SSM框架系列——注解开发
注解开发
为什么要使用注解
为了代替繁重的spring配置bean,注解得到了广泛的使用
由于本文仅是说明注解开发,所以不会带大家看注解的实现之类的,我会在SpringBoot系列中加上注解实现原理
Spring注解常用总览
| 注解 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| @Component | 使用在类上用于实例化Bean |
| @Controller | 使用在web层类上用于实例化Bean |
| @Service | 使用在service层类上用于实例化Bean |
| @Repository | 使用在dao层类上用于实例化Bean |
| @Autowired | 使用在字段上用于根据类型依赖注入 |
| @Qualifier | 结合@Autowired—起使用用于根据名称进行依赖注入 |
| @Resource | 相当于@Autowired+@Qualifier,按照名称进行注入 |
| @Value | 注入普通属性 |
| @Scope | 标注Bean的作用范国 |
| @PostConstruct | 使用在方法上标注该方法是Bean的销毁方法 |
| @PreDestroy | 使用在方法上标注该方法是Bean的销毁方法 |
Spring扩展注解常用总览
使用上面的注解还不能全部替代xml配置文件,还需要使用注解替代的配置如下
- 非自定义的Bean的配置:
<bean> - 加载properties文件的配置:
<contextproperty-placeholder> - 组件扫描的配置:
<context:component-scan> - 引入其他文件:
<import> - 等
| 注解 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| @Configuration | 用于指定当前类是一个Spring配置类,当创建容器时会从该类上加载注解 |
| @ComponentScan | 用于指定Spring在初始化容器时要扫描的包。作用和在Spring的xml配置文件中的< context:component-scan base-package=“com.itheima”/ >一样 |
| @Bean | 使用在方法上,标注将该方法的返回值存储到Spring容器中 |
| @PropertySource | 用于加载.properties文件中的配置 |
| @lmport | 用于导入其他配置类 |
| @Test | junit测试 |
注解替代
@Configuration标志核心配置类
@Configuration
public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {}
@ComponentScan配置组件扫描
可以代替
<context:component-scan base-package="com.example"></context:component-scan>
示例代码1(注解+配置文件)
一用到注解我就兴奋了,毕竟用的炒鸡熟
目录
applicationContext.xml
配置文件中需要配置组件扫描位置
<!-- 配置组件扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.example"></context:component-scan>
完整配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- 配置组件扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.example"></context:component-scan>
</beans>
baseMapper
其中@Component(“baseMapper”)代替了<bean id="baseMapper" class=" com.example.mapper.BaseMapper"></bean>
package com.example.mapper;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component("baseMapper")
public class BaseMapper {
public void show() {
System.out.println("baseMapper sout");
}
}
baseService
package com.example.service;
public interface BaseService {
void showBaseMapper();
}
baseServiceImpl
当然你可以用@Resource代替@Autowired和 @Qualifier
package com.example.service.impl;
import com.example.mapper.BaseMapper;
import com.example.service.BaseService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service(value = "baseService")
public class BaseServiceImpl implements BaseService {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("baseMapper")
private BaseMapper baseMapper;
@Override
public void showBaseMapper() {
baseMapper.show();
}
}
baseController
package com.example.controller;
import com.example.service.BaseService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
public class BaseController {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext app = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
BaseService baseService = (BaseService) app.getBean("baseService");
baseService.showBaseMapper();
}
}
结果
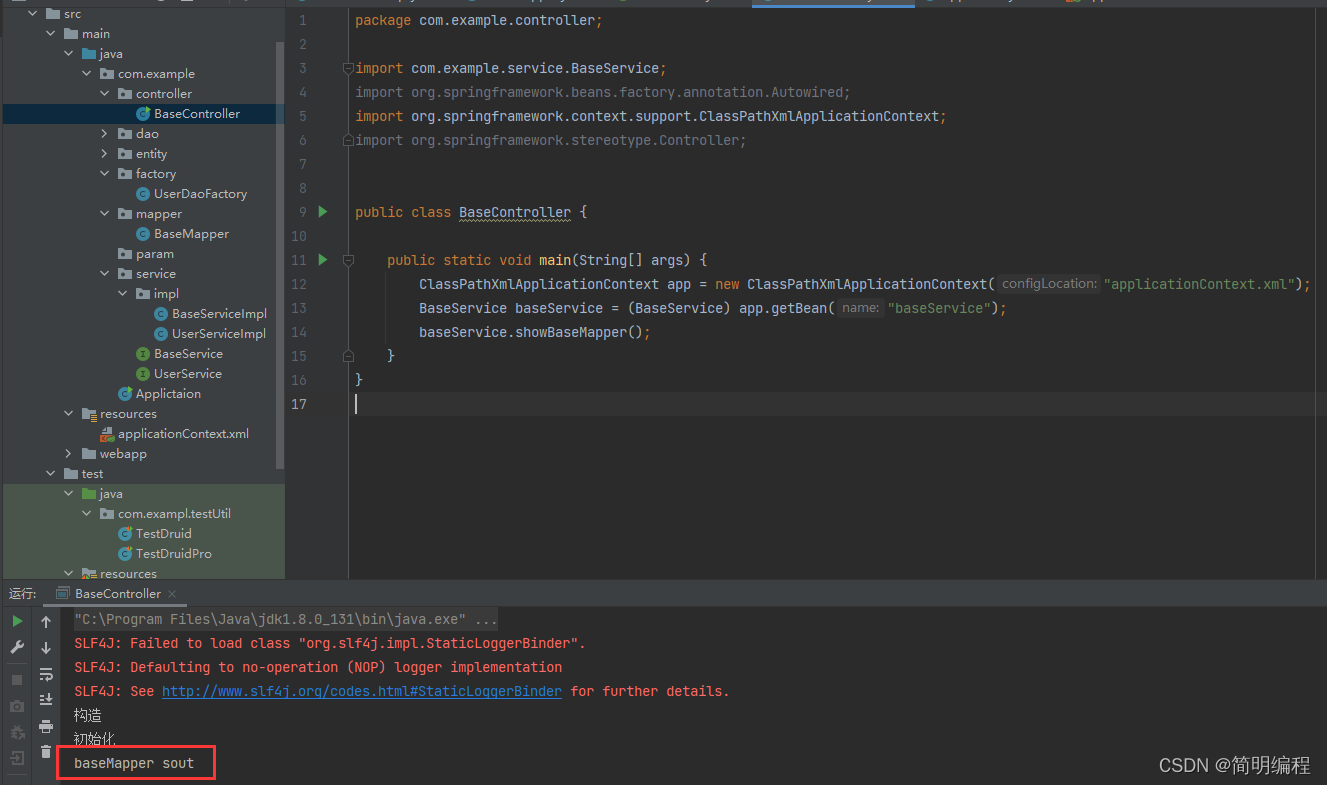
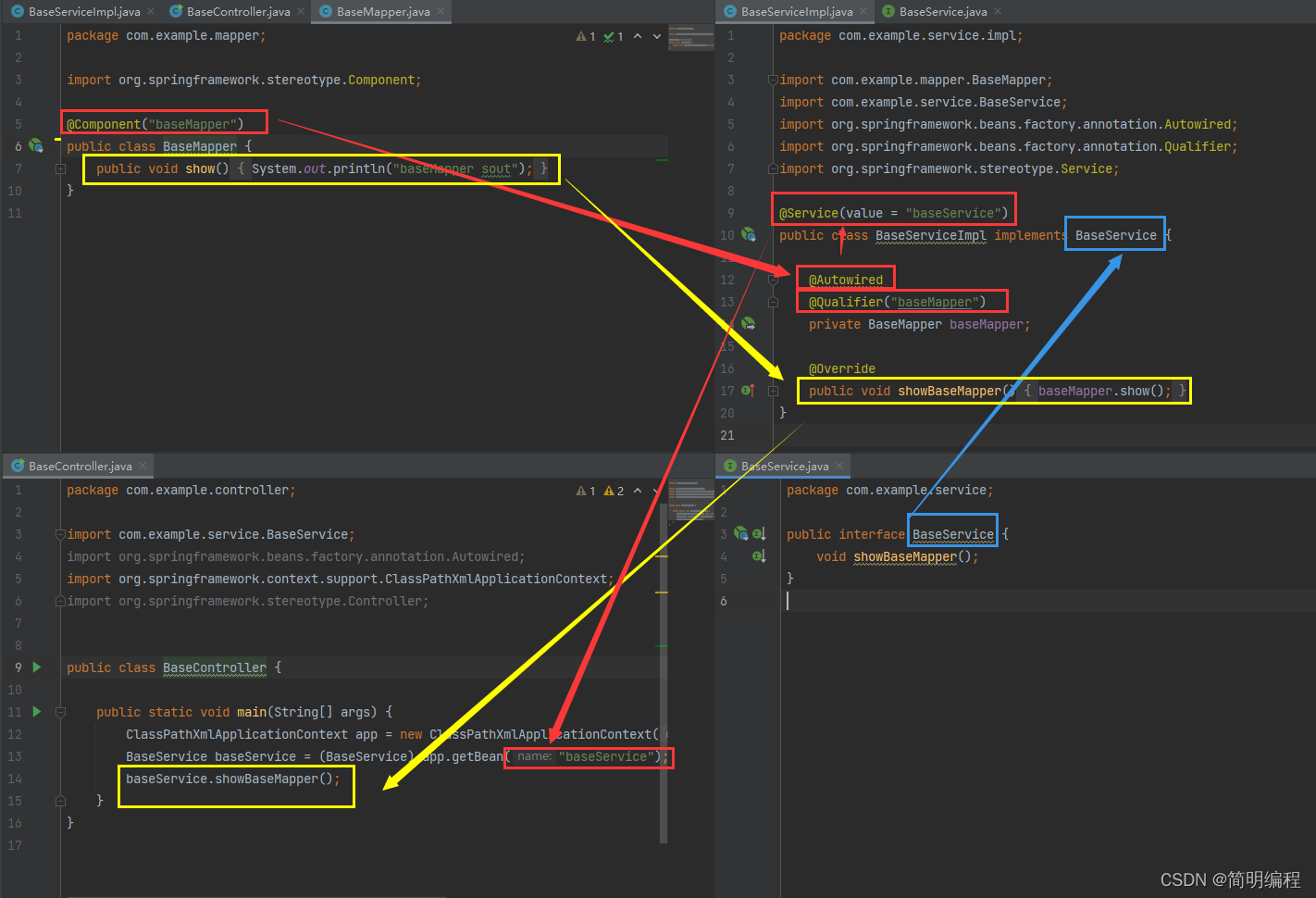
对应关系(重要)
看不同颜色的线大家应该可以看懂了
示例代码2(纯注解!我推荐这种)
这里我只列出和示例代码1不同的地方
目录
去除applicationContext.xml中的组件扫描
改用@ComponentScan("com.example")见下方baseConfiguration
baseConfiguration
package com.example.configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.example")
public class BaseConfiguration {
}
baseController
加载配置类
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext app = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(BaseConfiguration.class);
package com.example.controller;
import com.example.configuration.BaseConfiguration;
import com.example.service.BaseService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
public class BaseController {
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext app = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(BaseConfiguration.class);
BaseService baseService = (BaseService) app.getBean("baseService");
baseService.showBaseMapper();
}
}
结果
对应关系
前面的对应关系还是一样的,这里BaseConfiguration 代替示例代码1中baseController依赖配置文件的对应

