
历史文章(累计400+篇文章)
SpringBoot/Spring扩展点系列之初出茅庐ApplicationContextInitializer - 第426篇
SpringBoot/Spring扩展点BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor - 第427篇
SpringBoot/Spring扩展点系列之叱咤风云BeanFactoryPostProcessor - 第428篇SpringBoot扩展点系列之InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor模拟AOP - 第429篇
一款利用人工智能生成模型来合成代码的工具Copilot - 第430篇
SpringBoot配置文件内容加密,实现敏感信息保护 - 第431篇
?
悟纤:师傅,你说,当你的代码有多个构造方法的时候,Spring如何知道要执行哪一个构造方法呢?

师傅:这个就要归功于Spring的一个扩展点SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor。

悟纤:师傅,那你给徒儿讲讲呗。
师傅:那就给徒儿来稍微介绍一下,剩下的徒儿自己探索哦。
悟纤:师傅领进门,修行靠自身。

导读
一、SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor概述
1.1是什么?
SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor?继承自InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor;
但是SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor多了一个三个方法。
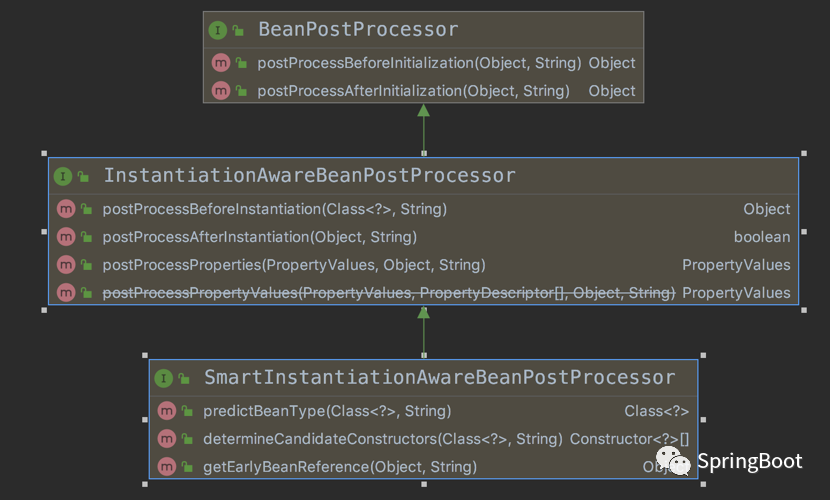
1.2三个方法详解
(1)getEarlyBeanReference
获得提前暴露的bean引用,主要用于解决循环引用的问题。
getEarlyBeanReference:该触发点发生在postProcessAfterInstantiation之后,当有循环依赖的场景,当bean实例化好之后,为了防止有循环依赖,会提前暴露回调方法,用于bean实例化的后置处理。这个方法就是在提前暴露的回调方法中触发。
(2)determineCandidateConstructors
检测Bean的构造器,可以检测出多个候选构造器,再有相应的策略决定使用哪一个,如AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor实现将自动扫描通过@Autowired/@Value注解的构造器从而可以完成构造器注入
执行时机是:?对象实例化之前执行。
determineCandidateConstructors:该触发点发生在postProcessBeforeInstantiation之后,用于确定该bean的构造函数之用,返回的是该bean的所有构造函数列表。用户可以扩展这个点,来自定义选择相应的构造器来实例化这个bean。
(3)predictBeanType
预测Bean的类型,返回第一个预测成功的Class类型,如果不能预测返回null;当你调用BeanFactory.getType(name)时当通过Bean定义无法得到Bean类型信息时就调用该回调方法来决定类型信息;BeanFactory.isTypeMatch(name, targetType)用于检测给定名字的Bean是否匹配目标类型(如在依赖注入时需要使用)。
predictBeanType:该触发点发生在postProcessBeforeInstantiation之前,这个方法用于预测Bean的类型,返回第一个预测成功的Class类型,如果不能预测返回null;当你调用BeanFactory.getType(name)时当通过bean的名字无法得到bean类型信息时就调用该回调方法来决定类型信息。
1.3?使用场景
SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor--determineCandidateConstructors处理器的应用场景:
当一个bean中有两个构造方法的时候,一个无参构造方法,一个有参构造方法,那么spring在进行bean初始化的时候回默认调用无参的构造方法:
例如:如下IndexServiceImpl中有两个构造方法
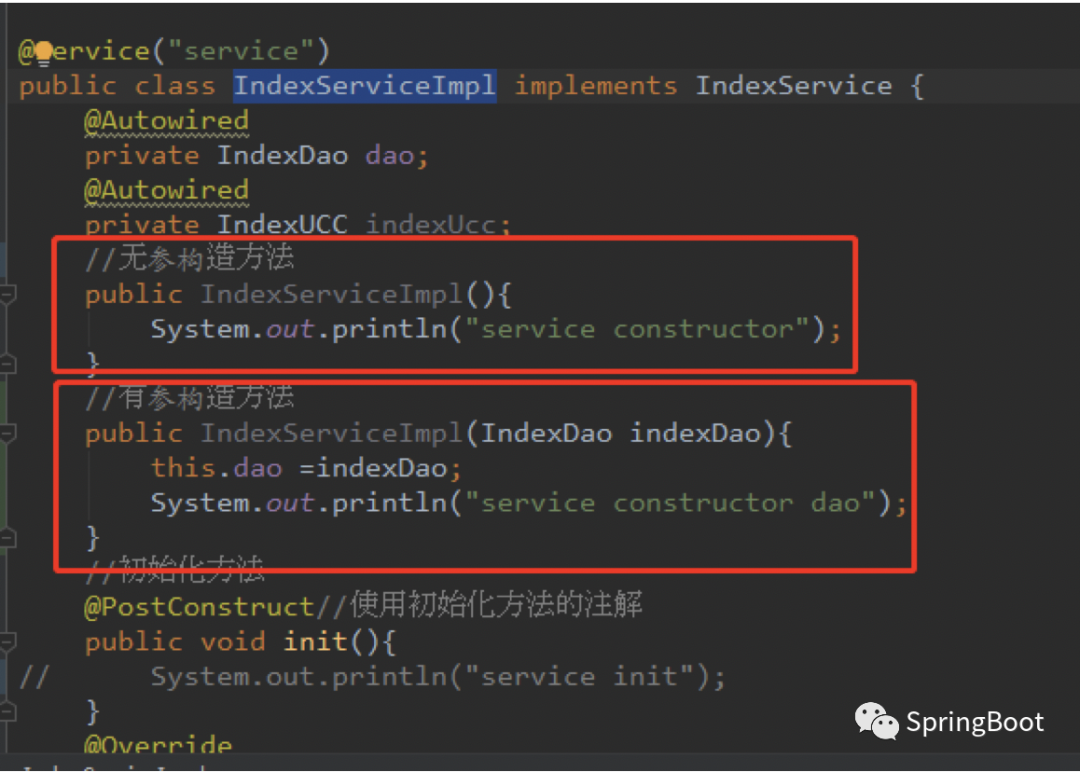
那么在spring进行实例化的过程中:
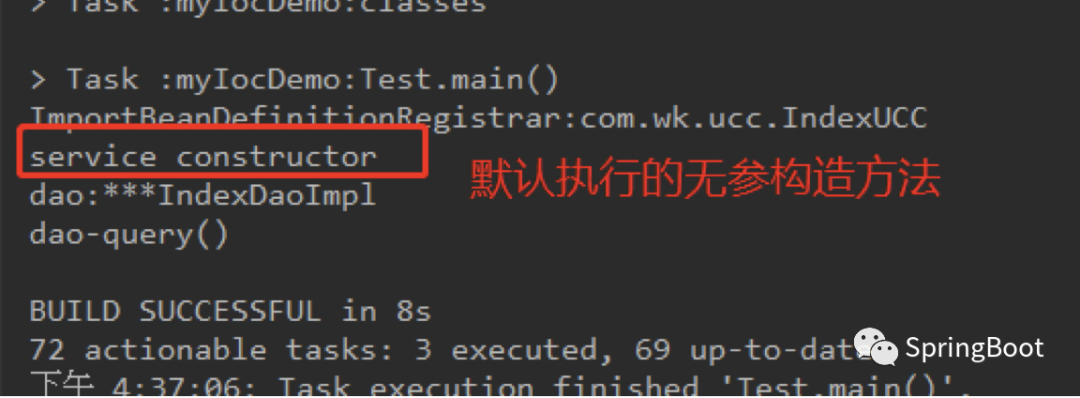
而如果我们想要执行有参的构造方法,则需要在有参构造方法上面加上@Autowired注解即可:
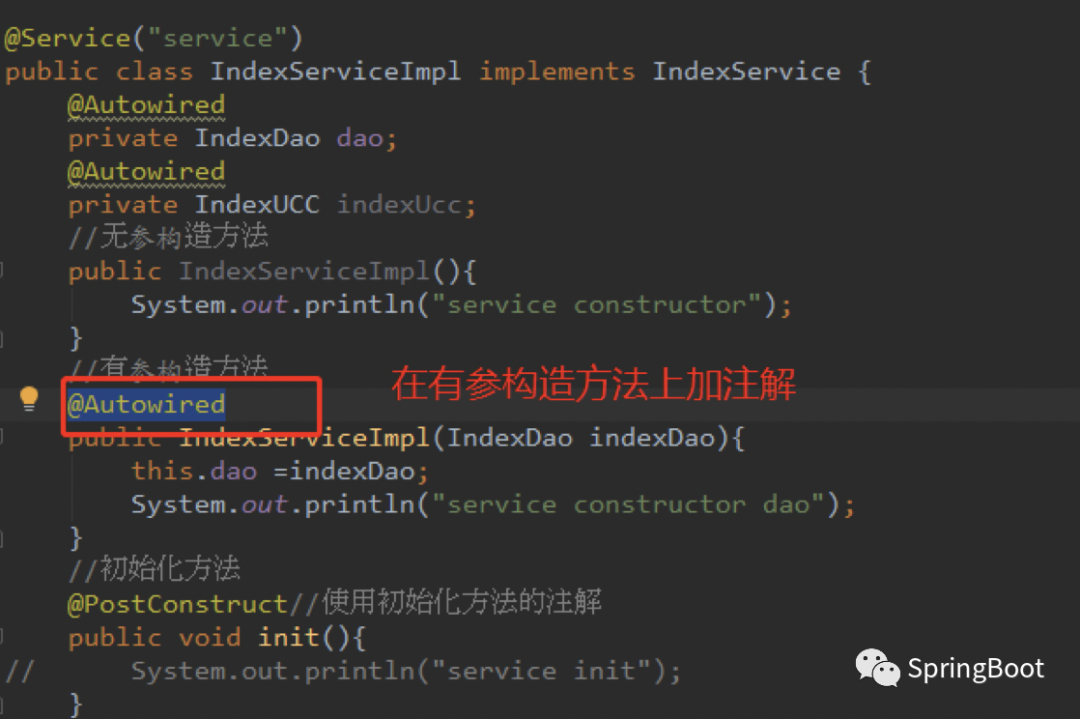
执行结果:发现spring执行了有参的构造方法
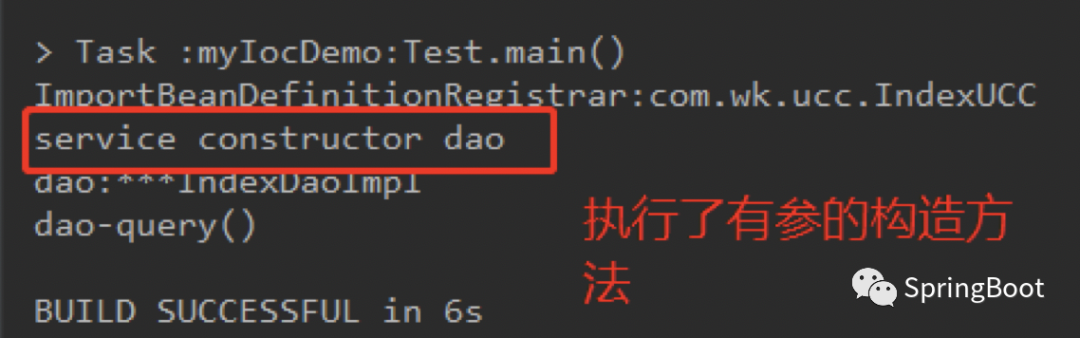
Spring推断构造方法的过程:在这个过程中,如果推断出有一个构造方法加了@Autowired注解,那么spring会把它放到一个临时变量当中,在判断临时变量是否为空,如果不为空,则把这个变量转换成临时数组返回出去,而如果构造方法都没有加@Autowired注解,那么spring就无法判断要把哪个加入到临时变量中,所以最后返回一个null,然后spring根据返回的null来使用默认的构造方法。
二、BeanFactoryPostProcessor扩展实现方式
方式一:使用@Configuration + @Bean?方式初始化
方式二:使用@ComponentScan + @Component方式初始化
接下来通过方式二来更深入的理解一下这个类的几个方法。
2.1?构建一个应用
这里使用了上一节构建的应用,你可以接着或者重新构建一个新的Spring Boot项目。
2.2?实现接口InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
创建一个类,实现接口SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor:
package com.kfit.config;?import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;?import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;?/*** SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor扩展点** @author 悟纤「公众号SpringBoot」* @date 2022-06-22* @slogan 大道至简 悟在天成*/@Componentpublic class MySmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor implements SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor {?/*** 预测Bean的类型,返回第一个预测成功的Class类型,如果不能预测返回null* @param beanClass* @param beanName* @return* @throws BeansException*/@Overridepublic Class<?> predictBeanType(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {System.out.println("MySmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.predictBeanType,beanName:"+beanName);return null;}?/*** 选择合适的构造器,比如目标对象有多个构造器,在这里可以进行一些定制化,选择合适的构造器** @param beanClass : beanClass参数表示目标实例的类型* @param beanName : beanName是目标实例在Spring容器中的name* @return : 返回值是个构造器数组,如果返回null,会执行下一个PostProcessor的determineCandidateConstructors方法;否则选取该PostProcessor选择的构造器* @throws BeansException*/@Overridepublic Constructor<?>[] determineCandidateConstructors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {System.out.println("MySmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.determineCandidateConstructors,beanName:"+beanName);return null;}?/*** 获得提前暴露的bean引用,主要用于解决循环引用的问题* (只有单例对象才会调用此方法)* @param bean* @param beanName* @return* @throws BeansException*/@Overridepublic Object getEarlyBeanReference(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {System.out.println("MySmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor.getEarlyBeanReference,beanName:"+beanName);return null;}}?
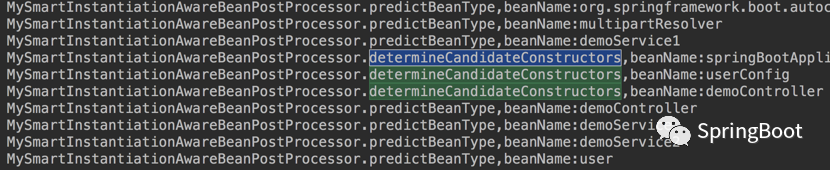
2.3?启动测试
运行项目,看下效果:
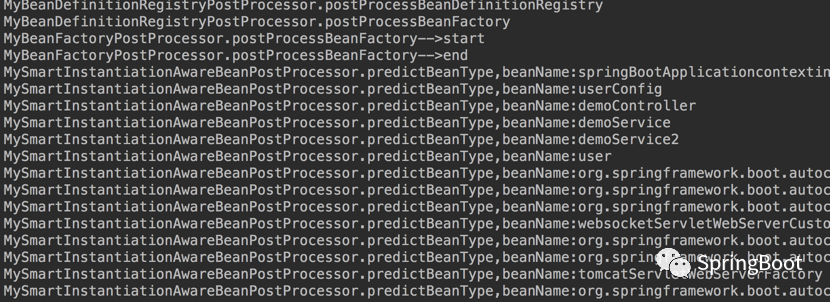
…
三、AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
接下来以AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor?来看看SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor是如何被使用的。
3.1?关键代码
以下为AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor应用SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor的关键代码:
@Override@Nullablepublic Constructor<?>[] determineCandidateConstructors(Class<?> beanClass, final String beanName)throws BeanCreationException {?// Let's check for lookup methods here...if (!this.lookupMethodsChecked.contains(beanName)) {try {ReflectionUtils.doWithMethods(beanClass, method -> {Lookup lookup = method.getAnnotation(Lookup.class);if (lookup != null) {Assert.state(this.beanFactory != null, "No BeanFactory available");LookupOverride override = new LookupOverride(method, lookup.value());try {RootBeanDefinition mbd = (RootBeanDefinition)this.beanFactory.getMergedBeanDefinition(beanName);mbd.getMethodOverrides().addOverride(override);}catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {throw new BeanCreationException(beanName,"Cannot apply @Lookup to beans without corresponding bean definition");}}});}catch (IllegalStateException ex) {throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Lookup method resolution failed", ex);}this.lookupMethodsChecked.add(beanName);}?// Quick check on the concurrent map first, with minimal locking.Constructor<?>[] candidateConstructors = this.candidateConstructorsCache.get(beanClass);if (candidateConstructors == null) {// Fully synchronized resolution now...synchronized (this.candidateConstructorsCache) {candidateConstructors = this.candidateConstructorsCache.get(beanClass);if (candidateConstructors == null) {Constructor<?>[] rawCandidates;try {//反射获取所有构造函数rawCandidates = beanClass.getDeclaredConstructors();}catch (Throwable ex) {throw new BeanCreationException(beanName,"Resolution of declared constructors on bean Class [" + beanClass.getName() +"] from ClassLoader [" + beanClass.getClassLoader() + "] failed", ex);}//候选构造方法List<Constructor<?>> candidates = new ArrayList<>(rawCandidates.length);Constructor<?> requiredConstructor = null;Constructor<?> defaultConstructor = null;//这个貌似是 Kotlin 上用的, 不用管它Constructor<?> primaryConstructor = BeanUtils.findPrimaryConstructor(beanClass);int nonSyntheticConstructors = 0;//遍历这些构造函数for (Constructor<?> candidate : rawCandidates) {//判断构造方法是否是合成的if (!candidate.isSynthetic()) {nonSyntheticConstructors++;}else if (primaryConstructor != null) {continue;}//查看是否有 @Autowired 注解//如果有多个构造方法, 可以通过标注 @Autowired 的方式来指定使用哪个构造方法AnnotationAttributes ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(candidate);if (ann == null) {Class<?> userClass = ClassUtils.getUserClass(beanClass);if (userClass != beanClass) {try {Constructor<?> superCtor =userClass.getDeclaredConstructor(candidate.getParameterTypes());ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(superCtor);}catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {// Simply proceed, no equivalent superclass constructor found...}}}//有 @Autowired 的情况if (ann != null) {if (requiredConstructor != null) {throw new BeanCreationException(beanName,"Invalid autowire-marked constructor: " + candidate +". Found constructor with 'required' Autowired annotation already: " +requiredConstructor);}boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);if (required) {if (!candidates.isEmpty()) {throw new BeanCreationException(beanName,"Invalid autowire-marked constructors: " + candidates +". Found constructor with 'required' Autowired annotation: " +candidate);}requiredConstructor = candidate;}candidates.add(candidate);}//无参构造函数的情况else if (candidate.getParameterCount() == 0) {//构造函数没有参数, 则设置为默认的构造函数defaultConstructor = candidate;}}//到这里, 已经循环完了所有的构造方法?//候选者不为空时if (!candidates.isEmpty()) {// Add default constructor to list of optional constructors, as fallback.if (requiredConstructor == null) {if (defaultConstructor != null) {candidates.add(defaultConstructor);}else if (candidates.size() == 1 && logger.isInfoEnabled()) {logger.info("Inconsistent constructor declaration on bean with name '" + beanName +"': single autowire-marked constructor flagged as optional - " +"this constructor is effectively required since there is no " +"default constructor to fall back to: " + candidates.get(0));}}candidateConstructors = candidates.toArray(new Constructor<?>[0]);}//类的构造方法只有1个, 且该构造方法有多个参数else if (rawCandidates.length == 1 && rawCandidates[0].getParameterCount() > 0) {candidateConstructors = new Constructor<?>[] {rawCandidates[0]};}//这里不会进, 因为 primaryConstructor = nullelse if (nonSyntheticConstructors == 2 && primaryConstructor != null &&defaultConstructor != null && !primaryConstructor.equals(defaultConstructor)) {candidateConstructors = new Constructor<?>[] {primaryConstructor, defaultConstructor};}//这里也不会进, 因为 primaryConstructor = nullelse if (nonSyntheticConstructors == 1 && primaryConstructor != null) {candidateConstructors = new Constructor<?>[] {primaryConstructor};}else {//如果方法进了这里, 就是没找到合适的构造方法//1. 类定义了多个构造方法, 且没有 @Autowired , 则有可能会进这里candidateConstructors = new Constructor<?>[0];}this.candidateConstructorsCache.put(beanClass, candidateConstructors);}}} //这里如果没找到, 则会返回 null, 而不会返回空数组return (candidateConstructors.length > 0 ? candidateConstructors : null);}?
3.2?代码说明
以上方法比较长,?但是仔细看,大致可以划分为几个步骤:
(1)获取类的所有构造方法
(2)遍历构造方法
-?只有一个无参构造方法,?则返回null。
-?只有一个有参构造方法,?则返回这个构造方法。
-?有多个构造方法且没有@Autowired,?此时spring则会蒙圈了,?不知道使用哪一个了.?这里的后置处理器,?翻译过来,?叫智能选择构造方法后置处理器。当选择不了的时候,?干脆返回?null。
-?有多个构造方法,?且在其中一个方法上标注了?@Autowired ,?则会返回这个标注的构造方法
-?有多个构造方法,?且在多个方法上标注了@Autowired,?则spring会抛出异常, spring会认为,?你指定了几个给我,?是不是你弄错了。
我就是我,是颜色不一样的烟火。
我就是我,是与众不同的小苹果。à悟空学院:https://t.cn/Rg3fKJD
学院中有Spring?Boot相关的课程!点击「阅读原文」进行查看!
SpringBoot视频:http://t.cn/A6ZagYTi
SpringBoot交流平台:https://t.cn/R3QDhU0
SpringSecurity5.0视频:http://t.cn/A6ZadMBe
ShardingJDBC分库分表:http://t.cn/A6ZarrqS
分布式事务解决方案:http://t.cn/A6ZaBnIr
JVM内存模型调优实战:http://t.cn/A6wWMVqG
Spring入门到精通:https://t.cn/A6bFcDh4
大话设计模式之爱你:https://dwz.cn/wqO0MAy7