Apache ShenYu 是一个异步的,高性能的,跨语言的,响应式的
API网关。
在ShenYu网关中,Apache ShenYu 利用 Java Agent 和 字节码增强 技术实现了无痕埋点,使得用户无需引入依赖即可接入第三方可观测性系统,获取 Traces、Metrics 和 Logging 。
本文基于
shenyu-2.4.2版本进行源码分析,官网的介绍请参考 可观测性 。
具体而言,就是shenyu-agent模块,它基于 Java Agent 机制,通过ByteBuddy字节码增强库,在类加载时增强对象,属于静态代理。
- AOP术语
在分析源码之前,介绍下AOP相关的术语,便于后续的理解:
-
JoinPoint:连接点,程序运行中的时间点,比如方法的执行点; -
PointCut:切入点,匹配JoinPoint的条件; -
Advice:通知,具体的执行逻辑; -
Target:目标对象; -
Proxy:代理对象。 -
关于Byte Buddy
Byte Buddy是一个代码生成和操作库,在Java应用程序的运行期间创建和修改Java类。可以利用它创建任何类,不像JDK动态代理那样强制实现一个接口。此外,Byte Buddy提供了方便的API,用于手动、使用Java代理或在构建期间改变类。
- 提供了非常方便的API接口,与强大的类,方法等匹配功能;
- 开箱即用,零学习成本,屏蔽了底层操作字节码技术;
- 强大的开放定制性功能,可以为任何实现的方法自定义字节码;
- 最少运行时生成代码原则,性能高效;
1. premain入口
premain()函数是javaagent 的入口函数,在 ShenYu由 ShenyuAgentBootstrap 提供并实现整个agent的逻辑。
/**
* agent 启动入口类
*/
public class ShenyuAgentBootstrap {
/**
* 入口函数 premain.
*/
public static void premain(final String arguments, final Instrumentation instrumentation) throws Exception {
// 1. 读取配置文件
ShenyuAgentConfigUtils.setConfig(ShenyuAgentConfigLoader.load());
// 2. 加载所有插件
ShenyuAgentPluginLoader.getInstance().loadAllPlugins();
// 3. 创建 agent
AgentBuilder agentBuilder = new AgentBuilder.Default().with(new ByteBuddy().with(TypeValidation.ENABLED))
.ignore(ElementMatchers.isSynthetic())
.or(ElementMatchers.nameStartsWith("org.apache.shenyu.agent."));
agentBuilder.type(ShenyuAgentTypeMatcher.getInstance())
.transform(new ShenyuAgentTransformer())
.with(AgentBuilder.RedefinitionStrategy.RETRANSFORMATION)
.with(new TransformListener()).installOn(instrumentation);
// 4. 启动插件
PluginLifecycleManager lifecycleManager = new PluginLifecycleManager();
lifecycleManager.startup(ShenyuAgentConfigUtils.getPluginConfigMap());
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(lifecycleManager::close));
}
}
premain函数的核心逻辑,就是上面的四步操作:
-
- 读取配置文件;
-
- 加载所有插件;
-
- 创建 agent;
-
- 启动插件。
接下来的源码分析就依次分析这四个操作。
2. 读取配置文件
- ShenyuAgentConfigLoader#load()
配置文件的处理由 ShenyuAgentConfigLoader 完成,代码实现如下:
public final class ShenyuAgentConfigLoader {
// 配置文件路径
private static final String CONFIG_PATH = "config-path";
/**
* 加载配置文件.
*/
public static ShenyuAgentConfig load() throws IOException {
// 读取配置文件路径
String configPath = System.getProperty(CONFIG_PATH);
// 如果没有配置,就读取默认的文件 shenyu-agent.yaml
File configFile = StringUtils.isEmpty(configPath) ? ShenyuAgentLocator.locatorConf("shenyu-agent.yaml") : new File(configPath);
// 读取配置文件并解析
return ShenyuYamlEngine.agentConfig(configFile);
}
}
可以通过config-path指定配置文件的路径,如果没有指定的话,就读取默认的配置文件 shenyu-agent.yaml,然后通过ShenyuYamlEngine来解析配置文件。
配置文件的格式是yaml格式,如何配置,请参考官网的介绍 可观测性 。
默认配置文件shenyu-agent.yaml的格式内容如下:
appName: shenyu-agent # 指定一个名称
supports: # 当前支持哪些功能
tracing: # 链路追踪的插件
# - jaeger
# - opentelemetry
- zipkin
metrics: # 统计度量插件
-
logging: # 日志信息插件
-
plugins: # 每个插件的具体配置信息
tracing: # 链路追踪的插件
jaeger: # jaeger的相关配置
host: "localhost"
port: 5775
props:
SERVICE_NAME: "shenyu-agent"
JAEGER_SAMPLER_TYPE: "const"
JAEGER_SAMPLER_PARAM: "1"
opentelemetry: # opentelemetry的相关配置
props:
otel.traces.exporter: jaeger #zipkin #otlp
otel.resource.attributes: "service.name=shenyu-agent"
otel.exporter.jaeger.endpoint: "http://localhost:14250/api/traces"
zipkin: # zipkin的相关配置
host: "localhost"
port: 9411
props:
SERVICE_NAME: "shenyu-agent"
URL_VERSION: "/api/v2/spans"
SAMPLER_TYPE: "const"
SAMPLER_PARAM: "1"
metrics: # 统计度量插件
prometheus: # prometheus的相关配置
host: "localhost"
port: 8081
props:
logging: # 日志信息插件
elasticSearch: # es的相关配置
host: "localhost"
port: 8082
props:
kafka: # kafka的相关配置
host: "localhost"
port: 8082
props:
需要开启哪个插件,就在supports中指定,然后再plugins指定插件的配置信息。
到目前为止,
Apache ShenYu发布的最新版本是2.4.2版本,可以支持tracing的插件有jaeger、opentelemetry和zipkin,metrics和logging将在后续的版本中陆续发布。
- ShenyuYamlEngine#agentConfig()
ShenyuYamlEngine提供了如何自定义加载yaml格式的文件。
public static ShenyuAgentConfig agentConfig(final File yamlFile) throws IOException {
try (
// 读取文件流
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(yamlFile);
InputStreamReader inputStreamReader = new InputStreamReader(fileInputStream)
) {
//指定对应的class
Constructor constructor = new Constructor(ShenyuAgentConfig.class);
//指定属性的class
TypeDescription customTypeDescription = new TypeDescription(AgentPluginConfig.class);
customTypeDescription.addPropertyParameters("plugins", Map.class);
constructor.addTypeDescription(customTypeDescription);
//通过Yaml工具包读取yaml文件
return new Yaml(constructor, new Representer(DUMPER_OPTIONS)).loadAs(inputStreamReader, ShenyuAgentConfig.class);
}
}
ShenyuAgentConfig是指定的Class类:
public final class ShenyuAgentConfig {
// appName 服务名称,默认是 shenyu-agent
private String appName = "shenyu-agent";
// supports 支持哪些插件
private Map<String, List<String>> supports = new LinkedHashMap<>();
// plugins 插件的属性信息
private Map<String, Map<String, AgentPluginConfig>> plugins = new LinkedHashMap<>();
}
AgentPluginConfig是指定插件的Class类:
public final class AgentPluginConfig {
// 指定插件的 host
private String host;
// 指定插件的 port
private int port;
// 指定插件的 password
private String password;
// 指定插件的 其他属性props
private Properties props;
}
通过配置文件,用户可以指定启用哪个插件,指定插件的属性信息。
3. 加载插件
- ShenyuAgentPluginLoader#loadAllPlugins()
读取配置文件后,需要根据用户自定义的配置信息,加载指定的插件。由ShenyuAgentPluginLoader来完成。
ShenyuAgentPluginLoader是一个自定义的类加载器,采用单例设计模式。
// 自定义类加载器,继承 ClassLoader
public final class ShenyuAgentPluginLoader extends ClassLoader implements Closeable {
// 私有变量
private static final ShenyuAgentPluginLoader AGENT_PLUGIN_LOADER = new ShenyuAgentPluginLoader();
// 私有构造器
private ShenyuAgentPluginLoader() {
super(ShenyuAgentPluginLoader.class.getClassLoader());
}
// 公开静态方法
public static ShenyuAgentPluginLoader getInstance() {
return AGENT_PLUGIN_LOADER;
}
/**
* 加载所有的插件.
*/
public void loadAllPlugins() throws IOException {
// 1.定位插件路径
File[] jarFiles = ShenyuAgentLocator.locatorPlugin().listFiles(file -> file.getName().endsWith(".jar"));
if (Objects.isNull(jarFiles)) {
return;
}
// 2.加载插件定义
Map<String, ShenyuAgentJoinPoint> pointMap = new HashMap<>();
try (ByteArrayOutputStream outputStream = new ByteArrayOutputStream()) {
for (File each : jarFiles) {
outputStream.reset();
JarFile jar = new JarFile(each, true);
jars.add(new PluginJar(jar, each));
}
}
loadAgentPluginDefinition(pointMap);
Map<String, ShenyuAgentJoinPoint> joinPointMap = ImmutableMap.<String, ShenyuAgentJoinPoint>builder().putAll(pointMap).build();
// 3.设置拦截点
ShenyuAgentTypeMatcher.getInstance().setJoinPointMap(joinPointMap);
}
}
3.1 定位插件路径
- ShenyuAgentLocator#locatorPlugin()
整个shenyu项目经过maven打包后(执行mvn clean install命令),agent打包目录如下:

插件文件都是jar包形式存在的。
conf目录是配置文件的目录位置;plugins目录是各个插件的目录位置。
相应的定位插件路径源码处理逻辑如下:
// 默认插件位于 /plugins 目录下
public static File locatorPlugin() {
return new File(String.join("", locatorAgent().getPath(), "/plugins"));
}
// 定位shenyu-agent.jar的绝对路径
public static File locatorAgent() {
// 找 ShenyuAgentLocator 所在的类路径(包名)
String classResourcePath = String.join("", ShenyuAgentLocator.class.getName().replaceAll("\\.", "/"), ".class");
// 找到 类 的绝对路径:磁盘路径+类路径
URL resource = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().getResource(classResourcePath);
assert resource != null;
String url = resource.toString();
// 是否是以jar包形式存在
int existFileInJarIndex = url.indexOf('!');
boolean isInJar = existFileInJarIndex > -1;
// 从jar包找到路径 或 从资源文件中找路径
return isInJar ? getFileInJar(url, existFileInJarIndex) : getFileInResource(url, classResourcePath);
}
// 从jar包找到路径
private static File getFileInJar(final String url, final int fileInJarIndex) {
// jar包所在的绝对路径
String realUrl = url.substring(url.indexOf("file:"), fileInJarIndex);
try {
// 以绝对路径创建File对象
File agentJarFile = new File(new URL(realUrl).toURI());
// 获取父文件
return agentJarFile.exists() ? agentJarFile.getParentFile() : null;
} catch (final MalformedURLException | URISyntaxException ex) {
return null;
}
}
拿到所有的插件文件后,会去加载插件定义,即拦截点。
3.2 加载拦截点
- ShenyuAgentPluginLoader#loadAgentPluginDefinition()
拦截点的默认配置是在 conf/tracing-point.yaml文件中,配置格式如下:
pointCuts:
- targetClass: org.apache.shenyu.plugin.global.GlobalPlugin # 拦截目标类
points:
- type: instanceMethod # 拦截点类型
name: execute # 拦截目标方法
handlers: # 处理器
jaeger: # 用于链路追踪的jaeger插件
- org.apache.shenyu.agent.plugin.tracing.jaeger.handler.JaegerGlobalPluginHandler
opentelemetry: # 用于链路追踪的opentelemetry插件
- org.apache.shenyu.agent.plugin.tracing.opentelemetry.handler.OpenTelemetryGlobalPluginHandler
zipkin: # 用于链路追踪的zipkin插件
- org.apache.shenyu.agent.plugin.tracing.zipkin.handler.ZipkinGlobalPluginHandler
// ......
加载拦截点的方式是通过SPI的方式进行加载的,然后再收集这些拦截点。
private void loadAgentPluginDefinition(final Map<String, ShenyuAgentJoinPoint> pointMap) {
SPILoader.loadList(AgentPluginDefinition.class) // SPI 加载拦截点
.forEach(each -> each.collector().forEach(def -> { // 收集拦截点
String classTarget = def.getClassTarget();
if (pointMap.containsKey(classTarget)) {
ShenyuAgentJoinPoint pluginInterceptorPoint = pointMap.get(classTarget);
pluginInterceptorPoint.getConstructorPoints().addAll(def.getConstructorPoints()); // 构造器类型拦截点
pluginInterceptorPoint.getInstanceMethodPoints().addAll(def.getInstanceMethodPoints()); // 实例方法类型拦截点
pluginInterceptorPoint.getStaticMethodPoints().addAll(def.getStaticMethodPoints()); // 静态方法类型拦截点
} else {
pointMap.put(classTarget, def);
}
}));
}
- SPILoader.loadList(AgentPluginDefinition.class)
AgentPluginDefinition是拦截点接口,由@SPI标记:
@SPI // 该接口通过SPI进行加载
public interface AgentPluginDefinition {
/**
* 收集拦截点
*/
Collection<ShenyuAgentJoinPoint> collector();
}
TracingAgentPluginDefinition是它的一个实现类,用于定义链路追踪的拦截点:
@Join // SPI的实现类
public final class TracingAgentPluginDefinition extends AbstractAgentPluginDefinition {
// 创建拦截点
@Override
protected Collection<JoinPointBuilder> joinPointBuilder() {
// ......
}
}
public abstract class AbstractAgentPluginDefinition implements AgentPluginDefinition {
// 创建拦截点
protected abstract Collection<JoinPointBuilder> joinPointBuilder();
// 收集拦截点信息
@Override
public final Collection<ShenyuAgentJoinPoint> collector() {
//......
}
}
类之间的继承关系如下:
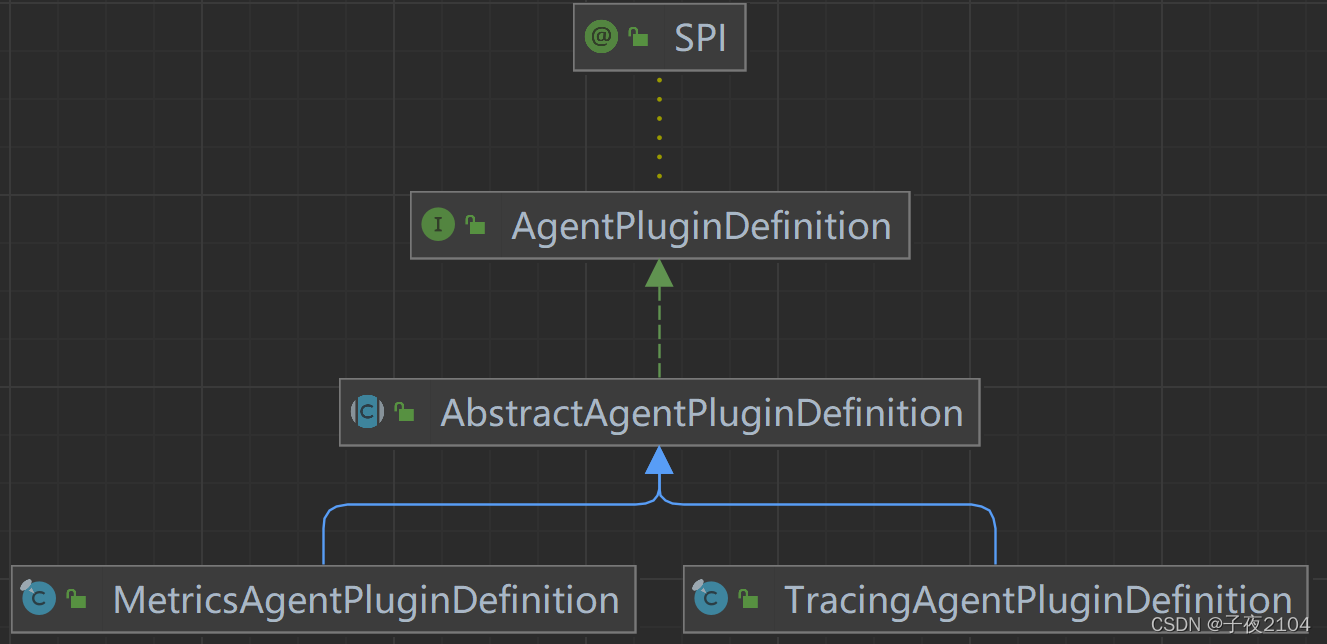
-
AgentPluginDefinition#collector()
AgentPluginDefinition只是一个接口,定义了收集拦截点的操作方法,具体实现交给了子类。
public abstract class AbstractAgentPluginDefinition implements AgentPluginDefinition {
// 子类去实现如何创建拦截点
protected abstract Collection<JoinPointBuilder> joinPointBuilder();
@Override
public final Collection<ShenyuAgentJoinPoint> collector() {
// 获取拦截点构建器
Collection<JoinPointBuilder> joinPointBuilders = joinPointBuilder();
// 创建拦截点对象 ShenyuAgentJoinPoint
return joinPointBuilders.stream().map(JoinPointBuilder::install).collect(Collectors.toList());
}
}
// 创建拦截点对象 ShenyuAgentJoinPoint
public ShenyuAgentJoinPoint install() {
// 四个构造参数分别是:目标对象,构造器拦截点,实例方法拦截点,静态方法拦截点
return new ShenyuAgentJoinPoint(classTarget, constructorPoints, instanceMethodPoints, classStaticMethodPoints);
}
-
TracingAgentPluginDefinition#joinPointBuilder()
创建用于链路追踪的拦截点。
@Join
public final class TracingAgentPluginDefinition extends AbstractAgentPluginDefinition {
// 创建拦截点
@Override
protected Collection<JoinPointBuilder> joinPointBuilder() {
PointCutConfig config = null;
try {
// 读取默认的拦截点配置文件
config = ShenyuYamlEngine.unmarshal(ShenyuAgentLocator.locatorConf("tracing-point.yaml"), PointCutConfig.class);
} catch (IOException e) {
LOG.error("Exception loader tracing point config is", e);
}
// 创建拦截点
return JoinPointBuilderFactory.create(config);
}
}
-
JoinPointBuilderFactory#create()
根据指定的配置文件创建拦截点 。
public static Collection<JoinPointBuilder> create(final PointCutConfig config) {
//如果没有配置文件或为空,则返回空集合
if (Objects.isNull(config) || config.getPointCuts().isEmpty()) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
return config.getPointCuts().stream() // 获取配置文件中定义的拦截点
.filter(pointCut -> StringUtils.isNotEmpty(pointCut.getTargetClass())
&& !pointCut.getPoints().isEmpty() && !pointCut.getHandlers().isEmpty()) // 拦截点必须要指定目标类,切入点,处理器
.map(pointCut -> {
JoinPointBuilder builder = ShenyuAgentJoinPoint.interceptClass(pointCut.getTargetClass()); // 设置需要拦截的目标类
Set<String> supports = ShenyuAgentConfigUtils.getSupports(); // 获取当前支持哪些插件
List<String> handlers = pointCut.getHandlers().entrySet().stream()
.filter(entry -> supports.contains(entry.getKey())) // 指定的处理器必须是当前可支持的插件
.flatMap(entry -> entry.getValue().stream())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
String[] instanceMethods = pointCut
.getPoints()
.stream()
.filter(point -> PointType.INSTANCE_METHOD.getName().equals(point.getType()))
.map(Point::getName) // 拦截实例方法
.toArray(String[]::new);
if (instanceMethods.length > 0) {
builder.aroundInstanceMethod(ElementMatchers.namedOneOf(instanceMethods)).handlers(handlers).build(); // 为实例方法添加匹配器用于后续运行时动态匹配,并添加对应的处理器
}
String[] staticMethods = pointCut
.getPoints()
.stream()
.filter(point -> PointType.STATIC_METHOD.getName().equals(point.getType()))
.map(Point::getName)
.toArray(String[]::new); // 拦截静态方法
if (staticMethods.length > 0) {
builder.aroundStaticMethod(ElementMatchers.namedOneOf(staticMethods)).handlers(handlers).build();// 为静态方法添加匹配器用于后续运行时动态匹配,并添加对应的处理器
}
String[] constructorPoints = pointCut
.getPoints()
.stream()
.filter(point -> PointType.CONSTRUCTOR.getName().equals(point.getType()))
.map(Point::getName)
.toArray(String[]::new); // 拦截构造器
if (constructorPoints.length > 0) {
builder.onConstructor(ElementMatchers.namedOneOf(constructorPoints)).handlers(handlers).build();// 为构造器添加匹配器用于后续运行时动态匹配,并添加对应的处理器
}
return builder;
}).collect(Collectors.toList()); // 返回匹配结果
}
创建拦截点的主要实现逻辑是:根据配置文件读取配置信息,为指定的目标对象的目标方法添加相应的处理器。处理器有三种:实例方法处理器,静态方法处理器,构造函数处理器。
这里用到了ElementMatchers.namedOneOf() 方法,它表示方法名称在指定的参数中,就可以匹配上这个方法。ElementMatchers是bytebuddy中的一个类,在ShenYu中,agent的创建也通过bytebuddy完成的。
后续将收集到的拦截点创建为拦截点对象ShenyuAgentJoinPoint。
public final Collection<ShenyuAgentJoinPoint> collector() {
// 获取拦截点
Collection<JoinPointBuilder> joinPointBuilders = joinPointBuilder();
// 创建拦截点对象
return joinPointBuilders.stream().map(JoinPointBuilder::install).collect(Collectors.toList());
}
收集完拦截点之后,用Map保存了这些拦截点信息。
// pointMap: Key和Value分别表示目标类,拦截点
private void loadAgentPluginDefinition(final Map<String, ShenyuAgentJoinPoint> pointMap) {
SPILoader.loadList(AgentPluginDefinition.class) // SPI 加载拦截点
.forEach(each -> each.collector().forEach(def -> { // 收集拦截点
String classTarget = def.getClassTarget();
if (pointMap.containsKey(classTarget)) {
ShenyuAgentJoinPoint pluginInterceptorPoint = pointMap.get(classTarget);
pluginInterceptorPoint.getConstructorPoints().addAll(def.getConstructorPoints()); // 构造器类型拦截点
pluginInterceptorPoint.getInstanceMethodPoints().addAll(def.getInstanceMethodPoints()); // 实例方法类型拦截点
pluginInterceptorPoint.getStaticMethodPoints().addAll(def.getStaticMethodPoints()); // 静态方法类型拦截点
} else {
pointMap.put(classTarget, def); // 将拦截点信息保存到Map中
}
}));
}
3.3 设置拦截点
在加载所有插件的过程中最后一步是设置拦截点。
public void loadAllPlugins() throws IOException {
// 1.定位插件路径
// ......
// 2.加载插件定义
// ......
// 3.设置拦截点
ShenyuAgentTypeMatcher.getInstance().setJoinPointMap(joinPointMap);
}
设置拦截点就是将拦截点集合保存到ShenyuAgentTypeMatcher类中。它实现了ElementMatcher接口,用于自定义匹配逻辑。ElementMatcher也是bytebuddy中的接口。
// 使用单例设计模式
public final class ShenyuAgentTypeMatcher extends ElementMatcher.Junction.AbstractBase<TypeDefinition> {
// 创建实例
private static final ShenyuAgentTypeMatcher SHENYU_AGENT_TYPE_MATCHER = new ShenyuAgentTypeMatcher();
// 拦截点集合
private Map<String, ShenyuAgentJoinPoint> joinPointMap;
private ShenyuAgentTypeMatcher() {
}
/**
* 获取单例
*/
public static ShenyuAgentTypeMatcher getInstance() {
return SHENYU_AGENT_TYPE_MATCHER;
}
//自定义匹配逻辑,目标类在拦截点集合中就匹配成功
@Override
public boolean matches(final TypeDefinition target) {
return joinPointMap.containsKey(target.getTypeName());
}
/**
* 设置拦截点集合
*/
public void setJoinPointMap(final Map<String, ShenyuAgentJoinPoint> joinPointMap) {
this.joinPointMap = joinPointMap;
}
}
4. 创建 agent
通过创建的agent,用于改变目标类的行为。
public static void premain(final String arguments, final Instrumentation instrumentation) throws Exception {
// 1. 读取配置文件
// ......
// 2. 加载所有插件
// ......
// 3. 创建 agent
AgentBuilder agentBuilder = new AgentBuilder.Default().with(new ByteBuddy().with(TypeValidation.ENABLED)) // 通过ByteBuddy创建Agent,开启类型校验
.ignore(ElementMatchers.isSynthetic()) // 忽略合成类
.or(ElementMatchers.nameStartsWith("org.apache.shenyu.agent.")); // 忽略org.apache.shenyu.agent 的类
agentBuilder.type(ShenyuAgentTypeMatcher.getInstance())//匹配加载类型,匹配器是ShenyuAgentTypeMatcher
.transform(new ShenyuAgentTransformer()) // 匹配成功的,通过ShenyuAgentTransformer改变其行为
.with(AgentBuilder.RedefinitionStrategy.RETRANSFORMATION) //指定重定义策略
.with(new TransformListener()) //指定一个监听器,监听运行过程中的事件
.installOn(instrumentation); // 将修改应用到instrumentation中
// 4. 启动插件
// ......
}
在创建agent的过程中,需要注意两个点:
- 是否匹配成功,由
ShenyuAgentTypeMatcher决定; - 匹配成功的类,通过
ShenyuAgentTransformer改变其行为;
接下来我们就来着重分析这两个类。
4.1 定义匹配逻辑
- ShenyuAgentTypeMatcher#matches()
ShenyuAgentTypeMatcher使用单例的设计模式,实现了ElementMatcher接口,重写了matches()方法。
是否能够匹配成功的逻辑是:如果目标类在拦截点joinPointMap集合中,就匹配成功。
public final class ShenyuAgentTypeMatcher extends ElementMatcher.Junction.AbstractBase<TypeDefinition> {
// ......
private Map<String, ShenyuAgentJoinPoint> joinPointMap;
// 自定义匹配逻辑:如果目标类在拦截点joinPointMap集合中,就匹配成功
@Override
public boolean matches(final TypeDefinition target) {
return joinPointMap.containsKey(target.getTypeName());
}
}
4.2 改变匹配类的行为
在加载目标类时,如果匹配成功,会通过ShenyuAgentTransformer改变其行为,它实现了Transformer接口,重写了transform()方法,Transformer也是bytebuddy的一个接口。
public final class ShenyuAgentTransformer implements Transformer {
//在匹配类中额外定义一个字段,传递上下文信息
private static final String EXTRA_DATA = "_$EXTRA_DATA$_";
//类型匹配器
private static final ShenyuAgentTypeMatcher MATCHER = ShenyuAgentTypeMatcher.getInstance();
//重写transform方法,重新定义匹配类的行为
//加载类期间,执行一次
@Override
public Builder<?> transform(final Builder<?> builder, final TypeDescription typeDescription, final ClassLoader classLoader, final JavaModule module) {
//不是匹配的类就跳过
if (!MATCHER.containsType(typeDescription)) {
return builder;
}
//为该类新增加一个字段
Builder<?> result = builder.defineField(EXTRA_DATA, Object.class, Opcodes.ACC_PRIVATE | Opcodes.ACC_VOLATILE).implement(TargetObject.class).intercept(FieldAccessor.ofField(EXTRA_DATA));
// 获取拦截点
ShenyuAgentJoinPoint joinPoint = MATCHER.loadShenyuAgentJoinPoint(typeDescription);
//拦截构造器
result = interceptorConstructorPoint(typeDescription, joinPoint.getConstructorPoints(), result);
//拦截静态方法
result = interceptorStaticMethodPoint(typeDescription, joinPoint.getStaticMethodPoints(), result);
//拦截实例方法
result = interceptorInstanceMethodPoint(typeDescription, joinPoint.getInstanceMethodPoints(), result);
return result;
}
// ......
}
在transform()方法中,重新定义了匹配类的行为:
- 新增了字段,是
TargetObject的子类,用于传递上下文; - 根据指定配置,是否拦截构造器;
- 根据指定配置,是否拦截静态方法;
- 根据指定配置,拦截实例方法;
4.2.3 拦截实例方法
- ShenyuAgentTransformer#interceptorInstanceMethodPoint()
根据切面构建实例方法拦截点,获取Builder对象。
private Builder<?> interceptorInstanceMethodPoint(final TypeDescription description, final Collection<InstanceMethodPointCut> pointCuts, final Builder<?> builder) {
Collection<ShenyuAgentTransformerPoint<?>> points = description.getDeclaredMethods().stream()
.filter(each -> !(each.isAbstract() || each.isSynthetic())) //过滤抽象方法,合成方法
.map(each -> buildInstanceMethodTransformationPoint(pointCuts, each)) //构建实例方法拦截点
.filter(Objects::nonNull)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
return getBuilder(description, builder, points); //获取Builder对象
}
- ShenyuAgentTransformer#buildInstanceMethodTransformationPoint()
过滤匹配上的方法,为方法获取对应的handler处理器,最后创建实例方法拦截点对象。
private ShenyuAgentTransformerPoint<?> buildInstanceMethodTransformationPoint(final Collection<InstanceMethodPointCut> pointCuts, final InDefinedShape methodDescription) {
List<InstanceMethodPointCut> points = pointCuts.stream().filter(point -> point.getMatcher().matches(methodDescription)).collect(Collectors.toList()); //过滤能够匹配上的方法
if (points.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
List<InstanceMethodHandler> handlers = points.stream()
.flatMap(pointCut -> pointCut.getHandlers().stream())
.map(handler -> (InstanceMethodHandler) MATCHER.getOrCreateInstance(handler)) //获取对应的handler处理器
.filter(Objects::nonNull)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
return new ShenyuAgentTransformerPoint<>(methodDescription, new InstanceMethodInterceptor(handlers));//创建实例方法拦截点对象,创建实例方法拦截器
}
方法能否匹配成功:当前方法名称是否是在tracing-point.yaml文件中配置的方法名称;
handler的获取:是根据tracing-point.yaml文件中配置的全限定名去加载对应的类。
- InstanceMethodInterceptor#intercept()
实例方法拦截器InstanceMethodInterceptor会在运行期间动态处理拦截方法。
public class InstanceMethodInterceptor {
// ......
/**
* 拦截目标对象.
*
* @param target 当前被拦截的目标对象
* @param method 目标对象的目标方法
* @param args 目标方法的参数
* @param callable 目标方法调用
* @return 目标方法调用结果
* @throws 异常信息
*/
@RuntimeType //定义运行时的目标方法
public Object intercept(@This final Object target, @Origin final Method method, @AllArguments final Object[] args, @SuperCall final Callable<?> callable) throws Exception {
//目标方法执行结果
Object result = null;
//目标对象
TargetObject instance = (TargetObject) target;
//依次调用handler
for (InstanceMethodHandler handler : handlerList) {
MethodResult methodResult = new MethodResult();
// 前置处理逻辑
try {
handler.before(instance, method, args, methodResult);
} catch (final Throwable ex) {
LOG.error("Failed to execute the before method of method {} in class {}", method.getName(), target.getClass(), ex);
}
//调用目标方法
try {
result = callable.call();
} catch (final Throwable ex) {
//处理异常
try {
handler.onThrowing(instance, method, args, ex);
} catch (final Throwable ignored) {
LOG.error("Failed to execute the error handler of method {} in class {}", method.getName(), target.getClass(), ex);
throw ex;
}
} finally {
//后置处理逻辑
try {
result = handler.after(instance, method, args, methodResult, result);
} catch (final Throwable ex) {
LOG.error("Failed to execute the after method of method {} in class {}", method.getName(), target.getClass(), ex);
}
}
}
//返回目标方法调用结果
return result;
}
}
实例方法拦截器在目标方法调用前,增加了前置处理逻辑,后置处理逻辑,以及异常处理逻辑。
这里用到了Byte Buddy的几个注解:
@RuntimeType: 定义运行时的目标方法,提示ByteBuddy禁用严格的类型检查;@This:当前被拦截的、动态生成的实例对象;@Origin:原有方法;@AllArguments:获取所有入参;@SuperCall:用于调用父类版本的方法。
实例方法处理器InstanceMethodHandler只是定义了三个接口,具体实现逻辑由具体插件去处理。
public interface InstanceMethodHandler {
// 前置处理逻辑
default void before(final TargetObject target, final Method method, final Object[] args, final MethodResult result) {
}
// 后置处理逻辑
default Object after(final TargetObject target, final Method method, final Object[] args, final MethodResult methodResult, final Object result) {
return result;
}
// 异常处理逻辑
default void onThrowing(final TargetObject target, final Method method, final Object[] args, final Throwable throwable) {
}
}
-
ShenyuAgentTransformer#getBuilder()
在
Agent的Builder获取时,为指定的目标方法指定对应的拦截器,在原有方法上添加新的逻辑,改变原有方法行为。
private static Builder<?> getBuilder(final TypeDescription description, final Builder<?> builder, final Collection<ShenyuAgentTransformerPoint<?>> points) {
final Builder<?>[] result = {builder};
points.forEach(point -> {
try {
result[0] = builder.method(ElementMatchers.is(point.getDescription()))//指定目标方法
.intercept(MethodDelegation.withDefaultConfiguration().to(point.getInterceptor()));//指定拦截器
// CHECKSTYLE:OFF
} catch (final Throwable ex) {
// CHECKSTYLE:ON
LOG.error("Failed to load handler class: {}", description.getTypeName(), ex);
}
});
return result[0];
}
通过以上的处理逻辑,就可以实现无侵入拦截实例方法了。
拦截方法intercept()的处理逻辑是:
- 依次处理每个
handler; - 调用
handler的前置方法; - 调用目标方法;
- 如果目标方法有异常,则调用
handler的异常处理方法; - 调用
handler的后置方法。
接下来看看拦截静态方法。
4.2.3 拦截静态方法
- ShenyuAgentTransformer#interceptorStaticMethodPoint()
过滤出静态方法,然后为静态方法构建静态方法拦截点。
private Builder<?> interceptorStaticMethodPoint(final TypeDescription description, final Collection<StaticMethodPointCut> pointCuts, final Builder<?> builder) {
Collection<ShenyuAgentTransformerPoint<?>> points = description.getDeclaredMethods().stream()
.filter(each -> each.isStatic() && !(each.isAbstract() || each.isSynthetic())) // 当前方法是静态方法,不是抽象方法,不是合成方法
.map(methodDescription -> buildStaticMethodTransformationPoint(pointCuts, methodDescription)) // 构建静态方法拦截点
.filter(Objects::nonNull)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
return getBuilder(description, builder, points);
}
- ShenyuAgentTransformer#buildStaticMethodTransformationPoint()
根据配置文件进行过滤,判断当前的静态方法是否需要拦截。然后获取对应的处理器,最后构建静态方法拦截器对象。
private ShenyuAgentTransformerPoint<?> buildStaticMethodTransformationPoint(final Collection<StaticMethodPointCut> pointCuts, final InDefinedShape methodDescription) {
List<StaticMethodPointCut> staticMethodPoints = pointCuts.stream().filter(point -> point.getMatcher().matches(methodDescription)).collect(Collectors.toList()); //根据配置文件进行过滤,判断当前的静态方法是否需要拦截
if (staticMethodPoints.isEmpty()) { // 如果没有配置,就直接返回了
return null;
}
List<StaticMethodHandler> handlers = staticMethodPoints.stream()
.flatMap(pointCut -> pointCut.getHandlers().stream())
.map(handler -> (StaticMethodHandler) MATCHER.getOrCreateInstance(handler)) //获取对应的处理器
.filter(Objects::nonNull)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
return new ShenyuAgentTransformerPoint<>(methodDescription, new StaticMethodInterceptor(handlers)); //构建静态方法拦截器对象
}
- StaticMethodInterceptor#intercept()
在运行时,会拦截目标方法,执行拦截器的处理逻辑 。
public class StaticMethodInterceptor {
//......
/**
* 拦截目标方法.
*/
@RuntimeType
public Object intercept(@Origin final Class<?> klass, @Origin final Method method, @AllArguments final Object[] args, @SuperCall final Callable<?> callable) throws Exception {
Object result = null;
// handler循环处理
for (StaticMethodHandler handler : handlerList) {
MethodResult methodResult = new MethodResult();
try {
//前置方法
handler.before(klass, method, args, new MethodResult());
} catch (final Throwable ex) {
LOG.error("Failed to execute the before method of method {} in class {}", method.getName(), klass, ex);
}
try {
// 调用当前方法
// 目标方法是不是应该只会被调用一次?
result = callable.call();
} catch (final Throwable ex) {
try {
//异常逻辑处理
handler.onThrowing(klass, method, args, ex);
} catch (final Throwable ignored) {
LOG.error("Failed to execute the error handler of method {} in class {}", method.getName(), klass, ex);
throw ex;
}
} finally {
try {
// 后置方法
handler.after(klass, method, args, methodResult);
} catch (final Throwable ex) {
LOG.error("Failed to execute the after method of method {} in class {}", method.getName(), klass, ex);
}
}
}
//返回方法调用结果
return result;
}
}
拦截方法intercept()的处理逻辑是:
- 依次处理每个
handler; - 调用
handler的前置方法; - 调用目标方法;
- 如果目标方法有异常,则调用
handler的异常处理方法; - 调用
handler的后置方法。
最后再看看如何拦截构造器。
4.2.3 拦截构造器
- ShenyuAgentTransformer#interceptorConstructorPoint()
过滤出构造器,然后构建构造器的拦截点,最后创建builder对象,为构造方法添加拦截器。
private Builder<?> interceptorConstructorPoint(final TypeDescription description, final Collection<ConstructorPointCut> constructorPoints, final Builder<?> builder) {
Collection<ShenyuAgentTransformerPoint<? extends ConstructorInterceptor>> constructorAdviceComposePoints = description.getDeclaredMethods().stream()
.filter(MethodDescription::isConstructor) //过滤出构造器
.map(each -> buildConstructorTransformerPoint(constructorPoints, each))//构建构造器的拦截点
.filter(Objects::nonNull)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
final Builder<?>[] result = {builder};
// 创建builder对象,为构造方法添加拦截器
constructorAdviceComposePoints.forEach(point -> {
try {
result[0] = builder.constructor(ElementMatchers.is(point.getDescription()))
.intercept(SuperMethodCall.INSTANCE.andThen(MethodDelegation.withDefaultConfiguration()
.to(point.getInterceptor())));//先调用父类构造器,然后添加拦截器
// CHECKSTYLE:OFF
} catch (final Throwable ex) {
// CHECKSTYLE:ON
LOG.error("Failed to load handler class: {}", description.getTypeName(), ex);
}
});
return result[0];
}
- ShenyuAgentTransformer#buildConstructorTransformerPoint()
先获取到构造器拦截点,然后为拦截点创建handler实例对象,最后创建构造器拦截器对象。
private ShenyuAgentTransformerPoint<? extends ConstructorInterceptor> buildConstructorTransformerPoint(
final Collection<ConstructorPointCut> constructorPoints, final InDefinedShape methodDescription) {
//获取构造器拦截点
List<ConstructorPointCut> constructorPointCutList = constructorPoints.stream().filter(each -> each.getMatcher().matches(methodDescription)).collect(Collectors.toList());
if (constructorPointCutList.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
List<ConstructorHandler> handlers = constructorPointCutList.stream()
.flatMap(pointCut -> pointCut.getHandlers().stream())
.map(handler -> (ConstructorHandler) MATCHER.getOrCreateInstance(handler)) //创建拦截点的handler实例对象
.filter(Objects::nonNull)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
return new ShenyuAgentTransformerPoint<>(methodDescription, new ConstructorInterceptor(handlers));//创建构造器拦截器
}
- ConstructorInterceptor#intercept()
构造器拦截器:在调用目标方法的构造器之前,执行每个handler的处理逻辑。
public class ConstructorInterceptor {
//......
/**
* 拦截方法.
*/
@RuntimeType
public void intercept(@This final TargetObject target, @AllArguments final Object[] args) {
for (ConstructorHandler handler : handlerList) {
try {
// handler处理逻辑
handler.onConstructor(target, args);
} catch (final Throwable throwable) {
LOG.error("Constructor advice execution error. class: {}", target.getClass().getTypeName(), throwable);
}
}
}
}
分析到此,我们分析完了创建agent的整个过程:
- 根据配置文件,定义匹配逻辑
ShenyuAgentTypeMatcher; - 定义
ShenyuAgentTransformer对象,改变匹配类的行为; - 通过
InstanceMethodInterceptor拦截实例对象方法; - 通过
StaticMethodInterceptor拦截静态方法; - 通过
ConstructorInterceptor拦截构造器。
这里没有提到每个handler的处理逻辑,是因为handler的实现逻辑由每个插件自定义。比如,当前实例方法拦截器InstanceMethodHandler的实现类就有jaeger,opentelemetry和zipkin。
[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-KFJdWGlT-1647258166340)(https://qiniu.midnight2104.com/20220216/instance_method_handler.png)]
5. 启动插件
创建完 agent之后,启动各个插件。
public static void premain(final String arguments, final Instrumentation instrumentation) throws Exception {
// 1. 读取配置文件
// ......
// 2. 加载所有插件
// ......
// 3. 创建 agent
// 4. 启动插件
PluginLifecycleManager lifecycleManager = new PluginLifecycleManager();
lifecycleManager.startup(ShenyuAgentConfigUtils.getPluginConfigMap());
//添加hook函数用于关闭插件
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(new Thread(lifecycleManager::close));
}
-
PluginLifecycleManager
PluginLifecycleManager负责插件的生命周期管理,用于启动插件和关闭插件。插件的启动,必须要在配置文件中指定。
public class PluginLifecycleManager {
//......
/**
* 启动插件.
*/
public void startup(final Map<String, AgentPluginConfig> configMap) {
//从配置文件中获取支持的插件名称
Set<String> support = ShenyuAgentConfigUtils.getSupports();
configMap.entrySet().stream()
.filter(entry -> support.contains(entry.getKey())) //包含在配置文件中
.forEach(entry -> Optional.ofNullable(SPILoader.load(AgentPluginBootService.class, entry.getKey())) //通过SPI加载插件启动类
.ifPresent(bootService -> {
try {
LOG.info("start shenyu plugin: {}", entry.getKey());
bootService.start(entry.getValue()); // 启动插件:执行插件的具体启动逻辑
} catch (final Throwable ex) {
LOG.error("Failed to start shenyu plugin", ex);
}
}));
}
/**
* 关闭插件
*/
public void close() {
//通过SPI加载插件启动类
SPILoader.loadList(AgentPluginBootService.class).forEach(each -> {
try {
each.close(); // 关闭插件:执行插件的具体关闭逻辑
} catch (final Throwable ex) {
LOG.error("Failed to close shenyu agent plugin", ex);
}
});
}
}
插件的启动和关闭也是有每个插件具体去实现的,然后通过SPI去加载。
6. 总结
shenyu-agent模块的实现主要是通过Byte Buddy工具包;- 在配置文件
shenyu-agent.yaml中,指定插件信息; - 插件加载过程通过
SPI完成; - 拦截点通过配置文件指定,设计灵活;
- 插件接口定义和实现分开,支持多种插件类型。