目录
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? Setter注入
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? Constructor注入
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 注入基本数据类型、字符串类型
?????????????????????????注入简单数据类型list集合
????????????????????????注入bean类型list集合
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 注入Properties对象
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? @Repository、@Service、@Controller
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? @Configuration
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? @ComponentScan
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? @PropertySource
????????????????编写POJO类、持久层、service层
????????????????Spring整合Junit进行单元测试
部分图片来自百战程序员
Spring简介
Spring是一个开源框架,为简化企业级开发而生。
它以IOC(控制反转)和AOP(面向切面)为思想内核,提供了控制层SpringMVC、数据层SpringData、服务层事务管理等众多技术,并可以整合众多第三方框架。
Spring将很多复杂的代码变得优雅简洁,有效的降低代码的耦合度,极大的方便项目的后期维护、升级和扩展。
Spring官网地址: Spring | Home
Spring结构
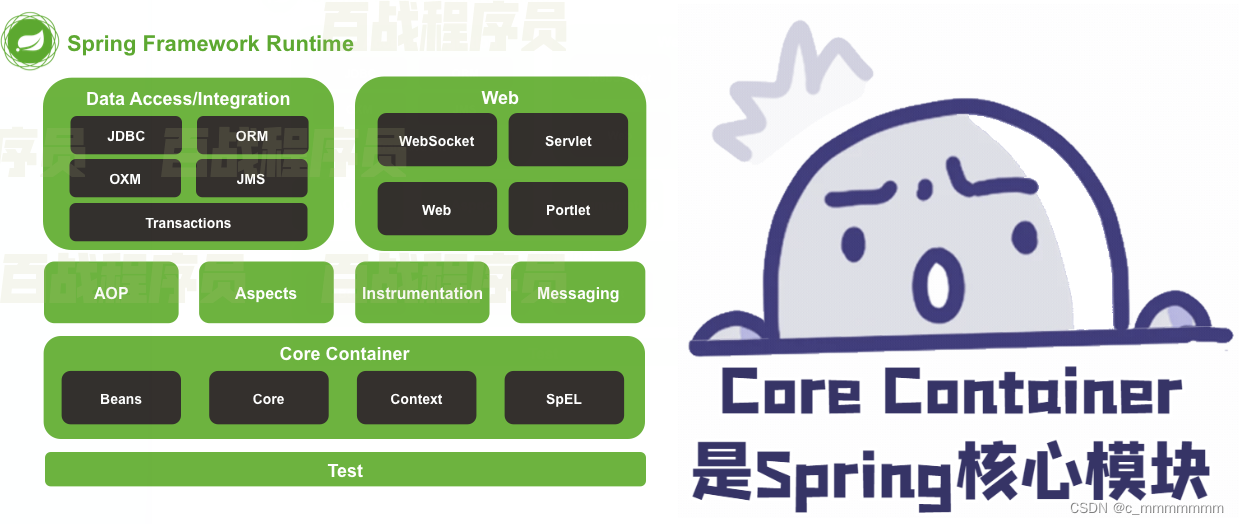
Spring框架根据不同的功能被划分成了多个模块,这些模块可以满足一切企业级应用开发的需求,在开发过程中可以根据需求有选择性地使用所需要的模块。
- Core Container:Spring核心模块,任何功能的使用都离不开该模块,是其他模块建立的基础。
- Data Access/Integration:该模块提供了数据持久化的相应功能。
- Web:该模块提供了web开发的相应功能。
- AOP:提供了面向切面编程实现
- Aspects:提供与AspectJ框架的集成,该框架是一个面向切面编程框架。
- Instrumentation:提供了类工具的支持和类加载器的实现,可以在特定的应用服务器中使用。
- Messaging:为Spring框架集成一些基础的报文传送应用
- Test:提供与测试框架的集成
IOC
? ? ? ? Spring容器类型
容器接口:
- BeanFactory:BeanFactory是Spring容器中的顶层接口,它可以对Bean对象进行管理。
- ApplicationContext:ApplicationContext是BeanFactory的子接口。它除了继承 BeanFactory的所有功能外,还添加了对国际化、资源访问、事件传播等方面的良好支持。
ApplicationContext有以下三个常用实现类:
容器实现类
- ClassPathXmlApplicationContext:该类可以从项目中读取配置文件
- FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:该类从磁盘中读取配置文件
- AnnotationConfigApplicationContext:使用该类不读取配置文件,而是会读取注解
? ? ? ? bean对象创建方式
1、默认根据POJO类的无参构造方法创建
<!--使用构造方法创建bean-->
<bean id="studentDao" class="com.itbaizhan.dao.StudentDaoImpl"></bean>
2、如果POJO类没有无参构造,那么就需要使用工厂类创建(普通方法)
<!--使用工厂类的方法创建bean-->
<bean id="studentDaoFactory" class="com.itbaizhan.dao.StudentDaoFactory"></bean>
<bean id="studentDao" factory-bean="studentDaoFactory" factory-method="getStudentDao"></bean>
3、使用工厂类的静态方法创建
<!--使用工厂的的静态方法创建bean-->
<bean id="studentDao" class="com.itbaizhan.dao.StudentDaoFactory2" factory-method="getStudentDao"></bean>
? ? ? ? 对象的创建策略
Spring通过配置<bean>中的scope属性设置对象的创建策略,共有五种创建策略:
- singleton:单例,默认策略。
整个项目只会创建一个对象,通过<bean>中的lazy-init属性可以设置单例对象的创建时机:
lazy-init="false"(默认):立即创建,在容器启动时会创建配置文件中的所有Bean对象。
lazy-init="true":延迟创建,第一次使用Bean对象时才会创建。
配置单例策略:
<bean id="studentDao" class="com.itbaizhan.dao.StudentDaoImpl2" scope="singleton"
lazy-init="false"></bean>- prototype:多例,每次从容器中获取时都会创建对象。
<!-- 配置多例策略 -->
<bean id="studentDao"? class="com.itbaizhan.dao.StudentDaoImpl2" scope="prototype"></bean>- request:每次请求创建一个对象,只在web环境有效。
- session:每次会话创建一个对象,只在web环境有效。
- gloabal-session:一次集群环境的会话创建一个对象,只在web环境有效。
? ? ? ? 对象的销毁方式
对象的创建策略不同,销毁时机也不同:
- singleton:对象随着容器的销毁而销毁。
- prototype:使用JAVA垃圾回收机制销毁对象。
- request:当处理请求结束,bean实例将被销毁。
- session:当HTTP Session最终被废弃的时候,bean也会被销毁掉。
- gloabal-session:集群环境下的session销毁,bean实例也将被销毁。
? ? ? ? 生命周期方法
bean对象的生命周期包含
创建——使用——销毁
,Spring可以配置Bean对象在创建和销毁时自动执行的方法:
?
配置生命周期方法
<!-- init-method:创建对象时执行的方法? destroy-method:销毁对象时执行的方法? -->
<bean id="studentDao" class="com.itbaizhan.dao.StudentDaoImpl2" scope="singleton"
?? init-method="init" destroy-method="destory"></bean>? ? ? ? 获取bean对象的方式
?1、通过id/name获取
配置文件
<bean name="studentDao" class="com.itbaizhan.dao.StudentDaoImpl2"></bean>
<bean id="studentDao" class="com.itbaizhan.dao.StudentDaoImpl2"></bean>
获取对象
StudentDao studentDao=(StudentDao) ac.getBean("studentDao");
2、通过类型获取?
配置文件
<bean name="studentDao" class="com.itbaizhan.dao.StudentDaoImpl2"></bean>
获取对象
StudentDao studentDao2=ac.getBean(StudentDao.class);
可以看到使用类型获取不需要强转。?
3、通过id/name+类型获取?
虽然使用类型获取不需要强转,但如果在容器中有一个接口的多个实现类对象,则获取时会报错,此时需要使用类型+id/name获取?
配置文件
<bean name="studentDao" class="com.itbaizhan.dao.StudentDaoImpl2"></bean>
<beann ame="studentDao1" class="com.itbaizhan.dao.StudentDaoImpl"></bean>
获取对象
StudentDao studentDao2 = ac.getBean("studentDao",StudentDao.class);
? ? ? ? 入门案例?
代码编写步骤
- 创建POJO类、持久层接口和实现类
- 编写配置文件,将实现类注入到Spring容器中
- 测试
1、创建Maven工程,引入依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.3.13</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>2、创建POJO类、持久层接口和实现类
package com.itbaizhan.pojo;
public class Student {
private int sid;
private String sname;
private int age;
private String sex;
public Student(int sid, String sname, int age, String sex) {
this.sid = sid;
this.sname = sname;
this.age = age;
this.sex = sex;
}
public Student() {
}
public int getSid() {
return sid;
}
public void setSid(int sid) {
this.sid = sid;
}
public String getSname() {
return sname;
}
public void setSname(String sname) {
this.sname = sname;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"sid=" + sid +
", sname='" + sname + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", sex='" + sex + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
package com.itbaizhan.dao;
import com.itbaizhan.pojo.Student;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
public interface StudentDao {
// 根据id查询学生
Student findById(int id);
}
package com.itbaizhan.dao;
import com.itbaizhan.pojo.Student;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class StudentDaoImpl implements StudentDao {
@Override
public Student findById(int id) {
return new Student(1,"路飞",16,"男");
}
}
?3、编写bean.xml配置文件,配置文件中配置需要Spring帮我们创建的对象。
?(id属性就是获取对象的key,class代表获取哪个对象)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<bean id="studentDao" class="com.itbaizhan.dao.StudentDaoImpl"></bean>
</beans>?测试从Spring容器中获取对象。?
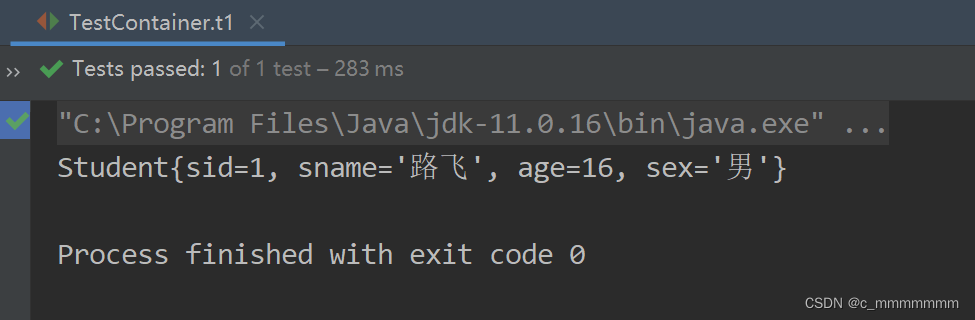
public class TestContainer{
@Test
public void t1(){
// 创建Spring容器
Application Contextac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
// 从容器获取对象
StudentDaostudent Dao1=(StudentDao) ac.getBean("studentDao");
StudentDaostudent Dao2=(StudentDao) ac.getBean("studentDao");
System.out.println(studentDao1.hashCode());
System.out.println(studentDao2.hashCode());
System.out.println(studentDao1.findById(1));
}
}
? ? ? ? 依赖注入DI
依赖注入(Dependency Injection,简称DI),它是Spring控制反转思想的具体实现。
控制反转将对象的创建交给了Spring,但是对象中可能会依赖其他对象。比如service类中要有dao类的属性,我们称service依赖于dao。之前需要手动注入属性值,
代码如下:

????????????????三种依赖注入的方式:
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? Setter注入
配置文件中,给需要注入属性值的<bean>中设置<property>
1、创建持久层接口和持久层接口实现类和POJO类
public interface StudentDao {
// 根据id查询学生
Student findById(int id);
}
public class StudentDaoImpl implements StudentDao {
@Override
public Student findById(int id) {
return new Student(1,"路飞",16,"男");
}
}
public class Student {
private int sid;
private String sname;
private int age;
private String sex;
public Student(int sid, String sname, int age, String sex) {
this.sid = sid;
this.sname = sname;
this.age = age;
this.sex = sex;
}
public Student() {
}
public int getSid() {
return sid;
}
public void setSid(int sid) {
this.sid = sid;
}
public String getSname() {
return sname;
}
public void setSname(String sname) {
this.sname = sname;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getSex() {
return sex;
}
public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"sid=" + sid +
", sname='" + sname + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", sex='" + sex + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
2、创建逻辑层
这个逻辑层中有一个StudentDao类型的属性,一定要为这个属性创建getter、setter方法
package com.itbaizhan.service;
import com.itbaizhan.dao.StudentDao;
import com.itbaizhan.pojo.Student;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Set;
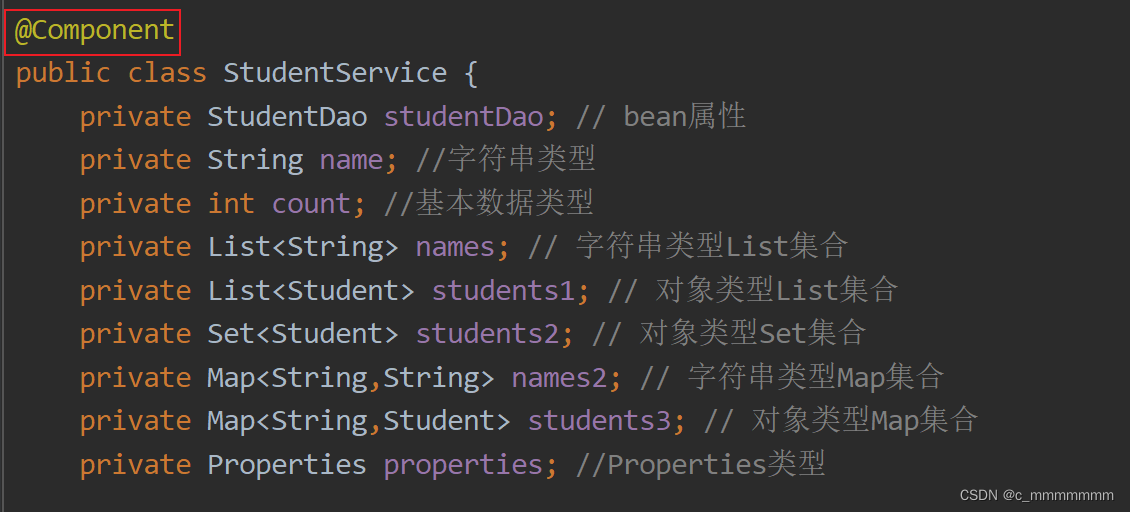
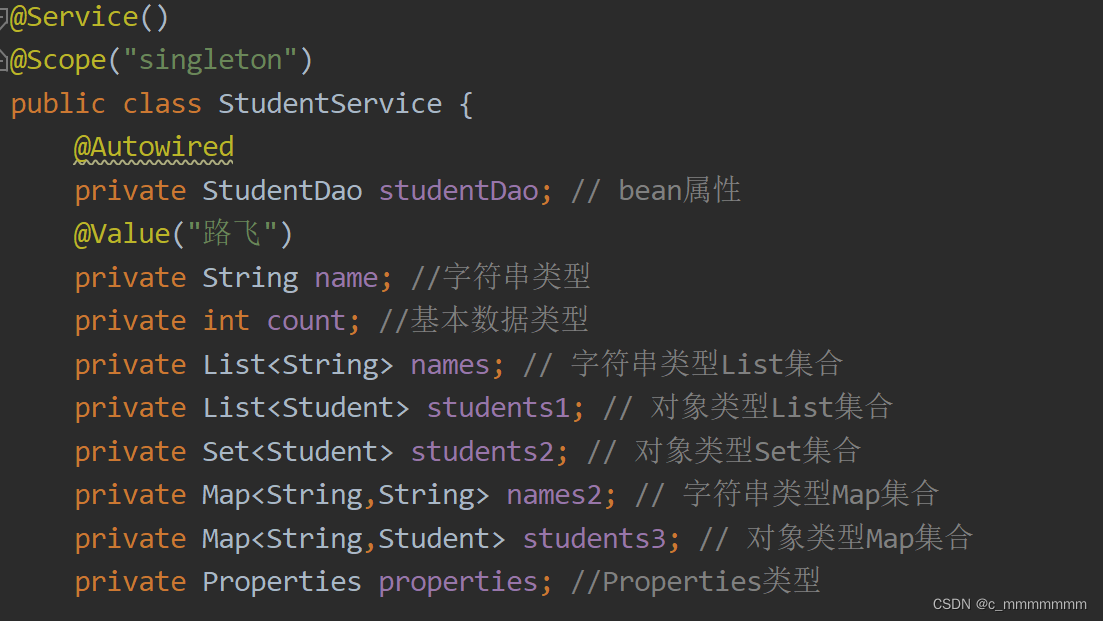
public class StudentService {
private StudentDao studentDao; // bean属性
private String name; //字符串类型
private int count; //基本数据类型
private List<String> names; // 字符串类型List集合
private List<Student> students1; // 对象类型List集合
private Set<Student> students2; // 对象类型Set集合
private Map<String,String> names2; // 字符串类型Map集合
private Map<String,Student> students3; // 对象类型Map集合
private Properties properties; //Properties类型
public StudentDao getStudentDao() {
return studentDao;
}
public void setStudentDao(StudentDao studentDao) {
this.studentDao = studentDao;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
public void setCount(int count) {
this.count = count;
}
public List<String> getNames() {
return names;
}
public void setNames(List<String> names) {
this.names = names;
}
public List<Student> getStudents1() {
return students1;
}
public void setStudents1(List<Student> students1) {
this.students1 = students1;
}
public Set<Student> getStudents2() {
return students2;
}
public void setStudents2(Set<Student> students2) {
this.students2 = students2;
}
public Map<String, String> getNames2() {
return names2;
}
public void setNames2(Map<String, String> names2) {
this.names2 = names2;
}
public Map<String, Student> getStudents3() {
return students3;
}
public void setStudents3(Map<String, Student> students3) {
this.students3 = students3;
}
public Properties getProperties() {
return properties;
}
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
}
public Student findById(int id){
return studentDao.findById(id);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "StudentService{" +
"studentDao=" + studentDao +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", count=" + count +
", names=" + names +
", students1=" + students1 +
", students2=" + students2 +
", names2=" + names2 +
", students3=" + students3 +
", properties=" + properties +
'}';
}
}
3、编写bean.xml文件(将StudentService类添加到Spring容器中)
?<!--name:对象的属性名 ref:容器中对象的id值-->
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<bean id="studentDaoImpl" class="com.itbaizhan.dao.StudentDaoImpl"></bean>
<bean id="studentService" class="com.itbaizhan.service.StudentService">
<!-- 使用setter方法实现依赖注入 -->
<property name="studentDao" ref="studentDaoImpl"></property>
</bean>
</beans>??4、测试
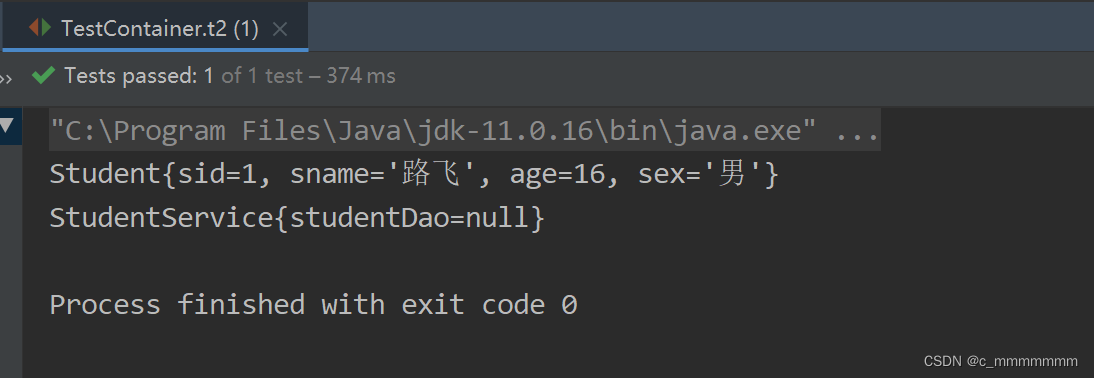
public class TestContainer {
@Test
public void t1(){
//创建Spring容器
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//获取对象
StudentService studentService = (StudentService) ac.getBean("studentService");
System.out.println(studentService.findById(1));
}
}
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? Constructor注入
给需要注入属性值的<bean>中设置<constructor-arg>
持久层接口和实现类和POJO类和Service类和测试类都延续上面的
bean.xml文件需要重新编写,将property标签改为constructor-arg标签,对应的被注入类需要添加构造方法
<bean id="studentDaoImpl" class="com.itbaizhan.dao.StudentDaoImpl"></bean>
<bean id="studentService" class="com.itbaizhan.service.StudentService">
<!-- 使用constructor方法实现依赖注入 -->
<constructor-arg name="studentDao" ref="studentDaoImpl"></constructor-arg>
</bean>public class TestContainer {
@Test
public void t1(){
//创建Spring容器
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//获取对象
StudentService studentService = (StudentService) ac.getBean("studentService");
System.out.println(studentService.findById(1));
}
}
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 自动注入
自动注入不需要在<bean>标签中添加其他标签注入属性值,而是自动从容器中找到相应的bean对象设置为属性值。
自动注入有两种配置方式:
- 全局配置:在<beans>中设置default-autowire属性可以定义所有bean对象的自动注入策略。
- 局部配置:在<bean>中设置autowire属性可以定义当前bean对象的自动注入策略。
autowire的取值如下:
- no:不会进行自动注入。
- default:全局配置default相当于no,局部配置default表示使用全局配置
- byName:在Spring容器中查找id与属性名相同的bean,并进行注入。需要提供set方法。
- byType:在Spring容器中查找类型与属性类型相同的bean,并进行注入。需要提供set方法。
- constructor:在Spring容器中查找id与属性名相同的bean,并进行注入。需要提供构造方法。
只需要修改bean.xml配置文件即可
<bean id="studentDao" class="com.itbaizhan.dao.StudentDaoImpl"></bean>
<!-- 使用自动注入实现依赖注入 -->
<bean id="studentService" class="com.itbaizhan.service.StudentService" autowire="byName"></bean>测试?
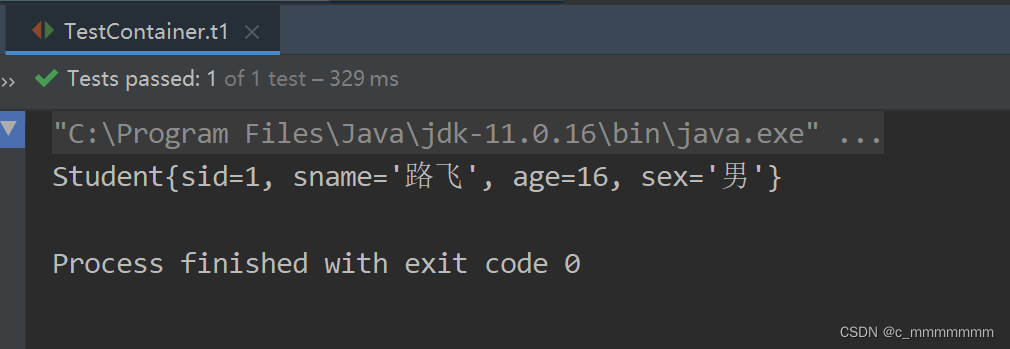
public class TestContainer {
@Test
public void t1(){
//创建Spring容器
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//获取对象
StudentService studentService = (StudentService) ac.getBean("studentService");
System.out.println(studentService.findById(1));
}
}
????????????????注入bean类型
使用property标签
name:对象的属性名 ?ref:容器中对象的id值
<bean id="studentDaoImpl" class="com.itbaizhan.dao.StudentDaoImpl"></bean>
<bean id="studentService" class="com.itbaizhan.service.StudentService">
<!-- 使用setter方法实现依赖注入 -->
<property name="studentDao" ref="studentDaoImpl"></property>
</bean>? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 注入基本数据类型、字符串类型
使用value标签
name:属性名? value:属性值
<bean id="studentDaoImpl" class="com.itbaizhan.dao.StudentDaoImpl"></bean>
<bean id="studentService" class="com.itbaizhan.service.StudentService">
<!-- 注入bean类型 -->
<property name="studentDao" ref="studentDaoImpl"></property>
<!-- 注入基本数据类型或字符串 -->
<property name="name" value="路飞"></property>
</bean>? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 注入list、set
根据StudentService类我们可以看到有List、Set类型的属性
package com.itbaizhan.service;
import com.itbaizhan.dao.StudentDao;
import com.itbaizhan.pojo.Student;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
import java.util.Set;
public class StudentService {
private StudentDao studentDao; // bean属性
private String name; //字符串类型
private int count; //基本数据类型
private List<String> names; // 字符串类型List集合
private List<Student> students1; // 对象类型List集合
private Set<Student> students2; // 对象类型Set集合
private Map<String,String> names2; // 字符串类型Map集合
private Map<String,Student> students3; // 对象类型Map集合
private Properties properties; //Properties类型
public StudentDao getStudentDao() {
return studentDao;
}
public void setStudentDao(StudentDao studentDao) {
this.studentDao = studentDao;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
public void setCount(int count) {
this.count = count;
}
public List<String> getNames() {
return names;
}
public void setNames(List<String> names) {
this.names = names;
}
public List<Student> getStudents1() {
return students1;
}
public void setStudents1(List<Student> students1) {
this.students1 = students1;
}
public Set<Student> getStudents2() {
return students2;
}
public void setStudents2(Set<Student> students2) {
this.students2 = students2;
}
public Map<String, String> getNames2() {
return names2;
}
public void setNames2(Map<String, String> names2) {
this.names2 = names2;
}
public Map<String, Student> getStudents3() {
return students3;
}
public void setStudents3(Map<String, Student> students3) {
this.students3 = students3;
}
public Properties getProperties() {
return properties;
}
public void setProperties(Properties properties) {
this.properties = properties;
}
public Student findById(int id){
return studentDao.findById(id);
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "StudentService{" +
"studentDao=" + studentDao +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", count=" + count +
", names=" + names +
", students1=" + students1 +
", students2=" + students2 +
", names2=" + names2 +
", students3=" + students3 +
", properties=" + properties +
'}';
}
}
1、property标签使用list标签注入list集合?
?????????????????????????注入简单数据类型list集合
<bean id="studentDaoImpl" class="com.itbaizhan.dao.StudentDaoImpl"></bean>
<bean id="studentService" class="com.itbaizhan.service.StudentService">
<!-- 注入bean类型 -->
<property name="studentDao" ref="studentDaoImpl"></property>
<!-- 注入基本数据类型或字符串 -->
<property name="name" value="路飞"></property>
<property name="count" value="1"></property>
<!-- 注入简单数据类型list -->
<property name="names">
<list>
<value>索隆</value>
<value>乔巴</value>
</list>
</property>
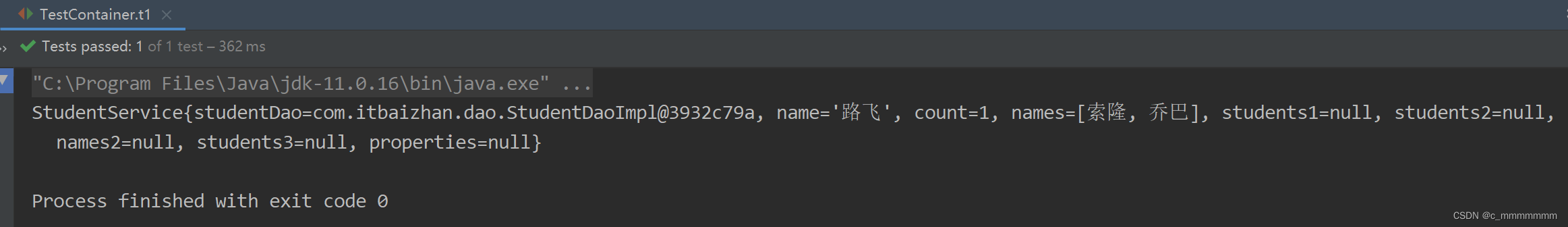
</bean>测试:
public class TestContainer {
@Test
public void t1(){
//创建Spring容器
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//获取对象
StudentService studentService = (StudentService) ac.getBean("studentService");
System.out.println(studentService);
}
}
????????????????????????注入bean类型list集合
<bean id="studentDaoImpl" class="com.itbaizhan.dao.StudentDaoImpl"></bean>
<bean id="studentService" class="com.itbaizhan.service.StudentService">
<!-- 注入bean类型 -->
<property name="studentDao" ref="studentDaoImpl"></property>
<!-- 注入基本数据类型或字符串 -->
<property name="name" value="路飞"></property>
<property name="count" value="1"></property>
<!-- 注入简单数据类型list -->
<property name="names">
<list>
<value>索隆</value>
<value>乔巴</value>
</list>
</property>
<!-- 注入bean类型list -->
<property name="students1">
<list>
<bean class="com.itbaizhan.pojo.Student">
<property name="sid" value="1"></property>
<property name="sname" value="索隆"></property>
<property name="sex" value="男"></property>
<property name="age" value="16"></property>
</bean>
<bean class="com.itbaizhan.pojo.Student">
<property name="sid" value="1"></property>
<property name="sname" value="娜美"></property>
<property name="sex" value="女"></property>
<property name="age" value="20"></property>
</bean>
</list>
</property>
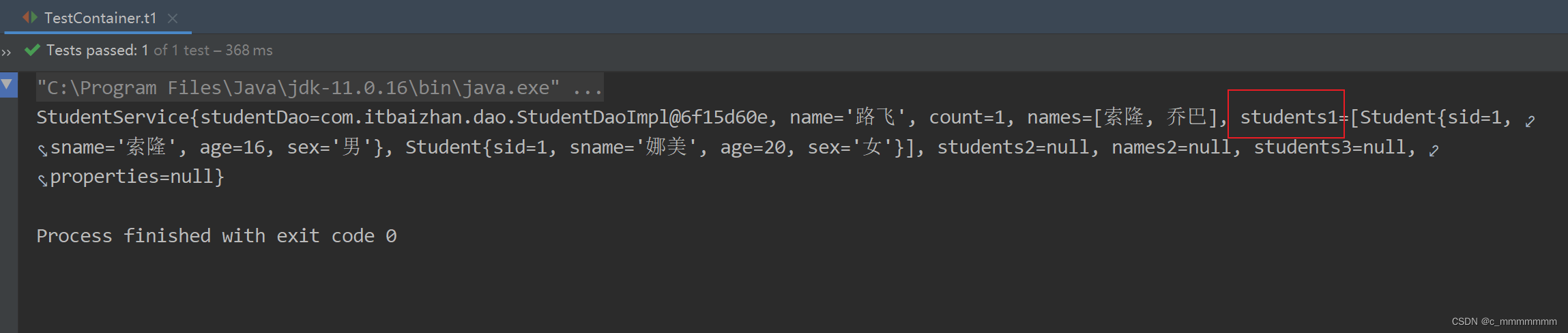
</bean>测试
public class TestContainer {
@Test
public void t1(){
//创建Spring容器
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//获取对象
StudentService studentService = (StudentService) ac.getBean("studentService");
System.out.println(studentService);
}
}
 ??
??
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 注入map
简单数据类型map集合:
简单数据类型Map集合:
<bean id="studentService" class="com.itbaizhan.service.StudentService">
<!-- 简单数据类型map集合 name:属性名 -->
<property name="names2">
<map>
<entry key="student1" value="bz"/>
<entry key="student2" value="sxt"/>
</map>
</property>
</bean>
对象类型map集合
对象类型Map集合:
<bean id="studentService" class="com.itbaizhan.service.StudentService">
<!-- 对象类型map集合 name:属性名 -->
<property name="students3">
<map>
<entry key="student1" value-ref="s1"/>
<entry key="student2" value-ref="s2"/>
</map>
</property>
</bean>
<bean id="s1" class="com.itbaizhan.domain.Student">
<property name="id" value="1"/>
<property name="name" value="尚学堂"/>
<property name="address" value="北京"/>
</bean>
<bean id="s2"class="com.itbaizhan.domain.Student">
<property name="id" value="2"/>
<property name="name" value="百战"/>
<property name="address" value="北京"/>
</bean>? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? 注入Properties对象
注入Properties对象
<bean id="studentService" class="com.itbaizhan.service.StudentService">
<property name="properties">
<props>
<prop key="配置1">值1</prop>
<prop key="配置2">值2</prop>
</props>
</property>
</bean>? ? ? ? 注解实现IOC
????????????????准备工作
注解配置和xml配置对于Spring的IOC要实现的功能都是一样的,只是配置的形式不一样。
- 创建一个新的Spring项目。(还是使用之前的)
- 编写pojo,dao,service类。(还是使用之前的)
- 编写空的配置文件,如果想让该文件支持注解,需要添加新的约束:
- 并且需要配置扫描包,只有被扫描的包的注解才能生效
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" ??? xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" ??? xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" ??? xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans ????????????? http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd ????????????? Index of /schema/context ????????????? http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!-- 要在配置文件中配置扫描的包,扫描到该注解才能生效。 --> <context:component-scan base-package="包名"></context:component-scan> </beans>
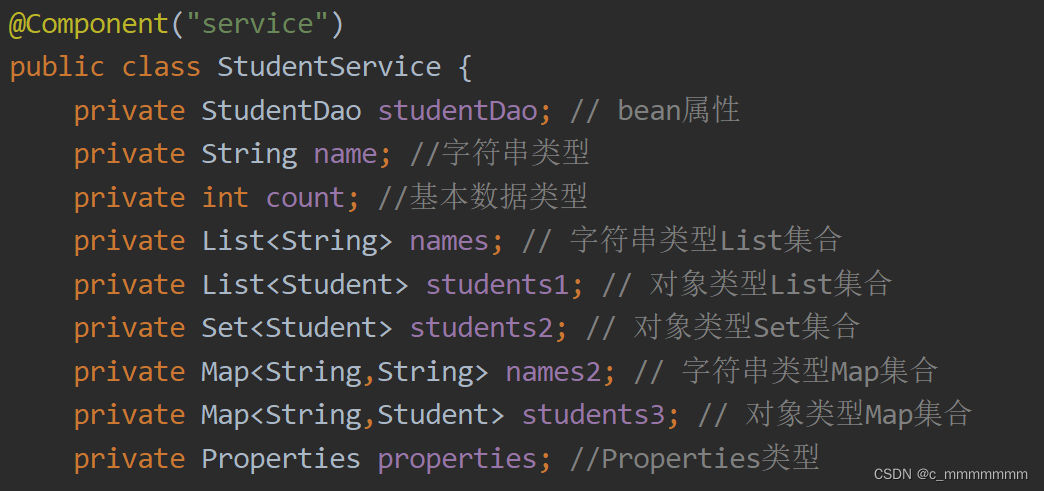
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? @Component
作用:用于创建对象,放入Spring容器,相当于<bean id="" class="">
位置:类上方
1、类上添加注解
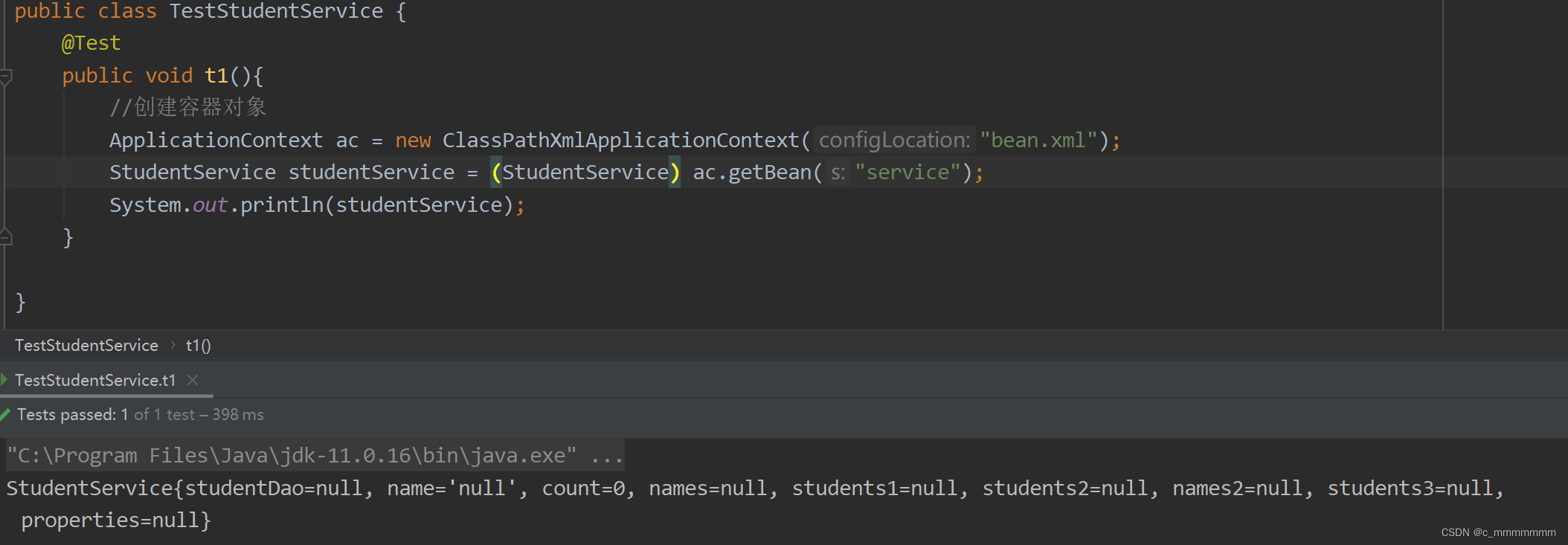
 ?2、测试
?2、测试
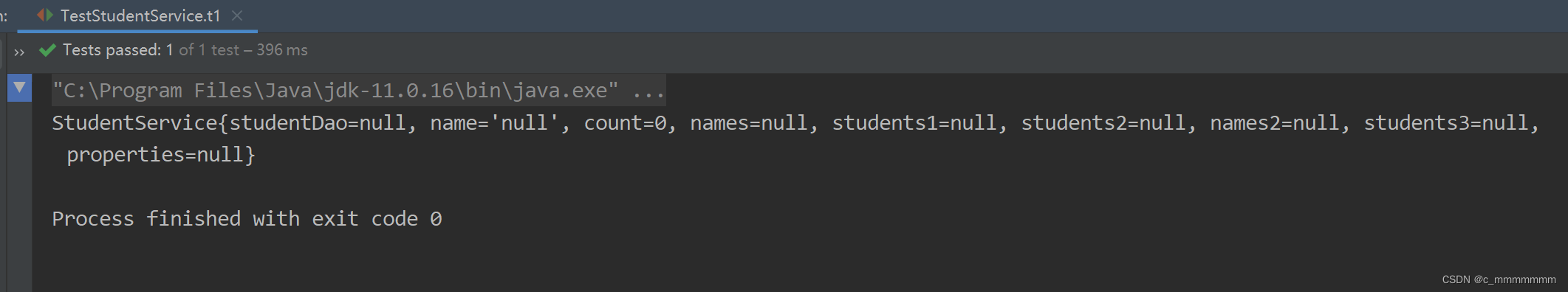
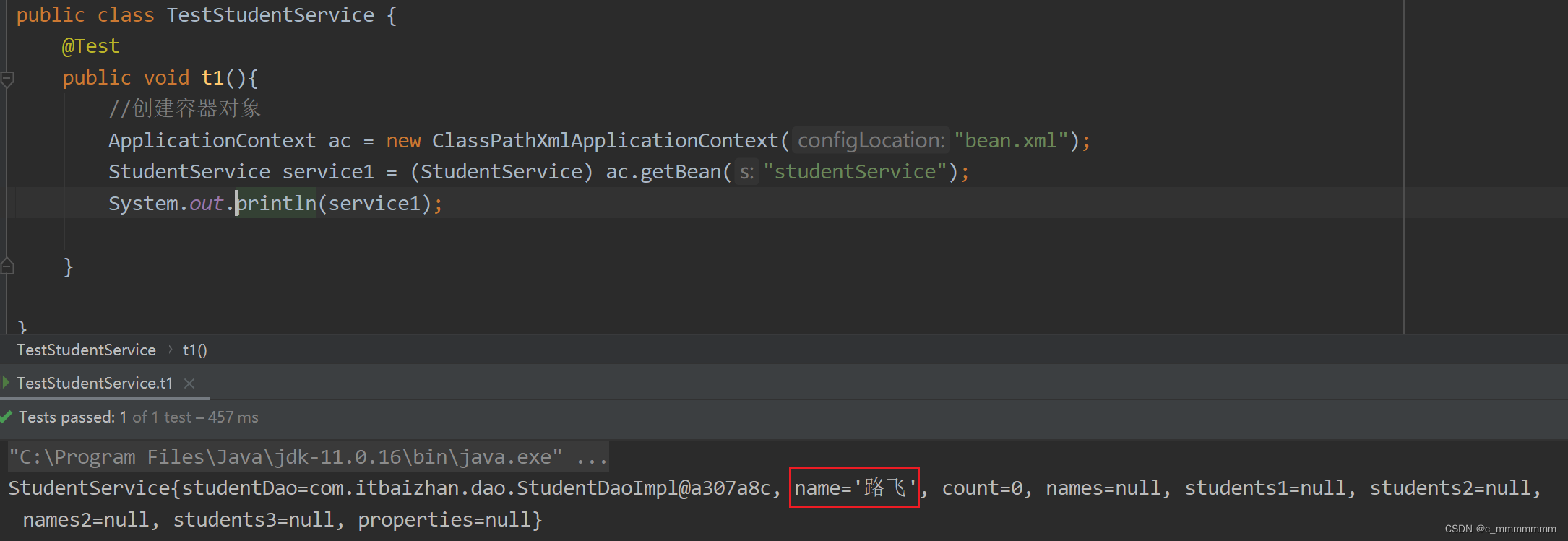
public class TestStudentService {
@Test
public void t1(){
//创建容器对象
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
StudentService studentService = (StudentService) ac.getBean("studentService");
System.out.println(studentService);
}
}
?????????
注意:
- 要在配置文件中配置扫描的包,扫描到该注解才能生效。
<context:component-scan base-package="com.itbaizhan"></context:component-scan> - @Component注解配置bean的默认id是首字母小写的类名。也可以手动设置bean的id值。
?
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? @Repository、@Service、@Controller
作用:这三个注解和@Component的用法和作用一样,
使用它们是为了区分该类属于什么层。
位置:
- @Repository用于Dao层
- @Service用于Service层
- @Controller用于Controller层
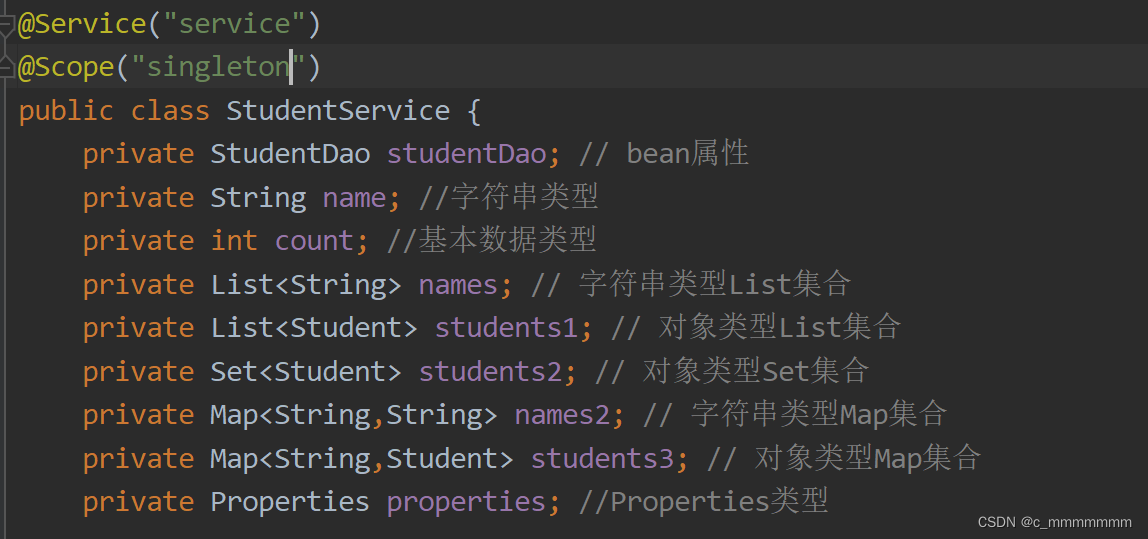
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? @Scope
作用:指定bean的创建策略
位置:类上方
?
取值:
singleton
prototype
request
session
globalsession
 ?
?
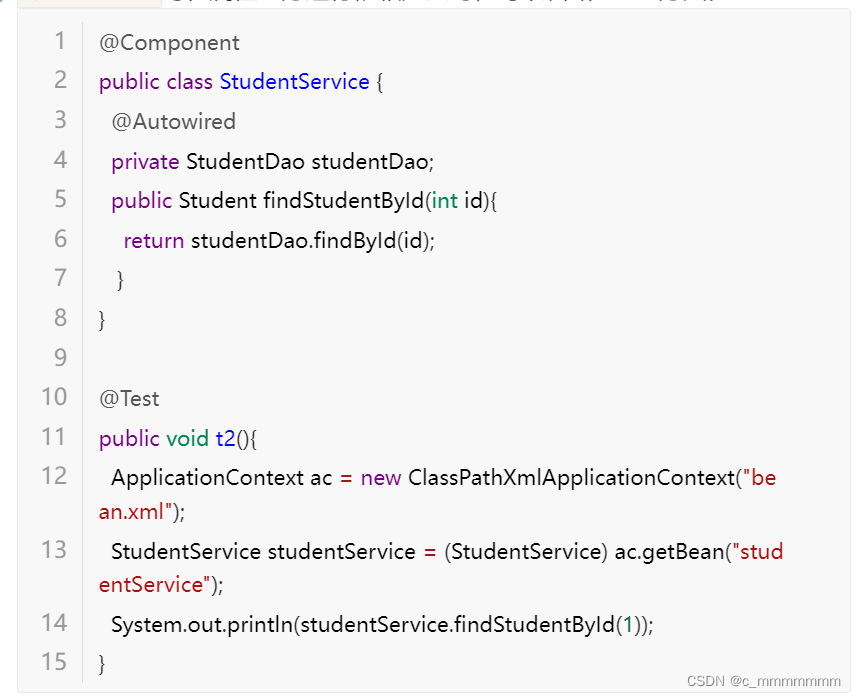
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? @Autowired
作用:从容器中查找符合属性类型的对象自动注入属性中。用于代替<bean>中的依赖注入配置。
位置:属性上方、setter方法上方、构造方法上方。
注意:?
- @Autowired写在属性上方进行依赖注入时,可以省略setter方法。
容器中没有对应类型的对象会报错?
// 如果StudentDaoImpl没有放到容器中会报错
//@Component("studentDao")
public class StudentDaoImpl implements StudentDao{
public StudentfindById(int id) {
// 模拟根据id查询学生
return new Student(1,"百战程序员","北京");
}
}容器中有多个对象匹配类型时,会找beanId等于属性名的对象,找不到会报错。?
// 如果容器中都多个同类型对象,会根据id值等于属性名找对象
@Component("studentDao")
public class StudentDaoImpl implements StudentDao{
public Student findById(int id) {
// 模拟根据id查询学生
return new Student(1,"百战程序员","北京");
}
}
@Component
public class StudentDaoImpl2 implements StudentDao{
public Student findById(int id) {
// 模拟根据id查询学生
return new Student(1,"百战程序员","北京");
}
}? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? @Qualifier
作用:在按照类型注入对象的基础上,再按照bean的id注入。
位置:属性上方
注意:@Qualifier必须和@Autowired一起使用。
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? @Value
作用:注入String类型和基本数据类型的属性值。
位置:属性上方
 ?
?
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? @Configuration
此时基于注解的IOC配置已经完成,但是我们依然离不开Spring的xml配置文件。接下来我们脱离bean.xml,使用纯注解实现IOC。
?
在真实开发中,我们一般还是会保留xml配置文件,很多情况下使用配置文件更加方便。
纯注解实现IOC需要一个Java类代替xml文件。这个Java类上方需要添加@Configuration,表示该类是一个配置类,作用是代替配置文件。
package com.itbaizhan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class SpringConfig {
}
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? @ComponentScan
作用:指定spring在初始化容器时扫描的包。
位置:配置类上方
只有被扫描的包下的注解才会生效
package com.itbaizhan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.itbaizhan")
public class SpringConfig {
}
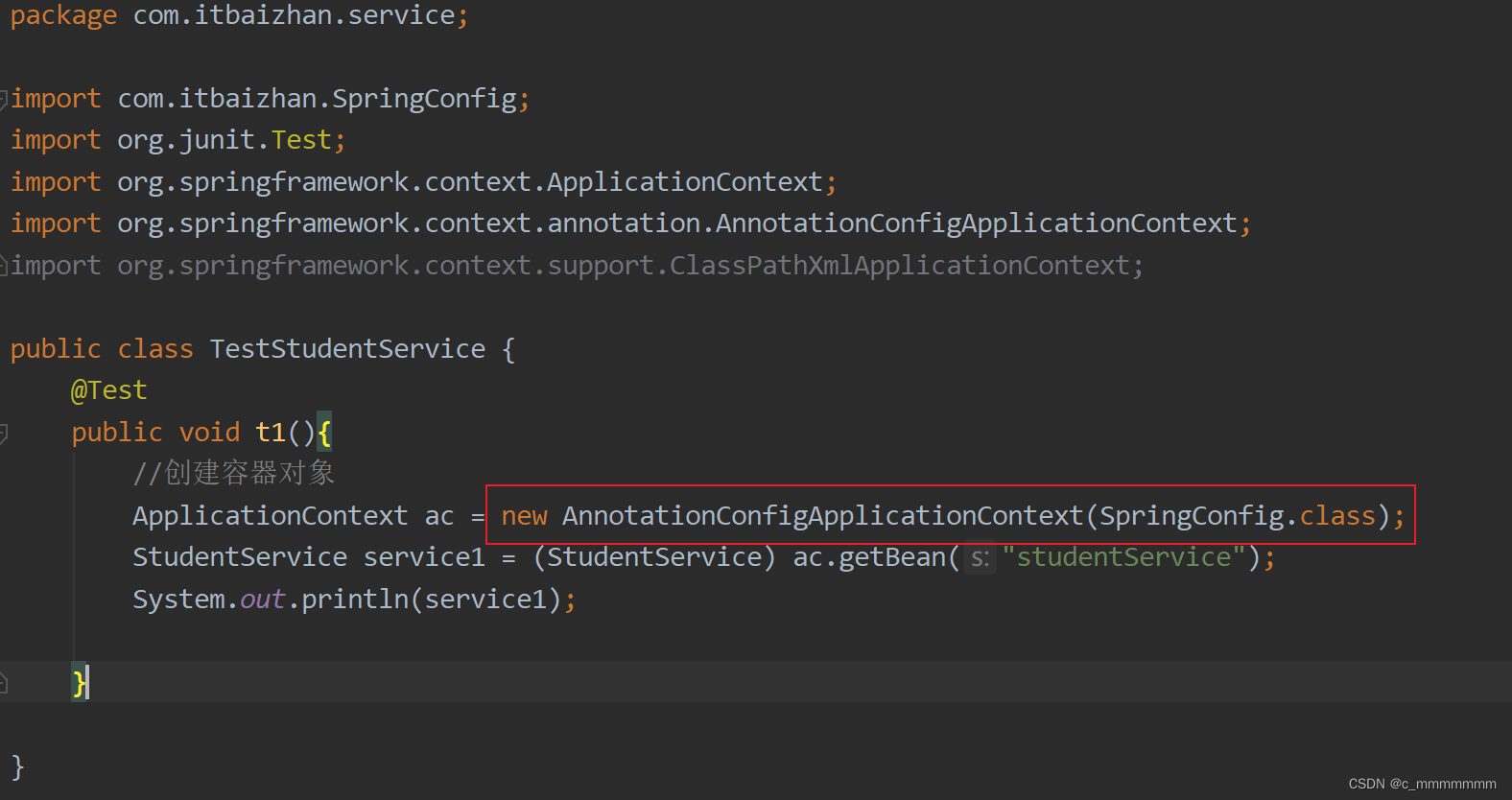
而如果使用配置类代替配置文件,那么创建容器对象使用的ApplicationContext实现类就需要使用AnnotationConfigApplicationContext,并传递配置类的class对象?
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? @PropertySource
作用:代替配置文件中的<context:property-placeholder>扫描配置文件
位置:配置类上方
注意:配置文件位置前要加关键字classpath
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? @Bean
作用:将方法的返回值对象放入Spring容器中。如果想将第三方类的对象放入容器,可以使用@Bean
位置:配置类的方法上方。
属性:name:给bean对象设置id
注意:@Bean修饰的方法如果有参数,spring会根据参数类型从容器中查找可用对象。
举例:如果想将jdbc连接对象放入Spring容器,我们无法修改Connection源码添加@Component,此时就需要使用将@Bean该对象放入Spring容器
package com.itbaizhan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.itbaizhan")
@PropertySource("classpath:db.properties")
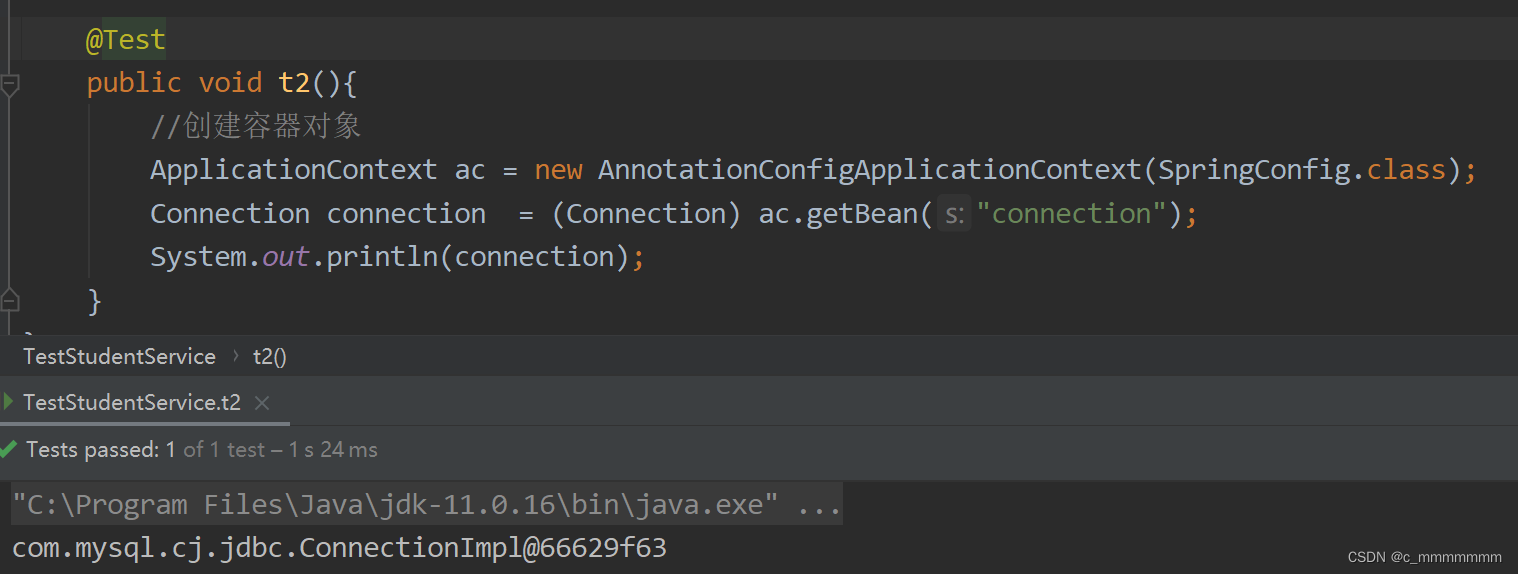
public class SpringConfig {
@Bean("connection")
public Connection getConnection(){
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
return DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql:///mysql","root","root");
}catch (Exception e){
return null;
}
}
}
? ? ? ? ? ? ? ? @Import
作用:如果配置过多,会有多个配置类,该注解可以为主配置类导入其他配置类
位置:主配置类上方

? ? ? ? Spring整合MyBatis
????????????????搭建环境
1、引入Junit和Spring整合Junit依赖
<!-- junit,如果Spring5整合junit,则junit版本至少在4.12以上 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- spring整合测试模块 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>5.3.13</version>
</dependency>
????????????????编写配置文件
1.在Spring整合MyBatis中,Spring提供的对SqlSessionFactory的封装类是SqlSessionFactoryBean
2.在Spring整合MyBatis中,Spring提供的对SqlSession的封装类是SqlSessionTemplate
1、?编写数据库配置文件db.properties
jdbc.driverClassName=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql:///student
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=root2、创建MyBatis配置文件SqlMapConfig.xml,数据源、扫描接口都交由Spring管理,不需要在MyBatis配置文件中设置。
<!-- mybatis配置文件 -->
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE configuration
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<configuration>
</configuration><!-- spring配置文件 -->
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- 包扫描 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.itbaizhan"></context:component-scan>
<!-- 读取配置文件 -->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:db.properties"></context:property-placeholder>
<!-- 创建druid数据源对象 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="${jdbc.driverClassName}"></property>
<property name="url" value="${jdbc.url}"></property>
<property name="username" value="${jdbc.username}"></property>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.password}"></property>
</bean>
<!-- Spring创建封装过的SqlSessionFactory -->
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!-- Spring创建封装过的SqlSession -->
<bean id="sqlSession" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionTemplate">
<constructor-arg name="sqlSessionFactory" ref="sqlSessionFactory"/>
</bean>
</beans>
????????????????编写POJO类、持久层、service层
准备数据库
CREATE DATABASE `student`;
USE `student`;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `student`;
CREATE TABLE `student` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`sex` varchar(10) DEFAULT NULL,
`address` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=3 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
insert into `student`(`id`,`name`,`sex`,`address`) values (1,'百战程序员','男','北京'),(2,'北京尚学堂','女','北京');
准备实体类
public class Student {
private int id;
private String name;
private String sex;
private String address;
// 省略构造方法/getter/setter/tostring
}
编写持久层接口
@Repository
public interface StudentDao {
// 查询所有学生
@Select("select * from student")
List<Student> findAll();
// 添加学生
@Insert("insert into student values(null,#{name},#{sex},#{address})")
void add(Student student);
}
编写service类
@Service
public class StudentService {
// SqlSession对象
@Autowired
private SqlSessionTemplate sqlSession;
// 使用SqlSession获取代理对象
public List<Student> findAllStudent(){
StudentDao studentDao = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentDao.class);
return studentDao.findAll();
}
}
?注:使用SqlSessionTemplate创建代理对象还是需要注册接口或者映射文件的。
在MyBatis配置文件注册接口
<configuration>
? <mappers>
??? <mapper class="com.itbaizhan.dao.StudentDao"></mapper>
? </mappers>
</configuration>
创建sqlSessionFactory时指定MyBatis配置文件
<!-- 创建Spring封装过的SqlSessionFactory -->
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
? <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
? <property name="configLocation" value="classpath:SqlMapConfig.xml"></property>
</bean>????????????????Spring整合Junit进行单元测试
之前进行单元测试时都需要手动创建Spring容器,能否在测试时让Spring自动创建容器呢?
引入Junit和Spring整合Junit依赖?
<!-- junit,如果Spring5整合junit,则junit版本至少在4.12以上 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- spring整合测试模块 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>5.3.13</version>
</dependency>
编写测试类
// JUnit使用Spring方式运行代码,即自动创建spring容器。
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
// 告知创建spring容器时读取哪个配置类或配置文件
// 配置类写法:@ContextConfiguration(classes=配置类.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations="classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class StudentServiceTest {
@Autowired
private StudentService studentService;
@Test
public void testFindAll(){
List<Student> allStudent = studentService.findAllStudent();
allStudent.forEach(System.out::println);
}
}
????????????????自动创建代理对象???
Spring提供了MapperScannerConfigurer对象,该对象可以自动扫描包创建代理对象,并将代理对象放入容器中,此时不需要使用SqlSession手动创建代理对象。
AOP
AOP的全称是Aspect Oriented Programming,即面向切面编程。是实现功能统一维护的一种技术,它将业务逻辑的各个部分进行隔离,使开发人员在编写业务逻辑时可以专心于核心业务,从而提高了开发效率。
- 作用:在不修改源码的基础上,对已有方法进行增强。
- 实现原理:动态代理技术。
- 优势:减少重复代码、提高开发效率、维护方便
- 应用场景:事务处理、日志管理、权限控制、异常处理等方面。
我们使用的是AspectJ框架实现的AOP,所以需要引入依赖
<!-- AspectJ -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.8.7</version>
</dependency>相关术语

为了更好地理解AOP,就需要对AOP的相关术语有一些了解
| 名称 | 说明 |
| Joinpoint(连接点) | 指能被拦截到的点,在Spring中只有方法能被拦截。 |
| Pointcut(切点) | 指要对哪些连接点进行拦截,即被增强的方法。 |
| Advice(通知) | 指拦截后要做的事情,即切点被拦截后执行的方法。 |
| Aspect(切面) | 切点+通知称为切面 |
| Target(目标) | 被代理的对象 |
| Proxy(代理) | 代理对象 |
| Weaving(织入) | 生成代理对象的过程 |
配置AOP流程
1、编写通知类
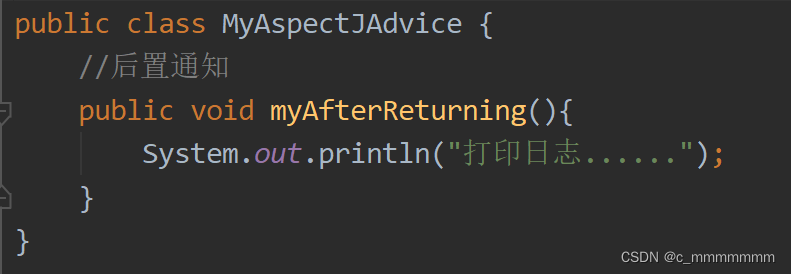
2、在bean.xml配置文件中,将通知类写入

3、配置aop
????????1、编写aop标签
????????2、配置切面以及切点的通知类
????????????????1、配置切点
????????????????2、配置通知类调用的方法和通知的切点id
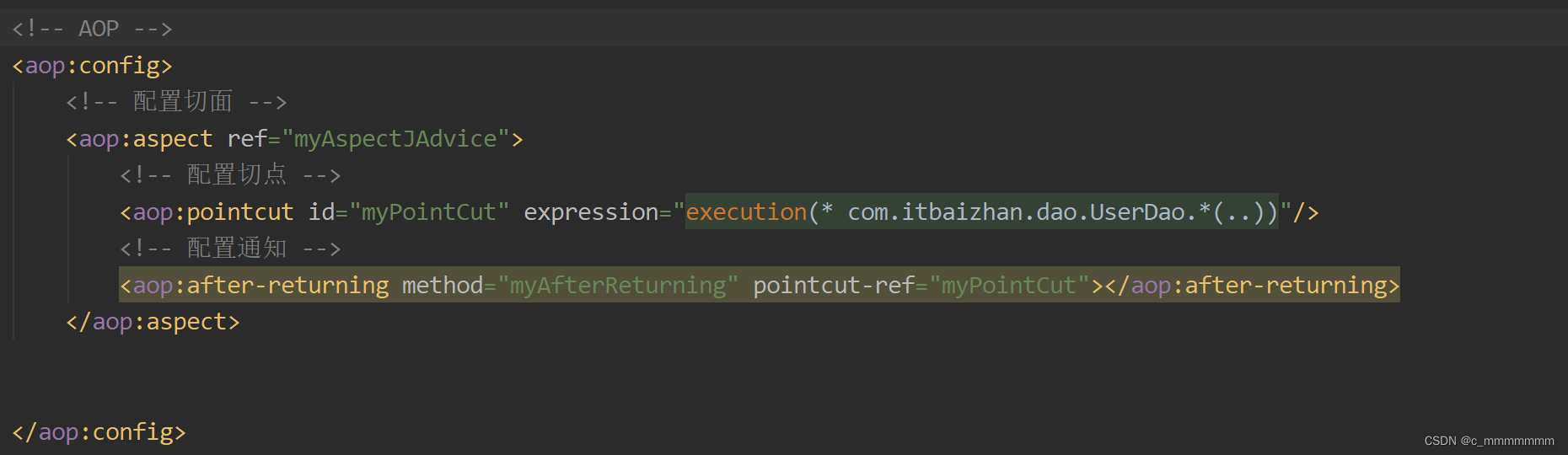
通知类型:?
AOP有以下几种常用的通知类型:
| 通知类型 | 描述 |
| 前置通知 | 在方法执行前添加功能 |
| 后置通知 | 在方法正常执行后添加功能 |
| 异常通知 | 在方法抛出异常后添加功能 |
| 最终通知 | 无论方法是否抛出异常,都会执行该通知 |
| 环绕通知 | 在方法执行前后添加功能 |
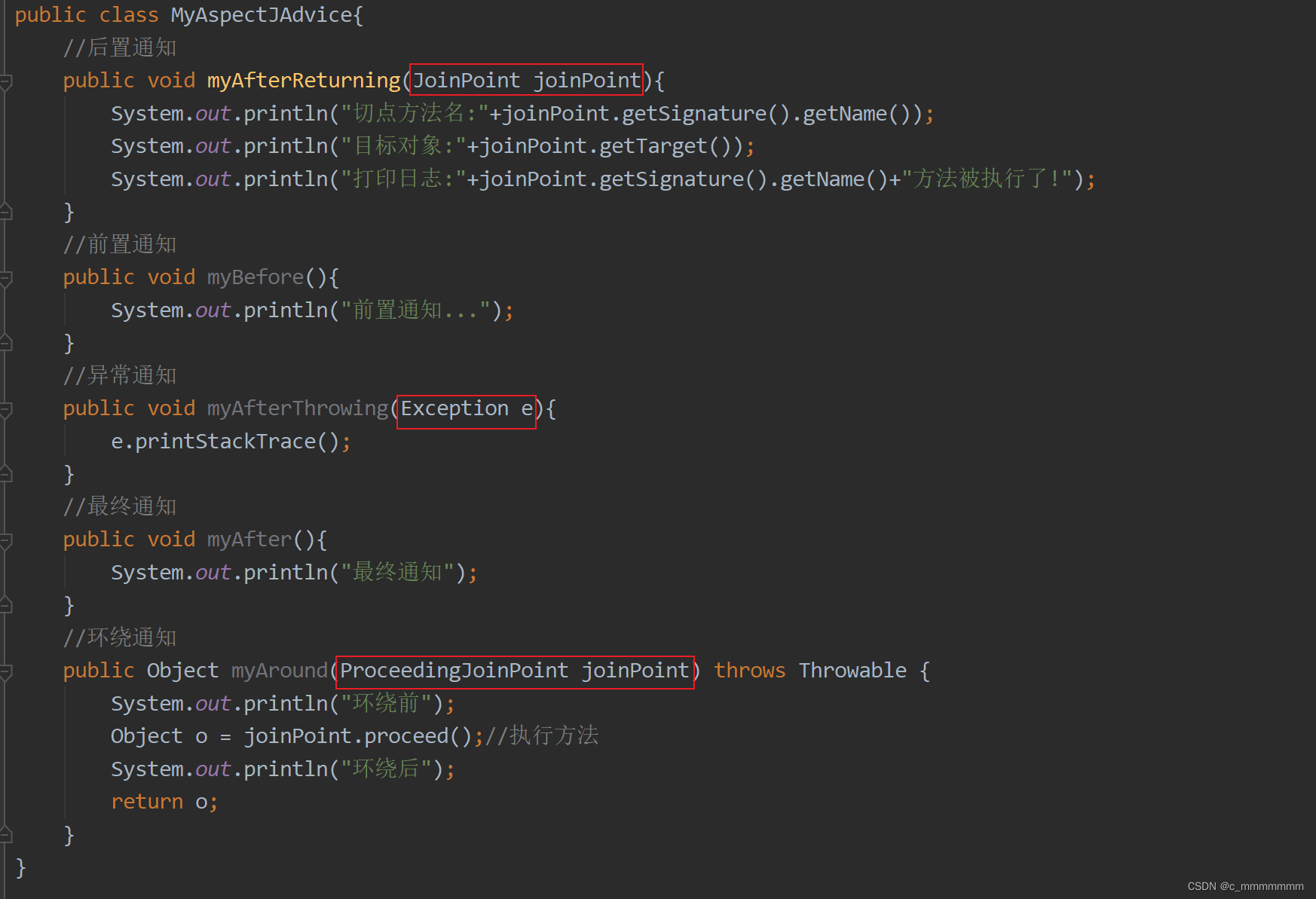
通知的各种类型的标签
<!-- 配置AOP -->
<aop:config>
<!-- 配置切面 -->
<aop:aspect ref="myAspectJAdvice">
<!-- 配置切点 -->
<aop:pointcut id="myPointcut" expression="execution(* com.itbaizhan.dao.UserDao.*(..))"/>
<!-- 前置通知 -->
<aop:before method="myBefore" pointcut-ref="myPointcut"></aop:before>
<!-- 后置通知 -->
<aop:after-returning method="myAfterReturning"pointcut-ref="myPointcut"/>
<!-- 异常通知 -->
<aop:after-throwing method="myAfterThrowing" pointcut-ref="myPointcut" throwing="ex"/>
<!-- 最终通知 -->
<aop:after method="myAfter" pointcut-ref="myPointcut"></aop:after>
<!-- 环绕通知 -->
<aop:around method="myAround" pointcut-ref="myPointcut"></aop:around>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
切点表达式
使用AspectJ需要使用切点表达式配置切点位置,写法如下:
- 标准写法:访问修饰符 返回值 包名.类名.方法名(参数列表)
- 访问修饰符可以省略。
- 返回值使用*代表任意类型。
- 包名使用*表示任意包,多级包结构要写多个*,使用*..表示任意包结构
- 类名和方法名都可以用*实现通配。
?
参数列表
- 基本数据类型直接写类型
- 引用类型写包名.类名
- *表示匹配一个任意类型参数
- ..表示匹配任意类型任意个数的参数
- 全通配:* *..*.*(..)
注解配置AOP
Spring可以使用注解代替配置文件配置切面:
- 在xml中开启AOP注解支持
<!-- 开启注解配置Aop -->
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy></aop:aspectj-autoproxy> - 在通知类上方加入注解@Aspect
- 在通知方法上方加入注解@Before/@AfterReturning/@AfterThrowing/@After/@Around
如果有多个el表达式是相同的那么可以编写一个方法,并在该方法头上添加@Pointcut注解,
设置值为el表达式
然后就可以在通知方法上直接调用该方法就行了
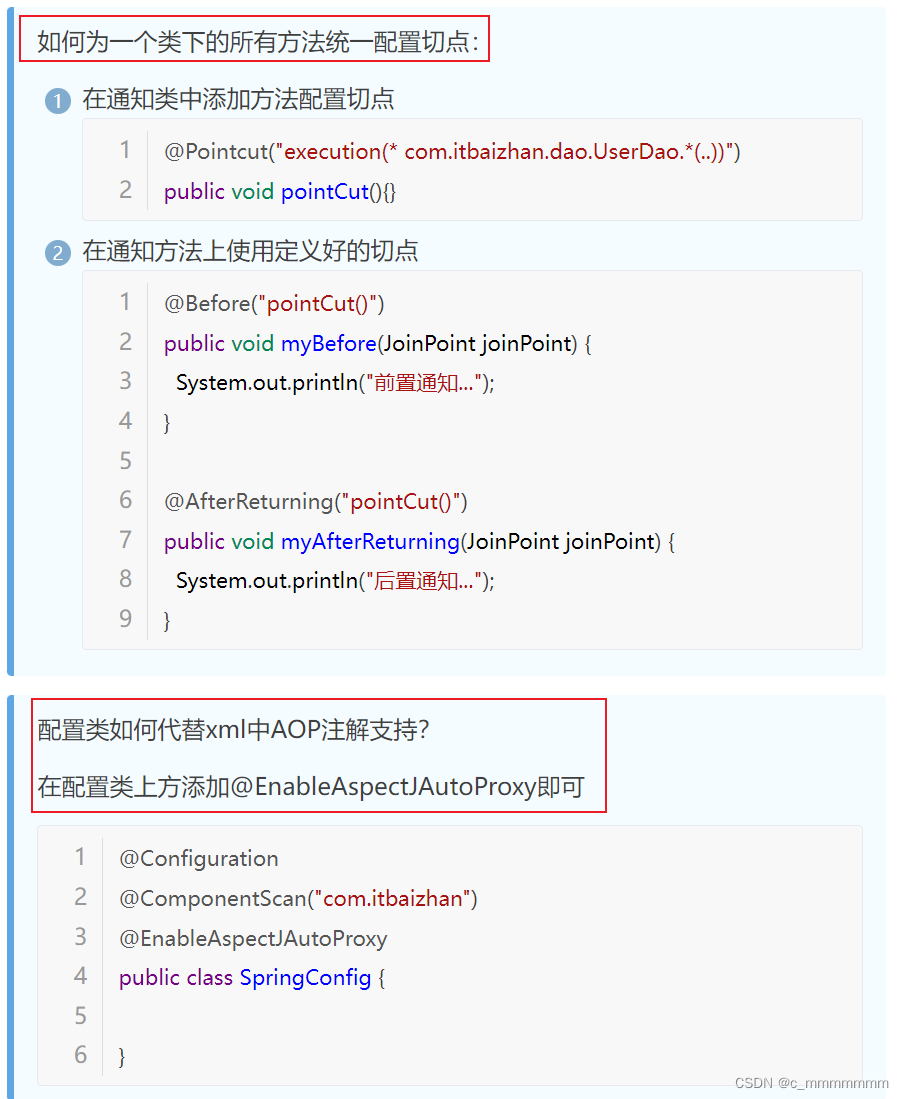
事务
? ? ? ? 案例:
????????????????准备工作:
1、准备数据库
CREATE DATABASE `spring` ;
USE `spring`;
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `account`;
CREATE TABLE `account` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`username` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`balance` double DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=3 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
insert into `account`(`id`,`username`,`balance`) values (1,'张三',1000),(2,'李四',1000);
2、创建maven项目,引入依赖
<dependencies>
<!-- mybatis -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.7</version>
</dependency>
<!-- mysql驱动包 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.26</version>
</dependency>
<!-- druid连接池 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.2.8</version>
</dependency>
<!-- spring -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.3.13</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId>
<version>5.3.13</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>5.3.13</version>
</dependency>
<!-- MyBatis与Spring的整合包,该包可以让Spring创建MyBatis的对象 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId>
<version>2.0.6</version>
</dependency>
<!-- junit,如果Spring5整合junit,则junit版本至少在4.12以上 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- spring整合测试模块 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>5.3.13</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
????????????????创建配置文件:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- 包扫描 -->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.itbaizhan"></context:component-scan>
<!-- 创建druid数据源对象 -->
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql:///spring"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="root"></property>
</bean>
<!-- Spring创建封装过的SqlSessionFactory -->
<bean id="sqlSessionFactory" class="org.mybatis.spring.SqlSessionFactoryBean">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 该对象可以自动扫描持久层接口,并为接口创建代理对象 -->
<bean id="mapperScanner" class="org.mybatis.spring.mapper.MapperScannerConfigurer">
<!-- 配置扫描的接口包 -->
<property name="basePackage" value="com.itbaizhan.dao"></property>
</bean>
</beans>????????????????编写代码步骤:
1、创建POJO类
2、创建持久层接口
3、创建逻辑层
4、编写配置文件
5、测试
????????????????编写代码:
1、编写POJO类
public class Account{
private Integer id;
private String username;
private Double balance;
省略构造方法、getter、setter
}
2、编写持久层接口?
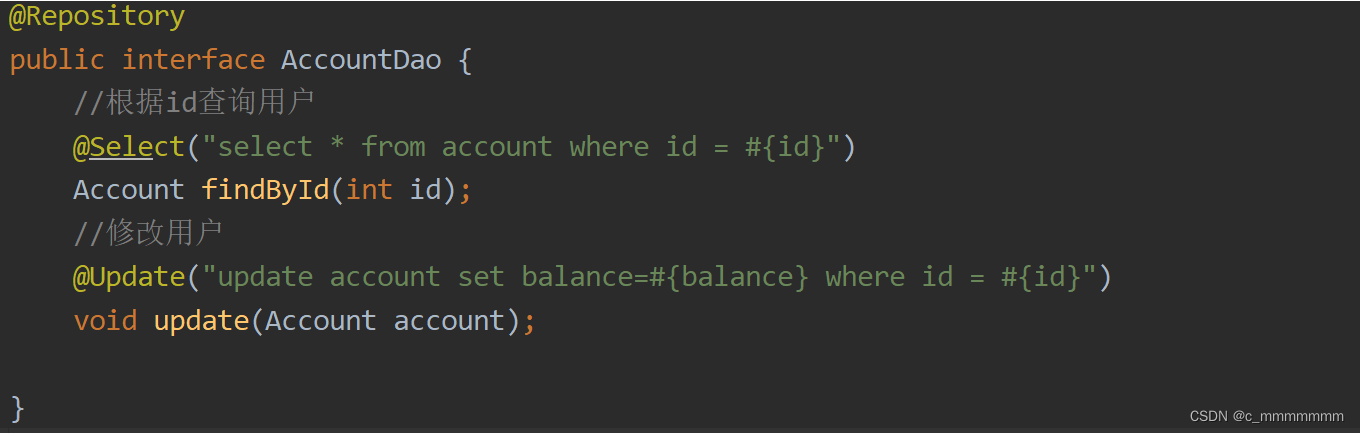
?3、编写逻辑层
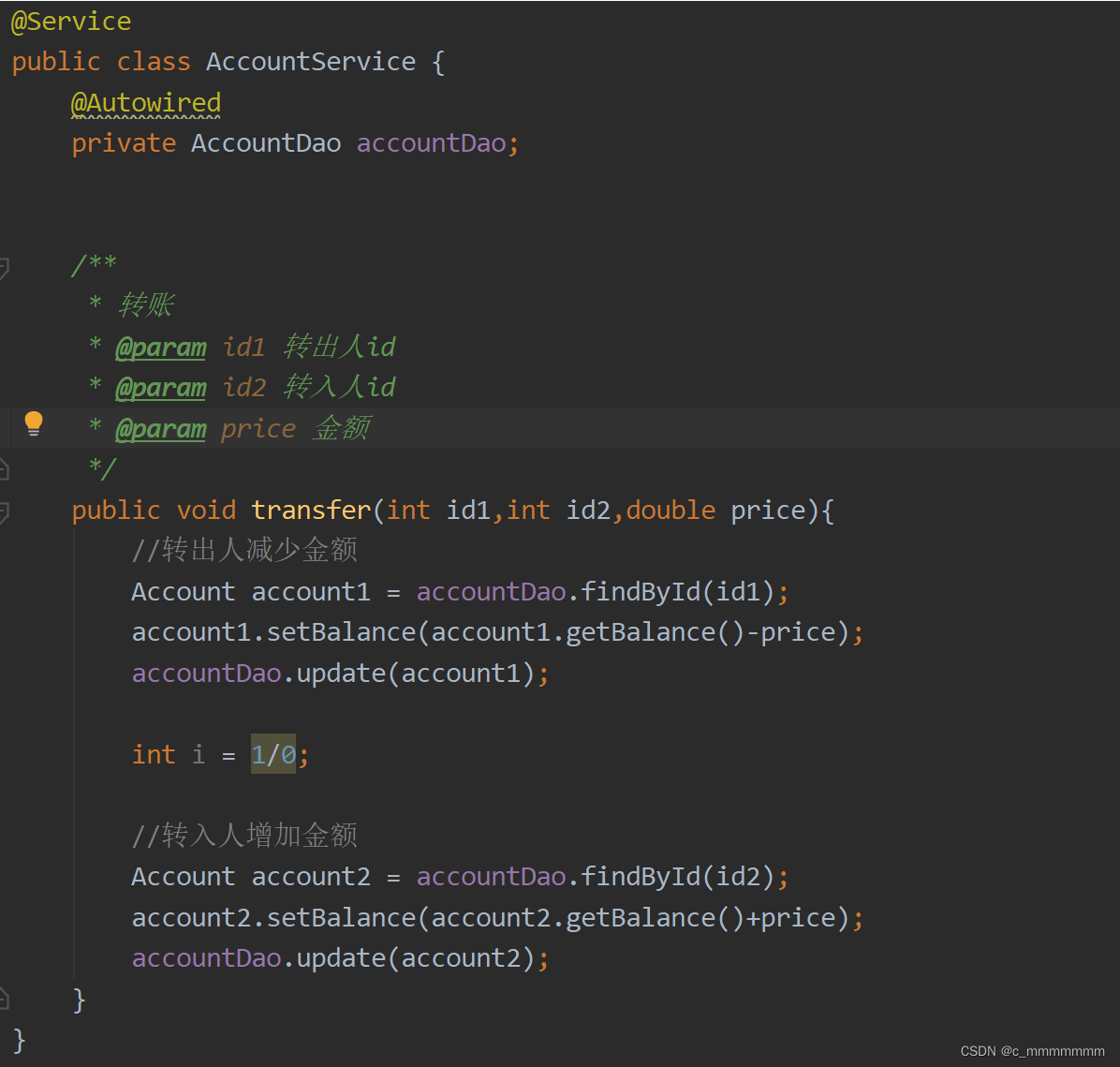
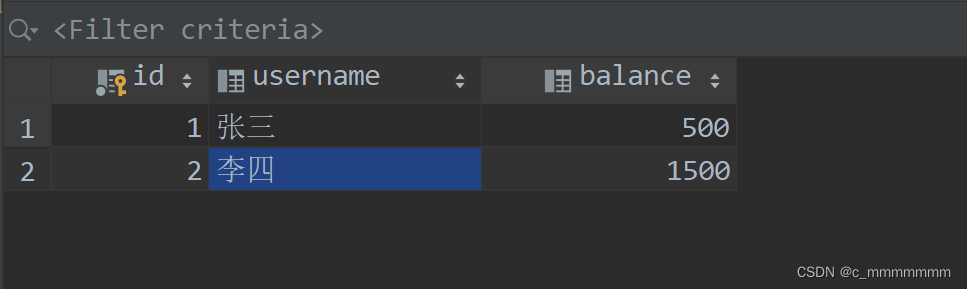
?测试?

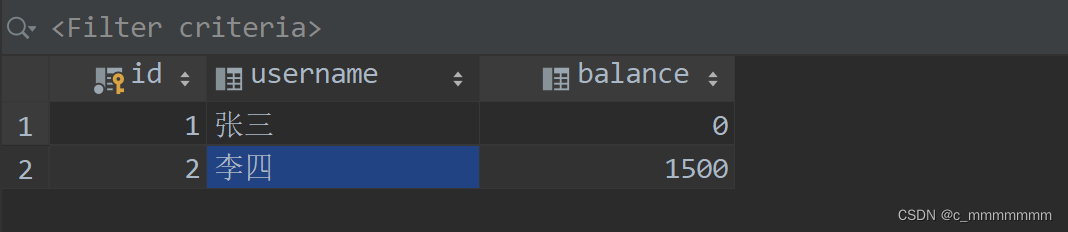
此时测试代码如果出现异常那么就导致数据出错,张三钱没了,但是李四钱没有增加,此时就需要使用事务来使程序具有原子性?
模拟转账出错:
@Service
public class AccountService {
@Autowired
private AccountDao accountDao;
public void transfer(int id1,int id2,double price){
Account a1 = accountDao.findById(id1);
a1.setBalance(a1.getBalance()-price);
accountDao.update(a1);
int i = 1/0;
Account a2 = accountDao.findById(id2);
a2.setBalance(a2.getBalance()+price);
accountDao.update(a2);
}
}
????????事务管理方案:
在service层手动添加事务可以解决该问题:
@Autowired
private SqlSessionTemplate sqlSession;
public void transfer(int id1, int id2, double price) {
try{
// account1修改余额
Account account1 = accountDao.findById(id1);
account1.setBalance(account1.getBalance()-price);
accountDao.update(account1);
int i = 1/0; // 模拟转账出错
// account2修改余额
Account account2 = accountDao.findById(id2);
account2.setBalance(account2.getBalance()+price);
accountDao.update(account2);
sqlSession.commit();
}catch(Exception ex){
sqlSession.rollback();
}
}
但在Spring管理下不允许手动提交和回滚事务。此时我们需要使用Spring的事务管理方案,在Spring框架中提供了两种事务管理方案:
- 编程式事务:通过编写代码实现事务管理。
- 声明式事务:基于AOP技术实现事务管理。
在Spring框架中,编程式事务管理很少使用,我们对声明式事务管理进行详细学习。
Spring的声明式事务管理在底层采用了AOP技术,其最大的优点在于无需通过编程的方式管理事务,只需要在配置文件中进行相关的规则声明,就可以将事务规则应用到业务逻辑中。
使用AOP技术为service方法添加如下通知:
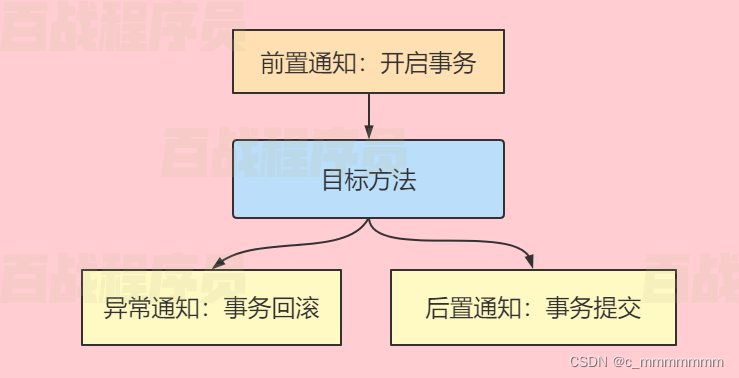
????????事务管理器:
Spring依赖事务管理器进行事务管理,事务管理器即一个通知类,我们为该通知类设置切点为service层方法即可完成事务自动管理。由于不同技术操作数据库,进行事务操作的方法不同。如:JDBC提交事务是connection.commit(),MyBatis提交事务是sqlSession.commit(),所以Spring提供了多个事务管理器。
| 事务管理器名称 | 作用 |
| org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager | 针对JDBC技术提供的事务管理器。适用于JDBC和MyBatis。 |
| org.springframework.orm.hibernate3.HibernateTransactionManager | 针对于Hibernate框架提供的事务管理器。适用于Hibernate框架。 |
| org.springframework.orm.jpa.JpaTransactionManager | 针对于JPA技术提供的事务管理器。适用于JPA技术。 |
| org.springframework.transaction.jta.JtaTransactionManager | 跨越了多个事务管理源。适用在两个或者是多个不同的数据源中实现事务控制。 |
我们使用MyBatis操作数据库,接下来使用DataSourceTransactionManager进行事务管理。
????????测试事务管理器:
引入依赖
<!-- 事务管理 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId>
<version>5.3.13</version>
</dependency>
<!-- AspectJ -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.8.7</version>
</dependency>
?编写配置文件
<!-- 事务管理器 -->
<bean id="transactionManager" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
<!-- 进行事务相关配置 -->
<tx:advice id= "txAdvice">
<tx:attributes>
<tx:method name="*"/>
</tx:attributes>
</tx:advice>
<!-- 配置切面 -->
<aop:config>
<!-- 配置切点 -->
<aop:pointcut id="pointcut" expression="execution(* com.itbaizhan.service.*.*(..))"/>
<!-- 配置通知 -->
<aop:advisor advice-ref="txAdvice" pointcut-ref="pointcut"></aop:advisor>
</aop:config>
?配置完事务过后,不管我们有没有出错他都会正常运行,出错自动回滚,没有出错提交事务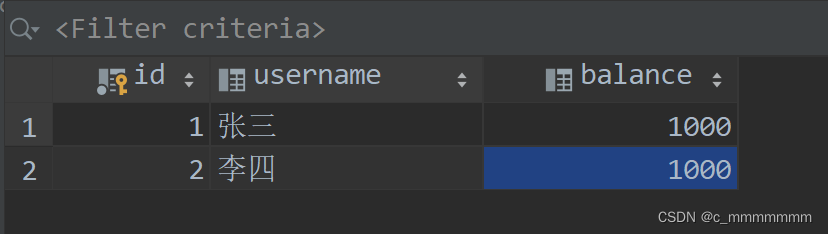
????????事务控制API:
Spring进行事务控制的功能是由三个接口提供的,这三个接口是Spring实现的,在开发中我们很少使用到,只需要了解他们的作用即可:
PlatformTransactionManager接口
PlatformTransactionManager是Spring提供的事务管理器接口,所有事务管理器都实现了该接口。该接口中提供了三个事务操作方法:
- TransactionStatus getTransaction(TransactionDefinition definition):获取事务状态信息。
- void commit(TransactionStatus status):事务提交
- void rollback(TransactionStatus status):事务回滚
?
TransactionDefinition接口
TransactionDefinition是事务的定义信息对象,它有如下方法:
- String getName():获取事务对象名称。
- int getIsolationLevel():获取事务的隔离级别。
- int getPropagationBehavior():获取事务的传播行为。
- int getTimeout():获取事务的超时时间。
- boolean isReadOnly():获取事务是否只读。
?
TransactionStatus接口
TransactionStatus是事务的状态接口,它描述了某一时间点上事务的状态信息。它有如下方法:
- void flush()?刷新事务
- boolean hasSavepoint()?获取是否存在保存点
- boolean isCompleted()?获取事务是否完成
- boolean isNewTransaction()?获取是否是新事务
- boolean isRollbackOnly()?获取是否回滚
- void setRollbackOnly()?设置事务回滚
? ? ? ? 事务的相关配置:
在<tx:advice>中可以进行事务的相关配置:
<tx:advice id="txAdvice">
? <tx:attributes>
??? <tx:method name="*"/>
??? <tx:method name="find*" read-only="true"/>
? </tx:attributes>
</tx:advice><tx:method>中的属性:?
- name:指定配置的方法。*表示所有方法,find*表示所有以find开头的方法。
- read-only:是否是只读事务,只读事务不存在数据的修改,数据库将会为只读事务提供一些优化手段,会对性能有一定提升,建议在查询中开启只读事务。
- timeout:指定超时时间,在限定的时间内不能完成所有操作就会抛异常。默认永不超时
- rollback-for:指定某个异常事务回滚,其他异常不回滚。默认所有异常回滚。
- no-rollback-for:指定某个异常不回滚,其他异常回滚。默认所有异常回滚。
- propagation:事务的传播行为
- isolation:事务的隔离级别
? ? ? ? 事务的传播行为:
事务的传播行为:
事务传播行为是指多个含有事务的方法相互调用时,事务如何在这些方法间传播。
如果在service层的方法中调用了其他的service方法,假设每次执行service方法都要开启事务,此时就无法保证外层方法和内层方法处于同一个事务当中。
// method1的所有方法在同一个事务中
public void method1(){
// 此时会开启一个新事务,这就无法保证method1()中所有的代码是在同一个事务中
method2();
System.out.println("method1");
}
public void method2(){
System.out.println("method2");
}
事务的传播特性就是解决这个问题的,Spring帮助我们将外层方法和内层方法放入同一事务中。
| 传播行为 | 介绍 |
| REQUIRED | 默认。支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就新建一个事务。这是最常见的选择。 |
| SUPPORTS | 支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就以非事务方式执行。 |
| MANDATORY | 支持当前事务,如果当前没有事务,就抛出异常。 |
| REQUIRES_NEW | 新建事务,如果当前存在事务,把当前事务挂起。 |
| NOT_SUPPORTED | 以非事务方式执行操作,如果当前存在事务,就把当前事务挂起。 |
| NEVER | 以非事务方式执行,如果当前存在事务,则抛出异常。 |
| NESTED | 必须在事务状态下执行,如果没有事务则新建事务,如果当前有事务则创建一个嵌套事务 |
? ? ? ? 事务的隔离级别:
事务隔离级别反映事务提交并发访问时的处理态度,隔离级别越高,数据出问题的可能性越低,但效率也会越低。
| 隔离级别 | 脏读 | 不可重复读 | 幻读 |
| READ_UNCOMMITED(读取未提交内容) | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| READ_COMMITED(读取提交内容) | No | Yes | Yes |
| REPEATABLE_READ(重复读) | No | No | Yes |
| SERIALIZABLE(可串行化) | No | No | No |
如果设置为DEFAULT会使用数据库的隔离级别。
- SqlServer , Oracle默认的事务隔离级别是READ_COMMITED
- Mysql的默认隔离级别是REPEATABLE_READ
? ? ? ? 注解配置声明式事务:
Spring支持使用注解配置声明式事务。用法如下:
1、注册事务注解驱动
<!-- 注册事务注解驱动 -->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager = "transactionManager"></tx:annotation-driven>2、在需要事务支持的方法或类上加@Transactional
@Service
// 作用于类上时,该类的所有public方法将都具有该类型的事务属性
@Transactional(propagation=Propagation.REQUIRED,isolation=Isolation.DEFAULT)
public class AccountService{
@Autowired
private AccountDao accountDao;
/**
* 转账
* @param id1 转出人id
* @param id2 转入人id
* @param price 金额
*/
// 作用于方法上时,该方法将都具有该类型的事务属性
@Transactional(propagation=Propagation.REQUIRED,isolation=Isolation.DEFAULT)
public void transfer(int id1, int id2, double price) {
// account1修改余额
Account account1 = accountDao.findById(id1);
account1.setBalance(account1.getBalance()-price);
accountDao.update(account1);
int i = 1/0; // 模拟转账出错
// account2修改余额
Accountaccount2=accountDao.findById(id2);
account2.setBalance(account2.getBalance()+price);
accountDao.update(account2);
}
}? ? ? ? 配置类代替xml中的注解事务支持:
在配置类上方写@EnableTranscationManagement
并将要用的对象添加到Spring容器中
public class SpringConfig{
@Bean
public DataSource getDataSource(){
DruidDataSource druidDataSource = new DruidDataSource();
druidDataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
druidDataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql:///spring");
druidDataSource.setUsername("root");
druidDataSource.setPassword("root");
return druidDataSource;
}
@Bean
public SqlSessionFactoryBean getSqlSession(DataSourcedataSource){
SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactoryBean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
sqlSessionFactoryBean.setDataSource(dataSource);
returns qlSessionFactoryBean;
}
@Bean
public MapperScannerConfigurer getMapperScanner(){
MapperScannerConfigurer mapperScannerConfigurer = new MapperScannerConfigurer();
mapperScannerConfigurer.setBasePackage("com.itbaizhan.dao");
return mapperScannerConfigurer;
}
@Bean
public DataSourceTransactionManagerget TransactionManager(DataSourcedata Source){
DataSourceTransaction Managermanager = new DataSourceTransactionManager();
manager.setDataSource(dataSource);
return manager;
}
}