一.SpringBoot2入门
1、系统要求
- Java 8?& 兼容java14 .
- Maven 3.3+
2、maven设置?
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.example</groupId>
<artifactId>myproject</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.7.4</version>
</parent>
<!-- Additional lines to be added here... -->
</project>3、HelloWorld
1.创建主程序
/**
* @author Chooker
* @create 2022-10-18 10:45
* 主程序类
*/
//告诉Springboot这是一个springboot应用
@SpringBootApplication
public class MainApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MainApplication.class,args);
}
}2.编写业务
//@Controller
//ResponseBody
@RestController
public class HelloContoller {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
return "hello,springboot";
}
}
3.测试
直接运行主程序类的main方法
4.简化配置
application.properties文件
比如想修改端口号
server.port=8888
5.简化部署?
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>4、了解自动配置原理
1.SpringBoot特点
1.1、依赖管理
<!--依赖管理--> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.3.4.RELEASE</version> </parent>他的父项目为:
<parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId> <version>2.3.4.RELEASE</version> </parent>里面为控制各种依赖的版本号:例如
<mysql.version>8.0.21</mysql.version>
如果想要修改其控制的版本号,改为自己的版本号,只需要在自己的pom文件中修改
? ? <properties>
? ? ? ? <mysql.version>5.1.43</mysql.version>
? ? </properties>?
starter场景启动器
1.见到很多spring-boot-starter-* :*就某种场景
2.只要引入starter,这个场景的所有常规需要的依赖我们都自动引入
3.SpringBoot所有支持的场景
4.见到的 thirdpartyproject-spring-boot-starter? 第三方为我们提供的starter
5.所有场景启动器最底层的依赖
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId> <version>2.3.4.RELEASE</version> <scope>compile</scope> </dependency>
例如:? ?Developing with Spring Boot

.无需关注版本号,自动版本仲裁
1、引入依赖默认都可以不写版本
2、引入非版本仲裁的jar,要写版本号。
?1.2、自动配置
- 自动配好Tomcat
-
- 引入Tomcat依赖。
- 配置Tomcat
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId> <version>2.3.4.RELEASE</version> <scope>compile</scope> </dependency>
- 自动配好SpringMVC
-
- 引入SpringMVC全套组件
- 自动配好SpringMVC常用组件(功能)
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-web</artifactId> <version>5.2.9.RELEASE</version> <scope>compile</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId> <version>5.2.9.RELEASE</version> <scope>compile</scope> </dependency>
- 自动配好Web常见功能,如:字符编码问题
-
- ? ? SpringBoot帮我们配置好了所有web开发的常见场景
- 默认的包结构
-
- 主程序所在包及其下面的所有子包里面的组件都会被默认扫描进来
- 无需以前的包扫描配置
也可以自己配置包的扫描

- 各种配置拥有默认值
-
- 默认配置最终都是映射到某个类上,如:MultipartProperties
- 配置文件的值最终会绑定每个类上,这个类会在容器中创建对象
- 按需加载所有自动配置项
-
- 非常多的starter
- 引入了哪些场景这个场景的自动配置才会开启
- SpringBoot所有的自动配置功能都在 spring-boot-autoconfigure 包里面
2、容器功能
2.1组件添加
@Configuration
- 基本使用
- Full模式与Lite模式
-
- 示例
- 最佳实战
-
-
- 配置 类组件之间无依赖关系用Lite模式加速容器启动过程,减少判断
- 配置类组件之间有依赖关系,方法会被调用得到之前单实例组件,用Full模式
-
//1.配置类中使用@Bean标注在方法上给容器注册组件,默认也是单实例的
//2.配置类本身也是组件
// 3、proxyBeanMethods : 代型bean的方法
// FuLL( proxyBeanMethods = true).
// Lite( proxyBeanMethods = false)
// 组件依赖
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) //告诉SpringBoot这是一个配置类
public class MyConfig {
/**
* 外部无论对配置类这个组件注册方法调用多少次,获取的都是之前注册到组件中的单实例
* @return
*/
@Bean("zxn") //给容器添加注解,以方法名作为组件的id,返回类型就是组件类型
//返回的值就是组件在容器中保存的实例
public User user01(){
return new User("zxn",15,"男","北京市");
}
}
@SpringBootApplication
public class MainApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext run = SpringApplication.run(MainApplication.class, args);
String[] beanDefinitionNames = run.getBeanDefinitionNames();
//查看容器中的组件
for (String beanDefinitionName : beanDefinitionNames) {
System.out.println(beanDefinitionName);
}
//从容器中获取组件
User zxn1 = run.getBean("zxn", User.class);
User zxn2 = run.getBean("zxn", User.class);
System.out.println("是否为单实例:"+(zxn1==zxn2));
MyConfig bean = run.getBean(MyConfig.class);
System.out.println(bean);
//Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = true )代理对象调用方法。SringBoot总会检杳这个组件是否在容器中的单实例
User user1 = bean.user01();
User user2 = bean.user01();
System.out.println("是否为单实例:"+(user1==user2));
}
}
输出:
是否为单实例:true
com.javastudy.boot.config.MyConfig@2c30b71f
是否为单实例:false
当proxyBeanMethods = true时,为true
@Import
@Import({User.class, DBHelper.class})

4、@Conditional
条件装配:满足Conditional指定的条件,则进行组件注入

?当pet没有@Bean注解时,在user上面加上
@ConditionalOnBean(name = "tom")?此时容器中就不会注册user01组件
2.2、原生配置文件引入
1、@ImportResource
在任意一个类上加
@ImportResource("classpath:bean.xml")bean.xml文件里面的组件就会到容器里面
2.3、配置绑定
1、@Component + @ConfigurationProperties
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mycar")
public class Car {
private String brand;
private Integer price;
public String getBrand() {
return brand;
}
public void setBrand(String brand) {
this.brand = brand;
}
public Integer getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(Integer price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Car{" +
"brand='" + brand + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
}application.properties
mycar.brand=BYD
mycar.price=10000
@RestController
public class HelloContoller {
@Autowired
Car car;
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
return "hello,springboot";
}
@RequestMapping("/car")
public Car car(){
return car;
}
}
2、@EnableConfigurationProperties + @ConfigurationProperties
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false) //告诉SpringBoot这是一个配置类
@ImportResource("classpath:bean.xml")
@EnableConfigurationProperties(Car.class)
//1、开启car配置绑定功能
//2、把这个car这个组件自动注入到容器中
public class MyConfig {
/**
* 外部无论对配置类这个组件注册方法调用多少次,获取的都是之前注册到组件中的单实例
* @return
*/
@Bean("zxn")
@ConditionalOnBean(name = "tom")
//给容器添加注解,以方法名作为组件的id,返回类型就是组件类型
//返回的值就是组件在容器中保存的实例
public User user01(){
return new User("zxn",15,"男","北京市");
}
@Bean("tom")
public Pet pettom(){
return new Pet("xcl");
}
}@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mycar")
public class Car {
}二、自动配置原理入门
3.1、引导加载自动配置类
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })1、@SpringBootConfiguration
@Configuration代表是一个配置类
2、@ComponentScan
指定扫描哪些,Spring注解;
3、@EnableAutoConfiguration
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import(AutoConfigurationPackages.Registrar.class)//给容器导入组件
public @interface AutoConfigurationPackage {
}static class Registrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar, DeterminableImports {
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata metadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
register(registry, new PackageImports(metadata).getPackageNames().toArray(new String[0]));
}
@Override
public Set<Object> determineImports(AnnotationMetadata metadata) {
return Collections.singleton(new PackageImports(metadata));
}
}
//利用Registrar给容器中导入一系列组件 //将指定的一个包下的所有组件导入进来 @Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
protected AutoConfigurationEntry getAutoConfigurationEntry(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return EMPTY_ENTRY;
}
AnnotationAttributes attributes = getAttributes(annotationMetadata);
List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes);
configurations = removeDuplicates(configurations);
Set<String> exclusions = getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes);
checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions);
configurations.removeAll(exclusions);
configurations = getConfigurationClassFilter().filter(configurations);
fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions);
return new AutoConfigurationEntry(configurations, exclusions);
}1、利用getAutoConfigurationEntrv(annotationMetadata);给容器中批量导入一些组件
2.调用List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes);
获取需要导入到容器中的组件
3.利用工厂加载private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader),得到所有的组件
4.从META-INF / spring.factories位置来加载一个文件。
默认扫描我们当前系统里面所有META-INF / spring.factories位置的文件
spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.3.4.RELEASE.jar包里面也有META-INF/spring.factories

?
?3.2、按需开启自动配置项
1.虽然我们127个场景的所有自动配置启动的时候默认全部加载。xxxxAutoConfiguration
2.按照条件装配规则(@Conditional),最终会按需配置。
3.3、修改默认配置
3.4、最佳实践
1.引入场景依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.查看自动配置了哪些(选做)
- 自己分析,引入场景对应的自动配置一般都生效了
- 配置文件中debug=true开启自动配置报告。Negative(不生效)\Positive(生效)
4.自定义加入或者替换组件?
?@Bean、@Component。。。
4、开发小技巧
4.1、Lombok
引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
在setting-plugins中搜索添加

?使用

?@Data为get和set方法,@ToString为tostring方法,@NoArgsConstructor无参构造器
@AllArgsConstructor 全参构造器? @EqualsAndHashCode是equals()andhashcode()
@Slf4j注解日志功能
@Slf4j
@RestController
public class HelloContoller {
@Autowired
Car car;
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hello(){
log.info("请求进来");
return "hello,springboot";
}
@RequestMapping("/car")
public Car car(){
return car;
}
}

?4.2、dev-tools
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
项目或者页面修改以后:Ctrl+F9;
4.3、Spring Initailizr(项目初始化向导)

?
?创建即可完成
x、配置文件
1、文件类型
1.1、properties
同以前的properties用法
1.2、yaml
1.2.1、简介
YAML 是 "YAML Ain't Markup Language"(YAML 不是一种标记语言)的递归缩写。在开发的这种语言时,YAML 的意思其实是:"Yet Another Markup Language"(仍是一种标记语言)。
非常适合用来做以数据为中心的配置文件
1.2.2、基本语法
- key: value;kv之间有空格
- 大小写敏感
- 使用缩进表示层级关系
- 缩进不允许使用tab,只允许空格
- 缩进的空格数不重要,只要相同层级的元素左对齐即可
- '#'表示注释
- 字符串无需加引号,如果要加,''与""表示字符串内容 会被 转义/不转义
1.2.3、数据类型
例如:
person:
username: zhangsan
boss: true
birth: 2009/01/25
age: 15
# interests: [足球,篮球]
interests:
- 篮球
- 乒乓球
- 羽毛球
animal: [张选宁,薛程朗]
# score:
# english: 80
# chinese: 90
# math: 60
score: {english: 80,chinese: 90,math: 10}
salary :
- 899.98
- 1455.5
pet:
name: 阿龙
weight: 99.99
allPets:
sick:
- {name: zxn,weight: 156}
- {name: ljl,weight: 156}
health: [{name: ql,weight: 153},{name: cr,weight: 155}]
注意:
username: "zxn \n lise" 双引号效果:?
{"userName":"zxn \n lise",}
username:'zxn \n lise' 单引号效果:?
{"userName":"zxn \\n lise"}
单引号会将ln 作为字符串输出
双引号会将\n作为换行输出
双引号不会转义,单引号会转义
2、配置提示
自定义的类和配置文件绑定一般没有提示。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<excludes>
<exclude>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
</exclude>
</excludes>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>1、SpringMVC自动配置概览
Spring Boot provides auto-configuration for Spring MVC that works well with most applications.(大多场景我们都无需自定义配置)
The auto-configuration adds the following features on top of Spring’s defaults:
- Inclusion of
ContentNegotiatingViewResolverandBeanNameViewResolverbeans.
-
- 内容协商视图解析器和BeanName视图解析器
- Support for serving static resources, including support for WebJars (covered later in this document)).
-
- 静态资源(包括webjars)
- Automatic registration of
Converter,GenericConverter, andFormatterbeans.
-
- 自动注册
Converter,GenericConverter,Formatter
- 自动注册
- Support for
HttpMessageConverters(covered later in this document).
-
- 支持
HttpMessageConverters(后来我们配合内容协商理解原理)
- 支持
- Automatic registration of
MessageCodesResolver(covered later in this document).
-
- 自动注册
MessageCodesResolver(国际化用)
- 自动注册
- Static
index.htmlsupport.
-
- 静态index.html 页支持
- Custom
Faviconsupport (covered later in this document).
-
- 自定义
Favicon
- 自定义
- Automatic use of a
ConfigurableWebBindingInitializerbean (covered later in this document).
-
- 自动使用
ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer,(DataBinder负责将请求数据绑定到JavaBean上)
- 自动使用
2、简单功能分析
2.1、静态资源访问
1、静态资源目录
只要静态资源放在类路径下: called?/static?(or?/public?or?/resources?or?/META-INF/resource
访问 : 当前项目根路径/ + 静态资源名
原理: 静态映射/**。
请求进来,先去找Controller看能不能处理。不能处理的所有请求又都交给静态资源处理器。静态资源也找不到则响应404页面
2、静态资源访问前缀
默认无前缀
spring:
mvc:
static-path-pattern: /resources/**?当前项目+static-path-pattern+静态资源名
3、webjar
自动映射 /webjars/**
WebJars - Web Libraries in Jars
<dependency>
<groupId>org.webjars</groupId>
<artifactId>jquery</artifactId>
<version>3.5.1</version>
</dependency>
?/webjars/jquery/3.5.1/jquery.js
2.2、欢迎页支持
- 静态资源路径下 index.html
-
- 可以配置静态资源路径
- 但是不可以配置静态资源的访问前缀。否则导致 index.html不能被默认访问
- controller能处理/index
2.3、自定义 Favicon
favicon.ico 放在静态资源目录下即可
记得要关闭static-path-pattern

2.4、静态资源配置原理
- SpringBoot启动默认加载 xxxAutoConfiguration 类(自动配置类)
- SpringMVC功能的自动配置类 WebMvcAutoConfiguration,生效
3、请求参数处理
0、请求映射
1、rest使用与原理
- @xxxMapping;
- Rest风格支持(使用HTTP请求方式动词来表示对资源的操作)
-
- 以前:/getUser ? 获取用户? /deleteUser 删除用户 ? /editUser ?修改用户 ? /saveUser 保存用户
- 现在: /user GET-获取用户 DELETE-删除用户 PUT-修改用户 POST-保存用户
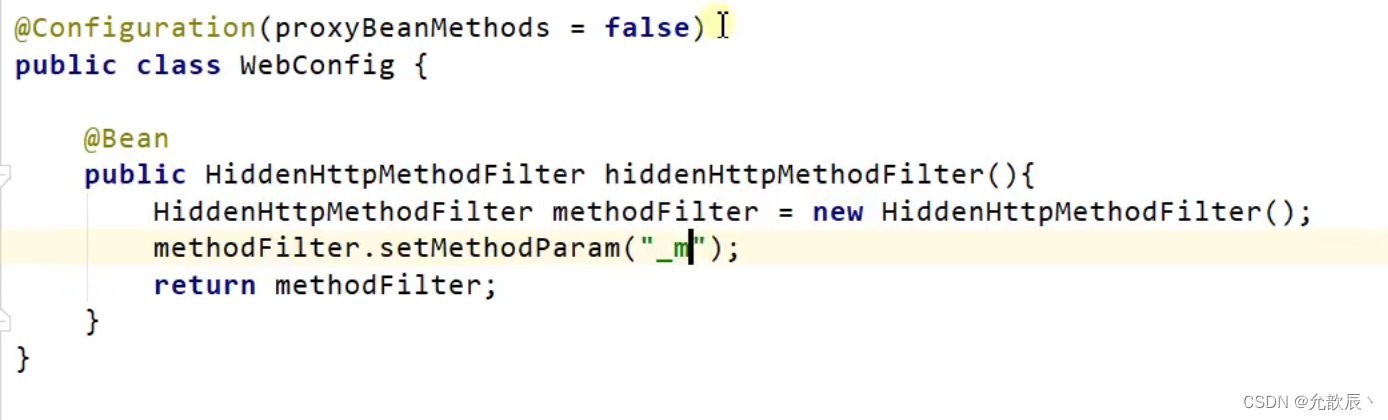
- 核心Filter;HiddenHttpMethodFilter
-
-
- 用法: 表单method=post,隐藏域 _method=put
- SpringBoot中手动开启
-
-
- 扩展:如何把_method 这个名字换成我们自己喜欢的。
Rest原理(表单提交要使用REST的时候)
●表单提交会带上_method=PUT
●请求过来被HiddenHttpMethodFilter拦截
○请求是否正常,并且是POST
■获取到_method的值。
■兼容以下请求;PUT.DELETE.PATCH
■原生request(post),包装模式requesWrapper重写了getMethod方法,返回的是传入的值。
■过滤器链放行的时候用wrapper。以后的方法调用getMethod是调用requesWrapper的。
Rest使用客户端工具,
●如PostMan直接发送Put、delete等方式请求,无需Filter。
spring:
mvc:
hiddenmethod:
filter:
enabled: true<form action="/user" method="get">
<input type="submit" value="GET-张三"/>
</form><br/>
<form action="/user" method="post">
<input type="submit" value="POST-张三"/>
</form><br/>
<form action="/user" method="post">
<input type="hidden" name="_method" value="put">
<input type="submit" value="PUT-张三"/>
</form><br/>
<form action="/user" method="post">
<input type="hidden" name="_method" value="delete">
<input type="submit" value="DELETE-张三"/>
</form><br/> @RequestMapping(value = "/user",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String getUser(){
return "GET-张三";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/user",method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String saveUser(){
return "POST-张三";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/user",method = RequestMethod.PUT)
public String putUser(){
return "PUT-张三";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/user",method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
public String deleteUser(){
return "DELETE-张三";
}
自定义? _method
?
?2、请求映射原理
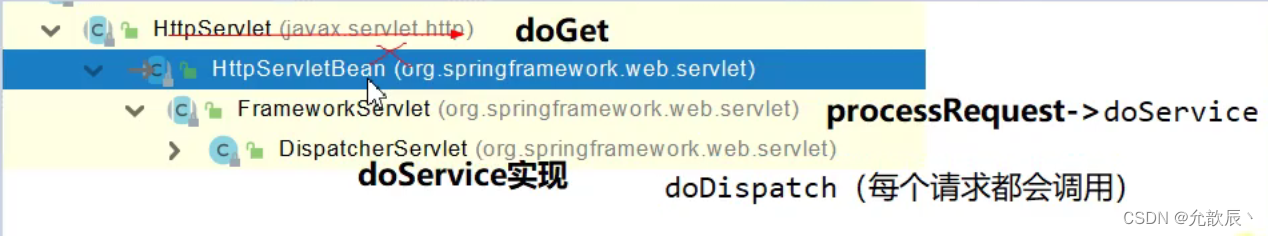
?SpringMVC功能分析都从 org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet--->doDispatch()
1、普通参数与基本注解
1.1、注解
@PathVariable、@RequestHeader、@ModelAttribute、@RequestParam、@MatrixVariable、@CookieValue、@RequestBody
@RestController
public class ParameterController {
@GetMapping("/car/{id}/owner/{name}")
public Map<String,Object> car(@PathVariable("id") Integer id, @PathVariable("name") String name,
@PathVariable Map<String,String> parameter,
@RequestHeader("User-Agent") String agent,
@RequestHeader Map<String,String> header,
@RequestParam("age") Integer age,
@RequestParam("hobby")List<String> hobby,
@RequestParam Map<String,String> param,
@CookieValue("Idea-1c60499a") String cookie){
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("id",id);
map.put("name",name);
map.put("map",parameter);
map.put("User-Agent",agent);
map.put("header",header);
map.put("age",age);
map.put("hobby",hobby);
map.put("param",param);
map.put("cookie",cookie);
return map;
}
}
@RequestBody
@PostMapping("/save")
public Map<String,Object> postMethod(@RequestBody String content){
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("content",content);
return map;
}<form action="/save" method="post">
username:<input type="text" name="username"/><br/>
password:<input type="password" name="password"/><br/>
<input type="submit" value="提交"/>
</form>![]()
?@RequestAttribute
@Controller
public class RequestController {
@RequestMapping("/request")
public String get(Model model){
model.addAttribute("name","张选宁");
model.addAttribute("age",15);
model.addAttribute("sex","男");
return "forward:/success";
}
@RequestMapping("/success")
@ResponseBody
public Map<String,Object> success(@RequestAttribute("name") String name,
@RequestAttribute("age") Integer age,
HttpServletRequest request){
Object sex = request.getAttribute("sex");
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("name",name);
map.put("age",age);
map.put("sex",sex);
return map;
}
}
注意:请求转发使用的是一个request,地址也不会发生改变
矩阵变量
/cars/{path}?XXX=xxx&aaa=ccc querystring查询字符串。------->@RequestParam; /cars/{path; low=34;brand=byd ,audi,yd};? 矩阵变量
或者/cars/sell; low=34 ; brand=byd; brand=audi;brand=yd
首先需要开启矩阵变量
@Configuration
public class MyConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void configurePathMatch(PathMatchConfigurer configurer) {
UrlPathHelper urlPathHelper = new UrlPathHelper();
//不移除;后面的内容。矩阵变量功能就可以生效
urlPathHelper.setRemoveSemicolonContent(false);
configurer.setUrlPathHelper(urlPathHelper);
}
}
<a href="/car/sell;low=34;brand=byd;brand=audi;brand=yd">测试</a>
// /cars/sell; low=34 ; brand=byd; brand=audi;brand=yd
//SpringBoot默认禁用了矩阵变量的功能
//需要手动开启
@RequestMapping("/car/{path}")
public Map<String,Object> carSell(@MatrixVariable("low") Integer low,@MatrixVariable("brand")List<String> brand,
@PathVariable("path") String path){
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("low",low);
map.put("brand",brand);
map.put("path",path);
return map;
}
}
?
1.2、Servlet API:
WebRequest、ServletRequest、MultipartRequest、 HttpSession、javax.servlet.http.PushBuilder、Principal、InputStream、Reader、HttpMethod、Locale、TimeZone、ZoneId
1.3、复杂参数:
Map、Model(map、model里面的数据会被放在request的请求域 request.setAttribute)、Errors/BindingResult、RedirectAttributes( 重定向携带数据)、ServletResponse(response)、SessionStatus、UriComponentsBuilder、ServletUriComponentsBuilder
4、数据响应与内容协商
1.1、jackson.jar+@ResponseBody
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
里面含有
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-json</artifactId>
<version>2.7.4</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>给前端自动返回json数据;
1.2、SpringMVC到底支持哪些返回值
ModelAndView
Model
View
ResponseEntity
ResponseBodyEmitter
StreamingResponseBody
HttpEntity
HttpHeaders
Callable
DeferredResult
ListenableFuture
CompletionStage
WebAsyncTask
1.3、HTTPMessageConverter原理?
2、内容协商
1.引入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-dataformat-xml</artifactId>
</dependency>
2、postman分别测试返回json和xml
只需要改变请求头中Accept字段。Http协议中规定的,告诉服务器本客户端可以接收的数据类型


5、视图解析与模板引擎
视图解析:SpringBoot默认不支持 JSP,需要引入第三方模板引擎技术实现页面渲染。
1、视图解析
2、模板引擎-Thymeleaf
1、thymeleaf简介
Thymeleaf is a modern server-side Java template engine for both web and standalone environments, capable of processing HTML, XML, JavaScript, CSS and even plain text.
2、基本语法
1、表达式

3、thymeleaf使用
1、引入Starter
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf</artifactId>
</dependency>自动配好的策略
- 1、所有thymeleaf的配置值都在 ThymeleafProperties
- 2、配置好了 SpringTemplateEngine
- 3、配好了 ThymeleafViewResolver
- 4、我们只需要直接开发页面
默认的前缀和后缀
??? public static final String DEFAULT_PREFIX = "classpath:/templates/";
?? ?public static final String DEFAULT_SUFFIX = ".html";? //xxx.html
6、拦截器
1、HandlerInterceptor 接口
/**
* 登录检查
* 1.配置好拦截哪些请求
* 2.把这些配置放在容器中
* @author Chooker
* @create 2022-10-25 17:36
*/
public class LoginInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor {
@Override //目标方法完成之前
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
//登录检查逻辑
HttpSession session = request.getSession();
Object loginUser = session.getAttribute("loginUser");
if(loginUser!=null)
return true;
else {
//未登录,重定向跳转到登录页面
request.setAttribute("msg","未登录");
request.getRequestDispatcher("/").forward(request,response);
return false;
}
}
@Override //目标方法完成之后
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
HandlerInterceptor.super.postHandle(request, response, handler, modelAndView);
}
@Override //页面渲染之后
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
HandlerInterceptor.super.afterCompletion(request, response, handler, ex);
}
}
2、配置拦截器?
@Configuration
public class AdminWebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(new LoginInterceptor()).addPathPatterns("/**").//所有请求包括静态资源
excludePathPatterns("/","/login","/css/**","/fonts/**","/images/**","/js/**");
}
}
3、拦截器原理
1、根据当前请求,找到HandlerExecutionChain【可以处理请求的handler以及handler的所有 拦截器】
2、先来顺序执行 所有拦截器的 preHandle方法
- 1、如果当前拦截器prehandler返回为true。则执行下一个拦截器的preHandle
- 2、如果当前拦截器返回为false。直接 倒序执行所有已经执行了的拦截器的 afterCompletion;
3、如果任何一个拦截器返回false。直接跳出不执行目标方法
4、所有拦截器都返回True。执行目标方法
5、倒序执行所有拦截器的postHandle方法。
6、前面的步骤有任何异常都会直接倒序触发 afterCompletion
7、页面成功渲染完成以后,也会倒序触发 afterCompletion
7、文件上传
1、页面表单
<form role="form" th:action="@{/upload}" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleInputEmail1">邮箱</label>
<input type="email" name="email" class="form-control" id="exampleInputEmail1" placeholder="Enter email">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleInputPassword1">名字</label>
<input type="text" name="username" class="form-control" id="exampleInputPassword1" placeholder="Password">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleInputFile">头像</label>
<input type="file" name="headerImg" id="exampleInputFile">
</div>
<div class="form-group">
<label for="exampleInputFile">生活照</label>
<input type="file" name="photos" multiple>
</div>
<div class="checkbox">
<label>
<input type="checkbox"> Check me out
</label>
</div>
<button type="submit" class="btn btn-primary">提交</button>
</form>2、文件上传代码
@GetMapping("/form_layouts")
public String form_layouts(){
return "/form/form_layouts";
}
@PostMapping("/upload")
public String upload(@RequestParam("email")String email,
@RequestParam("username")String username,
@RequestPart("headerImg") MultipartFile headImage,
@RequestPart("photos")MultipartFile[] photos) throws IOException {
log.info("上传的信息: email={},username={},headImage={},photos={}",
email,username,headImage.getSize(),photos.length);
if(!headImage.isEmpty()){
String fileName = headImage.getOriginalFilename();
headImage.transferTo(new File("D:\\photos\\"+fileName));
}
if(photos.length>0){
for (MultipartFile photo : photos) {
if(!photo.isEmpty()){
String fileName = photo.getOriginalFilename();
photo.transferTo(new File("D:\\photos\\"+fileName));
}
}
}
return "main";
}3.上传信息大小的改变
spring:
mvc:
hiddenmethod:
filter:
enabled: true
servlet:
multipart:
max-file-size: 10MB
max-request-size: 100MB8、异常处理
1、错误处理
1、默认规则
- 默认情况下,Spring Boot提供
/error处理所有错误的映射 - 对于机器客户端,它将生成JSON响应,其中包含错误,HTTP状态和异常消息的详细信息。对于浏览器客户端,响应一个“ whitelabel”错误视图,以HTML格式呈现相同的数据
浏览器
 postman
postman
?要对其进行自定义,添加View解析为erro


9、Web原生组件注入(Servlet、Filter、Listener)
1、使用Servlet API
//指定原生Servlet组件都放在哪里
@SpringBootApplication //默认扫描boot包下的所有
@ServletComponentScan
public class Boot05Web02Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Boot05Web02Application.class, args);
}
}?Servlet
//直接响应,没有经过Servlet的拦截器
@WebServlet(urlPatterns = "/my")
public class MyServlet extends HttpServlet {
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
resp.getWriter().write("66666666");
}
}Filter
@Slf4j
@WebFilter(urlPatterns = {"/css/*","/images/*"})
public class MyFilter implements Filter {
@Override
public void doFilter(ServletRequest servletRequest, ServletResponse servletResponse, FilterChain filterChain) throws IOException, ServletException {
log.info("filter起作用");
filterChain.doFilter(servletRequest,servletResponse);
}
@Override
public void init(FilterConfig filterConfig) throws ServletException {
log.info("Filter创建");
}
@Override
public void destroy() {
log.info("filter的销毁");
}
}
Listener
@Slf4j
@WebListener
public class MyListener implements ServletContextListener {
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent sce) {
log.info("监听到listenr的初始化");
}
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent sce) {
log.info("监听到listenr的销毁");
}
}
推荐使用这种方式
2、使用RegistrationBean
ServletRegistrationBean,?FilterRegistrationBean, and?ServletListenerRegistrationBean
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = true) //保证依赖的组件是单实例的
public class MyRegisterConfig {
@Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean myServlet(){
MyServlet myServlet = new MyServlet();
return new ServletRegistrationBean(myServlet,"/my","/my02");
}
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean myFilter(){
MyFilter myFilter = new MyFilter();
//拦截myServlet的路径
// return new FilterRegistrationBean(myFilter,myServlet());
FilterRegistrationBean filterRegistrationBean = new FilterRegistrationBean(myFilter);
filterRegistrationBean.setUrlPatterns(Arrays.asList("my","/css/*"));
return filterRegistrationBean;
}
@Bean
public ServletListenerRegistrationBean myListener(){
MyListener myListener = new MyListener();
return new ServletListenerRegistrationBean(myListener);
}
}10、嵌入式Servlet容器
1、切换嵌入式Servlet容器
- 默认支持的webServer
-
Tomcat,?Jetty, or?UndertowServletWebServerApplicationContext?容器启动寻找ServletWebServerFactory?并引导创建服务器
2、定制Servlet容器
- 实现 WebServerFactoryCustomizer<ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory>
-
- 把配置文件的值和
ServletWebServerFactory 进行绑定
- 把配置文件的值和
- 修改配置文件 server.xxx
- 直接自定义 ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory
xxxxxCustomizer:定制化器,可以改变xxxx的默认规则
import org.springframework.boot.web.server.WebServerFactoryCustomizer;
import org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.server.ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class CustomizationBean implements WebServerFactoryCustomizer<ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory> {
@Override
public void customize(ConfigurableServletWebServerFactory server) {
server.setPort(9000);
}
}?
?
11、定制化原理
1、定制化的常见方式
- 修改配置文件;
- xxxxxCustomizer;
- 编写自定义的配置类 xxxConfiguration;+ @Bean替换、增加容器中默认组件;视图解析器
- Web应用 编写一个配置类实现 WebMvcConfigurer 即可定制化web功能;+ @Bean给容器中再扩展一些组件
@Configuration
public class AdminWebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
registry.addInterceptor(new LoginInterceptor()).addPathPatterns("/**").//所有请求包括静态资源
excludePathPatterns("/","/login","/css/**","/fonts/**","/images/**","/js/**");
}
}
- @EnableWebMvc + WebMvcConfigurer —— @Bean 可以全面接管SpringMVC,所有规则全部自己重新配置; 实现定制和扩展功能
?
2、原理分析套路
场景starter - xxxxAutoConfiguration - 导入xxx组件 - 绑定xxxProperties -- 绑定配置文件项
?
06、数据访问
1、SQL
1、数据源的自动配置-HikariDataSource
1、导入JDBC场景
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
数据库驱动?
为什么导入JDBC场景,官方不导入驱动?官方不知道我们接下要操作什么数据库。
数据库版本和驱动版本对应
<!-- 数据库驱动-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
</dependency>
如果是mysql5版本的话:直接导入版本号,不需要springboot的版本仲裁
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.47</version>
</dependency>直接在properties改掉属性
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<mysql-version>5.1.49</mysql-version>
</properties>3、修改配置项
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/eesy_mybatis?characterEncoding=utf8&useUnicode=true&useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC
username: root
password: woaini520
type: com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource4、测试
@Slf4j
@SpringBootTest
class Boot05Web02ApplicationTests {
@Autowired
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
List<Map<String, Object>> maps = jdbcTemplate.queryForList("select * from user");
for (Map<String, Object> map : maps) {
System.out.println(map);
}
}
}
2、使用Druid数据源
1、druid官方github地址
https://github.com/alibaba/druid
整合第三方技术的两种方式
- 自定义
- 找starter
1.创建数据源
@Configuration
public class MyDataSourceConfig {
@Bean // 容器中没有DataSource才会自动配置Hikari
// @ConditionalOnMissingBean({ DataSource.class})
@ConfigurationProperties("spring.datasource")
public DataSource myDataSource(){
DruidDataSource druidDataSource = new DruidDataSource();
return druidDataSource;
}
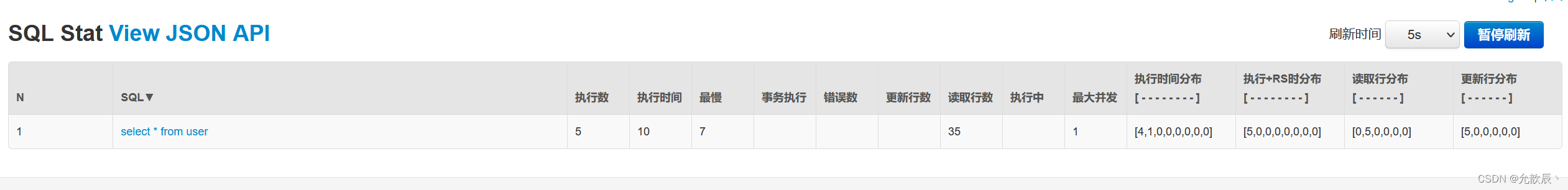
}2、StatViewServlet
StatViewServlet的用途包括:
- 提供监控信息展示的html页面
- 提供监控信息的JSON API
<servlet>
<servlet-name>DruidStatView</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>com.alibaba.druid.support.http.StatViewServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>DruidStatView</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/druid/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping> @Bean
public ServletRegistrationBean statViewServlet(){
StatViewServlet statViewServlet = new StatViewServlet();
ServletRegistrationBean<StatViewServlet> view = new ServletRegistrationBean<>(statViewServlet,"/druid/*");
return view;
} @Bean // 容器中没有DataSource才会自动配置Hikari
// @ConditionalOnMissingBean({ DataSource.class})
@ConfigurationProperties("spring.datasource")
public DataSource myDataSource() throws SQLException {
DruidDataSource druidDataSource = new DruidDataSource();
//加入监控功能
druidDataSource.setFilters("stat");
return druidDataSource;
}
?
?
3、StatFilter?
用于统计监控信息;如SQL监控、URI监控
@Bean
public FilterRegistrationBean webStatFilter(){
WebStatFilter webStatFilter = new WebStatFilter();
FilterRegistrationBean<WebStatFilter> webStatFilterFilterRegistrationBean = new FilterRegistrationBean<>(webStatFilter);
webStatFilterFilterRegistrationBean.setUrlPatterns(Arrays.asList("/*"));
webStatFilterFilterRegistrationBean.addInitParameter("exclusions","*.js,*.gif,*.jpg,*.png,*.css,*.ico,/druid/*");
return webStatFilterFilterRegistrationBean;
}?
3、使用官方starter方式
1、引入druid-starter
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.17</version>
</dependency>
2、配置示例
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db_account
username: root
password: 123456
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
druid:
aop-patterns: com.atguigu.admin.* #监控SpringBean
filters: stat,wall # 底层开启功能,stat(sql监控),wall(防火墙)
stat-view-servlet: # 配置监控页功能
enabled: true
login-username: admin
login-password: admin
resetEnable: false
web-stat-filter: # 监控web
enabled: true
urlPattern: /*
exclusions: '*.js,*.gif,*.jpg,*.png,*.css,*.ico,/druid/*'
filter:
stat: # 对上面filters里面的stat的详细配置
slow-sql-millis: 1000
logSlowSql: true
enabled: true
wall:
enabled: true
config:
drop-table-allow: false3、整合MyBatis操作
<!-- springboot整合mybatis-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.1.4</version>
</dependency>4、整合 MyBatis-Plus
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.5.2</version>
</dependency>
5、单元测试
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>