初步认识AbstractQueuedSynchonizer
文章目录
源码采用JDK8
什么是AQS
AQS是用来构建锁或者其他同步组件的基础框架,它使用了一个int的变量表示同步状态,通过内置的FIFO队列来完成资源获取线程的排队工作。
它的主要使用方式是继承,子类通过继承AQS并实现他的抽象方法来管理同步状态,在抽象方法的实现过程中免不了要对同步状态进行修改,AQS为此提供了三个方法(getState() 、setState(int newState)、compareAndSetState(int expect, int update))来操进行作操作,它们可以保证修改是安全的。使用自定义同步组件的静态内部类来实现子类,同步器自身没有实现任何同步接口,它仅仅定义了一些关于同步状态获取和释放的方法来使用。AQS既支持抢占式的获取同步状态,也支持共享式的获取同步状态。
AQS的接口和示例
AQS的设计基于模板方法模式的,这就需要我们继承AQS并重写指定的方法,随后AQS组合在自定义的组件实现中,并调用同步器提供的模板方法,而这些模板方法会调用我们重写的方法。子类需要重写的三个方法:
- getState() :获取当前同步状态
- setState(int newState):设置当前同步状态
- compareAndSetState(int expect, int update):使用CAS设置当前状态,该方法能够保证状态设置的原子性
AQS可以被重写的方法
| 方法名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| protected boolean tryAcquire(int arg) | 独占式获取同步状态,实现的时候需要查询当前状态并判断是否符合预期,再使用CAS设置同步状态 |
| protected boolean tryRelease(int arg) | 独占式释放同步状态,等待获取同步状态的线程将有机会获取同步状态 |
| protected int tryAcquireShared(int arg) | 共享式获取同步状态,返回大于等于0的值,表示获取成功,否知失败 |
| protected boolean tryReleaseShared(int arg) | 共享式释放同步状态 |
| protected boolean isHeldExclusively() | 当前AQS是否在独占模式下被线程占用,一般该方法表示是否被当前线程所独占 |
AQS提供的模板方法基本分为3类
- 独占式获取与释放同步状态
- 共享式获取与释放同步状态
- 查询同步队列中的等待线程情况
| 方法名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| void acquire(int arg) | 独占式获取同步状态,如果当前线程获取同步状态成功则返回,否则进入同步队列等待,该发放会去调用重写的tryAcquire(int arg) |
| void acquireInterruptibly(int arg) throws InterruptedException | 与acquire(int arg)的差异是 这个方法响应中断,当前线程在等待队列中,如果被中断,那么该方法会抛出异常并返回 |
| boolean tryAcquireNanos(int arg, long nanosTimeout) throws InterruptedException | 在acquireInterruptibly(int arg)基础上增加了超时机制,在规定时间内取不到同步状态,也会以false返回。 |
| boolean release(int arg) | 独占式释放同步状态,在释放同步状态后,会将等待队列的第一个节点对应的线程唤醒 |
| void acquireShared(int arg) | 共享式获取同步状态,如果当前线程获取同步状态成功则返回,否则进入同步队列等待,该发放会去调用重写的tryAcquire(int arg),与独占式不同,可以有多个线程获取到同步状态。 |
| void acquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg) throws InterruptedException | 与acquireShared(int arg)的差异是 这个方法响应中断,当前线程在等待队列中,如果被中断,那么该方法会抛出异常并返回 |
| boolean tryAcquireSharedNanos(int arg, long nanosTimeout) throws InterruptedException | 在acquireSharedInterruptibly(int arg)基础上增加了超时机制,在规定时间内取不到同步状态,也会以false返回。 |
| boolean releaseShared(int arg) | 共享式释放同步状态, |
| Collection getQueuedThreads() | 获取等待队列中的线程集合 |
官网例子
在JDK1.8源码里面有提供了一个独占锁的实现例子Mutex自定义同步组件,它在同一时刻只能有一个线程能获取到锁。在Mutex中定义一个静态内部类Sync。
Sync继承了AQS,并使用getState() 、setState(int newState)、compareAndSetState(int expect, int update)重写了isHeldExclusively() 、tryAcquire(int acquires)、tryRelease(int releases)方法。
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.AbstractQueuedSynchronizer;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
public class Mutex implements Lock, java.io.Serializable {
// 继承AQS的子类,静态内部类形式
private static class Sync extends AbstractQueuedSynchronizer {
// 是否是独占的
@Override
protected boolean isHeldExclusively() {
return getState() == 1;
}
// 当同步状态是0时,获取锁
@Override
public boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
assert acquires == 1; // Otherwise unused
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 释放锁将 同步状态改为0
@Override
protected boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
assert releases == 1; // Otherwise unused
if (getState() == 0) {
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
}
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
setState(0);
return true;
}
// 提供一个ConditionObject
Condition newCondition() {
return new ConditionObject();
}
// Deserializes properly
private void readObject(ObjectInputStream s)
throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
s.defaultReadObject();
setState(0); // reset to unlocked state
}
}
// sync完成所有艰苦的工作。 我们是需要将操作代理到sync上。
private final Sync sync = new Sync();
@Override
public void lock() {
sync.acquire(1);
}
@Override
public void lockInterruptibly() throws InterruptedException {
sync.acquireInterruptibly(1);
}
@Override
public boolean tryLock() {
return sync.tryAcquire(1);
}
@Override
public boolean tryLock(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
return sync.tryAcquireNanos(1, unit.toNanos(time));
}
@Override
public void unlock() {
sync.release(1);
}
@Override
public Condition newCondition() {
return sync.newCondition();
}
}
编写测试MutexTest类,会使用AQS的模板方法进行操作。通过lock()进行获取锁(内部调用了Sync的tryAcquire),unlock()(Sync的tryRelease)解锁。
public class MutexTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Mutex lock = new Mutex();
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
executorService.execute(() -> {
lock.lock();
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " get lock");
Thread.sleep(1000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " release lock");
lock.unlock();
}
});
}
executorService.shutdown();
}
}
通过结果,可以看出一次只有一个线程获取到锁。
Thread[pool-1-thread-1,5,main] get lock. 17:21:23
Thread[pool-1-thread-1,5,main] release lock. 17:21:24
Thread[pool-1-thread-2,5,main] get lock. 17:21:24
Thread[pool-1-thread-2,5,main] release lock. 17:21:25
Thread[pool-1-thread-3,5,main] get lock. 17:21:25
Thread[pool-1-thread-3,5,main] release lock. 17:21:26
Thread[pool-1-thread-4,5,main] get lock. 17:21:26
Thread[pool-1-thread-4,5,main] release lock. 17:21:27
Thread[pool-1-thread-5,5,main] get lock. 17:21:27
Thread[pool-1-thread-5,5,main] release lock. 17:21:28
AQS实现分析
核心思想
如果被请求的共享资源空闲,则将当前请求资源的线程设置为有效的工作线程,并且将共享资源设置为锁定状态。如果被请求的共享资源被占用,那么就需要一套线程阻塞等待以及被唤醒时锁分配的机制,这个机制在AQS是用CLH队列锁实现的,即将暂时获取不到锁的线程加入到队列中。队列有同步队列(sync queue)和条件队列(condition queue)。
CLH(Craig,Landin,and Hagersten)队列是一个虚拟的双向队列(虚拟的双向队列,即不存在队列实例,仅存在结点之间的关联关系)。AQS是将每条请求共享资源的线程封装成一个CLH锁队列的一个结点(Node)来实现锁的分配。
我的理解就是没有用类似QUEUE那样的队列的实例,而是通过NODE中存放前后结点PreNode和NextNode形成一种双向链表似的关系
sync queue 同步队列
AQS使用一个int成员变量来表示同步状态,通过内置的FIFO队列来完成获取资源线程的排队工作。AQS使用CAS操作对该同步状态进行原子操作实现对其值的修改。CAS操作主要借助sun.misc.Unsafed类来实现。
// 代表同步状态的变量
private volatile int state;
同步队列中的结点用来保存获取同步状态失败的线程引用、等待状态以及前驱和后继结点,结点的属性类型与名称, 源码如下
static final class Node {
// 模式,分为共享与独占
// 共享模式
static final Node SHARED = new Node();
// 独占模式
static final Node EXCLUSIVE = null;
// 结点状态的值
// CANCELLED,值为1,表示当前的线程被取消(由于等待超时或者中断)
// SIGNAL,值为-1,表示当前结点的后继结点包含的线程需要唤醒(处于等待状态),也就是unpark。当前结点的线程释放同步状态或者取消了,将唤醒后继结点的线程
// CONDITION,值为-2,表示当前节点在等待condition,也就是在condition队列中。
// PROPAGATE,值为-3,表示当前场景下后续的acquireShared能够得以执行。共享式同步状态获取的时候将会无条件传播下去
// 值为0,初始值。表示当前节点在sync队列中,等待着获取锁
static final int CANCELLED = 1;
static final int SIGNAL = -1;
static final int CONDITION = -2;
static final int PROPAGATE = -3;
// 结点状态
volatile int waitStatus;
/**
* 前驱结点
*/
volatile Node prev;
/**
* 后继结点
*/
volatile Node next;
/**
* 结点所对应的线程
*/
volatile Thread thread;
/**
* 下一个等待者 后继结点
*/
Node nextWaiter;
/**
* 节点是否在共享模式下等待 当Returns true if node is waiting in shared mode.
*/
final boolean isShared() {
return nextWaiter == SHARED;
}
/**
* 获取前驱结点,若前驱结点为空,抛出异常
*/
final Node predecessor() throws NullPointerException {
Node p = prev;
if (p == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
else
return p;
}
//无参构造方法
Node() { // 用于建立初始头部或共享标记
}
Node(Thread thread, Node mode) { // Used by addWaiter
this.nextWaiter = mode;
this.thread = thread;
}
Node(Thread thread, int waitStatus) { // Used by Condition
this.waitStatus = waitStatus;
this.thread = thread;
}
}
同步队列的数据结构
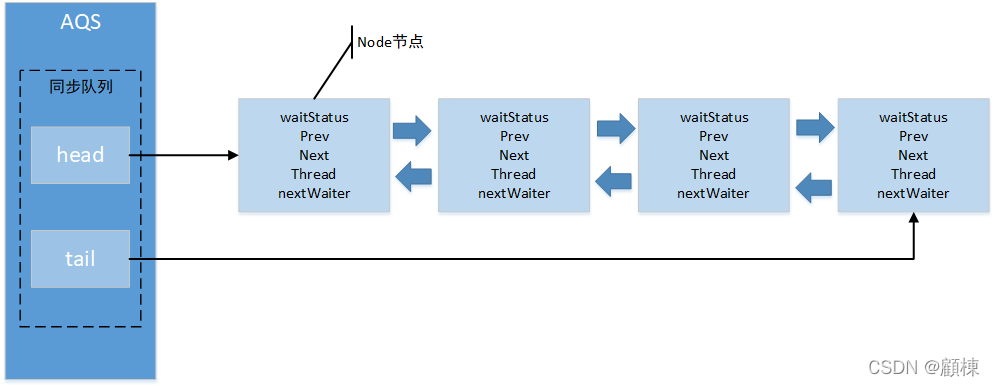
在AQS中有两个结点类型的引用,head是指向头结点(状态值不会是1),tail是指向尾结点。
/**
* Head of the wait queue, lazily initialized. Except for
* initialization, it is modified only via method setHead. Note:
* If head exists, its waitStatus is guaranteed not to be
* CANCELLED.
*/
private transient volatile Node head;
/**
* Tail of the wait queue, lazily initialized. Modified only via
* method enq to add new wait node.
*/
private transient volatile Node tail;
独占式同步状态获取与释放
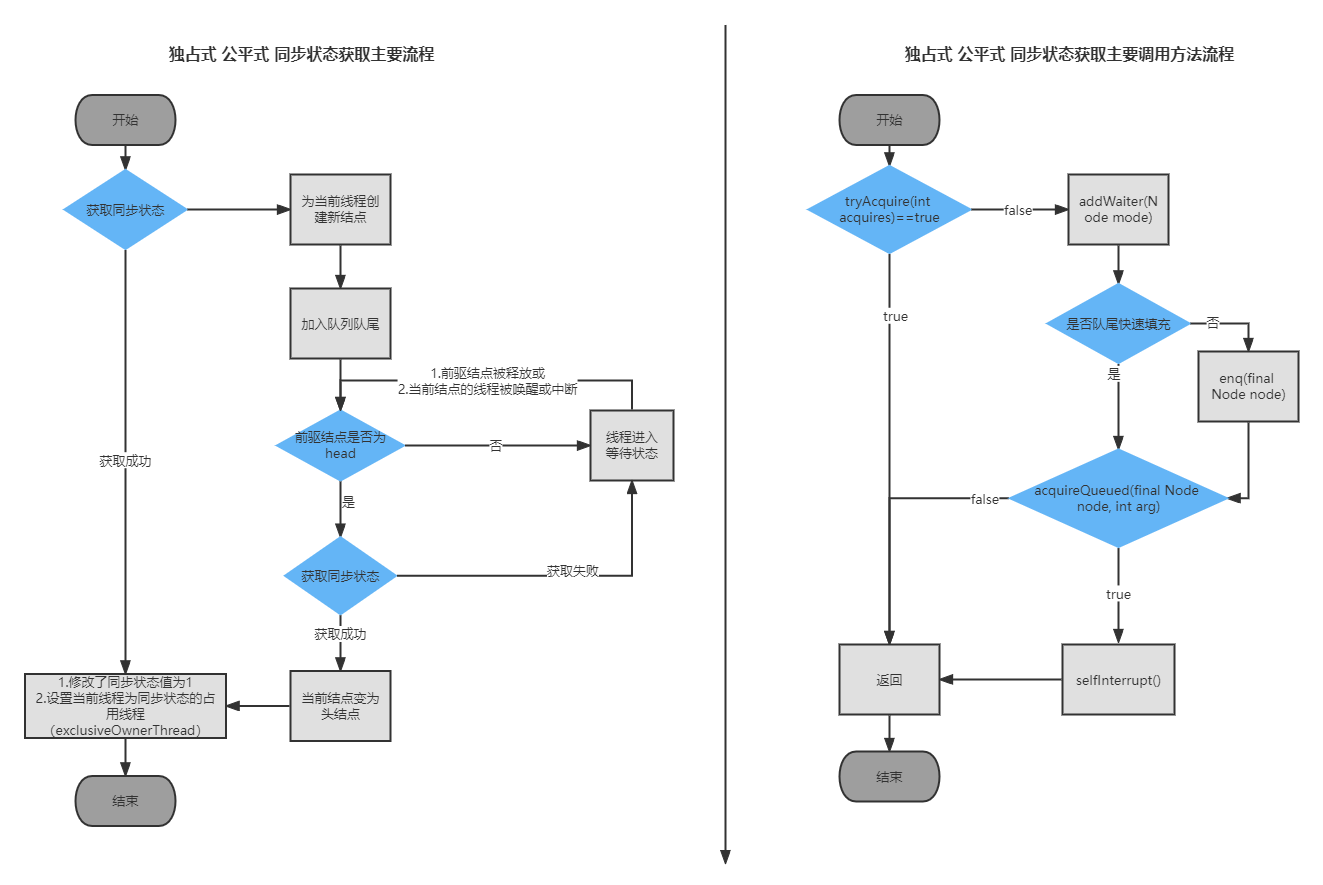
以上述官网独占式获取同步状态为例,在使用sync.acquire(1);获取同步状态失败的时候,会执行addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg),先通过compareAndSetTail(pred, node)尝试快速填充队尾,如果填充失败或者当没有尾结点时,去调用enq(final Node node)进行队列初始化,通过compareAndSetHead(Node update)和compareAndSetTail(Node expect, Node update)来设置AQS的head结点和tail结点。在完成addWaiter之后,继续执行acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg),如果当前结点的前驱结点是首结点,再次尝试获同步状态,若成功,将当前结点更新head结点,若失败,进行线程park,等待前驱结点释放锁唤醒当前线程,若期间当前线程中断,也会被唤醒。若发生异常情况, 会通过cancelAcquire(Node node) 取消继续获取(资源)。
锁获取的主要流程图如下:
独占锁的释放主要通过调用release(int arg)来释放锁。
源码部分
addWaiter(Node mode)
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
// 为当前线程构建一个Node,独占模式
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
// Try the fast path of enq; backup to full enq on failure
Node pred = tail;
// 当队列尾结点不为空,快速填充队尾
if (pred != null) {
node.prev = pred;
// 比较pred是否为尾结点,是则将尾结点设置为node
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {
pred.next = node;
return node;
}
}
// 尾结点为空(即还没有被初始化过),或者是compareAndSetTail操作失败,则入队列
enq(node);
return node;
}
enq(final Node node)
private Node enq(final Node node) {
// 无限循环 势必将结点加入队列中
for (;;) {
// 获取AQS当前尾结点
Node t = tail;
// 如果尾结点是null,则进行初始化,新建一个空Node同时作为head结点和tail结点
if (t == null) { // Must initialize
if (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))
tail = head;
} else {
// 尾结点不为空,即已经被初始化过
// 将当前尾结点作为node结点的前置结点
node.prev = t;
// 比较结点t是否为尾结点,若是则将尾结点设置为node
if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {
t.next = node;
return t;
}
}
}
}
acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg)
// 以独占不间断模式获取已在队列中的线程。
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
// 中断标志
boolean interrupted = false;
// 无限循环
for (;;) {
// 获取前置结点
final Node p = node.predecessor();
// 如果前置结点是head且当前线程成功获取到同步状态,将自身结点变为head结点,返回中断标记
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
// 当获取资源失败,更新结点状态并阻塞线程,返回其中断标识
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
// 取消加入队列失败的节点的资源获取
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node)
// 当获取(资源)失败后,检查并且更新结点状态--只有当该节点的前驱结点的状态为SIGNAL时,才可以对该结点所封装的线程进行park操作。否则,将不能进行park操作。
private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) {
// 前置结点的状态
int ws = pred.waitStatus;
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL)
/*
* 前置节点已经设置了使后置结点阻塞等待的信号,因此它可以安全地park。
*/
return true;
if (ws > 0) {
/*
* 前置结点已经取消了等待该锁,从前置结点向前遍历,找到未取消的节点,设置为当前节点的前置结点
*/
do {
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
} while (pred.waitStatus > 0);
pred.next = node;
} else {
/*
* waitStatus必须为0或PROPAGATE。我们需要信号,不是立即park。调用者将需要重试,以确保在park前。它不能获得同步状态。
* 尝试将前驱结点的信号变为SIGNAL
*/
compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL);
}
return false;
}
parkAndCheckInterrupt()
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {
// 将其线程阻塞--线程被唤醒后或中断后会在此后继续执行
LockSupport.park(this);
// 返回当前线程是否已被中断,并对中断标识位进行复位
return Thread.interrupted();
}
cancelAcquire(Node node)
// 取消继续获取(资源)
private void cancelAcquire(Node node) {
// 忽略结点已经不存在的情况
if (node == null)
return;
// 清空node结点的thread
node.thread = null;
// Skip cancelled predecessors
// 保存node的前驱结点,如果前驱节点已经是取消的状态,则一直向前遍历,取不是取消状态的结点作为当前结点的前驱结点
Node pred = node.prev;
while (pred.waitStatus > 0)
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
// predNext is the apparent node to unsplice. CASes below will
// fail if not, in which case, we lost race vs another cancel
// or signal, so no further action is necessary.
// 获取前驱结点的下一个节点(此时应该就是当前结点)
Node predNext = pred.next;
// Can use unconditional write instead of CAS here.
// After this atomic step, other Nodes can skip past us.
// Before, we are free of interference from other threads.
// 将当前结点的状态变为取消
node.waitStatus = Node.CANCELLED;
// If we are the tail, remove ourselves.
// 如果当前结点是尾结点,且将前驱节点成功设置为尾结点,则将前驱节点的下一个节点变为null
if (node == tail && compareAndSetTail(node, pred)) {
compareAndSetNext(pred, predNext, null);
} else {
// If successor needs signal, try to set pred's next-link
// so it will get one. Otherwise wake it up to propagate.
// 当前结点不为尾结点,或者将前驱结点设置为尾结点失败了
int ws;
// 当前驱结点既不是head,它的thread又不为空时,如果前驱节点的状态是SIGNAL或可以讲前驱结点的状态变为SIGNAL,那么可以去获取当前结点的后置结点,如果后置结点不为空,且状态不是取消的话,可以将前驱结点的后置结点直接变为当前结点的后置结点。这样就从队列中去掉了当前结点。
if (pred != head &&
((ws = pred.waitStatus) == Node.SIGNAL ||
(ws <= 0 && compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL))) &&
pred.thread != null) {
Node next = node.next;
if (next != null && next.waitStatus <= 0)
compareAndSetNext(pred, predNext, next);
} else {
// 唤醒node的下一个结点
unparkSuccessor(node);
}
node.next = node; // help GC
}
}
unparkSuccessor(Node node)
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {
/*
* If status is negative (i.e., possibly needing signal) try
* to clear in anticipation of signalling. It is OK if this
* fails or if status is changed by waiting thread.
*/
int ws = node.waitStatus;
// 只要状态不是初始状态或者取消状态,则重置成初始化状态
if (ws < 0)
compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);
/*
* 要取消阻塞的线程在后继节点中,通常是下一个节点。 但如果后继结点已经取消或明显为空,则从尾部向前遍历以找到实际未取消的结点。
* 获取当前结点的后置结点,若后置结点为null或者状态为已取消,则从队尾向前遍历,找到当前结点之后的状态不是已取消的结点,如果此结点不为空,则唤醒。
*/
Node s = node.next;
if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {
// 清空s,重新寻找
s = null;
for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)
if (t.waitStatus <= 0)
s = t;
}
if (s != null)
LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);
}
独占锁的释放主要通过调用release(int arg)来释放锁。
public final boolean release(int arg) {
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
// 释放锁成功,则唤醒head结点的后继结点
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
// 唤醒head结点的后继结点(可能是next,也可能是从tail往前找合适的结点唤醒)
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}
共享式同步状态获取与释放
在阅读这块内容时,可以先读Semaphore和CountDownLatch
共享式的锁是从acquireShared(int arg)方法开始尝试获取。对于获取同步状态失败的线程会进入到doAcquireShared(int arg)中继续执行,同样使用addWaiter(Node.SHARED)填充队列,不过结点是共享模式的。如果当前结点的前驱结点是首结点,尝试获取锁,若成功获取,则执行setHeadAndPropagate(node, r)设置首结点和可能唤醒后继结点;若获取失败,会判断是否park线程和中断标记,等待前驱结点释放锁唤醒当前线程,若期间当前线程中断,也会被唤醒。若发生异常情况, 会通过cancelAcquire(Node node) 取消继续获取(资源)。
acquireShared(int arg)
public final void acquireShared(int arg) {
if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0)
doAcquireShared(arg);
}
doAcquireShared(int arg)
private void doAcquireShared(int arg) {
// 以共享模式的结点填充队列
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED);
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
// 无限循环-以独占不间断模式获取已在队列中的线程。
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();、
// 如果前驱结点是head,尝试获取共享锁
if (p == head) {
int r = tryAcquireShared(arg);
// 获取到锁
if (r >= 0) {
// 更新首结点和共享锁的个数,并可能释放锁
setHeadAndPropagate(node, r);
p.next = null; // help GC
if (interrupted)
selfInterrupt();
failed = false;
return;
}
}
// 当获取资源失败,更新结点状态并阻塞线程,返回其中断标识
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
// 取消加入队列失败的节点的资源获取
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
setHeadAndPropagate(Node node, int propagate)
private void setHeadAndPropagate(Node node, int propagate) {
// 获取调整之前的head结点
Node h = head; // Record old head for check below
// 将结点设置为head结点
setHead(node);
/*
* Try to signal next queued node if:
* Propagation was indicated by caller,
* or was recorded (as h.waitStatus either before
* or after setHead) by a previous operation
* (note: this uses sign-check of waitStatus because
* PROPAGATE status may transition to SIGNAL.)
* and
* The next node is waiting in shared mode,
* or we don't know, because it appears null
*
* The conservatism in both of these checks may cause
* unnecessary wake-ups, but only when there are multiple
* racing acquires/releases, so most need signals now or soon
* anyway.
*/
// 1.若还有共享锁的可用propagate > 0,
// 2.或者原首结点为空
// 3.或者原首结点的状态既没有取消又不是初始状态(其他线程释放了共享锁,存在共享锁可用),
// 4.亦或者现首结点的为空
// 5.或者状态既没有取消又不是初始状态(当新的首结点不是尾结点的时候,它的waitStatus应该为SIGNAL)
if (propagate > 0 || h == null || h.waitStatus < 0 ||
(h = head) == null || h.waitStatus < 0) {
// 获取当前结点的后继结点
Node s = node.next;
// 若后继结点为空或者是共享结点,则触发锁的释放唤醒线程
if (s == null || s.isShared())
doReleaseShared();
}
}
setHead(Node node)
// 将结点设置为head结点-node赋给变量head,并且将线程和前置结点置空
private void setHead(Node node) {
head = node;
node.thread = null;
node.prev = null;
}
doReleaseShared()
private void doReleaseShared() {
// 无限循环
for (;;) {
// 取得首结点
Node h = head;
// 如果首结点不为空且首结点尾结点不是同一个节点的情况下,
if (h != null && h != tail) {
int ws = h.waitStatus;
// 如果首结点的状态是SIGNAL,则尝试将首结点的状态变为初始化状态。如果失败,则继续循环
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) {
if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, Node.SIGNAL, 0))
continue; // loop to recheck cases
// 如果重置状态成功,则唤醒首结点的“后继结点”
unparkSuccessor(h);
}
// 如果首结点的状态是初始化状态且无法将首结点的状态变为PROPAGATE,则继续循环
else if (ws == 0 &&
!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, 0, Node.PROPAGATE))
continue; // loop on failed CAS
}
// 检查首结点有没有发生变化,如果发生变化就需要跳出循环了
if (h == head) // loop if head changed
break;
}
}
共享锁的释放可以通过调用releaseShared(int arg)完成。
public final boolean releaseShared(int arg) {
if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) {
// 释放锁成功,则唤醒head结点的后继结点
doReleaseShared();
return true;
}
return false;
}
独占式与共享式的主要区别
共享式获取允许同一时刻多个线程获取到同步状态。
共享式可以允许其他共享式的访问,独占式不允许其他任何访问。
condition queue 等待队列
ConditionObject实现了Condition接口,可以与Lock配合实现等待/通知模式。它与Object的监视器方法有些区别。
| 对比项 | Object monitor methods | condition |
|---|---|---|
| 前置条件 | 获取对象的锁 | 调用Lock.lock()获取锁 调用Lock.newCondition()获取Condition对象 |
| 调用方式 | 直接调用 如object.wait() | 直接调用 如condition.await() |
| 等待队列个数 | 一个 | 多个 |
| 当前线程释放锁并进入等待状态 | 支持 | 支持 |
| 当前线程释放锁并进入等待状态,在等待状态中不响应中断 | 不支持 | 支持 |
| 当前线程释放锁并进入超时等待状态 | 支持 | 支持 |
| 当前线程释放锁并进入等待状态到将来的某个时间 | 不支持 | 支持 |
| 唤醒等待队列的一个线程 | 支持 | 支持 |
| 唤醒等待队列的全部线程 | 支持 | 支持 |
当前线程在调用这些方法的时候需要提前获取Condition对象关联的锁,Condition对象是由Lock对象创建出来的,由于Condition依赖Lock对象,所以采用了内部类的实现方式,将ConditionObject作为AQS的内部类。
ConditionObject的主要方法
| 方法名称 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| void await() throws InterruptedException | 当前线程进入等待状态(释放锁)直至被通知(signal)或者中断,当前线程将进入运行状态且从await()方法返回的情况,包括 其让线程调用该condition的signal()或者signalAll()方法,而当前线程被选中唤醒 1.其他线程(调用interrupt()方法)中断当前线程 2.如果当前等待线程从await()方法返回,那么表明该线程已经获取了Condition对象对应的锁 |
| long awaitNanos(long nanosTimeout) throws InterruptedException | 当前线程进入等待状态(释放锁)直至被通知(signal)、中断或者超时。返回值表示还有多少时间超时,如果值为负数或0,认定为已经超时。 |
| boolean awaitUntil(Date deadline) throws InterruptedException | 当前线程进入等待状态(释放锁)直至被通知(signal)、中断或者到某个时间。如果到了指定时间还没有被通知唤醒,方法返回false,还没到指定时间被唤醒,方法返回true。 |
| boolean await(long time, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException | 当前线程进入等待状态(释放锁)直至被通知(signal)、中断或者超时。返回true代表超时,返回false代表未超时。 |
| void awaitUninterruptibly() | 当前线程进入等待状态(释放锁)直至被通知(signal),对中断不敏感 |
| void signalAll() | 唤醒所有等待在condition上的线程,能够从等待方法返回的线程必须获得与condition相关联的锁 |
| void signal() | 唤醒一个等待在condition上的线程,该线程能够从等待方法返回,必须获得与condition相关联的锁 |
条件队列的数据结构
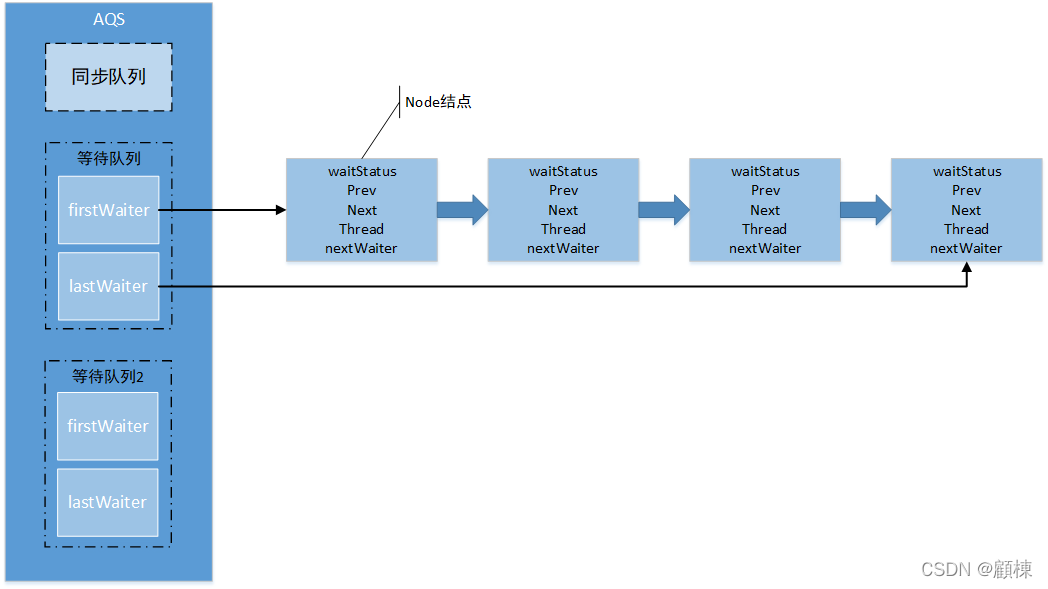
每一个Condition对象都包含一个队列,它是一个单向队列,主要有两个结点对象,firstWaiter指首个结点,lastWaiter指最后一个结点。
等待与通知模式示例
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
public class BoundedQueue<T> {
private Object[] items;
private int addindex, removeindex, count;
private Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private Condition notEmpty = lock.newCondition();
private Condition notFull = lock.newCondition();
public BoundedQueue(int size) {
items = new Object[size];
}
public void add(T t) throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
try {
while (count == items.length) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " is full. " + new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss").format(new Date()));
notFull.await();
}
items[addindex] = t;
if (++addindex == items.length) {
addindex = 0;
}
++count;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " is not empty. " + new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss").format(new Date()));
notEmpty.signal();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public T remove() throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
try {
while (count == 0) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " is empty. " + new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss").format(new Date()));
notEmpty.await();
}
Object x = items[removeindex];
if (++removeindex == items.length) {
removeindex = 0;
}
--count;
notFull.signal();
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread() + " is not full. " + new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss").format(new Date()));
return (T) x;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BoundedQueue m = new BoundedQueue(2);
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
int finalI = i;
executorService.execute(() -> {
try {
m.add(finalI);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
executorService.shutdown();
}
等待
调用condition的await()方法(或者以await开头的方法),会使当前线程进入等待队列并释放锁,同时线程变为等待状态,当从await方法返回时,当前线程一定获取了condition的相关锁。
以await()为例。
await() throws InterruptedException
/**实现可中断条件等待。
1.如果当前线程被中断,则抛出 InterruptedException。
2.保存 getState 返回的锁定状态。
3.使用保存状态作为参数调用释放,如果失败则抛出 IllegalMonitorStateException。
4.阻塞直到发出信号或中断。
5.通过以保存状态作为参数调用特定版本的获取来重新获取。
6.如果在步骤 4 中被阻塞时被中断,则抛出 InterruptedException。*/
public final void await() throws InterruptedException {
// 线程被中断,退出等待
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
// 等待队列中新增结点
Node node = addConditionWaiter();
// 获取当前锁的状态,同时释放锁
int savedState = fullyRelease(node);
int interruptMode = 0;
// 如果结点不在同步队列,则挂起对应线程,直到被唤醒或者发生中断退出循环--等待发生在此
while (!isOnSyncQueue(node)) {
LockSupport.park(this);
if ((interruptMode = checkInterruptWhileWaiting(node)) != 0)
break;
}
// 获取锁 且在退出等待时 不需要抛出中断异常,退出等待时需要重新中断
if (acquireQueued(node, savedState) && interruptMode != THROW_IE)
interruptMode = REINTERRUPT;
// 结点还存在后继结点时,在condition队列中从首结点开始遍历队列,清除状态不为CONDITION的结点
if (node.nextWaiter != null) // clean up if cancelled
unlinkCancelledWaiters();
// 如果发生过中则需要根据中断类型,进行重新中断或者中断异常抛出处理
if (interruptMode != 0)
reportInterruptAfterWait(interruptMode);
}
addConditionWaiter()
// 从队尾填充等待队列
private Node addConditionWaiter() {
Node t = lastWaiter;
// 如果发现尾结点已经被取消了,则动态清理整个队列并寻找新尾结点
if (t != null && t.waitStatus != Node.CONDITION) {
// 在condition队列中从首结点开始遍历队列,清除状态不为CONDITION的结点
unlinkCancelledWaiters();
t = lastWaiter;
}
// 构建等待队列节点
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), Node.CONDITION);
// 队列为空用当前结点作为首结点
if (t == null)
firstWaiter = node;
// 为尾结点增加后继结点
else
t.nextWaiter = node;
// 更新尾结点
lastWaiter = node;
return node;
}
unlinkCancelledWaiters()
// 在condition队列中从首结点开始遍历队列,清除状态为不为CONDITION的结点
private void unlinkCancelledWaiters() {
// 首结点开始遍历队列 获取接结点
Node t = firstWaiter;
// 临时尾结点
Node trail = null;
// 当首结点不为空,
while (t != null) {
// 获取后继结点
Node next = t.nextWaiter;
// 结点的不是在condition队列上
if (t.waitStatus != Node.CONDITION) {
// 清空首结点的后继结点
t.nextWaiter = null;
// 新的队列还没有首结点进行初始化:将后继结点变为新首结点
if (trail == null)
firstWaiter = next;
// 填充新链表
else
trail.nextWaiter = next;
// 后继结点是空,说明当前首结点也是尾结点,那么新链表的首尾结点都是空(trail)
if (next == null)
lastWaiter = trail;
}
// 如果节点在condition队列上,将这个结点作为临时尾结点
else
trail = t;
// 遍历下一个结点
t = next;
}
}
fullyRelease(Node node)
final int fullyRelease(Node node) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
int savedState = getState();
// 尝试释放锁,唤醒首结点的线程
if (release(savedState)) {
failed = false;
return savedState;
} else {
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
}
} finally {
if (failed)
node.waitStatus = Node.CANCELLED;
}
}
boolean isOnSyncQueue(Node node)
// 如果一个节点(始终是最初放置在条件队列中的节点)现在正在等待重新获取同步队列,则返回 true。
final boolean isOnSyncQueue(Node node) {
if (node.waitStatus == Node.CONDITION || node.prev == null)
return false;
if (node.next != null) // If has successor, it must be on queue
return true;
/*
* node.prev 可以是非空的,但尚未在队列中,因为将其放入队列的 CAS 可能会失败。 所以我们必须从尾部遍历以确保它确实成功了。 在调用这个方法时它总是 * 在尾部附近,除非 CAS 失败(这不太可能),它会在那里,所以我们几乎不会遍历太多
*/
return findNodeFromTail(node);
}
唤醒
signalAll唤醒条件队列全部结点
public final void signalAll() {
// 如果不是独占,即异常
if (!isHeldExclusively())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
Node first = firstWaiter;
// 只要队列不空,就执行唤醒
if (first != null)
doSignalAll(first);
}
doSignalAll(Node first)
private void doSignalAll(Node first) {
lastWaiter = firstWaiter = null;
do {
// 获取首结点的后继结点
Node next = first.nextWaiter;
// 清空首结点的后继结点域
first.nextWaiter = null;
// 唤醒首结点
transferForSignal(first);
// 更替首结点
first = next;
} while (first != null);
}
transferForSignal(Node node)
final boolean transferForSignal(Node node) {
/*
* If cannot change waitStatus, the node has been cancelled.
* 结点已经取消后,不需要唤醒
*/
if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, Node.CONDITION, 0))
return false;
/*
* Splice onto queue and try to set waitStatus of predecessor to
* indicate that thread is (probably) waiting. If cancelled or
* attempt to set waitStatus fails, wake up to resync (in which
* case the waitStatus can be transiently and harmlessly wrong).
*/
// 将结点加入同步队列,取出结点的前驱结点,如果前驱结点的状态不是初始化或将无法将前驱结点的状态更新为SIGNAL,则唤醒结点线程。
Node p = enq(node);
int ws = p.waitStatus;
if (ws > 0 || !compareAndSetWaitStatus(p, ws, Node.SIGNAL))
LockSupport.unpark(node.thread);
return true;
}
signal唤醒单个结点
signal()
public final void signal() {
if (!isHeldExclusively())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
Node first = firstWaiter;
if (first != null)
doSignal(first);
}
doSignal(Node first)
private void doSignal(Node first) {
do {
// 更新首结点 将首结点后移一位
if ( (firstWaiter = first.nextWaiter) == null)
// 新首结点为null则尾结点也为null
lastWaiter = null;
// 分离旧首结点与链表
first.nextWaiter = null;
} while (!transferForSignal(first) && // 唤醒首结点失败且新的首结点不是null则继续唤醒
(first = firstWaiter) != null);
}
同步队列与条件队列的关系
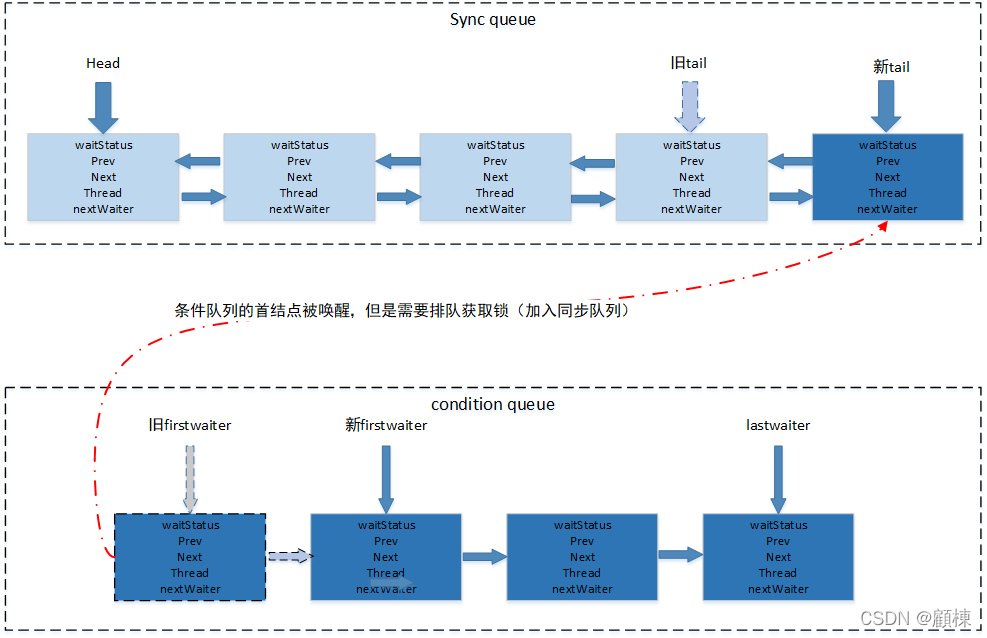
上图简单体现了节点从从condition queue转移到sync queue上去的过程。即使是调用signalAll时,节点也是一个一个转移过去的,因为每个节点都需要重新建立sync queue的链接。
