mysql8 实现读写分离有很多种方法。本文比较全面的总结了目前可用的方法。
其中原生的jdbc负载均衡和读写分离推荐使用,再则是基于mysql router 的方式也推荐使用,这两种方法稳定,且轻量级。
mysql8 读写分离负载均衡方法总结
1. spring 多数动态据源负载均衡

源码如下:
com.common.spring.db.DynamicDataSource
public class DynamicDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
@Override
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
return DsHolder.get();
}
}
定义切面
<bean id="dataSourceAdvice" class="com.common.spring.db.DataSourceAdvice"></bean>
<!-- 动态切换数据源 方法拦截器
1. 注解形式切换数据源
1.1此拦截器只会拦截以*DAO 结尾的类
1.2. 在DAO 中用以下方法切换,方法签名如下
@DataSource("read")
public List<TSSysUserinf> queryAllBybm();
1.3. mapper 文件的写法没有变化
1.4. 目前不支持分布式事务
2. 如何用代码切换数据源:
List<TSSysUserinf> result=DsHolder.execute("read", new IChangeDsCallback<List<TSSysUserinf>>() {
@Override
public List<TSSysUserinf> execute(String dsName) {
return service.queryByAll(params);
}
} );
-->
<bean id="dataSourceAdviceBeanNameAutoProxyCreator" class="org.springframework.aop.framework.autoproxy.BeanNameAutoProxyCreator" >
<property name="proxyTargetClass" value="true"></property>
<property name="beanNames" value="*Service,I*Service" />
<property name="interceptorNames">
<list>
<value>dataSourceAdvice</value>
</list>
</property>
<property name="order" value="99"/>
</bean>
2. 第三方库 ShardingSphere-JDBC,myCat 负载均衡
参考文档 https://shardingsphere.apache.org/document/current/cn/overview/#shardingsphere-proxy
https://dbaplus.cn/news-11-1854-1.html 对比总结,分析的很好

3. 原生jdbc 负载均衡(推荐使用)
支持复制的jdbc
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/connector-j/8.0/en/connector-j-source-replica-replication-connection.html
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/connector-j/8.0/en/connector-j-usagenotes-j2ee-concepts-managing-load-balanced-connections.html
https://blog.csdn.net/li_xiang_996/article/details/106195812
https://blog.51cto.com/xsunday/2049682 使用样例
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/62279901 参数解释
1、readFromMasterWhenNoSlaves readFromSourceWhenNoReplicas 当所有的salve死掉后,此参数用来控制主库是否参与读。如果从库的流量很大,配置此参数对主库有很大风险;但如果你关掉,请求则会快速失败。
2、loadBalanceStrategy 策略用来指定从库的轮询规则。有轮询,也有权重,也可以指定具体的策略实现。当你维护或者迁移某个实例时,先置空流量,这会非常有用。或许,你会给某DB一个预热的可能。
3、allowMasterDownConnections allowSourceDownConnections如果主机当机,当连接池获取新的连接时,会失败。但如果打开此参数,则虚拟连接只会创建Slave连接组,整个连接会降级为只读,不论你设置了什么注解。
4、allowSlavesDownConnections allowReplicasDownConnections=true如果没有只读库了,是否允许创建新的连接。在这种情况下,此参数开启,读操作有很大可能会失败。
5、retriesAllDown 当所有的hosts都无法连接时重试的最大次数(依次循环重试),默认为120。重试次数达到阈值仍然无法获取有效链接,将会抛出SQLException。
6、autoReconnect 实例既然有下线、就有上线。上线以后要能够继续服务,此参数用来控制断线情况下自动重连而不抛出异常。这会破坏事务的完整性,但还是默认开启。
Seamless Reconnection
Although not recommended, you can make the driver perform failovers without invalidating the active Statement or ResultSet instances by setting either the parameter autoReconnect or autoReconnectForPools to true. This allows the client to continue using the same object instances after a failover event, without taking any exceptional measures. This, however, may lead to unexpected results: for example, if the driver is connected to the primary host with read/write access mode and it fails-over to a secondary host in real-only mode, further attempts to issue data-changing queries will result in errors, and the client will not be aware of that. This limitation is particularly relevant when using data streaming: after the failover, the ResultSet looks to be alright, but the underlying connection may have changed already, and no backing cursor is available anymore.
详细的参数配置请参考
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/connector-j/8.0/en/connector-j-source-replica-replication-connection.html
添加jdbc
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.23</version>
</dependency>
Connector/J supports multi-source replication topographies.
The connection URL for replication discussed earlier
(i.e., in the format of jdbc:mysql:replication://source,replica1,replica2,replica3/test)
assumes that the first (and only the first) host is the source host. Supporting deployments with an arbitrary number of sources and replicas requires the “address-equals” URL syntax for multiple host connection discussed in Section 6.2, “Connection URL Syntax”, with the property type=[source|replica];
for example:
jdbc:mysql:replication://address=(type=source)(host=source1host),address=(type=source)(host=source2host),address=
比如以下url:
url : jdbc:mysql:replication://localhost:8024,localhost:8025,localhost:8026,localhost:8024/test?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF8&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&autoReconnect=false&failOverReadOnly=true&roundRobinLoadBalance=true&readFromSourceWhenNoReplicas=true&allowSourceDownConnections=true&allowReplicasDownConnections=true&retriesAllDown=3&connectionLifecycleInterceptors=com.app.common.core.MySqlConnectionLifecycleInterceptor
参数意思解释如下:
allowSourceDownConnections=true
to allow Connection objects to be created even though no source hosts are reachable. Such Connection objects report they are read-only, and isSourceConnection() returns false for them. The Connection tests for available source hosts when Connection.setReadOnly(false) is called, throwing an SQLException if it cannot establish a connection to a source, or switching to a source connection if the host is available
allowReplicasDownConnections=true
to allow Connection objects to be created even though no replica hosts are reachable. A Connection then, at runtime, tests for available replica hosts when Connection.setReadOnly(true) is called (see explanation for the method below), throwing an SQLException if it cannot establish a connection to a replica, unless the property readFromSourceWhenNoReplicas is set to be “true” (see below for a description of the property)
重要:
if you want to allow connection to a source when no replicas are available, set the property readFromSourceWhenNoReplicas to “true.”
Notice that the source host will be used in read-only state in those cases, as if it is a replica host. Also notice that setting readFromSourceWhenNoReplicas=true might result in an extra load for the source host in a transparent manner.
readFromSourceWhenNoReplicas
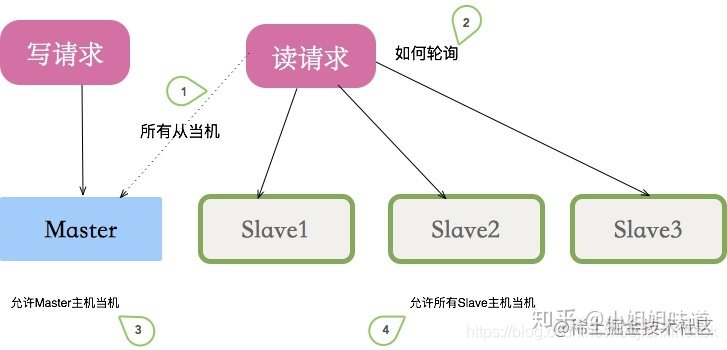
需要把master 放到读库列表中,一般放到最后
协议的第一个连接,表示主库Master
后面的一堆连接,表示从库Slave,当然可以有多个
当你把Master的连接也放在后面的一堆里,那么它也拥有了“读库“的属性了
测试方法如下:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
Properties props = new Properties();
props.put("autoReconnect", "true");
props.put("roundRobinLoadBalance", "true");
props.put("user", "test");
props.put("password", "123456");
String url = "jdbc:mysql:replication://localhost:8024,localhost:8025,localhost:8026/test";
int i = 1;
while (i < 100) {
// 每次获取新的连接,测试是否负载均衡
try (Connection connection = DriverManager.getConnection(url, props)) {
if ((i % 5) == 0) {
PreparedStatement rwStmt = connection.prepareStatement("insert into demo values(?,?)");
connection.setReadOnly(false);// 非只读
connection.setAutoCommit(false);// 只读
rwStmt.setString(1, String.valueOf(i));
rwStmt.setString(2, LocalDateTime.now().toString());
rwStmt.execute();
connection.commit();
rwStmt.close();
} else {
connection.setReadOnly(true);// 只读
}
Statement roStmt = connection.createStatement();
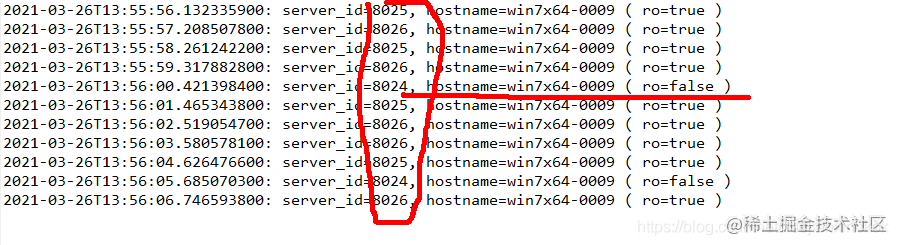
ResultSet rs = roStmt.executeQuery("select @@server_id server_id, @@hostname hostname ");
if (rs.next()) {
String output = LocalDateTime.now().toString() + ": server_id=" + rs.getString("server_id")
+ ", hostname=" + rs.getString("hostname");
output += " ( ro=" + connection.isReadOnly() + " )";
System.out.println(output);
}
rs.close();
roStmt.close();
Thread.sleep(1000);
i++;
} // end try
} // end while
}
注意事项: 复制库对于超级用户root 来说是可写入的,在应用中需要创建一个普
通用户,防止从库被写入
需要访问普通用户
CREATE USER 'test'@'%' IDENTIFIED BY '123456';
--授权 test 数据库给 'test'@'%'
GRANT ALL ON test.* TO 'test'@'%';
在mysql 配置文件中从库需要配置
#对普通用户只读,对超级用户root没用
read_only=ON
如果是注解式事物添加注解
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
@Bean("myTransactionInterceptor")
public TransactionInterceptor myTransactionInterceptor() {
NameMatchTransactionAttributeSource source = new NameMatchTransactionAttributeSource();
// 只读事务,不做更新操作
RuleBasedTransactionAttribute readOnlyTx = new RuleBasedTransactionAttribute();
readOnlyTx.setReadOnly(true);
//PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS 如果当前有事务则加入,如果没有则不用事务
//readOnlyTx.setPropagationBehavior(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS);
//支持当前事务,如果当前有事务, 那么加入事务, 如果当前没有事务则新建一个(默认情况)
readOnlyTx.setPropagationBehavior(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED); //需要重新设置事物的传播属性
//支持当前事务,如果当前有事务, 那么加入事务, 如果当前没有事务则新建一个(默认情况)
RuleBasedTransactionAttribute requiredTx = new RuleBasedTransactionAttribute(
TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED,
Collections.singletonList(new RollbackRuleAttribute(Exception.class)));
// requiredTx.setTimeout(5);//设置超时
Map<String, TransactionAttribute> txMap = new HashMap<>();
txMap.put("*", readOnlyTx);// 只读事务
txMap.put("save*", requiredTx);
txMap.put("insert*", requiredTx);
txMap.put("update*", requiredTx);
txMap.put("delete*", requiredTx);
source.setNameMap(txMap);
return new TransactionInterceptor(transactionManager, source);
}
生命周期管理 connectionLifecycleInterceptors
接口
com.mysql.cj.jdbc.interceptors.ConnectionLifecycleInterceptor
样例
&connectionLifecycleInterceptors=com.app.common.core.MySqlConnectionLifecycleInterceptor
A comma-delimited list of classes that implement “com.mysql.cj.jdbc.interceptors.ConnectionLifecycleInterceptor” that should notified of connection lifecycle events
(creation, destruction, commit, rollback, setting the current database and changing the autocommit mode) and potentially alter the execution of these commands.
ConnectionLifecycleInterceptors are “stackable”, more than one interceptor may be specified via the configuration property as a comma-delimited list,
with the interceptors executed in order from left to right

查询拦截 queryInterceptors
queryInterceptors, where you specify the fully qualified names of classes that implement the com.mysql.cj.interceptors.QueryInterceptor interface. In these kinds of interceptor classes, you might change or augment the processing done by certain kinds of statements, such as automatically checking for queried data in a memcached server, rewriting slow queries, logging information about statement execution, or route requests to remote servers
A comma-delimited list of classes that implement “com.mysql.cj.interceptors.QueryInterceptor” that should be placed “in between” query execution to influence the results. QueryInterceptors are “chainable”, the results returned by the “current” interceptor will be passed on to the next in in the chain, from left-to-right order, as specified in this property.

连接验证
https://dev.mysql.com/doc/connector-j/8.0/en/connector-j-usagenotes-j2ee-concepts-connection-pooling.html
specify a validation query in your connection pool that starts with /* ping */. Note that the syntax must be exactly as specified. This will cause the driver send a ping to the server and return a dummy lightweight result set. When using a ReplicationConnection or LoadBalancedConnection, the ping will be sent across all active connections.
————————————————
4. nginx tcp 代理负载均衡 和 HAProxy 代理
4.1 NGINX 配置
stream {
upstream tcp8021 {
#hash $remote_addr consistent; #负载方法
server localhost:8025 max_fails=5 fail_timeout=30s;
server localhost:8026 max_fails=5 fail_timeout=30s;
}
server {
listen 8021;
proxy_connect_timeout 60;
proxy_timeout 300s;
proxy_pass tcp8021;
}
}
4.2 HAPROXY 配置
#vi /etc/kubernetes/haproxy.cfg
global
log 127.0.0.1 local2
chroot /var/lib/haproxy
pidfile /var/run/haproxy.pid
maxconn 4096
user haproxy
group haproxy
daemon
stats socket /var/lib/haproxy/stats
defaults
mode http
log global
option httplog
option dontlognull
option http-server-close
option forwardfor except 127.0.0.0/8
option redispatch
retries 3
timeout http-request 10s
timeout queue 1m
timeout connect 10s
timeout client 1m
timeout server 1m
timeout http-keep-alive 10s
timeout check 10s
maxconn 3000
frontend mysql-server
mode tcp
bind *:3306
option tcplog
default_backend mysql-server-backend
listen stats
mode http
bind *:8888
stats auth admin:password
stats refresh 5s
stats realm HAProxy\ Statistics
stats uri /stats
log 127.0.0.1 local3 err
backend mysql-server-backend
mode tcp
balance roundrobin
server mysql01 172.16.10.138:3306 check
server mysql02 172.16.10.137:3306 check
server mysql03 172.16.10.139:3306 check
5. mysql router 读写分离负载均衡(推荐)
[DEFAULT]
base_dir = D:/soft/mysql/mysqlrouter8023
logging_folder={base_dir}/data/log
runtime_folder={base_dir}/data/run
data_folder ={base_dir}/data/data
[logger]
#level = INFO
level = DEBUG
[routing:db1]
bind_address=0.0.0.0
bind_port=8020
destinations=127.0.0.1:8024
mode=read-write
client_connect_timeout=6
connect_timeout=3
max_connections=2048
[routing:db2]
bind_address=0.0.0.0
bind_port=8021
destinations=127.0.0.1:8025,127.0.0.1:8026
mode=read-only
client_connect_timeout=6
connect_timeout=3
max_connections=1024
