一 CompletableFuture
1 CompletableFuture简介
CompletableFuture是一种任务编排工具,每个任务都以CompletableFuture内部函数的方式存在,比如下面创建了三个任务future1、future2、future3,任务的具体逻辑就是函数式接口的执行逻辑。future1、2、3之间以串行的方式连接。
// CompletableFuture测试
@Test
public void test() throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
CompletableFuture<String> future1 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "hello");
CompletableFuture<String> future2 = future1.thenApply(h -> h + " completableFuture");
CompletableFuture<String> future3 = future2.whenComplete((r, cause) -> System.out.println(r));
System.out.println(future3.get());
}
2 supplyAsync原理分析
CompletableFuture属性
volatile Object result; // Either the result or boxed AltResult
volatile Completion stack; // Top of Treiber stack of dependent actions
- result 属性
每个CompletableFuture代表一个任务,任务【传入的函数】执行结果保存在result中,并且会返回当前CompletableFuture供后续任务编排使用,比如上面future1执行完能够通过future1.get()获取内部的result,并且通过返回的future1执行future1.thenApply进行后面的任务编排。
- stack属性
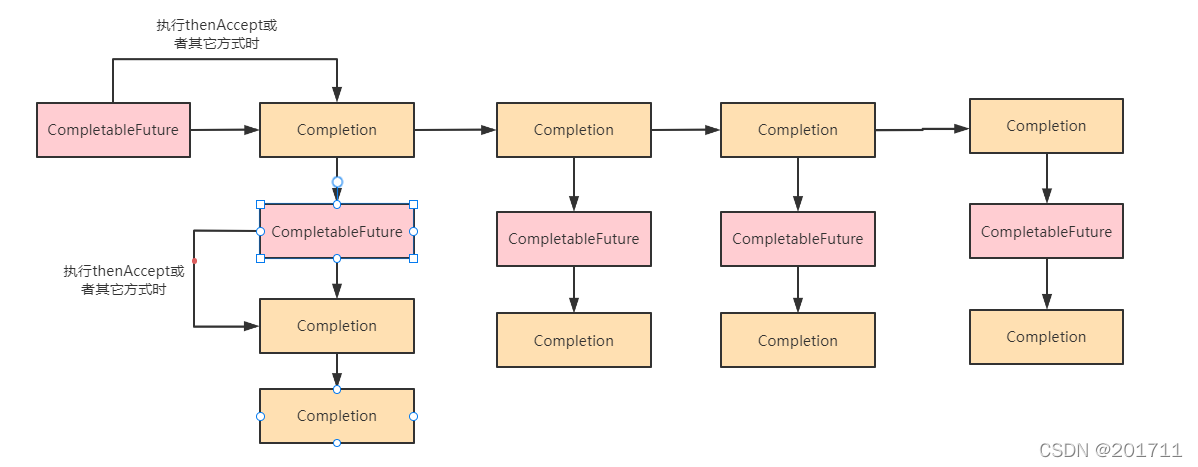
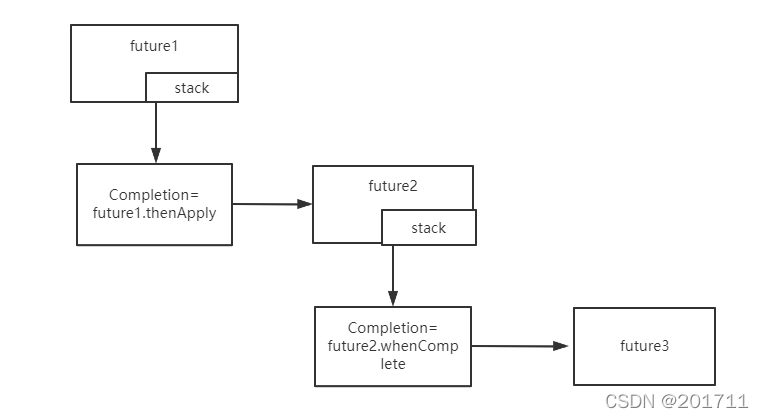
每个CompletableFuture中存在stack栈,该stack通过next方式连接下一个Completion对象。比如上面 future1.thenApply、future2.whenComplete都会生成Completion栈,只不过 future1.thenApply生成的栈放入到了 future1的stack属性中,future2.whenComplete放入到了future2的stack属性中。
上面的方法生成的stack结构如下所示
3 执行流程分析
future1.thenApply(fn)
private <V> CompletableFuture<V> uniApplyStage(
Executor e, Function<? super T,? extends V> f) {
if (f == null) throw new NullPointerException();
CompletableFuture<V> d = new CompletableFuture<V>();
// d.uniApply尝试运行一次
if (e != null || !d.uniApply(this, f, null)) {
// 生成completion放入到future1的stack中
UniApply<T,V> c = new UniApply<T,V>(e, d, this, f);
// 这里采用的链表头部插入,先进后出
push(c);
c.tryFire(SYNC);
}
// 这里返回当前future2
return d;
}
future2.whenComplete(fn)
private CompletableFuture<T> uniWhenCompleteStage(
Executor e, BiConsumer<? super T, ? super Throwable> f) {
if (f == null) throw new NullPointerException();
CompletableFuture<T> d = new CompletableFuture<T>();
// 实现Completion的子类方法大致一样,都会尝试先运行一次
if (e != null || !d.uniWhenComplete(this, f, null)) {
// 运行失败则压入当前future2的栈中,注意压入的是future2【调用者】
UniWhenComplete<T> c = new UniWhenComplete<T>(e, d, this, f);
push(c);
c.tryFire(SYNC);
}
return d;
}
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(fn)
static final class AsyncSupply<T> extends ForkJoinTask<Void>
implements Runnable, AsynchronousCompletionTask {
CompletableFuture<T> dep; Supplier<T> fn;
AsyncSupply(CompletableFuture<T> dep, Supplier<T> fn) {
this.dep = dep; this.fn = fn;
}
public final Void getRawResult() { return null; }
public final void setRawResult(Void v) {}
public final boolean exec() { run(); return true; }
public void run() {
CompletableFuture<T> d; Supplier<T> f;
if ((d = dep) != null && (f = fn) != null) {
dep = null; fn = null;
if (d.result == null) {
try {
d.completeValue(f.get());
} catch (Throwable ex) {
d.completeThrowable(ex);
}
}
// 这里主要是当前future1执行完成后,执行future1后面stack中关联的阶段任务
d.postComplete();
}
}
}
d.postComplete()
final void postComplete() {
CompletableFuture<?> f = this; Completion h;
// 返回的如果是当前的future,则执行future stack中的Completion链表对象
while ((h = f.stack) != null ||
// 如果下面返回的不是当前的future则执行stack中的Completion链表对象
(f != this && (h = (f = this).stack) != null)) {
CompletableFuture<?> d; Completion t;
// f.casStack取f的stack,然后把stack.next放到stack位置。
// 这里其实是一个个取future后面的stack并执行 d = h.tryFire(NESTED))
if (f.casStack(h, t = h.next)) {
if (t != null) {
if (f != this) {
pushStack(h);
continue;
}
h.next = null; // detach
}
// 返回当前的future,调用哪个Completion则返回对应的future
f = (d = h.tryFire(NESTED)) == null ? this : d;
}
}
}
4 CompletableFuture总结
CompletableFuture在调用方法时,会返回一个future对象,通过该future对象和后面的future对象进行连接,并对任务进行编排。任务编排后会形成链表形状的数据结构。