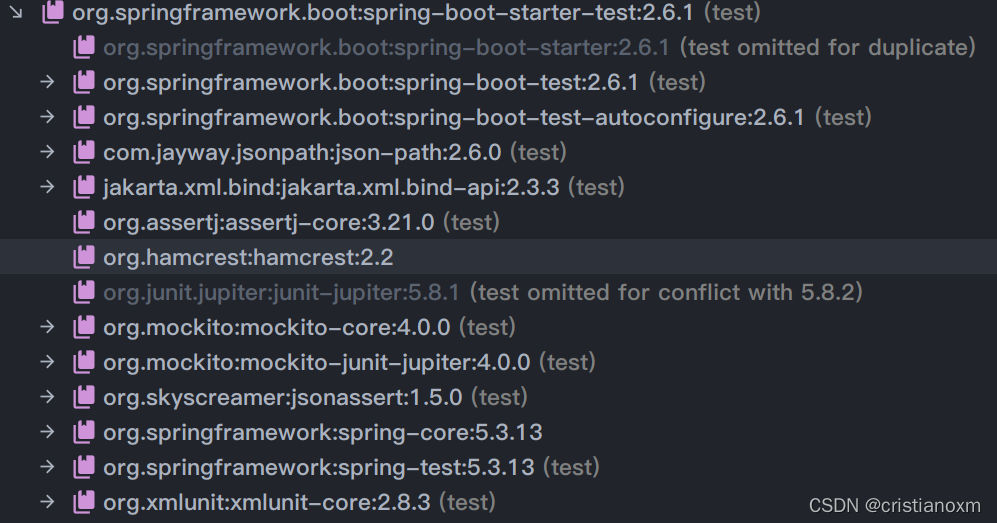
可以看到,SpringBootTest默认集成了以下功能:
- JUnit 5: Java单元测试框架
- Spring Test & Spring Boot Test: Spring Boot的测试工具和支持
- AssertJ: 流式断言
- Hamcrest: Hamcrest断言
- Mockito: Java Mock框架
- JSONassert: JSON断言
- JsonPath: XPath for JSON
二、SpringBootTest和Junit5的使用
整体上,Spring Boot Test支持的测试种类,大致可以分为如下三类:
- 单元测试:
一般面向方法,编写一般业务代码时,测试成本较大。涉及到的注解有@Test。- 切片测试:一般面向难于测试的边界功能,介于单元测试和功能测试之间。涉及到的注解有 @WebMvcTest等。
主要就是对于Controller的测试,分离了Service层,这里就涉及到Moc控制层所依赖的组件了- 功能测试:一般
面向某个完整的业务功能,同时也可以使用切面测试中的mock能力,推荐使用。涉及到的注解有@SpringBootTest等。
- 单元测试
集成测试,不启动server,以创建项目后自动生成的默认测试类为例:
@SpringBootTest
class TestDemoApplicationTests {
@Test
void contextLoads() {
}
}
默认无参数的@SpringBootTest 注解会加载一个Web Application Context并提供Mock Web Environment,但是不会启动内置的server。这点从日志中没有打印Tomcat started on port(s)可以佐证。
- 集成测试,启动server
新建一个测试类如下:
//指定@SpringBootTest的Web Environment为RANDOM_PORT
//此时,将会加载Applicaiton Context,并启动server,server侦听在随机端口上。在测试类中通过@LocalServerPort获取该端口值。
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
public class DemoTest {
@LocalServerPort
private Integer port;
@Test
@DisplayName("should access application")
void shouldAccessApplication() {
assertThat(port).isGreaterThan(1024);
}
}
也可以通过指定@SpringBootTest的Web Environment为DEFINED_PORT 来指定server侦听应用程序配置的端口,默认为8080。不过这种指定端口的方式很少使用,因为如果本地同时启动应用时,会导致端口冲突。
- 更多关系JUnit5集成SpringBootTest的例子,参考这个文档,我这里不在啰嗦
三、Spring Boot Test中的主要注解
- 在说Mockito之前,先看一下SpringBootTest的注解,
Mockito是一个独立的框架,被springboot集成了而已。
从功能上讲,Spring Boot Test中的注解主要分如下几类
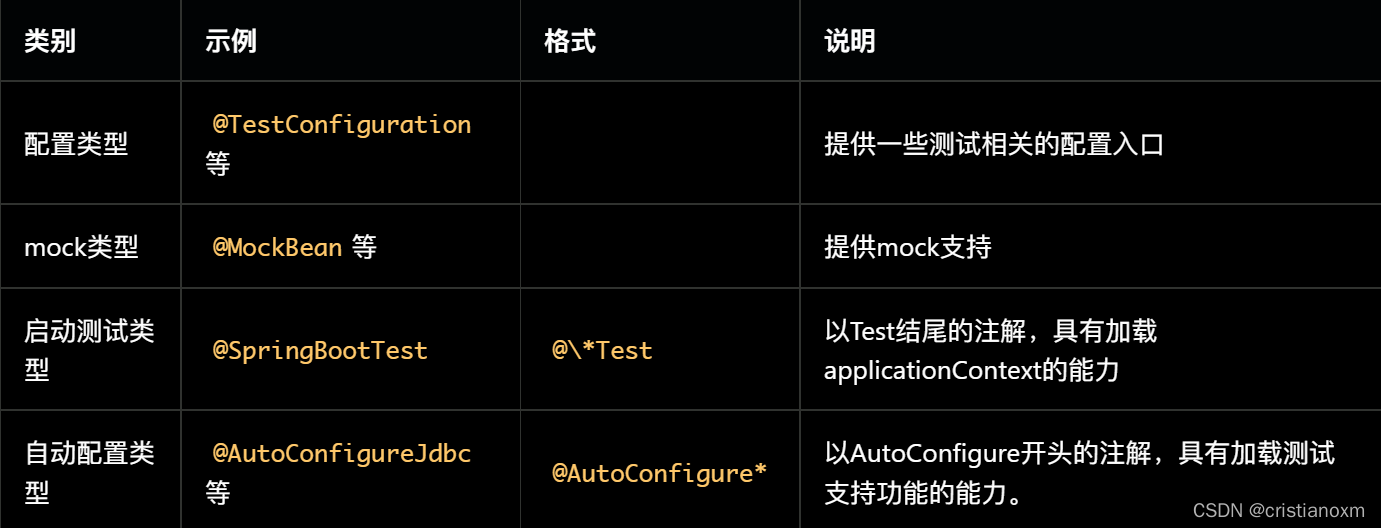
- 配置类型的注解:
使用@SpringBootApplication启动测试或者生产代码,被@TestComponent描述的Bean会自动被排除掉。如果不是则需要向@SpringBootApplication添加TypeExcludeFilter。
- mock类型的注解

@MockBean和@SpyBean这两个注解,在mockito框架中本来已经存在,且功能基本相同。Spring Boot Test又定义一份重复的注解,目的在于使MockBean和SpyBean被ApplicationContext管理,从而方便使用。
MockBean和SpyBean功能非常相似,都能模拟方法的各种行为。不同之处在于MockBean是全新的对象,跟正式对象没有关系;
而SpyBean与正式对象紧密联系,可以模拟正式对象的部分方法,没有被模拟的方法仍然可以运行正式代码。
- 自动配置类型的注解(@AutoConfigure*)
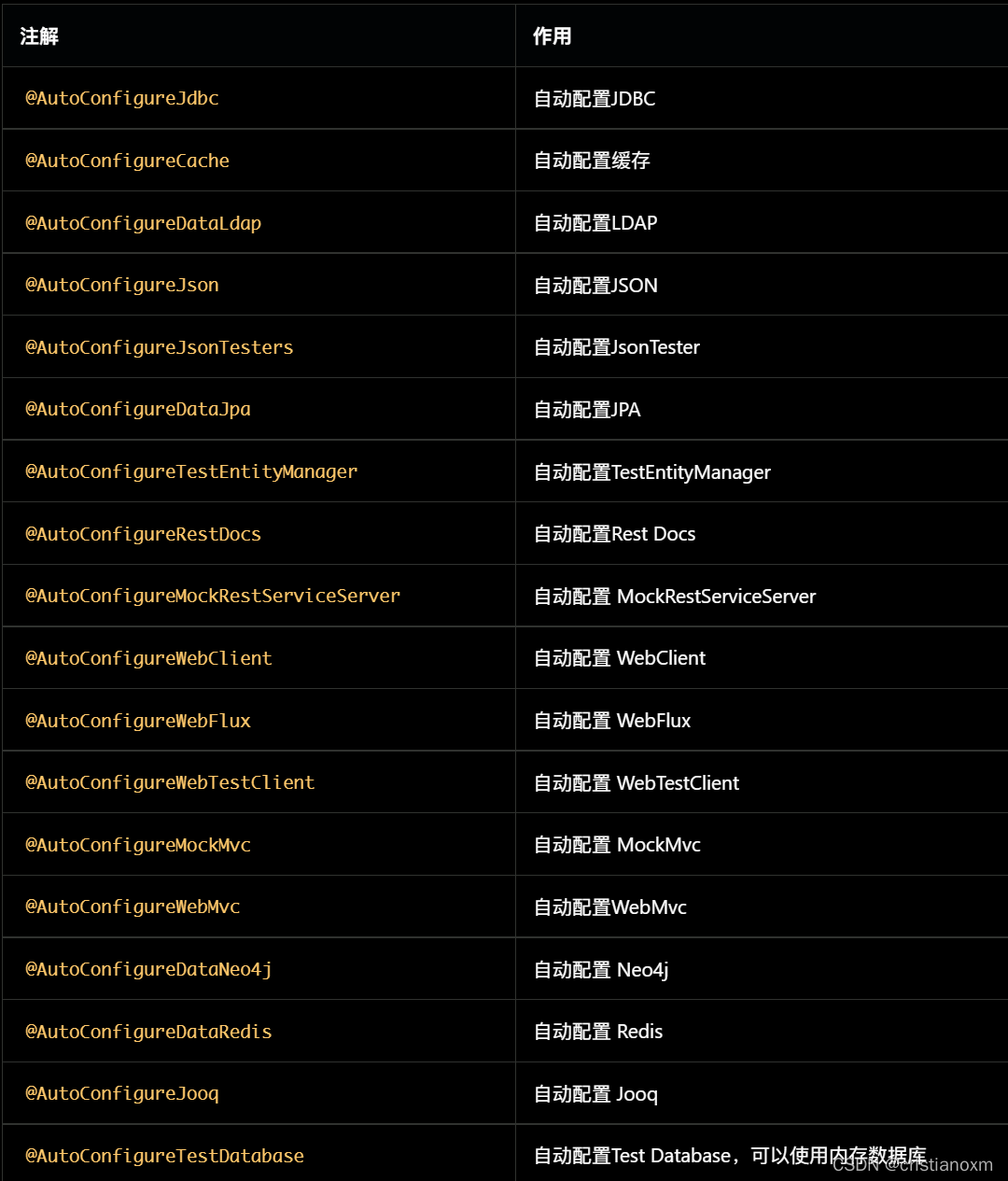
这些注解可以搭配@\*Test使用,用于开启在@\*Test中未自动配置的功能。例如@SpringBootTest和@AutoConfigureMockMvc组合后,就可以注入org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc。
“自动配置类型”有两种使用方式:
- 在功能测试(即使用@SpringBootTest)时显示添加。
一般在切片测试中被隐式使用,例如@WebMvcTest注解时,隐式添加了@AutoConfigureCache、@AutoConfigureWebMvc、@AutoConfigureMockMvc。
- 启动测试类型的注解
所有的@*Test注解都被@BootstrapWith注解,它们可以启动ApplicationContext,是测试的入口,所有的测试类必须声明一个@*Test注解。
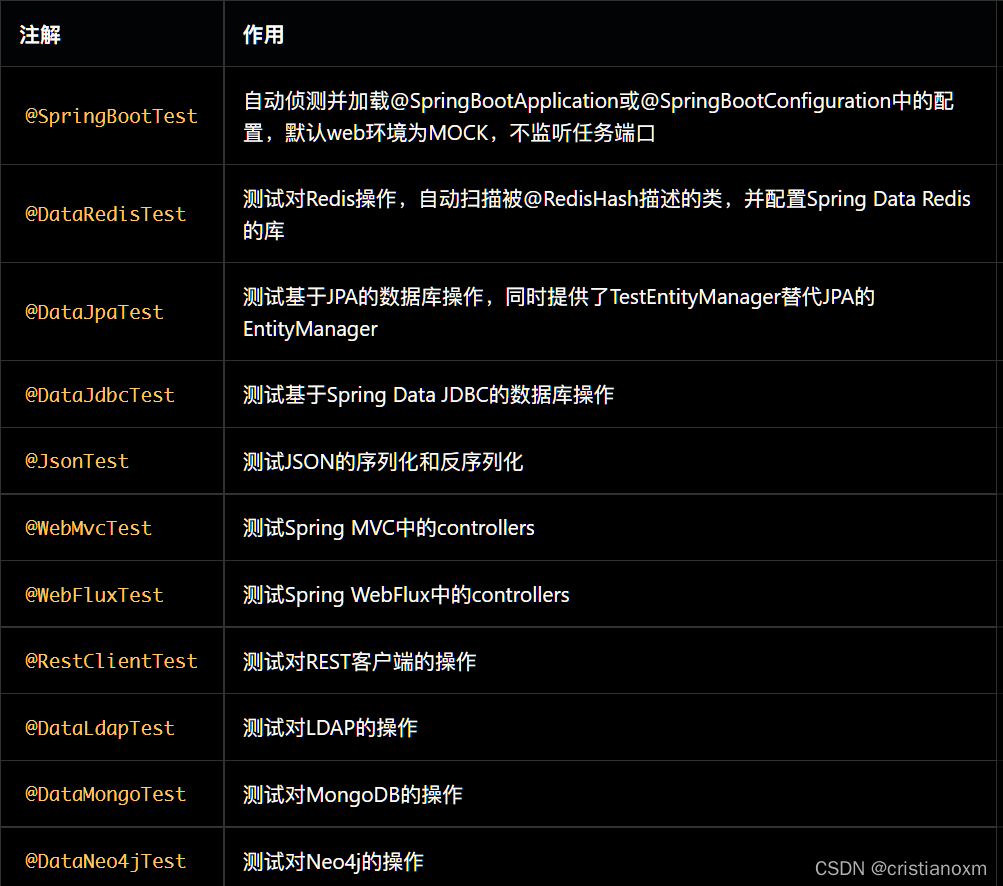
除了@SpringBootTest之外的注解都是用来进行切面测试的,他们会默认导入一些自动配置,点击官方docs查看详情。一般情况下,推荐使用@SpringBootTest而非其它切片测试的注解,简单有效。若某次改动仅涉及特定切片,可以考虑使用切片测试。SpringBootTest是这些注解中最常用的一个,其中包含的配置项如下:
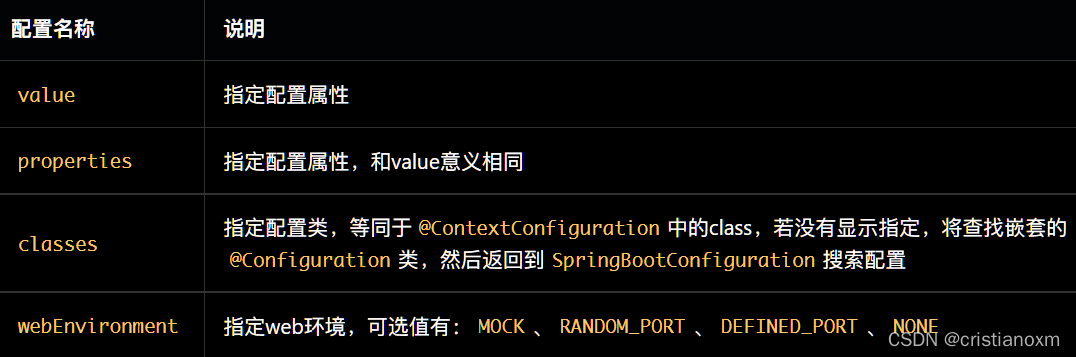
webEnvironment详细说明:
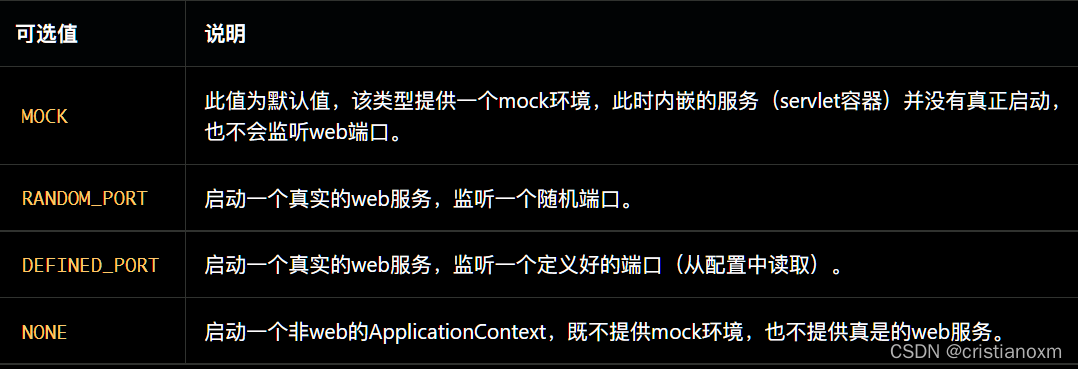
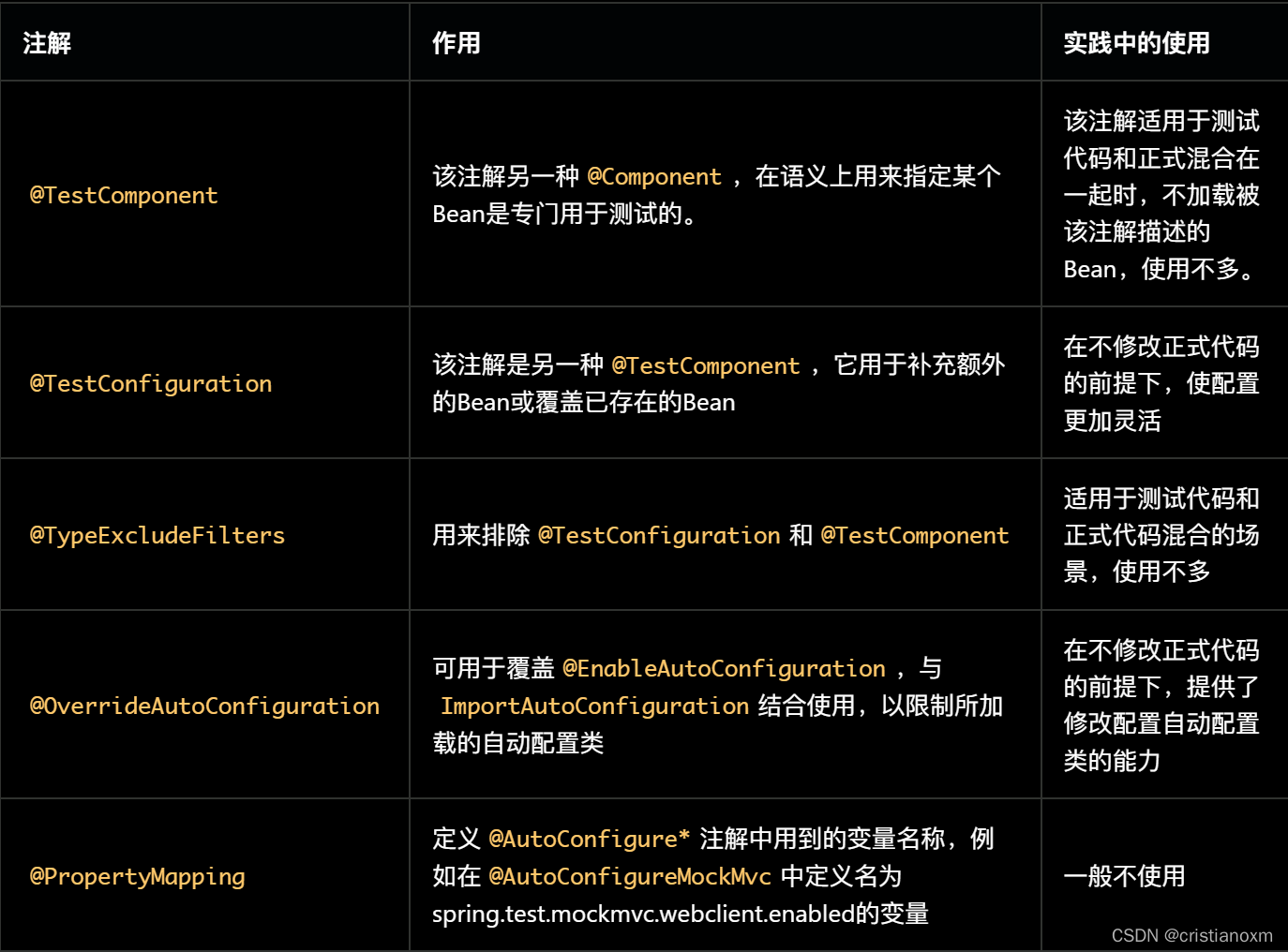
- 相似注解的区别和联系
@TestComment vs @Comment:
@TestComponent是另一种@Component,在语义上用来指定某个Bean是专门用于测试的。使用@SpringBootApplication服务时,@TestComponent会被自动排除@TestConfiguration vs @Configuration:
@TestConfiguration是Spring Boot Boot Test提供的,@Configuration是Spring Framework提供的。@TestConfiguration实际上是也是一种@TestComponent,只是这个@TestComponent专门用来做配置用。
@TestConfiguration和@Configuration不同,它不会阻止@SpringBootTest的查找机制,相当于是对既有配置的补充或覆盖。@SpringBootTest vs @WebMvcTest(或@*Test):
都可以启动Spring的ApplicationContext @SpringBootTest自动侦测并加载@SpringBootApplication或@SpringBootConfiguration中的配置,@WebMvcTest不侦测配置,只是默认加载一些自动配置。
@SpringBootTest测试范围一般比@WebMvcTest大。@MockBean vs @SpyBean:
都能模拟方法的各种行为。不同之处在于MockBean是全新的对象,跟正式对象没有关系;而SpyBean与正式对象紧密联系,可以模拟正式对象的部分方法,没有被模拟的方法仍然可以运行正式代码
四、Mockito的使用
- 简单的一个例子
public class MyMockitoTest {
private static UserServiceImpl mockUserService;
private static List<String> mockedList;
@BeforeAll
public static void beforeMock() throws Exception {
//使用Mock,模拟UserServiceImpl对象
mockUserService = mock(UserServiceImpl.class);
// mock creation 创建mock对象
mockedList = mock(List.class);
/*
* 默认情况下,所有的函数都有返回值。mock函数默认返回的是null,
* 一个空的集合或者一个被对象类型包装的内置类型,
* 例如0、false对应的对象类型为Integer、Boolean
*/
//做一些测试桩(stubbing),也即是定义行为,如果是getOneUser(3),则返回的是null,2则抛出异常
when(mockUserService.getOneUser(1)).thenReturn(new User("a",1));
//注意该抛出异常的stubbing,一定是UserServiceImpl真的有抛出这个异常,Mockito才能编译通过,并执行
when(mockUserService.getOneUser(2)).thenThrow(new IllegalAccessException());
when(mockUserService.getOneUser(3)).thenReturn(new User("a",1));
when(mockUserService.update(isA(User.class))).thenReturn(true);
}
@Test
@DisplayName("GetOneUser")
public void testGet() throws Exception {
//使用mock模拟出来的mockUserService进行操作
User user = mockUserService.getOneUser(1);
User oneUser = mockUserService.getOneUser(2);
User oneUser1 = mockUserService.getOneUser(3);
System.out.println(user);
System.out.println(oneUser);
mockUserService.update(user);
//验证是否执行过一次getOneUser(1)
verify(mockUserService, times(1)).getOneUser(eq(1));
//验证是否执行过一次update
verify(mockUserService, times(1)).update(isA(User.class));
}
@Test
public void testMatcher(){
//使用内置的anyInt()参数匹配器,也可以使用自定义的参数处理器
when(mockedList.get(anyInt())).thenReturn("element");
System.out.println(mockedList.get(999));
}
//验证函数的确切、最少、从未调用次数
@Test
@DisplayName("testUsingTime")
public void testUsingTime(){
//using mock
mockedList.add("once");
mockedList.add("twice");
mockedList.add("twice");
mockedList.add("three times");
mockedList.add("three times");
mockedList.add("three times");
// 下面的两个验证函数效果一样,因为verify默认验证的就是times(1)
// verify函数默认验证的是执行了times(1),也就是某个测试函数是否执行了1次.因此,times(1)通常被省略了。
verify(mockedList).add("once");
verify(mockedList, times(1)).add("once");
// 验证具体执行次数
verify(mockedList, times(2)).add("twice");
verify(mockedList, times(3)).add("three times");
// 使用never()进行验证,never相当于times(0)
verify(mockedList, never()).add("never happened");
// 使用atLeast()/atMost()
verify(mockedList, atLeastOnce()).add("three times");
verify(mockedList, atLeast(2)).add("five times");
verify(mockedList, atMost(5)).add("three times");
}
}
- 主要看一下使用mockito进行切面测试(Controller)
public class Keywords implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String keyword;
private String notes;
public Keywords(){}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Keywords{" +
"id=" + id +
", keyword='" + keyword + '\'' +
", notes='" + notes + '\'' +
'}';
}
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public String getKeyword() {
return keyword;
}
public String getNotes() {
return notes;
}
private Keywords(Builder builder){
this.id=builder.id;
this.keyword = builder.keyword;
this.notes = builder.notes;
}
public static class Builder{
private Integer id;
private String keyword;
private String notes;
public Builder setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
return this;
}
public Builder setKeyword(String keyword) {
this.keyword = keyword;
return this;
}
public Builder setNotes(String notes) {
this.notes = notes;
return this;
}
public Keywords build(){
return new Keywords(this);
}
}
}
@Controller
public class KeywordController {
@Autowired
private KeywordsService keywordsService;
@Autowired
private KeywordsServiceImpl keywordsServiceImpl;
@GetMapping(value = "/api/keywords")
public Keywords findKeywordById(@RequestParam(value = "id") Integer id) {
return keywordsService.findKeywordById(id);
}
@PostMapping("/api/add")
@ResponseBody
public Boolean addOne(@RequestBody Keywords keywords){
//调用被spy注解的类的方法,就会直接使用真实的方法
return keywordsServiceImpl.addOne(keywords);
}
}
@Repository
public interface KeywordsService {
Keywords findKeywordById(int i);
Boolean addOne(Keywords keywords);
}
@Service
public class KeywordsServiceImpl implements KeywordsService {
@Override
public Keywords findKeywordById(int i) {
return null;
}
@Override
public Boolean addOne(Keywords keywords) {
System.out.println("invoke spy class method");
System.out.println(keywords);
return false;
}
}
public class MvcMockitoTest {
//定义MockMvc对象
protected MockMvc mockMvc;
@Mock
//要mock被测类中依赖的对象使用@Mock注解
private KeywordsService keywordsService;
@Spy
//被 spy 的对象,调用其方法时默认会走真实方法。
private KeywordsServiceImpl keywordsServiceImpl;
@InjectMocks
//被测类本身使用@InjectMocks注解
private KeywordController controller;
@BeforeEach()
public void setup() {
MockitoAnnotations.openMocks(this);
//初始化MockMvc对象,将KeywordController加载进Spring容器
mockMvc = MockMvcBuilders.standaloneSetup(controller).build();
}
@Test
@DisplayName("findKeywordByIdTest")
public void findKeywordByIdTest() throws Exception {
Keywords keywords = new Builder().setId(666).setKeyword("tester").setNotes("notes").build();
//打桩,当执行findKeywordById(1)时,就返回上面创建的keywords对象
Mockito.when(keywordsService.findKeywordById(1)).thenReturn(keywords);
//执行一个RequestBuider请求,自动执行SpringMvc的流程并映射到相应的控制器执行处理
MvcResult mvcResult = mockMvc.perform(
get("/api/keywords?id=1") //请求的url,请求的方法是Get
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)) //数据的格式
//添加ResultMatcher验证规则,验证perform执行完成后的结果是否正确(对返回的数据进行判断)
.andExpect(status().isOk()) //期待的返回状态是200
//添加ResultHandler结果处理器,比如调试打印结果到控制台print()
.andDo(print())//打印出请求和相应的内容
//最后返回相应的MvcResult,然后进行自定义验证/进行下一步的异步处理
.andReturn();
System.out.println(mvcResult.getResponse().getContentAsString());
}
@Test
@DisplayName("addOne")
public void testAddOne() throws Exception {
Keywords build = new Builder().setId(1).setKeyword("addOne").setNotes("testAddOne").build();
Gson gson = new Gson();
String jsonString =gson.toJson(build);
System.out.println(jsonString);
MvcResult mvcResult = mockMvc.perform(
MockMvcRequestBuilders.post("/api/add")
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)//发送的文本格式
.content(jsonString)
.accept(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)//接受的文本格式
)
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk())
.andDo(MockMvcResultHandlers.print()).andReturn();
int status = mvcResult.getResponse().getStatus();
assertEquals(status,200);
System.out.println("输出 " + mvcResult.getResponse().getContentAsString());
}
}
结果:
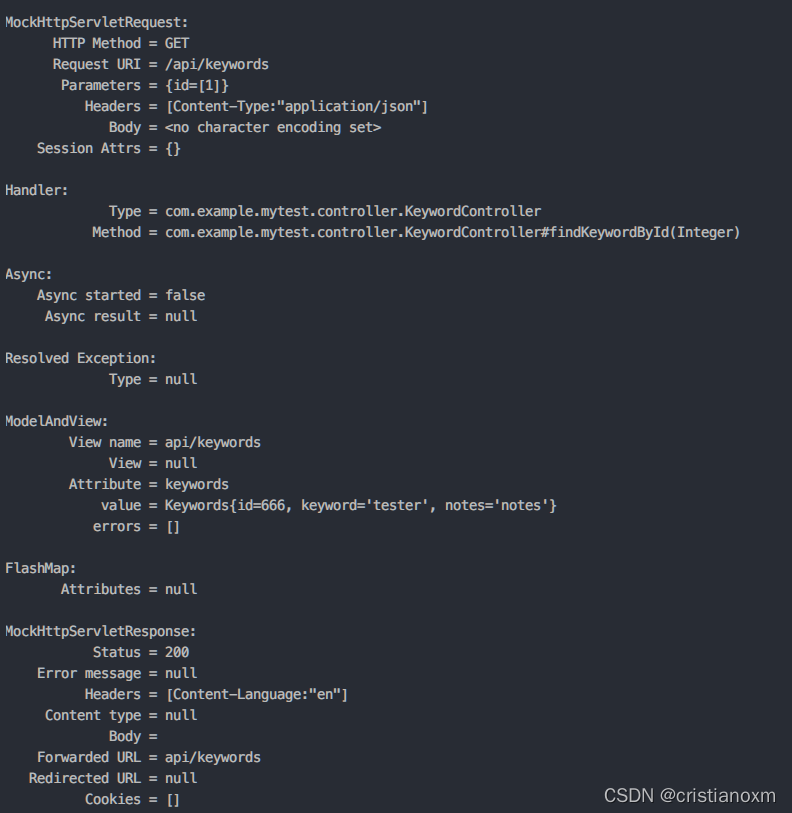
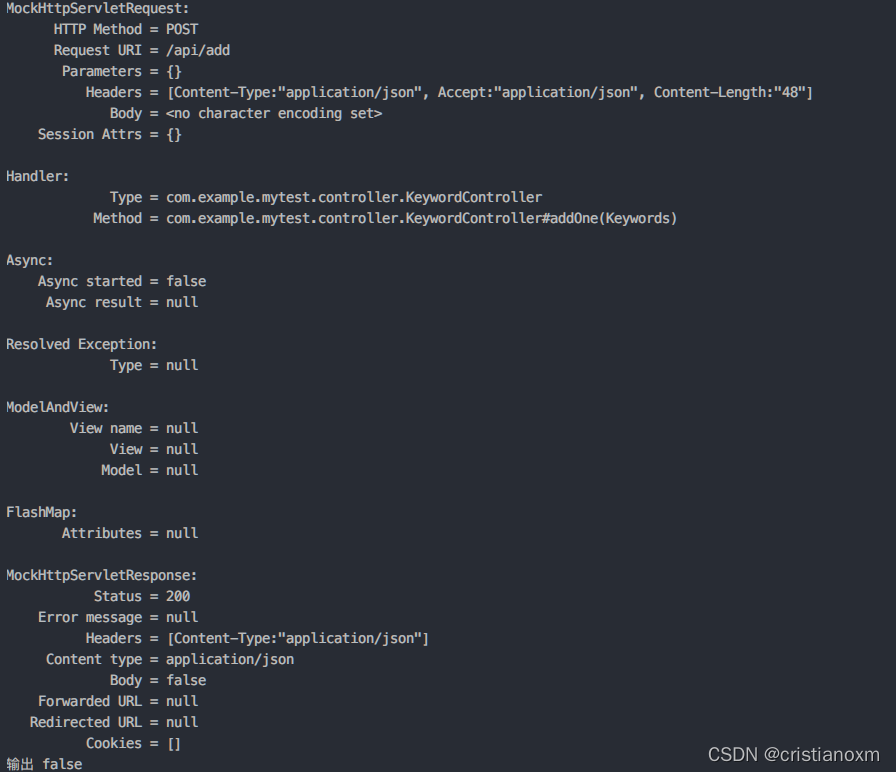

mockito可以配合junit5的断言功能使用。更多用法可以参考官方文档