目录
1. 创建Spring 项目
1)?创建?个普通 Maven 项?。
2.)添加 Spring 框架?持(spring-context、spring-beans)。
3)?添加启动类。
1.1?创建?个 Maven 项?
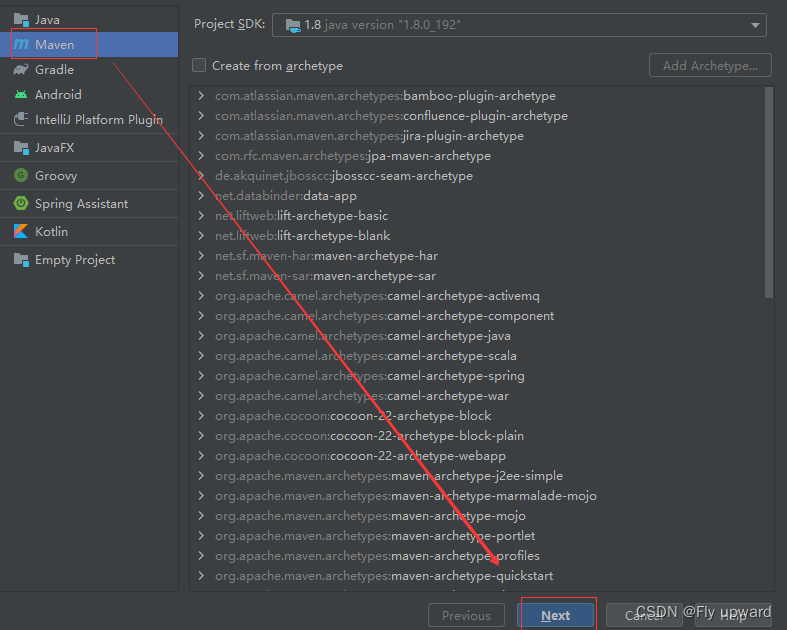
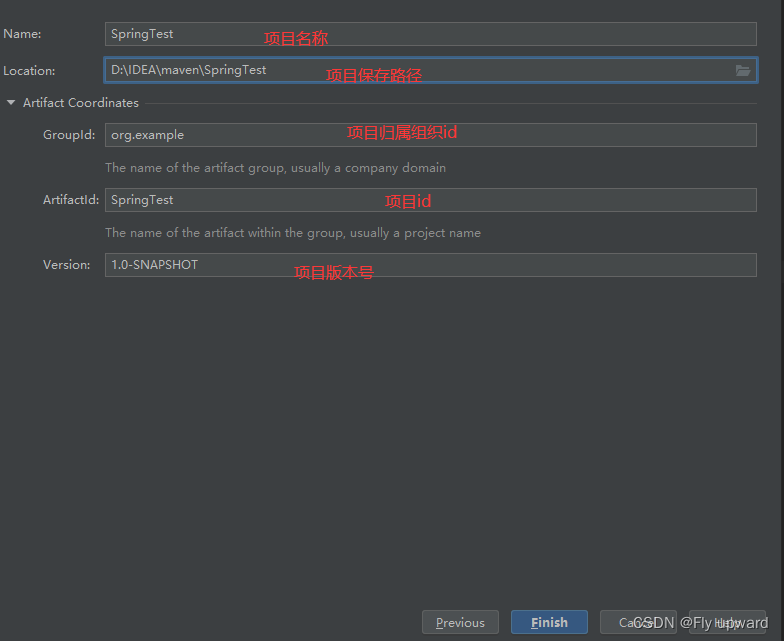
?1.2 添加 Spring 框架支持
在项?的 pom.xml 中添加 Spring 框架的?持,xml 配置如下:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.2.3.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-beans</artifactId>
<version>5.2.3.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
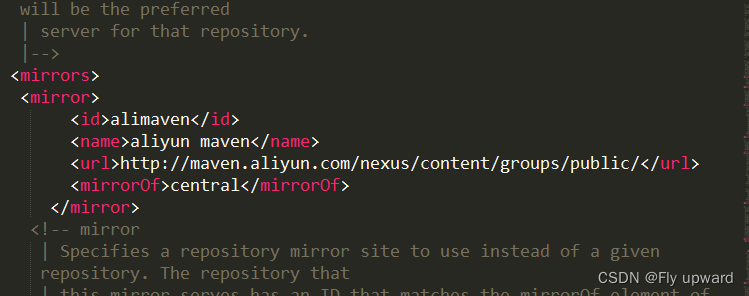
</dependencies>配置国内源
将下面两个框都要勾选上
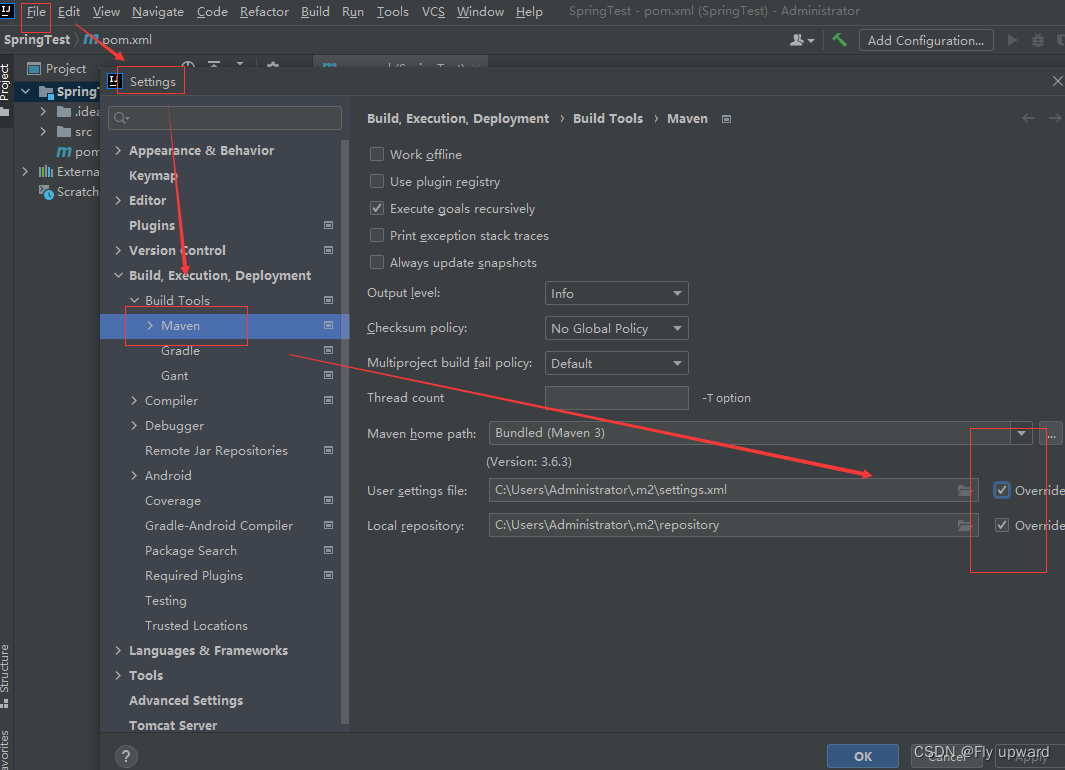
?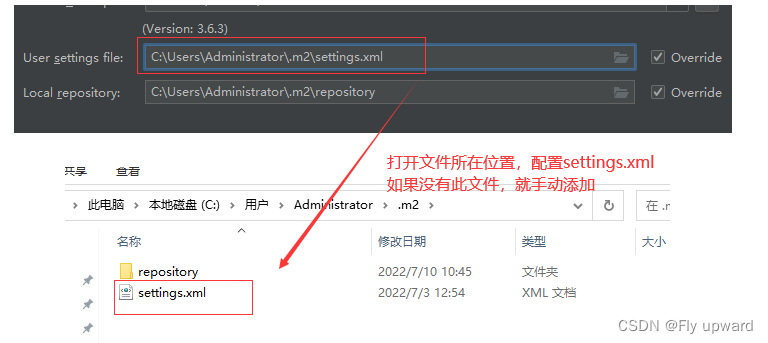
?settings.xml 文件配置代码:
<mirrors>
<mirror>
<id>alimaven</id>
<name>aliyun maven</name>
<url>http://maven.aliyun.com/nexus/content/groups/public/</url>
<mirrorOf>central</mirrorOf>
</mirror>修改位置如下
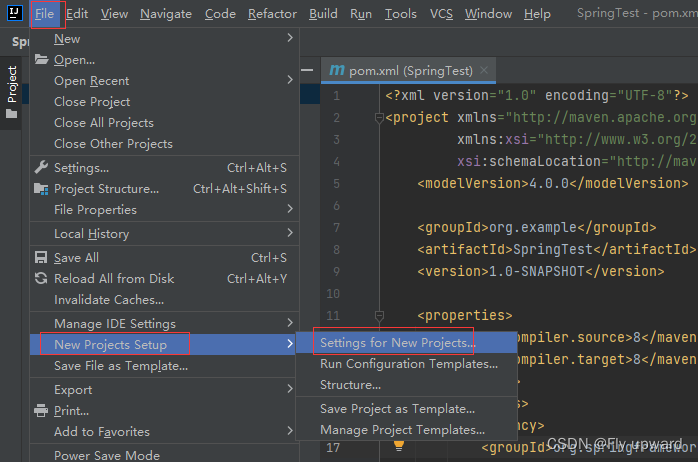
?配置好之后,如果想下一次的项目也使用该国内源,则需下面的配置
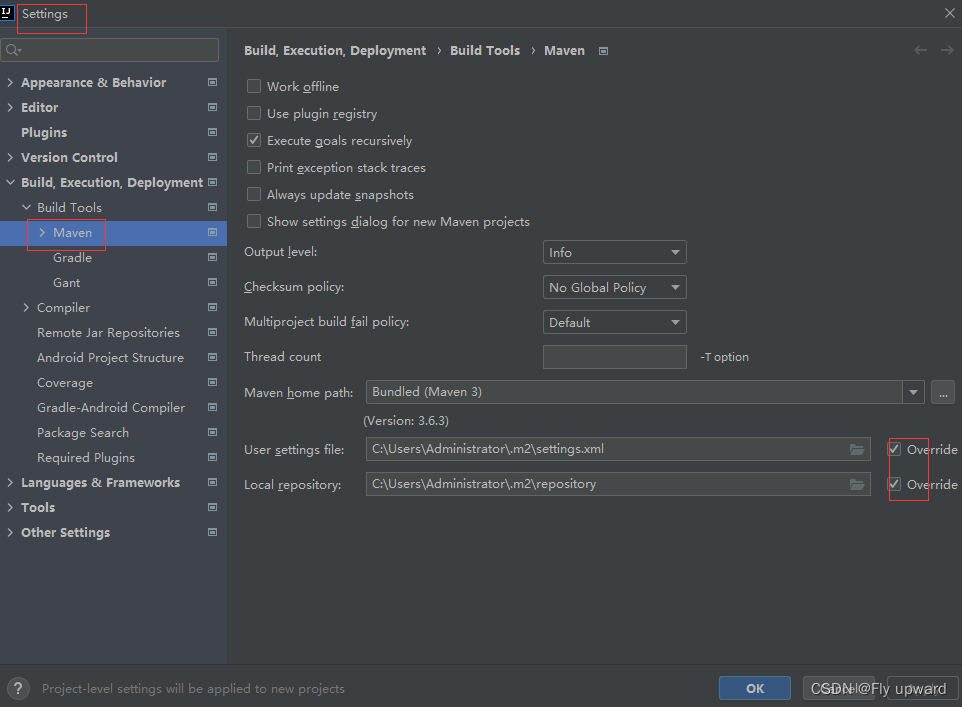
?
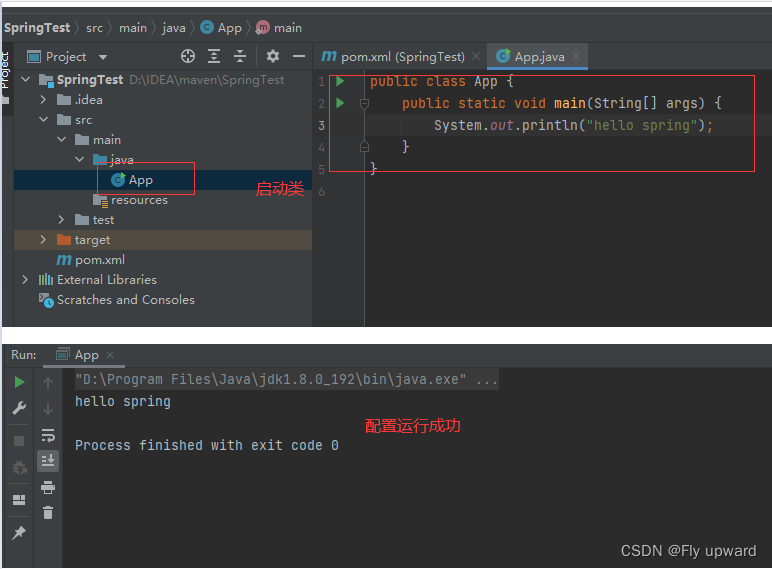
?1.3 添加启动类
最后在创建好的项? java ?件夹下创建?个启动类,包含 main ?法即可
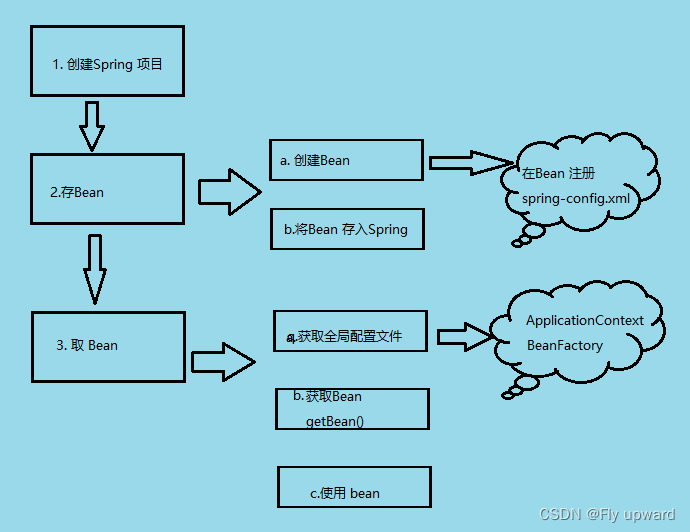
2. 存储 Bean 对象
存储 Bean 分为以下 3步:
1)存储 Bean 之前,先得有 Bean 才?,因此先要创建?个 Bean。
2)?配置?件 spring-config.xml
3)将创建的 Bean 注册到 Spring 容器中。
2.1?创建Bean?
Bean 就是 Java 语?中的?个普通对象,实现代码如下:
public class User {
public static void say(String name){
System.out.println("hello " + name);
}
}2.2?配置?spring-config.xml
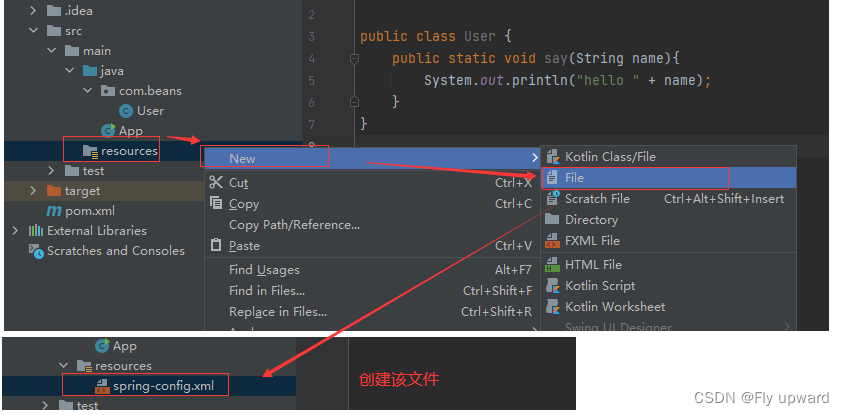
在文件中添加以下代码
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
</beans>再将 User 对象注册到spring-config.xml 中就可以,具体操作是在 <beans> 中添加如下配置:
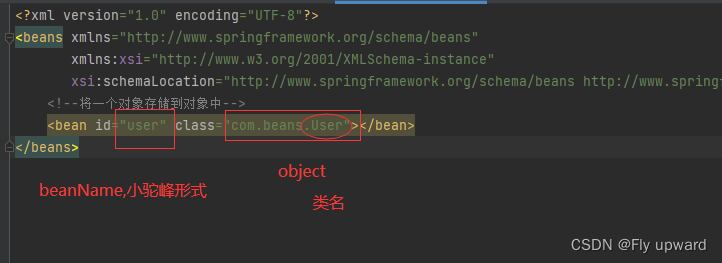
3. 获取并使用?Bean 对象
获取并使? Bean 对象,分为以下 3 步:
1. 得到 Spring 上下?对象,因为对象都交给 Spring 管理了,所以获取对象要从 Spring 中获取,那么就得先得到 Spring 的上下?。
2. 通过 Spring 上下?,获取某?个指定的 Bean 对象。
3. 使? Bean 对象。
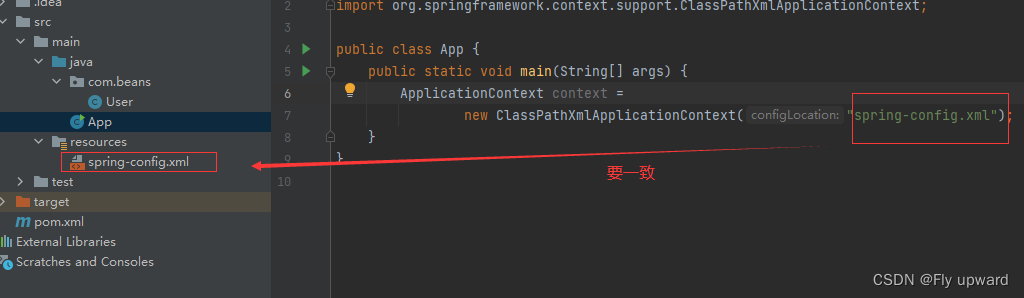
3.1 创建Sprign 上下文
Spring 上下?对象可使? ApplicationContext,代码如下
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml");
}
除了 ApplicationContext 之外,我们还可以使? BeanFactory 来作为 Spring 的上下?,如下代码所示
// 1.得到 bean 工厂
BeanFactory factory = new XmlBeanFactory(
new ClassPathResource("spring-config.xml"));
// 2.获取 bean
User user = (User) factory.getBean("user");
// 3.使用 bean
user.say("黄小小");ApplicationContext 和 BeanFactory 效果是?样的,ApplicationContext 属于 BeanFactory 的?类, 它们的区别如下
1)继承关系和功能??来说:Spring 容器有两个顶级的接?:BeanFactory 和ApplicationContext。
其中 BeanFactory 提供了基础的访问容器的能?,? ApplicationContext 属于 BeanFactory 的?类,它除了继承了 BeanFactory 的所有功能之外,它还拥有独特的特性,还添加了对国际化?持、资源访问?持、以及事件传播等??的?持。
2)从性能??来说:ApplicationContext 是?次性加载并初始化所有的 Bean 对象,? BeanFactory是需要那个才去加载那个,因此更加轻量。
?3.2??获取指定的 Bean 对象
//2.根据上下文对象提供的方法获取到 bean
//User user = (User) context.getBean("user");//与spring-config.xml 中的id 一致
//User user = context.getBean(User.class);//不需要强转,但不建议使用
User user = context.getBean("user",User.class);//精准并不需要强转,推荐使用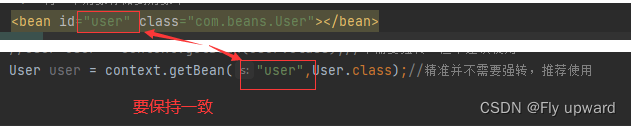

?3.3 使用Bean
//3.使用
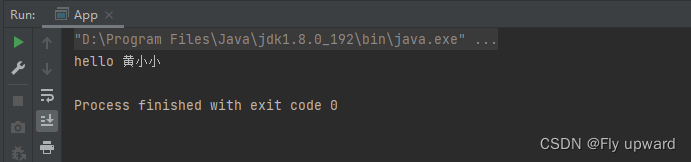
user.say("黄小小");总代码:
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.得到 spring 上下文对象
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml");
//2.根据上下文对象提供的方法获取到 bean
//User user = (User) context.getBean("user");//与spring-config.xml 中的id 一致
//User user = context.getBean(User.class);//不需要强转,但不建议使用
User user = context.getBean("user",User.class);//精准并不需要强转,推荐使用
//3.使用
user.say("黄小小");
}
}
4.总结
更简单的获取和存储对象
5.配置扫描路径
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:content="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<content:component-scan base-package="com.beans"></content:component-scan>
</beans>
6.添加注解存储 bean对象
1)? 类注解:@Controller、@Service、@Repository、@Component、@Configuration。2)? ?法注解:@Bean
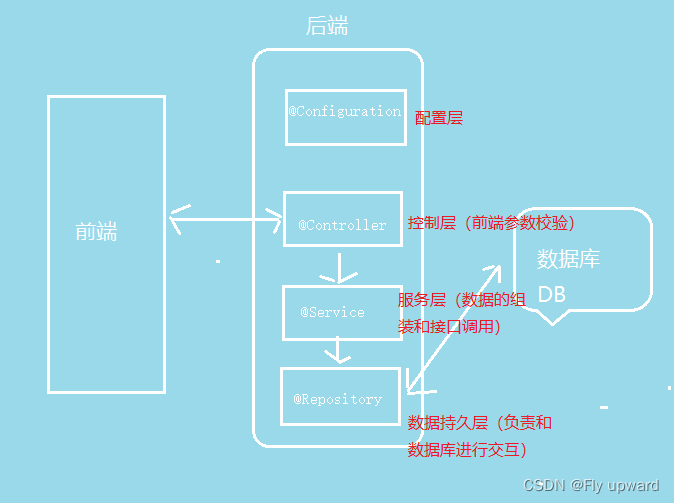
6.1 @Controller(控制器存储)?
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
@Controller//将对象存储到Spring中
public class UserController {
public void sayHi() {
System.out.println("hello controller");
}
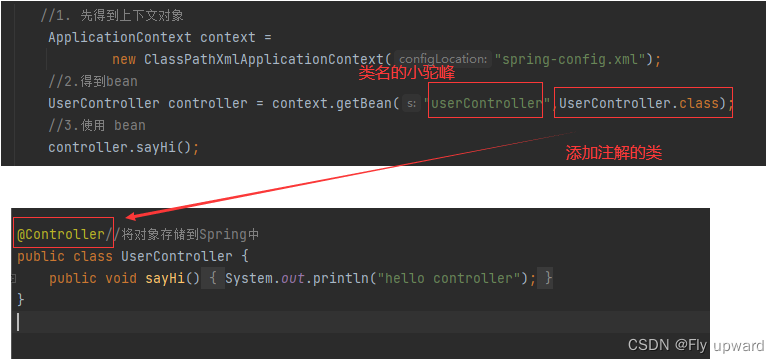
}public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 先得到上下文对象
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml");
//2.得到bean
UserController controller = context.getBean("userController",UserController.class);
//3.使用 bean
controller.sayHi();
}
}代码注入解释:
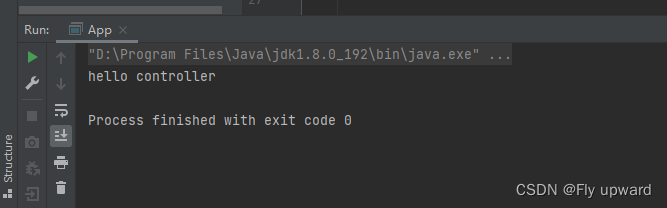
获取结果
?6.2 @Service (服务器存储)
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class UserService {
public void sayHi() {
System.out.println("hello service");
}
}在main 方法中用读取对象的?式来读取上?的 UserService 对象,如下代码所示
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 先得到上下文对象
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml");
//2.得到bean
UserService service = context.getBean("userService",UserService.class);
//3.使用 bean
service.sayHi();
}
}6.3 @Repository (仓库存储)
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class UserRepository {
public void sayHi() {
System.out.println("hello repository");
}
}在main 方法中用读取对象的?式来读取上?的 UserController 对象,如下代码所示
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 先得到上下文对象
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml");
//2.得到bean
UserRepository repository = context.getBean("userRepository",UserRepository.class);
//3.使用 bean
repository.sayHi();
}
}6.4 @Component (组件存储)
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class UserComponent {
public void sayHi() {
System.out.println("hello component");
}
}在main 方法中用读取对象的?式来读取上?的 UserComponent 对象,如下代码所示
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 先得到上下文对象
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml");
//2.得到bean
UserComponent component = context.getBean("userComponent",UserComponent.class);
//3.使用 bean
component.sayHi();
}
}6.5?@Configuration(配置存储)
使用?@Configuration 存储 bean 的代码如下所示:
@Configuration
public class UserConfig {
public void sayHi() {
System.out.println("hello Configuration");
}
}在main 方法中用读取对象的?式来读取上?的 UserConfig 对象,如下代码所示
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 先得到上下文对象
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml");
//2.得到bean
UserConfig config = context.getBean("userConfig",UserConfig.class);
//3.使用 bean
config.sayHi();
}
}?6.6 为什么需要五大注解
让代码可读性提高,能直观的判断当前类的用途

6.7 方法注解 @Bean
6.7.1 方法注解配合类注解使用
1)创建一个 bean
在要扫描的根路径(com.beans)下创建一个? UserBeans 类
@Component
public class UserBeans {
@Bean
public User user1() {
User user = new User();
user.setId(1);
user.setName("黄小小");
return user;
}
}然后创建一个User对象
public class User {
private int id;
private String name;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"id=" + id +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
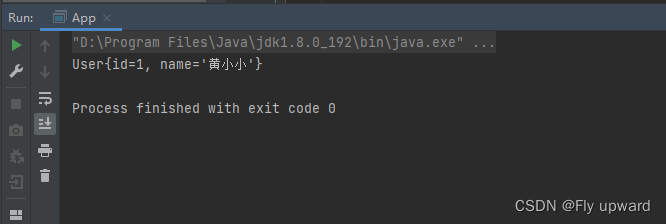
}在main 方法中用读取对象的?式来读取上?的 User?对象,如下代码所示
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 先得到上下文对象
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml");
User user = context.getBean("user1",User.class);
System.out.println(user);
}
}
6.7.2 重命名Bean
当 User 类里面有多个对象时,可以通过设置 name 属性给 Bean 对象进?重命名操作,如下代码
@Component
public class UserBeans {
@Bean(name = "in")
public User user1() {
User user1 = new User();
user1.setId(1);
user1.setName("黄小小");
return user1;
}
@Bean(name = "to")
public User user2() {
User user2 = new User();
user2.setId(2);
user2.setName("杨通达");
return user2;
}
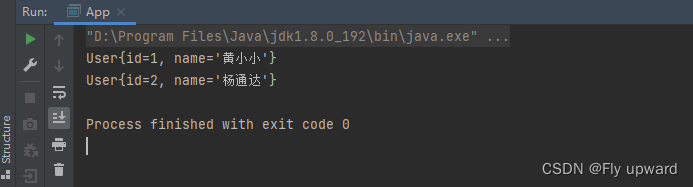
}?通过使用 Bean 里面的 name 就可以获取对象了
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 先得到上下文对象
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml");
User user1 = context.getBean("in",User.class);
System.out.println(user1);
User user2 = context.getBean("to",User.class);
System.out.println(user2);
}
}
8.获取 Bean 对象
1. 属性注?2. 构造?法注?3. Setter 注?
8.1 属性注入
UserService类
@Service
public class UserService {
public void sayHi() {
System.out.println("hello service");
}
}UserController2 类
@Controller
public class UserController2 {
//对象注入方式1:属性注入
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
public void sayHi() {
userService.sayHi();
}
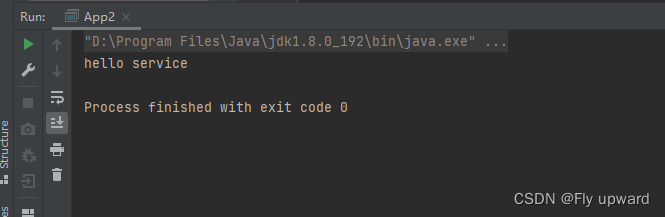
}main方法
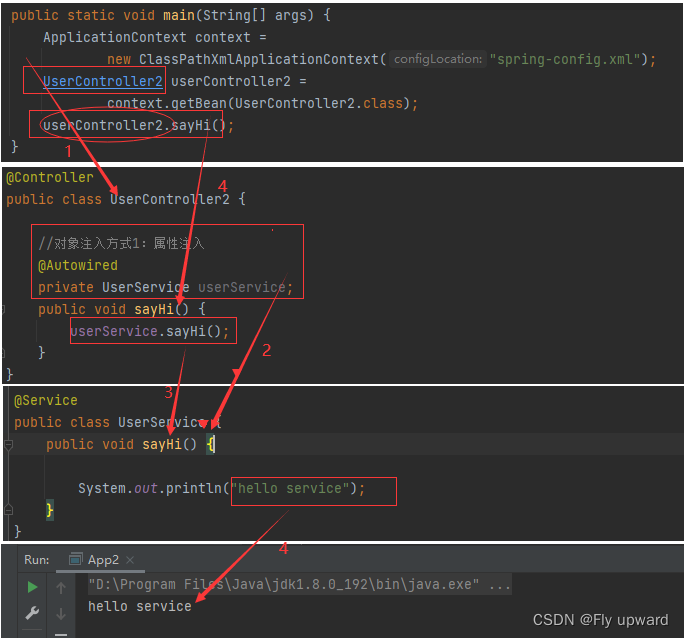
public class App2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-config.xml");
UserController2 userController2 =
context.getBean(UserController2.class);
userController2.sayHi();
}
}获取结果
?整个获取的调用链过程:
?8.2 构造方法注入
其中UserService类和上面属性注入的一样。
@Controller
public class UserController3 {
private UserService userService;
//构造方法注入(官方推荐)
@Autowired
public UserController3(UserService userService) {
this.userService = userService;
}
/*
//当有多个构造方法时,上面的 @Autowired 不能省略
public UserController3(UserService userService, int num) {
this.userService = userService;
}*/
public void sayHi() {
userService.sayHi();
}
}8.3 Setter 注入
@Controller
public class UserController4 {
private UserService userService;
//Setter 注?
@Autowired
public void setUserService(UserService userService) {
this.userService = userService;
}
public void sayHi() {
userService.sayHi();
}
}8.4?三种注?优缺点分析
1)属性注?的优点是简洁,使??便;缺点是只能?于 IoC 容器,如果是? IoC 容器不可?,并且只有在使?的时候才会出现 NPE(空指针异常)。2)构造?法注?是 Spring 推荐的注??式,它的缺点是如果有多个注?会显得?较臃肿,但出现这种情况你应该考虑?下当前类是否符合程序的单?职责的设计模式了,它的优点是通?性,在使?之前?定能把保证注?的类不为空。3)Setter ?式是 Spring 前期版本推荐的注??式,但通?性不如构造?法,所有 Spring 现版本已经推荐使?构造?法注?的?式来进?类注?了
8.5 @Resource:另一种注入关键字
@Controller
public class UserController4 {
private UserService userService;
//Setter 注?
//@Autowired
@Resource
public void setUserService(UserService userService) {
this.userService = userService;
}
public void sayHi() {
userService.sayHi();
}
}1)出身不同:@Resource 来自于 JDK ,@Autowrired 是Spring 框架提供的2)用法不同:@Autowired 支持属性注入、构造方法注入和Setter 注入,而 @Resource 不支持构造方法注入。3)支持的参数不同:@Resource 支持更多的参数设置,比如 name 、type 设置,而@Autowired 只支持required 参数设置。