目录
1.认识文件
我们先来认识狭义上的文件(file)。针对硬盘这种持久化存储的I/O设备,当我们想要进行数据保存时, 往往不是保存成一个整体,而是独立成一个个的单位进行保存,这个独立的单位就被抽象成文件的概 念,就类似办公桌上的一份份真实的文件一般。
文件除了有数据内容之外,还有一部分信息,例如文件名、文件类型、文件大小等并不作为文件的数据 而存在,我们把这部分信息可以视为文件的元信息。
1.1 文件结构组织和目录
随着文件越来越多,对文件的系统管理也被提上了日程,如何进行文件的组织呢,一种合乎自然 的想法出现了,就是按照层级结构进行组织 —— 也就是我们数据结构中学习过的树形结构。这样,一 种专门用来存放管理信息的特殊文件诞生了,也就是我们平时所谓文件夹(folder)或者目录(directory)的 概念。
1.2 文件路径(Path)
- 从树型结构的角度来看,树中的每个结点都可以被一条从根开始,一直到达的结点的路径所描述,而这种描述方式就被称为文件的
绝对路径(absolute path)。 - 从任意结点出发,进行路径的描述,而这种描述方式就被称为
相对路径(relative path),相对于当前所在结点的一条路径。
1.3 文件类型
根据其保存数据的不同,经常被分为不同的类型,我们一般简单的划分为文本文件和二进制文件,分别指代保存被字符集编码的文本和按照标准格式保存的非被字符集编码过的文件。
1.4 文件权限
文件由于被操作系统进行了管理,所以根据不同的用户,会赋予用户不同的对待该文件的权限,一般地可以认为有可读、可写、可执行权限。
2.Java 中操作文件
Java 中通过 java.io.File 类来对一个文件(包括目录)进行抽象的描述。注意,有 File 对象,并不代表真实存在该文件。
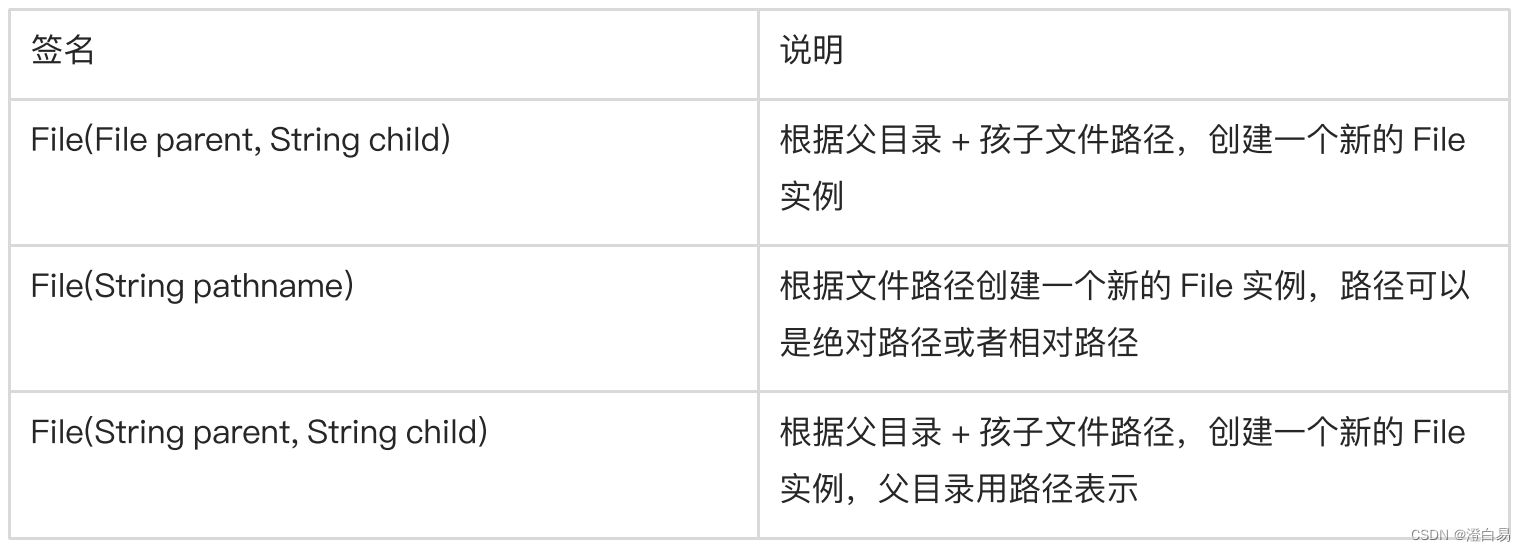
2.1 File常用构造方法
示例代码:
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 构造方法1
File file1 = new File(new File("E:\\"), "\\a.txt");
System.out.println(file1.getPath());
// 构造方法2
File file2 = new File("E:\\a.txt");
System.out.println(file2.getPath());
// 构造方法3
File file3 = new File("E:\\", "a.txt");
System.out.println(file3.getPath());
}
2.2 常用方法
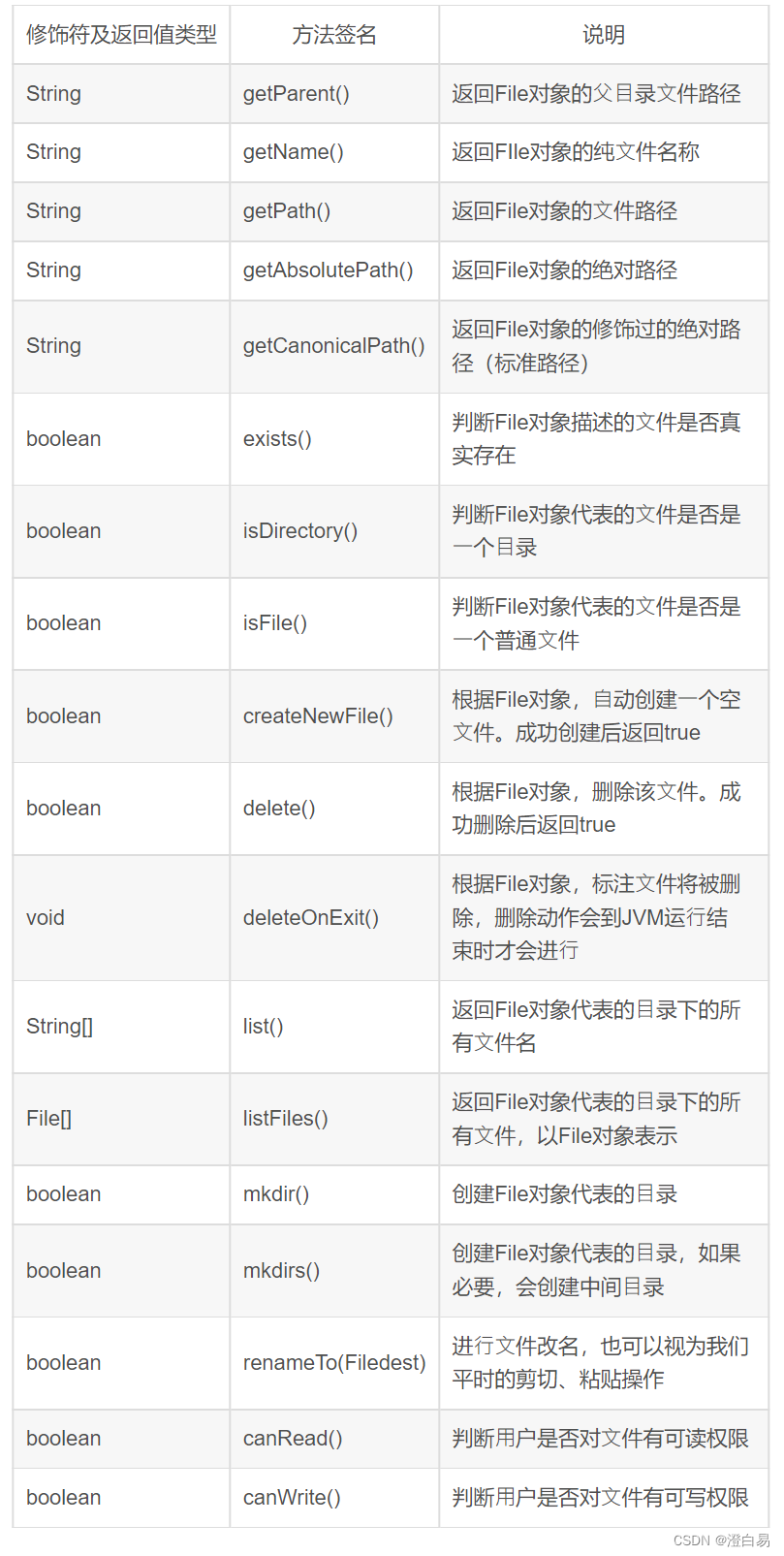
示例1: 文件路径
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File("../a.txt");
System.out.println("文件名称:" + file.getName());
System.out.println("文件目录:" + file.getPath());
System.out.println("绝对路径:" + file.getAbsolutePath());
System.out.println("标准路径:" + file.getCanonicalPath());
}
运行结果:
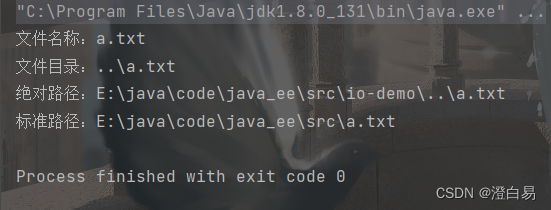
示例2: 文件判断与创建
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File("a.txt");
if (!file.exists()) {
// 文件不存在,创建文件
System.out.println("创建文件:" + file.createNewFile());
}
System.out.println("是否为文件夹:" + file.isDirectory());
System.out.println("是否为文件:" + file.isFile());
}
运行结果:
示例3: 文件存在删除/不存在创建
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 先得到一个 file 对象
File file = new File("a.txt");
// 判断 file 对象是否存在
if (file.exists()) {
// 如果存在就删除文件
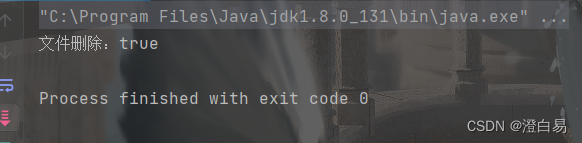
boolean result = file.delete();
System.out.println("文件删除:" + result);
} else {
// 不存在就创建文件
boolean result = file.createNewFile();
System.out.println("文件创建:" + result);
}
}
运行结果:
示例4: 观察deleteOnExit
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
File file = new File("a.txt");
if (!file.exists()) {
// 不存在就创建文件
boolean result = file.createNewFile();
System.out.println("新建文件:" + result);
}
// System.out.println("删除文件:" + file.delete());
file.deleteOnExit();
Thread.sleep(5 * 1000);
System.out.println("删除成功!");
}
运行结果:
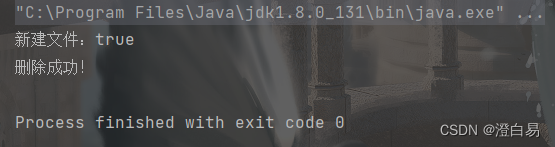
程序运行结束后,文件被删除。
示例5: 观察目录的创建
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("a/b");
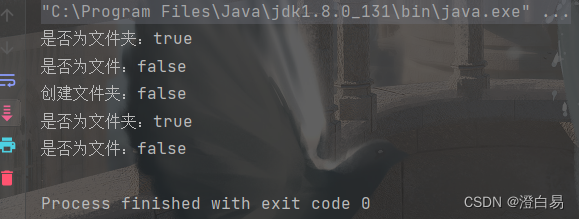
System.out.println("是否为文件夹:" + file.isDirectory());
System.out.println("是否为文件:" + file.isFile());
// 创建单级目录
// boolean result = file.mkdir();
// 创建多级目录
boolean result = file.mkdirs();
System.out.println("创建文件夹:" + result);
System.out.println("是否为文件夹:" + file.isDirectory());
System.out.println("是否为文件:" + file.isFile());
}
运行结果:
示例6: 重命名
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
// 将 a.txt 命名为 b.txt
File file = new File("a.txt");
File tarFile = new File("d.txt");
// 文件不存在先创建文件
if (!file.exists()) {
System.out.println("创建文件:" + file.createNewFile());
}
// 重命名文件
System.out.println("重命名文件:" + file.renameTo(tarFile));
}
运行结果:
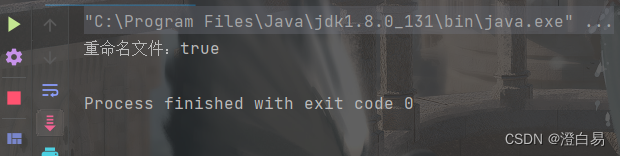
如果renameTo的文件不存在,那么可以重命名成功,反之则不成功。
3.文件内容的读写——数据流
3.1 InputStream:输入流
InputStream输入流是用来读取数据的。
3.1.1 InputStream常用方法
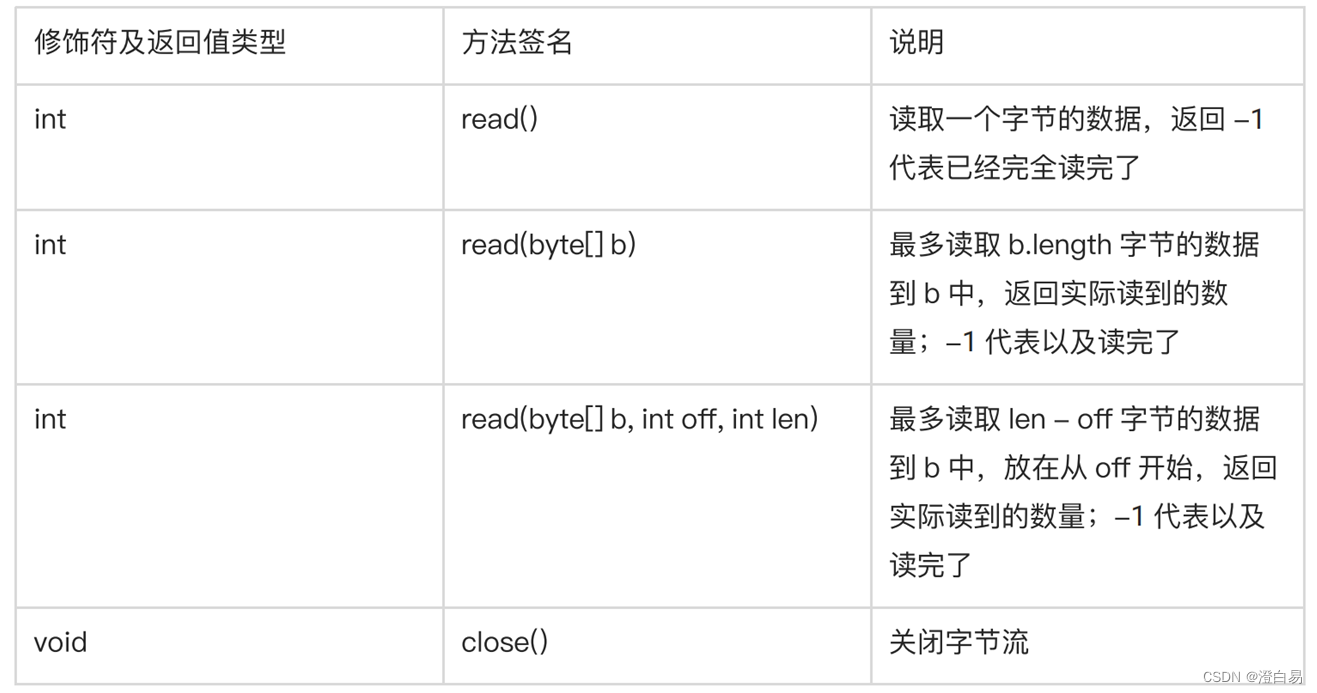
说明:
InputStream 只是一个抽象类,要使用还需要具体的实现类。关于InputStream 的实现类有很多,基本可以认为不同的输入设备都可以对应一个 InputStream 类,我们现在只关心从文件中读取,所以使用FileInputStream
3.1.2 FileInputStream
构造方法:
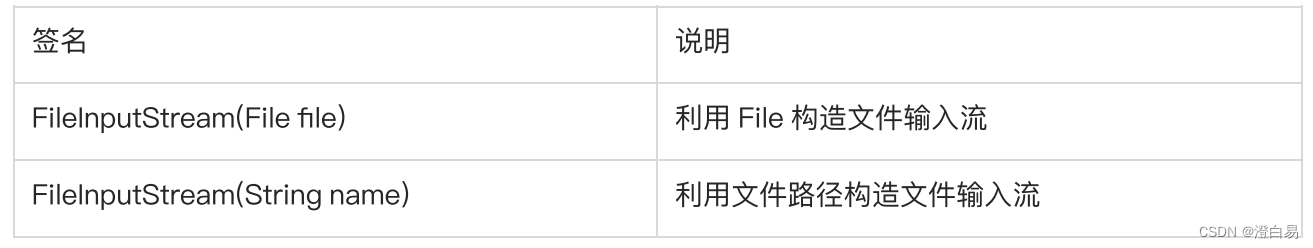
读取文件中的内容:
将文件完全读完的两种方式:
- 方式1
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建流对象(try-catch-resource) JDK1.7
try (InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("b.txt")) {
// 读写操作
while (true) {
int c = inputStream.read();
if (c == -1) break;
Thread.sleep(200);
System.out.printf("%c", c);
}
} catch (InterruptedException | IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
- 方式2
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("b.txt")) {
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
while (true) {
// 如果数据超过了byte容量,会读取多次
int c = inputStream.read(bytes);
if (c == -1) break;
System.out.println(new String(bytes, StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
Thread.sleep(200);
}
} catch (InterruptedException | IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
3.1.3 使用Scanner进行数据读取
可以使?Scanner进行数据读取,它有一个构造方法:
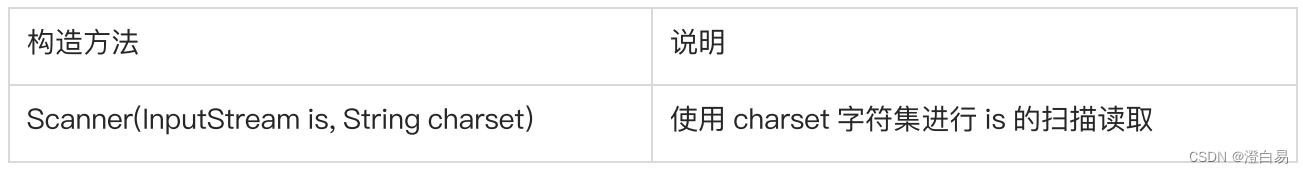
示例:
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (InputStream inputStream = new FileInputStream("b.txt")) {
try (Scanner scanner = new Scanner(inputStream, "utf-8")) {
while (scanner.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(scanner.nextLine());
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
3.2 OutputStream:输出流
OutputStream 输出流是进行数据写入的。
3.2.1 OutputStream常用方法
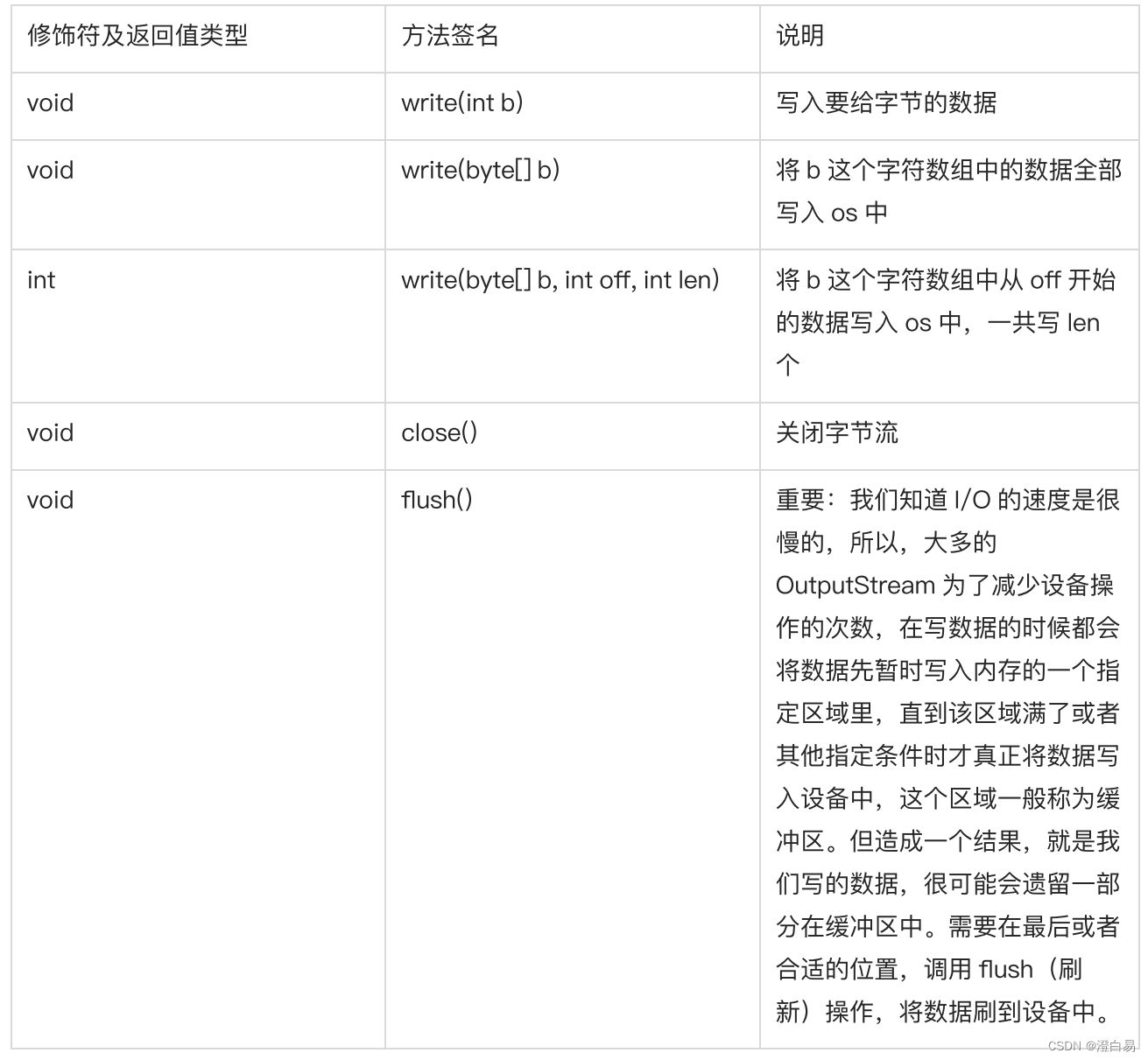
说明:
OutputStream 同样只是一个抽象类,要使用还需要具体的实现类。我们现在还是只关心写入文件中,所以使用 FileOutputStream
3.2.2 实现数据写入
一个一个字符写入:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File("c.txt");
if (!file.exists()) System.out.println("新建文件:" + file.createNewFile());
// 写入数据
try (OutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(file)) {
outputStream.write('h');
outputStream.write('e');
outputStream.write('l');
outputStream.write('l');
outputStream.write('o');
outputStream.flush();
}
}
字节数组批量写入:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File("c.txt");
if (!file.exists()) System.out.println("创建文件:" + file.createNewFile());
// 写入数据
try (OutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(file)){
byte[] bytes = new byte[]{
'h', 'e', 'e'
};
outputStream.write(bytes);
outputStream.flush();
}
}
字符串写入:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File("c.txt");
if (!file.exists()) System.out.println("创建文件:" + file.createNewFile());
// 写入数据
try (OutputStream outputStream = new FileOutputStream(file)) {
String msg = "hello, world";
outputStream.write(msg.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
outputStream.flush();
}
}
3.2.3 使用PrintWriter进行写入
除了上述的写入方式之外,JDK还提供了一个类 PrintWriter 可以很方便的实现数据写入。 PrintWriter类中提供了我们熟悉的 print/println/printf 方法。
示例:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File("c.txt");
if (!file.exists()) {
System.out.println("创建文件:" + file.createNewFile());
}
try (PrintWriter printWriter = new PrintWriter(file)) {
printWriter.println("这是第一行数据");
printWriter.println("这是第二行数据");
printWriter.flush();
}
}
3.2.4 使用FileWriter追加数据
示例:
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File("c.txt");
if (!file.exists()) System.out.println("创建文件:" + file.createNewFile());
// 数据追加
try (FileWriter fileWriter = new FileWriter(file, true)) {
fileWriter.append("\n我是追加的数据");
fileWriter.flush();
}
}
4.练习
示例1
扫描指定目录,并找到名称中包含指定字符的所有普通文件(不包含目录),并且后续询问用户是否要删除该文件。
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入要扫描的根目录(绝对路径 OR 相对路径): ");
String rootDirPath = scanner.next();
File rootDir = new File(rootDirPath);
if (!rootDir.isDirectory()) {
System.out.println("您输入的根目录不存在或者不是目录,退出");
return;
}
System.out.print("请输入要找出的文件名中的字符: ");
String token = scanner.next();
List<File> result = new ArrayList<>();
// 因为文件系统是树形结构,所以我们使用深度优先遍历(递归)完成遍历
scanDir(rootDir, token, result);
System.out.println("共找到了符合条件的文件 " + result.size() + " 个,它们分别
是");
for (File file : result) {
System.out.println(file.getCanonicalPath() + " 请问您是否要删除该文
件?y/n");
String in = scanner.next();
if (in.toLowerCase().equals("y")) {
file.delete();
}
}
}
private static void scanDir(File rootDir, String token, List<File> result) {
File[] files = rootDir.listFiles();
if (files == null || files.length == 0) {
return;
}
for (File file : files) {
if (file.isDirectory()) {
scanDir(file, token, result);
} else {
if (file.getName().contains(token)) {
result.add(file.getAbsoluteFile());
}
}
}
}
}
示例2
进行普通文件的复制。
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入要复制的文件(绝对路径 OR 相对路径): ");
String sourcePath = scanner.next();
File sourceFile = new File(sourcePath);
if (!sourceFile.exists()) {
System.out.println("文件不存在,请确认路径是否正确");
return;
}
if (!sourceFile.isFile()) {
System.out.println("文件不是普通文件,请确认路径是否正确");
return;
}
System.out.print("请输入要复制到的目标路径(绝对路径 OR 相对路径): ");
String destPath = scanner.next();
File destFile = new File(destPath);
if (destFile.exists()) {
if (destFile.isDirectory()) {
System.out.println("目标路径已经存在,并且是一个目录,请确认路径是否正
确");
return;
}
if (destFile.isFile()) {
System.out.println("目录路径已经存在,是否要进行覆盖?y/n");
String ans = scanner.next();
if (!ans.toLowerCase().equals("y")) {
System.out.println("停止复制");
return;
}
}
}
try (InputStream is = new FileInputStream(sourceFile)) {
try (OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream(destFile)) {
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len;
while (true) {
len = is.read(buf);
if (len == -1) {
break;
}
os.write(buf, 0, len);
}
os.flush();
}
}
System.out.println("复制已完成");
}
}
示例3
扫描指定目录,并找到名称或者内容中包含指定字符的所有普通文件(不包含目录)。
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("请输入要扫描的根目录(绝对路径 OR 相对路径): ");
String rootDirPath = scanner.next();
File rootDir = new File(rootDirPath);
if (!rootDir.isDirectory()) {
System.out.println("您输入的根目录不存在或者不是目录,退出");
return;
}
System.out.print("请输入要找出的文件名中的字符: ");
String token = scanner.next();
List<File> result = new ArrayList<>();
// 因为文件系统是树形结构,所以我们使用深度优先遍历(递归)完成遍历
scanDirWithContent(rootDir, token, result);
System.out.println("共找到了符合条件的文件 " + result.size() + " 个,它们分别
是");
for (File file : result) {
System.out.println(file.getCanonicalPath());
}
}
private static void scanDirWithContent(File rootDir, String token,
List<File> result) throws IOException {
File[] files = rootDir.listFiles();
if (files == null || files.length == 0) {
return;
}
for (File file : files) {
if (file.isDirectory()) {
scanDirWithContent(file, token, result);
} else {
if (isContentContains(file, token)) {
result.add(file.getAbsoluteFile());
}
}
}
}
// 我们全部按照utf-8的字符文件来处理
private static boolean isContentContains(File file, String token) throws
IOException {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
try (InputStream is = new FileInputStream(file)) {
try (Scanner scanner = new Scanner(is, "UTF-8")) {
while (scanner.hasNextLine()) {
sb.append(scanner.nextLine());
sb.append("\r\n");
}
}
}
return sb.indexOf(token) != -1;
}
}