这节的话就更简单了,主要实现bean的单例(创建一个对象),多例(可创建多个对象),怎么可以实现如果单例的话第一次存储容器里,第二次获取从容器里获取就可呢,非常非常简单,直接进入代码吧
1.首先第一步是需要在BeanDefination里去添加设置Scope的值,等待解析xml的时候通过set注入到BeanDefination对象里就可以在处理时使用了。
public class BeanDefinition {
// 按上一章的话这里已经把Object改成了Class,这样就可以把bean的实例化操作放到容器中处理了
private Class beanClass;
String SCOPE_SINGLETON = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_SINGLETON;
String SCOPE_PROTOTYPE = ConfigurableBeanFactory.SCOPE_PROTOTYPE;
private PropertyValues propertyValues;
// 初始化方法名称
private String initMethodName;
// 销毁方法名称
private String destroyMethodName;
// 目的把xml中的bean对象作用范围填充到属性中
private String scope = SCOPE_SINGLETON;
// 默认是单例
private boolean singleton = true;
private boolean prototype = false;
public void setScope(String scope) {
this.scope = scope;
this.singleton = SCOPE_SINGLETON.equals(scope);
this.prototype = SCOPE_PROTOTYPE.equals(scope);
}
public boolean isSingleton() {
return singleton;
}
public boolean isPrototype() {
return prototype;
}
public BeanDefinition(Class beanClass) {
this.beanClass = beanClass;
// 此处加入new PropertyValues()目的是在Bean对象没有属性时后续获取会报空错,在此处理
this.propertyValues = new PropertyValues();
}
public BeanDefinition(Class beanClass, PropertyValues propertyValues) {
this.beanClass = beanClass;
this.propertyValues = propertyValues != null ? propertyValues : new PropertyValues();
}
public Class getBeanClass() {
return beanClass;
}
public void setBeanClass(Class beanClass) {
this.beanClass = beanClass;
}
public PropertyValues getPropertyValues() {
return propertyValues;
}
public void setPropertyValues(PropertyValues propertyValues) {
this.propertyValues = propertyValues;
}
public String getInitMethodName() {
return initMethodName;
}
public void setInitMethodName(String initMethodName) {
this.initMethodName = initMethodName;
}
public String getDestroyMethodName() {
return destroyMethodName;
}
public void setDestroyMethodName(String destroyMethodName) {
this.destroyMethodName = destroyMethodName;
}
}beanDefiniton里加了,我们需要考虑配置文件设置需要加载到对象里供处理中使用,所以需要去修改加载xml里能够将socpe范围设置单例和多例的情况,这里只放入doLoadBeanDefiniion添加如下代码即可
?String beanScope = bean.getAttribute("scope");
?if (StrUtil.isNotEmpty(beanScope)) {
? ? ?beanDefination.setScope(beanScope);
?}
// 核心方法-从xml中取出bean和属性信息进行bean的注册
protected void doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputStream inputStream) throws ClassNotFoundException {
Document doc = XmlUtil.readXML(inputStream);
Element root = doc.getDocumentElement();
NodeList childNodes = root.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < childNodes.getLength(); i++) {
// 判断元素
if (!(childNodes.item(i) instanceof Element)) continue;
// 判断对象
if (!"bean".equals(childNodes.item(i).getNodeName())) continue;
// 解析标签
Element bean = (Element) childNodes.item(i);
String id = bean.getAttribute("id");
String name = bean.getAttribute("name");
String classname = bean.getAttribute("class");
String initMethod = bean.getAttribute("init-method");
String destroyMethodName = bean.getAttribute("destroy-method");
String beanScope = bean.getAttribute("scope");
// 获取Class,方便获取类中的名称
// Class.forName装入类并对类做初始化
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(classname);
// 优先级 id > name
String beanName = StrUtil.isNotEmpty(id) ? id : name;
if (StrUtil.isEmpty(beanName)) {
beanName = StrUtil.lowerFirst(clazz.getSimpleName());
}
// 将解析出来的Bean放入BeanDefination的beanClass
BeanDefinition beanDefination = new BeanDefinition(clazz);
// 从xml解析出来需要初始化调用的方法名称设置
beanDefination.setInitMethodName(initMethod);
// 从xml解析出来需要调用销毁方法名称的设置
beanDefination.setDestroyMethodName(destroyMethodName);
if (StrUtil.isNotEmpty(beanScope)) {
beanDefination.setScope(beanScope);
}
// 读取属性并填充
for (int j = 0; j < bean.getChildNodes().getLength(); j++) {
if (!(bean.getChildNodes().item(j) instanceof Element)) continue;
if (!"property".equals(bean.getChildNodes().item(j).getNodeName())) continue;
// 解析标签
Element property = (Element) bean.getChildNodes().item(j);
String attrName = property.getAttribute("name");
String attrValue = property.getAttribute("value");
String attrRef = property.getAttribute("ref");
// 获取属性值:引入对象、值对象
Object value = StrUtil.isNotEmpty(attrRef) ? new BeanReference(attrRef) : attrValue;
// 创建属性信息
PropertyValue propertyValue = new PropertyValue(attrName, value);
// 添加到属性集合里去
beanDefination.getPropertyValues().addPropertyValue(propertyValue);
}
if (getRegistry().containsBeanDefinition(beanName)) {
throw new BeansException("Duplicate beanName[" + beanName + "] is not allowed");
}
// 注册beanDefinition
getRegistry().registerBeanDefinition(beanName, beanDefination);
}
}xml处理完,BeanDefinition就有数据了,然后我们去找创建完对象以后存储单例对象里的操作,我们要判断单例存储,多例不存储,这样在getBean时,单例就从单例容器中获取就可以是同一个对象,多例需要在重新创建对象,这样就是多个实例了
AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory类里修改如下:
只展示createBean的方法里边添加了如下判断
if (beanDefinition.isSingleton()) {?
}
@Override
protected Object createBean(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition, Object[] args) throws BeansException {
Object bean = null;
try {
// 第四节注释调此种获取bean实例方式,因为对于有构造函数的bean会报错
// 获得beanDefination里beanClass的字段的新实例
//bean = beanDefinition.getBeanClass().newInstance();
// 第四节更改
bean = createBeanInstance(beanDefinition, beanName, args);
applyPropertyValues(beanName, bean, beanDefinition);
// 执行bean的初始化方法和BeanPostProcessor的前置和后置处理方法。(都是用户自定义的哦)
bean = initializeBean(beanName, bean, beanDefinition);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BeansException("Instantiation of bean failed", e);
}
registerDisposableBeanIfNecessary(beanName, bean, beanDefinition);
// 单例要存储容器里
if (beanDefinition.isSingleton()) {
// 获取bean实例以后添加到单例对象中
addSingleton(beanName, bean);
}
return bean;
}2.测试提前准备
xml配置文件如下,添加了scope="prototype",这里的prototype也可以改成singleton,看自己想要测什么
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<beans>
<bean id="userService" class="com.spring.sourcecode.springframework.test.UserService" scope="prototype">
<property name="uId" value="10001"/>
<property name="company" value="腾讯"/>
<property name="location" value="深圳"/>
</bean>
</beans>UserService添加如下实体
public class UserService {
private String uId;
private String company;
private UserDao userDao;
private String location;
public void queryUserInfo() {
System.out.println("查询用户信息:" + userDao.queryUserName(uId)
+ ",公司名称:" + company + ",地址:" + location);
}
public String getuId() {
return uId;
}
public void setuId(String uId) {
this.uId = uId;
}
public UserDao getUserDao() {
return userDao;
}
public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
public String getLocation() {
return location;
}
public void setLocation(String location) {
this.location = location;
}
public String getCompany() {
return company;
}
public void setCompany(String company) {
this.company = company;
}
}单元测试-测试多例
@Test
public void test_xml() {
// 1.初始化BeanFactory
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:spring.xml");
applicationContext.registerShutdownHook();
// 2.获取bean对象调用方法
UserService userService1 = applicationContext.getBean("userService", UserService.class);
// 2. 获取Bean对象调用方法
UserService userService2 = applicationContext.getBean("userService", UserService.class);
System.out.println(userService1);
System.out.println(userService2);
}
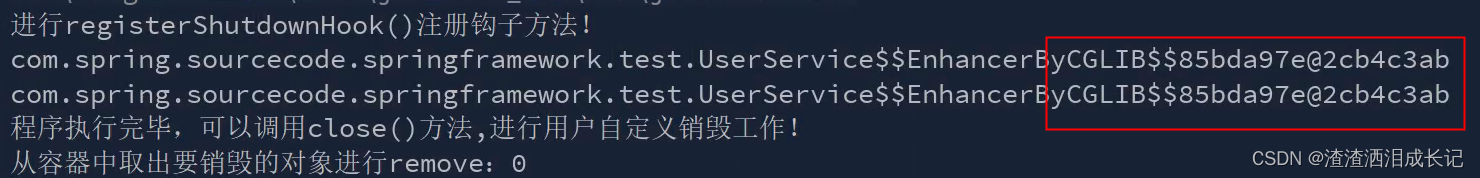
}?测试结果,发现是不同的对象
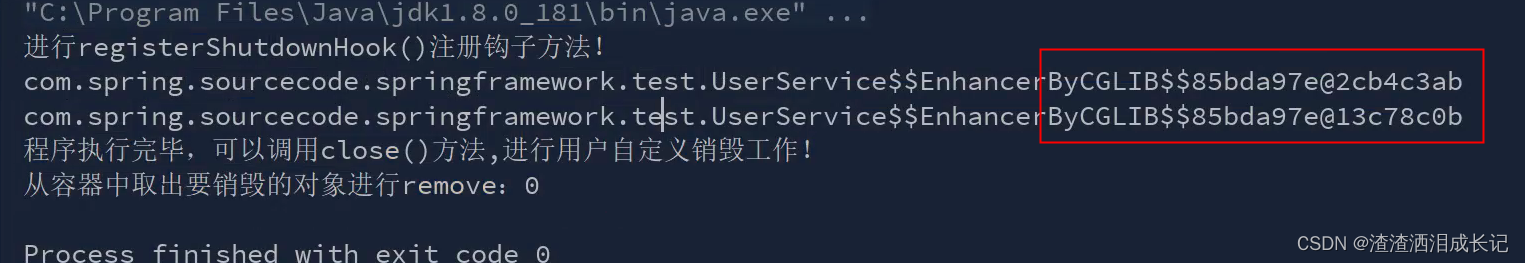
单元测试-测试单例(将配置文件改为单例 scope="singleton")
发现都是同一个对象