什么时候执行:
1、容器初始化完成后调用(spring自己的事件监听)
源码分析
springBoot的启动类中调用了run方法
springboot的启动类
public class StarterApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
SpringApplication.run(StarterApplication.class, args);
log.info("启动成功");
} catch (Exception ex) {
log.error("运行异常:{}",ex);
}
}
}
?run方法在各个阶段都会发布时间,触发监听事件的执行,例如:
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication#run(java.lang.String...)
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
// 发布启动开始监听事件
listeners.starting();
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(
args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners,
applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
context = createApplicationContext();
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(
SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments,
printedBanner);
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass)
.logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
// 发布启动完成监听事件
listeners.started(context);
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
// 发布运行中监听事件
listeners.running(context);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}追踪代码可以看到各个事件都调用了
listener.onApplicationEvent(event);2、自定义事件监听
比如业务完成后需要进行某个耗时比较久的操作,除了mq也可以用spring的事件监听功能
ApplicationEvent和ApplicationListener。
为什么要使用ApplicationEvent和ApplicationListener?
Spring事件需要遵循以下程序,我们就按着这几个步奏一一道来:
(1)自定义事件:继承ApplicationEvent
(2)定义事件监听器:实现ApplicationListener
(3)使用容器发布事件
?
那么不发布事件是否也可以执行onApplicationEvent呢?
查看源码可以发现,spring也有自己的一些监听器都是会默认执行的,这些监听器都是配置在spring.factories 配置文件中,也就是说只要在这个文件中的监听器项目启动过程中就会执行
实现方式:
在META-INF中自定义配置文件spring.factories,spring就能识别到,具体写法可以搜索spring自带的spring.factories文件
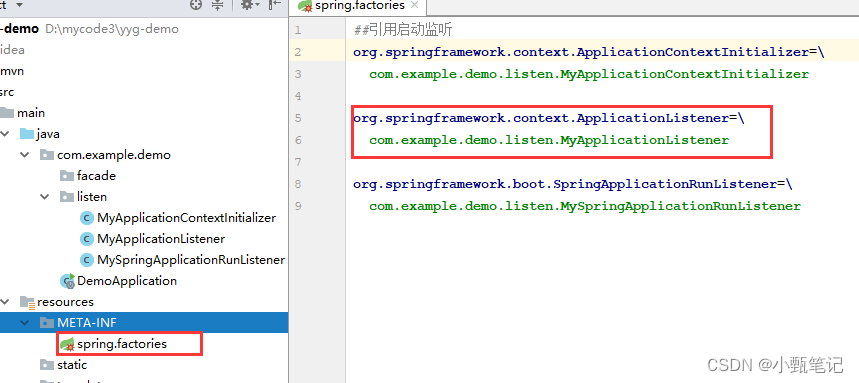
?具体就可以编写代码了
public class MyApplicationListener implements ApplicationListener {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
System.out.println("MyApplicationListener...onApplicationEvent...");
}
}发布事件的方式:
方式1:自己获取容器发布
ApplicationContext context = ContextLoader.getCurrentWebApplicationContext();
// ResponseEvent 继承了springEvent的实体类,具体自己定义
ResponseEvent event = new ResponseEvent(source, ResponseLog);
context.publishEvent(event);
方式2:ApplicationEventPublisher是ApplicationContext的父接口之一
功能就是发布事件,也就是把某个事件告诉的所有与这个事件相关的监听器。
这个方法会通知的所有与事件相匹配的监听器。这些监听可能是spring框架的监听器,也有可能是特定的监听器
package org.springframework.context;
@FunctionalInterface
public interface ApplicationEventPublisher {
// 方法一
default void publishEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
this.publishEvent((Object)event);
}
// 方法二
void publishEvent(Object var1);
}方法一使用案例
1、定义实体类继承ApplicationEvent
public class CallbackSendMsgEvent extends ApplicationEvent {
public CallbackSendMsgEvent(SendMsgReqDto sendMsgReqDto){
super(sendMsgReqDto);
}
}?2、事件发布
@Resource
private ApplicationEventPublisher eventPublisher;
// 业务方法
public void test (){
eventPublisher.publishEvent(new CallbackSendMsgEvent(reqDto));
}
3、监听
@Service
public class CallbackMsgSender implements ApplicationListener<CallbackSendMsgEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(CallbackSendMsgEvent callbackSendMsgEvent) {
// 具体业务处理
}
}方法二使用案例
1、定义实体类
// 普通的实体类
public class CallbackSendMsgEvent {
}2、事件发布
// 具体发布什么就传入什么对象
applicationEventPublisher.publishEvent(new CallbackSendMsgEvent ());3、监听
import org.springframework.context.event.EventListener;
// 通过注解来监听
@EventListener
public void listener(CallbackSendMsgEvent event) {
// 业务逻辑
}另外也可以实现自定义的publiser
在自定义事件发布器MyEventPublisher中,我们需要通过ApplicationEventPublisher来发布事件,所以我们实现了ApplicationEventPublisherAware接口,通过回调方法setApplicationEventPublisher为MyEventPublisher的ApplicationEventPublisher属性赋值;同样的,我们自定义的事件MyEvent构造函数需要传入Spring上下文,所以MyEventPublisher还实现了ApplicationContextAware接口,注入了上下文对象ApplicationContext。
@Component
public class MyEventPublisher implements ApplicationEventPublisherAware, ApplicationContextAware {
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
private ApplicationEventPublisher applicationEventPublisher;
private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
@Override
public void setApplicationEventPublisher(ApplicationEventPublisher applicationEventPublisher) {
this.applicationEventPublisher = applicationEventPublisher;
}
public void publishEvent() {
logger.info("开始发布自定义事件MyEvent");
MyEvent myEvent = new MyEvent(applicationContext);
applicationEventPublisher.publishEvent(myEvent);
logger.info("发布自定义事件MyEvent结束");
}
}