1 jdbc操作数据库
1.1 jdbc操作数据库步骤
在springboot中要使用jdbc操作数据库,按以下步骤进行:
(1)导入jdbc的场景启动器
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
(2)导入数据库驱动
由于不同的数据库使用的驱动不同,因此springboot框架没有自动导入数据库驱动。但是springboot底层对不同数据库驱动的版本进行了版本仲裁,可以直接导入驱动无需定义版本号。
由于驱动的版本有可能比本机安装的mysql版本高,驱动版本过高需要自定义驱动版本号。
自定义版本两种方法:第一种是在依赖引入具体版本,这利用了maven的就近依赖原则;第二种是重新在properties属性中声明版本,利用了maven的属性就近优先原则。
<properties>
<!--第二种改版本的方法-->
<mysql.version>5.1.25</mysql.version>
</properties>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.25</version>
<!--第一种改版本的方法-->
</dependency>
(3)在配置文件中设置数据库连接的基本信息
# 设置数据库连接信息
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db1
username: root
password: "root"
1.2 更换数据源
导入jdbc的场景启动器后,springboot底层已经自动配置了Hikari数据源,如果想要修改数据源,可以用以下两种方法完成:自定义配置类、引入相应的场景启动器再配置配置文件。
1.2.1 自定义配置类实现更换数据源
(1)引入druid依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.10</version>
</dependency>
(2)自定义配置类往容器中注册datasource组件,并在组件上完成配置绑定解决硬编码问题。
@Configuration
public class DataSourceConfig {
@ConfigurationProperties("spring.datasource")
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
/* dataSource.setUrl();
dataSource.setDriverClassName();
dataSource.setUsername();
dataSource.setPassword();
用配置绑定替代
*/
return dataSource;
}
}
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db1
username: root
password: root
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
1.2.2 引入相应的场景启动器更换数据源
(1)引入druid场景启动器
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.17</version>
</dependency>
(2) 配置配置文件
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db1
username: root
password: "1234"
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
2 springboot整合mybatis
mybatis的使用:可以使用配置文件进行开发,也可以纯注解开发,配置文件适合处理SQL语句复杂的情况,注解适合处理SQL语句简单的情况,二者各有优劣,实际使用时可以混合使用。
2.1 基于配置文件的mybatis开发
实现步骤:(1)引入mybatis的场景启动器,(mybatis的启动器内部引用了jdbc的启动器,无需重复引用)。
查看源码可知:容器中已经自动配置了sqlsessionFactory和sqlsessionTemplate(sqlsessionTemplate里面组合了sqlsession),同时只要我们写的操作mybatis的接口上标注了@Mapper,mapper就会被自动扫描进来,底层开启了配置绑定,配置项前缀是mybatis
补充:springboot官方的场景启动器的命名是spring-boot-starter-xxx,第三方的启动器命名是xxx-spring-boot-starter
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.1.4</version>
</dependency>
(2)在resource下新建mybatis文件夹,并在mybatis文件夹下创建mybatis全局配置文件mybatis-config.xml,mybatis-config.xml中什么都不用写,底层已经自动配好了
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
</configuration>
(3)创建mapper文件夹,在其中创建UserMapper接口,在接口上方标注@Mapper
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper {
public User getUser(int id);
}
(4)编写mapper映射文件并绑定mapper接口
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!--namespace名称空间-->
<mapper namespace="com.example.mapper.UserMapper">
<select id="getUser" resultType="com.example.domain.User">
select * from user where id=#{id}
</select>
</mapper>
(5)在application.yml中声明mybatis全局配置文件和mapper映射文件的位置,这里要特别注意位置容易写错,报的错是Invalid bound statement
mybatis:
config-location: classpath:mybatis/mybatis-config.xml #全局配置文件位置
mapper-locations: classpath:mybatis/mapper/*.xml #mapper映射文件位置
(6)数据库中的字段名有的是user_id,封装不到实体中,需要开启驼峰命名规则(开启后数据库中字段值的下划线‘_’加字母会被认为是大写),即将user_id视为userId。可以在mybatis全局配置文件中开启;也可以在application.yml中配置,不过这时就不能创建mybatis全局配置文件了,原先在mybatis全局配置文件中配的内容都可以在application.yml中配置。
以后配置mybatis的相关属性建议用第二种,这样可以少创建一个mybatis核心配置文件
<!--这是在mybatis全局配置文件-->
<configuration>
<settings>
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="true"/>
</settings>
</configuration>
#这是在application.yml中
mybatis:
configuration:
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true
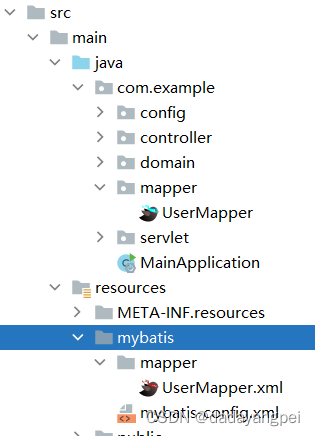
整个文件结构如下图
总结一下,springboot整合mybatis的步骤如下:
- 导入mybatis的场景启动器
- 编写mapper接口,在接口上标注@Mapper
- 编写mapper映射文件,并绑定mapper接口
- 在application.yml中指定mapper映射文件的位置,同时,如果创建了mybatis核心配置文件用来配置mybatis的相关属性要在application.yml中指定其位置,不过可以在application.yml中配置mybatis.configuration替代mybaits的相关属性配置,这样就不用创建mybatis核心配置文件了
2.2 基于注解的mybatis开发
实现步骤:(1)引入mybatis的场景启动器
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.1.4</version>
</dependency>
(2)编写mapper接口,在接口上标注@Mapper
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper {
@Select("select * from user where id=#{id}")
public User getUser(int id);
}
2.3 混合使用
实际使用时可以混合使用上述两种方式。
另外,如果写的mapper接口很多,每个接口上都要标@Mapper很麻烦,可以在任意一个配置类上用@MapperScan(指定要扫描的mapper接口所在的包)简化书写
3 springboot整合MybatisPlus
MybatisPlus是一个mybatis的增强工具,在mybatis的基础上进行增强,简化开发。
3.1 整合步骤
(1)引入mybatisplus场景启动器,mybatisplus场景启动器中包含了mybatis和jdbc的场景启动器,无需重复引用
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.4.1</version>
<dependency>
导入mybatisplus场景启动器后,自动配好了sqlsessionfactory、mapperlocations、sqlsessiontemplate,@Mapper标注的接口也会被自动扫描
mapperlocations默认值是classpath*:/mapper/**/*.xml,是指任意包的类路径下的所有mapper文件夹下任意路径下的xml文件,建议以后mappper映射文件写在类路径下的mapper文件夹下。
(2)编写mapper接口标注@Mapper注解,并继承BaseMapper类,类的泛型写具体要操作的JavaBean。BaseMapper有一些简单的crud方法,mapper接口继承后,可以直接使用父类中已经写好的简单CRUD方法,但是一些复杂的SQL业务还是需要使用映射文件来实现的。
@Mapper
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User> {
}
javabean中的属性必须与数据库中表的字段对应,如果存在表中没有的属性,可以在实体类使用注解标识。
@Data
@TableName("user")//指定数据库的表名是user
public class User {
// 表名该字段是定义的临时变量,并不存在于数据库的表中
@TableField(exist = false)
private int age;
private int sid;
private String name;
private Double money;
private int id;
}
(3)service接口继承IService类
service的实现类继承ServiceImpl并传两个泛型(mapper接口,实体类),然后实现service接口
public interface UserService extends IService<User> {
}
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<UserMapper, User> implements UserService {
}
(4)controller层注入service接口,直接使用service继承类的方法进行增删改查
3.2 mybatisplus的分页功能
自定义一个配置类,向容器中注册一个Interceptor
@Configuration
public class MyBatisConfig {
@Bean
public MybatisPlusInterceptor mybatisPlusInterceptor() {
MybatisPlusInterceptor interceptor = new MybatisPlusInterceptor();
PaginationInnerInterceptor paginationInnerInterceptor = new PaginationInnerInterceptor();
paginationInnerInterceptor.setOverflow(true);//true表示当请求的页面超过最后一页,自动跳回第一页
paginationInnerInterceptor.setMaxLimit(500L);//最大单页显示数量
interceptor.addInnerInterceptor(paginationInnerInterceptor);
return interceptor;
}
}
在service继承类中使用分页的相关方法
@GetMapping("/dynamic_table")
public String dynamic_table(@RequestParam(value = "pn", defaultValue = "1")Integer pn, Model model) {
Page<User> userPage = new Page<>(pn, 2);// // 当前页是pn,每页显示两条
Page<User> page = userService.page(userPage);
model.addAttribute("page", page);
return "/table/dynamic_table";
}