1、Redis在实际业务场景中的用途
- 缓存
- 分布式锁
- 接口限流
- 处理请求接口幂等性
- 其他
2、springboot项目使用Redis实现接口限流的完整案例
2.1 项目结构
2.2 pom.xml依赖
需要以下依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.6.8</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.kkarma</groupId>
<artifactId>interface-ratelimiter</artifactId>
<version>1.0.0</version>
<name>interface-ratelimiter</name>
<description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.80</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
2.3 application.yml配置文件
我这里的redis设置了密码, 如果你的redis没有设置密码, 这里密码可以不配置, 如果配置文件中redis配置了密码, 你的redis服务必须也要设置密码, 主要就是在redis.conf配置文件中设置requirepass字段之后重启redis服务即可
server:
port: 6001
spring:
application:
name: interface-ratelimiter
profiles:
active: dev
redis:
host: localhost
port: 6379
password: 111111
database: 6
lettuce:
pool:
min-idle: 0
max-idle: 8
max-active: 8
max-wait: -1ms
timeout: 10s
2.4 限流核心流程实现
真实的业务场景下, 我们的限流策略不一样,例如一下业务场景:
1】所有的API接口统一设置限制, 一分钟之后只能被访问10000次
2】针对某一个用户, 该用户的Ip地址在 1 分钟内只能问指定接口10 次
定义一个限流策略的枚举类, 可以设置接口的限流策略
2.4.1 限流策略枚举类
package com.kkarma.common.enums;
/**
* @Author: karma
* @Date: 2022/5/25 0025 - 05 - 25 - 14:29
* @Description: com.kkarma.common.enums
* @version: 1.0
*/
public enum RateLimiterEnum {
/**
* 默认策略全局限流
*/
DEFAULT,
/**
* 根据请求用户的IP地址进行限流
*/
IP;
}
2.4.2 自定义限流器注解
@Documented
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface RateLimiter {
/**
* 限流key
*/
String key() default "rate_limiter:";
/**
* 限流时间,单位秒
*/
int time() default 60;
/**
* 限流次数
*/
int count() default 100;
/**
* 限流类型
*/
RateLimiterEnum limitType() default RateLimiterEnum.DEFAULT;
}
2.4.3 Redis的配置类设置
主要是设置RedisTemplate的自定义序列化器、redisTemplatede bean对象注入到容器, 同时设置限流脚本等等。
- 自定义redis序列化器FastJson2JsonRedisSerializer
package com.kkarma.config;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSON;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.parser.ParserConfig;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.serializer.SerializerFeature;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.JavaType;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.type.TypeFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.SerializationException;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
/**
* Redis使用FastJson序列化
*
* @author kkarma
*/
public class FastJson2JsonRedisSerializer<T> implements RedisSerializer<T>
{
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
private ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper();
public static final Charset DEFAULT_CHARSET = Charset.forName("UTF-8");
private Class<T> clazz;
static
{
ParserConfig.getGlobalInstance().setAutoTypeSupport(true);
}
public FastJson2JsonRedisSerializer(Class<T> clazz)
{
super();
this.clazz = clazz;
}
@Override
public byte[] serialize(T t) throws SerializationException
{
if (t == null)
{
return new byte[0];
}
return JSON.toJSONString(t, SerializerFeature.WriteClassName).getBytes(DEFAULT_CHARSET);
}
@Override
public T deserialize(byte[] bytes) throws SerializationException
{
if (bytes == null || bytes.length <= 0)
{
return null;
}
String str = new String(bytes, DEFAULT_CHARSET);
return JSON.parseObject(str, clazz);
}
public void setObjectMapper(ObjectMapper objectMapper)
{
Assert.notNull(objectMapper, "'objectMapper' must not be null");
this.objectMapper = objectMapper;
}
protected JavaType getJavaType(Class<?> clazz)
{
return TypeFactory.defaultInstance().constructType(clazz);
}
}
- 定义Redis的配置类
设置限流脚本的两种方式任意使用一种都可以, 这里两种都给大家写上,随便选用
package com.kkarma.config;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonAutoDetect;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonTypeInfo;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.PropertyAccessor;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.jsontype.impl.LaissezFaireSubTypeValidator;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.io.ClassPathResource;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.script.DefaultRedisScript;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.scripting.support.ResourceScriptSource;
/**
* @Author: karma
* @Date: 2022/5/25 0025 - 05 - 25 - 14:33
* @Description: com.kkarma.config
* @version: 1.0
*/
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory)
{
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
template.setConnectionFactory(connectionFactory);
FastJson2JsonRedisSerializer serializer = new FastJson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper();
mapper.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
mapper.activateDefaultTyping(LaissezFaireSubTypeValidator.instance, ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL, JsonTypeInfo.As.PROPERTY);
serializer.setObjectMapper(mapper);
// 使用StringRedisSerializer来序列化和反序列化redis的key值
template.setKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
template.setValueSerializer(serializer);
// Hash的key也采用StringRedisSerializer的序列化方式
template.setHashKeySerializer(new StringRedisSerializer());
template.setHashValueSerializer(serializer);
template.afterPropertiesSet();
return template;
}
@Bean
public DefaultRedisScript<Long> limitScript() {
DefaultRedisScript<Long> redisScript = new DefaultRedisScript<>();
// 第一种方式:从项目的classpath路径下的lua脚本中获取脚本内容获取源
redisScript.setScriptSource(new ResourceScriptSource(new ClassPathResource("lua/rate_limiter.lua")));
// 第二种方式:直接在配置文件中写死脚本的文本, 设置redisScript脚本
redisScript.setScriptText(limitScriptLuaText());
redisScript.setResultType(Long.class);
return redisScript;
}
/**
* redis限流需要使用的lua脚本
*/
private String limitScriptLuaText()
{
return "local key = KEYS[1]\n" +
"local count = tonumber(ARGV[1])\n" +
"local time = tonumber(ARGV[2])\n" +
"local current = redis.call('get', key);\n" +
"if current and tonumber(current) > count then\n" +
" return tonumber(current);\n" +
"end\n" +
"current = redis.call('incr', key)\n" +
"if tonumber(current) == 1 then\n" +
" redis.call('expire', key, time)\n" +
"end\n" +
"return tonumber(current);";
}
}
2.4.4 定义解析自定义限流注解的切面
package com.kkarma.common.aspect;
import com.kkarma.common.annotation.RateLimiter;
import com.kkarma.common.enums.RateLimiterEnum;
import com.kkarma.common.exception.ServiceException;
import com.kkarma.common.utils.IpUtils;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.script.RedisScript;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.ServletRequestAttributes;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @Author: karma
* @Date: 2022/5/25 0025 - 05 - 25 - 14:49
* @Description: com.kkarma.common.aspect
* @version: 1.0
*/
@Aspect
@Component
public class RateLimiterAspect {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RateLimiterAspect.class);
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate;
@Autowired
private RedisScript<Long> limitScript;
@Before("@annotation(rateLimiter)")
public void doBefore(JoinPoint point, RateLimiter rateLimiter) throws Throwable {
String key = rateLimiter.key();
int time = rateLimiter.time();
int count = rateLimiter.count();
String combineKey = getCombineKey(rateLimiter, point);
List<Object> keys = Collections.singletonList(combineKey);
try {
Long number = redisTemplate.execute(limitScript, keys, count, time);
if (number == null || number.intValue() > count) {
throw new ServiceException("访问过于频繁,请稍候再试");
}
log.info("限制请求'{}',当前请求'{}',缓存key'{}'", count, number.intValue(), key);
} catch (ServiceException e) {
throw e;
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException("服务器限流异常,请稍候再试");
}
}
public String getCombineKey(RateLimiter rateLimiter, JoinPoint point) {
StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer(rateLimiter.key());
if (rateLimiter.limitType() == RateLimiterEnum.IP) {
stringBuffer.append(IpUtils.getIpAddr(((ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.currentRequestAttributes()).getRequest())).append("-");
}
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) point.getSignature();
Method method = signature.getMethod();
Class<?> targetClass = method.getDeclaringClass();
stringBuffer.append(targetClass.getName()).append("-").append(method.getName());
return stringBuffer.toString();
}
}
这个自定义的切面拦截所有加了 @RateLimiter 注解的方法,在前置通知doBefore方法中中对注解进行处理。核心的判断限流逻辑就在doBefore方法中,回去限流脚本质性的返回值和限流生效的默认次数参数count作比较,如果超过count设置的值,抛异常,拒绝访问接口, 这样就实现了限流,是不是很简单。
- 定义自定义异常类
package com.kkarma.common.exception;
/**
* @Author: karma
* @Date: 2022/5/25 0025 - 05 - 25 - 15:00
* @Description: com.kkarma.common.exception
* @version: 1.0
*/
public final class ServiceException extends RuntimeException {
/**
* 错误码
*/
private Integer code;
/**
* 错误提示
*/
private String message;
/**
* 错误明细,内部调试错误
*
* 和 {@link #getDetailMessage()} 一致的设计
*/
private String detailMessage;
/**
* 空构造方法,避免反序列化问题
*/
public ServiceException()
{
}
public ServiceException(String message)
{
this.message = message;
}
public ServiceException(String message, Integer code)
{
this.message = message;
this.code = code;
}
public String getDetailMessage()
{
return detailMessage;
}
@Override
public String getMessage()
{
return message;
}
public Integer getCode()
{
return code;
}
public ServiceException setMessage(String message)
{
this.message = message;
return this;
}
public ServiceException setDetailMessage(String detailMessage)
{
this.detailMessage = detailMessage;
return this;
}
}
- 定义全局异常处理
package com.kkarma.common.exception;
import com.kkarma.common.constants.ResponseEntity;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestControllerAdvice;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
/**
* @Author: karma
* @Date: 2022/5/25 0025 - 05 - 25 - 15:26
* @Description: com.kkarma.common.exception
* @version: 1.0
*/
@RestControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(GlobalExceptionHandler.class);
/**
* 业务异常
*/
@ExceptionHandler(ServiceException.class)
public ResponseEntity handleServiceException(ServiceException ex)
{
log.error(ex.getMessage(), ex);
Integer code = ex.getCode();
return !StringUtils.isEmpty(code) ? ResponseEntity.error(code, ex.getMessage()) : ResponseEntity.error(ex.getMessage());
}
/**
* 系统异常
*/
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public ResponseEntity handleException(Exception e, HttpServletRequest request)
{
String requestURI = request.getRequestURI();
log.error("请求地址'{}',发生系统异常.", requestURI, e);
return ResponseEntity.error(e.getMessage());
}
}
2.5 测试限流实现是否正确
定义一个测试接口
package com.kkarma.controller;
import com.kkarma.common.annotation.RateLimiter;
import com.kkarma.common.enums.RateLimiterEnum;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* @Author: karma
* @Date: 2022/5/25 0025 - 05 - 25 - 15:03
* @Description: com.kkarma.controller
* @version: 1.0
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/rate/limiter")
public class TestController {
@GetMapping("test")
@RateLimiter(time = 10, count = 3, limitType = RateLimiterEnum.IP)
public String testRateLimiter() {
return "rate limiter is valid at: " +
new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date());
}
}
启动项目测试, 验证访问10秒之内访问3次之后,再次访问页面是否可以正确抛出异常。
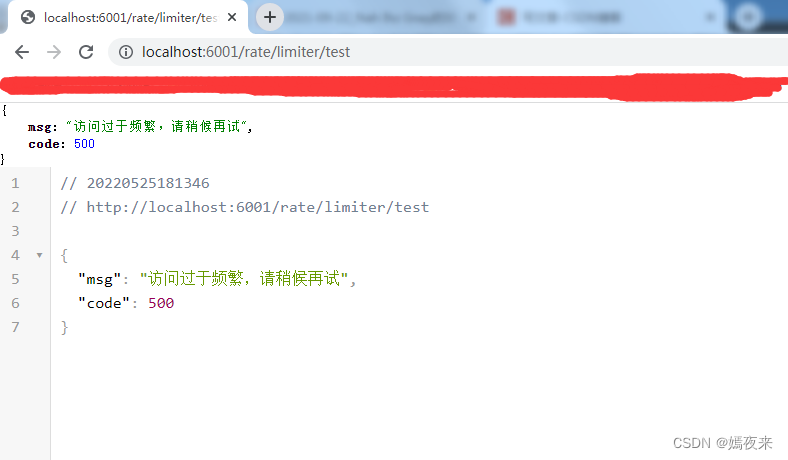
OK, 没问题~
2.6 源码获取
这里我把项目上传到gitee, 需要的同学可以自取,觉得有帮助到你的话点赞收藏哦~???
gitee仓库地址:https://gitee.com/karma0704/springboot-interface-ratelimiter
