Refactor:Duplicated code
02重复代码
什么是重复代码?
定义:在一个以上的地点看到相同或相似的代码结构。
影响:想要修改其中一段代码逻辑需要修改多次,易遗漏,难维护。
改进目标:消除重复,提升可维护性的目标。
方法:提炼函数,移动语句,函数上移等重构方法。
案例1:同一个类的两个函数含有相同的表达式
/**
* 计算水果总价(同一个类的两个函数含有相同的表达式)
*
* @since 2021-08-18
*/
public class FruitsCost {
public double computeMoneyWithoutPrivileges(String type, int numbers) {
double prices;
switch (type) {
case "apple":
prices = 5.5;
break;
case "banana":
prices = 4.0;
break;
case "strawberry":
prices = 10.5;
break;
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal type : " + type);
}
return prices * numbers;
}
public double computeMoneyWithPrivileges(String type, double numbers, double discount) {
double prices;
switch (type) {
case "apple":
prices = 5.5;
break;
case "banana":
prices = 4.0;
break;
case "strawberry":
prices = 10.5;
break;
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal type : " + type);
}
return prices * numbers * discount;
}
}
代码背景:两个函数根据水果类型获得单价并计算水果费用;其中一个函数全价购买,一个函数打折购买;
症状/问题:两个函数在获得水果单价的代码是一致的,如果其中一
种水果单价出现变化,则需要同时修改两处
重构方法:
我们重构的方法是这样,把相同部分的代码提取出来成一个方法,然后原代码处调用这个提取代码的方法即可。
如果你用的是idea,可以这样做:
选中重复的代码,按ctrl+shift+M(提取方法),出现一个窗口,我们可以修改访问级别,一般用private,毕竟是在类的内部使用,可以给方法命名,下面还有预览方法,确定好最后点refactor
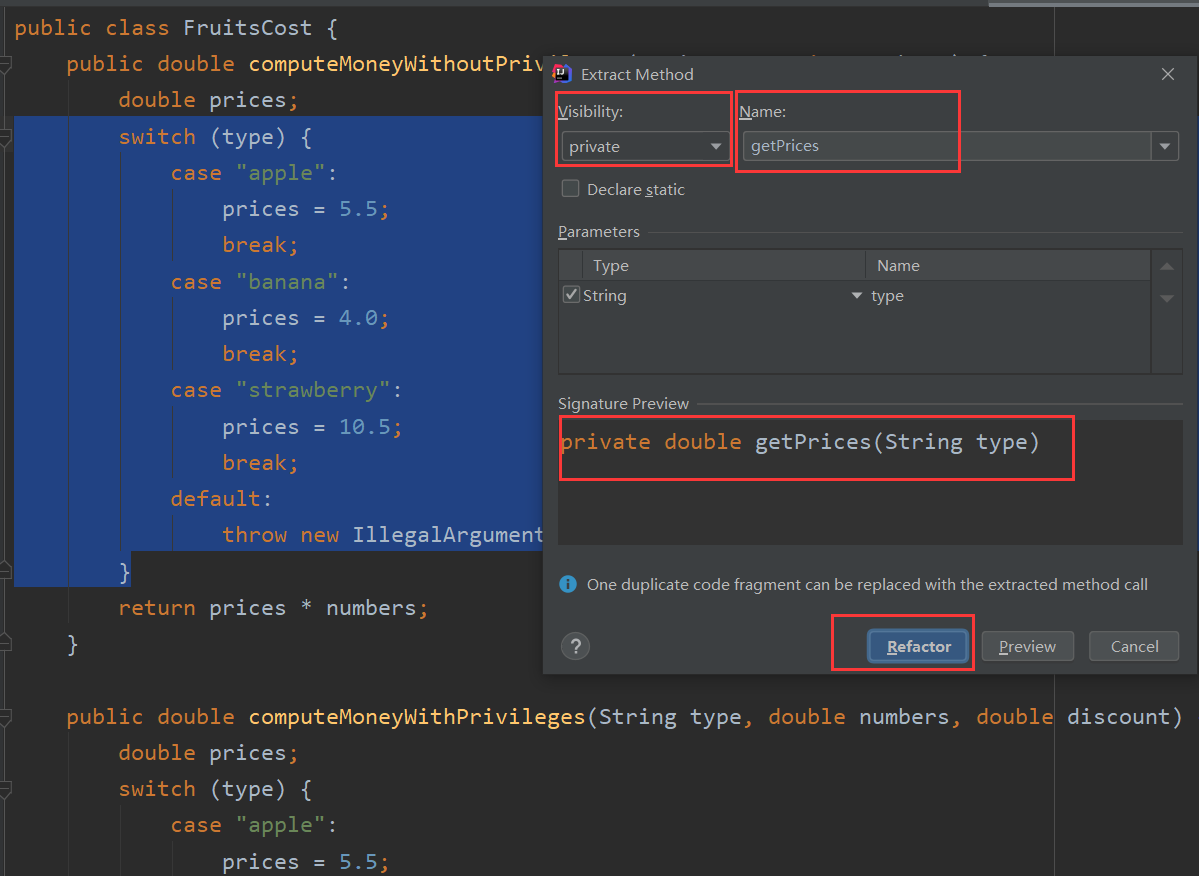
然后他会提示其它方法的相同的代码(绿色部分),点replaces一起提取即可。
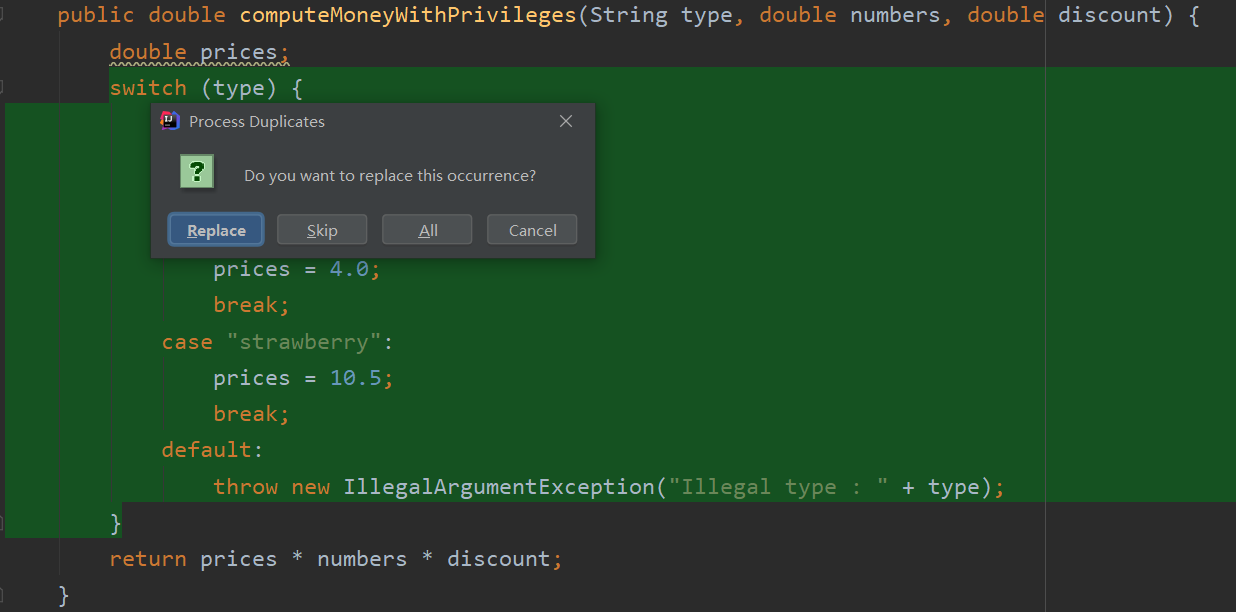
重构后
public class FruitsCost {
public double computeMoneyWithoutPrivileges(String type, int numbers){
return getPrices(type) * numbers;
}
public double computeMoneyWithPrivileges(String type, double numbers, double discount){
return getPrices(type) * numbers * discount;
}
private double getPrices(String type) {
double prices;
switch (type) {
case "apple":
prices = 5.5;
break;
case "banana":
prices = 4.0;
break;
case "strawberry":
prices = 10.5;
break;
default:
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal type : " + type);
}
return prices;
}
}
案例2:两个互为兄弟的子类含有相同的表达式
/**
* 水果利润(两个互为兄弟的子类含有相同的表达式)
*
* @since 2021-08-18
*/
class Fruits {
// 成本单价
public double costPrices;
// 出售单价
public double prices;
// 最小出货量
public double minSaleableNum;
}
/**
* 苹果利润(两个互为兄弟的子类含有相同的表达式)
*
* @since 2021-08-18
*/
class Apple extends Fruits {
public Apple(double costPrices, double prices, double minSaleableNum) {
this.costPrices = costPrices;
this.minSaleableNum = minSaleableNum;
this.prices = prices;
}
public double profitMoney(int number) {
return Math.max(0, number - minSaleableNum) * this.prices - this.costPrices * number;
}
}
/**
* 香蕉利润(两个互为兄弟的子类含有相同的表达式)
*
* @since 2021-08-18
*/
class Banana extends Fruits {
public Banana(double costPrices, double prices, double minSaleableNum) {
this.costPrices = costPrices;
this.minSaleableNum = minSaleableNum;
this.prices = prices;
}
public double profitMoney(int number) {
return Math.max(0, number - minSaleableNum) * this.prices - this.costPrices * number;
}
}
代码背景:代码由水果父类,以及苹果香蕉两个子类组成。计算每种水果的销售利润。考虑运费、存储、破损等成本,计算毛利润时,需要从销量中减去最小出货量。
症状:两个子类计算利润的方法完全一致,如果计算利润方式出现变化,则需要修改多个子类。
重构方法
我们可以把这些子类都有的方法提取,放到父类中。比如这个例子,把所有水果类中的profitMoney方法都提取到Fruits类中,只写一次。当我们添加新的水果子类时,不需要再写该方法;当计算利润方式发生变化时,我们只需要修改Fruits类中的方法即可,只需要修改一次;当其中某中水果有特殊的计算方式,我们只需要重写该子类的方法。这正好适应了面向对象继承和方法重写的特性。
如果你用idea,你可以用快捷键来重构。
将鼠标光标放到需要提取的方法上,按ctrl+shift+alt+T,或者右键到refator中,找到Pull Members Up,点击Refoctor,这样代码就提取到父类中了。
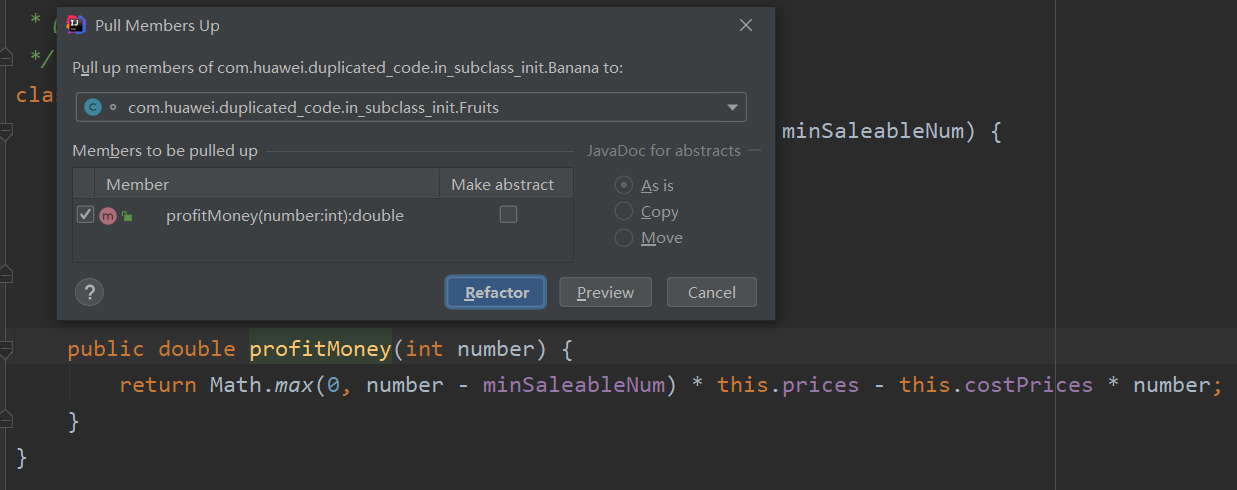
重构后代码
把子类中的重复方法提取到父类中
class Fruits {
// 成本单价
public double costPrices;
// 出售单价
public double prices;
// 最小出货量
public double minSaleableNum;
public double profitMoney(int number) {
return Math.max(0, number - minSaleableNum) * this.prices - this.costPrices * number;
}
}
案例3:代码片段中语句有可能增删改,功能不变
/**
* 月份判断(代码片段中语句有可能增删改,功能不变)
*
* @since 2021-08-18
*/
class MonthJudgement {
public boolean judgeMonth() {
Long timeStamp = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 获取当前时间戳
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
String date = sdf.format(new Date(Long.parseLong(String.valueOf(timeStamp))));
String month = date.split(" ")[0].split("-")[1];
return "12".equals(month);
}
}
/**
* 年份判断(代码片段中语句有可能增删改,功能不变)
*
* @since 2021-08-18
*/
class YearJudgement {
public boolean judgeYear() {
Long time = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 获取当前时间戳
System.out.println("获得当前时间戳");
SimpleDateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
String date = dateFormat.format(new Date(Long.parseLong(String.valueOf(time))));
return date.startsWith("2021");
}
}
代码背景
重复代码出现在不同的类中。代码逻辑不完全一致,变量名不同分别为time和timeState, judgeYear多 了一条打印语句。
症状
两个类中函数judgeMonth和judgeYear函数逻辑基本上是一致,只是个别不相同的地方,如果修改时间格式,需要同时修改两处。
重构方法
把鼠标放在代码上,按ctrl+shift+上/下,可以移动语句,在方法上可以调动位置。注意你需要先确认这样不会改变业务逻辑,才可进行。然后才可以提取相同的代码。还可以搬移函数,放到其他的类中,如果使用快捷键(F6),需要先将抽取出来的方法改为静态。
重构后代码
/**
* 日期转换
*
* @since 2021-08-18
*/
public class DateFormatter {
public static String getDate() {
Long timeStamp = System.currentTimeMillis(); // 获取当前时间戳
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
return sdf.format(new Date(Long.parseLong(String.valueOf(timeStamp))));
}
}
/**
* 月份判断(代码片段中语句有可能增删改,功能不变)
*
* @since 2021-08-18
*/
class MonthJudgement {
public boolean judgeMonth() {
String date = DateFormatter.getDate();
String month = date.split(" ")[0].split("-")[1];
return "12".equals(month);
}
}
/**
* 年份判断(代码片段中语句有可能增删改,功能不变)
*
* @since 2021-08-18
*/
class YearJudgement {
public boolean judgeYear() {
System.out.println("获得当前时间戳");
String date = DateFormatter.getDate();
return date.startsWith("2021");
}
}
