不一样的视角来学习Spring源码之AOP---下
系列文章:
jdk 和 cglib 在 Spring 中的统一
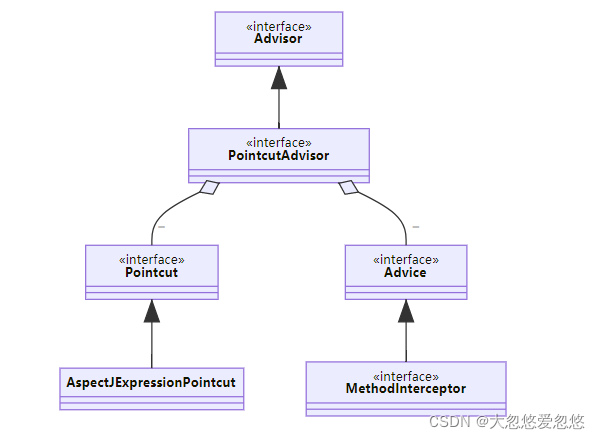
Spring 中对切点、通知、切面的抽象如下
- 切点:接口 Pointcut,典型实现 AspectJExpressionPointcut
- 通知:典型接口为 MethodInterceptor 代表环绕通知
- 切面:Advisor,包含一个 Advice 通知,PointcutAdvisor 包含一个 Advice 通知和一个 Pointcut
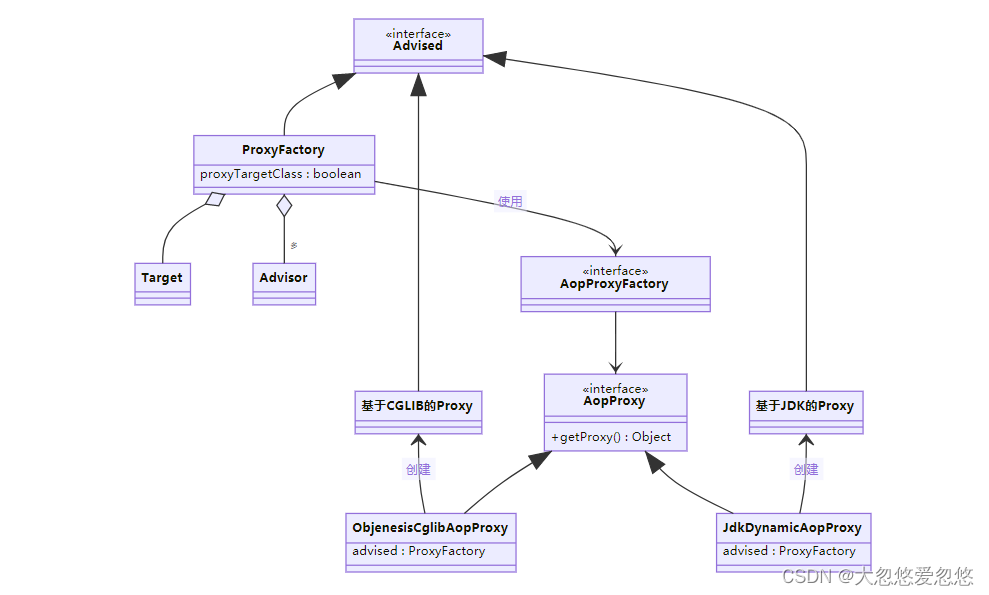
代理相关类图
- AopProxyFactory 根据 proxyTargetClass 等设置选择 AopProxy 实现
- AopProxy 通过 getProxy 创建代理对象
- 图中 Proxy 都实现了 Advised 接口,能够获得关联的切面集合与目标(其实是从 ProxyFactory 取得)
- 调用代理方法时,会借助 ProxyFactory 将通知统一转为环绕通知:MethodInterceptor
底层切点、通知、切面使用演示
public class A15 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
两个切面概念
aspect =
通知1(advice) + 切点1(pointcut)
通知2(advice) + 切点2(pointcut)
通知3(advice) + 切点3(pointcut)
...
advisor = 更细粒度的切面,包含一个通知和切点
*/
// 1. 备好切点
AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut = new AspectJExpressionPointcut();
pointcut.setExpression("execution(* foo())");
// 2. 备好通知
MethodInterceptor advice = invocation -> {
System.out.println("before...");
Object result = invocation.proceed(); // 调用目标
System.out.println("after...");
return result;
};
// 3. 备好切面----只包含一个pointcut和advice
DefaultPointcutAdvisor advisor = new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(pointcut, advice);
/*
4. 创建代理
a. proxyTargetClass = false, 目标实现了接口, 用 jdk 实现
b. proxyTargetClass = false, 目标没有实现接口, 用 cglib 实现
c. proxyTargetClass = true, 总是使用 cglib 实现
*/
Target2 target = new Target2();
ProxyFactory factory = new ProxyFactory();
factory.setTarget(target);
factory.addAdvisor(advisor);
factory.setInterfaces(target.getClass().getInterfaces());
factory.setProxyTargetClass(false);
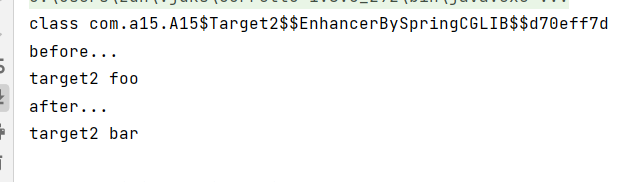
Target2 proxy = (Target2) factory.getProxy();
System.out.println(proxy.getClass());
proxy.foo();
proxy.bar();
/*
学到了什么
a. Spring 的代理选择规则
b. 底层的切点实现
c. 底层的通知实现
d. ProxyFactory 是用来创建代理的核心实现, 用 AopProxyFactory 选择具体代理实现
- JdkDynamicAopProxy
- ObjenesisCglibAopProxy
*/
}
interface I1 {
void foo();
void bar();
}
static class Target1 implements I1 {
public void foo() {
System.out.println("target1 foo");
}
public void bar() {
System.out.println("target1 bar");
}
}
static class Target2 {
public void foo() {
System.out.println("target2 foo");
}
public void bar() {
System.out.println("target2 bar");
}
}
}
收获💡
- 底层的切点实现
- 底层的通知实现
- 底层的切面实现
- ProxyFactory 用来创建代理
- 如果指定了接口,且 proxyTargetClass = false,使用 JdkDynamicAopProxy
- 如果没有指定接口,或者 proxyTargetClass = true,使用 ObjenesisCglibAopProxy
- 例外:如果目标是接口类型或已经是 Jdk 代理,使用 JdkDynamicAopProxy
注意
- 要区分本章节提到的 MethodInterceptor,它与之前 cglib 中用的的 MethodInterceptor 是不同的接口
切点匹配
切点匹配演示
public class A16 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException {
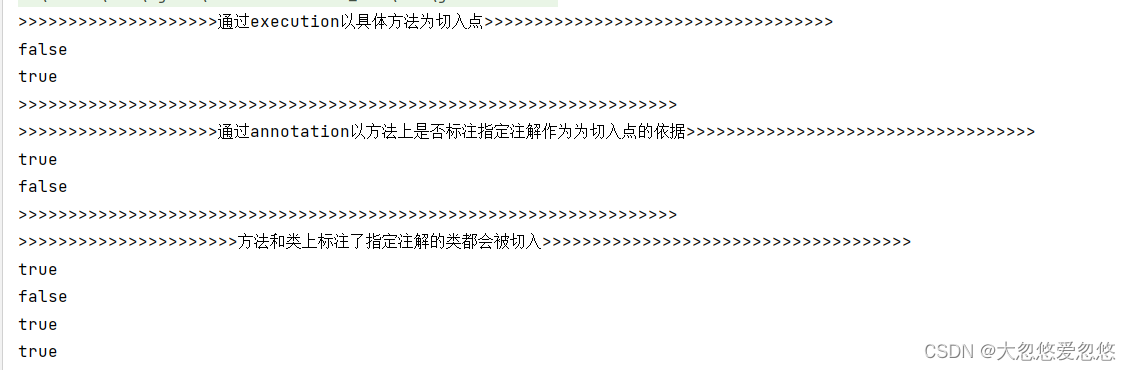
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>通过execution以具体方法为切入点>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>");
AspectJExpressionPointcut pt1 = new AspectJExpressionPointcut();
pt1.setExpression("execution(* bar())");
System.out.println(pt1.matches(T1.class.getMethod("foo"), T1.class));
System.out.println(pt1.matches(T1.class.getMethod("bar"), T1.class));
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>");
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>通过annotation以方法上是否标注指定注解作为为切入点的依据>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>");
AspectJExpressionPointcut pt2 = new AspectJExpressionPointcut();
pt2.setExpression("@annotation(org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional)");
System.out.println(pt2.matches(T1.class.getMethod("foo"), T1.class));
System.out.println(pt2.matches(T1.class.getMethod("bar"), T1.class));
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>");
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>方法和类上标注了指定注解的类都会被切入>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>");
StaticMethodMatcherPointcut pt3 = new StaticMethodMatcherPointcut() {
@Override
public boolean matches(Method method, Class<?> targetClass) {
// 检查方法上是否加了 Transactional 注解
MergedAnnotations annotations = MergedAnnotations.from(method);
if (annotations.isPresent(Transactional.class)) {
return true;
}
// 查看类上是否加了 Transactional 注解----到继承树上去寻找---本类---父类--接口上有也算
annotations = MergedAnnotations.from(targetClass, MergedAnnotations.SearchStrategy.TYPE_HIERARCHY);
if (annotations.isPresent(Transactional.class)) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
};
System.out.println(pt3.matches(T1.class.getMethod("foo"), T1.class));
System.out.println(pt3.matches(T1.class.getMethod("bar"), T1.class));
System.out.println(pt3.matches(T2.class.getMethod("foo"), T2.class));
System.out.println(pt3.matches(T3.class.getMethod("foo"), T3.class));
/*
学到了什么
a. 底层切点实现是如何匹配的: 调用了 aspectj 的匹配方法
b. 比较关键的是它实现了 MethodMatcher 接口, 用来执行方法的匹配
*/
}
static class T1 {
@Transactional
public void foo() {
}
public void bar() {
}
}
@Transactional
static class T2 {
public void foo() {
}
}
@Transactional
interface I3 {
void foo();
}
static class T3 implements I3 {
public void foo() {
}
}
}
收获💡
- 常见 aspectj 切点用法
- aspectj 切点的局限性,实际的 @Transactional 切点实现
从 @Aspect 到 Advisor
/**
* @author 大忽悠
* @create 2022/3/30 9:17
*/
public class A17 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//不会自动注册相关后置处理器的干净的容器
GenericApplicationContext applicationContext=new GenericApplicationContext();
applicationContext.registerBean("aspectJ",AspectJ.class);
applicationContext.registerBean("config",Config.class);
applicationContext.registerBean(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class);
applicationContext.registerBean(Target.class);
applicationContext.refresh();
for (String beanDefinitionName : applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
System.out.println(beanDefinitionName);
}
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>");
Target bean = applicationContext.getBean(Target.class);
bean.foo();
}
static class Target{
public void foo()
{
System.out.println("foo");
}
}
@Aspect//高级切面
static class AspectJ{
@Before("execution(* foo())")
public void Before()
{
System.out.println("aspect1 before");
}
@After("execution(* foo())")
public void after()
{
System.out.println("aspect1 after");
}
}
@Configuration
static class Config{
@Bean//低级切面
public Advisor advisor(MethodInterceptor advice)
{
AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut=new AspectJExpressionPointcut();
pointcut.setExpression("execution(* foo())");
return new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(pointcut,advice);
}
@Bean
public MethodInterceptor advice()
{
return new MethodInterceptor() {
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation methodInvocation) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("advice before");
Object proceed = methodInvocation.proceed();
System.out.println("advice after");
return proceed;
}
} ;
}
}
}
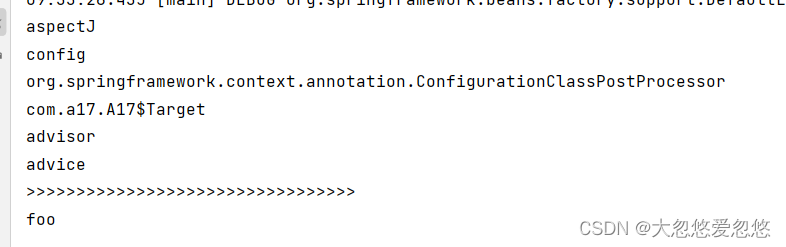
可以看到,我们注册了一个高级切面类AspectJ和低级切面Advisor到容器中,但是此时运行,发现目标对象方法没有被代理,说明光有切面没用,还少了点啥子,让切面能够运作起来
代理创建器
少了神魔呢?—》少了下面这个自动代理的后置处理器
//自动代理
applicationContext.registerBean(AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator.class);
该后置处理器: 创建bean----> 上面的后置处理器干点事 ---->依赖注入----->初始化—>上面的后置处理器干点事
此时再进行测试:
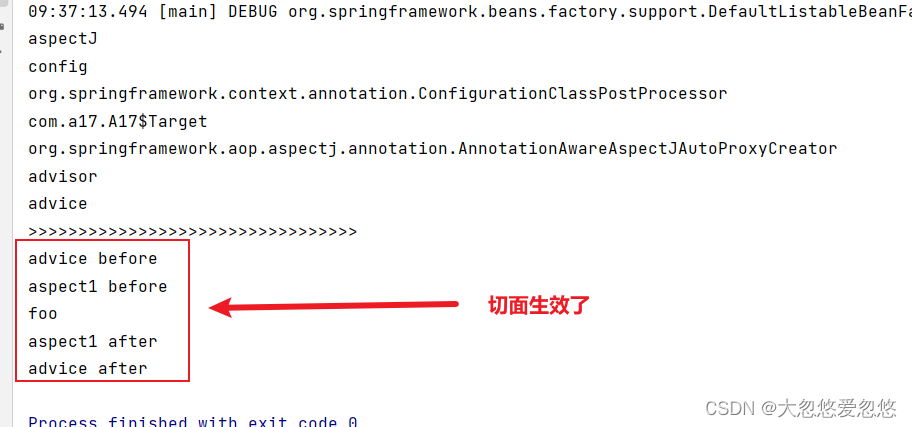
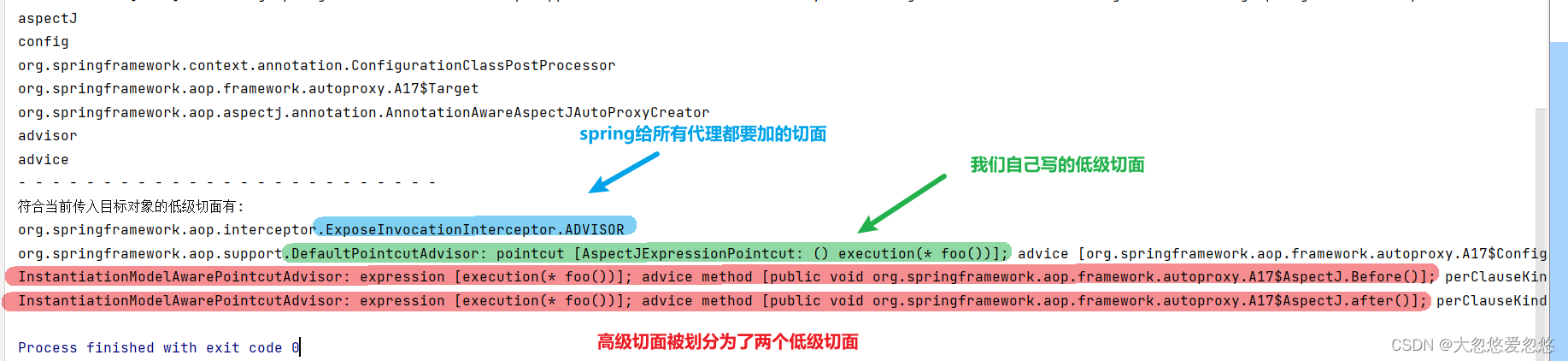
findEligibleAdvisors—找出符合当前目标对象的所有切面
这里不直接翻源码,而是通过调用该后置处理器中的方法来模拟一下源码中的思路:
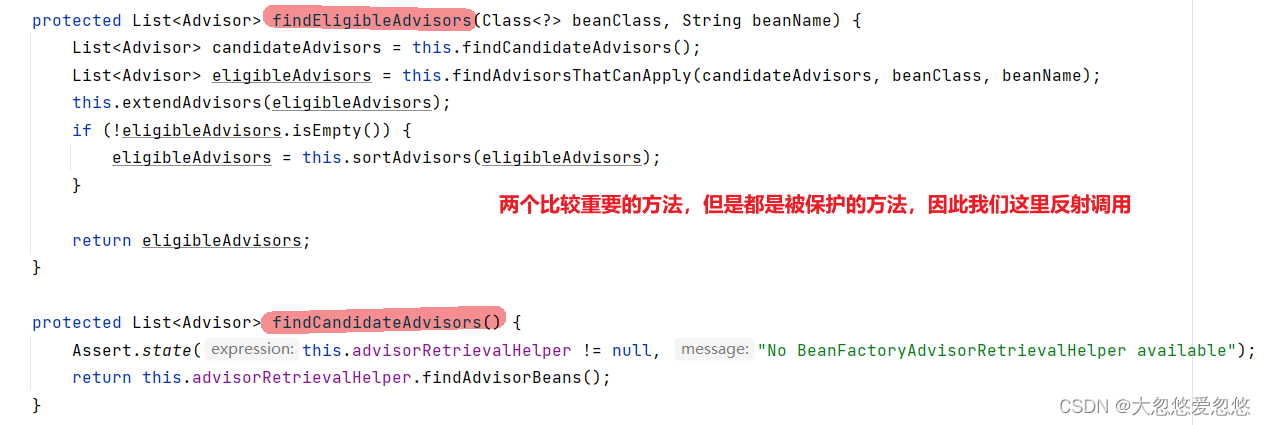
这里因为是受保护的方法,所以除了反射调用之外,还可以把我们的测试类所在包名改为上面这个后置处理器包名相同,也可以直接调用
//包名改为这个即可
package org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy;
public class A17 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
//不会自动注册相关后置处理器的干净的容器
GenericApplicationContext applicationContext=new GenericApplicationContext();
applicationContext.registerBean("aspectJ",AspectJ.class);
applicationContext.registerBean("config",Config.class);
applicationContext.registerBean(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class);
applicationContext.registerBean(Target.class);
//自动代理
applicationContext.registerBean(AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator.class);
applicationContext.refresh();
for (String beanDefinitionName : applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
System.out.println(beanDefinitionName);
}
System.out.println("- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - ");
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator annotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator = applicationContext.getBean(AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator.class);
List<Advisor> advisors = annotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator.findEligibleAdvisors(Target.class, "target");
System.out.println("符合当前传入目标对象的低级切面有:");
advisors.forEach(advisor -> System.out.println(advisor));
}
static class Target{
public void foo()
{
System.out.println("foo");
}
}
@Aspect//高级切面
static class AspectJ{
@Before("execution(* foo())")
public void Before()
{
System.out.println("aspect1 before");
}
@After("execution(* foo())")
public void after()
{
System.out.println("aspect1 after");
}
}
@Configuration
static class Config{
@Bean//低级切面
public Advisor advisor(MethodInterceptor advice)
{
AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut=new AspectJExpressionPointcut();
pointcut.setExpression("execution(* foo())");
return new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(pointcut,advice);
}
@Bean
public MethodInterceptor advice()
{
return new MethodInterceptor() {
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation methodInvocation) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("advice before");
Object proceed = methodInvocation.proceed();
System.out.println("advice after");
return proceed;
}
} ;
}
}
}
输出结果:
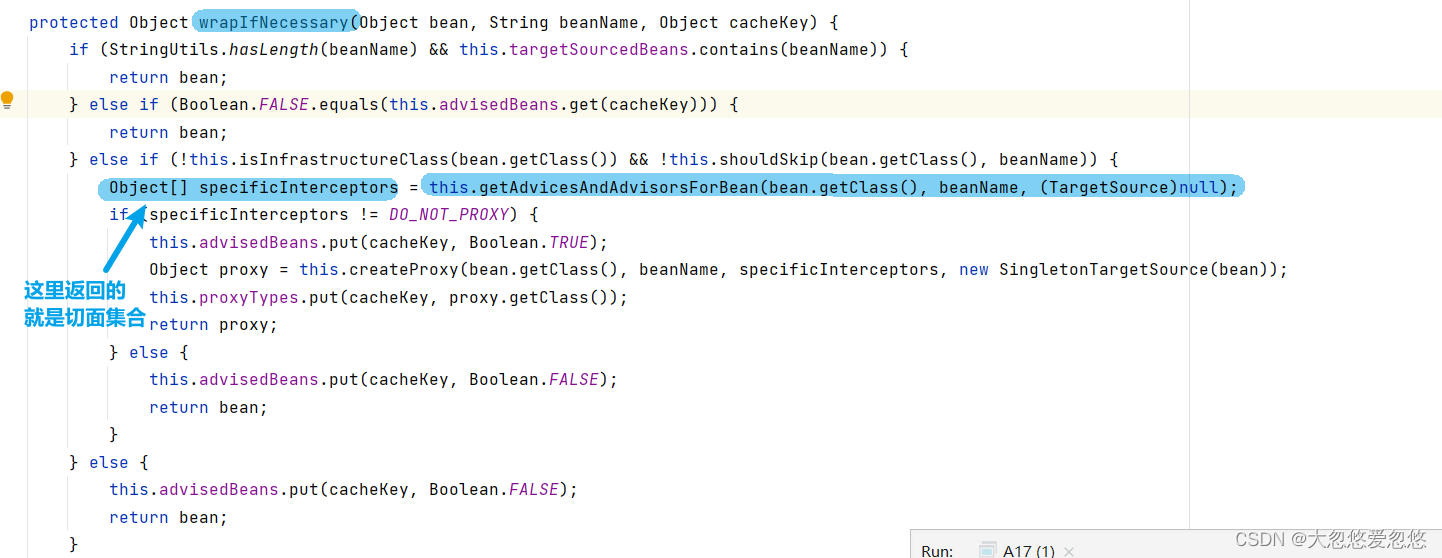
wrapIfNecessary—判断目标对象是否需要被代理----用的就是上面的findEligibleAdvisors方法
/**
* @author 大忽悠
* @create 2022/3/30 9:17
*/
public class A17 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
//不会自动注册相关后置处理器的干净的容器
GenericApplicationContext applicationContext=new GenericApplicationContext();
applicationContext.registerBean("aspectJ",AspectJ.class);
applicationContext.registerBean("config",Config.class);
applicationContext.registerBean(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class);
applicationContext.registerBean(Target.class);
//自动代理
applicationContext.registerBean(AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator.class);
applicationContext.refresh();
for (String beanDefinitionName : applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames()) {
System.out.println(beanDefinitionName);
}
System.out.println("- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - ");
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator annotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator = applicationContext.getBean(AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator.class);
List<Advisor> advisors = annotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator.findEligibleAdvisors(Target.class, "target");
System.out.println("符合当前传入目标对象的低级切面有:");
advisors.forEach(advisor -> System.out.println(advisor));
System.out.println("- - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - - ");
//是否需要给当前Bean创建代理对象
//查找当前Bean相关符合的切面调用的是findEligibleAdvisors方法
//如果当前Bean找到了相关符合的切面--那么就需要代理--返回的是代理对象
Object o1 = annotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator.wrapIfNecessary(new Target(), "target", "target");
System.out.println(o1.getClass());
//如果当前Bean没有找的找到相关符合的切面---那么就不需要代理--返回原对象即可
Object o2 = annotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator.wrapIfNecessary(new Target1(), "target", "target");
System.out.println(o2.getClass());
}
static class Target{
public void foo()
{
System.out.println("foo");
}
}
static class Target1{
public void bar()
{
System.out.println("foo");
}
}
@Aspect//高级切面
static class AspectJ{
@Before("execution(* foo())")
public void Before()
{
System.out.println("aspect1 before");
}
@After("execution(* foo())")
public void after()
{
System.out.println("aspect1 after");
}
}
@Configuration
static class Config{
@Bean//低级切面
public Advisor advisor(MethodInterceptor advice)
{
AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut=new AspectJExpressionPointcut();
pointcut.setExpression("execution(* foo())");
return new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(pointcut,advice);
}
@Bean
public MethodInterceptor advice()
{
return new MethodInterceptor() {
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation methodInvocation) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("advice before");
Object proceed = methodInvocation.proceed();
System.out.println("advice after");
return proceed;
}
} ;
}
}
}

源码小探
这两个方法比较重要,大家从上面的源码也可以看出来
收获💡
- AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator 的作用
- 将高级 @Aspect 切面统一为低级 Advisor 切面
- 在合适的时机创建代理
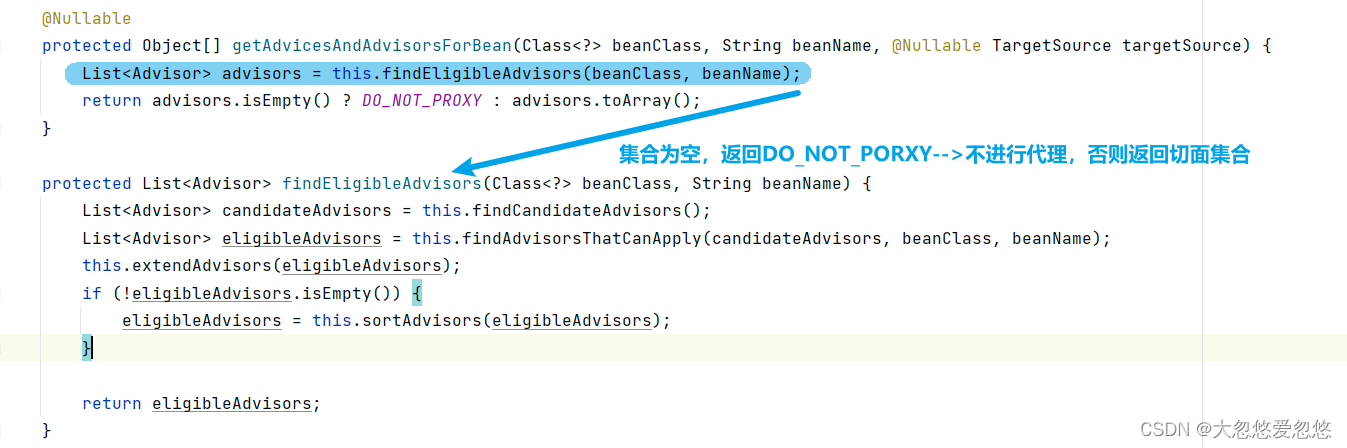
- findEligibleAdvisors 找到有【资格】的 Advisors
- 有【资格】的 Advisor 一部分是低级的, 可以由自己编写
- 有【资格】的 Advisor 另一部分是高级的, 由解析 @Aspect 后获得
- wrapIfNecessary
- 它内部调用 findEligibleAdvisors, 只要返回集合不空, 则表示需要创建代理
- 它的调用时机通常在原始对象初始化后执行, 但碰到循环依赖会提前至依赖注入之前执行
代理创建时机
public class A17 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
//不会自动注册相关后置处理器的干净的容器
GenericApplicationContext applicationContext=new GenericApplicationContext();
//注册一个工厂Bean的后置处理器
//负责解析@ComponentScan @Bean @Import @ImportResource
applicationContext.registerBean(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class);
applicationContext.registerBean(Config.class);
applicationContext.refresh();
applicationContext.close();
}
static class Bean1{
public void foo()
{
System.out.println("foo");
}
public Bean1(){
System.out.println("Bean1()");
}
@PostConstruct
public void init()
{
System.out.println("Bean1 init()");
}
}
static class Bean2{
public void bar()
{
System.out.println("foo");
}
public Bean2() {
System.out.println("Bean2()");
}
@Autowired
public void setBean1(Bean1 bean1)
{
System.out.println("bean1 class: "+bean1);
}
@PostConstruct
public void init()
{
System.out.println("Bean2 init()");
}
}
@Configuration
static class Config{
@Bean//解析@AspectJ注解,产生代理
public AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator annotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator()
{
return new AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator();
}
@Bean//解析@Autowired注解
public AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor autowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor()
{
return new AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor();
}
@Bean//解析@PostConStruct注解
public CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor commonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor()
{
return new CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor();
}
@Bean
public Advisor advisor(MethodInterceptor advice)
{
AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut=new AspectJExpressionPointcut();
pointcut.setExpression("execution(* foo())");
return new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(pointcut,advice);
}
@Bean
public MethodInterceptor advice()
{
return new MethodInterceptor() {
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation methodInvocation) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("advice before");
Object proceed = methodInvocation.proceed();
System.out.println("advice after");
return proceed;
}
} ;
}
@Bean
public Bean1 bean1()
{
return new Bean1();
}
@Bean
public Bean2 bean2()
{
return new Bean2();
}
}
}
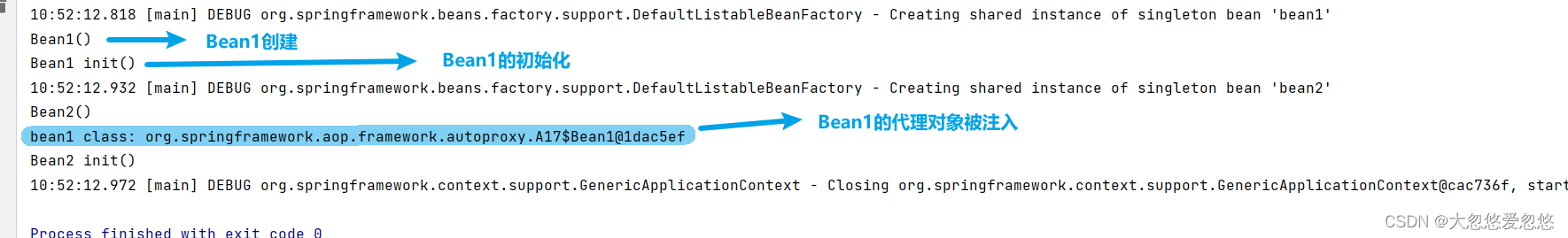
代理对象创建的日志输出是Trace级别,如果大家想要看到的话,需要调整输出的日志级别。
默认顺序是: Bean1()对象的创建----->Bean1 init()初始化方法的调用---->判断是否需要创建代理对象,如果需要就进行包装---->后续的依赖注入注入的都是代理对象
如果是循环依赖的情况下,代理对象的创建时机?
static class Bean1{
public void foo()
{
System.out.println("foo");
}
public Bean1(){
System.out.println("Bean1()");
}
@PostConstruct
public void init()
{
System.out.println("Bean1 init()");
}
@Autowired
public void setBean2(Bean2 bean2)
{
System.out.println("bean2 class: "+bean2);
}
}
static class Bean2{
public void bar()
{
System.out.println("foo");
}
public Bean2() {
System.out.println("Bean2()");
}
@Autowired
public void setBean1(Bean1 bean1)
{
System.out.println("bean1 class: "+bean1);
}
@PostConstruct
public void init()
{
System.out.println("Bean2 init()");
}
}
其余不变,下面测试:
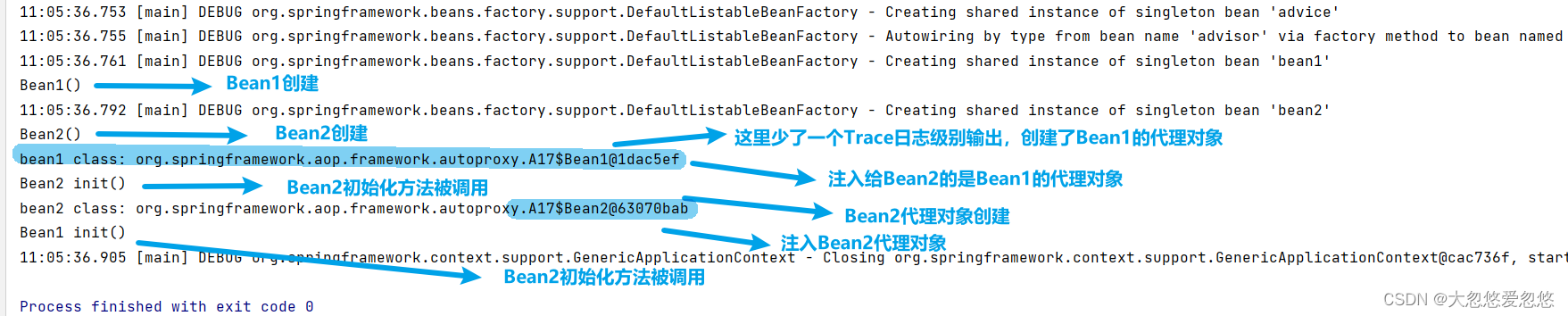
收获💡
- 代理的创建时机
- 初始化之后 (无循环依赖时)
- 实例创建后, 依赖注入前 (有循环依赖时), 并暂存于二级缓存
- 依赖注入与初始化不应该被增强, 仍应被施加于原始对象
@Order指定切面运行顺序
@Order(1) //只能在这里指定切面顺序
@Aspect
static class AspectJ{
@Before("execution(* foo())")
public void Before()
{
System.out.println("aspect1 before");
}
@After("execution(* foo())")
public void after()
{
System.out.println("aspect1 after");
}
}
//@Order(2)----没有用的---该注解不会被解析
@Bean
public Advisor advisor(MethodInterceptor advice)
{
AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut=new AspectJExpressionPointcut();
pointcut.setExpression("execution(* foo())");
DefaultPointcutAdvisor advisor = new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(pointcut, advice);
//只能在这里指定切面顺序
advisor.setOrder(2);
return advisor;
}

如果我们想在同一个Apsect切面里面指定两个before的顺序,通过order注解也是没办法完成的
@Aspect
static class AspectJ{
@Before("execution(* foo())")
@Order(2) //不会生效的
public void Before()
{
System.out.println("aspect1 before1");
}
@Order(1)//不会生效的
@Before("execution(* foo())")
public void Before1()
{
System.out.println("aspect1 before2");
}
}
高级切面转换为低级切面演示
public class A17_2 {
@Aspect
static class AspectJ{
@Before("execution(* foo())")
public void Before()
{
System.out.println("aspect1 before1");
}
@Before("execution(* foo())")
public void Before1()
{
System.out.println("aspect1 before2");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//切面的实例工厂
AspectInstanceFactory factory=new SingletonAspectInstanceFactory(new AspectJ());
Method[] methods = AspectJ.class.getMethods();
List<Advisor> advisorList=new ArrayList<>();
for (Method method : methods) {
if(method.isAnnotationPresent(Before.class))
{
//解析切点
String expression = method.getAnnotation(Before.class).value();
AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut=new AspectJExpressionPointcut();
pointcut.setExpression(expression);
//通知类
AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice methodBeforeAdvice=new AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice(method,pointcut,factory);
//切面
Advisor advisor=new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(pointcut,methodBeforeAdvice);
advisorList.add(advisor);
}
}
advisorList.forEach(advisor -> System.out.println(advisor));
}
}

这里只对@Before注解进行了解析,其他注解类似
收获💡
- @Before 前置通知会被转换为原始的 AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice 形式, 该对象包含了如下信息
- 通知代码从哪儿来
- 切点是什么(这里为啥要切点, 后面解释)
- 通知对象如何创建, 本例共用同一个 Aspect 对象
- 类似的还有
- AspectJAroundAdvice (环绕通知)
- AspectJAfterReturningAdvice
- AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice (环绕通知)
- AspectJAfterAdvice (环绕通知)
统一转换为环绕通知
无论ProxyFactory采用哪种方式创建代理,最后干活的advice都是一个MethodInvocation对象,即所有没有继承MethodInvocation对象的advice,最终都会被封装为对应的MethodInvocation环绕对象
为什么都要转换为环绕通知呢?
- 因为Advisor有多个,且都是一个套一个调用,因此你需要一个调用链对象,即MethodInvocation
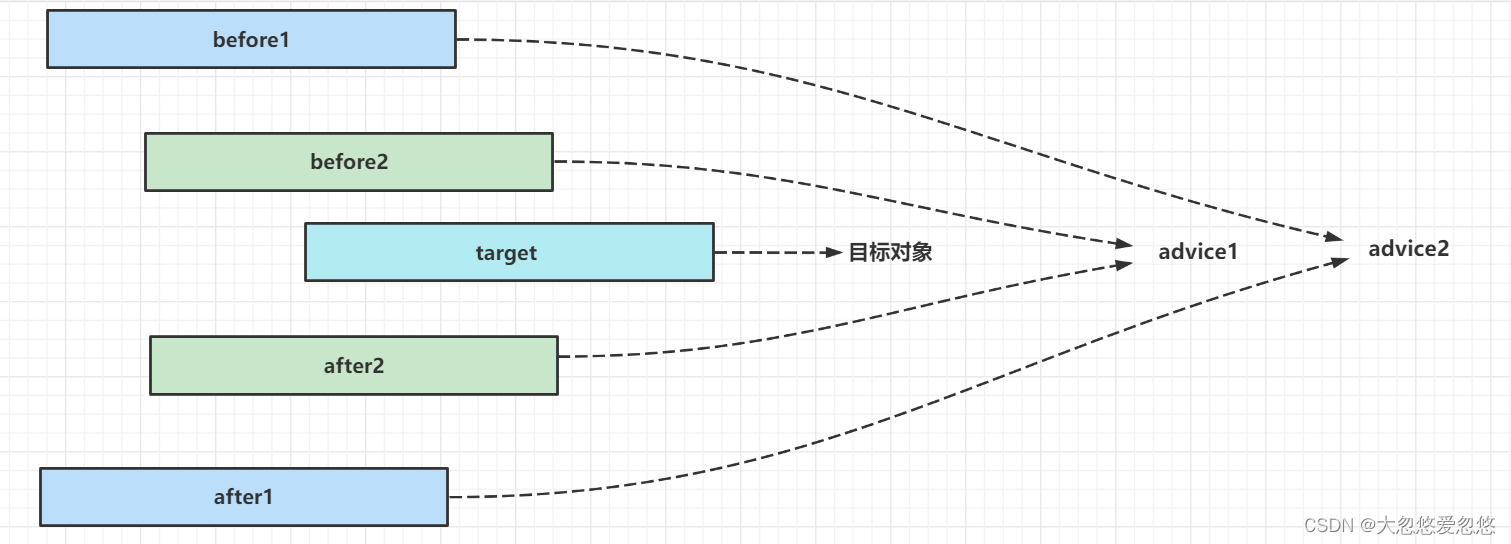
从上图看出,只有环绕通知才适合作为advice,因此其他before,afterreturing都会被转换为环绕通知
看下面的例子演示:
public class A17_2 {
@Aspect
static class AspectJ{
@Before("execution(* foo())")
public void Before()
{
System.out.println("aspect1 before1");
}
@After("execution(* foo())")
public void After()
{
System.out.println("aspect1 After");
}
@AfterThrowing("execution(* foo())")
public void AfterThrowing()
{
System.out.println("aspect1 AfterThrowing");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException {
//1.高级切面转换为低级切面---在解析AspectJ类的时候创建
//切面的实例工厂
AspectInstanceFactory factory=new SingletonAspectInstanceFactory(new AspectJ());
Method[] methods = AspectJ.class.getMethods();
List<Advisor> advisorList=new ArrayList<>();
for (Method method : methods) {
if(method.isAnnotationPresent(Before.class))
{
//解析切点
String expression = method.getAnnotation(Before.class).value();
AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut=new AspectJExpressionPointcut();
pointcut.setExpression(expression);
//通知类
AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice methodBeforeAdvice=new AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice(method,pointcut,factory);
//切面
Advisor advisor=new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(pointcut,methodBeforeAdvice);
advisorList.add(advisor);
}else if(method.isAnnotationPresent(After.class))
{
//解析切点
String expression = method.getAnnotation(After.class).value();
AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut=new AspectJExpressionPointcut();
pointcut.setExpression(expression);
//通知类
AspectJAfterAdvice aspectJAfterAdvice=new AspectJAfterAdvice(method,pointcut,factory);
//切面
Advisor advisor=new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(pointcut,aspectJAfterAdvice);
advisorList.add(advisor);
}else if(method.isAnnotationPresent(AfterThrowing.class))
{
//解析切点
String expression = method.getAnnotation(AfterThrowing.class).value();
AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut=new AspectJExpressionPointcut();
pointcut.setExpression(expression);
//通知类
AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice afterThrowingAdvice=new AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice(method,pointcut,factory);
//切面
Advisor advisor=new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(pointcut,afterThrowingAdvice);
advisorList.add(advisor);
}
}
System.out.println("原始advisor切面类: ");
advisorList.forEach(advisor -> System.out.println(advisor));
//统一转换为环绕通知 MethodInterceptor---在方法执行时转换
ProxyFactory proxyFactory=new ProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.setTarget(new A17.Target());
proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisorList);
System.out.println("统一转换为环绕通知");
List<Object> interceptionAdvice = proxyFactory.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(A17.Target.class.getMethod("foo"), A17.Target.class);
interceptionAdvice.forEach(advisor-> System.out.println(advisor));
}
}
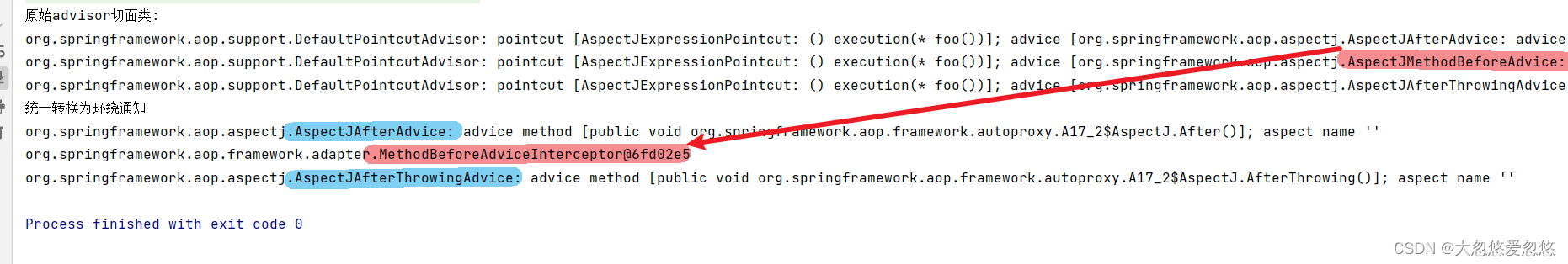



适配器模式
//该适配器负责将MethodBeforeAdvice转换为MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor
class MethodBeforeAdviceAdapter implements AdvisorAdapter, Serializable {
MethodBeforeAdviceAdapter() {
}
public boolean supportsAdvice(Advice advice) {
return advice instanceof MethodBeforeAdvice;
}
public MethodInterceptor getInterceptor(Advisor advisor) {
MethodBeforeAdvice advice = (MethodBeforeAdvice)advisor.getAdvice();
return new MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor(advice);
}
}
class AfterReturningAdviceAdapter implements AdvisorAdapter, Serializable {
AfterReturningAdviceAdapter() {
}
public boolean supportsAdvice(Advice advice) {
return advice instanceof AfterReturningAdvice;
}
public MethodInterceptor getInterceptor(Advisor advisor) {
AfterReturningAdvice advice = (AfterReturningAdvice)advisor.getAdvice();
return new AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor(advice);
}
}
通过适配器转换的过程在getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice方法中完成
调用链执行
解析切面类---->将所有解析后的切面加入切面列表---->将所有不是环绕通知的低级切面都通过适配器转换为对应的环绕通知形式的切面---->创建调用链—>执行调用链
import org.aopalliance.intercept.MethodInvocation;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterThrowing;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.springframework.aop.Advisor;
import org.springframework.aop.aspectj.*;
import org.springframework.aop.support.DefaultPointcutAdvisor;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author 大忽悠
* @create 2022/3/30 11:24
*/
public class A17_2 {
static class Target{
public void foo(){
System.out.println("foo");
}
}
@Aspect
static class AspectJ{
@Before("execution(* foo())")
public void Before()
{
System.out.println("aspect1 before1");
}
@After("execution(* foo())")
public void After()
{
System.out.println("aspect1 After");
}
@AfterThrowing("execution(* foo())")
public void AfterThrowing()
{
System.out.println("aspect1 AfterThrowing");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Throwable {
//切面的实例工厂
AspectInstanceFactory factory=new SingletonAspectInstanceFactory(new AspectJ());
Method[] methods = AspectJ.class.getMethods();
List<Advisor> advisorList=new ArrayList<>();
for (Method method : methods) {
if(method.isAnnotationPresent(Before.class))
{
//解析切点
String expression = method.getAnnotation(Before.class).value();
AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut=new AspectJExpressionPointcut();
pointcut.setExpression(expression);
//通知类
AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice methodBeforeAdvice=new AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice(method,pointcut,factory);
//切面
Advisor advisor=new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(pointcut,methodBeforeAdvice);
advisorList.add(advisor);
}else if(method.isAnnotationPresent(After.class))
{
//解析切点
String expression = method.getAnnotation(After.class).value();
AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut=new AspectJExpressionPointcut();
pointcut.setExpression(expression);
//通知类
AspectJAfterAdvice aspectJAfterAdvice=new AspectJAfterAdvice(method,pointcut,factory);
//切面
Advisor advisor=new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(pointcut,aspectJAfterAdvice);
advisorList.add(advisor);
}else if(method.isAnnotationPresent(AfterThrowing.class))
{
//解析切点
String expression = method.getAnnotation(AfterThrowing.class).value();
AspectJExpressionPointcut pointcut=new AspectJExpressionPointcut();
pointcut.setExpression(expression);
//通知类
AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice afterThrowingAdvice=new AspectJAfterThrowingAdvice(method,pointcut,factory);
//切面
Advisor advisor=new DefaultPointcutAdvisor(pointcut,afterThrowingAdvice);
advisorList.add(advisor);
}
}
System.out.println("原始advisor切面类: ");
advisorList.forEach(advisor -> System.out.println(advisor));
//统一转换为环绕通知 MethodInterceptor
Target target=new Target();
ProxyFactory proxyFactory=new ProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.setTarget(target);
proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisorList);
System.out.println("统一转换为环绕通知");
List<Object> interceptionAdvice = proxyFactory.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(Target.class.getMethod("foo"), Target.class);
interceptionAdvice.forEach(advisor-> System.out.println(advisor));
System.out.println(">>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>>");
//创建并执行调用链(环绕通知+目标对象)
//这里ReflectiveMethodInvocation的构造方法是受保护的,可以采取反射或者将当前测试类放在和它同名的包下
MethodInvocation methodInvocation=new ReflectiveMethodInvocation(
//代理类---这里用不到传入null
null,
//目标对象
target,
//目标对象被代理的方法
Target.class.getMethod("foo"),
//方法执行时的参数数组
new Object[0],
//目标类型
Target.class,
//环绕通知---传入的是转换为环绕通知的所有低级切面
interceptionAdvice
);
//执行调用链
methodInvocation.proceed();
}
}
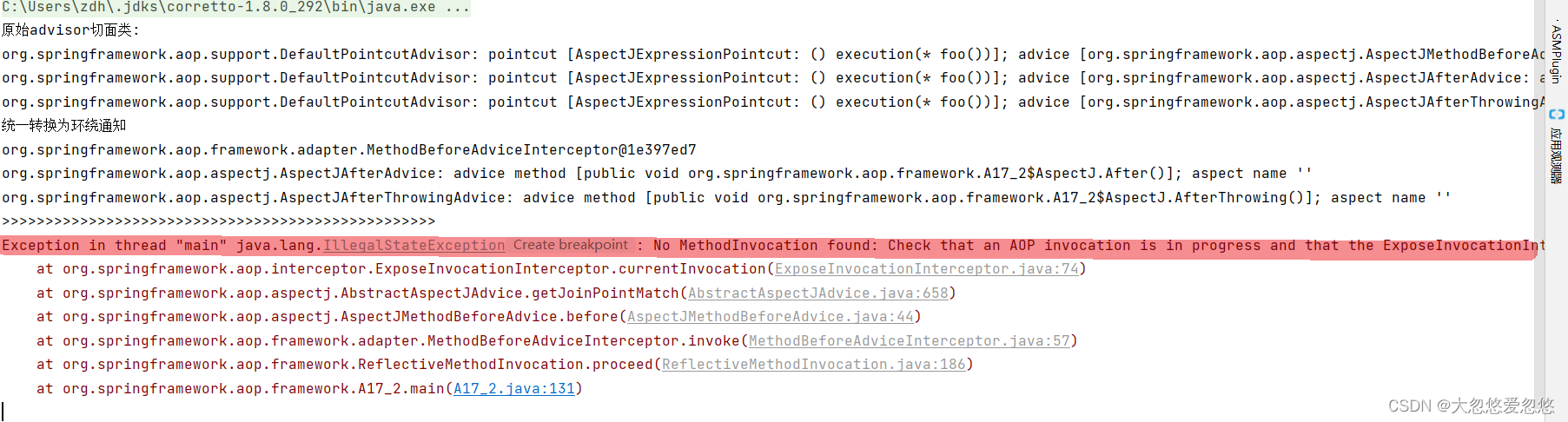
这里报错了,原因是某些通知内部会用到调用链对象,所以我们在执行的时候需要将调用链放在让所有通知都能获取到的一个地方,哪里呢?
- 当前线程内,因为当前调用链肯定是在同一个线程内执行的,因此每个切面都可以获取到当前线程内的调用链
放入当前线程的工作是由spring自动添加的一个外层环绕通知完成的,这里也解释了为什么上面的例子中,会显示有一个spring默认添加的最外层的通知

ExposeInvocationInterceptor该切面类完成调用链添加进当前线程的功能
//统一转换为环绕通知 MethodInterceptor
Target target=new Target();
ProxyFactory proxyFactory=new ProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.setTarget(target);
//准备把ExposeInvocationInterceptor放入当前线程
proxyFactory.addAdvice(ExposeInvocationInterceptor.INSTANCE);
proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisorList);
此时再次测试:

静态通知调用
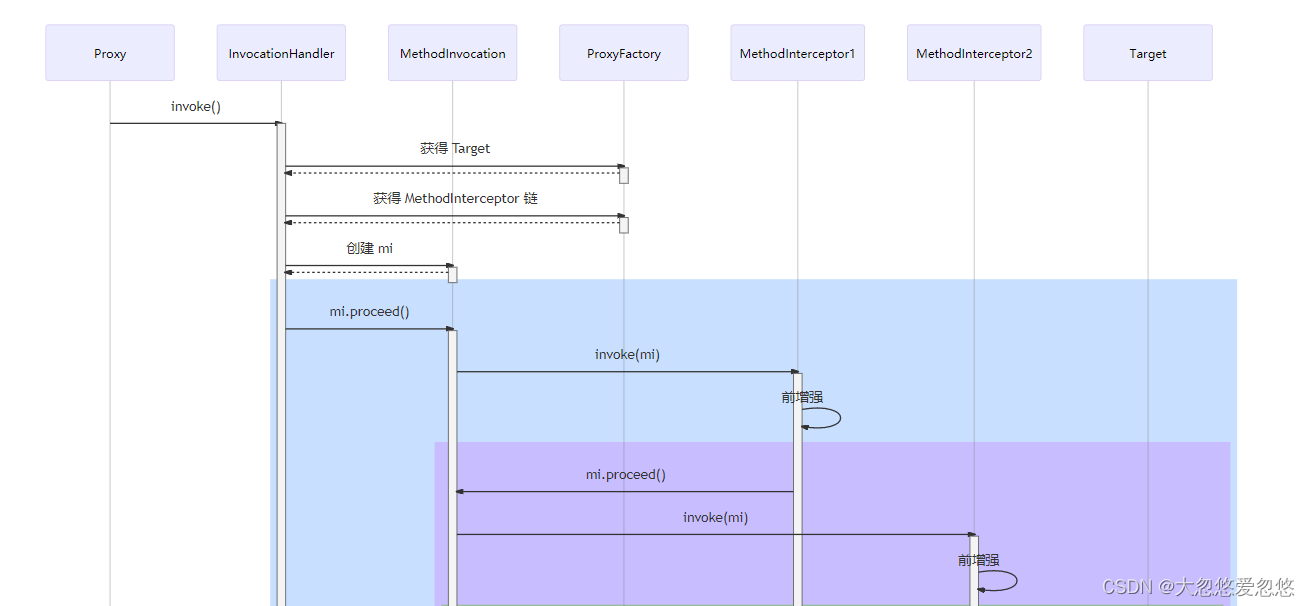
代理对象调用流程如下(以 JDK 动态代理实现为例)
- 从 ProxyFactory 获得 Target 和环绕通知链,根据他俩创建 MethodInvocation,简称 mi
- 首次执行 mi.proceed() 发现有下一个环绕通知,调用它的 invoke(mi)
- 进入环绕通知1,执行前增强,再次调用 mi.proceed() 发现有下一个环绕通知,调用它的 invoke(mi)
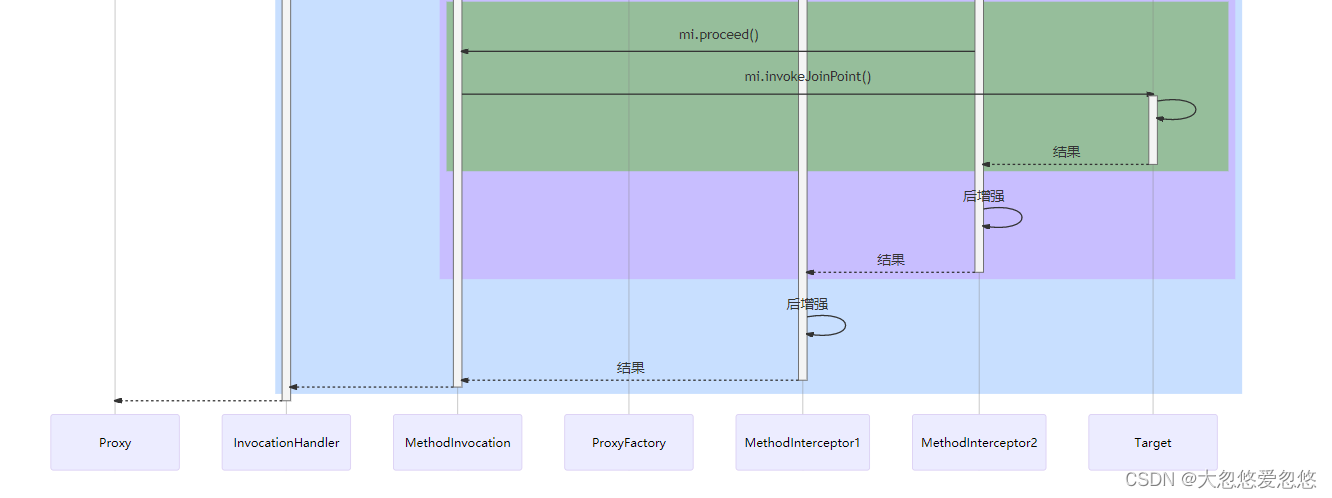
- 进入环绕通知2,执行前增强,调用 mi.proceed() 发现没有环绕通知,调用 mi.invokeJoinPoint() 执行目标方法
- 目标方法执行结束,将结果返回给环绕通知2,执行环绕通知2 的后增强
- 环绕通知2继续将结果返回给环绕通知1,执行环绕通知1 的后增强
- 环绕通知1返回最终的结果
图中不同颜色对应一次环绕通知或目标的调用起始至终结
收获💡
代理方法执行时会做如下工作
- 通过 proxyFactory 的 getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice() 将其他通知统一转换为 MethodInterceptor 环绕通知
- MethodBeforeAdviceAdapter 将 @Before AspectJMethodBeforeAdvice 适配为 MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor
- AfterReturningAdviceAdapter 将 @AfterReturning AspectJAfterReturningAdvice 适配为 AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor
- 这体现的是适配器设计模式
- 所谓静态通知,体现在上面方法的 Interceptors 部分,这些通知调用时无需再次检查切点,直接调用即可
- 结合目标与环绕通知链,创建 MethodInvocation 对象,通过它完成整个调用
模拟 MethodInvocation
/**
* <P>
* 模拟调用链执行
* </P>
* @author 大忽悠
* @create 2022/3/30 22:30
*/
public class MyInvocationHandler implements MethodInvocation {
/**
* 目标对象
*/
private Object target;
/**
* 被调用的方法
*/
private Method method;
/**
* 方法参数
*/
private Object[] args;
/**
* 环绕通知集合
*/
private List<MethodInterceptor> methodInterceptorList;
/**
* 调用次数
*/
private int count=1;
public MyInvocationHandler(Object target, Method method, Object[] args, List<MethodInterceptor> methodInterceptorList) {
this.target = target;
this.method = method;
this.args = args;
this.methodInterceptorList = methodInterceptorList;
}
@Override
public Method getMethod() {
return method;
}
@Override
public Object[] getArguments() {
return args;
}
/**
* 责任链模式的核心体现: 先调用每一个环绕通知,然后调用目标对象的方法
*/
@Override
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
//调用链的长度
int size = methodInterceptorList.size();
if(count>size)
{
//调用链执行完毕,可以执行目标方法
return method.invoke(target,args);
}
//逐一调用每个环绕通知
MethodInterceptor methodInterceptor = methodInterceptorList.get(count++ - 1);
return methodInterceptor.invoke(this);
}
/**
* @return 返回调用链对象
*/
@Override
public Object getThis() {
return target;
}
@Override
public AccessibleObject getStaticPart() {
//暂时不管
return method;
}
}
测试:
/**
* @author 大忽悠
* @create 2022/3/30 22:53
*/
public class Advice1 implements MethodInterceptor {
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation methodInvocation) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("advice1 before");
Object proceed = methodInvocation.proceed();
System.out.println("advice1 after");
return proceed;
}
}
/**
* @author 大忽悠
* @create 2022/3/30 22:54
*/
public class Advice2 implements MethodInterceptor {
@Override
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation methodInvocation) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("advice2 before");
Object proceed = methodInvocation.proceed();
System.out.println("advice2 after");
return proceed;
}
}
public class Main {
static class Target{
public void foo()
{
System.out.println("foo");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Throwable {
Target target=new Target();
List<MethodInterceptor> methodInterceptorList=
Arrays.asList(new Advice1(),new Advice2());
MyInvocationHandler invocationHandler = new MyInvocationHandler(target
, target.getClass().getMethod("foo"),
null,methodInterceptorList);
invocationHandler.proceed();
}
}
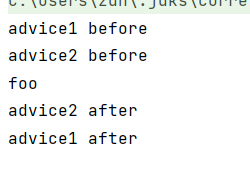
收获💡
- proceed() 方法调用链中下一个环绕通知
- 每个环绕通知内部继续调用 proceed()
- 调用到没有更多通知了, 就调用目标方法
MethodInvocation 的编程技巧在实现拦截器、过滤器时能用上
动态通知调用
动态调用的例子:
@Aspect
class AspectJ {
//静态通知调用,执行时不带参数绑定,执行时不需要切点
@Before("execution(* foo())")
public void Before() {
System.out.println("aspect1 before1");
}
//动态通知调用,需要参数绑定,执行时还需要切点对象
@Before("execution(* foo(..)) && args(x)")
public void Before1(int x) {
System.out.println("aspect1 before2,x="+x);
}
}
使用演示:
package org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.springframework.aop.Advisor;
import org.springframework.aop.aspectj.annotation.AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator;
import org.springframework.aop.framework.ProxyFactory;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassPostProcessor;
import org.springframework.context.support.GenericApplicationContext;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author 大忽悠
* @create 2022/3/30 22:54
*/
public class Main {
@Aspect
static class AspectJ {
//静态通知调用,执行时不带参数绑定,执行时不需要切点
@Before("execution(* foo())")
public void Before() {
System.out.println("aspect1 before1");
}
//动态通知调用,需要参数绑定,执行时还需要切点对象
@Before("execution(* foo(..)) && args(x)")
public void Before1(int x) {
System.out.println("aspect1 before2,x="+x);
}
}
static class Target{
public void foo(int x)
{
System.out.println("foo的参数x为: "+x);
}
}
@Configuration
static class Config{
@Bean
public AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator proxyCreator()
{
return new AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator();
}
@Bean
public AspectJ aspectJ()
{
return new AspectJ();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Throwable {
GenericApplicationContext context=new GenericApplicationContext();
//解析@Bean,@PostContruct等注解
context.registerBean(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class);
context.registerBean(Config.class);
context.refresh();
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator aspectJAutoProxyCreator = context.getBean(AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator.class);
//找到和当前Target类型Bean相关联的切面
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = aspectJAutoProxyCreator.findEligibleAdvisors(Target.class, "target");
System.out.println("=======================================");
System.out.println("原始通知:");
eligibleAdvisors.forEach(advisor -> System.out.println(advisor));
System.out.println("=======================================");
Target target=new Target();
ProxyFactory proxyFactory=new ProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.setTarget(target);
proxyFactory.addAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
//获取代理
Object proxy = proxyFactory.getProxy();
System.out.println("得到的代理对象为: "+proxy);
System.out.println("=======================================");
//将所有切面都转换为环绕通知
List<Object> interceptionAdvice = proxyFactory.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(Target.class.getMethod("foo", int.class), Target.class);
interceptionAdvice.forEach(advice-> System.out.println(advice));
}
}

主要看转换后生成的这个类:
class InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher {
//拥有一个环绕通知
final MethodInterceptor interceptor;
//和一个方法匹配器
final MethodMatcher methodMatcher;
public InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher(MethodInterceptor interceptor, MethodMatcher methodMatcher) {
this.interceptor = interceptor;
this.methodMatcher = methodMatcher;
}
}
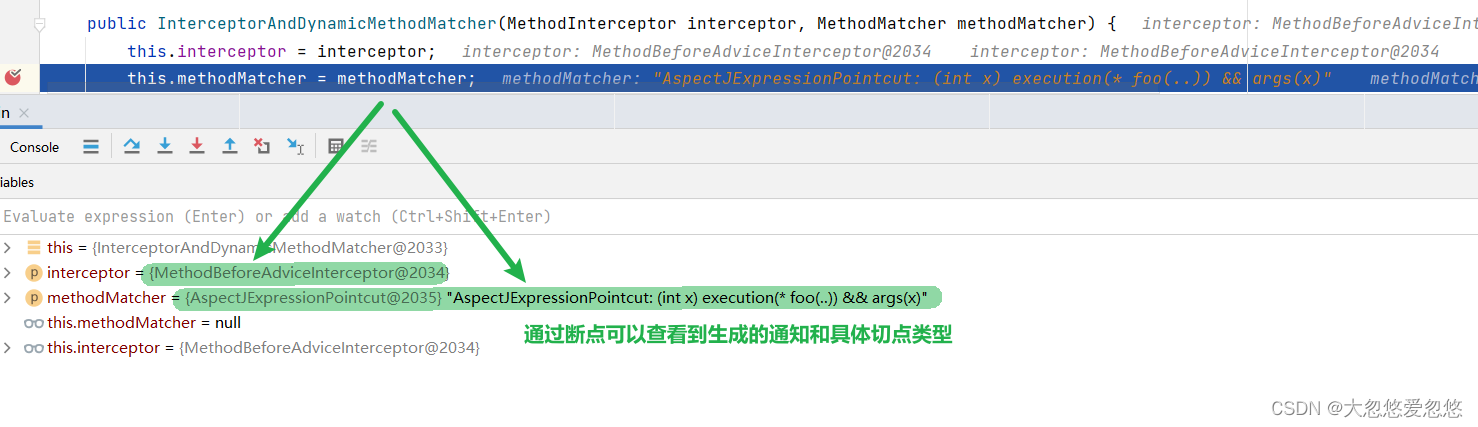
模拟调用测试:
/**
* @author 大忽悠
* @create 2022/3/30 22:54
*/
public class Main {
@Aspect
static class AspectJ {
//静态通知调用,执行时不带参数绑定,执行时不需要切点
@Before("execution(* foo())")
public void Before() {
System.out.println("aspect1 before1");
}
//动态通知调用,需要参数绑定,执行时还需要切点对象
@Before("execution(* foo(..)) && args(x)")
public void Before1(int x) {
System.out.println("aspect1 before2,x="+x);
}
}
static class Target{
public void foo(int x)
{
System.out.println("foo的参数x为: "+x);
}
}
@Configuration
static class Config{
@Bean
public AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator proxyCreator()
{
return new AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator();
}
@Bean
public AspectJ aspectJ()
{
return new AspectJ();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Throwable {
GenericApplicationContext context=new GenericApplicationContext();
//解析@Bean,@PostContruct等注解
context.registerBean(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class);
context.registerBean(Config.class);
context.refresh();
AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator aspectJAutoProxyCreator = context.getBean(AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator.class);
//找到和当前Target类型Bean相关联的切面
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = aspectJAutoProxyCreator.findEligibleAdvisors(Target.class, "target");
System.out.println("=======================================");
System.out.println("原始通知:");
eligibleAdvisors.forEach(advisor -> System.out.println(advisor));
System.out.println("=======================================");
Target target=new Target();
ProxyFactory proxyFactory=new ProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.setTarget(target);
proxyFactory.addAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
//获取代理
Object proxy = proxyFactory.getProxy();
System.out.println("得到的代理对象为: "+proxy);
System.out.println("=======================================");
//将所有切面都转换为环绕通知
List<Object> interceptionAdvice = proxyFactory.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(Target.class.getMethod("foo", int.class), Target.class);
interceptionAdvice.forEach(advice-> System.out.println(advice));
System.out.println("=======================================");
//生成调用链
Constructor<ReflectiveMethodInvocation> constructor = ReflectiveMethodInvocation.class.getDeclaredConstructor(Object.class,Object.class,Method.class, Object[].class, Class.class, List.class);
constructor.setAccessible(true);
//代理对象,目标对象,目标方法,参数,目标对象类型,环绕通知数组
ReflectiveMethodInvocation methodInvocation = constructor.newInstance(proxy, target,Target.class.getMethod("foo", int.class), new Object[]{100}, Target.class, interceptionAdvice);
//执行过滤器链
methodInvocation.proceed();
}
}
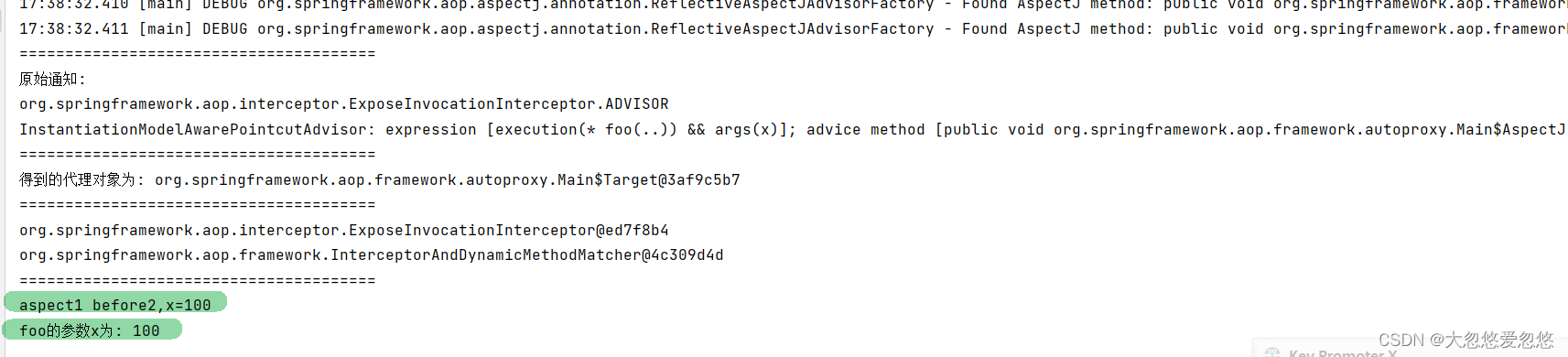
收获💡
- 通过 proxyFactory 的 getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice() 将其他通知统一转换为 MethodInterceptor 环绕通知
- 所谓动态通知,体现在上面方法的 DynamicInterceptionAdvice 部分,这些通知调用时因为要为通知方法绑定参数,还需再次利用切点表达式
- 动态通知调用复杂程度高,性能较低