1.Bean的发现
????????????????spring boot默认扫描启动类所在的包下的主类与子类的所有组件,但并没有包括依赖包中的类,那么依赖包中的bean是如何被发现和加载的?
我们需要从Spring Boot项目的启动类开始跟踪,在启动类上我们一般会加入SpringBootApplication注解
????????
重点介绍如下四个注解:
????????**SpringBootConfiguration**:作用就相当于**Configuration**注解,被注解的类将成为一个bean配置类
????????**ComponentScan**:作用就是自动扫描并加载符合条件的组件,最终将这些bean加载到spring容器中
????????**EnableAutoConfiguration** :这个注解很重要,借助@**Import**的支持,收集和注册依赖包中相关的bean定义
????????**EnableConfigurationProperties**:?启用配置属性
2.自动配置实现方法? ?
????????1、@Configuration与@Bean:基于Java代码的bean配置
????????2、@Conditional:设置自动配置条件依赖
????????3、@EnableConfigurationProperties与@ConfigurationProperties:读取配置文件转换为bean
????????4、@EnableAutoConfiguration与@Import:实现bean发现与加载
3.案例一
????????第一步:创建starter工程hello-spring-boot-starter并配置pom.xml文件
~~~xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<groupId>cn.itcast</groupId>
<artifactId>hello-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-autoconfigure</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
~~~????????第二步:创建配置属性类HelloProperties
package com.laoyang.config;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
/**
* @author:Kevin
* @create: 2022-09-17 09:27
* @Description: 创建数据源配置类,用于封装配置文件的配置属性
*/
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "hello")
public class HelloProties {
private String name;
private String adress;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAdress() {
return adress;
}
public void setAdress(String adress) {
this.adress = adress;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HelloProties{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", adress='" + adress + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
????????第三步:创建服务类HelloService
package com.laoyang.service;
/**
* @author:Kevin
* @create: 2022-09-17 09:34
* @Description: 服务类
*/
public class HelloService {
private String name;
private String address;
public HelloService(String name, String address) {
this.name = name;
this.address = address;
}
public String sayHello(){
return "你好!我的名字叫 " + name + ",我来自 " + address;
}
}
????????第四步:创建自动配置类HelloServiceAutoConfiguration
package com.laoyang.config;
import com.laoyang.service.HelloService;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnMissingBean;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @author:Kevin
* @create: 2022-09-17 09:37
* @Description: helloservice的自动配置类,很关键
*/
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(value = HelloProties.class) //启用配置属性
public class HelloServiceAutoConfiguration {
private HelloProties helloProperties;
//通过构造方法注入配置属性对象HelloProperties
public HelloServiceAutoConfiguration(HelloProties helloProperties) {
this.helloProperties = helloProperties;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean // 不存在这个实例才去创建这个实例bean
public HelloService helloService(){
return new HelloService(helloProperties.getName(), helloProperties.getAdress());
}
}
????????第五步:在resources目录下创建META-INF/spring.factories
????????
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
com.laoyang.config.HelloServiceAutoConfiguration3.1????????以下开始测试(hello-spring-boot-starter)已经封装完毕
????????第一步:创建maven工程myapp并配置pom.xml文件,这里需要导入我们刚才那个maven,注意刚才那个maven不要忘了install
????????
~~~xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<groupId>cn.itcast</groupId>
<artifactId>myapp</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--导入自定义starter-->
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.itcast</groupId>
<artifactId>hello-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
~~~????????第二步:创建application.yml文件
server:
port: 8080
hello:
name: kevin
address: sx????????第三步:创建HelloController
package com.laoyang.controller;
import com.laoyang.service.HelloService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @author:Kevin
* @create: 2022-09-17 09:57
* @Description:
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public class hellocontroller {
@Autowired
private HelloService helloService;
@GetMapping("/say")
public String sayHello(){
return helloService.sayHello();
}
}
????????第四步:创建启动类HelloApplication
package com.laoyang;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
/**
* @author:Kevin
* @create: 2022-09-17 09:59
* @Description: 启动类
*/
@SpringBootApplication
public class HelloApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(HelloApplication.class, args);
}
}
???????????????执行启动类main方法
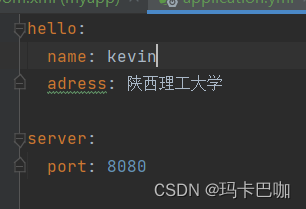
总结:我们创建了两个maven工程,第一个是实现spring boot-starter的自动装配原理,第一步,创建了数据源配置类,用于封装配置文件的配置属性,通过@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "hello")
这个注解标识了数据源的初始化名称,相当于yml文件的前缀,如图:
?另外配置了helloservice类,保证自动装配生效来验证,最关键的一步,helloservice的自动配置类,很关键,
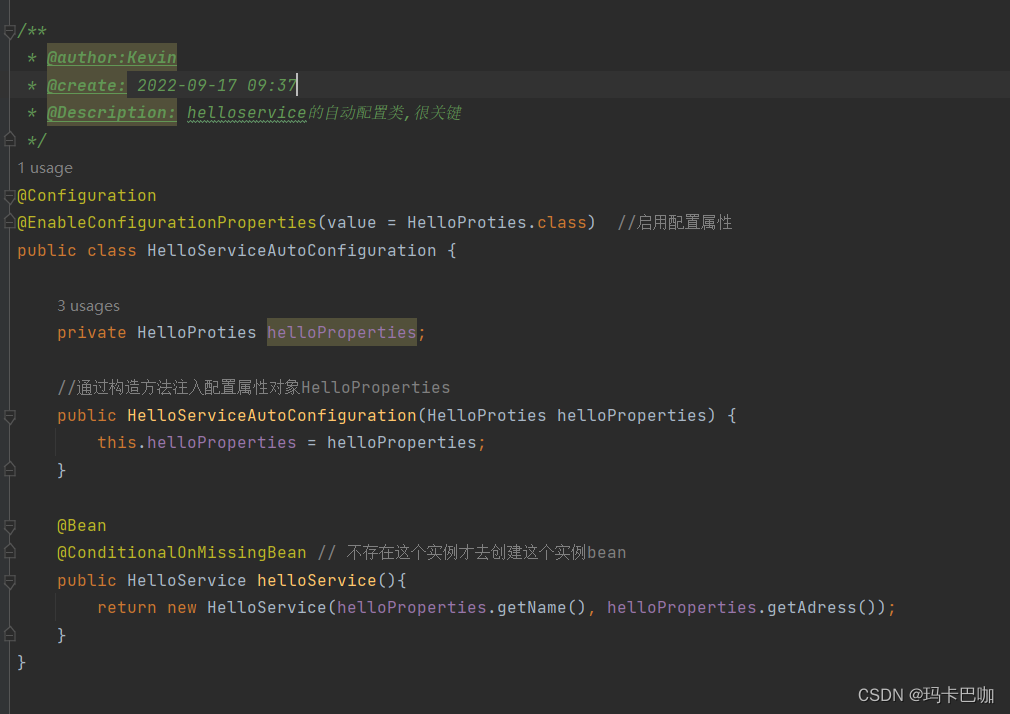
@Configuration //配置文件类 @EnableConfigurationProperties(value = HelloProties.class) //启用配置属性
?最后成功的将这个配置类对象封装成了bean对象放到了spring容器中。
??2.3.2 案例二??
????????在前面的案例一中我们通过定义starter,自动配置了一个HelloService实例。本案例我们需要通过自动配置来创建一个拦截器对象,通过此拦截器对象来实现记录日志功能。
????????第一步:在hello-spring-boot-starter的pom.xml文件中追加如下maven坐标
????????
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
</dependency>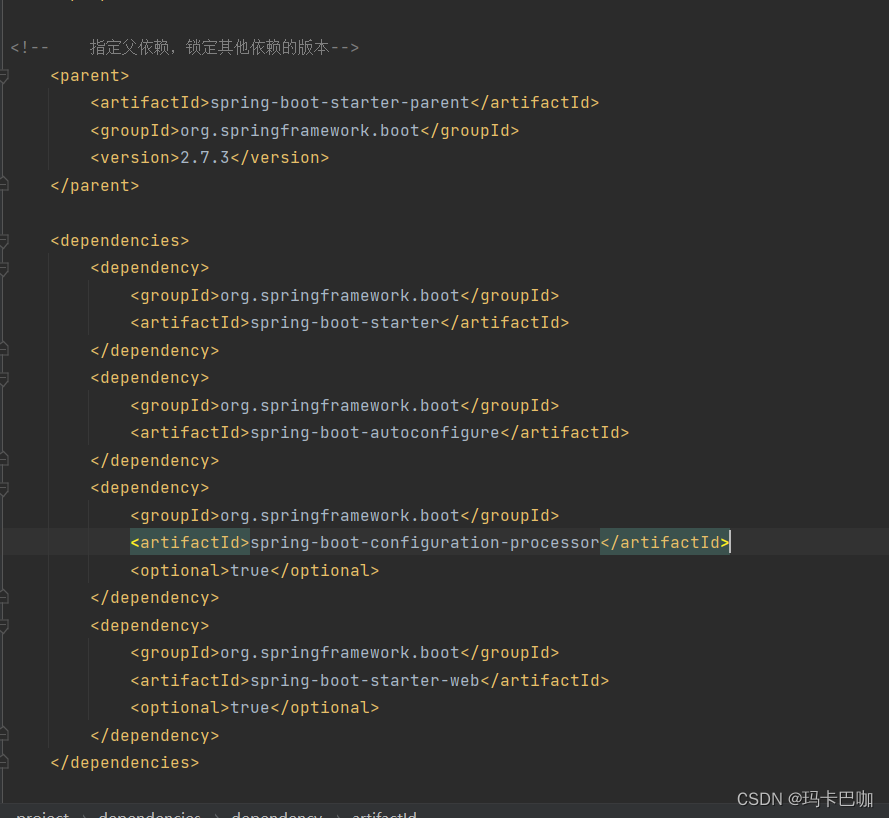
?
?
第二步:自定义MyLog注解
? ? ? ? 注解上的两个注解方法作用:
@Target(ElementType.METHOD) //这个注解加在方法上,通过ElementType的枚举指定这个注解加在什么位置 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) //这个注解运行时生效
????????
package com.laoyang.log;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* 自定义日志注解
*/
@Target(ElementType.METHOD) //这个注解加在方法上,通过ElementType的枚举指定这个注解加在什么位置
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) //这个注解运行时生效
public @interface MyLog {
/**
* 方法描述
*/
String desc() default "";
}
????????????????第三步:自定义日志拦截器MyLogInterceptor,用来计算加了MyLog注解后的方法从开始到结束总共的运行时间。
????????
package com.laoyang.log;
import org.springframework.web.method.HandlerMethod;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.HandlerInterceptorAdapter;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
/**
* @author:Kevin
* @create: 2022-09-17 10:41
* @Description: 自定义拦截器
*/
public class MylogInterceptor extends HandlerInterceptorAdapter {
private static final ThreadLocal<Long> startTimeThreadLocal = new ThreadLocal<>();
/**
* controller方法执行之前
* @param request
* @param response
* @param handler
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = (HandlerMethod)handler; //转换成方法处理器
Method method = handlerMethod.getMethod(); //获得被拦截的方法对象
MyLog annotation = method.getAnnotation(MyLog.class); //获得方法上的MyLog注解
if (annotation != null){
//说明当前拦截的方法加入了MyLog注解
long currentTimeMills = System.currentTimeMillis();
startTimeThreadLocal.set(currentTimeMills);
}
return true;
}
/**
* controller方法执行之后
* @param request
* @param response
* @param handler
* @param modelAndView
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
HandlerMethod handlerMethod = (HandlerMethod)handler; //转换成方法处理器
Method method = handlerMethod.getMethod(); //获得被拦截的方法对象
MyLog annotation = method.getAnnotation(MyLog.class); //获得方法上的MyLog注解
if (annotation!=null){
//说明当前拦截的方法加入了MyLog注解
long endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
Long startTime = startTimeThreadLocal.get();
long optTime = endTime - startTime; //计算controller方法执行时间
String requestUri = request.getRequestURI(); //获取当前请求的地址
String methodName = method.getDeclaringClass().getName() + "." +
method.getName(); //获取当前请求的方法名称
String methodDesc = annotation.desc(); //获取注解的声明
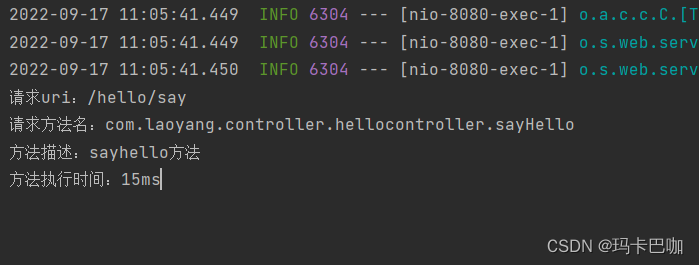
System.out.println("请求uri:" + requestUri);
System.out.println("请求方法名:" + methodName);
System.out.println("方法描述:" + methodDesc);
System.out.println("方法执行时间:" + optTime + "ms");
}
super.postHandle(request, response, handler, modelAndView);
}
}
????????第四步:创建自动配置类MyLogAutoConfiguration,用于自动配置拦截器、参数解析器等web组件,?用于自动创建拦截器对象,但此时只是创建了实例,还需要自动配置
????????
package com.laoyang.config;
import com.laoyang.log.MylogInterceptor;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.InterceptorRegistry;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurer;
/**
* @author:Kevin
* @create: 2022-09-17 10:56
* @Description: 拦截器自动配置类,用于自动创建拦截器对象
* 因为配置为web层的拦截器对象,所以要实现WebMvcConfigurer
*/
@Configuration
public class MyLogAutoConfiguration implements WebMvcConfigurer {
/**
* 添加注册拦截器配置
* @param registry
*/
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(new MylogInterceptor());
}
}
????????第五步:在spring.factories中追加MyLogAutoConfiguration配置,放入自动配置创库实现springboot的自动配置
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
com.laoyang.config.HelloServiceAutoConfiguration,\
com.laoyang.config.MyLogAutoConfiguration?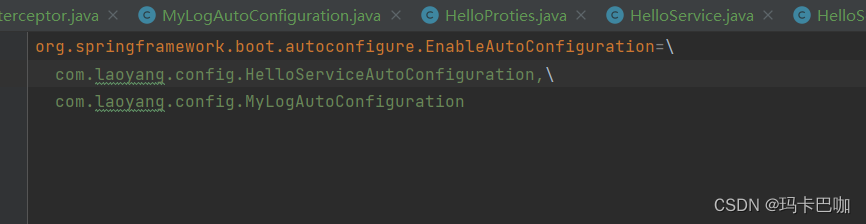
? ? ? ? 欧克,最后install,打包,在我们的另一个maven项目稍加修改。
? ? ? ? 注意,这里是另一个maven项目,用来测试的。
package com.laoyang.controller;
import com.laoyang.log.MyLog;
import com.laoyang.service.HelloService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
/**
* @author:Kevin
* @create: 2022-09-17 09:57
* @Description:
*/
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public class hellocontroller {
@Autowired
private HelloService helloService;
@MyLog(desc = "sayhello方法")
@GetMapping("/say")
public String sayHello(){
return helloService.sayHello();
}
}
? ? ? ? 启动并运行即可
gitee:https://gitee.com/kewen-yang/springboot-starter.git???????