? ? ? ? 众所周知Spring Boot是由Pivotal团队提供的全新框架,其设计目的是用来简化新Spring应用的初始搭建以及开发过程.该框架使用了特定的方式来进行配置,从而使开发人员不再需要定义样板化的配置.由于 Spring 项目的"配置地狱"导致开发者们急需一个更加轻量级的,无需繁重配置的框架,SpringBoot 项目由此应运而生.? ? ??
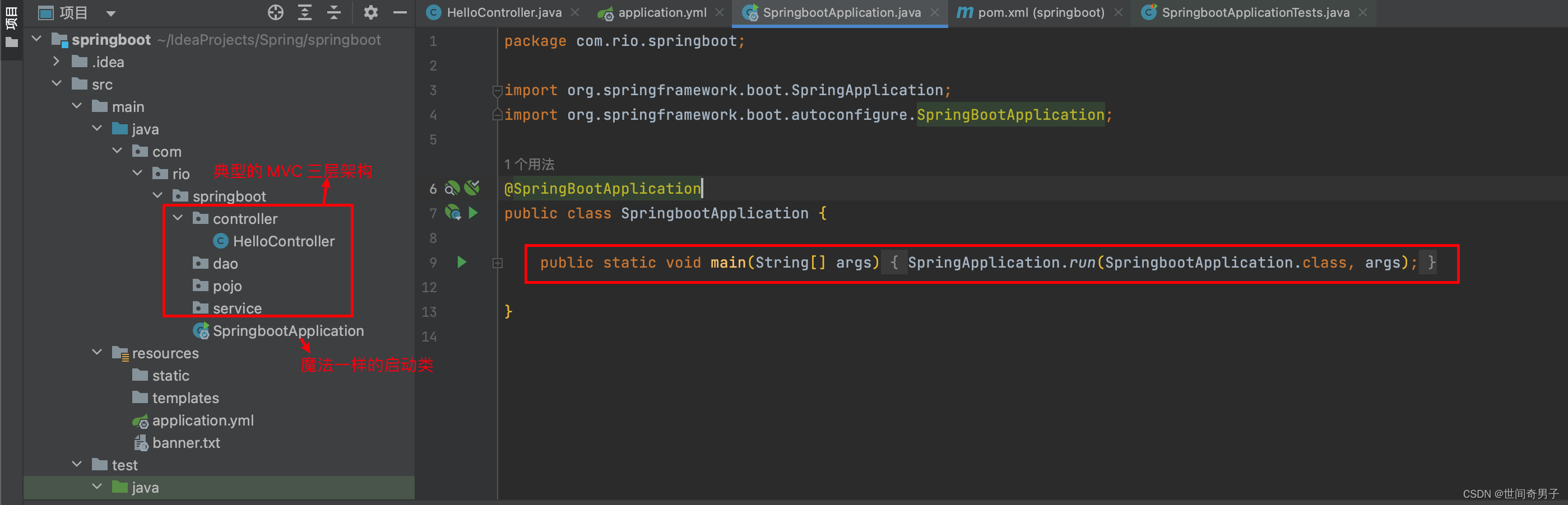
????????以上是一个典型的 SpringBoot 项目结构,在这里 controller,dao,pojo,service 等包都如我们在 Spring 项目中写的一样没什么讲的,但问题是像一个典型的 Spring 项目却没有一个类似SpringBootApplication 这样的启动类,要启动一个 Spring 项目我们需要将项目打包成 war 或 jar 包并依赖外部的 web 服务器启动 (例如 tomcat),一个典型的 Spring 项目结构如下

????????那么,SpringBoot 究竟是如何做到 "可以轻松创建可以'直接运行'的独立的、生产级的基于 Spring 的应用程序。"的呢?(Spring Boot makes it easy to create stand-alone, production-grade Spring based Applications that you can "just run".) 就让我们来看看被 @SpringBootApplication 注解标注的主程序类是究竟如何实现这神奇的一切吧.
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringbootApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringbootApplication.class, args);
}
}????????古人云:相由心生. 这句话在 SpringBoot 启动类上形容在合适不过,SpringApplication类提供一个静态方法run() 该方法接收第一个参数为SpringBoot 主类的class对象,第二个参数是args[]再通过反射执行.?
run 方法概览
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = createBootstrapContext();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
context = createApplicationContext();
context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup);
prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
Duration timeTakenToStartup = Duration.ofNanos(System.nanoTime() - startTime);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), timeTakenToStartup);
}
listeners.started(context, timeTakenToStartup);
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
Duration timeTakenToReady = Duration.ofNanos(System.nanoTime() - startTime);
listeners.ready(context, timeTakenToReady);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}????????不难看出,run 方法只是做一些 setup 和启动的工作,并不是本篇想要讨论的自动配置,有兴趣的同学可以看一下这篇文章:?http://t.csdn.cn/ZZKU1
/*
* Copyright 2012-2020 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Inherited;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanNameGenerator;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringBootConfiguration;
import org.springframework.boot.context.TypeExcludeFilter;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationBeanNameGenerator;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan.Filter;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.FilterType;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AliasFor;
import org.springframework.data.repository.Repository;
/**
* Indicates a {@link Configuration configuration} class that declares one or more
* {@link Bean @Bean} methods and also triggers {@link EnableAutoConfiguration
* auto-configuration} and {@link ComponentScan component scanning}. This is a convenience
* annotation that is equivalent to declaring {@code @Configuration},
* {@code @EnableAutoConfiguration} and {@code @ComponentScan}.
*
* @author Phillip Webb
* @author Stephane Nicoll
* @author Andy Wilkinson
* @since 1.2.0
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
/**
* Exclude specific auto-configuration classes such that they will never be applied.
* @return the classes to exclude
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class)
Class<?>[] exclude() default {};
/**
* Exclude specific auto-configuration class names such that they will never be
* applied.
* @return the class names to exclude
* @since 1.3.0
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = EnableAutoConfiguration.class)
String[] excludeName() default {};
/**
* Base packages to scan for annotated components. Use {@link #scanBasePackageClasses}
* for a type-safe alternative to String-based package names.
* <p>
* <strong>Note:</strong> this setting is an alias for
* {@link ComponentScan @ComponentScan} only. It has no effect on {@code @Entity}
* scanning or Spring Data {@link Repository} scanning. For those you should add
* {@link org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.domain.EntityScan @EntityScan} and
* {@code @Enable...Repositories} annotations.
* @return base packages to scan
* @since 1.3.0
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = ComponentScan.class, attribute = "basePackages")
String[] scanBasePackages() default {};
/**
* Type-safe alternative to {@link #scanBasePackages} for specifying the packages to
* scan for annotated components. The package of each class specified will be scanned.
* <p>
* Consider creating a special no-op marker class or interface in each package that
* serves no purpose other than being referenced by this attribute.
* <p>
* <strong>Note:</strong> this setting is an alias for
* {@link ComponentScan @ComponentScan} only. It has no effect on {@code @Entity}
* scanning or Spring Data {@link Repository} scanning. For those you should add
* {@link org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.domain.EntityScan @EntityScan} and
* {@code @Enable...Repositories} annotations.
* @return base packages to scan
* @since 1.3.0
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = ComponentScan.class, attribute = "basePackageClasses")
Class<?>[] scanBasePackageClasses() default {};
/**
* The {@link BeanNameGenerator} class to be used for naming detected components
* within the Spring container.
* <p>
* The default value of the {@link BeanNameGenerator} interface itself indicates that
* the scanner used to process this {@code @SpringBootApplication} annotation should
* use its inherited bean name generator, e.g. the default
* {@link AnnotationBeanNameGenerator} or any custom instance supplied to the
* application context at bootstrap time.
* @return {@link BeanNameGenerator} to use
* @see SpringApplication#setBeanNameGenerator(BeanNameGenerator)
* @since 2.3.0
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = ComponentScan.class, attribute = "nameGenerator")
Class<? extends BeanNameGenerator> nameGenerator() default BeanNameGenerator.class;
/**
* Specify whether {@link Bean @Bean} methods should get proxied in order to enforce
* bean lifecycle behavior, e.g. to return shared singleton bean instances even in
* case of direct {@code @Bean} method calls in user code. This feature requires
* method interception, implemented through a runtime-generated CGLIB subclass which
* comes with limitations such as the configuration class and its methods not being
* allowed to declare {@code final}.
* <p>
* The default is {@code true}, allowing for 'inter-bean references' within the
* configuration class as well as for external calls to this configuration's
* {@code @Bean} methods, e.g. from another configuration class. If this is not needed
* since each of this particular configuration's {@code @Bean} methods is
* self-contained and designed as a plain factory method for container use, switch
* this flag to {@code false} in order to avoid CGLIB subclass processing.
* <p>
* Turning off bean method interception effectively processes {@code @Bean} methods
* individually like when declared on non-{@code @Configuration} classes, a.k.a.
* "@Bean Lite Mode" (see {@link Bean @Bean's javadoc}). It is therefore behaviorally
* equivalent to removing the {@code @Configuration} stereotype.
* @since 2.2
* @return whether to proxy {@code @Bean} methods
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = Configuration.class)
boolean proxyBeanMethods() default true;
}
?? ? ? ? 自动配置的工作其实主要依赖于@SpringBootApplication 注解,代码如上 前三个注解无需过多解释?@Inherited 则是为了继承类启动的实现添加的元注解(http://t.csdn.cn/V6CHx),@ComponentScan 用来支持自动扫描包的 bean 配个 @Filter 实现不过多赘述,让我们重点关注一下@SpringBootConfiguration 与?@EnableAutoConfiguration
@SpringBootConfiguration
/*
* Copyright 2012-2021 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.boot;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AliasFor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Indexed;
/**
* Indicates that a class provides Spring Boot application
* {@link Configuration @Configuration}. Can be used as an alternative to the Spring's
* standard {@code @Configuration} annotation so that configuration can be found
* automatically (for example in tests).
* <p>
* Application should only ever include <em>one</em> {@code @SpringBootConfiguration} and
* most idiomatic Spring Boot applications will inherit it from
* {@code @SpringBootApplication}.
*
* @author Phillip Webb
* @author Andy Wilkinson
* @since 1.4.0
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Configuration
@Indexed
public @interface SpringBootConfiguration {
/**
* Specify whether {@link Bean @Bean} methods should get proxied in order to enforce
* bean lifecycle behavior, e.g. to return shared singleton bean instances even in
* case of direct {@code @Bean} method calls in user code. This feature requires
* method interception, implemented through a runtime-generated CGLIB subclass which
* comes with limitations such as the configuration class and its methods not being
* allowed to declare {@code final}.
* <p>
* The default is {@code true}, allowing for 'inter-bean references' within the
* configuration class as well as for external calls to this configuration's
* {@code @Bean} methods, e.g. from another configuration class. If this is not needed
* since each of this particular configuration's {@code @Bean} methods is
* self-contained and designed as a plain factory method for container use, switch
* this flag to {@code false} in order to avoid CGLIB subclass processing.
* <p>
* Turning off bean method interception effectively processes {@code @Bean} methods
* individually like when declared on non-{@code @Configuration} classes, a.k.a.
* "@Bean Lite Mode" (see {@link Bean @Bean's javadoc}). It is therefore behaviorally
* equivalent to removing the {@code @Configuration} stereotype.
* @return whether to proxy {@code @Bean} methods
* @since 2.2
*/
@AliasFor(annotation = Configuration.class)
boolean proxyBeanMethods() default true;
}
? ? ? ? 可以看到这个注解很简单,首先@Configuration定义了被该注解标注的类是一个被 Spring 托管的组件说明SpringBoot主启动类也是一个 Spring 组件 @Indexed 则索引模式(http://t.csdn.cn/oHcge), @SpringBootConfiguration 完😇
@EnableAutoConfiguration
/*
* Copyright 2012-2022 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Inherited;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnBean;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnClass;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnMissingBean;
import org.springframework.boot.context.annotation.ImportCandidates;
import org.springframework.boot.web.embedded.tomcat.TomcatServletWebServerFactory;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.server.ServletWebServerFactory;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Conditional;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.SpringFactoriesLoader;
/**
* Enable auto-configuration of the Spring Application Context, attempting to guess and
* configure beans that you are likely to need. Auto-configuration classes are usually
* applied based on your classpath and what beans you have defined. For example, if you
* have {@code tomcat-embedded.jar} on your classpath you are likely to want a
* {@link TomcatServletWebServerFactory} (unless you have defined your own
* {@link ServletWebServerFactory} bean).
* <p>
* When using {@link SpringBootApplication @SpringBootApplication}, the auto-configuration
* of the context is automatically enabled and adding this annotation has therefore no
* additional effect.
* <p>
* Auto-configuration tries to be as intelligent as possible and will back-away as you
* define more of your own configuration. You can always manually {@link #exclude()} any
* configuration that you never want to apply (use {@link #excludeName()} if you don't
* have access to them). You can also exclude them via the
* {@code spring.autoconfigure.exclude} property. Auto-configuration is always applied
* after user-defined beans have been registered.
* <p>
* The package of the class that is annotated with {@code @EnableAutoConfiguration},
* usually via {@code @SpringBootApplication}, has specific significance and is often used
* as a 'default'. For example, it will be used when scanning for {@code @Entity} classes.
* It is generally recommended that you place {@code @EnableAutoConfiguration} (if you're
* not using {@code @SpringBootApplication}) in a root package so that all sub-packages
* and classes can be searched.
* <p>
* Auto-configuration classes are regular Spring {@link Configuration @Configuration}
* beans. They are located using {@link ImportCandidates} and the
* {@link SpringFactoriesLoader} mechanism (keyed against this class). Generally
* auto-configuration beans are {@link Conditional @Conditional} beans (most often using
* {@link ConditionalOnClass @ConditionalOnClass} and
* {@link ConditionalOnMissingBean @ConditionalOnMissingBean} annotations).
*
* @author Phillip Webb
* @author Stephane Nicoll
* @since 1.0.0
* @see ConditionalOnBean
* @see ConditionalOnMissingBean
* @see ConditionalOnClass
* @see AutoConfigureAfter
* @see SpringBootApplication
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
/**
* Environment property that can be used to override when auto-configuration is
* enabled.
*/
String ENABLED_OVERRIDE_PROPERTY = "spring.boot.enableautoconfiguration";
/**
* Exclude specific auto-configuration classes such that they will never be applied.
* @return the classes to exclude
*/
Class<?>[] exclude() default {};
/**
* Exclude specific auto-configuration class names such that they will never be
* applied.
* @return the class names to exclude
* @since 1.3.0
*/
String[] excludeName() default {};
}
@AutoConfigurationPackage
/*
* Copyright 2012-2020 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Inherited;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Import;
/**
* Registers packages with {@link AutoConfigurationPackages}. When no {@link #basePackages
* base packages} or {@link #basePackageClasses base package classes} are specified, the
* package of the annotated class is registered.
*
* @author Phillip Webb
* @since 1.3.0
* @see AutoConfigurationPackages
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class)
public @interface AutoConfigurationPackage {
/**
* Base packages that should be registered with {@link AutoConfigurationPackages}.
* <p>
* Use {@link #basePackageClasses} for a type-safe alternative to String-based package
* names.
* @return the back package names
* @since 2.3.0
*/
String[] basePackages() default {};
/**
* Type-safe alternative to {@link #basePackages} for specifying the packages to be
* registered with {@link AutoConfigurationPackages}.
* <p>
* Consider creating a special no-op marker class or interface in each package that
* serves no purpose other than being referenced by this attribute.
* @return the base package classes
* @since 2.3.0
*/
Class<?>[] basePackageClasses() default {};
}
可以看到该类中也有一个@Import 注解也是@AutoConfigurationPackage的主要实现方式 从参数AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class可以看出这个注解应该是帮助 SpringBoot 做了自动包的配置,那么@Import 究竟是何方神圣呢,让我们一探究竟.
@Import
/*
* Copyright 2002-2019 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.context.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* Indicates one or more <em>component classes</em> to import — typically
* {@link Configuration @Configuration} classes.
*
* <p>Provides functionality equivalent to the {@code <import/>} element in Spring XML.
* Allows for importing {@code @Configuration} classes, {@link ImportSelector} and
* {@link ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar} implementations, as well as regular component
* classes (as of 4.2; analogous to {@link AnnotationConfigApplicationContext#register}).
*
* <p>{@code @Bean} definitions declared in imported {@code @Configuration} classes should be
* accessed by using {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired @Autowired}
* injection. Either the bean itself can be autowired, or the configuration class instance
* declaring the bean can be autowired. The latter approach allows for explicit, IDE-friendly
* navigation between {@code @Configuration} class methods.
*
* <p>May be declared at the class level or as a meta-annotation.
*
* <p>If XML or other non-{@code @Configuration} bean definition resources need to be
* imported, use the {@link ImportResource @ImportResource} annotation instead.
*
* @author Chris Beams
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 3.0
* @see Configuration
* @see ImportSelector
* @see ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar
* @see ImportResource
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
public @interface Import {
/**
* {@link Configuration @Configuration}, {@link ImportSelector},
* {@link ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar}, or regular component classes to import.
*/
Class<?>[] value();
}
@Import是一个元注解,从注释文档可以看出来这个注解的功能与 Spring 配置文件中的<import/>差不多,让我们跳出@AutoConfigurationPackage 也就是回到 @EnableAutoConfiguration 注解中的最后一个@Import 中
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class
/*
* Copyright 2012-2022 the original author or authors.
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* https://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.LinkedHashSet;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.function.Predicate;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import org.apache.commons.logging.Log;
import org.apache.commons.logging.LogFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.Aware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanClassLoaderAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.boot.context.annotation.ImportCandidates;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.bind.Binder;
import org.springframework.context.EnvironmentAware;
import org.springframework.context.ResourceLoaderAware;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.DeferredImportSelector;
import org.springframework.core.Ordered;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AnnotationAttributes;
import org.springframework.core.env.ConfigurableEnvironment;
import org.springframework.core.env.Environment;
import org.springframework.core.io.ResourceLoader;
import org.springframework.core.io.support.SpringFactoriesLoader;
import org.springframework.core.type.AnnotationMetadata;
import org.springframework.core.type.classreading.CachingMetadataReaderFactory;
import org.springframework.core.type.classreading.MetadataReaderFactory;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
import org.springframework.util.ClassUtils;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
/**
* {@link DeferredImportSelector} to handle {@link EnableAutoConfiguration
* auto-configuration}. This class can also be subclassed if a custom variant of
* {@link EnableAutoConfiguration @EnableAutoConfiguration} is needed.
*
* @author Phillip Webb
* @author Andy Wilkinson
* @author Stephane Nicoll
* @author Madhura Bhave
* @author Moritz Halbritter
* @since 1.3.0
* @see EnableAutoConfiguration
*/
public class AutoConfigurationImportSelector implements DeferredImportSelector, BeanClassLoaderAware,
ResourceLoaderAware, BeanFactoryAware, EnvironmentAware, Ordered {
private static final AutoConfigurationEntry EMPTY_ENTRY = new AutoConfigurationEntry();
private static final String[] NO_IMPORTS = {};
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class);
private static final String PROPERTY_NAME_AUTOCONFIGURE_EXCLUDE = "spring.autoconfigure.exclude";
private ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory;
private Environment environment;
private ClassLoader beanClassLoader;
private ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
private ConfigurationClassFilter configurationClassFilter;
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return NO_IMPORTS;
}
AutoConfigurationEntry autoConfigurationEntry = getAutoConfigurationEntry(annotationMetadata);
return StringUtils.toStringArray(autoConfigurationEntry.getConfigurations());
}
@Override
public Predicate<String> getExclusionFilter() {
return this::shouldExclude;
}
private boolean shouldExclude(String configurationClassName) {
return getConfigurationClassFilter().filter(Collections.singletonList(configurationClassName)).isEmpty();
}
/**
* Return the {@link AutoConfigurationEntry} based on the {@link AnnotationMetadata}
* of the importing {@link Configuration @Configuration} class.
* @param annotationMetadata the annotation metadata of the configuration class
* @return the auto-configurations that should be imported
*/
protected AutoConfigurationEntry getAutoConfigurationEntry(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return EMPTY_ENTRY;
}
AnnotationAttributes attributes = getAttributes(annotationMetadata);
List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes);
configurations = removeDuplicates(configurations);
Set<String> exclusions = getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes);
checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions);
configurations.removeAll(exclusions);
configurations = getConfigurationClassFilter().filter(configurations);
fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions);
return new AutoConfigurationEntry(configurations, exclusions);
}
@Override
public Class<? extends Group> getImportGroup() {
return AutoConfigurationGroup.class;
}
protected boolean isEnabled(AnnotationMetadata metadata) {
if (getClass() == AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class) {
return getEnvironment().getProperty(EnableAutoConfiguration.ENABLED_OVERRIDE_PROPERTY, Boolean.class, true);
}
return true;
}
/**
* Return the appropriate {@link AnnotationAttributes} from the
* {@link AnnotationMetadata}. By default this method will return attributes for
* {@link #getAnnotationClass()}.
* @param metadata the annotation metadata
* @return annotation attributes
*/
protected AnnotationAttributes getAttributes(AnnotationMetadata metadata) {
String name = getAnnotationClass().getName();
AnnotationAttributes attributes = AnnotationAttributes.fromMap(metadata.getAnnotationAttributes(name, true));
Assert.notNull(attributes, () -> "No auto-configuration attributes found. Is " + metadata.getClassName()
+ " annotated with " + ClassUtils.getShortName(name) + "?");
return attributes;
}
/**
* Return the source annotation class used by the selector.
* @return the annotation class
*/
protected Class<?> getAnnotationClass() {
return EnableAutoConfiguration.class;
}
/**
* Return the auto-configuration class names that should be considered. By default
* this method will load candidates using {@link ImportCandidates} with
* {@link #getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass()}. For backward compatible reasons it
* will also consider {@link SpringFactoriesLoader} with
* {@link #getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass()}.
* @param metadata the source metadata
* @param attributes the {@link #getAttributes(AnnotationMetadata) annotation
* attributes}
* @return a list of candidate configurations
*/
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
List<String> configurations = new ArrayList<>(
SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), getBeanClassLoader()));
ImportCandidates.load(AutoConfiguration.class, getBeanClassLoader()).forEach(configurations::add);
Assert.notEmpty(configurations,
"No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories nor in META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports. If you "
+ "are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
}
/**
* Return the class used by {@link SpringFactoriesLoader} to load configuration
* candidates.
* @return the factory class
*/
protected Class<?> getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass() {
return EnableAutoConfiguration.class;
}
private void checkExcludedClasses(List<String> configurations, Set<String> exclusions) {
List<String> invalidExcludes = new ArrayList<>(exclusions.size());
for (String exclusion : exclusions) {
if (ClassUtils.isPresent(exclusion, getClass().getClassLoader()) && !configurations.contains(exclusion)) {
invalidExcludes.add(exclusion);
}
}
if (!invalidExcludes.isEmpty()) {
handleInvalidExcludes(invalidExcludes);
}
}
/**
* Handle any invalid excludes that have been specified.
* @param invalidExcludes the list of invalid excludes (will always have at least one
* element)
*/
protected void handleInvalidExcludes(List<String> invalidExcludes) {
StringBuilder message = new StringBuilder();
for (String exclude : invalidExcludes) {
message.append("\t- ").append(exclude).append(String.format("%n"));
}
throw new IllegalStateException(String.format(
"The following classes could not be excluded because they are not auto-configuration classes:%n%s",
message));
}
/**
* Return any exclusions that limit the candidate configurations.
* @param metadata the source metadata
* @param attributes the {@link #getAttributes(AnnotationMetadata) annotation
* attributes}
* @return exclusions or an empty set
*/
protected Set<String> getExclusions(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
Set<String> excluded = new LinkedHashSet<>();
excluded.addAll(asList(attributes, "exclude"));
excluded.addAll(asList(attributes, "excludeName"));
excluded.addAll(getExcludeAutoConfigurationsProperty());
return excluded;
}
/**
* Returns the auto-configurations excluded by the
* {@code spring.autoconfigure.exclude} property.
* @return excluded auto-configurations
* @since 2.3.2
*/
protected List<String> getExcludeAutoConfigurationsProperty() {
Environment environment = getEnvironment();
if (environment == null) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
if (environment instanceof ConfigurableEnvironment) {
Binder binder = Binder.get(environment);
return binder.bind(PROPERTY_NAME_AUTOCONFIGURE_EXCLUDE, String[].class).map(Arrays::asList)
.orElse(Collections.emptyList());
}
String[] excludes = environment.getProperty(PROPERTY_NAME_AUTOCONFIGURE_EXCLUDE, String[].class);
return (excludes != null) ? Arrays.asList(excludes) : Collections.emptyList();
}
protected List<AutoConfigurationImportFilter> getAutoConfigurationImportFilters() {
return SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactories(AutoConfigurationImportFilter.class, this.beanClassLoader);
}
private ConfigurationClassFilter getConfigurationClassFilter() {
if (this.configurationClassFilter == null) {
List<AutoConfigurationImportFilter> filters = getAutoConfigurationImportFilters();
for (AutoConfigurationImportFilter filter : filters) {
invokeAwareMethods(filter);
}
this.configurationClassFilter = new ConfigurationClassFilter(this.beanClassLoader, filters);
}
return this.configurationClassFilter;
}
protected final <T> List<T> removeDuplicates(List<T> list) {
return new ArrayList<>(new LinkedHashSet<>(list));
}
protected final List<String> asList(AnnotationAttributes attributes, String name) {
String[] value = attributes.getStringArray(name);
return Arrays.asList(value);
}
private void fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(List<String> configurations, Set<String> exclusions) {
List<AutoConfigurationImportListener> listeners = getAutoConfigurationImportListeners();
if (!listeners.isEmpty()) {
AutoConfigurationImportEvent event = new AutoConfigurationImportEvent(this, configurations, exclusions);
for (AutoConfigurationImportListener listener : listeners) {
invokeAwareMethods(listener);
listener.onAutoConfigurationImportEvent(event);
}
}
}
protected List<AutoConfigurationImportListener> getAutoConfigurationImportListeners() {
return SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactories(AutoConfigurationImportListener.class, this.beanClassLoader);
}
private void invokeAwareMethods(Object instance) {
if (instance instanceof Aware) {
if (instance instanceof BeanClassLoaderAware) {
((BeanClassLoaderAware) instance).setBeanClassLoader(this.beanClassLoader);
}
if (instance instanceof BeanFactoryAware) {
((BeanFactoryAware) instance).setBeanFactory(this.beanFactory);
}
if (instance instanceof EnvironmentAware) {
((EnvironmentAware) instance).setEnvironment(this.environment);
}
if (instance instanceof ResourceLoaderAware) {
((ResourceLoaderAware) instance).setResourceLoader(this.resourceLoader);
}
}
}
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
Assert.isInstanceOf(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory.class, beanFactory);
this.beanFactory = (ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) beanFactory;
}
protected final ConfigurableListableBeanFactory getBeanFactory() {
return this.beanFactory;
}
@Override
public void setBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader classLoader) {
this.beanClassLoader = classLoader;
}
protected ClassLoader getBeanClassLoader() {
return this.beanClassLoader;
}
@Override
public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) {
this.environment = environment;
}
protected final Environment getEnvironment() {
return this.environment;
}
@Override
public void setResourceLoader(ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
}
protected final ResourceLoader getResourceLoader() {
return this.resourceLoader;
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE - 1;
}
private static class ConfigurationClassFilter {
private final AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata;
private final List<AutoConfigurationImportFilter> filters;
ConfigurationClassFilter(ClassLoader classLoader, List<AutoConfigurationImportFilter> filters) {
this.autoConfigurationMetadata = AutoConfigurationMetadataLoader.loadMetadata(classLoader);
this.filters = filters;
}
List<String> filter(List<String> configurations) {
long startTime = System.nanoTime();
String[] candidates = StringUtils.toStringArray(configurations);
boolean skipped = false;
for (AutoConfigurationImportFilter filter : this.filters) {
boolean[] match = filter.match(candidates, this.autoConfigurationMetadata);
for (int i = 0; i < match.length; i++) {
if (!match[i]) {
candidates[i] = null;
skipped = true;
}
}
}
if (!skipped) {
return configurations;
}
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>(candidates.length);
for (String candidate : candidates) {
if (candidate != null) {
result.add(candidate);
}
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
int numberFiltered = configurations.size() - result.size();
logger.trace("Filtered " + numberFiltered + " auto configuration class in "
+ TimeUnit.NANOSECONDS.toMillis(System.nanoTime() - startTime) + " ms");
}
return result;
}
}
private static class AutoConfigurationGroup
implements DeferredImportSelector.Group, BeanClassLoaderAware, BeanFactoryAware, ResourceLoaderAware {
private final Map<String, AnnotationMetadata> entries = new LinkedHashMap<>();
private final List<AutoConfigurationEntry> autoConfigurationEntries = new ArrayList<>();
private ClassLoader beanClassLoader;
private BeanFactory beanFactory;
private ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
private AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata;
@Override
public void setBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader classLoader) {
this.beanClassLoader = classLoader;
}
@Override
public void setBeanFactory(BeanFactory beanFactory) {
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
}
@Override
public void setResourceLoader(ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
}
@Override
public void process(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata, DeferredImportSelector deferredImportSelector) {
Assert.state(deferredImportSelector instanceof AutoConfigurationImportSelector,
() -> String.format("Only %s implementations are supported, got %s",
AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class.getSimpleName(),
deferredImportSelector.getClass().getName()));
AutoConfigurationEntry autoConfigurationEntry = ((AutoConfigurationImportSelector) deferredImportSelector)
.getAutoConfigurationEntry(annotationMetadata);
this.autoConfigurationEntries.add(autoConfigurationEntry);
for (String importClassName : autoConfigurationEntry.getConfigurations()) {
this.entries.putIfAbsent(importClassName, annotationMetadata);
}
}
@Override
public Iterable<Entry> selectImports() {
if (this.autoConfigurationEntries.isEmpty()) {
return Collections.emptyList();
}
Set<String> allExclusions = this.autoConfigurationEntries.stream()
.map(AutoConfigurationEntry::getExclusions).flatMap(Collection::stream).collect(Collectors.toSet());
Set<String> processedConfigurations = this.autoConfigurationEntries.stream()
.map(AutoConfigurationEntry::getConfigurations).flatMap(Collection::stream)
.collect(Collectors.toCollection(LinkedHashSet::new));
processedConfigurations.removeAll(allExclusions);
return sortAutoConfigurations(processedConfigurations, getAutoConfigurationMetadata()).stream()
.map((importClassName) -> new Entry(this.entries.get(importClassName), importClassName))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
private AutoConfigurationMetadata getAutoConfigurationMetadata() {
if (this.autoConfigurationMetadata == null) {
this.autoConfigurationMetadata = AutoConfigurationMetadataLoader.loadMetadata(this.beanClassLoader);
}
return this.autoConfigurationMetadata;
}
private List<String> sortAutoConfigurations(Set<String> configurations,
AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata) {
return new AutoConfigurationSorter(getMetadataReaderFactory(), autoConfigurationMetadata)
.getInPriorityOrder(configurations);
}
private MetadataReaderFactory getMetadataReaderFactory() {
try {
return this.beanFactory.getBean(SharedMetadataReaderFactoryContextInitializer.BEAN_NAME,
MetadataReaderFactory.class);
}
catch (NoSuchBeanDefinitionException ex) {
return new CachingMetadataReaderFactory(this.resourceLoader);
}
}
}
protected static class AutoConfigurationEntry {
private final List<String> configurations;
private final Set<String> exclusions;
private AutoConfigurationEntry() {
this.configurations = Collections.emptyList();
this.exclusions = Collections.emptySet();
}
/**
* Create an entry with the configurations that were contributed and their
* exclusions.
* @param configurations the configurations that should be imported
* @param exclusions the exclusions that were applied to the original list
*/
AutoConfigurationEntry(Collection<String> configurations, Collection<String> exclusions) {
this.configurations = new ArrayList<>(configurations);
this.exclusions = new HashSet<>(exclusions);
}
public List<String> getConfigurations() {
return this.configurations;
}
public Set<String> getExclusions() {
return this.exclusions;
}
}
}
一眼定钟情
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
List<String> configurations = new ArrayList<>(
SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), getBeanClassLoader()));
ImportCandidates.load(AutoConfiguration.class, getBeanClassLoader()).forEach(configurations::add);
Assert.notEmpty(configurations,
"No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories nor in META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports. If you "
+ "are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
}getCandidateConfigurations() 方法名已经预示了一切😋?这个方法又调用了 ?SpringFactoriesLoader 类的静态方法!我们进入SpringFactoriesLoader类loadFactoryNames() 方法
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
ClassLoader classLoaderToUse = classLoader;
if (classLoaderToUse == null) {
classLoaderToUse = SpringFactoriesLoader.class.getClassLoader();
}
String factoryTypeName = factoryType.getName();
return loadSpringFactories(classLoaderToUse).getOrDefault(factoryTypeName, Collections.emptyList());
}我们继续点击查看 loadSpringFactories 方法
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(ClassLoader classLoader) {
Map<String, List<String>> result = cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
result = new HashMap<>();
try {
Enumeration<URL> urls = classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION);
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
for (Map.Entry<?, ?> entry : properties.entrySet()) {
String factoryTypeName = ((String) entry.getKey()).trim();
String[] factoryImplementationNames =
StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) entry.getValue());
for (String factoryImplementationName : factoryImplementationNames) {
result.computeIfAbsent(factoryTypeName, key -> new ArrayList<>())
.add(factoryImplementationName.trim());
}
}
}
// Replace all lists with unmodifiable lists containing unique elements
result.replaceAll((factoryType, implementations) -> implementations.stream().distinct()
.collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.toList(), Collections::unmodifiableList)));
cache.put(classLoader, result);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [" +
FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex);
}
return result;
}
classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION); 告诉我们他加载了FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION 即 "META-INF/spring.factories"
全局搜索找到我们需要的配置文件
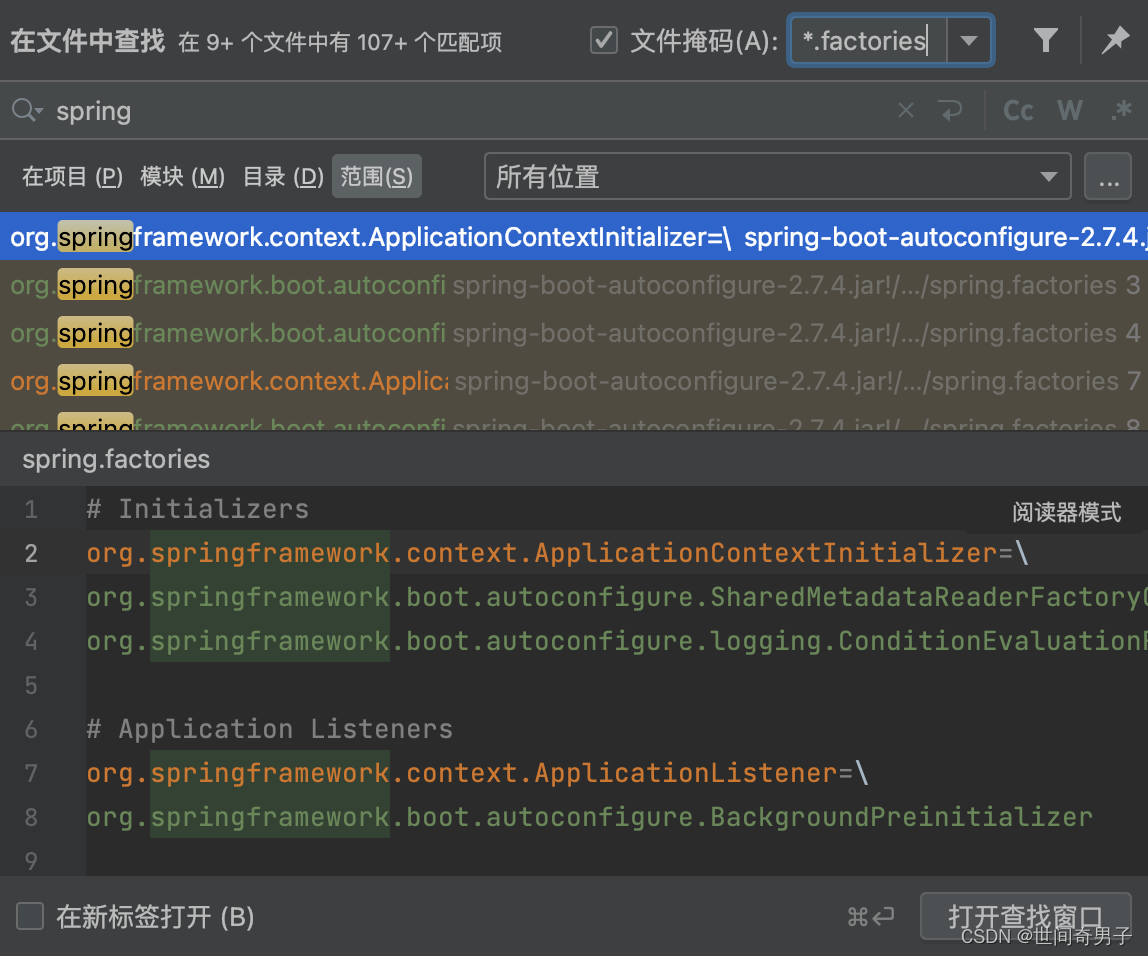
# Initializers
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SharedMetadataReaderFactoryContextInitializer,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.logging.ConditionEvaluationReportLoggingListener
# Application Listeners
org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.BackgroundPreinitializer
# Environment Post Processors
org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessor=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.integration.IntegrationPropertiesEnvironmentPostProcessor
# Auto Configuration Import Listeners
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportListener=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionEvaluationReportAutoConfigurationImportListener
# Auto Configuration Import Filters
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigurationImportFilter=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnBeanCondition,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnClassCondition,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.OnWebApplicationCondition
# Failure analyzers
org.springframework.boot.diagnostics.FailureAnalyzer=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisUrlSyntaxFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.diagnostics.analyzer.NoSuchBeanDefinitionFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.flyway.FlywayMigrationScriptMissingFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceBeanCreationFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.HikariDriverConfigurationFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jooq.NoDslContextBeanFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.r2dbc.ConnectionFactoryBeanCreationFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.r2dbc.MissingR2dbcPoolDependencyFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.r2dbc.MultipleConnectionPoolConfigurationsFailureAnalzyer,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.r2dbc.NoConnectionFactoryBeanFailureAnalyzer,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.session.NonUniqueSessionRepositoryFailureAnalyzer
# Template availability providers
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.template.TemplateAvailabilityProvider=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.freemarker.FreeMarkerTemplateAvailabilityProvider,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.mustache.MustacheTemplateAvailabilityProvider,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.groovy.template.GroovyTemplateAvailabilityProvider,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.thymeleaf.ThymeleafTemplateAvailabilityProvider,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.web.servlet.JspTemplateAvailabilityProvider
# DataSource initializer detectors
org.springframework.boot.sql.init.dependency.DatabaseInitializerDetector=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.flyway.FlywayMigrationInitializerDatabaseInitializerDetector
# Depends on database initialization detectors
org.springframework.boot.sql.init.dependency.DependsOnDatabaseInitializationDetector=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.batch.JobRepositoryDependsOnDatabaseInitializationDetector,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.quartz.SchedulerDependsOnDatabaseInitializationDetector,\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.session.JdbcIndexedSessionRepositoryDependsOnDatabaseInitializationDetector
我们根据源头打开spring.factories , 看到了很多自动配置的文件;这就是自动配置根源所在!
WebMvcAutoConfiguration
我们在上面的自动配置类随便找一个打开看看,比如 :WebMvcAutoConfiguration

可以看到这些一个个的都是JavaConfig配置类,而且都注入了一些Bean,可以找一些自己认识的类,看着熟悉一下!
所以,自动配置真正实现是从classpath中搜寻所有的META-INF/spring.factories配置文件 ,并将其中对应的 org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure. 包下的配置项,通过反射实例化为对应标注了 @Configuration的JavaConfig形式的IOC容器配置类 , 然后将这些都汇总成为一个实例并加载到IOC容器中。
结论:
-
SpringBoot在启动的时候从类路径下的META-INF/spring.factories中获取EnableAutoConfiguration指定的值
-
将这些值作为自动配置类导入容器 , 自动配置类就生效 , 帮我们进行自动配置工作;
-
整个J2EE的整体解决方案和自动配置都在springboot-autoconfigure的jar包中;
-
它会给容器中导入非常多的自动配置类 (xxxAutoConfiguration), 就是给容器中导入这个场景需要的所有组件 , 并配置好这些组件 ;
-
有了自动配置类 , 免去了我们手动编写配置注入功能组件等的工作;
?