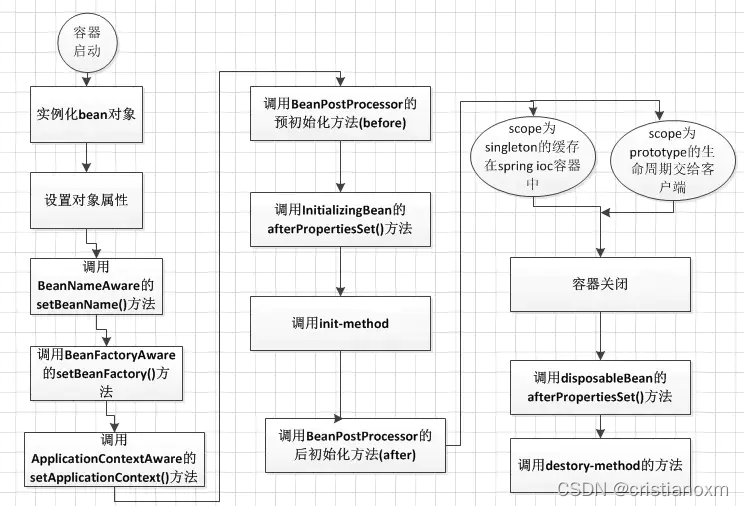
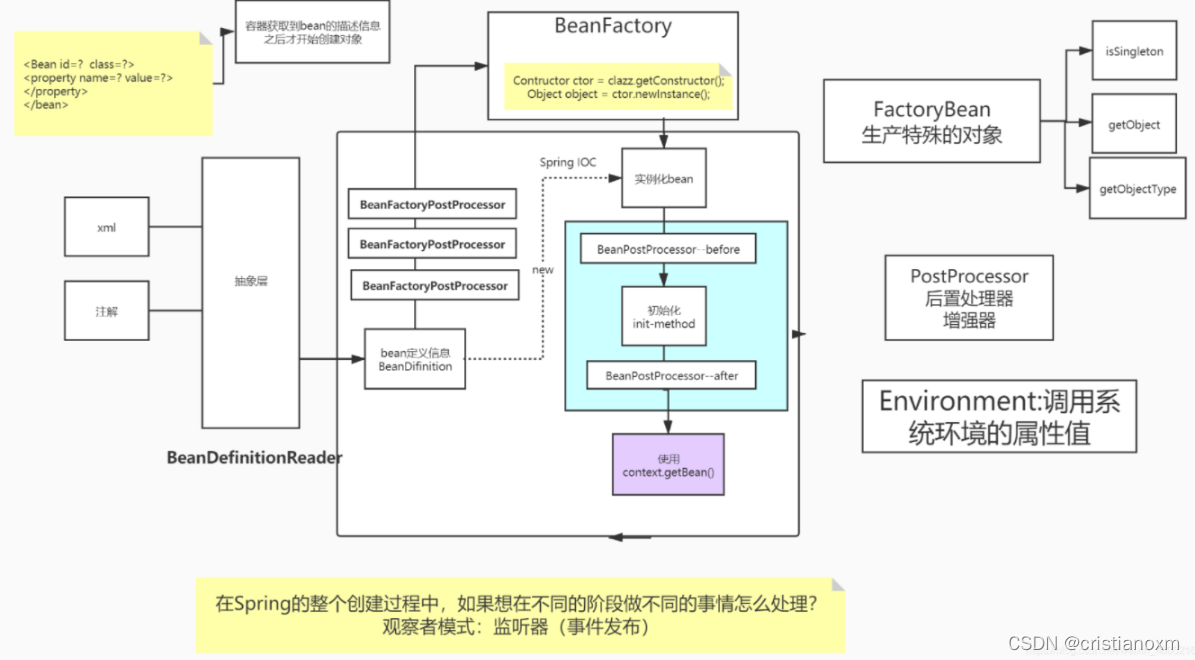
一、从AbstractApplicationContext的体系说起
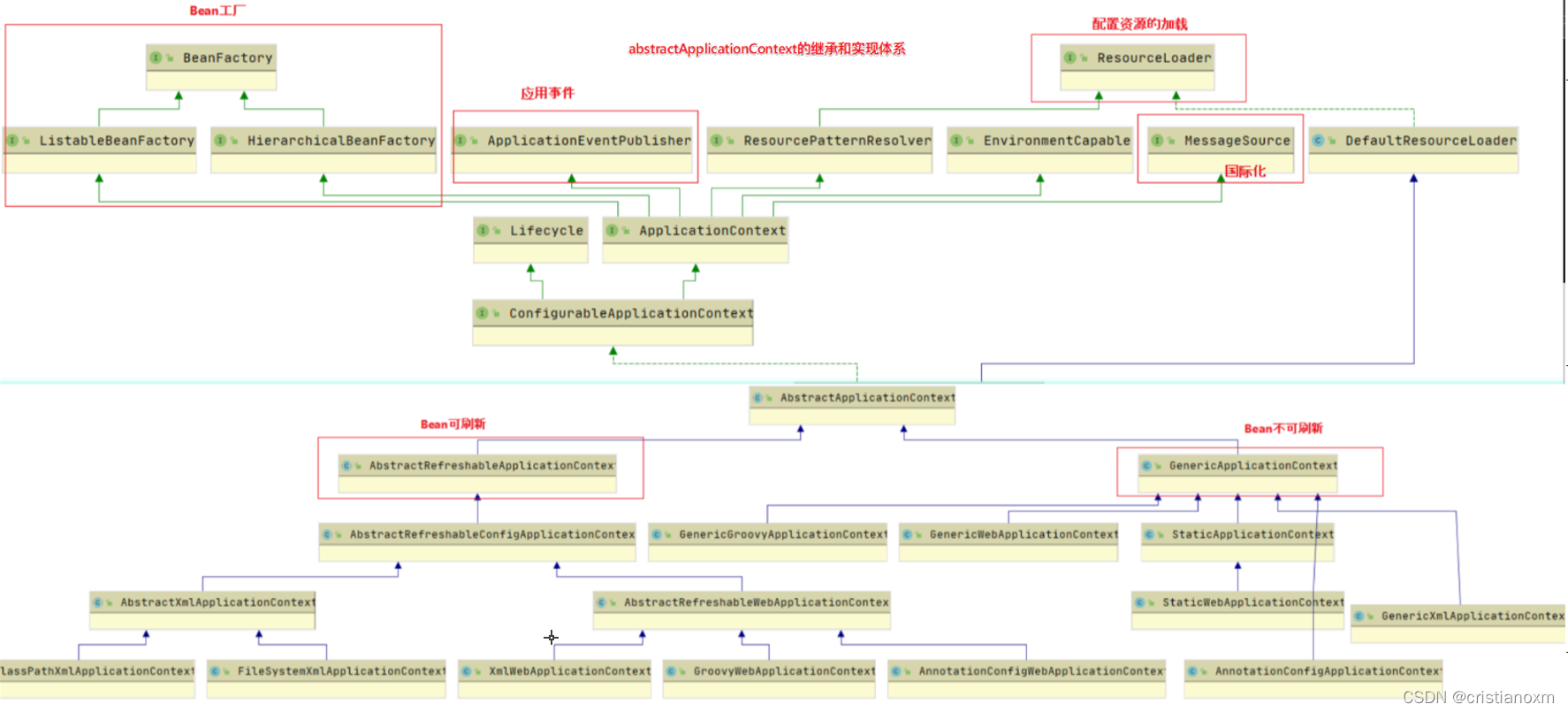
- 第一,从类结构设计上看, 围绕着是否需要Refresh容器衍生出两个抽象类:
- GenericApplicationContext: 是初始化的时候就创建容器,往后的每次refresh都不会更改
- AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext:AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext及子类的每次refresh都是先清除已有(如果不存在就创建)的容器,然后再重新创建;
AbstractRefreshableApplicationContext及子类无法做到GenericApplicationContext混合搭配从不同源头获取bean的定义信息
- 第二, 从加载的源来看(比如xml,groovy,annotation等), 衍生出众多类型的ApplicationContext, 典型比如:
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:从文件系统下的
一个或多个xml配置文件中加载上下文定义,也就是说系统盘符中加载xml配置文件。
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext: 从类路径下的一个或多个xml配置文件中加载上下文定义,适用于xml配置的方式。AnnotationConfigApplicationContext:从一个或多个基于java的配置类中加载上下文定义,适用于java注解的方式。
ConfigurableApplicationContext: 扩展于 ApplicationContext,
它新增加了两个主要的方法: refresh()和 close(),让ApplicationContext 具有启动、刷新和关闭应用上下文的能力。在应用上下文关闭的情况下调用refresh()即可启动应用上下文,在已经启动的状态下,调用refresh()则清除缓存并重新装载配置信息,而调用close()则可关闭应用上下文。这些接口方法为容器的控制管理带来了便利,但作为开发者,我们并不需要过多关心这些方法。XmlWebApplicationContext: 继承自AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext,
接受能被XmlBeanDefinitionReader所理解的XML文档配置。对于根上下文,默认的配置文件路径是/WEB-INF/applicationContext.xml,对于命名空间为test-servlet的上下文,默认的配置文件路径是/WEB-INF/test-servlet.xml(就像servlet-name为test的DispatcherServlet实例)。AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext: 继承自AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext,接受注解的类作为输入(特殊的@Configuration注解类,一般的@Component注解类,与JSR-330兼容的javax.inject注解)。允许一个一个的注入,同样也能使用类路径扫描。
对于web环境,基本上是和AnnotationConfigApplicationContext等价的。使用AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader来对注解的bean进行处理,使用ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner来对类路径下的bean进行扫描
这里可以参考这篇文章
二、本文以ClassPathXmlApplicationContext为例,这种方式包含了多种spring加载bean的方式
//如下:开启spring应用
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ac =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
User bean = ac.getBean("user",User.class);
System.out.println(bean);
}
从ClassPathXmlApplicationContext的构造方法开始查看
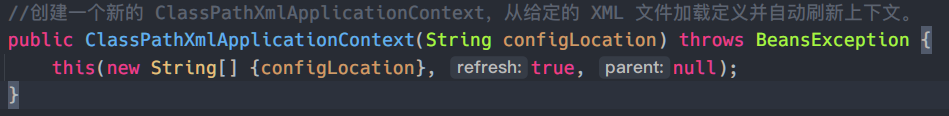
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, ApplicationContext parent)
throws BeansException {
// 1.初始化父类,这里一路加载到顶层父类AbstractApplicationContext中的构造方法
// 才不再显示的super(parent)
super(parent);
// 2.设置本地的配置信息
setConfigLocations(configLocations);
// 3.完成Spring容器的初始化
if (refresh) {
refresh();
}
}
- super(parent)
public AbstractApplicationContext(ApplicationContext parent) {
this();
setParent(parent);
}
- 那么看一下this()
public AbstractApplicationContext() {
//在该构造方法对resourcePatternResolver 变量赋值。resourcePatternResolver 的作用是根据路径得到类的Resource对象
this.resourcePatternResolver = getResourcePatternResolver();
}
protected ResourcePatternResolver getResourcePatternResolver() {
//创建PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver对象的时候
//AbstractApplicationContext将自身作为ResourceLoader传递给了PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver
return new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver(this);
}
public PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver(ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
Assert.notNull(resourceLoader, "ResourceLoader must not be null");
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
}
@Override
public Resource getResource(String location) {
return getResourceLoader().getResource(location);
}
- 再看一下setParent(parent)
@Override
public void setParent(ApplicationContext parent) {
this.parent = parent; // null
//因为parent为null所以if语句中的代码不会执行,所以此if中的代码在此逻辑中不会执行,所以在此就没有分析的必要了。
//初始化的第一部分就分析完毕了,这部分的主要工作是为后续Resource处理准备好处理类
if (parent != null) {
Environment parentEnvironment = parent.getEnvironment();
if (parentEnvironment instanceof ConfigurableEnvironment) {
getEnvironment().merge((ConfigurableEnvironment) parentEnvironment);
}
}
}
- setConfigLocations(configLocations)
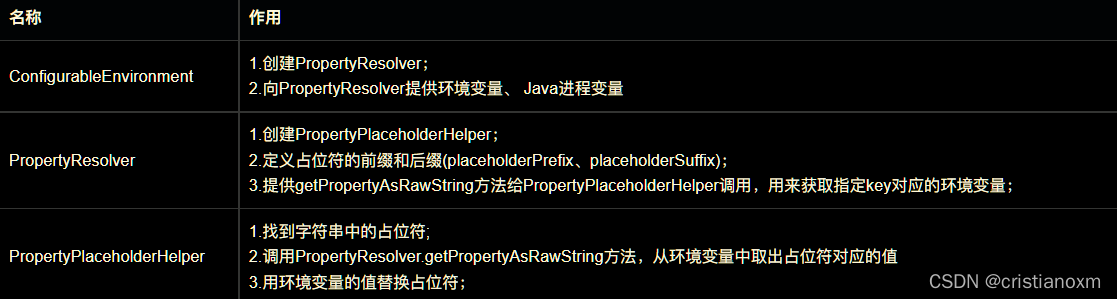
//1.setConfigLocations主要工作有两个:创建环境对象ConfigurableEnvironment 、处理ClassPathXmlApplicationContext传入的字符串中的占位符;
//2.环境对象ConfigurableEnvironment中包含了当前JVM的profile配置信息、环境变量、 Java进程变量;
//3.处理占位符的关键是ConfigurableEnvironment、PropertyResolver、PropertyPlaceholderHelper之间的配合
public void setConfigLocations(String... locations) {
if (locations != null) {
Assert.noNullElements(locations, "Config locations must not be null");
this.configLocations = new String[locations.length];
for (int i = 0; i < locations.length; i++) {
//循环取出每一个path参数,在此处我们就只有一个“applicationContext.xml“”
this.configLocations[i] = resolvePath(locations[i]).trim();
}
}
else {
this.configLocations = null;
}
}
// 这个方法的目的是替换掉path字符串中的占位符${XXX}这样的内容
protected String resolvePath(String path) {
// 1.进入getEnvironment()
// 2.进入resolveRequiredPlaceholders方法
return getEnvironment().resolveRequiredPlaceholders(path);
}
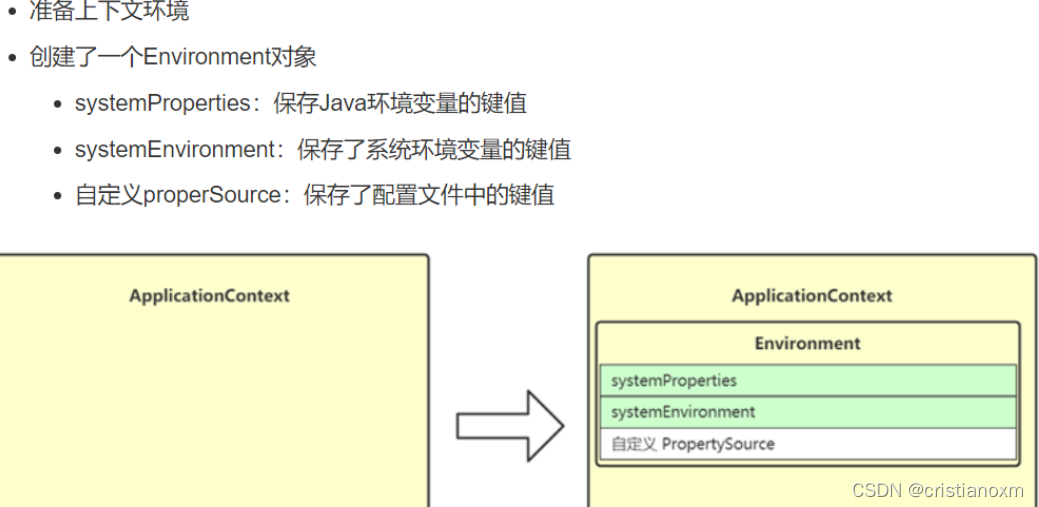
- getEnvironment():创建了ConfigurableEnvironment 对象
public ConfigurableEnvironment getEnvironment() {
if (this.environment == null) {
this.environment = createEnvironment();
}
return this.environment;
}

从提供的方法中可以看出两个功能
- 处理profile:
Profile是对测试、生产等不同环境下的bean配置,这里我们没有特别设置,所以用到的profile是AbstractEnvironment的defaultProfiles- 处理property
- 获取系统环境信息
- 合并环境信息
- PropertyResolver:resolveRequiredPlaceholders(path)

@Override
public String resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException {
if (this.strictHelper == null) {
this.strictHelper = createPlaceholderHelper(false);
}
return doResolvePlaceholders(text, this.strictHelper);
}
处理占位符的方法:
- PropertyPlaceholderHelper
@Override
public String resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException {
if (this.strictHelper == null) {
// 创建PropertyPlaceholderHelper对象
this.strictHelper = createPlaceholderHelper(false);
}
return doResolvePlaceholders(text, this.strictHelper);
}
进入doResolvePlaceholders继续查看
private String doResolvePlaceholders(String text, PropertyPlaceholderHelper helper) {
return helper.replacePlaceholders(text, new PropertyPlaceholderHelper.PlaceholderResolver() {
@Override
public String resolvePlaceholder(String placeholderName) {
return getPropertyAsRawString(placeholderName);
}
});
}
getPropertyAsRawString的具体实现在PropertySourcesPropertyResolver类中
@Override
protected String getPropertyAsRawString(String key) {
return getProperty(key, String.class, false);
}
继续跟踪helper.replacePlaceholders(),到了PropertyPlaceholderHelper.parseStringValue方法,这里面逐一找出每个占位符去做替换:
public String replacePlaceholders(String value, PlaceholderResolver placeholderResolver) {
Assert.notNull(value, "'value' must not be null");
return parseStringValue(value, placeholderResolver, new HashSet<String>());
}
parseStringValue方法中,找到了占位符后,会调用入参placeholderResolver的resolvePlaceholder(placeholder)方法,也就是上面匿名类的getPropertyAsRawString方法(实际上就是PropertySourcesPropertyResolver.getPropertyAsRawString方法),最终会在PropertySourcesPropertyResolver.getProperty方法中找出所有的属性来匹配占位符
protected String parseStringValue(
String strVal, PlaceholderResolver placeholderResolver, Set<String> visitedPlaceholders) {
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder(strVal);
int startIndex = strVal.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix);
while (startIndex != -1) {
int endIndex = findPlaceholderEndIndex(result, startIndex);
if (endIndex != -1) {
String placeholder = result.substring(startIndex + this.placeholderPrefix.length(), endIndex);
String originalPlaceholder = placeholder;
if (!visitedPlaceholders.add(originalPlaceholder)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Circular placeholder reference '" + originalPlaceholder + "' in property definitions");
}
// Recursive invocation, parsing placeholders contained in the placeholder key.
placeholder = parseStringValue(placeholder, placeholderResolver, visitedPlaceholders);
// Now obtain the value for the fully resolved key...
String propVal = placeholderResolver.resolvePlaceholder(placeholder);
if (propVal == null && this.valueSeparator != null) {
int separatorIndex = placeholder.indexOf(this.valueSeparator);
if (separatorIndex != -1) {
String actualPlaceholder = placeholder.substring(0, separatorIndex);
String defaultValue = placeholder.substring(separatorIndex + this.valueSeparator.length());
propVal = placeholderResolver.resolvePlaceholder(actualPlaceholder);
if (propVal == null) {
propVal = defaultValue;
}
}
}
if (propVal != null) {
// Recursive invocation, parsing placeholders contained in the
// previously resolved placeholder value.
propVal = parseStringValue(propVal, placeholderResolver, visitedPlaceholders);
result.replace(startIndex, endIndex + this.placeholderSuffix.length(), propVal);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Resolved placeholder '" + placeholder + "'");
}
startIndex = result.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix, startIndex + propVal.length());
}
else if (this.ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders) {
// Proceed with unprocessed value.
startIndex = result.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix, endIndex + this.placeholderSuffix.length());
}
else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Could not resolve placeholder '" +
placeholder + "'" + " in string value \"" + strVal + "\"");
}
visitedPlaceholders.remove(originalPlaceholder);
}
else {
startIndex = -1;
}
}
return result.toString();
}
总结:
剩下最核心的refresh()方法,单开一章
三、核心refresh()方法
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
//做容器刷新前的准备工作
//1.设置容器的启动时间
//2.设置活跃状态为true
//3.设置关闭状态为false
//4.获取Environment对象,并加载当前系统的属性值到Environment对象中
//5.准备监听器和事件的集合对象,默认为空的集合
prepareRefresh();
//创建容器对象:DefaultListableFactory
//加载xml配置文件的属性值到当前工厂中,最重要的就是BeanDefinition
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
//beanFactory的准备工作,对各种属性进行填充
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// 允许在上下文子类中对 bean 工厂进行后处理。此处我们一般不做任何扩展工作
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// 调用在上下文中注册为 beanFactory 处理器。
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
//注册能拦截 bean 创建的 bean 处理器,此处只是注册功能,真正调用的是getBean
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
//为上下文初始化message源,即不同语言的消息体,国际化处理
initMessageSource();
//为此上下文初始化事件多播器
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
//留给子类来初始化其他bean
onRefresh();
//在所有注册的bean中查找listener bean,注册到消息广播器中
registerListeners();
// 初始化剩下的单实例(非懒加载),多例是在getBean时才初始化
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
//完成刷新过程,通知生命周期处理器lifecycleProcessor刷新过程,同时发出ContextRefreshEvent通知别人
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
//销毁已经创建的单例以避免悬空资源
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
//重置active标志
cancelRefresh(ex);
throw ex;
}
finally {
//重置 Spring 核心中的常见自省缓存,因为我们可能不再需要单例 bean 的元数据
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
- 步骤:
- prepareRefresh
- obtainFreshBeanFactory
- prepareBeanFactory
- postProcessBeanFactory
- invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors
- registerBeanPostProcessors
- initMessageSource
- initApplicationEventMulticaster
- onRefresh
- registerListeners
- finishBeanFactoryInitialization
- finishRefresh
- resetCommonCaches()
-
prepareRefresh()
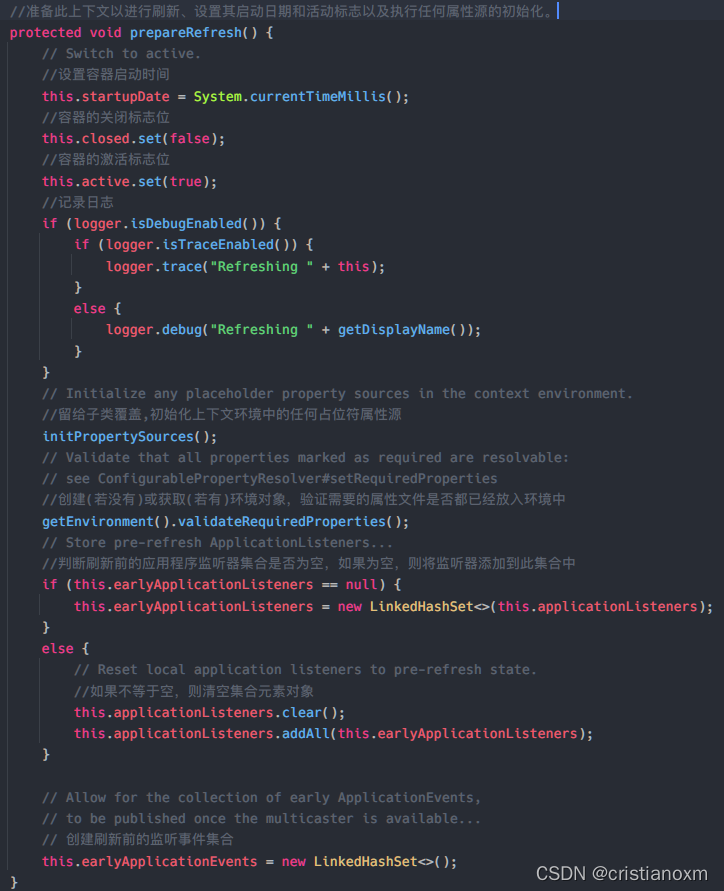
作用:
-
obtainFreshBeanFactory()

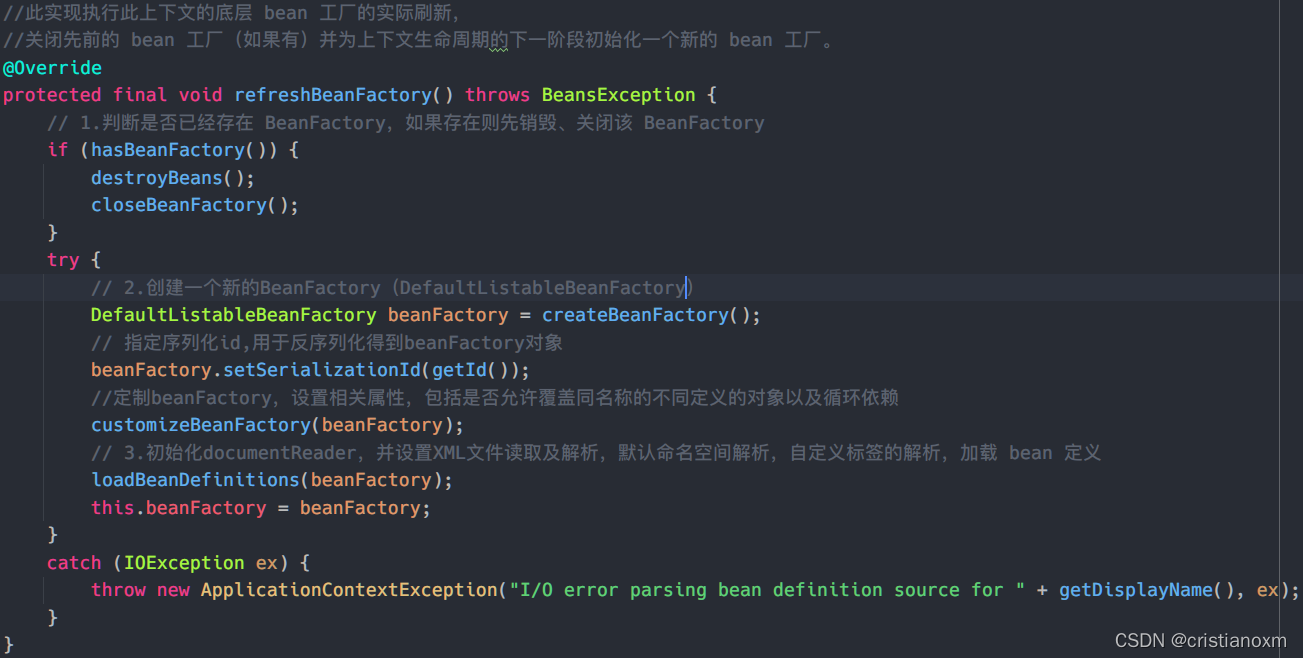
createBeanFactory----创建bean工厂

进入loadBeanDefinition
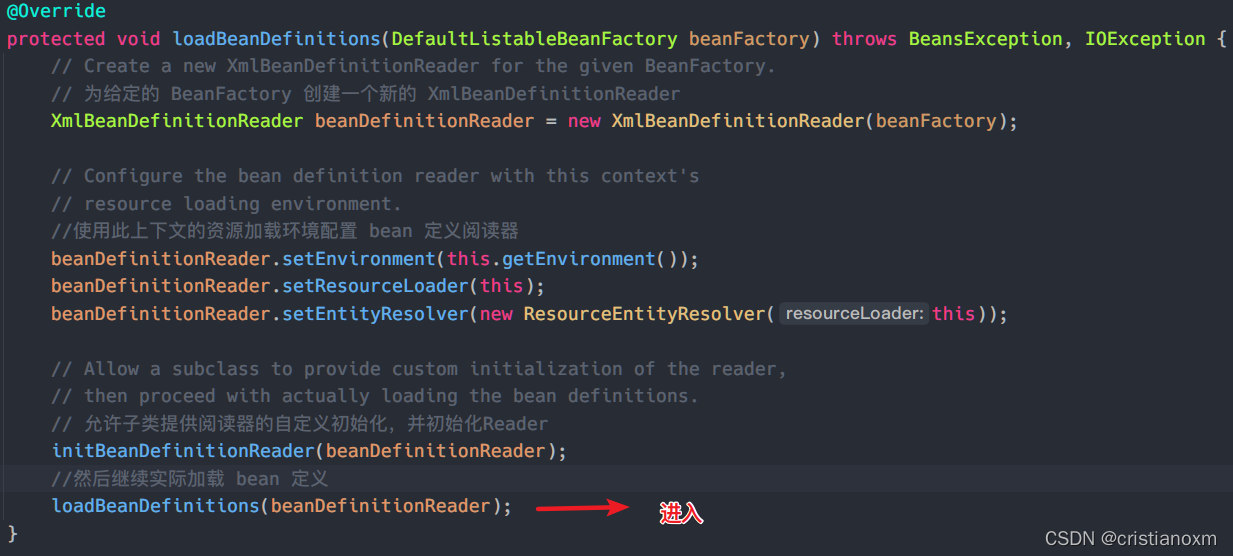
走完loadBeanDefinitons后,beanFactory中的beandefinitionMap就不会为空了
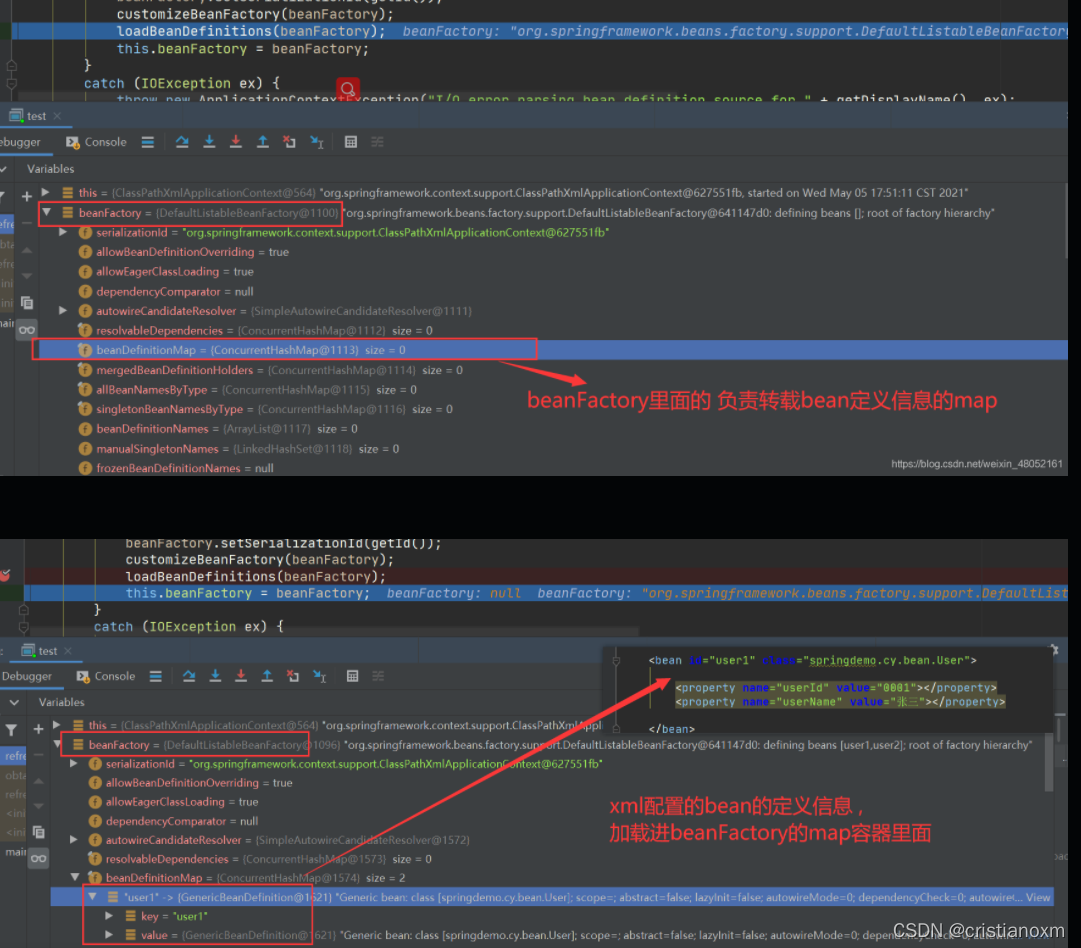
然后一路再返回到AbstractApplicationContext
作用:
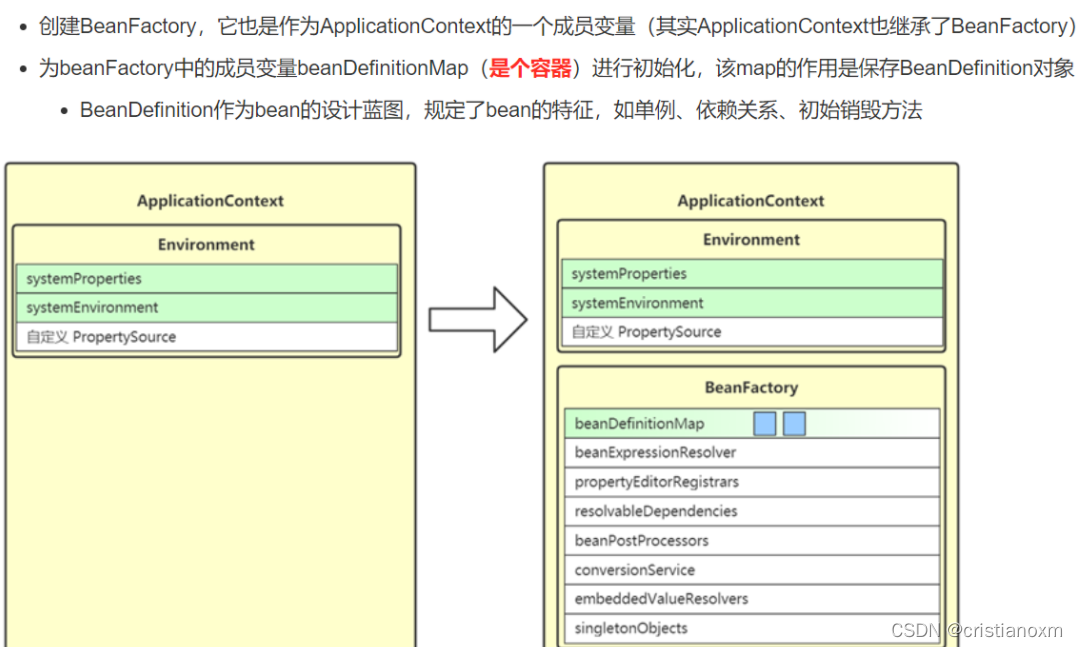
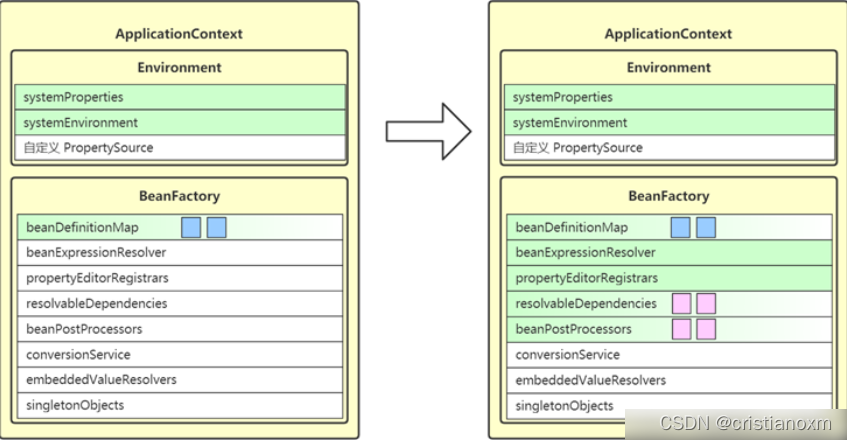
- prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory):beanFactory的准备工作,对各种属性进行填充
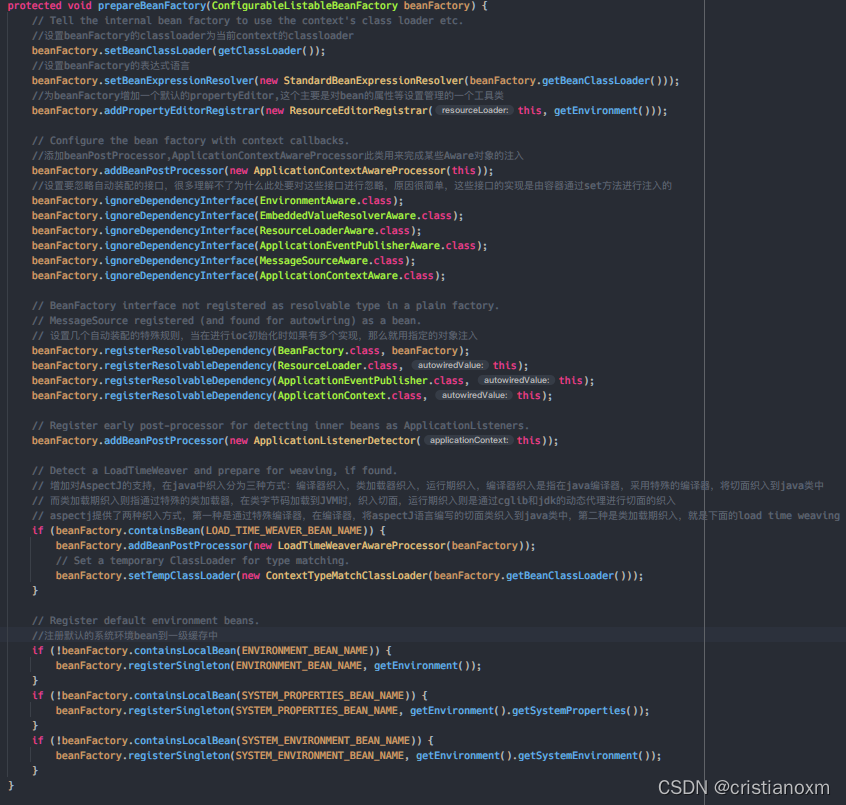
作用:

- postProcessBeanFactory(BeanFactory的后置处理器,留给其子类做扩展用的)
postProcessBeanFactory方法是留给子类扩展的,可以在bean实例初始化之前注册后置处理器(类似prepareBeanFactory方法中的beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor),空实现且没有子类覆盖。
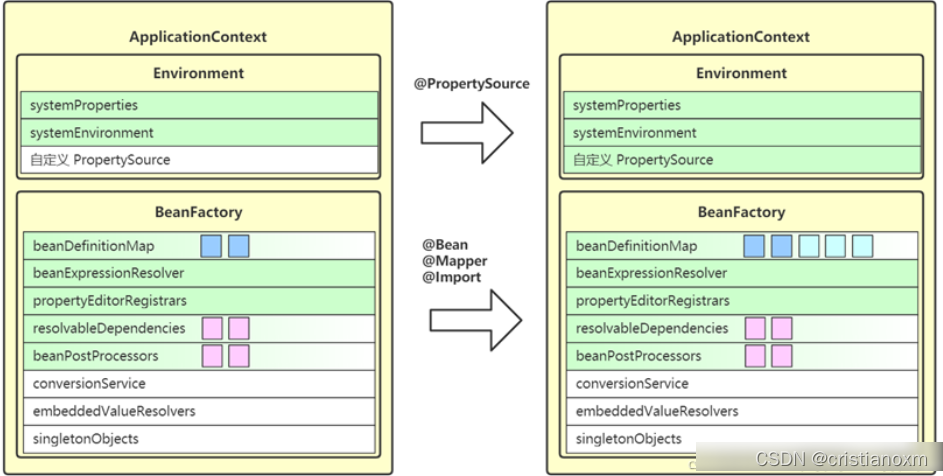
- invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(调用各种beanFactory处理器)
该方法执行BeanFactoryPostProcessor执行器

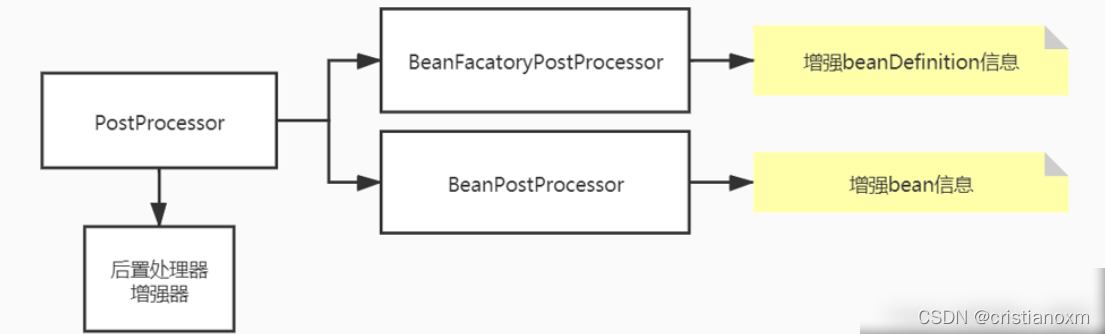
执行BeanFactoryPostProcessor 执行器
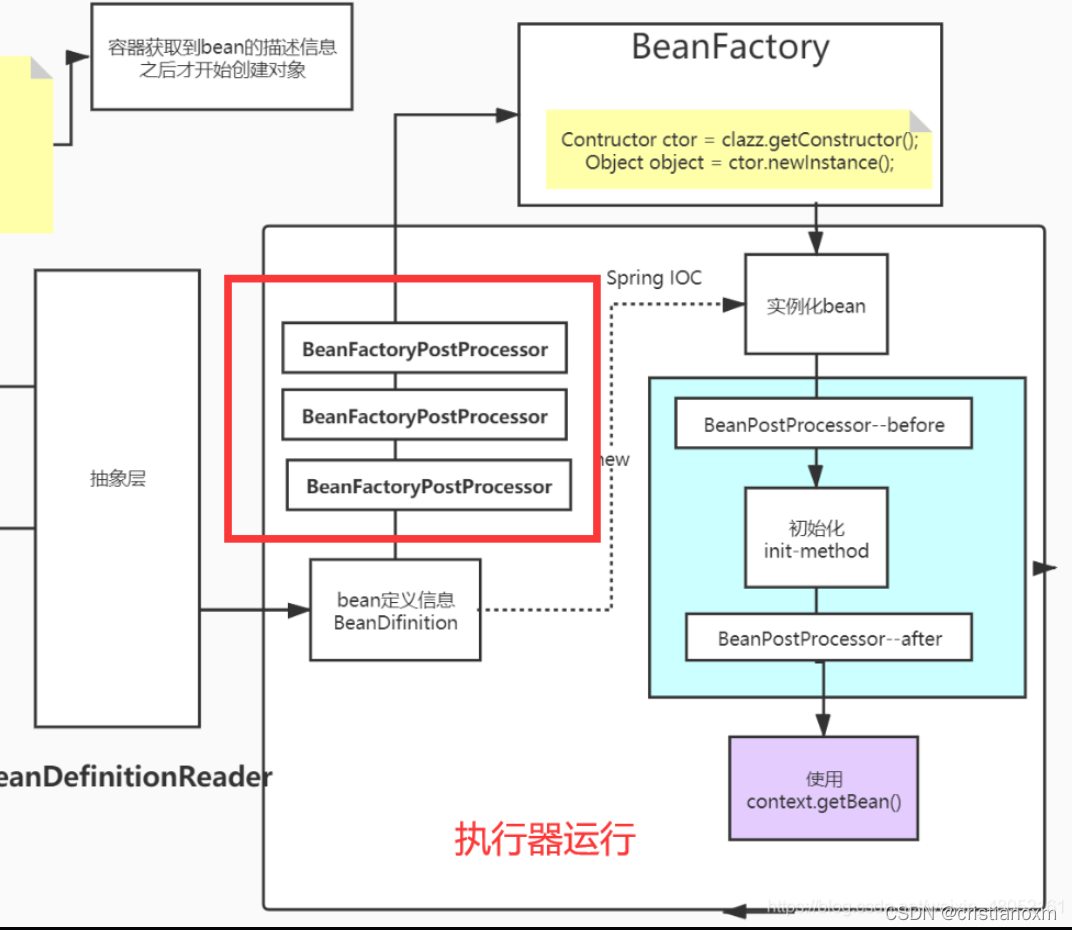
作用:

附表:常用的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
| BeanFactoryPostProcessor类 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| CachingMetadataReaderFactoryPostProcessor(也实现了接口BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor | |
| ConfigurationWarningsPostProcessor(也实现了接口BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor | 主要作用就是把在注册BeanDefinition实例过程中产生的告警信息传给Check接口的实例进行处理,ConfigurationWarningsApplicationContextInitializer中只提供了一个Check的实现 ComponentScanPackageCheck,ConfigurationWarningsApplicationContextInitializer的作用是用来报告Spring容器的一些常见的错误配置的 |
| ConfigurationClassPostProcessor (也实现了接口BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) | 主要功能是参与BeanFactory的建造,主要功能如下: 解析加了@Configuration的配置类 解析@ComponentScan扫描的包 解析@ComponentScans扫描的包 |
| PropertySourceOrderingPostProcessor | Bean工厂结束后对环境里的属性源进行重排序 -> 把名字叫defaultProperties的属性源放在最末位 |
注意: BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 继承自 BeanFactoryPostProcessor,比 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 具有更高的优先级,主要用来在常规的 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 激活之前注册一些 bean 定义。
- registerBeanPostProcessors
注册bean处理器,这里只是注册功能,真正调用的是getBean方法

registerBeanPostProcessors方法的代码略多,就不在此贴出来了,简单的说,就是找出所有的bean的后置处理器(注意,是bean的后置处理器,不是beanFactory的后置处理器,bean后置处理器处理的是bean实例,beanfactory后置处理器处理的是bean的定义),然后将这些bean的后置处理器分为三类:
- 实现了顺序接口Ordered.class的,先放入orderedPostProcessors集合,排序后顺序加入beanFactory的bean后处理集合中;
- 既没有实现Ordered.class,也没有实现PriorityOrdered.class的后置处理器,也加入到beanFactory的bean后处理集合中;
- 最后是实现了优先级接口PriorityOrdered.class的,排序后顺序加入beanFactory的bean后处理集合中;
registerBeanPostProcessors方法执行完毕后,beanFactory中已经保存了有序的bean后置处理器,在bean实例化之后,会依次使用这些后置处理器对bean实例来做对应的处理;
作用:

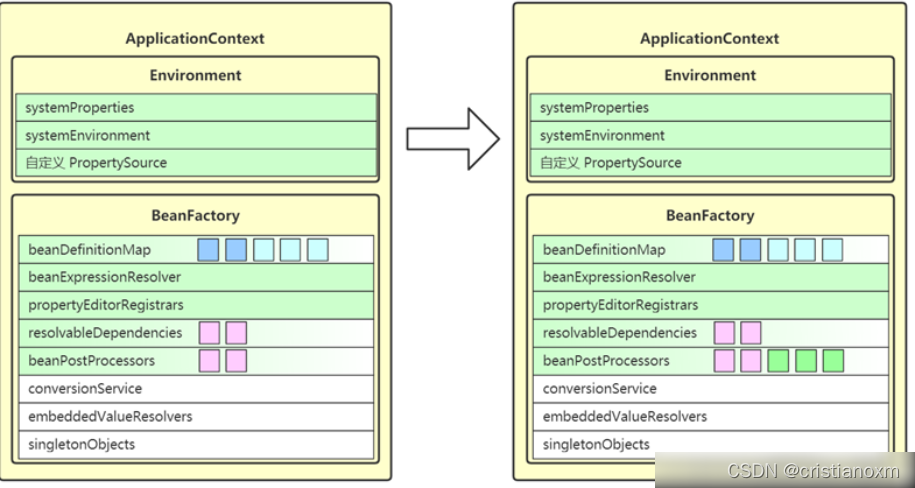
- initMessageSource
为上下文初始化message源,即不同语言的消息体,国际化处理

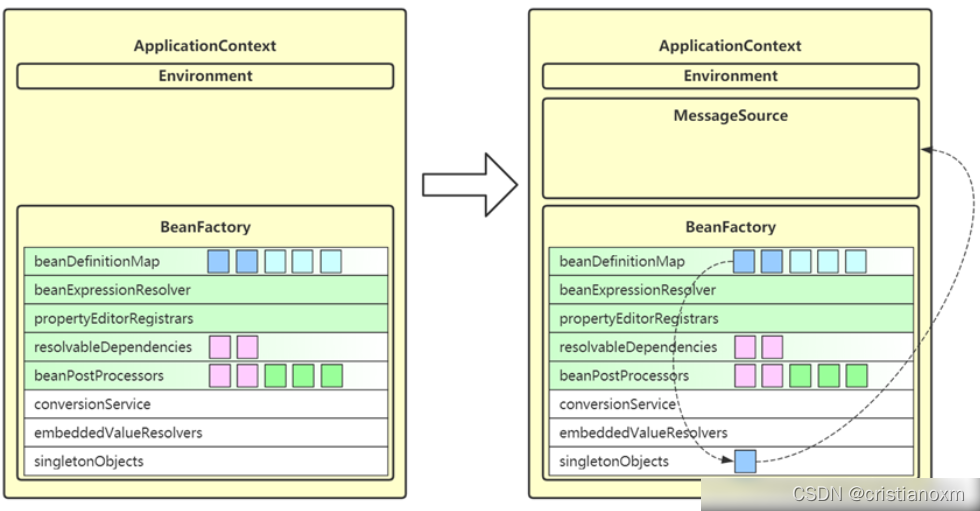
- initApplicationEventMulticaster
初始化事件监听多路广播器
作用:

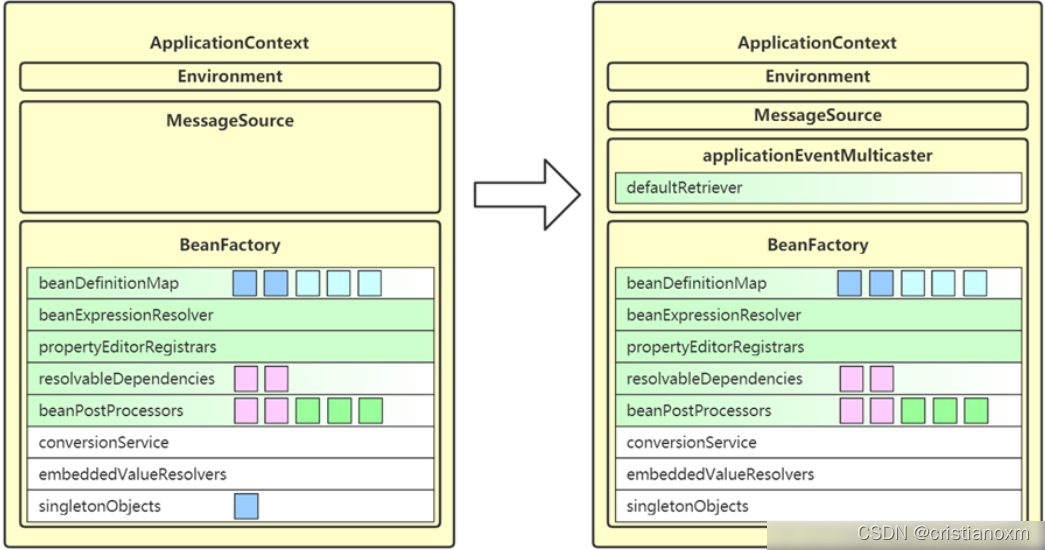
- onRefresh
onRefresh是个空方法,留给子类自己实现的,在实例化bean之前做一些ApplicationContext相关的操作,以子类AbstractRefreshableWebApplicationContext为例,看看它的onRefresh方法
/**
* Initialize the theme capability.
*/
@Override
protected void onRefresh() {
this.themeSource = UiApplicationContextUtils.initThemeSource(this);
}
- registerListeners
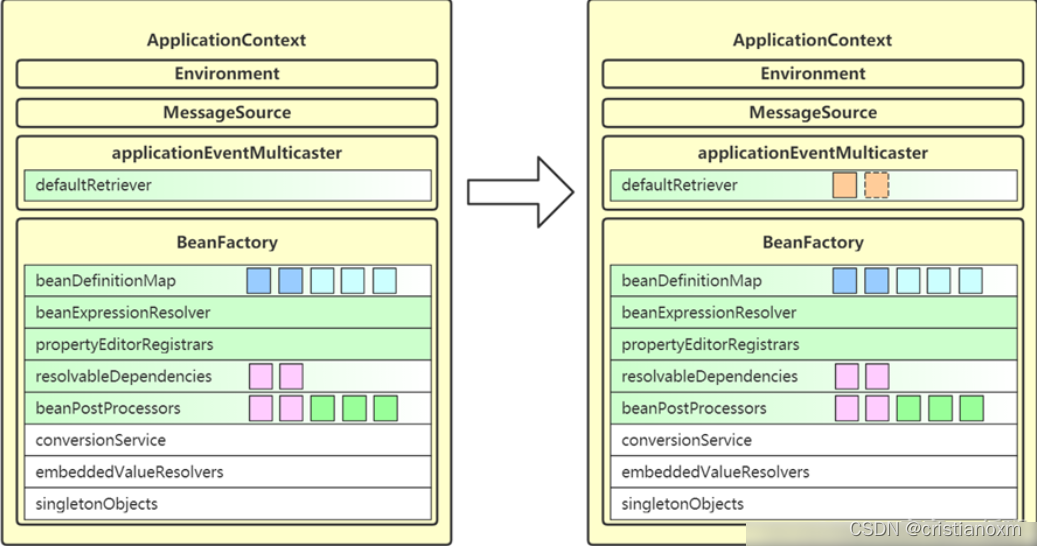
方法名为registerListeners,看名字像是将监听器注册在事件广播器中,但实际情况并非如此,只有一些特殊的监听器被注册了,那些在bean配置文件中实现了ApplicationListener接口的类还没有实例化,所以此处只是将其name保存在广播器中,将这些监听器注册在广播器的操作是在bean的后置处理器中完成的,那时候bean已经实例化完成了,我们看代码
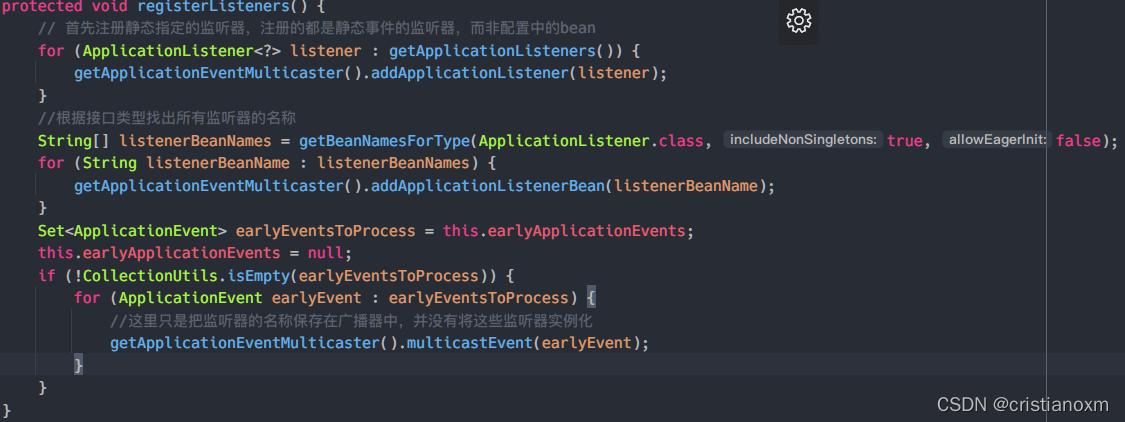
作用:

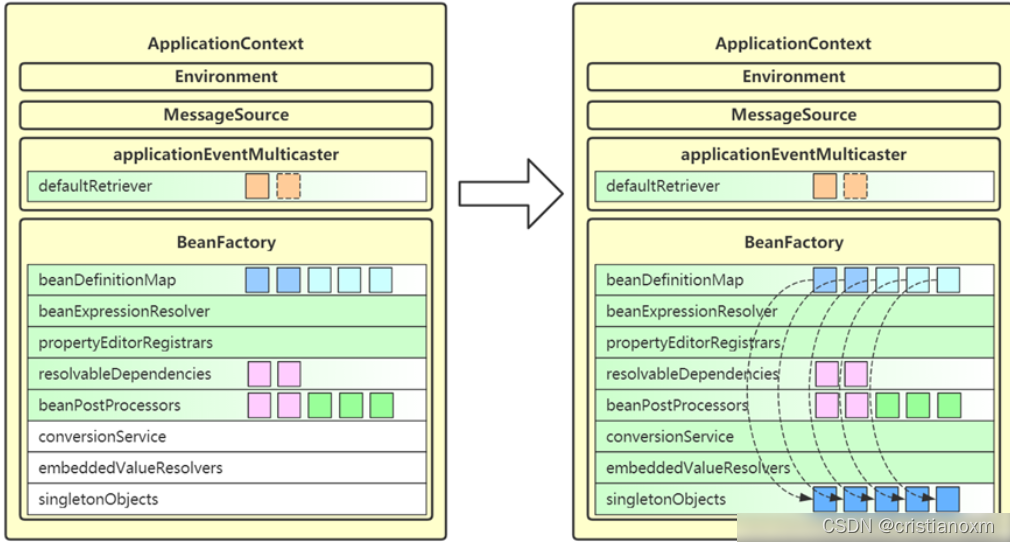
- finishBeanFactoryInitialization
初始化剩下的单实例(非懒加载的),多例在getBean时才初始化
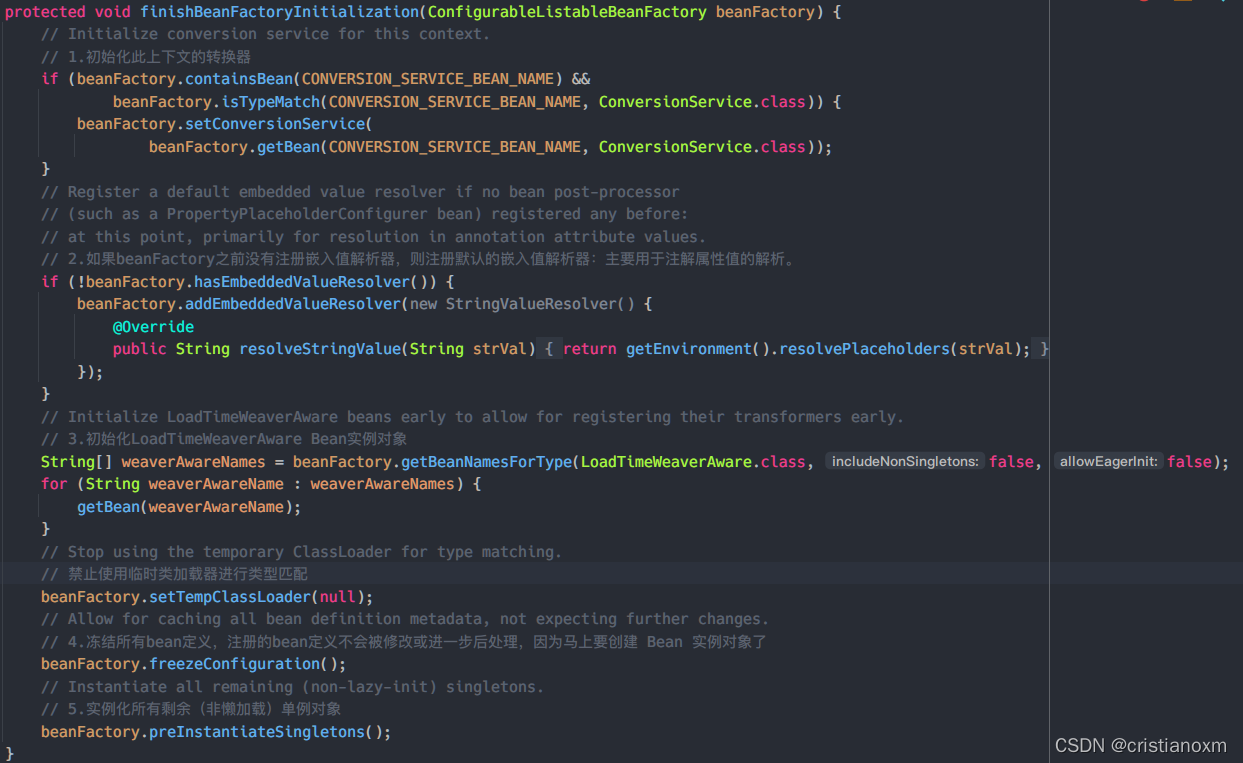
- preInstantiateSingletons方法这个方法里就解决了循环依赖的问题
@Override
public void preInstantiateSingletons() throws BeansException {
if (this.logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
this.logger.debug("Pre-instantiating singletons in " + this);
}
// Iterate over a copy to allow for init methods which in turn register new bean definitions.
// While this may not be part of the regular factory bootstrap, it does otherwise work fine.
// 1.创建beanDefinitionNames的副本beanNames用于后续的遍历,以允许init等方法注册新的bean定义
List<String> beanNames = new ArrayList<String>(this.beanDefinitionNames);
// Trigger initialization of all non-lazy singleton beans...
// 2.遍历beanNames,触发所有非懒加载单例bean的初始化
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
// 3.获取beanName对应的MergedBeanDefinition
RootBeanDefinition bd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
// 4.bd对应的Bean实例:不是抽象类 && 是单例 && 不是懒加载
if (!bd.isAbstract() && bd.isSingleton() && !bd.isLazyInit()) {
// 5.判断beanName对应的bean是否为FactoryBean
if (isFactoryBean(beanName)) {
// 5.1 通过beanName获取FactoryBean实例
// 通过getBean(&beanName)拿到的是FactoryBean本身;通过getBean(beanName)拿到的是FactoryBean创建的Bean实例
final FactoryBean<?> factory = (FactoryBean<?>) getBean(FACTORY_BEAN_PREFIX + beanName);
// 5.2 判断这个FactoryBean是否希望急切的初始化
boolean isEagerInit;
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null && factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean) {
isEagerInit = AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Boolean>() {
@Override
public Boolean run() {
return ((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit();
}
}, getAccessControlContext());
} else {
isEagerInit = (factory instanceof SmartFactoryBean &&
((SmartFactoryBean<?>) factory).isEagerInit());
}
if (isEagerInit) {
// 5.3 如果希望急切的初始化,则通过beanName获取bean实例
getBean(beanName);
}
} else {
// 6.如果beanName对应的bean不是FactoryBean,只是普通Bean,通过beanName获取bean实例
getBean(beanName);
}
}
}
// Trigger post-initialization callback for all applicable beans...
// 7.遍历beanNames,触发所有SmartInitializingSingleton的后初始化回调
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
// 7.1 拿到beanName对应的bean实例
Object singletonInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
// 7.2 判断singletonInstance是否实现了SmartInitializingSingleton接口
if (singletonInstance instanceof SmartInitializingSingleton) {
final SmartInitializingSingleton smartSingleton = (SmartInitializingSingleton) singletonInstance;
// 7.3 触发SmartInitializingSingleton实现类的afterSingletonsInstantiated方法
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
AccessController.doPrivileged(new PrivilegedAction<Object>() {
@Override
public Object run() {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
return null;
}
}, getAccessControlContext());
} else {
smartSingleton.afterSingletonsInstantiated();
}
这里接下来的调用链条是:
getBean() -> doGetBean() -> createBean() -> doCreateBean() -> populateBean()//填充属性 -> initializeBean()//初始化(这里涉及到代理的创建)
initializeBean方法中会执行applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization方法
applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization具体的代码如下:
@Override
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
Object current = processor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName);
if (current == null) {
return result;
}
result = current;
}
return result;
}
逻辑比较简单,就是遍历所有实现了BeanPostProcessor接口的类,其中AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator(由EnableAspectJAutoProxy导入的)就是会实现AOP动态代理,然后返回代理对象。所以如果没有导入@EnableAspectJAutoProxy,自然不会创建代理. 这里也可以看出applicationContext构造的过程,就会创建好代理.而且在创建代理的过程中,如果涉及到循环依赖还是提前创建代理并放入earlyProxyReferences集合,用于表示进行了提前的动态代理.这里可以参考这篇文章.注意,多实例对象并不会提前创建,当两个多实例对象循环引用且设计代理的创建时,就会报错
附表:SpringBoot常用的BeanPostProcessor清单
| BeanPostProcessor类 | 介绍 |
|---|---|
| ApplicationContextAwareProcessor | 功能:bean创建时调用bean所实现的各种Aware接口方法设置相应的属性 |
| WebApplicationContextServletContextAwareProcessor | 功能:Springboot Servlet Web应用中bean创建时调用bean实现的ServletContextAware或者ServletConfigAware接口为bean设置ServletContext或者ServletConfig属性引入时机:在ServletWebServerApplicationContex#postProcessBeanFactory中登记到应用上下文 |
| PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate$BeanPostProcessorChecker | TBD |
| ConfigurationPropertiesBindingPostProcessor | 功能: 绑定配置文件中的配置属性项到配置属性对象,比如server开头的配置项设置到配置属性bean对象ServerProperties上 |
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator | 功能: 如果某个bean匹配了某些定义的切面advise或者Spring Advisor,则为这个bean创建AOP代理对象 |
| DataSourceInitializerPostProcessor | 功能: 一旦检测到数据源DataSource bean被初始化,执行数据源的初始化:创建相应的表格(create schema)和填充相应的数据(init schema) |
| MethodValidationPostProcessor | 默认不添加,需要手动添加。支持方法级别的JSR-303规范。需要在类上加上@Validated注解,以及在方法的参数中加上验证注解,比如@Max,@Min,@NotEmpty …。 |
| BeanValidationPostProcessor | 默认不添加,需要手动添加。主要提供对JSR-303验证的支持,内部有个boolean类型的属性afterInitialization,默认是false。如果是false,在postProcessBeforeInitialization过程中对bean进行验证,否则在postProcessAfterInitialization过程对bean进行验证。 |
| PersistenceExceptionTranslationPostProcessor | 它将每个Repository组件bean包装成一个代理对象并为该代理对象添加一个PersistenceExceptionTranslationAdvisor。该PersistenceExceptionTranslationAdvisor会拦截Repository组件bean的方法调用产生的异常并将其转换成Spring框架标准异常 |
| WebServerFactoryCustomizerBeanPostProcessor | 这个处理器类会获取TomcatServletWebServerFactoryCustomizer定制器,并调用customize方法进行定制,这时候工厂类起作用,调用getWebServer方法进行Tomcat属性配置和引擎设置等等,再创建TomcatWebServer启动Tomcat容器 |
| ErrorPageRegistrarBeanPostProcessor | 功能: 在ErrorPageRegistry bean创建时初始化前将容器中的所有ErrorPageRegistrar bean注册进来。 |
| DataSourceInitializedPublisher | 用于发布DataSourceInitializedEvent事件 |
| PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor | 功能: 识别bean上的持久化注解@PersistenceUnit/@PersistenceContext,并完成相应的属性EntityManagerFactory/EntityManager注入。 |
| CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor | 功能: 对JSR-250 @Resource、@PostConstruct 、@PreDestroy等注解的处理 |
| AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor | 功能: 对每个bean执行真正的依赖"注入",缺省支持三种自动装配注解@Autowired,@Value @Inject |
| ApplicationListenerDetector | 功能: 检测单例ApplicationListener bean将它们注册到应用上下文的事件多播器上,并在这些bean销毁之前将它们从事件多播器上移除 |
| RequiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor | 主要处理@Required注解的实现(@Required注解只能修饰方法) |
| ScheduledAnnotationBeanPostProcessor | 默认不添加,使用@EnableScheduling注解后,会被注册到Spring容器中。主要使用Spring Scheduling功能对bean中使用了@Scheduled注解的方法进行调度处理。 |
| AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor | 默认不添加,使用@EnableAsync注解后,会被注册到Spring容器中。AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor内部使用aop处理方法的调用。 |
protected <T> T doGetBean(
final String name, final Class<T> requiredType, final Object[] args, boolean typeCheckOnly)
throws BeansException {
// 1.解析beanName,主要是解析别名、去掉FactoryBean的前缀“&”
final String beanName = transformedBeanName(name);
Object bean;
// Eagerly check singleton cache for manually registered singletons.
// 2.尝试从缓存中获取beanName对应的实例
Object sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName);
if (sharedInstance != null && args == null) {
// 3.如果beanName的实例存在于缓存中,
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
if (isSingletonCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
logger.debug("Returning eagerly cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName +
"' that is not fully initialized yet - a consequence of a circular reference");
} else {
logger.debug("Returning cached instance of singleton bean '" + beanName + "'");
}
}
// 3.1 返回beanName对应的实例对象(主要用于FactoryBean的特殊处理,普通Bean会直接返回sharedInstance本身)
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, null);
} else {
// Fail if we're already creating this bean instance:
// We're assumably within a circular reference.
// 4.scope为prototype的循环依赖校验:如果beanName已经正在创建Bean实例中,而此时我们又要再一次创建beanName的实例,则代表出现了循环依赖,需要抛出异常。
// 例子:如果存在A中有B的属性,B中有A的属性,那么当依赖注入的时候,就会产生当A还未创建完的时候因为对于B的创建再次返回创建A,造成循环依赖
if (isPrototypeCurrentlyInCreation(beanName)) {
throw new BeanCurrentlyInCreationException(beanName);
}
// Check if bean definition exists in this factory.
// 5.获取parentBeanFactory
BeanFactory parentBeanFactory = getParentBeanFactory();
// 5.1 如果parentBeanFactory存在,并且beanName在当前BeanFactory不存在Bean定义,则尝试从parentBeanFactory中获取bean实例
if (parentBeanFactory != null && !containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) {
// Not found -> check parent.
// 5.2 将别名解析成真正的beanName
String nameToLookup = originalBeanName(name);
// 5.3 尝试在parentBeanFactory中获取bean对象实例
if (args != null) {
// Delegation to parent with explicit args.
return (T) parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, args);
} else {
// No args -> delegate to standard getBean method.
return parentBeanFactory.getBean(nameToLookup, requiredType);
}
}
if (!typeCheckOnly) {
// 6.如果不是仅仅做类型检测,而是创建bean实例,这里要将beanName放到alreadyCreated缓存
markBeanAsCreated(beanName);
}
try {
// 7.根据beanName重新获取MergedBeanDefinition(步骤6将MergedBeanDefinition删除了,这边获取一个新的)
final RootBeanDefinition mbd = getMergedLocalBeanDefinition(beanName);
// 7.1 检查MergedBeanDefinition
checkMergedBeanDefinition(mbd, beanName, args);
// Guarantee initialization of beans that the current bean depends on.
// 8.拿到当前bean依赖的bean名称集合,在实例化自己之前,需要先实例化自己依赖的bean
String[] dependsOn = mbd.getDependsOn();
if (dependsOn != null) {
// 8.1 遍历当前bean依赖的bean名称集合
for (String dep : dependsOn) {
// 8.2 检查dep是否依赖于beanName,即检查是否存在循环依赖
if (isDependent(beanName, dep)) {
// 8.3 如果是循环依赖则抛异常
throw new BeanCreationException(mbd.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Circular depends-on relationship between '" + beanName + "' and '" + dep + "'");
}
// 8.4 将dep和beanName的依赖关系注册到缓存中
registerDependentBean(dep, beanName);
// 8.5 获取dep对应的bean实例,如果dep还没有创建bean实例,则创建dep的bean实例
getBean(dep);
}
}
// Create bean instance.
// 9.针对不同的scope进行bean的创建
if (mbd.isSingleton()) {
// 9.1 scope为singleton的bean创建(新建了一个ObjectFactory,并且重写了getObject方法)
sharedInstance = getSingleton(beanName, new ObjectFactory<Object>() {
@Override
public Object getObject() throws BeansException { //
try {
// 9.1.1 创建Bean实例
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
} catch (BeansException ex) {
// Explicitly remove instance from singleton cache: It might have been put there
// eagerly by the creation process, to allow for circular reference resolution.
// Also remove any beans that received a temporary reference to the bean.
destroySingleton(beanName);
throw ex;
}
}
});
// 9.1.2 返回beanName对应的实例对象
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(sharedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
} else if (mbd.isPrototype()) {
// 9.2 scope为prototype的bean创建
// It's a prototype -> create a new instance.
Object prototypeInstance = null;
try {
// 9.2.1 创建实例前的操作(将beanName保存到prototypesCurrentlyInCreation缓存中)
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
// 9.2.2 创建Bean实例
prototypeInstance = createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
} finally {
// 9.2.3 创建实例后的操作(将创建完的beanName从prototypesCurrentlyInCreation缓存中移除)
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
// 9.2.4 返回beanName对应的实例对象
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(prototypeInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
} else {
// 9.3 其他scope的bean创建,可能是request之类的
// 9.3.1 根据scopeName,从缓存拿到scope实例
String scopeName = mbd.getScope();
final Scope scope = this.scopes.get(scopeName);
if (scope == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("No Scope registered for scope name '" + scopeName + "'");
}
try {
// 9.3.2 其他scope的bean创建(新建了一个ObjectFactory,并且重写了getObject方法)
Object scopedInstance = scope.get(beanName, new ObjectFactory<Object>() {
@Override
public Object getObject() throws BeansException {
// 9.3.3 创建实例前的操作(将beanName保存到prototypesCurrentlyInCreation缓存中)
beforePrototypeCreation(beanName);
try {
// 9.3.4 创建bean实例
return createBean(beanName, mbd, args);
} finally {
// 9.3.5 创建实例后的操作(将创建完的beanName从prototypesCurrentlyInCreation缓存中移除)
afterPrototypeCreation(beanName);
}
}
});
// 9.3.6 返回beanName对应的实例对象
bean = getObjectForBeanInstance(scopedInstance, name, beanName, mbd);
} catch (IllegalStateException ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName,
"Scope '" + scopeName + "' is not active for the current thread; consider " +
"defining a scoped proxy for this bean if you intend to refer to it from a singleton",
ex);
}
}
} catch (BeansException ex) {
// 如果创建bean实例过程中出现异常,则将beanName从alreadyCreated缓存中移除
cleanupAfterBeanCreationFailure(beanName);
throw ex;
}
}
// Check if required type matches the type of the actual bean instance.
// 10.检查所需类型是否与实际的bean对象的类型匹配
if (requiredType != null && bean != null && !requiredType.isInstance(bean)) {
try {
// 10.1 类型不对,则尝试转换bean类型
return getTypeConverter().convertIfNecessary(bean, requiredType);
} catch (TypeMismatchException ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Failed to convert bean '" + name + "' to required type '" +
ClassUtils.getQualifiedName(requiredType) + "'", ex);
}
throw new BeanNotOfRequiredTypeException(name, requiredType, bean.getClass());
}
}
// 11.返回创建出来的bean实例对象
return (T) bean;
}
作用:

- finishRefresh
最后一个方法是finishRefresh,这是在bean的实例化、初始化等完成后的一些操作
- 完成刷新过程,通知生命周期处理器lifecycleProcessor刷新过程,
- 同时发出ContextRefreshEvent通知别人\
protected void finishRefresh() {
// Clear context-level resource caches (such as ASM metadata from scanning).
// 清除上下文级别的资源缓存(如扫描的ASM元数据)
// 清空在资源加载器中所有的资源缓存
clearResourceCaches();
// Initialize lifecycle processor for this context.
// 为这个上下文初始化生命周期处理器
// 初始化LifecycleProcessor,如果上下文中找到LifecycleProcessor的LifecycleProcessor bean对象,则使用DefaultLifecycleProcessor
initLifecycleProcessor();
// Propagate refresh to lifecycle processor first.
// 首先将刷新传播到生命周期处理器,上下文刷新的通知,例如自启动的组件
getLifecycleProcessor().onRefresh();
// Publish the final event.
// 发布最终事件
// 新建ContextRefreshEvent事件对象,将其发布到所有监听器
publishEvent(new ContextRefreshedEvent(this));
// Participate in LiveBeansView MBean, if active.
// 参与LiveBeansView MBean,如果是活动的。LiveBeansView :Spring用于支持JMX服务的类
// 注册当前上下文LiveBeansView,以支持JMX服务
LiveBeansView.registerApplicationContext(this);
}
作用:

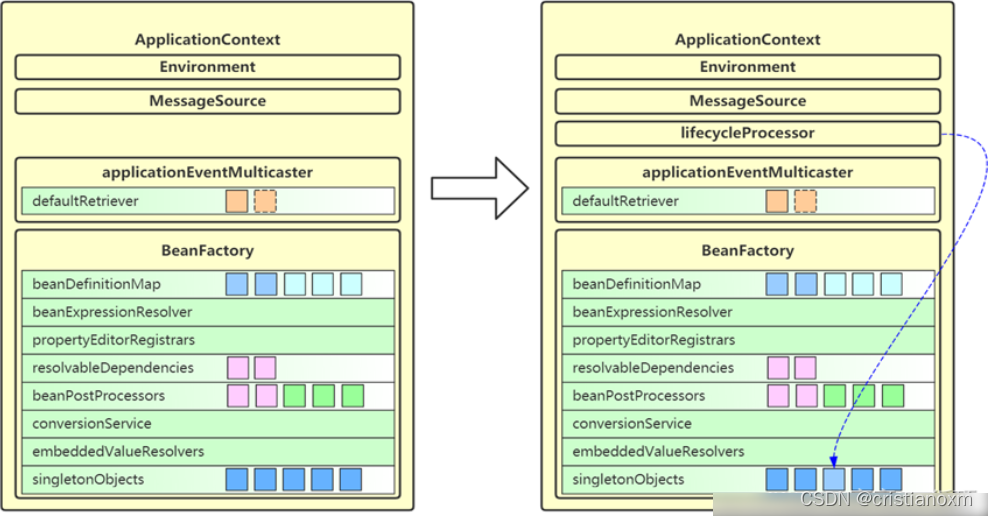
- resetCommonCaches()
在spring的核心中重置常见的内省缓存,因为我们可能不再需要singleton bean的元数据了
四、总结
- prepareRefresh:准备好环境变量,配置变量
- obtainFreshBeanFactory:创建或获取bean工厂,并加载BeanDefinition
- prepareBeanFactory:beanFactory的准备工作,对各种属性进行填充
- postProcessBeanFactory:留给子类子类去扩展bean工厂
- invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors:自定义beanFactory后置处理器去扩展bean工厂
- registerBeanPostProcessors:注册bean后置处理器
- initMessageSource:为spring容器提供国际化功能
- initApplicationEventMulticaster:为spring容器提供事件发布器
- onRefresh:留给子类对spring容器进行扩展
- registerListeners:为spring容器注册监听器
- finishBeanFactoryInitialization:初始化剩余的非懒加载单例bean,执行bean后置处理器扩展
- finishRefresh:准备spring容器生命周期管理器,发布contextRefreshed事件
- resetCommonCaches: 缓存重置