spring中有太多的扩展点,总记得很零散,有些扩展点也只简单知道用途,不知其所以然,所以写篇博客总结归纳一下,如果有遗漏欢迎告知,会进行补充~
1.Spring中扩展点
1.BeanFactoryProcessor
容器扩展接口,调用时机在Spring读取BeanDefinition信息之后,实例化bean之前。
可用作修改已经注册的BeanDefinition,比如修改类的属性、是否懒加载、类名等。
/**
* 一个接口方法用于
**/
void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException;
子接口 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
这个接口也只有一个实现方法,这个方法参数是BeanDefinitionRegistry,我们的容器是实现了这个接口,所以可以对容器中的beandefinition进行增删查改。
void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException;
2.BeanPostProcessor
Bean的后置处理器,在bean的生命周期各个阶段起到扩展和应用,常见的应用有初始化前@postConstruct解析执行,初始化后aop的动态代理。
/**
* 初始化前的扩展
**/
@Nullable
default Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
@Nullable
default Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
1.子接口InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
Bean实例化处理器,相当于在创建这个bean的前后做扩展,在bean通过反射创建前后的扩展。
- postProcessAfterInstantiation:注意它的返回值是boolean而不是obj,因为它的返回值是决定要不要调用postProcessPropertyValues方法。
- postProcessProperties: 顾名思义处理属性值 作用:对属性值进行修改,如果postProcessAfterInstantiation方法返回false,该方法可能不会被调用。可以在该方法内对属性值进行修改。
@Nullable
default Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return null;
}
default boolean postProcessAfterInstantiation(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return true;
}
@Nullable
default PropertyValues postProcessProperties(PropertyValues pvs, Object bean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
return null;
}
2.子接口SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor的子接口,比父类多了三个方法,我们常用的AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator用于aop和提前暴露解决循环依赖的就是该接口的实现。
- predictBeanType:该触发点发生在postProcessBeforeInstantiation之前,这个方法用于预测Bean的类型,返回第一个预测成功的Class类型,如果不能预测返回null;当你调用BeanFactory.getType(name)时当通过bean的名字无法得到bean类型信息时就调用该回调方法来决定类型信息。
- determineCandidateConstructors:该触发点发生在postProcessBeforeInstantiation之后,用于确定该bean的构造函数之用,返回的是该bean的所有构造函数列表。用户可以扩展这个点,来自定义选择相应的构造器来实例化这个bean。
- getEarlyBeanReference:该触发点发生在postProcessAfterInstantiation之后,当有循环依赖的场景,当bean实例化好之后,为了防止有循环依赖,会提前暴露回调方法,用于bean实例化的后置处理。这个方法就是在提前暴露的回调方法中触发。
@Nullable
default Class<?> predictBeanType(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return null;
}
@Nullable
default Constructor<?>[] determineCandidateConstructors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
return null;
}
default Object getEarlyBeanReference(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
return bean;
}
3.MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor
这个用于收集bean上的注解,比如我们常见的@Value、@NacosValue、@Mapper等,收集了,收集好的数据缓存在injectionMetadataCache中,以便后续比如属性注入的时候使用。
public interface MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor extends BeanPostProcessor {
void postProcessMergedBeanDefinition(RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition, Class<?> beanType, String beanName);
default void resetBeanDefinition(String beanName) {
}
}
3.ApplicationListener
ApplicationListener可以监听某个事件的event,触发时机可以穿插在业务方法执行过程中,用户可以自定义某个业务事件。但是spring内部也有一些内置事件,这种事件,可以穿插在启动调用中。我们也可以利用这个特性,来自己做一些内置事件的监听器来达到和前面一些触发点大致相同的事情。最常见的Spring Cloud中的注册就是通过监听WebServerInitializedEvent事件来进行服务注册。
当然还有很多不同的事件,在Spring生命周期过程中。会进行触发。
| 事件 | 触发时期 |
|---|---|
| ContextRefreshedEvent | ApplicationContext 被初始化或刷新时 |
| ContextStartedEvent | 当使用 ConfigurableApplicationContext (ApplicationContext子接口)接口中的 start() 方法启动 ApplicationContext时,该事件被发布。 |
| ContextStoppedEvent | 当使用 ConfigurableApplicationContext接口中的 stop()停止ApplicationContext 时,发布这个事件 |
| ContextClosedEvent | 当使用 ConfigurableApplicationContext接口中的 close()方法关闭 ApplicationContext 时,该事件被发布。 |
| RequestHandledEvent | 当Spring处理用户请求结束后,系统会自动触发该事件 |
3.xxxxAware
资源注入,一般我们常用的有BeannameAware用于设置bean名字、BeanFactoryAware用于设置beanFactory等,还有很多aware接口,我们根据bean对应所需的属性设置即可。
4.InitializingBean/DisposableBean
InitializingBean 初始化Bean时候判断bean是否实现该接口,如果实现则会调用afterPropertiesSet方法,它的调用时机在BeanPostProcessor的before、after方法中间。用于bean的初始化
public class CustomizeInitializing implements InitializingBean{
// 用法,实现对应afterPropertiesSet方法。
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("[InitializingBean] bean");
}
}
DisposableBean 销毁bean的是判断是否实现该接口,如果实现就会调用destroy方法。
public class CustomizeDestroy implements DisposableBean {
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
System.out.println("[DisposableBean] bean");
}
}
5.FactoryBean
顾名思义工厂bean,当我们调用getBean获取bean的时候,如果判断该bean是工厂bean那么就会调用工厂的getObject方法来获取。本质就是避免了我们创建bean所需要提供的大量配置,用工厂bean简洁创建。避免底层繁琐实现。
最常用的实现就是mybatis中sqlSessionFactory,用工厂方法帮助我们创建每个连接器。
public interface FactoryBean<T> {
@Nullable
T getObject() throws Exception;
@Nullable
Class<?> getObjectType();
default boolean isSingleton() {
return true;
}
}
6.SmartInitializingSingleton
这个类的作用是在spring容器管理的所有**单例对象(非懒加载对象)**初始化完成之后调用的回调接口。它只有一个方法afterSingletonsInstantiated
public class TestSmartInitializingSingleton implements SmartInitializingSingleton {
@Override
public void afterSingletonsInstantiated() {
System.out.println("[TestSmartInitializingSingleton]");
}
}
7.@postConstruct
这个注解是用于实例化后的初始化操作的,和InitializingBean作用很像,但两者的实现位置不一样,
postConstruct是在BeanPostProcessor的前置方法中判断和回调的。
而InitializingBean则是前置方法执行完进行初始化操作中回调的。
我们定位到CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor这个处理器,在父类postProcessBeforeInitialization通过反射回调。
public CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor() {
setOrder(Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE - 3);
// 注入了postConstruct和preDestroy注解
setInitAnnotationType(PostConstruct.class);
setDestroyAnnotationType(PreDestroy.class);
ignoreResourceType("javax.xml.ws.WebServiceContext");
}
8.CommandLineRunner
这个接口也只有一个方法:run(String… args),触发时机为整个项目启动完毕后,自动执行。如果有多个CommandLineRunner,可以利用@Order来进行排序。
使用场景:用户扩展此接口,进行启动项目之后一些业务的预处理。
public class TestCommandLineRunner implements CommandLineRunner {
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("[TestCommandLineRunner]");
}
}
总结
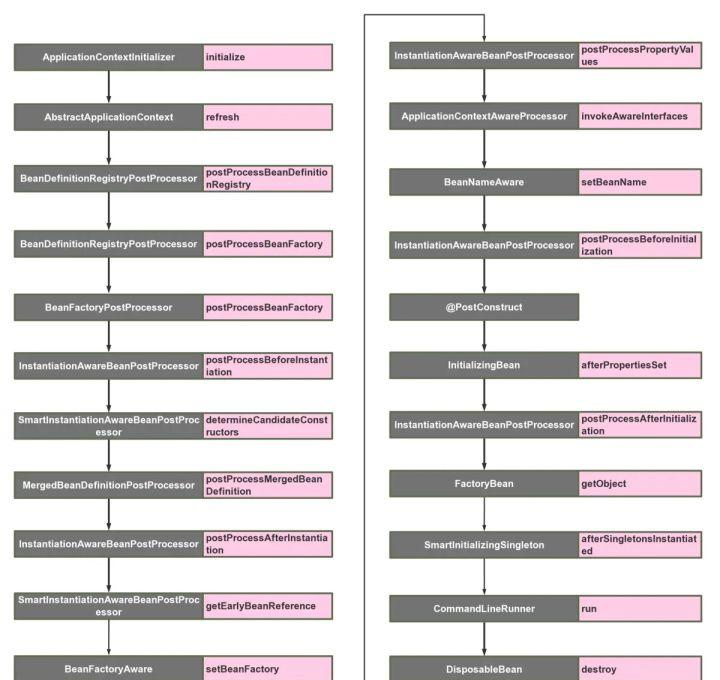
最后附上一张流程图,在bean生命周期的各个位置的扩展点,bean是spring关键的功能,所以主要扩展点也都在bean的生命周期上。这就是Spring和SpringBoot所有的扩展点,如果有遗漏欢迎留言告知,我们会后续补充~
另外SpringApplicationRunListener这个是SpringBoot的监听器,主要作用是在SB的执行过程的各个阶段进行回调,但我们如果自己进行实现并引入容器是无法进行回调的。所以和Spring的ApplicationListener是有所区别的。