测试代码
public class ContextApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:spring.xml");
IUserService userService = context.getBean("userService", IUserService.class);
System.out.println(userService);
}
}
1 构造函数
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext() {
}
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(ApplicationContext parent) {
super(parent);
}
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String configLocation) throws BeansException {
this(new String[] {configLocation}, true, null);
}
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String... configLocations) throws BeansException {
this(configLocations, true, null);
}
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, @Nullable ApplicationContext parent)
throws BeansException {
this(configLocations, true, parent);
}
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String[] configLocations, boolean refresh) throws BeansException {
this(configLocations, refresh, null);
}
public ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
String[] configLocations, boolean refresh, @Nullable ApplicationContext parent)
throws BeansException {
super(parent);
setConfigLocations(configLocations);
if (refresh) {
refresh();
}
}
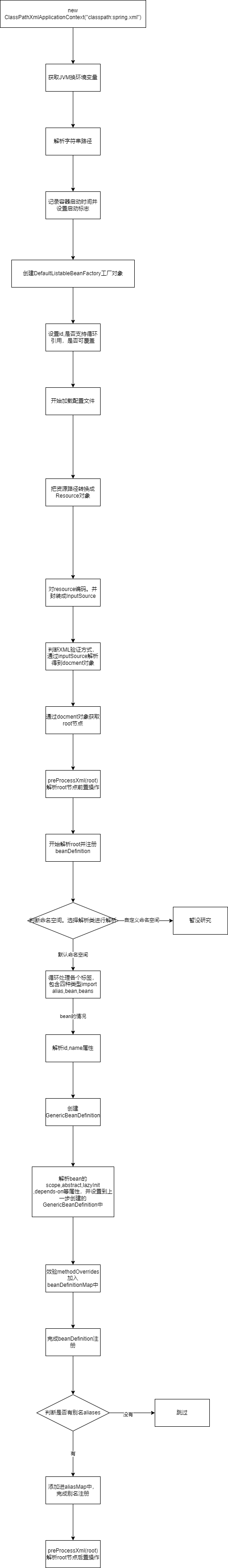
这里用了重载,最终会调用最后一个构造函数,三个参数分别是资源路径,是否自动刷新,默认为true,父容器,这里默认为空
先看看super方法做了哪些工作,一路点进去,发现只有下面两个方法做了点东西
2.super(parent)
/**
* Create a new AbstractApplicationContext with no parent. */
public AbstractApplicationContext() {
this.resourcePatternResolver = getResourcePatternResolver();
}
public void setParent(@Nullable ApplicationContext parent) {
this.parent = parent;
if (parent != null) {
Environment parentEnvironment = parent.getEnvironment();
if (parentEnvironment instanceof ConfigurableEnvironment) {
getEnvironment().merge((ConfigurableEnvironment) parentEnvironment);
}
}
}
第一个方法是设置资源解析的类,这个类实现了用来把字符串格式的资源文件转换为Resource对象
第二个方法设置父容器,做合并操作,我们这里没有会直接跳过
3:setConfigLocations(configLocations)
public void setConfigLocations(@Nullable String... locations) {
if (locations != null) {
Assert.noNullElements(locations, "Config locations must not be null");
this.configLocations = new String[locations.length];
for (int i = 0; i < locations.length; i++) {
this.configLocations[i] = resolvePath(locations[i]).trim();
}
}
else {
this.configLocations = null;
}
}
循环资源文件数组,重点看一下resolvePath方法
protected String resolvePath(String path) {
return getEnvironment().resolveRequiredPlaceholders(path);
}
这里先获取环境变量然后解析路径
注意在创建环境变量的时候,会先进入他的父类
protected ConfigurableEnvironment createEnvironment() {
return new StandardEnvironment();
}

执行父类的构造器
public AbstractEnvironment() {
customizePropertySources(this.propertySources);
}
然后执行子类覆盖的这个方法获取JVM环境属性和系统环境变量属性
@Override
protected void customizePropertySources(MutablePropertySources propertySources) {
propertySources.addLast(
new PropertiesPropertySource(SYSTEM_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, getSystemProperties()));
propertySources.addLast(
new SystemEnvironmentPropertySource(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, getSystemEnvironment()));
}
到此环境变量和JDK属性都已经获取到了,开始解析地址
@Override
public String resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException {
return this.propertyResolver.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(text);
}
交给propertyResolver来处理解析
@Override
public String resolveRequiredPlaceholders(String text) throws IllegalArgumentException {
if (this.strictHelper == null) {
this.strictHelper = createPlaceholderHelper(false);
}
return doResolvePlaceholders(text, this.strictHelper);
}
doResolvePlaceholders
private String doResolvePlaceholders(String text, PropertyPlaceholderHelper helper) {
return helper.replacePlaceholders(text, this::getPropertyAsRawString);
}
replacePlaceholders
public String replacePlaceholders(String value, PlaceholderResolver placeholderResolver) {
Assert.notNull(value, "'value' must not be null");
return parseStringValue(value, placeholderResolver, null);
}
走了一路终于开始真正解析了
protected String parseStringValue(
String value, PlaceholderResolver placeholderResolver, @Nullable Set<String> visitedPlaceholders) {
int startIndex = value.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix);
if (startIndex == -1) {
return value;
}
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder(value);
while (startIndex != -1) {
int endIndex = findPlaceholderEndIndex(result, startIndex);
if (endIndex != -1) {
String placeholder = result.substring(startIndex + this.placeholderPrefix.length(), endIndex);
String originalPlaceholder = placeholder;
if (visitedPlaceholders == null) {
visitedPlaceholders = new HashSet<>(4);
}
if (!visitedPlaceholders.add(originalPlaceholder)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Circular placeholder reference '" + originalPlaceholder + "' in property definitions");
}
// Recursive invocation, parsing placeholders contained in the placeholder key.
placeholder = parseStringValue(placeholder, placeholderResolver, visitedPlaceholders);
// Now obtain the value for the fully resolved key...
String propVal = placeholderResolver.resolvePlaceholder(placeholder);
if (propVal == null && this.valueSeparator != null) {
int separatorIndex = placeholder.indexOf(this.valueSeparator);
if (separatorIndex != -1) {
String actualPlaceholder = placeholder.substring(0, separatorIndex);
String defaultValue = placeholder.substring(separatorIndex + this.valueSeparator.length());
propVal = placeholderResolver.resolvePlaceholder(actualPlaceholder);
if (propVal == null) {
propVal = defaultValue;
}
}
}
if (propVal != null) {
// Recursive invocation, parsing placeholders contained in the
// previously resolved placeholder value. propVal = parseStringValue(propVal, placeholderResolver, visitedPlaceholders);
result.replace(startIndex, endIndex + this.placeholderSuffix.length(), propVal);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Resolved placeholder '" + placeholder + "'");
}
startIndex = result.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix, startIndex + propVal.length());
}
else if (this.ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders) {
// Proceed with unprocessed value.
startIndex = result.indexOf(this.placeholderPrefix, endIndex + this.placeholderSuffix.length());
}
else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Could not resolve placeholder '" +
placeholder + "'" + " in value \"" + value + "\"");
}
visitedPlaceholders.remove(originalPlaceholder);
}
else {
startIndex = -1;
}
}
return result.toString();
}
我们这里没有${,所以会直接返回,到此设置资源路径完成了,开始下一步refresh
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
/**
* 前置动作
* 1:记录容器开始时间
* 2:设置关闭标志为false,活跃标志为true
* 3:获取Environment对象,并加载当前系统的属性值到Environment对象中
* 4:准备监听器和事件的集合对象,默认为空
* 提供扩展点添加容器环境属性{@link org.springframework.context.support.AbstractApplicationContext#initPropertySources}
*/ prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
// 刷新BeanFactory,得到一个空的BeanFactory-Default
/**
* 1.创建容器对象:DefaultListableBeanFactory
* 2:加载配置文件的属性值到当前工厂中,最重要的是BeanFactory
*/ ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // co
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. // 准备BeanFactory
// 1. 设置BeanFactory的类加载器、表达式解析器、类型转化注册器
// 2. 添加三个BeanPostProcessor,注意是具体的BeanPostProcessor实例对象
// 3. 记录ignoreDependencyInterface
// 4. 记录ResolvableDependency
// 5. 添加三个单例Bean
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
// 子类可以对BeanFactory进行进一步初始化
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
// BeanFactory准备好了之后,执行BeanFactoryPostProcessor,开始对BeanFactory进行处理
// 默认情况下:
// 此时beanFactory的beanDefinitionMap中有6个BeanDefinition,5个基础BeanDefinition+AppConfig的BeanDefinition
// 而这6个中只有一个BeanFactoryPostProcessor:ConfigurationClassPostProcessor
// 这里会执行ConfigurationClassPostProcessor进行@Component的扫描,扫描得到BeanDefinition,并注册到beanFactory中
// 注意:扫描的过程中可能又会扫描出其他的BeanFactoryPostProcessor,那么这些BeanFactoryPostProcessor也得在这一步执行
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); //BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor ,BeanFactoryPostProcessors
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation. // 从BeanFactory找出扫描得到得BeanPostProcessor,实例化并注册到BeanFactory中
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
// 初始化MessageSource,如果配置了一个名字叫做“messageSource”的BeanDefinition
// 就会把这个Bean创建出来,并赋值给ApplicationContext的messageSource属性
// 这样ApplicationContext就可以使用国际化的功能了
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
// 设置ApplicationContext的applicationEventMulticaster
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
// 执行子类的onRefresh方法
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
// 注册Listener
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
// 完成beanFactory的初始化(实例化非懒加载的单例bean)
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
// 发布事件
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore... resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
里面一共13个方法,是spring的核心,第一个方法是前置准备,记录容器开始时间,设置关闭标志为false,活跃标志为true 等,本篇文章主要看第二个方法
obtainFreshBeanFactory
@Override
protected final void refreshBeanFactory() throws BeansException {
if (hasBeanFactory()) {
destroyBeans();
closeBeanFactory();
}
try {
//创建DefaultListableBeanFactory工厂对象
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = createBeanFactory();
//设置ID
beanFactory.setSerializationId(getId());
// 设置是否覆盖,循环引用属性值
customizeBeanFactory(beanFactory);
//读取配置文件
loadBeanDefinitions(beanFactory);
synchronized (this.beanFactoryMonitor) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new ApplicationContextException("I/O error parsing bean definition source for " + getDisplayName(), ex);
}
}
重点看loadBeanDefinitions,这个会注册DeanDefintions
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException, IOException {
// Create a new XmlBeanDefinitionReader for the given BeanFactory.
XmlBeanDefinitionReader beanDefinitionReader = new XmlBeanDefinitionReader(beanFactory);
// Configure the bean definition reader with this context's
// resource loading environment. beanDefinitionReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment());
beanDefinitionReader.setResourceLoader(this);
beanDefinitionReader.setEntityResolver(new ResourceEntityResolver(this));
// Allow a subclass to provide custom initialization of the reader,
// then proceed with actually loading the bean definitions. initBeanDefinitionReader(beanDefinitionReader);
loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader);
}
先创建一个beanDefinitionReader,这个是负责读取DeanDefintions的
重点看loadBeanDefinitions方法
protected void loadBeanDefinitions(XmlBeanDefinitionReader reader) throws BeansException, IOException {
Resource[] configResources = getConfigResources();
if (configResources != null) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configResources);
}
String[] configLocations = getConfigLocations();
if (configLocations != null) {
reader.loadBeanDefinitions(configLocations);
}
}
这里getConfigLocations()会获取到我们上面第三步设置的资源
@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String... locations) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.notNull(locations, "Location array must not be null");
int count = 0;
for (String location : locations) {
count += loadBeanDefinitions(location);
}
return count;
}
因为可能有多个,所以循环遍历读取
public int loadBeanDefinitions(String location, @Nullable Set<Resource> actualResources) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = getResourceLoader();
if (resourceLoader == null) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Cannot load bean definitions from location [" + location + "]: no ResourceLoader available");
}
if (resourceLoader instanceof ResourcePatternResolver) {
// Resource pattern matching available.
try {
Resource[] resources = ((ResourcePatternResolver) resourceLoader).getResources(location);
int count = loadBeanDefinitions(resources);
if (actualResources != null) {
Collections.addAll(actualResources, resources);
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Loaded " + count + " bean definitions from location pattern [" + location + "]");
}
return count;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Could not resolve bean definition resource pattern [" + location + "]", ex);
}
}
else {
// Can only load single resources by absolute URL.
Resource resource = resourceLoader.getResource(location);
int count = loadBeanDefinitions(resource);
if (actualResources != null) {
actualResources.add(resource);
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Loaded " + count + " bean definitions from location [" + location + "]");
}
return count;
}
}
这里通过判断resourceLoader的类型,选取相应的加载器,把字符串资源转换成Resource资源,进入loadBeanDefinitions(resource)方法,把resourse转换成BeanDefinition并注册
@Override
public int loadBeanDefinitions(Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
return loadBeanDefinitions(new EncodedResource(resource));
}
这里用了重载,将resource进行了编码,继续调用loadBeanDefinitions
public int loadBeanDefinitions(EncodedResource encodedResource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Set<EncodedResource> currentResources = this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.get();
if (currentResources == null) {
currentResources = new HashSet<>(4);
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.set(currentResources);
}
if (!currentResources.add(encodedResource)) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"Detected cyclic loading of " + encodedResource + " - check your import definitions!");
}
try {
InputStream inputStream = encodedResource.getResource().getInputStream();
try {
InputSource inputSource = new InputSource(inputStream);
if (encodedResource.getEncoding() != null) {
inputSource.setEncoding(encodedResource.getEncoding());
}
return doLoadBeanDefinitions(inputSource, encodedResource.getResource());
}
finally {
inputStream.close();
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(
"IOException parsing XML document from " + encodedResource.getResource(), ex);
}
finally {
currentResources.remove(encodedResource);
if (currentResources.isEmpty()) {
this.resourcesCurrentlyBeingLoaded.remove();
}
}
}
把inputStream封装成InputSource,进入真正的doLoadBeanDefinitions
protected int doLoadBeanDefinitions(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
try {
Document doc = doLoadDocument(inputSource, resource);
int count = registerBeanDefinitions(doc, resource);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Loaded " + count + " bean definitions from " + resource);
}
return count;
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (SAXParseException ex) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Line " + ex.getLineNumber() + " in XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (SAXException ex) {
throw new XmlBeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"XML document from " + resource + " is invalid", ex);
}
catch (ParserConfigurationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Parser configuration exception parsing XML from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"IOException parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(resource.getDescription(),
"Unexpected exception parsing XML document from " + resource, ex);
}
}
除去异常捕获,就干了两件事,
1:通过inputSource和resource得到Docment对象
2:通过docment和resource注册Definition
doLoadDocument
protected Document doLoadDocument(InputSource inputSource, Resource resource) throws Exception {
return this.documentLoader.loadDocument(inputSource, getEntityResolver(), this.errorHandler,
getValidationModeForResource(resource), isNamespaceAware());
}
getValidationModeForResource(resource)会返回XML的验证模式,XML的验证模式分为DTD和XSD,底层是通过判断是否包含DOCTYPE来决定的,包含就是DTD否则就是XSD
boolean hasDoctype(String content) {
return content.contains(DOCTYPE);
}
getEntityResolver()默认返回DelegatingEntityResolver的实例,他的主要作用是把
通过网络加载验证文件转换成自己工程对应的地址文件,这样可以提供用户体验,避免在没有网络的情况也能加载验证文件
DTD转换规则
@Override
@Nullable
public InputSource resolveEntity(@Nullable String publicId, @Nullable String systemId) throws IOException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Trying to resolve XML entity with public ID [" + publicId +
"] and system ID [" + systemId + "]");
}
if (systemId != null && systemId.endsWith(DTD_EXTENSION)) {
int lastPathSeparator = systemId.lastIndexOf('/');
int dtdNameStart = systemId.indexOf(DTD_NAME, lastPathSeparator);
if (dtdNameStart != -1) {
String dtdFile = DTD_NAME + DTD_EXTENSION;
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Trying to locate [" + dtdFile + "] in Spring jar on classpath");
}
try {
Resource resource = new ClassPathResource(dtdFile, getClass());
InputSource source = new InputSource(resource.getInputStream());
source.setPublicId(publicId);
source.setSystemId(systemId);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Found beans DTD [" + systemId + "] in classpath: " + dtdFile);
}
return source;
}
catch (FileNotFoundException ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Could not resolve beans DTD [" + systemId + "]: not found in classpath", ex);
}
}
}
}
// Fall back to the parser's default behavior.
return null;
}
截取systemId最后的xx.dtd然后去当前路径下寻找
XSD转换规则
@Override
@Nullable
public InputSource resolveEntity(@Nullable String publicId, @Nullable String systemId) throws IOException {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Trying to resolve XML entity with public id [" + publicId +
"] and system id [" + systemId + "]");
}
if (systemId != null) {
String resourceLocation = getSchemaMappings().get(systemId);
if (resourceLocation == null && systemId.startsWith("https:")) {
// Retrieve canonical http schema mapping even for https declaration
resourceLocation = getSchemaMappings().get("http:" + systemId.substring(6));
}
if (resourceLocation != null) {
Resource resource = new ClassPathResource(resourceLocation, this.classLoader);
try {
InputSource source = new InputSource(resource.getInputStream());
source.setPublicId(publicId);
source.setSystemId(systemId);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Found XML schema [" + systemId + "] in classpath: " + resourceLocation);
}
return source;
}
catch (FileNotFoundException ex) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Could not find XML schema [" + systemId + "]: " + resource, ex);
}
}
}
}
// Fall back to the parser's default behavior.
return null;
}
加载XSD类型的是PluggableSchemaResolver类的resolveEntity是默认到META-INF/Spring.schemas文件中找到systemid所对应的XSD文件并加载
解析inputSouce
@Override
public Document loadDocument(InputSource inputSource, EntityResolver entityResolver,
ErrorHandler errorHandler, int validationMode, boolean namespaceAware) throws Exception {
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = createDocumentBuilderFactory(validationMode, namespaceAware);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Using JAXP provider [" + factory.getClass().getName() + "]");
}
DocumentBuilder builder = createDocumentBuilder(factory, entityResolver, errorHandler);
return builder.parse(inputSource);
}
通过SAX解析XML文档的套路大致都差不多,Spring在这里并没有什么特殊的地方,先创建DocumentBuilderFactory,再通过DocumentBuilderFactory创建DocumentBuilder,进而解析inputSource来返回Document对象
获取到document对象,下面看注册过程
public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader();
int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount();
documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource));
return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore;
}
创建一个BeanDefinitionDocumentReader来负责注册,并记录一下注册之前的数量,进入注册,最后返回本次注册的数量
registerBeanDefinitions
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, XmlReaderContext readerContext) {
this.readerContext = readerContext;
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(doc.getDocumentElement());
}
获取root节点,进入doRegisterBeanDefinitions方法
protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) {
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate;
//专门处理解析
this.delegate = createDelegate(getReaderContext(), root, parent);
if (this.delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
//处理profile属性
String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE);
if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) {
String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(
profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
if (!getReaderContext().getEnvironment().acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Skipped XML bean definition file due to specified profiles [" + profileSpec +
"] not matching: " + getReaderContext().getResource());
}
return;
}
}
}
//解析前处理,留给子类实现
preProcessXml(root);
parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate);
//解析后处理,留给子类实现
postProcessXml(root);
this.delegate = parent;
}
profile属性是用来定义环境的,根据当前环境判断是否需要注册bean
preProcessXml(root),postProcessXml(root)用了模板方法模式,如果继承自DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader的子类需要在Bean解析前后做一些处理的话,那么只需要重写这两个方法就可以了
看一下注册解析的流程:parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate)
protected void parseBeanDefinitions(Element root, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(root)) {
NodeList nl = root.getChildNodes();
for (int i = 0; i < nl.getLength(); i++) {
Node node = nl.item(i);
if (node instanceof Element) {
Element ele = (Element) node;
if (delegate.isDefaultNamespace(ele)) {
parseDefaultElement(ele, delegate);
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(ele);
}
}
}
}
else {
delegate.parseCustomElement(root);
}
}
通过判断命名空间选择解析方式,spring默认的命名空间为 http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans,我们主要看一下默认的解析方式,自定义不去探究
parseDefaultElement
private void parseDefaultElement(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
//对import标签做处理
if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, IMPORT_ELEMENT)) {
importBeanDefinitionResource(ele);
}
//对alias标签做处理
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, ALIAS_ELEMENT)) {
processAliasRegistration(ele);
}
//对bean标签做处理
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, BEAN_ELEMENT)) {
processBeanDefinition(ele, delegate);
}
//beans标签做处理
else if (delegate.nodeNameEquals(ele, NESTED_BEANS_ELEMENT)) {
// recurse
doRegisterBeanDefinitions(ele);
}
}
判断标签名称来进入不同的解析方法,一共有四种标签,分别是import,alias,bean,beans,我们这里会进入bean标签的解析方法
protected void processBeanDefinition(Element ele, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate delegate) {
BeanDefinitionHolder bdHolder = delegate.parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele);
if (bdHolder != null) {
bdHolder = delegate.decorateBeanDefinitionIfRequired(ele, bdHolder);
try {
// Register the final decorated instance.
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, getReaderContext().getRegistry());
}
catch (BeanDefinitionStoreException ex) {
getReaderContext().error("Failed to register bean definition with name '" +
bdHolder.getBeanName() + "'", ele, ex);
}
// Send registration event.
getReaderContext().fireComponentRegistered(new BeanComponentDefinition(bdHolder));
}
}
把root对象解析成BeanDefinitionHolder,如果不为空,然后解析标签里面的自定义属性,最后使用BeanDefinitionReaderUtils注册,先看一下解析过程parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele)
@Nullable
public BeanDefinitionHolder parseBeanDefinitionElement(Element ele, @Nullable BeanDefinition containingBean) {
//解析id属性
String id = ele.getAttribute(ID_ATTRIBUTE);
//解析name属性
String nameAttr = ele.getAttribute(NAME_ATTRIBUTE);
List<String> aliases = new ArrayList<>();
if (StringUtils.hasLength(nameAttr)) {
String[] nameArr = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(nameAttr, MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
aliases.addAll(Arrays.asList(nameArr));
}
String beanName = id;
if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName) && !aliases.isEmpty()) {
beanName = aliases.remove(0);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No XML 'id' specified - using '" + beanName +
"' as bean name and " + aliases + " as aliases");
}
}
if (containingBean == null) {
checkNameUniqueness(beanName, aliases, ele);
}
AbstractBeanDefinition beanDefinition = parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele, beanName, containingBean);
if (beanDefinition != null) {
if (!StringUtils.hasText(beanName)) {
try {
if (containingBean != null) {
beanName = BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.generateBeanName(
beanDefinition, this.readerContext.getRegistry(), true);
}
else {
beanName = this.readerContext.generateBeanName(beanDefinition);
// Register an alias for the plain bean class name, if still possible,
// if the generator returned the class name plus a suffix. // This is expected for Spring 1.2/2.0 backwards compatibility. String beanClassName = beanDefinition.getBeanClassName();
if (beanClassName != null &&
beanName.startsWith(beanClassName) && beanName.length() > beanClassName.length() &&
!this.readerContext.getRegistry().isBeanNameInUse(beanClassName)) {
aliases.add(beanClassName);
}
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Neither XML 'id' nor 'name' specified - " +
"using generated bean name [" + beanName + "]");
}
}
catch (Exception ex) {
error(ex.getMessage(), ele);
return null; }
}
String[] aliasesArray = StringUtils.toStringArray(aliases);
return new BeanDefinitionHolder(beanDefinition, beanName, aliasesArray);
}
return null;
}
提取id,name属性,使用parseBeanDefinitionElement解析其他属性,判断beanName是否存在,如果不存在则使用默认规则生成,最后将信息封装到 BeanDefinitionHolder中,重点看一下解析其他属性
parseBeanDefinitionElement(ele, beanName, containingBean)
@Nullable
public AbstractBeanDefinition parseBeanDefinitionElement(
Element ele, String beanName, @Nullable BeanDefinition containingBean) {
this.parseState.push(new BeanEntry(beanName));
String className = null;
//解析class属性
if (ele.hasAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE)) {
className = ele.getAttribute(CLASS_ATTRIBUTE).trim();
}
String parent = null;
//解析parent属性
if (ele.hasAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE)) {
parent = ele.getAttribute(PARENT_ATTRIBUTE);
}
try {
//创建用于承载属性的GenericBeanDefinition实例
AbstractBeanDefinition bd = createBeanDefinition(className, parent);
//解析bean标签的各种属性
parseBeanDefinitionAttributes(ele, beanName, containingBean, bd);
//提取description
bd.setDescription(DomUtils.getChildElementValueByTagName(ele, DESCRIPTION_ELEMENT));
//解析元数据
parseMetaElements(ele, bd);
// 解析lookup-method属性
parseLookupOverrideSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides());
// 解析replaced-method属性
parseReplacedMethodSubElements(ele, bd.getMethodOverrides());
//解析构造函数参数
parseConstructorArgElements(ele, bd);
//解析property子元素
parsePropertyElements(ele, bd);
//解析qualifier属性
parseQualifierElements(ele, bd);
bd.setResource(this.readerContext.getResource());
bd.setSource(extractSource(ele));
return bd;
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
error("Bean class [" + className + "] not found", ele, ex);
}
catch (NoClassDefFoundError err) {
error("Class that bean class [" + className + "] depends on not found", ele, err);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
error("Unexpected failure during bean definition parsing", ele, ex);
}
finally {
this.parseState.pop();
}
return null;
}
这个方法逻辑很清晰,调用不同的方法解析不同的属性,先看一下创建过程
createBeanDefinition
public static AbstractBeanDefinition createBeanDefinition(
@Nullable String parentName, @Nullable String className, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) throws ClassNotFoundException {
GenericBeanDefinition bd = new GenericBeanDefinition();
bd.setParentName(parentName);
if (className != null) {
if (classLoader != null) {
bd.setBeanClass(ClassUtils.forName(className, classLoader));
}
else {
bd.setBeanClassName(className);
}
}
return bd;
}
parentName可能为空,创建完成后看前面的解析bean标签的各种属性
parseBeanDefinitionAttributes
public AbstractBeanDefinition parseBeanDefinitionAttributes(Element ele, String beanName,
@Nullable BeanDefinition containingBean, AbstractBeanDefinition bd) {
//解析singleton
if (ele.hasAttribute(SINGLETON_ATTRIBUTE)) {
error("Old 1.x 'singleton' attribute in use - upgrade to 'scope' declaration", ele);
}
//解析scope
else if (ele.hasAttribute(SCOPE_ATTRIBUTE)) {
bd.setScope(ele.getAttribute(SCOPE_ATTRIBUTE));
}
//在有父类beanDifition情况下,没有单独指定scope属性则使用父类默认的属性
else if (containingBean != null) {
// Take default from containing bean in case of an inner bean definition.
bd.setScope(containingBean.getScope());
}
//解析abstract
if (ele.hasAttribute(ABSTRACT_ATTRIBUTE)) {
bd.setAbstract(TRUE_VALUE.equals(ele.getAttribute(ABSTRACT_ATTRIBUTE)));
}
//解析lazyInit
String lazyInit = ele.getAttribute(LAZY_INIT_ATTRIBUTE);
if (isDefaultValue(lazyInit)) {
lazyInit = this.defaults.getLazyInit();
}
bd.setLazyInit(TRUE_VALUE.equals(lazyInit));
// 解析autowire
String autowire = ele.getAttribute(AUTOWIRE_ATTRIBUTE);
bd.setAutowireMode(getAutowireMode(autowire));
// 解析depends-on
if (ele.hasAttribute(DEPENDS_ON_ATTRIBUTE)) {
String dependsOn = ele.getAttribute(DEPENDS_ON_ATTRIBUTE);
bd.setDependsOn(StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(dependsOn, MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS));
}
//解析autowire-candidate
String autowireCandidate = ele.getAttribute(AUTOWIRE_CANDIDATE_ATTRIBUTE);
if (isDefaultValue(autowireCandidate)) {
String candidatePattern = this.defaults.getAutowireCandidates();
if (candidatePattern != null) {
String[] patterns = StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(candidatePattern);
bd.setAutowireCandidate(PatternMatchUtils.simpleMatch(patterns, beanName));
}
}
else {
bd.setAutowireCandidate(TRUE_VALUE.equals(autowireCandidate));
}
//解析primary
if (ele.hasAttribute(PRIMARY_ATTRIBUTE)) {
bd.setPrimary(TRUE_VALUE.equals(ele.getAttribute(PRIMARY_ATTRIBUTE)));
}
//解析init-method
if (ele.hasAttribute(INIT_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE)) {
String initMethodName = ele.getAttribute(INIT_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE);
bd.setInitMethodName(initMethodName);
}
else if (this.defaults.getInitMethod() != null) {
bd.setInitMethodName(this.defaults.getInitMethod());
bd.setEnforceInitMethod(false);
}
//解析destroy-method
if (ele.hasAttribute(DESTROY_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE)) {
String destroyMethodName = ele.getAttribute(DESTROY_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE);
bd.setDestroyMethodName(destroyMethodName);
}
else if (this.defaults.getDestroyMethod() != null) {
bd.setDestroyMethodName(this.defaults.getDestroyMethod());
bd.setEnforceDestroyMethod(false);
}
//解析factory-method
if (ele.hasAttribute(FACTORY_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE)) {
bd.setFactoryMethodName(ele.getAttribute(FACTORY_METHOD_ATTRIBUTE));
}
//解析factory-bean
if (ele.hasAttribute(FACTORY_BEAN_ATTRIBUTE)) {
bd.setFactoryBeanName(ele.getAttribute(FACTORY_BEAN_ATTRIBUTE));
}
return bd;
}
解析bean里面的各种属性,注释写的很清楚,自此BeanDefinition终于创建完成了,接下来就是注册了
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bdHolder, getReaderContext().getRegistry())
public static void registerBeanDefinition(
BeanDefinitionHolder definitionHolder, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
// Register bean definition under primary name.
String beanName = definitionHolder.getBeanName();
registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, definitionHolder.getBeanDefinition());
// Register aliases for bean name, if any.
String[] aliases = definitionHolder.getAliases();
if (aliases != null) {
for (String alias : aliases) {
registry.registerAlias(beanName, alias);
}
}
}
注册beanDefinition和别名aliases,重点看注册beanDefinition
registerBeanDefinition
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition)
throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
Assert.hasText(beanName, "Bean name must not be empty");
Assert.notNull(beanDefinition, "BeanDefinition must not be null");
if (beanDefinition instanceof AbstractBeanDefinition) {
try {
((AbstractBeanDefinition) beanDefinition).validate();
}
catch (BeanDefinitionValidationException ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(beanDefinition.getResourceDescription(), beanName,
"Validation of bean definition failed", ex);
}
}
BeanDefinition existingDefinition = this.beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
if (existingDefinition != null) {
if (!isAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding()) {
throw new BeanDefinitionOverrideException(beanName, beanDefinition, existingDefinition);
}
else if (existingDefinition.getRole() < beanDefinition.getRole()) {
// e.g. was ROLE_APPLICATION, now overriding with ROLE_SUPPORT or ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE
if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) {
logger.info("Overriding user-defined bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with a framework-generated bean definition: replacing [" +
existingDefinition + "] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
else if (!beanDefinition.equals(existingDefinition)) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with a different definition: replacing [" + existingDefinition +
"] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Overriding bean definition for bean '" + beanName +
"' with an equivalent definition: replacing [" + existingDefinition +
"] with [" + beanDefinition + "]");
}
}
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
}
else {
if (hasBeanCreationStarted()) {
// Cannot modify startup-time collection elements anymore (for stable iteration)
synchronized (this.beanDefinitionMap) {
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
List<String> updatedDefinitions = new ArrayList<>(this.beanDefinitionNames.size() + 1);
updatedDefinitions.addAll(this.beanDefinitionNames);
updatedDefinitions.add(beanName);
this.beanDefinitionNames = updatedDefinitions;
removeManualSingletonName(beanName);
}
}
else {
// Still in startup registration phase
this.beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName, beanDefinition);
this.beanDefinitionNames.add(beanName);
removeManualSingletonName(beanName);
}
this.frozenBeanDefinitionNames = null;
}
if (existingDefinition != null || containsSingleton(beanName)) {
resetBeanDefinition(beanName);
}
}
这个方法就是最后的注册过程了,分为四步
1对AbstractBeanDefinition的校验。对于AbstractBean Definition的methodOverrides属性
2对beanName已经注册的情况的处理。如果设置了不允许bean的覆盖,则需要抛出异常,否则直接覆盖。
3加入map缓存。
4清除解析之前留下的对应beanName的缓存。
到此终于完成了BeanDefinition的注册
然后是注册别名
@Override
public void registerAlias(String name, String alias) {
synchronized (this.aliasMap) {
if (alias.equals(name)) {
this.aliasMap.remove(alias);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Alias definition '" + alias + "' ignored since it points to same name");
}
}
else {
String registeredName = this.aliasMap.get(alias);
if (registeredName != null) {
if (registeredName.equals(name)) {
// An existing alias - no need to re-register
return;
}
if (!allowAliasOverriding()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot define alias '" + alias + "' for name '" +
name + "': It is already registered for name '" + registeredName + "'.");
}
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Overriding alias '" + alias + "' definition for registered name '" +
registeredName + "' with new target name '" + name + "'");
}
}
checkForAliasCircle(name, alias);
this.aliasMap.put(alias, name);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Alias definition '" + alias + "' registered for name '" + name + "'");
}
}
}
}
(1)alias与beanName相同情况处理。若alias与beanName并名称相同则不需要处理并删除掉原有alias。
(2)alias覆盖处理。若aliasName已经使用并已经指向了另一beanName则需要用户的设置进行处理。
(3)alias循环检查。当A->B存在时,若再次出现A->C->B时候则会抛出异常。(4)注册alias。
最后简单总结一下流程图