文章目录
正则表达式
笔记来自b站韩顺平-正则表达式
Java里的正则相关
Regexp_
package cn.imlql.regexp;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
/**
* @author
* @version 1.0
* 体验正则表达式的威力,给我们文本处理带来哪些便利
*/
public class Regexp_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String content = "私有地址(Private address)属于非注册地址,专门为组织机构内部使用。\n" +
"以下列出留用的内部私有地址\n" +
"A类 10.0.0.0--10.255.255.255\n" +
"B类 172.16.0.0--172.31.255.255\n" +
"C类 192.168.0.0--192.168.255.255";
//提取文章中所有的英文单词
//提取文章中所有的数字
//提取文章中所有的英文单词和数字
//提取百度热榜 标题
//(1). 传统方法. 使用遍历方式,代码量大,效率不高
//(2). 正则表达式技术
//1. 先创建一个Pattern对象 , 模式对象, 可以理解成就是一个正则表达式对象
//Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("[a-zA-Z]+");
//Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("[0-9]+");
//Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("([0-9]+)|([a-zA-Z]+)");
//Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("<a target=\"_blank\" title=\"(\\S*)\"");
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("\\d+\\.\\d+\\.\\d+\\.\\d+");
//2. 创建一个匹配器对象
//理解: 就是 matcher 匹配器按照 pattern(模式/样式), 到 content 文本中去匹配
//找到就返回true, 否则就返回false
int no = 0;
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(content);
//3. 可以开始循环匹配
while (matcher.find()) {
//匹配内容,文本,放到 m.group(0)
System.out.println("找到: " + (++no) + " " +matcher.group(0));
}
}
}
输出:
找到: 1 10.0.0.0
找到: 2 10.255.255.255
找到: 3 172.16.0.0
找到: 4 172.31.255.255
找到: 5 192.168.0.0
找到: 6 192.168.255.255
Process finished with exit code 0
RegTheory
package cn.imlql.regexp;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
/**
* @author
* @version 1.0
* 分析java的正则表达式的底层实现(重要.)
*/
public class RegTheory {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String content = "1998年12月8日,第二代Java平台的企业版J2EE发布。1999年6月,Sun公司发布了" +
"第二代Java平台(简称为Java2)的3个版本:J2ME(Java2 Micro Edition,Java2平台的微型" +
"版),应用于移动、无线及有限资源的环境;J2SE(Java 2 Standard Edition,Java 2平台的" +
"标准版),应用于桌面环境;J2EE(Java 2Enterprise Edition,Java 2平台的企业版),应" +
"用3443于基于Java的应用服务器。Java 2平台的发布,是Java发展过程中最重要的一个" +
"里程碑,标志着Java的应用开始普及9889 ";
//目标:匹配所有四个数字
//说明
//1. \\d 表示一个任意的数字
String regStr = "(\\d\\d)(\\d\\d)";
//2. 创建模式对象[即正则表达式对象]
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regStr);
//3. 创建匹配器
//说明:创建匹配器matcher, 按照 正则表达式的规则 去匹配 content字符串
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(content);
//4.开始匹配
/**
*
* matcher.find() 完成的任务 (考虑分组)
* 什么是分组,比如 (\d\d)(\d\d) ,正则表达式中有() 表示分组,第1个()表示第1组,第2个()表示第2组...
* 1. 根据指定的规则 ,定位满足规则的子字符串(比如(19)(98))
* 2. 找到后,将 子字符串的开始的索引记录到 matcher对象的属性 int[] groups;
* 2.1 groups[0] = 0 , 把该子字符串的结束的索引+1的值记录到 groups[1] = 4
* 2.2 记录1组()匹配到的字符串 groups[2] = 0 groups[3] = 2
* 2.3 记录2组()匹配到的字符串 groups[4] = 2 groups[5] = 4
* 2.4.如果有更多的分组.....
* 3. 同时记录oldLast 的值为 子字符串的结束的 索引+1的值即35, 即下次执行find时,就从35开始匹配
*
* matcher.group(0) 分析
*
* 源码:
* public String group(int group) {
* if (first < 0)
* throw new IllegalStateException("No match found");
* if (group < 0 || group > groupCount())
* throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("No group " + group);
* if ((groups[group*2] == -1) || (groups[group*2+1] == -1))
* return null;
* return getSubSequence(groups[group * 2], groups[group * 2 + 1]).toString();
* }
* 1. 根据 groups[0]=31 和 groups[1]=35 的记录的位置,从content开始截取子字符串返回
* 就是 [31,35) 包含 31 但是不包含索引为 35的位置
*
* 如果再次指向 find方法.仍然安上面分析来执行
*/
while (matcher.find()) {
//小结
//1. 如果正则表达式有() 即分组
//2. 取出匹配的字符串规则如下
//3. group(0) 表示匹配到的子字符串
//4. group(1) 表示匹配到的子字符串的第一组字串
//5. group(2) 表示匹配到的子字符串的第2组字串
//6. ... 但是分组的数不能越界.
System.out.println("找到: " + matcher.group(0));
System.out.println("第1组()匹配到的值=" + matcher.group(1));
System.out.println("第2组()匹配到的值=" + matcher.group(2));
}
}
}
输出:
找到: 1998
第1组()匹配到的值=19
第2组()匹配到的值=98
找到: 1999
第1组()匹配到的值=19
第2组()匹配到的值=99
找到: 3443
第1组()匹配到的值=34
第2组()匹配到的值=43
找到: 9889
第1组()匹配到的值=98
第2组()匹配到的值=89
Process finished with exit code 0
PatternMethod
public class PatternMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String content = "hello abc hello, 教育";
//String regStr = "hello";
String regStr = "hello.*";
boolean matches = Pattern.matches(regStr, content);
System.out.println("整体匹配= " + matches);
}
}
MatcherMethod

package cn.imlql.regexp;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
/**
* @author
* @version 1.0
* Matcher 类的常用方法
*/
public class MatcherMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String content = "hello edu jack hspedutom hello smith hello hspedu hspedu";
String regStr = "hello";
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regStr);
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(content);
while (matcher.find()) {
System.out.println("=================");
System.out.println(matcher.start());
System.out.println(matcher.end());
System.out.println("找到: " + content.substring(matcher.start(), matcher.end()));
}
//整体匹配方法,常用于,去校验某个字符串是否满足某个规则
System.out.println("整体匹配=" + matcher.matches());
//完成如果content 有 hspedu 替换成 教育
regStr = "hspedu";
pattern = Pattern.compile(regStr);
matcher = pattern.matcher(content);
//注意:返回的字符串才是替换后的字符串 原来的 content 不变化
String newContent = matcher.replaceAll("教育");
System.out.println("newContent=" + newContent);
System.out.println("content=" + content);
}
}
输出:
=================
0
5
找到: hello
=================
25
30
找到: hello
=================
37
42
找到: hello
整体匹配=false
newContent=hello edu jack 教育tom hello smith hello 教育 教育
content=hello edu jack hspedutom hello smith hello hspedu hspedu
Process finished with exit code 0
基本介绍

元字符-转义符


public class RegExp02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String content = "abc$(a.bc(123( )";
//匹配( => \\(
//匹配. => \\.
//String regStr = "\\.";
//String regStr = "\\d\\d\\d";
String regStr = "\\d{3}";
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regStr);
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(content);
while (matcher.find()) {
System.out.println("找到 " + matcher.group(0));
}
}
}
元字符-匹配符


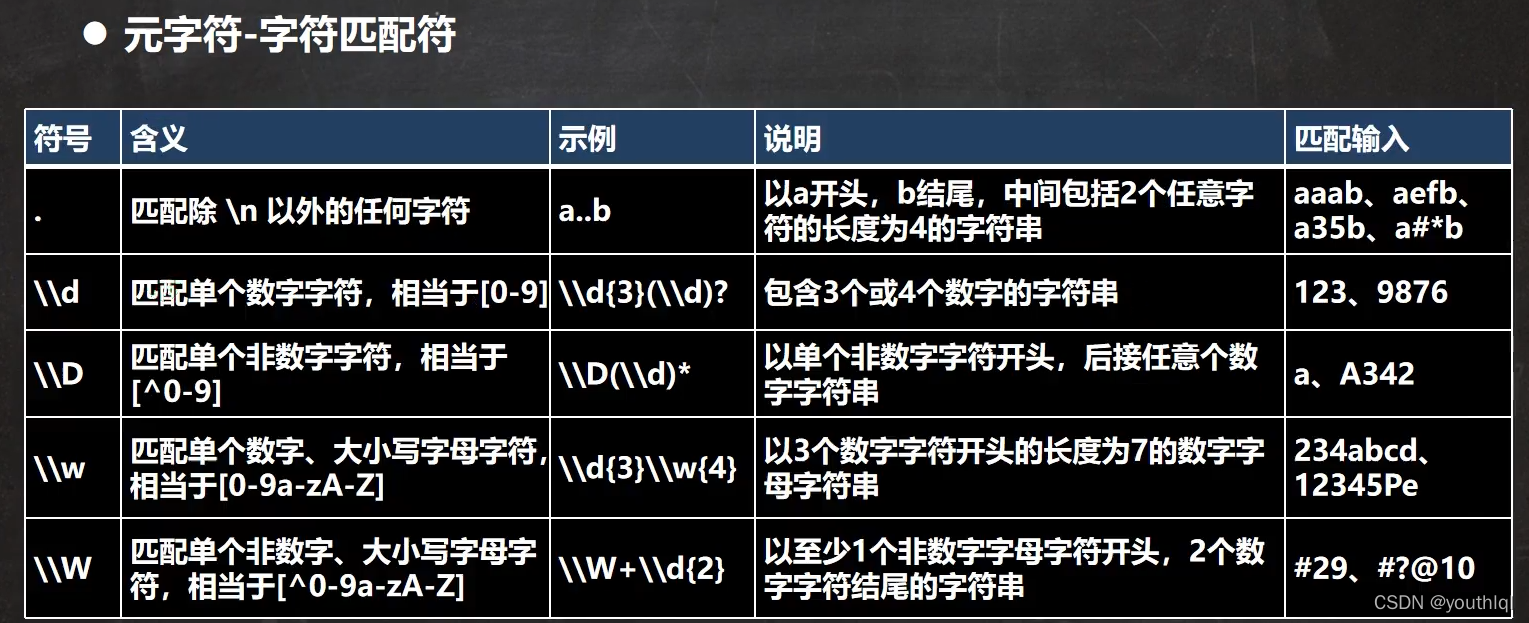

public class RegExp03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String content = "a11c8abc _ABCy @";
//String regStr = "[a-z]";//匹配 a-z之间任意一个字符
//String regStr = "[A-Z]";//匹配 A-Z之间任意一个字符
//String regStr = "abc";//匹配 abc 字符串[默认区分大小写]
//String regStr = "(?i)abc";//匹配 abc 字符串[不区分大小写]
//String regStr = "[0-9]";//匹配 0-9 之间任意一个字符
//String regStr = "[^a-z]";//匹配 不在 a-z之间任意一个字符
//String regStr = "[^0-9]";//匹配 不在 0-9之间任意一个字符
//String regStr = "[abcd]";//匹配 在 abcd中任意一个字符
//String regStr = "\\D";//匹配 不在 0-9的任意一个字符
//String regStr = "\\w";//匹配 大小写英文字母, 数字,下划线
//String regStr = "\\W";//匹配 等价于 [^a-zA-Z0-9_]
//\\s 匹配任何空白字符(空格,制表符等)
//String regStr = "\\s";
//\\S 匹配任何非空白字符 ,和\\s刚好相反
//String regStr = "\\S";
//. 匹配出 \n 之外的所有字符,如果要匹配.本身则需要使用 \\.
String regStr = ".";
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regStr/*, Pattern.CASE_INSENSITIVE*/);
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(content);
while (matcher.find()) {
System.out.println("找到 " + matcher.group(0));
}
}
}
元字符-选择匹配符

public class RegExp04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String content = "hanshunping 韩 寒冷";
String regStr = "han|韩|寒";
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regStr/*, Pattern.CASE_INSENSITIVE*/);
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(content);
while (matcher.find()) {
System.out.println("找到 " + matcher.group(0));
}
}
}
元字符-限定符
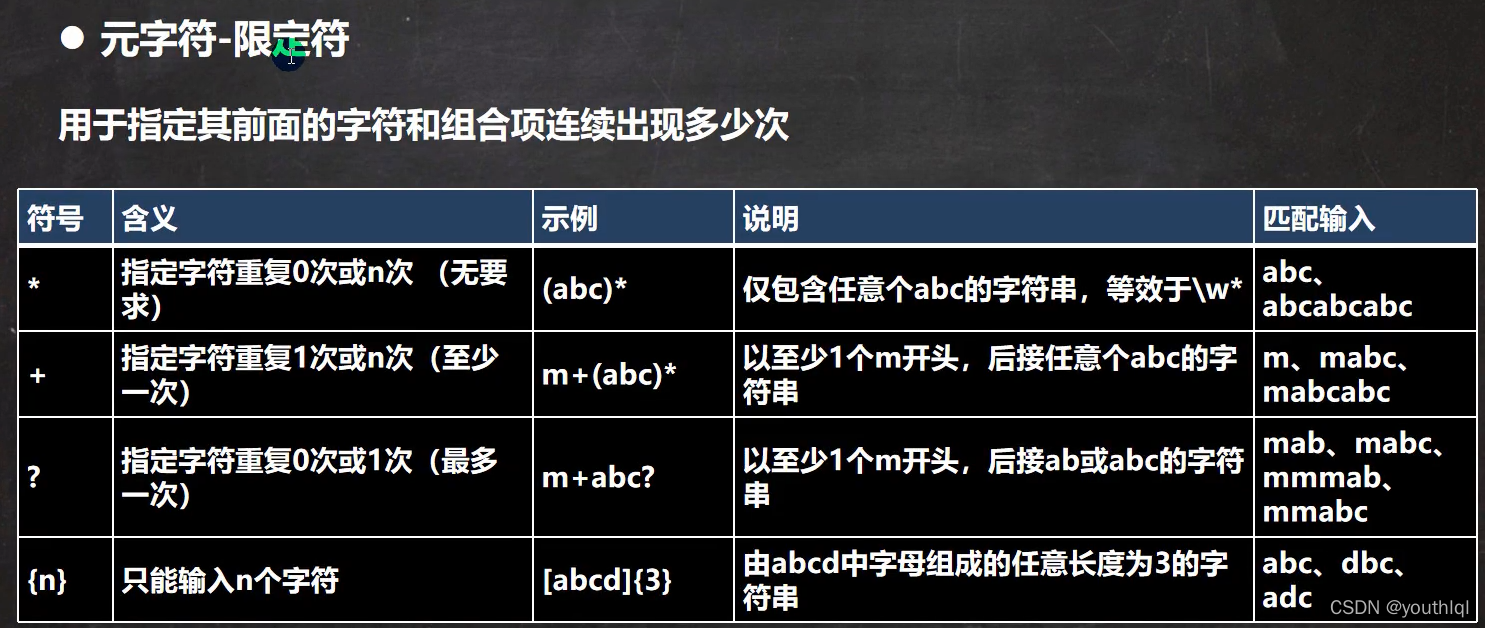

public class RegExp05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String content = "a211111aaaaaahello";
//a{3},1{4},\\d{2}
//String regStr = "a{3}";// 表示匹配 aaa
//String regStr = "1{4}";// 表示匹配 1111
//String regStr = "\\d{2}";// 表示匹配 两位的任意数字字符
//a{3,4},1{4,5},\\d{2,5}
//细节:java匹配默认贪婪匹配,即尽可能匹配多的
//String regStr = "a{3,4}"; //表示匹配 aaa 或者 aaaa
//String regStr = "1{4,5}"; //表示匹配 1111 或者 11111
//String regStr = "\\d{2,5}"; //匹配2位数或者3,4,5
//1+
//String regStr = "1+"; //匹配一个1或者多个1
//String regStr = "\\d+"; //匹配一个数字或者多个数字
//1*
//String regStr = "1*"; //匹配0个1或者多个1
//演示?的使用, 遵守贪婪匹配
String regStr = "a1?"; //匹配 a 或者 a1
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regStr/*, Pattern.CASE_INSENSITIVE*/);
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(content);
while (matcher.find()) {
System.out.println("找到 " + matcher.group(0));
}
}
}
元字符-定位符
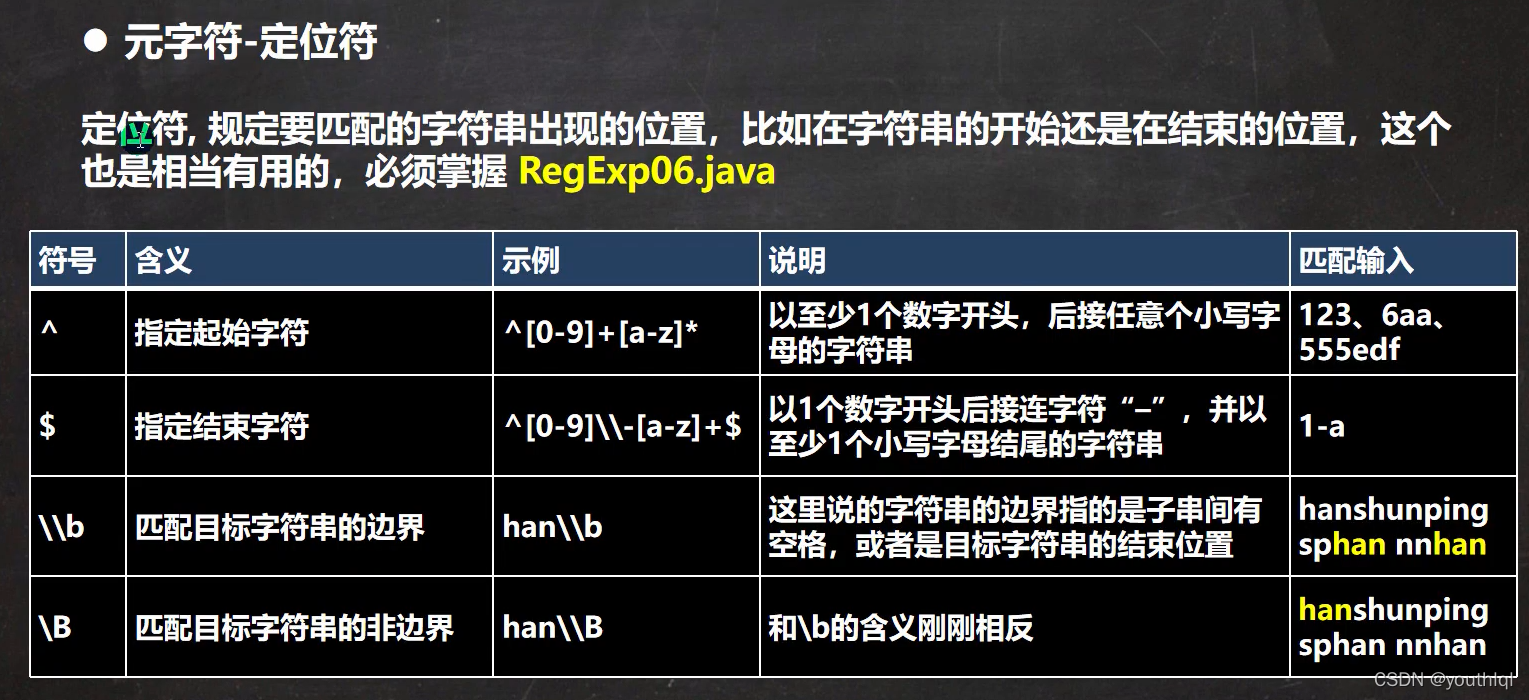
public class RegExp06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String content = "hanshunping sphan nnhan";
//String content = "123-abc";
//以至少1个数字开头,后接任意个小写字母的字符串
//String regStr = "^[0-9]+[a-z]*";
//以至少1个数字开头, 必须以至少一个小写字母结束
//String regStr = "^[0-9]+\\-[a-z]+$";
//表示匹配边界的han[这里的边界是指:被匹配的字符串最后,
// 也可以是空格的子字符串的后面]
//String regStr = "han\\b";
//和\\b的含义刚刚相反
String regStr = "han\\B";
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regStr);
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(content);
while (matcher.find()) {
System.out.println("找到=" + matcher.group(0));
}
}
}
分组
捕获分组

public class RegExp07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String content = "hanshunping s7789 nn1189han";
//下面就是非命名分组
//说明
// 1. matcher.group(0) 得到匹配到的字符串
// 2. matcher.group(1) 得到匹配到的字符串的第1个分组内容
// 3. matcher.group(2) 得到匹配到的字符串的第2个分组内容
//String regStr = "(\\d\\d)(\\d\\d)";//匹配4个数字的字符串
//命名分组: 即可以给分组取名
String regStr = "(?<g1>\\d\\d)(?<g2>\\d\\d)";//匹配4个数字的字符串
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regStr);
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(content);
while (matcher.find()) {
System.out.println("找到=" + matcher.group(0));
System.out.println("第1个分组内容=" + matcher.group(1));
System.out.println("第1个分组内容[通过组名]=" + matcher.group("g1"));
System.out.println("第2个分组内容=" + matcher.group(2));
System.out.println("第2个分组内容[通过组名]=" + matcher.group("g2"));
}
}
}
非捕获分组

public class RegExp08 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String content = "hello韩顺平教育 jack韩顺平老师 韩顺平同学hello韩顺平学生";
// 找到 韩顺平教育 、韩顺平老师、韩顺平同学 子字符串
//String regStr = "韩顺平教育|韩顺平老师|韩顺平同学";
//上面的写法可以等价非捕获分组, 注意:不能 matcher.group(1)
//String regStr = "韩顺平(?:教育|老师|同学)";
//找到 韩顺平 这个关键字,但是要求只是查找韩顺平教育和 韩顺平老师 中包含有的韩顺平
//下面也是非捕获分组,不能使用 matcher.group(1)
//String regStr = "韩顺平(?=教育|老师)";
//找到 韩顺平 这个关键字,但是要求只是查找 不是 (韩顺平教育 和 韩顺平老师) 中包含有的韩顺平
//下面也是非捕获分组,不能使用 matcher.group(1)
String regStr = "韩顺平(?!教育|老师)";
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regStr);
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(content);
while (matcher.find()) {
System.out.println("找到: " + matcher.group(0));
}
}
}
非贪婪匹配
| ? | 当此字符紧随任何其他限定符(*、+、?、{n}、{n,}、{n,m})之后时,匹配模式是"非贪心的"。"非贪心的"模式匹配搜索到的、尽可能短的字符串,而默认的"贪心的"模式匹配搜索到的、尽可能长的字符串。例如,在字符串"oooo"中,"o+?“只匹配单个"o”,而"o+“匹配所有"o”。 |
|---|
public class RegExp09 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String content = "hello111111 ok";
// String regStr = "\\d+"; //默认是贪婪匹配,输出是111111
String regStr = "\\d+?"; //非贪婪匹配 输出6行1
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regStr);
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(content);
while (matcher.find()) {
System.out.println("找到: " + matcher.group(0));
}
}
}
反向引用

内部反向引用的意思是:在正则表达式里使用了反向引用
外部反向引用的意思是:没有在正则表达式里使用,而是在其他行代码里用到了反向引用。RegExp13的例子
public class RegExp12 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String content = "h1234el9876lo33333 j12324-333999111a1551ck14 tom11 jack22 yyy12345 xxx";
//要匹配两个连续的相同数字 : (\\d)\\1
//String regStr = "(\\d)\\1";
//要匹配五个连续的相同数字: (\\d)\\1{4} 反向引用第一个表达式的值,再出现4次
//String regStr = "(\\d)\\1{4}";
//要匹配个位与千位相同,十位与百位相同的数 5225 , 1551 (\\d)(\\d)\\2\\1
//String regStr = "(\\d)(\\d)\\2\\1";
/**
* (\\d)(\\d)\\2\\1 这里的2,1就是第2个组,第一个组
* \\2反向引用第二组表达式的值
* \\1反向引用第一组表达式的值
*/
/**
* 请在字符串中检索商品编号,形式如:12321-333999111 这样的号码,
* 要求满足前面是一个五位数,然后一个-号,然后是一个九位数,连续的每三位要相同
*/
String regStr = "\\d{5}-(\\d)\\1{2}(\\d)\\2{2}(\\d)\\3{2}";
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regStr);
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(content);
while (matcher.find()) {
System.out.println("找到 " + matcher.group(0));
}
}
}
package cn.imlql.regexp;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
/**
* @author
* @version 1.0
*/
public class RegExp13 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String content = "我....我要....学学学学....编程java!";
//1. 去掉所有的.
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("\\.");
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(content);
content = matcher.replaceAll("");
System.out.println("content=" + content);
//2. 去掉重复的字 我我要学学学学编程java!
// 思路
//(1) 使用 (.)\\1+ ==》解释:首先.是匹配所有; \\1反向引用(.); +就是反向引用的字符可以出现多次
//(2) 使用 反向引用$1 来替换匹配到的内容
// 注意:因为正则表达式变化,所以需要重置 matcher
pattern = Pattern.compile("(.)\\1+");//分组的捕获内容记录到$1
matcher = pattern.matcher(content);
while (matcher.find()) {
System.out.println("找到=" + matcher.group(0));
}
//
// //使用 反向引用$1 来替换匹配到的内容
content = matcher.replaceAll("$1");
System.out.println("content=" + content);
// //3. 使用一条语句 去掉重复的字 我我要学学学学编程java!
// content = Pattern.compile("(.)\\1+").matcher(content).replaceAll("$1");
//
// System.out.println("content=" + content);
}
}
输出:
content=我我要学学学学编程java!
找到=我我
找到=学学学学
content=我要学编程java!
Process finished with exit code 0
String类使用正则表达式
public class StringReg {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String content = "2000年5月,JDK1.3、JDK1.4和J2SE1.3相继发布,几周后其" +
"获得了Apple公司Mac OS X的工业标准的支持。2001年9月24日,J2EE1.3发" +
"布。" +
"2002年2月26日,J2SE1.4发布。自此Java的计算能力有了大幅提升";
//使用正则表达式方式,将 JDK1.3 和 JDK1.4 替换成JDK
content = content.replaceAll("JDK1\\.3|JDK1\\.4", "JDK");
System.out.println(content);
//要求 验证一个 手机号, 要求必须是以138 139 开头的
content = "13888889999";
if (content.matches("1(38|39)\\d{8}")) {
System.out.println("验证成功");
} else {
System.out.println("验证失败");
}
//要求按照 # 或者 - 或者 ~ 或者 数字 来分割
System.out.println("===================");
content = "hello#abc-jack12smith~北京";
String[] split = content.split("#|-|~|\\d+");
for (String s : split) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
输出:
2000年5月,JDK、JDK和J2SE1.3相继发布,几周后其获得了Apple公司Mac OS X的工业标准的支持。2001年9月24日,J2EE1.3发布。2002年2月26日,J2SE1.4发布。自此Java的计算能力有了大幅提升
验证成功
===================
hello
abc
jack
smith
北京
Process finished with exit code 0
实例
匹配URL
public class RegExp11 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//String content = "https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1fh411y7R8?from=search&seid=1831060912083761326";
String content = "http://edu.3dsmax.tech/yg/bilibili/my6652/pc/qg/05-51/index.html#201211-1?track_id=jMc0jn-hm-yHrNfVad37YdhOUh41XYmjlss9zocM26gspY5ArwWuxb4wYWpmh2Q7GzR7doU0wLkViEhUlO1qNtukyAgake2jG1bTd23lR57XzV83E9bAXWkStcAh4j9Dz7a87ThGlqgdCZ2zpQy33a0SVNMfmJLSNnDzJ71TU68Rc-3PKE7VA3kYzjk4RrKU";
/**
* 思路
* 1. 先确定 url 的开始部分 https:// | http://
* 2.然后通过 ([\w-]+\.)+[\w-]+ 匹配 www.bilibili.com
* 3. /video/BV1fh411y7R8?from=sear 匹配(\/[\w-?=&/%.#]*)?
*/
String regStr = "^((http|https)://)?([\\w-]+\\.)+[\\w-]+(\\/[\\w-?=&/%.#]*)?$";//注意:[. ? *]表示匹配就是.本身
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regStr);
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(content);
if(matcher.find()) {
System.out.println("满足格式");
} else {
System.out.println("不满足格式");
}
//这里如果使用Pattern的matches 整体匹配 比较简洁
System.out.println(Pattern.matches(regStr, content));//
}
}
验证电子邮件是否合法
package cn.imlql.regexp;
/**
* @author
* @version 1.0
*/
public class Homework01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//规定电子邮件规则为
//只能有一个@
//@前面是用户名,可以是a-z A-Z 0-9 _-字符
//@后面是域名,并且域名只能是英文字母, 比如 sohu.com 或者 tsinghua.org.cn
// 写出对应的正则表达式, 验证输入的字符串是否为满足规则
String content = "hsp@tsinghua.org.cn kkk";
String regStr = "^[\\w-]+@([a-zA-Z]+\\.)+[a-zA-Z]+$";
//老师说明
//1. String 的 matches 是整体匹配
//2. 看看这个matches 底层
/**
* String 的 matches
* public boolean matches(String regex) {
* return Pattern.matches(regex, this);
* }
*
* Pattern
* public static boolean matches(String regex, CharSequence input) {
* Pattern p = Pattern.compile(regex);
* Matcher m = p.matcher(input);
* return m.matches();
* }
*
* Mather类 match
* Attempts to match the entire region against the pattern
* public boolean matches() {
* return match(from, ENDANCHOR);
* }
*/
if (content.matches(regStr)) {
System.out.println("匹配成功");
} else {
System.out.println("匹配失败");
}
}
}
验证是不是整数或者小数
package cn.imlql.regexp;
/**
* @author
* @version 1.0
*/
public class Homework02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//要求验证是不是整数或者小数
//提示: 这个题要考虑正数和负数
//比如: 123 -345 34.89 -87.9 -0.01 0.45 等
/**
* 老师的思路
* 1. 先写出简单的正则表达式
* 2. 在逐步的完善[根据各种情况来完善]
*/
String content = "-0.89"; //
String regStr = "^[-+]?([1-9]\\d*|0)(\\.\\d+)?$";
if(content.matches(regStr)) {
System.out.println("匹配成功 是整数或者小数");
} else {
System.out.println("匹配失败");
}
}
}
解析URL
package cn.imlql.regexp;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
/**
* @author
* @version 1.0
*/
public class Homework03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String content = "http://www.sohu.com:8080/abc/xxx/yyy/inde@#$%x.htm";
//因为正则表达式是根据要求来编写的,所以,如果需求需要的话,可以改进.
String regStr = "^([a-zA-Z]+)://([a-zA-Z.]+):(\\d+)[\\w-/]*/([\\w.@#$%]+)$";
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(regStr);
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(content);
if(matcher.matches()) {//整体匹配, 如果匹配成功,可以通过group(x), 获取对应分组的内容
System.out.println("整体匹配=" + matcher.group(0));
System.out.println("协议: " + matcher.group(1));
System.out.println("域名: " + matcher.group(2));
System.out.println("端口: " + matcher.group(3));
System.out.println("文件: " + matcher.group(4));
} else {
System.out.println("没有匹配成功");
}
}
}
输出:
整体匹配=http://www.sohu.com:8080/abc/xxx/yyy/inde@#$%x.htm
协议: http
域名: www.sohu.com
端口: 8080
文件: inde@#$%x.htm
Process finished with exit code 0
资料
常用正则表达式大全
一、校验数字的表达式
1 数字:^[0-9]*$
2 n位的数字:^\d{n}$
3 至少n位的数字:^\d{n,}$
4 m-n位的数字:^\d{m,n}$
5 零和非零开头的数字:^(0|[1-9][0-9]*)$
6 非零开头的最多带两位小数的数字:^([1-9][0-9]*)+(.[0-9]{1,2})?$
7 带1-2位小数的正数或负数:^(\-)?\d+(\.\d{1,2})?$
8 正数、负数、和小数:^(\-|\+)?\d+(\.\d+)?$
9 有两位小数的正实数:^[0-9]+(.[0-9]{2})?$
10 有1~3位小数的正实数:^[0-9]+(.[0-9]{1,3})?$
11 非零的正整数:^[1-9]\d*$ 或 ^([1-9][0-9]*){1,3}$ 或 ^\+?[1-9][0-9]*$
12 非零的负整数:^\-[1-9][]0-9"*$ 或 ^-[1-9]\d*$
13 非负整数:^\d+$ 或 ^[1-9]\d*|0$
14 非正整数:^-[1-9]\d*|0$ 或 ^((-\d+)|(0+))$
15 非负浮点数:^\d+(\.\d+)?$ 或 ^[1-9]\d*\.\d*|0\.\d*[1-9]\d*|0?\.0+|0$
16 非正浮点数:^((-\d+(\.\d+)?)|(0+(\.0+)?))$ 或 ^(-([1-9]\d*\.\d*|0\.\d*[1-9]\d*))|0?\.0+|0$
17 正浮点数:^[1-9]\d*\.\d*|0\.\d*[1-9]\d*$ 或 ^(([0-9]+\.[0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*)|([0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*\.[0-9]+)|([0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*))$
18 负浮点数:^-([1-9]\d*\.\d*|0\.\d*[1-9]\d*)$ 或 ^(-(([0-9]+\.[0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*)|([0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*\.[0-9]+)|([0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*)))$
19 浮点数:^(-?\d+)(\.\d+)?$ 或 ^-?([1-9]\d*\.\d*|0\.\d*[1-9]\d*|0?\.0+|0)$
二、校验字符的表达式
1 汉字:^[\u4e00-\u9fa5]{0,}$
2 英文和数字:^[A-Za-z0-9]+$ 或 ^[A-Za-z0-9]{4,40}$
3 长度为3-20的所有字符:^.{3,20}$
4 由26个英文字母组成的字符串:^[A-Za-z]+$
5 由26个大写英文字母组成的字符串:^[A-Z]+$
6 由26个小写英文字母组成的字符串:^[a-z]+$
7 由数字和26个英文字母组成的字符串:^[A-Za-z0-9]+$
8 由数字、26个英文字母或者下划线组成的字符串:^\w+$ 或 ^\w{3,20}$
9 中文、英文、数字包括下划线:^[\u4E00-\u9FA5A-Za-z0-9_]+$
10 中文、英文、数字但不包括下划线等符号:^[\u4E00-\u9FA5A-Za-z0-9]+$ 或 ^[\u4E00-\u9FA5A-Za-z0-9]{2,20}$
11 可以输入含有^%&',;=?$\"等字符:[^%&',;=?$\x22]+
12 禁止输入含有~的字符:[^~\x22]+
三、特殊需求表达式
1 Email地址:^\w+([-+.]\w+)*@\w+([-.]\w+)*\.\w+([-.]\w+)*$
2 域名:[a-zA-Z0-9][-a-zA-Z0-9]{0,62}(/.[a-zA-Z0-9][-a-zA-Z0-9]{0,62})+/.?
3 InternetURL:[a-zA-z]+://[^\s]* 或 ^https://([\w-]+\.)+[\w-]+(/[\w-./?%&=]*)?$
4 手机号码:^(13[0-9]|14[5|7]|15[0|1|2|3|5|6|7|8|9]|18[0|1|2|3|5|6|7|8|9])\d{8}$
5 电话号码("XXX-XXXXXXX"、"XXXX-XXXXXXXX"、"XXX-XXXXXXX"、"XXX-XXXXXXXX"、"XXXXXXX"和"XXXXXXXX):^(\(\d{3,4}-)|\d{3.4}-)?\d{7,8}$
6 国内电话号码(0511-4405222、021-87888822):\d{3}-\d{8}|\d{4}-\d{7}
7 身份证号:
15或18位身份证:^\d{15}|\d{18}$
15位身份证:^[1-9]\d{7}((0\d)|(1[0-2]))(([0|1|2]\d)|3[0-1])\d{3}$
18位身份证:^[1-9]\d{5}[1-9]\d{3}((0\d)|(1[0-2]))(([0|1|2]\d)|3[0-1])\d{4}$
8 短身份证号码(数字、字母x结尾):^([0-9]){7,18}(x|X)?$ 或 ^\d{8,18}|[0-9x]{8,18}|[0-9X]{8,18}?$
9 帐号是否合法(字母开头,允许5-16字节,允许字母数字下划线):^[a-zA-Z][a-zA-Z0-9_]{4,15}$
10 密码(以字母开头,长度在6~18之间,只能包含字母、数字和下划线):^[a-zA-Z]\w{5,17}$
11 强密码(必须包含大小写字母和数字的组合,不能使用特殊字符,长度在8-10之间):^(?=.*\d)(?=.*[a-z])(?=.*[A-Z]).{8,10}$
12 日期格式:^\d{4}-\d{1,2}-\d{1,2}
13 一年的12个月(01~09和1~12):^(0?[1-9]|1[0-2])$
14 一个月的31天(01~09和1~31):^((0?[1-9])|((1|2)[0-9])|30|31)$
15 钱的输入格式:
16 1.有四种钱的表示形式我们可以接受:"10000.00" 和 "10,000.00", 和没有 "分" 的 "10000" 和 "10,000":^[1-9][0-9]*$
17 2.这表示任意一个不以0开头的数字,但是,这也意味着一个字符"0"不通过,所以我们采用下面的形式:^(0|[1-9][0-9]*)$
18 3.一个0或者一个不以0开头的数字.我们还可以允许开头有一个负号:^(0|-?[1-9][0-9]*)$
19 4.这表示一个0或者一个可能为负的开头不为0的数字.让用户以0开头好了.把负号的也去掉,因为钱总不能是负的吧.下面我们要加的是说明可能的小数部分:^[0-9]+(.[0-9]+)?$
20 5.必须说明的是,小数点后面至少应该有1位数,所以"10."是不通过的,但是 "10" 和 "10.2" 是通过的:^[0-9]+(.[0-9]{2})?$
21 6.这样我们规定小数点后面必须有两位,如果你认为太苛刻了,可以这样:^[0-9]+(.[0-9]{1,2})?$
22 7.这样就允许用户只写一位小数.下面我们该考虑数字中的逗号了,我们可以这样:^[0-9]{1,3}(,[0-9]{3})*(.[0-9]{1,2})?$
23 8.1到3个数字,后面跟着任意个 逗号+3个数字,逗号成为可选,而不是必须:^([0-9]+|[0-9]{1,3}(,[0-9]{3})*)(.[0-9]{1,2})?$
24 备注:这就是最终结果了,别忘了"+"可以用"*"替代如果你觉得空字符串也可以接受的话(奇怪,为什么?)最后,别忘了在用函数时去掉去掉那个反斜杠,一般的错误都在这里
25 xml文件:^([a-zA-Z]+-?)+[a-zA-Z0-9]+\\.[x|X][m|M][l|L]$
26 中文字符的正则表达式:[\u4e00-\u9fa5]
27 双字节字符:[^\x00-\xff] (包括汉字在内,可以用来计算字符串的长度(一个双字节字符长度计2,ASCII字符计1))
28 空白行的正则表达式:\n\s*\r (可以用来删除空白行)
29 HTML标记的正则表达式:<(\S*?)[^>]*>.*?|<.*? /> (网上流传的版本太糟糕,上面这个也仅仅能部分,对于复杂的嵌套标记依旧无能为力)
30 首尾空白字符的正则表达式:^\s*|\s*$或(^\s*)|(\s*$) (可以用来删除行首行尾的空白字符(包括空格、制表符、换页符等等),非常有用的表达式)
31 腾讯QQ号:[1-9][0-9]{4,} (腾讯QQ号从10000开始)
32 中国邮政编码:[1-9]\d{5}(?!\d) (中国邮政编码为6位数字)
33 IP地址:\d+\.\d+\.\d+\.\d+ (提取IP地址时有用)
正则表达式元字符-详细说明
| 字符 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| \ | 将下一字符标记为特殊字符、文本、反向引用或八进制转义符。例如,“n"匹配字符"n”。“\n"匹配换行符。序列”\\“匹配”\“,”\(“匹配”("。 |
| ^ | 匹配输入字符串开始的位置。如果设置了 RegExp 对象的 Multiline 属性,^ 还会与"\n"或"\r"之后的位置匹配。 |
| $ | 匹配输入字符串结尾的位置。如果设置了 RegExp 对象的 Multiline 属性,$ 还会与"\n"或"\r"之前的位置匹配。 |
| * | 零次或多次匹配前面的字符或子表达式。例如,zo* 匹配"z"和"zoo"。 *等效于 {0,}。 |
| + | 一次或多次匹配前面的字符或子表达式。例如,"zo+"与"zo"和"zoo"匹配,但与"z"不匹配。+ 等效于 {1,}。 |
| ? | 零次或一次匹配前面的字符或子表达式。例如,"do(es)?“匹配"do"或"does"中的"do”。? 等效于 {0,1}。 |
| {n} | n 是非负整数。正好匹配 n 次。例如,"o{2}"与"Bob"中的"o"不匹配,但与"food"中的两个"o"匹配。 |
| {n,} | n 是非负整数。至少匹配 n 次。例如,"o{2,}“不匹配"Bob"中的"o”,而匹配"foooood"中的所有 o。"o{1,}“等效于"o+”。"o{0,}“等效于"o*”。 |
| {n,m} | m 和 n 是非负整数,其中 n <= m。匹配至少 n 次,至多 m 次。例如,"o{1,3}"匹配"fooooood"中的头三个 o。‘o{0,1}’ 等效于 ‘o?’。注意:您不能将空格插入逗号和数字之间。 |
| ? | 当此字符紧随任何其他限定符(*、+、?、{n}、{n,}、{n,m})之后时,匹配模式是"非贪心的"。"非贪心的"模式匹配搜索到的、尽可能短的字符串,而默认的"贪心的"模式匹配搜索到的、尽可能长的字符串。例如,在字符串"oooo"中,"o+?“只匹配单个"o”,而"o+“匹配所有"o”。 |
| . | 匹配除"\r\n"之外的任何单个字符。若要匹配包括"\r\n"在内的任意字符,请使用诸如"[\s\S]"之类的模式。 |
| (pattern) | 匹配 pattern 并捕获该匹配的子表达式。可以使用 $0…$9 属性从结果"匹配"集合中检索捕获的匹配。若要匹配括号字符 ( ),请使用"(“或者”)"。 |
| (?:pattern) | 匹配 pattern 但不捕获该匹配的子表达式,即它是一个非捕获匹配,不存储供以后使用的匹配。这对于用"or"字符 (|) 组合模式部件的情况很有用。例如,'industr(?:y|ies) 是比 ‘industry|industries’ 更经济的表达式。 |
| (?=pattern) | 执行正向预测先行搜索的子表达式,该表达式匹配处于匹配 pattern 的字符串的起始点的字符串。它是一个非捕获匹配,即不能捕获供以后使用的匹配。例如,‘Windows (?=95|98|NT|2000)’ 匹配"Windows 2000"中的"Windows",但不匹配"Windows 3.1"中的"Windows"。预测先行不占用字符,即发生匹配后,下一匹配的搜索紧随上一匹配之后,而不是在组成预测先行的字符后。 |
| (?!pattern) | 执行反向预测先行搜索的子表达式,该表达式匹配不处于匹配 pattern 的字符串的起始点的搜索字符串。它是一个非捕获匹配,即不能捕获供以后使用的匹配。例如,‘Windows (?!95|98|NT|2000)’ 匹配"Windows 3.1"中的 “Windows”,但不匹配"Windows 2000"中的"Windows"。预测先行不占用字符,即发生匹配后,下一匹配的搜索紧随上一匹配之后,而不是在组成预测先行的字符后。 |
| x|y | 匹配 x 或 y。例如,‘z|food’ 匹配"z"或"food"。‘(z|f)ood’ 匹配"zood"或"food"。 |
| [xyz] | 字符集。匹配包含的任一字符。例如,"[abc]“匹配"plain"中的"a”。 |
| [^xyz] | 反向字符集。匹配未包含的任何字符。例如,"[^abc]“匹配"plain"中"p”,“l”,“i”,“n”。 |
| [a-z] | 字符范围。匹配指定范围内的任何字符。例如,"[a-z]"匹配"a"到"z"范围内的任何小写字母。 |
| [^a-z] | 反向范围字符。匹配不在指定的范围内的任何字符。例如,"[^a-z]"匹配任何不在"a"到"z"范围内的任何字符。 |
| \b | 匹配一个字边界,即字与空格间的位置。例如,“er\b"匹配"never"中的"er”,但不匹配"verb"中的"er"。 |
| \B | 非字边界匹配。“er\B"匹配"verb"中的"er”,但不匹配"never"中的"er"。 |
| \cx | 匹配 x 指示的控制字符。例如,\cM 匹配 Control-M 或回车符。x 的值必须在 A-Z 或 a-z 之间。如果不是这样,则假定 c 就是"c"字符本身。 |
| \d | 数字字符匹配。等效于 [0-9]。 |
| \D | 非数字字符匹配。等效于 [^0-9]。 |
| \f | 换页符匹配。等效于 \x0c 和 \cL。 |
| \n | 换行符匹配。等效于 \x0a 和 \cJ。 |
| \r | 匹配一个回车符。等效于 \x0d 和 \cM。 |
| \s | 匹配任何空白字符,包括空格、制表符、换页符等。与 [ \f\n\r\t\v] 等效。 |
| \S | 匹配任何非空白字符。与 [^ \f\n\r\t\v] 等效。 |
| \t | 制表符匹配。与 \x09 和 \cI 等效。 |
| \v | 垂直制表符匹配。与 \x0b 和 \cK 等效。 |
| \w | 匹配任何字类字符,包括下划线。与"[A-Za-z0-9_]"等效。 |
| \W | 与任何非单词字符匹配。与"[^A-Za-z0-9_]"等效。 |
| \xn | 匹配 n,此处的 n 是一个十六进制转义码。十六进制转义码必须正好是两位数长。例如,“\x41"匹配"A”。“\x041"与”\x04"&"1"等效。允许在正则表达式中使用 ASCII 代码。 |
| \num | 匹配 num,此处的 num 是一个正整数。到捕获匹配的反向引用。例如,"(.)\1"匹配两个连续的相同字符。 |
| \n | 标识一个八进制转义码或反向引用。如果 \n 前面至少有 n 个捕获子表达式,那么 n 是反向引用。否则,如果 n 是八进制数 (0-7),那么 n 是八进制转义码。 |
| \nm | 标识一个八进制转义码或反向引用。如果 \nm 前面至少有 nm 个捕获子表达式,那么 nm 是反向引用。如果 \nm 前面至少有 n 个捕获,则 n 是反向引用,后面跟有字符 m。如果两种前面的情况都不存在,则 \nm 匹配八进制值 nm,其中 n 和 m 是八进制数字 (0-7)。 |
| \nml | 当 n 是八进制数 (0-3),m 和 l 是八进制数 (0-7) 时,匹配八进制转义码 nml。 |
| \un | 匹配 n,其中 n 是以四位十六进制数表示的 Unicode 字符。例如,\u00A9 匹配版权符号 (?)。 |



