本文主要围绕三个问题展开?
- 1.spirng是怎么和mybatis关联起来的?
- 2.xml和mapper是如何解析的
- 3.mapper中的方法是怎么和xml中的方法关联起来的?
Spirng是怎么和mybatis关联起来的
在基本的 MyBatis 中,session 工厂可以使用 SqlSessionFactoryBuilder 来创建。而在MyBatis-Spring 中,则使用 SqlSessionFactoryBean 来替代。
spring-mybatis包中有一个类SqlSessionFactoryBean
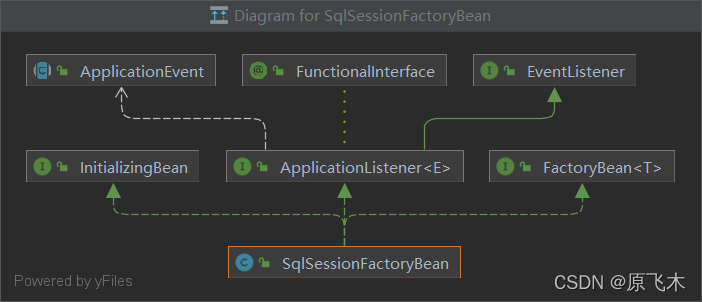
SqlSessionFactoryBean 实现了 Spring 的 FactoryBean 接口这就说明了由 Spring 最终创建的 bean 不是 SqlSessionFactoryBean 本身,。而是工厂类的 getObject()返回的方法的结果。
@Override
public SqlSessionFactory getObject() throws Exception {
if (this.sqlSessionFactory == null) {
// sqlSessionFactory默认为空,直接走afterPropertiesSet()方法
// 实际不是这样的,由于SqlSessionFactoryBean实现了InitializingBean,则再该bean生成之后,
// 会直接调用afterPropertiesSet()方法,来创建sqlSessionFactory,故sqlSessionFactory应该
// 是已经被创建好的
afterPropertiesSet();
}
return this.sqlSessionFactory;
}
如果sqlSessionFactory为空的话就调用afterPropertiesSet();方法,该方法是重写InitializingBean的方法,在bean初始化的时候就会执行。
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
notNull(dataSource, "Property 'dataSource' is required");
notNull(sqlSessionFactoryBuilder, "Property 'sqlSessionFactoryBuilder' is required");
state((configuration == null && configLocation == null) || !(configuration != null && configLocation != null),
"Property 'configuration' and 'configLocation' can not specified with together");
this.sqlSessionFactory = buildSqlSessionFactory();
}
做了一些环境前置的判断。然后执行buildSqlSessionFactory();构建sqlSessionFactory
核心内容是对于 mapperLocations 的解析,如下代码
protected SqlSessionFactory buildSqlSessionFactory() throws Exception {
final Configuration targetConfiguration;
XMLConfigBuilder xmlConfigBuilder = null;
//....省略代码
/**
* mapperLocations里面就是xml文件
* 把xml文件进行解析(重要)
*/
if (this.mapperLocations != null) {
if (this.mapperLocations.length == 0) {
LOGGER.warn(() -> "Property 'mapperLocations' was specified but matching resources are not found.");
} else {
for (Resource mapperLocation : this.mapperLocations) {
if (mapperLocation == null) {
continue;
}
try {
XMLMapperBuilder xmlMapperBuilder = new XMLMapperBuilder(mapperLocation.getInputStream(),
targetConfiguration, mapperLocation.toString(), targetConfiguration.getSqlFragments());
//解析mapper文件
xmlMapperBuilder.parse();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new NestedIOException("Failed to parse mapping resource: '" + mapperLocation + "'", e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Parsed mapper file: '" + mapperLocation + "'");
}
}
} else {
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Property 'mapperLocations' was not specified.");
}
return this.sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(targetConfiguration);
}
这里主要就是构建一个Configuration对象,在最后利用这个对象去构建一个sqlSessionFactory。
this.sqlSessionFactoryBuilder.build(targetConfiguration)
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder支持不同的方式去创建SqlSessionFactory。(SqlSessionFactoryBuilder是mybatis源码里面的类了)
- 如通过配置文件,如:mybatis-config.xml,以前ssm那一套
- 通过IO流
- 通过Configuration参数
public SqlSessionFactory build(Configuration config) {
return new DefaultSqlSessionFactory(config);
}
xml和mapper是如何解析的
进入xmlMapperBuilder.parse();
public void parse() {
// 1.如果 resource 没被加载过才进行加载
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
// 1.1 解析 mapper 文件
configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));
// 1.2 将 resource 添加到已加载列表
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
// 1.3 绑定 namespace 的 mapper
bindMapperForNamespace();
}
parsePendingResultMaps();
parsePendingCacheRefs();
parsePendingStatements();
}
configurationElement
//context就是一个mapper.xml的内容
private void configurationElement(XNode context) {
try {
// 1.获取namespace属性
String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");
if (namespace == null || namespace.isEmpty()) {
throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty");
}
// 2.设置currentNamespace属性
builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);
// 3.解析parameterMap、resultMap、sql等节点
cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref"));
cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache"));
parameterMapElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap"));
resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap"));
sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql"));
// 4.解析增删改查节点,封装成 Statement
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing Mapper XML. The XML location is '" + resource + "'. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
private void buildStatementFromContext(List<XNode> list) {
if (configuration.getDatabaseId() != null) {
buildStatementFromContext(list, configuration.getDatabaseId());
}
// 解析增删改查节点,封装成Statement
buildStatementFromContext(list, null);
}
这里的每个Xnode就是对应一个方法
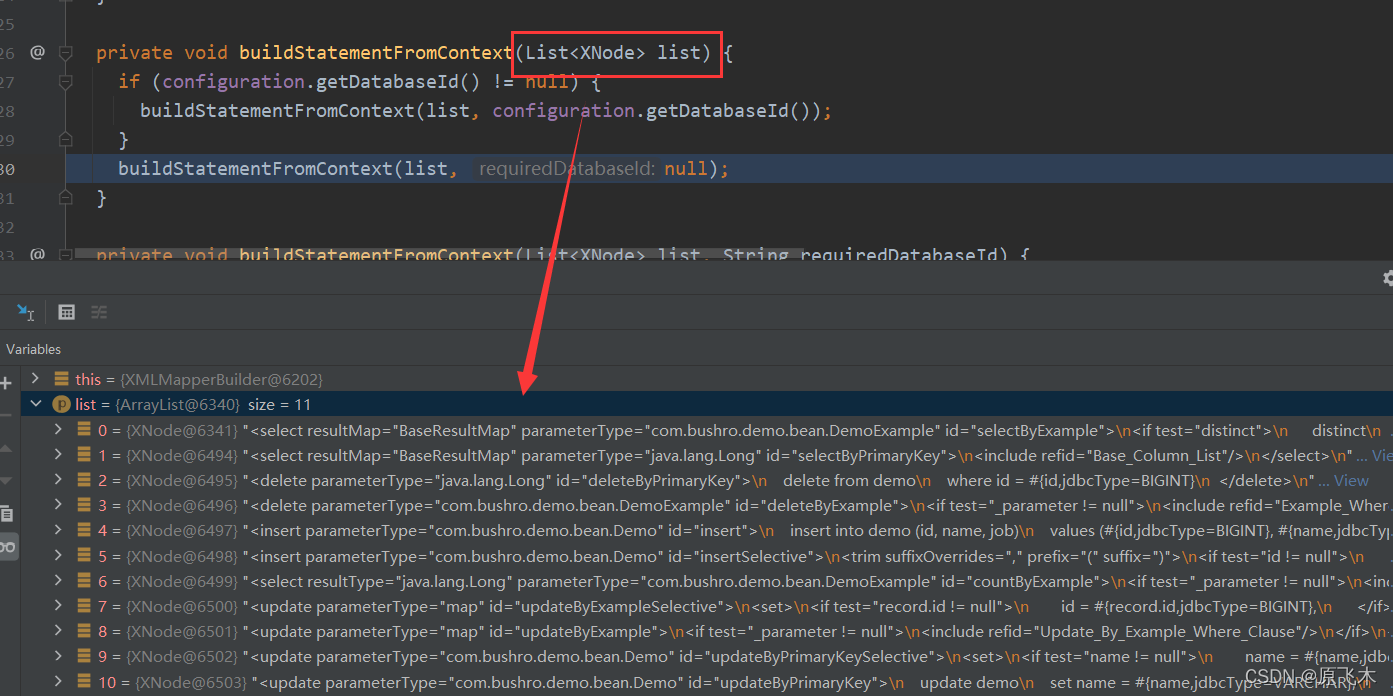
解析节点构建成一个MappedStatement对象,最后 放到Configuration中的Map<String, MappedStatement> mappedStatements变量中
private void buildStatementFromContext(List<XNode> list, String requiredDatabaseId) {
for (XNode context : list) {
// 1.构建XMLStatementBuilder
final XMLStatementBuilder statementParser = new XMLStatementBuilder(configuration, builderAssistant, context, requiredDatabaseId);
try {
// 2.解析节点
statementParser.parseStatementNode();
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteStatement(statementParser);
}
}
}
一次put会放入两个值,key不同但是value是一样的。MappedStatement就是一个sql方法。所以通过这两种key都可以找到对应的sql。
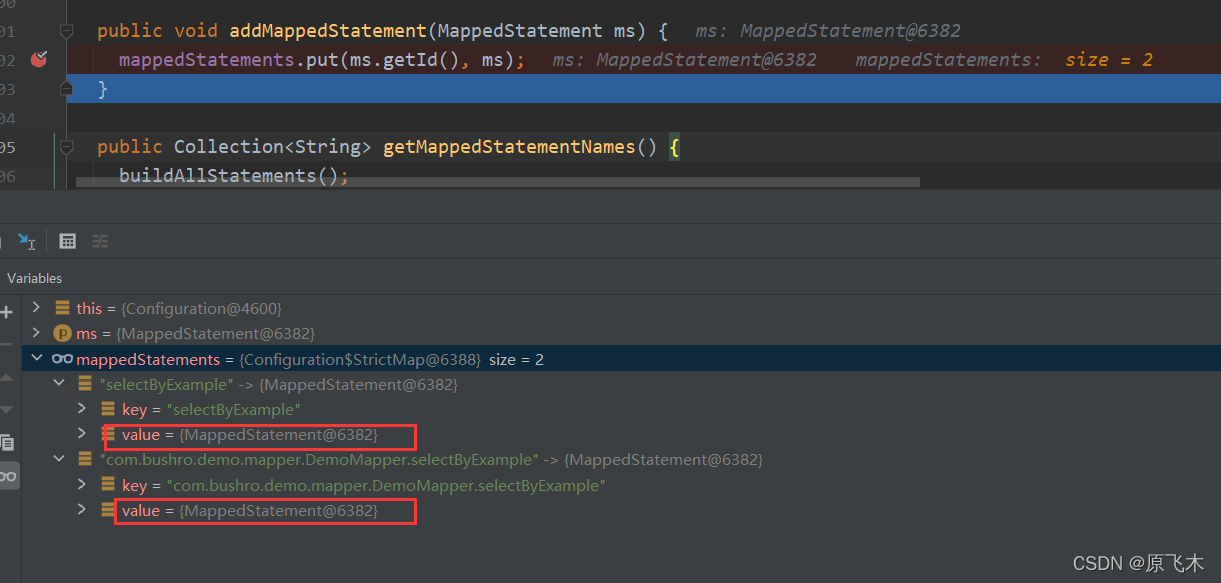
bindMapperForNamespace
- 通过之前解析xml得到的namespace获取到对应的Class
- 放到
Map<Class<?>, MapperProxyFactory<?>> knownMappers变量中
private void bindMapperForNamespace() {
// 找出当前的命名空间
String namespace = builderAssistant.getCurrentNamespace();
if (namespace != null) {
Class<?> boundType = null;
try {
// 1.找到对应的mapper类
boundType = Resources.classForName(namespace);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {}
if (boundType != null && !configuration.hasMapper(boundType)) {
// 2.boundType不为空,并且configuration还没有添加boundType,
// 则将namespace添加到已加载列表,将boundType添加到knownMappers缓存
configuration.addLoadedResource("namespace:" + namespace);
configuration.addMapper(boundType);
}
}
}
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
mapperRegistry.addMapper(type);
}
public <T> void addMapper(Class<T> type) {
if (type.isInterface()) {
if (hasMapper(type)) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is already known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
boolean loadCompleted = false;
try {
// 放到knownMappers缓存中去,value是一个MapperProxyFactory的代理
knownMappers.put(type, new MapperProxyFactory<>(type));
MapperAnnotationBuilder parser = new MapperAnnotationBuilder(config, type);
//解析mapper类
parser.parse();
loadCompleted = true;
} finally {
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
}
}
}
解析mapper类
public void parse() {
// Class对象的唯一标识,如:
// 类似"interface com.xxx.mapper.xxxMapper"
String resource = type.toString();
// 如果当前Class对象已经解析过,则不在解析
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
// 加载并解析指定的xml配置文件,Class所在的包对应文件路径,Class类名对应文件名称,如:
// com.xxx.mapper.xxxMapper类对应的配置文件为com/xxx/mapper/xxxMapper.xml
loadXmlResource();
// 把Class对应的标识添加到已加载的资源列表中
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
// 设置当前namespace为接口Class的全限定名
assistant.setCurrentNamespace(type.getName());
// 解析@CacheNamespace注解对应mapper.xml配置文件中的<cache>元素
parseCache();
// 解析缓存引用,会覆盖之前解析的缓存对象
parseCacheRef();
// 获取mapper接口所有方法,解析方法上的注解
Method[] methods = type.getMethods();
// 遍历所有获取到的方法
for (Method method : methods) {
try {
// 主要是针对注解的 例如:方法上的@Select
// 解析一个方法生成对应的MapperedStatement对象
// 并添加到配置对象中
parseStatement(method);
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteMethod(new MethodResolver(this, method));
}
}
}
// 解析挂起的方法
parsePendingMethods();
}
mapper中的方法是怎么和xml中的方法关联起来的
在上篇文章说到用@MapperScan扫描到的bean,BeanDefinition中的beanClass会被替换成MapperFactoryBean.class
我们来看一看MapperFactoryBean的类图
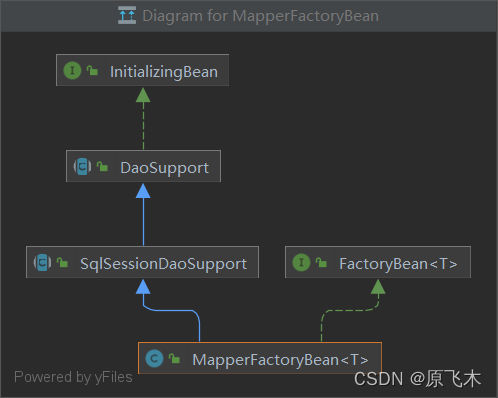
- SqlSessionDaoSupport:提供SqlSessionTemplate模版,这个变量会在初始化mapper bean的时候属性填充的时候设置进去
- DaoSupport:实现了InitializingBean,具体方法有子类实现,做一些检查,初始化工作
MapperFactoryBean也是一个FactoryBean,也就是说spirng真正返回的是getObject()中的bean。
@Override
public T getObject() throws Exception {
return getSqlSession().getMapper(this.mapperInterface);
}
使用mapper来执行方法的流程
首先就要先获取到mapper,这个mapper是一个被代理的对象
SqlSessionTemplate
@Override
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type) {
return getConfiguration().getMapper(type, this);
}
Configuration中的getMapper方法。mapper是哪里来的呢?
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession);
}
mapper是从knownMappers变量中获取,也就是上面在bindMapperForNamespace方法中就放进入了
public <T> T getMapper(Class<T> type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxyFactory<T> mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory<T>) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
最后调用MapperProxyFactory里面的newInstance方法
protected T newInstance(MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy) {
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(mapperInterface.getClassLoader(), new Class[] { mapperInterface }, mapperProxy);
}
public T newInstance(SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxy<T> mapperProxy = new MapperProxy<>(sqlSession, mapperInterface, methodCache);
return newInstance(mapperProxy);
}
MapperProxy实现了InvocationHandler,是基于jdk动态代理的。里面的invoke方法。最后执行的是MapperMethod中的execute方法。
// MapperProxy.invoke()
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// Object的方法执行
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
try {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
}
// 获取MapperMethod
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
// 真正的处理在这里
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
private MapperMethod cachedMapperMethod(Method method) {
MapperMethod mapperMethod = methodCache.get(method);
if (mapperMethod == null) {
mapperMethod = new MapperMethod(mapperInterface, method, sqlSession.getConfiguration());
methodCache.put(method, mapperMethod);
}
return mapperMethod;
}
MapperMethod.execute()方法执行
// MapperMethod.execute()
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
// 具体的增删改查操作,都有具体的执行,
if (SqlCommandType.INSERT == command.getType()) {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
} else if (SqlCommandType.UPDATE == command.getType()) {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
} else if (SqlCommandType.DELETE == command.getType()) {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
// 在这里我们主要看本例中的查询操作
} else if (SqlCommandType.SELECT == command.getType()) {
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
// 本例就返回一个结果值,看这里
// 封装参数值,最后还是交给SqlSession来处理
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
}
} else if (SqlCommandType.FLUSH == command.getType()) {
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
} else {
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
比如说这样一个方法。通过断点看看
@Autowired
private DemoMapper demoMapper;
@Test
public void test() {
Demo demo1 = demoMapper.selectByPrimaryKey(1L);
System.out.println(demo1.toString());
}
我们可以很清楚的看到demoMapper就是一个被代理的类。
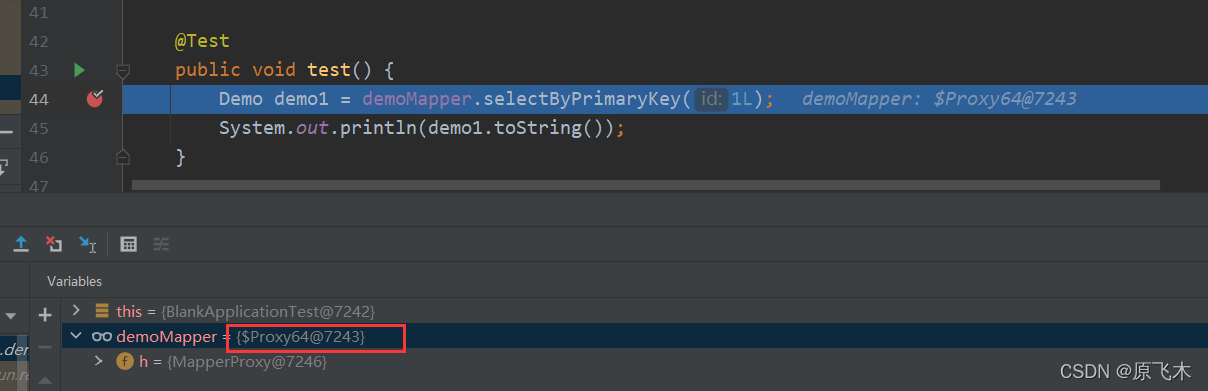
经过SqlSessionTemplate-selectOne->DefaultSqlSession-selectOne最后到selectList中
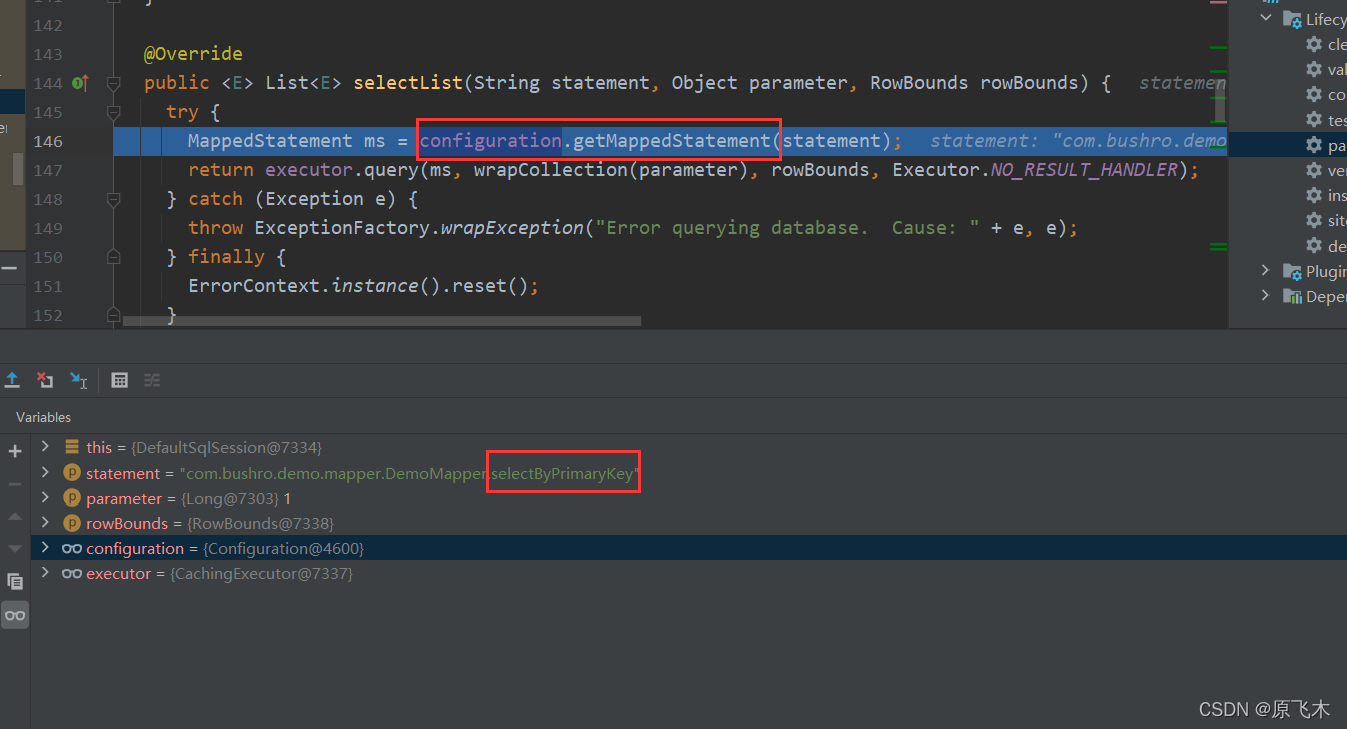
就是从Map<String, MappedStatement> mappedStatements这个变量中去获取的,而这个变量中的值在解析xml文件的时候已经放进去了。
我们都知道在mapper里面写的方法名称,在xml里面的id要一致才可以。Configuration中的mappedStatements是一个map。把xml里面的方法解析后放到这里面。然后这样就把mapper和xml对应起来了。
总结
- 通过xml的namespace和mapper接口的类路径一直绑定
- 然后通过在mapper里面写的方法名称和xml中的id一致这样就把xml和mapper绑定起来了
