前言
前面两个章节我们把Kafka给安装起来然后使用命令演示是生产和消费的过程,以及Kafka的架构原理,接下来就是Kafka的实战使用,顺应如今企业流行的开发模式,当然要使用SpringBoot和Kafka进行整合。
SpringBoot整合Kafka
第一步:我们基于SpringBoot来快速入门Kafka,我这里使用的SpringBoot版本是2.2.5.RELEASE ,对应spring-kafka的版本是2.3.6,具体依赖如下:
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.5.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.kafka</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-kafka</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>1.2.28</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
第二步:导入依赖之后需要为SpringBoot创建启动类,在启动类中我们通过注解的方式创建一个Topic,如下
@SpringBootApplication
public class KafkaApplication {
//Topic的名字
public static final String TOPIC_NAME = "topic-test";
//通过定义Bean的方式创建Topic
@Bean
public NewTopic topicHello(){
//创建Topic : topic名字, partition数量 , replicas副本数量
return TopicBuilder.name(TOPIC_NAME).build();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(KafkaApplication.class , args);
}
}
第三步:因为是基于SpringBoot开发,所以需要在yml对kafka做一些常规配置,如下:
spring:
application:
name: application-kafka
kafka:
bootstrap-servers: localhost:9092 #这个是kafka的地址,对应你server.properties中配置的
producer:
key-serializer: org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer #序列化
value-serializer: org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer
retries: 1 # 消息发送重试次数
acks: 1 #应答级别:多少个分区副本备份完成时向生产者发送ack确认(可选0、1、all/-1)
batch-size: 16384 #批量大小
properties:
linger:
ms: 0 #提交延迟
consumer:
key-deserializer: org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer
value-deserializer: org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer
group-id: test-consumer-group #消费者的ID,这个对应 config/consumer.properties中的group.id
- bootstrap-servers :kafka服务器的链接地址
- producer :对生产者的配置
- acks :生产者发送消息到Kafka的应答模式,值为0、1、all/-1 ,
- acks = 0:设置成 表示 producer 完全不理睬 leader broker 端的处理结果。此时producer 发送消息后立即开启下 条消息的发送,根本不等待 leader broker 端返回结果
- acks= all 或者-1 :表示当发送消息时, leader broker 不仅会将消息写入本地日志,同时还会等待所有其他副本都成功写入它们各自的本地日志后,才发送响应结果给,消息安全但是吞吐量会比较低。
- acks = 1:默认的参数值。 producer 发送消息后 leader broker 仅将该消息写入本地日志,然后便发送响应结果给producer ,而无须等待其他副本写入该消息。折中方案,只要leader一直活着消息就不会丢失,同时也保证了吞吐量
- consumer :是对消费者的配置 ,group-id 是消费者组的ID。
生产者发送消息
编写生产者案例 ,Kafka提供了 KafkaTemplate 用来向Kafka发送消息,直接在查询中注入即可使用。KafkaTemplate提供了很多个重载的send方法,方法返回ListenableFuture对象,即发送的结果对象。下面我编写了一个controller作为生产者
@RestController
public class HelloProducer {
@Autowired
private KafkaTemplate<String,String> kafkaTemplate;
@PostMapping("/send/{msg}")
public String sendMsg(@PathVariable("msg")String msg) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ListenableFuture<SendResult<String, String>> future = kafkaTemplate.send(KafkaApplication.TOPIC_NAME, msg);
System.out.println("发送结果:"+future.get().toString());
return "发送成功";
}
}
同步阻塞
需要特别注意的是: future.get()方法会阻塞,他会一直尝试获取发送结果,如果Kafka迟迟没有返回发送结果那么程序会阻塞到这里。所以这种发送方式是同步的。
当然如果你的消息不重要允许丢失你也可以直接执行 : kafkaTemplate.send ,不调用get()方法获取发送结果,程序就不会阻塞,当然你也就不知道消息到底有没有发送成功。
异步非阻塞
幸好Kafka为 ListenableFuture 提供了Callback异步回调,我们可以通过异步回调来接收发送结果,如下:
@PostMapping("/send/syn/{msg}")
public String sendMsgSyn(@PathVariable("msg")String msg) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ListenableFuture<SendResult<String, String>> future = kafkaTemplate.send(KafkaApplication.TOPIC_NAME, msg);
future.addCallback(new ListenableFutureCallback(){
@Override
public void onSuccess(Object result) {
System.out.println("发送成功 result = "+result);
}
@Override
public void onFailure(Throwable ex) {
System.out.println("发送异常");
ex.printStackTrace();
}
});
return "发送成功";
}
生产者监听器
Kafka提供了ProducerListener 监听器来异步监听生产者消息是否发送成功,我们可以自定义一个kafkaTemplate添加ProducerListener,当消息发送失败我们可以拿到消息进行重试或者把失败消息记录到数据库定时重试。
@Configuration
public class KafkaConfig{
//生产者工厂
@Autowired
ProducerFactory producerFactory;
@Bean
public KafkaTemplate<String,String> kafkaTemplate(){
KafkaTemplate<String, String> kafkaTemplate = new KafkaTemplate<String, String>(producerFactory);
//生产者监听器
kafkaTemplate.setProducerListener(new ProducerListener(){
@Override
public void onError(ProducerRecord producerRecord, Exception exception) {
System.out.println("发送失败"+producerRecord.toString());
System.out.println(exception.getMessage());
}
@Override
public void onError(String topic, Integer partition, Object key, Object value, Exception exception) {
System.out.println("发送失败"+"topic = "+topic +" ; partion = "+partition +"; key = "+key + " ; value="+value);
System.out.println(exception.getMessage());
}
@Override
public void onSuccess(ProducerRecord producerRecord, RecordMetadata recordMetadata) {
System.out.println("发送成功 "+producerRecord.toString());
}
@Override
public void onSuccess(String topic, Integer partition, Object key, Object value, RecordMetadata recordMetadata) {
System.out.println("发送成功 topic = "+topic +" ; partion = "+partition +"; key = "+key + " ; value="+value);
}
});
return kafkaTemplate;
}
}
当我们发送一条消息,既会走 ListenableFutureCallback 回调,也会走ProducerListener回调。
执行测试方法,查看控制台效果:

消费者接收消息
我们可以通过定义一个 KafkaMessageListenerContainer 的Bean,为他添加 MessageListener 来消费消息,但是这种很麻烦,具体用法可以看 SpringBoot文档 ,Kafka另外提供了 @KafkaListener注释来接收消息,用法比较简单,我们演示注解方式如下:
@Component
public class HelloConsumer {
//监听一个或者多个Topic
@KafkaListener(topics = KafkaApplication.TOPIC_NAME)
public void handler(String message){
System.out.println("收到消息:"+message);
}
}
不出意外你应该可以收到生产者发送过来的消息了。
手动确认消息
默认情况下Kafka的消费者是自动确认消息的,通常情况下我们需要在业务处理成功之后手动触发消息的签收,否则可能会出现:消息消费到一半消费者异常,消息并未消费成功但是消息已经自动被确认,也不会再投递给消费者,也就导致消息丢失了。
第一步:添加kafka配置,把 spring.kafka.listener.ack-mode = manual 设置为手动
spring:
kafka:
listener:
ack-mode: manual #手動確認消息
第二步:消费消息的时候,给 方法添加 Acknowledgment 参数用来签收消息
@Component
public class HelloConsumer {
//监听一个或者多个Topic
@KafkaListener(topics = KafkaApplication.TOPIC_NAME,containerFactory = "kafkaManualAckListenerContainerFactory")
public void handler(String message, Acknowledgment ack){
System.out.println("收到消息:"+message);
//确认收到消息
ack.acknowledge();
}
}
- ack.acknowledge() : 签收消息
事务消息
在某些场景中我们需要同时向kafka发送多条消息,而且这些消息必须是原子性要么都成功,要么都失败,Kafka提供了事务机制保证多个消息的原子性。那这就要要求kafka的leader和其副本都收到消息之后才应答生产者。
第一步:在yaml配置生产者的应答acks=all ,同时随着事务前缀,如下
spring:
kafka:
producer:
acks: all #应答级别:kafka多少个分区副本备份完成时向生产者发送ack确认(可选0、1、all/-1)
transaction-id-prefix: "transaction-id-xx" #事务ID前缀
第二步:发送消息,需要在方法上使用 @Transactional(rollbackFor = RuntimeException.class) 标记事务支持
@PostMapping("/send/ts/{msg}")
//增加事務,保證kafka多次發送的原子性,呀麼都成功,要麼都失敗
@Transactional(rollbackFor = RuntimeException.class)
public String sendMsgTs(@PathVariable("msg")String msg) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
kafkaTemplate.send(KafkaApplication.TOPIC_NAME, msg);
if(msg.length() > 5){
kafkaTemplate.send(KafkaApplication.TOPIC_NAME, msg);
}else{
throw new RuntimeException("演示異常");
}
return "发送成功";
}
使用postmain发送请求,当msg长度大于5 两条消息都可以发送成功,当msg长度小于5,第一条消息也发送不了,会被撤销,效果如下;
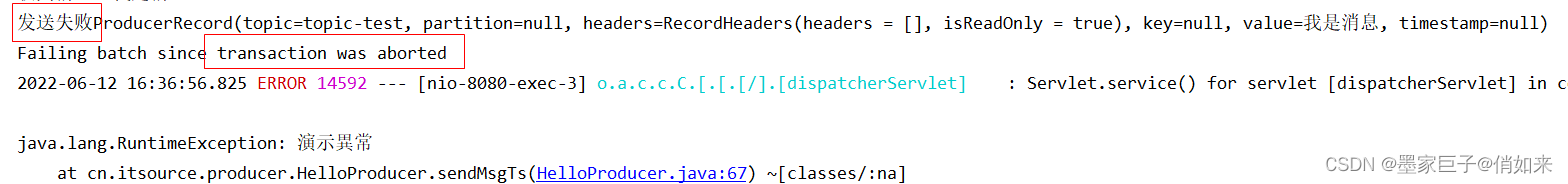
另外除了使用 @Transactional 来支持事务,还可以使用 template.executeInTransaction 回调的方式如下:
boolean result = kafkaTemplate.executeInTransaction(t -> {
t.sendDefault("thing1", "thing2");
t.sendDefault("cat", "hat");
return true;
});
文章就写到这里把,点赞还是要求一下的,万一屏幕面前的大帅哥或者大漂亮就评论收藏了呢?