? ? ? ?Spring Boot 提供了大量的自动配置,极大地简化了spring 应用的开发过程,当用户创建了一个 Spring Boot 项目后,即使不进行任何配置,该项目也能顺利的运行起来。当然,用户也可以根据自身的需要使用配置文件修改 Spring Boot 的默认设置。
SpringBoot 默认使用以下 2 种全局的配置文件,其文件名是固定的。
- application.properties
- application.yml
application.properties与 application.yaml都可以作为Spring Boot的配置文件,只是书写格式不同而已,在 Spring Boot 启动时被自动读取。当然也可以同时使用,但同级目录下读取的顺序是先读取application.properties,读取application.yaml。该配置文件的存放路径如下图所示。
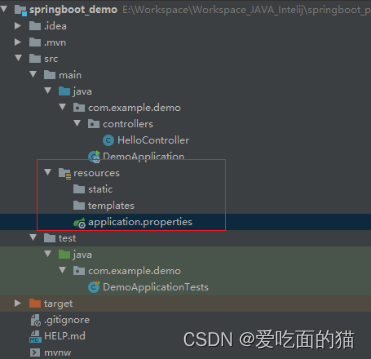
本节我们将详细介绍 application.properties的语法及使用
下面是一个简单的 application.properties属性配置文件。
server.port=8080?
properties 语法
properties的语法如下:
- 使用properties的key=value形式
- 使用层级递进关系。
- 从最高层到最低层逐个低级,中间使用点"."间隔
例如:?
server.address=localhost/170.20.10.112 #可以写IP或域名 server.port=80 #表示监听的80端口,默认是8080 spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver #数据库驱动 spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/cqyddx?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&allowPublicKeyRetrieval=true&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai spring.datasource.username=root spring.datasource.password=root
properties常用写法
properties支持以下三种数据结构:
- 对象:键值对的集合
- 数组:一组按次序排列的值
- 字面量:单个的、不可拆分的值
properties字面量写法
字面量是指单个的,不可拆分的值,例如:数字、字符串、布尔值、以及日期等。
在 properties中,使用“key[=]value”的形式表示一对键值对(空格不能省略),如 name=?"xiatian",age=?32。
字面量直接写在键值对的“value”中即可,且默认情况下字符串是不需要使用单引号或双引号的。
name="xiatian"age=32
若字符串使用单引号,则会转义特殊字符。
name="zhangsan '\n'?lisi"输出结果为:zhangsan \n lisi
若字符串使用单引号,则会转义特殊字符。
name="zhangsan \n?lisi"输出结果为:
- zhangsan
- lisi
properties对象写法
在 properties中,对象可能包含多个属性,每一个属性都是一对键值对。
properties 为对象提供了 以下写法:
使用递进表示对象与属性的层级关系。
user.name="xiatian"user.age=32
properties?数组写法
properties 使用[x]表示数组中的元素,普通写法如下:
user.books[0]="biancheng0"user.books[1]="biancheng1"
user.books[2]="biancheng2"
user.books[3]="biancheng3"
复合结构
以上三种数据结构可以任意组合使用,以实现不同的用户需求,例如:
user.name="xiatian"
user.age=32
user.books[0]="biancheng0"
user.books[1]="biancheng1"
user.books[2]="biancheng2"
user.books[3]="biancheng3"
user.cat.name="diudiu"
