文章目录
1.🍧异常的基本概念
🍰Java中异常是以类的形式存在,每一个异常都可以创建异常对象
现实中的例子:
火灾(异常类)
2008年1月1日,小明家着火了。(异常类对象)
2008年1月2日,小亮家着火了。(异常类对象)
2008年1月3日,小红家着火了。(异常类对象)
public class ExceptionTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArithmeticException x = new ArithmeticException("/ by zero");
System.out.println(x);
}
}
编译结果
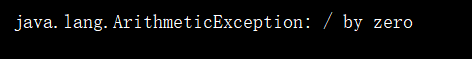
🍰当Java程序遇到异常时都会创建一个异常对象并抛出
public class ExceptionTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a = 5 / 0;
/*
运行时会抛出以下结果:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
at exception.ExceptionTest01.main(ExceptionTest01.java:5)
实则程序在运行到这里时会创建异常对象: new ArithmeticException("/ by zero");然后将异常抛出*/
}
}
2. 🍡异常的分类
2.1🍬异常继承关系图
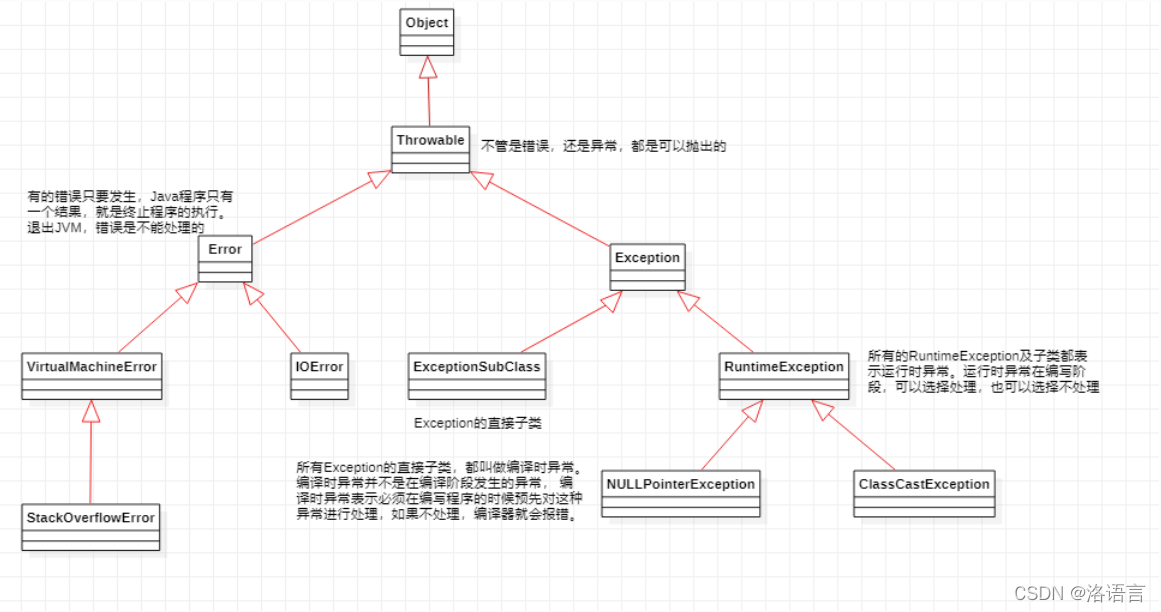
2.2🍚异常的分类
Java中异常大致分为:错误、编译时异常、运行时异常。
-
错误(Error)
如果应用程序出现了Error,那么将无法恢复,只能重新启动应用程序,最典型的Error的异常是:OutOfMemoryError -
编译时异常(ExceptionSubClass)
又称受检异常或受控异常,Exception的直接子类都是编译时异常,编译时异常的子类也都是编译时子类。编译时异常并不是编译阶段发生的异常,而是必须要在编译的时候预先处理的异常,如果不处理,程序就会报错,典型的编译时异常:FileNotFoundException,IOException。 -
运行时异常(RuntimeException)
又称非受检异常或非受控异常RuntimeException及其子类都是运行时异常,在程序编写时,运行时异常可以选择处理,也可以选择不处理。典型的运行时异常:NullPointerException,ArithmeticException。
2.3🍚error和exception的区别
Error类和Exception类的父类都是Throwable类,他们的区别如下:
-
Error类一般是指与虚拟机相关的问题,如系统崩溃,虚拟机错误,内存空间不足,方法调用栈溢出等。对于这类错误的导致的应用程序中断,仅靠程序本身无法恢复和预防,遇到这样的错误,建议让程序终止。 -
Exception类表示程序可以处理的异常,可以捕获且可能恢复。这种异常是由与程序设计的不完善而出现的问题,遇到这类异常,应该尽可能处理异常,使程序恢复运行,而不应该随意终止异常。
3.🍯异常处理
Java语言处理异常的两种方式
- 异常上抛:在方法声明的位置上,使用 throws 关键字,抛给上一级(抛给方法掉用着)。
- 异常捕捉:使用 try…catch 进行对异常的捕捉。
3.1🍝异常上抛
- 谁调用上抛异常的方法,谁就负责处理该异常
- 在定义方法时,把异常抛出就是为了提醒方法的使用者,有异常需要预处理
在处理异常时,是选择捕获处理还是抛出处理 - 异常上抛可以同时上抛多个异常,用逗号隔开。
- 采用上抛的方式处理异常,遇到异常时会将异常上抛,并且该方法后继的代码不在执行
- 在main方法中可以选择将异常上抛,但是并不建议这样做, 因为当程序中出现了该错误,在main方法中将异常抛给JVM,然后JVM就会终止该程序,这样做并不利于程序的健壮性。
阅读以下程序,体会异常的上抛:
public class ExceptionTest04 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException{
//调用了m1方法,所以m1的异常被抛给了main方法
//main方法将异常继续上抛,抛给JVM
System.out.println("main begin!");
m1();
System.out.println("main end!");
}
public static void m1()throws FileNotFoundException {
//调用了m2方法,所以m3的异常被抛给了m2
//m2将异常继续上抛
System.out.println("m1 bengin!");
m2();
System.out.println("m1 end!");
}
public static void m2()throws FileNotFoundException {
//调用了m3方法,所以m3的异常被抛给了m2
//m2将异常继续上抛
System.out.println("m2 bengin!");
m3();
System.out.println("m2 end!");
}
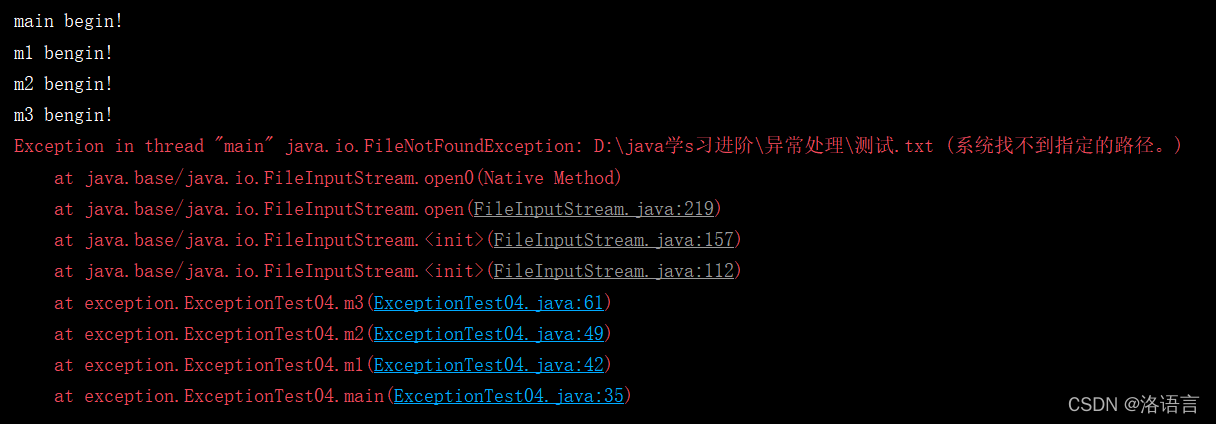
public static void m3()throws FileNotFoundException {
//FileInputStream 抛出了异常FileNotFoundException
//FileNotFoundException 继承了 IOException
//IOException继承了Exception
//所以FileNotFoundException是编译时异常
//在m3方法中需要对该异常进行提前处理
//在这里可以选择将异常FileNotFoundException上抛,也可以将它的父类IOException上抛
//可以理解为:子类异常都是包含在父类异常中的
System.out.println("m3 bengin!");
new FileInputStream("D:\\java学习d进阶\\异常处理\\测试.txt");
System.out.println("m3 end!");
}
}
如果创建流时传参传的是正确路径,程序编译结果如下:

如果创建流时传参传的是错误路径,程序编译结果如下:
3.2🥯异常捕捉
- 异常捕捉语法如下:
try{
//试着执行,如果遇到异常则停止执行
}catch(异常名 引用名){
//该引用保存的是异常对象的地址
//如果成功捕捉到该异常,则会执行这里面的语句
}
- 一般情况下,在调用其他方法时,如果被调用的方法有受检(编译时)异常需要预处理,选择捕获处理,因为你调用了方法, 你负责处理该异常。
- 采用捕捉的方式处理异常,遇到异常会将异常对象捕捉,并不会影响后继代码的执行。
- catch的后面的小括号可以是具体的异常类型,也可以是父类型异常,但是建议使用具体异常类型,有利于程序的调试。
- try中代码抛出多个异常时,可以写多个catch,但是catch内的异常必须从小到大(继承关系)。
- jdk8之后支持:用try…catch处理多个异常时,catch后面的括号可以拿 | 连接,引用写在最后面,拿 | 来连接的异常不能具有继承关系。
样例代码1:
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println("main begin!");
try{
new FileInputStream("D:\\java学习d进阶.txt");
System.out.println("try内代码全部执行!");
}catch(FileNotFoundException a){
//遇到异常时一定会创建一个异常对象,这个对象的地址会保存在a中。
System.out.println("文件不存在");
}
m1();
System.out.println("main end!");
}
若以上代码创建流时传参传的是正确路径,编译结果如下:

如果传参传的是错误路径,编译结果如下:

样例代码2:
public class ExceptionTest05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
new FileInputStream("D:\\java学习d进阶\\异常处理\\测试.txt");
}catch(Exception x){
//catch后面写父类型异常——多态
//Exception x = new FileNotFoundException();
}
}
当以上代码创建流出错时,就会创建异常对象 new FileNotFoundException(),然后异常就会被引用Exception x捕捉,这里就是多态。
样例代码3:
try{
//创建输入流 —— 会抛出 FileNotFoundException 异常(编译时异常)
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\java学习d进阶\\异常处理\\测试.txt");
//读文件 —— 会抛出 IOException 异常(编译时异常)
fis.read();
}catch(FileNotFoundException f){
}catch(IOException i){
//IOException不能放在FileNotFoundException之前,因为IOException是FileNotFountException的父类
}
FileNotFoundException 是IOException的子类,所以在异常捕捉时IOException不能放在FileNotFoundException 的前面。
样例代码4:
//jdk8之后支持:用try..catch处理多个异常时,catch后面的括号可以拿 | 连接,引用写在最后面
//注意:拿 | 来连接的异常不能具有继承关系
try{
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream("D:\\java学习d进阶\\异常处理\\测试.txt");
System.out.println(100 / 0);
}catch(FileNotFoundException | ArithmeticException x){
}
##3.3 finally与try…catch的联合使用
- try不能单独使用,try可以和catch联合使用,try也可以和fianlly联合使用,try,catch,fianlly三个也可以一块联合使用
- finally使用在try或try…catch的后边,无论是否捕捉到异常,都会最后执行finally子句中的代码。
测试代码1:
//try和finally的联合使用
try{
System.out.println("111");
//这里的return并不会影响222的打印
return;
}finally{
System.out.println("222");
}
编译结果:

测试代码2:
public class ExceptionTest07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileInputStream x = null;
try {
//创建输入流
x = new FileInputStream("D:\\java学习d进阶\\异常处理\\测试.txt");
String s = null;
//这里会出现NuLLPointException,下面的代码将不会在执行
s.toString();
//流使用完要关闭,即使程序出现异常也要关闭,所以将x.close放在这里十分危险
x.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException a) {
a.printStackTrace();
} catch (NullPointerException b) {
b.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException c) {
c.printStackTrace();
} finally {
//在这里关闭流比较保险
if (x != null) {
try {
x.close();
} catch (IOException d) {
d.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
以上代码就展现了finally在实际开发中的重要作用。
4🍿常用类中重要的重要方法
异常类中的两个常用方法:getMessage() , printStackTrace()。
4.1🍜getMessage()方法
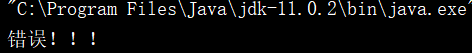
getMessage():获取异常的简单描述信息,该描述信息是创建异常对象时传给构造方法的String参数
public static void main(String[] args) {
//getMessage():获取异常的简单描述信息,该描述信息是创建异常对象时传给构造方法的String参数
FileNotFoundException x = new FileNotFoundException("错误!!!");
System.out.println(x.getMessage());
}
编译结果:
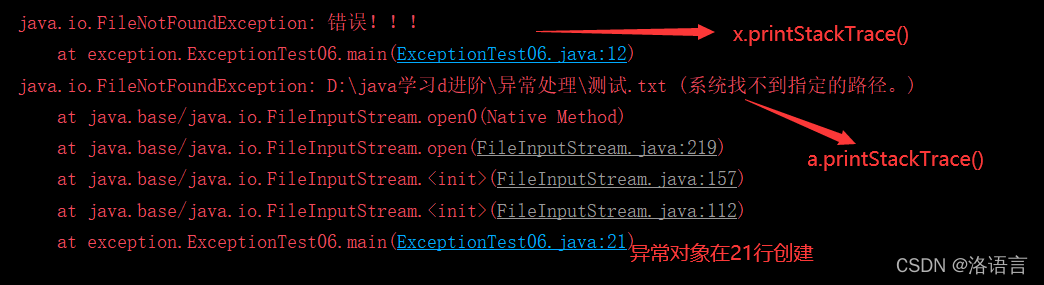
4.2🦪printStackTrace()方法
printStackTrace(): 打印异常的堆栈信息,可以在堆栈信息找到异常对象在Java源代码中的位置
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileNotFoundException x = new FileNotFoundException("错误!!!");
//printStackTrace(): 打印异常的堆栈信息,可以在堆栈信息找到异常对象在Java源代码中的位置
x.printStackTrace();
//该方法时常与try..catch连用
try{
new FileInputStream("D:\\java学习d进阶\\异常处理\\测试.txt");
}catch(FileNotFoundException a){
//当捕捉到异常后,为了程序员知道出错了,并且找到出错的位置,就可以使用该方法。
a.printStackTrace();
}
}
编译结果如下:
5🥡自定义异常类
Java中允许使用者自定义异常类
步骤:
- 编译时异常要继承Exception,运行时异常继承RunTimeException。
- 要创建一个无参构造和一个有参构造(带一个String参数)
//编译时异常
public class MyException extends Exception{
public MyException(){
}
public MyException(String s){
super(s);
}
}
