?下期开始更Mybatis啦~~~
目录
1.获取参数
本节内容接上期所讲的Spring MVC(上)
1.1获取cookie/header
我们前面讲过SpringMVC是基于Servlet的,所以,在MVC中,方法中的HttpServletRequest 与HttpServletResponse参数默认是隐藏的,如果想要使用,直接写上即可。所以,在这里我们的cookie和header都会有两种获取方式,一种是基于Servlet的,另一种是基于Spring本身的,下面我们来一一演示:
①cookie:
(1)servlet获取cookie的方法:
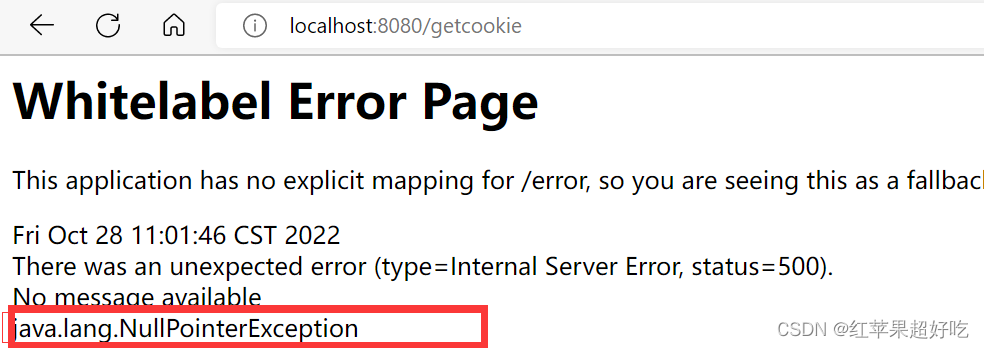
为了防止以下这种空指针异常的情况,我们手动地添加一项cookie
添加如下:
?代码:
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody; import javax.servlet.http.Cookie; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; @Slf4j @Controller @ResponseBody public class UserController6 { @RequestMapping("/getcookie") public void getCookie(HttpServletRequest req){ //得到全部的cookie Cookie[]cookies= req.getCookies(); for (Cookie a:cookies){ log.info("CookieKey:" + a.getName() + " CookieValue:" + a.getValue()); } }?输出结果:
同时我们可以通过抓包看到此时的cookie:
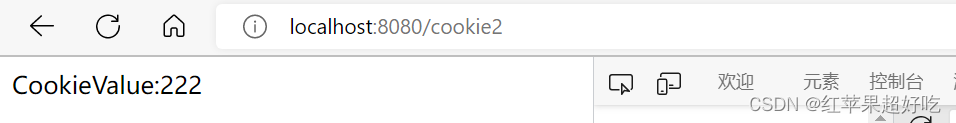
?(2)使用@CookieValue注解获取cookie的方法:
代码:
@RequestMapping("/cookie2") public String getCookie2(@CookieValue("111") String cookie) { return "CookieValue:" + cookie; }输出结果:
注意:对于第一种方法来说会把所有的cookies都给读出来,而第二种的话更有针对性的拿出某个cookie,具体用哪种根据我们自己的需求
②header:(我们这里以获取header中的UA为例)
(1)通过servlet来获取
代码如下:
@RequestMapping("/getheader") public String getHeader(HttpServletRequest request){ return "header"+request.getHeader("User-Agent"); }结果如下:
(2)通过@RequestHeader注解来获取
代码如下:
@RequestMapping("/getheader2") public String getHeader2(@RequestHeader("User-Agent")String UA){ return "header"+UA; }结果如下:
1.2存储并获取session
我们知道,在获取session之前需要先存入session,而在Spring MVC中存取session和在servlet阶段的存入是一致的。
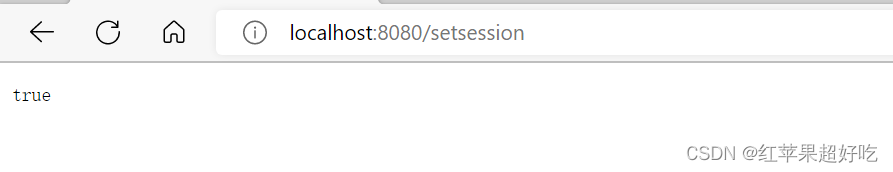
①存储session:
@RequestMapping("/setsession") public boolean setSession(HttpServletRequest req){ boolean result=false; //1.得到HTTPsession HttpSession session= req.getSession(true);//此处的true,如果有session就直接用,没有就进行创建 //2.使用setAtribute设置值 session.setAttribute("Student对象", "这是一个Student对象"); result=true; return result; }②获取session:
(注意!此处一定要先setSession,即访问设置会话,否则是不会返回的)
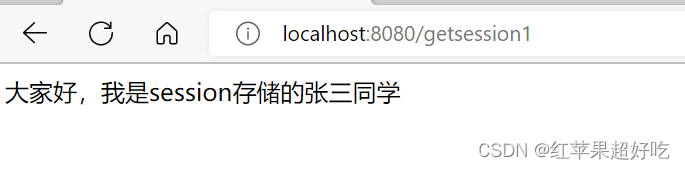
(1)存储session的代码:
@RequestMapping("/setsession") public boolean setSession(HttpServletRequest req){ boolean result=false; //1.得到HTTPsession HttpSession session= req.getSession(true);//此处的true,如果有session就直接用,没有就进行创建 //2.使用setAtribute设置值 session.setAttribute("name", "大家好,我是session存储的张三同学"); result=true; return result; }(2)用servlet来获取session:
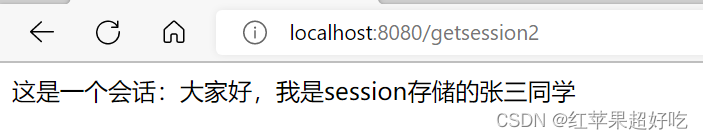
@RequestMapping("/getsession1") public String getSession(HttpServletRequest req){ String result=null; //1.得到HTTPSession对象 HttpSession session= req.getSession(false);//如果会话不为空就可以拿到,不新建一个会话 //2.利用getAtrribute得到会话信息 if ((session!=null)&&session.getAttribute("name")!=null){ result= (String)session.getAttribute("name"); } return result; }(3)用@RequestSession注解来获取session:
@RequestMapping("/getsession2") public String getSession2(@SessionAttribute(value = "name",required = false)String name){ return "这是一个会话:"+name; }结果如下:
设置会话:
?获取会话:
2.将结果返回给用户
前面的三部曲,我们已经进行了两步,下面将是最后的环节,即从服务器返回给客户端(用户)
2.1返回一个静态html文件
首先,我们先了解@ResponseBody这个注解的意思是返回一个非静止页面,也就是说,当我们不加这个注解的时候,服务器会去找我们返回的值是否存在一个页面,若不存在,就会出现以下情况报错:
代码:
package com.example.demo.test; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; @Controller public class UserController { @RequestMapping("/gettext") public String gettext(){ return "hello"; } }结果:
①创建一个html文件,来看是否能够读取到:
package com.example.demo.test; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; @Controller public class UserController { @RequestMapping("/gettext") public String gettext(){ return "test.html"; } }输出结果:
②此时如果想要返回一个数据,则需要使用注解@ResponseBody修饰对应的方法或者修饰类才能实现:
代码如下:
package com.example.demo.test; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody; @Controller @ResponseBody public class UserController { @RequestMapping("/gettext") public String gettext(){ return "test.html"; } }输出结果:?
③关于ResponseBody的一些说明:
(1)ResponseBody可以修饰类,表示当前类中的所有方法都会返回一个非静态页面的数据;当然其也可以修饰方法,修饰方法时表示当前方法返回的是一个非静态页面的数据。说白了,就是作用域的问题。
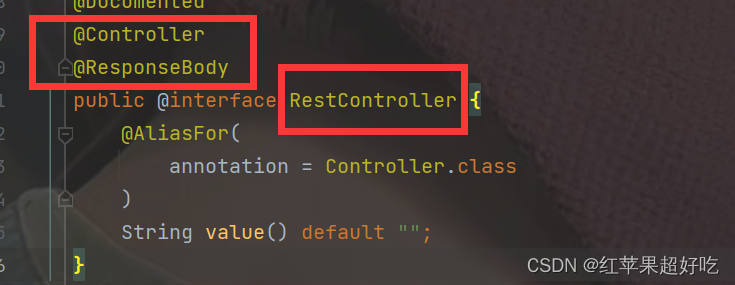
(2)@RestController是@ResponseBody和@Controller的集合,所以写这一个就表示了它们两个
2.2返回json对象
此处我们通过一个ajax来构造一个登陆页面的案例,来返回json对象。在开始之前,我们先说几点需要注意的地方
(1)不要忘了设置ajax对象参数中的contentType:"application/json;charset=utf8"
(2)将对象转换成json格式的字符串需要用到JSON.Stringify
①前端通过ajax来构造:
<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, user-scalable=no, initial-scale=1.0, maximum-scale=1.0, minimum-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <script src="https://apps.bdimg.com/libs/jquery/2.1.4/jquery.min.js"></script> <title>Document</title> <script> // ajax 提交 function mysub(){ // 1.判空 var username = jQuery("#username").val(); var password = jQuery("#password").val(); if(jQuery.trim(username)==""){ alert("请先输入用户名!"); username.focus(); // 光标重制到此元素 return; } if(jQuery.trim(password)==""){ alert("请先输入密码!"); password.focus(); // 光标重制到此元素 return; } jQuery.ajax({ url:"/test", type:"POST", contentType:"application/json", data:JSON.stringify({"username":name, "password":password}), success:function(result){ alert(JSON.stringify(result)); } }); } </script> </head> <body> <div style="text-align: center;"> <h1>登录</h1> 用户:<input id="username"> <br> 密码:<input id="password" type="password"> <br> <input type="button" value=" 提交 " onclick="mysub()" style="margin-top: 20px;margin-left: 50px;"> </div> </body> </html>②后端java代码:
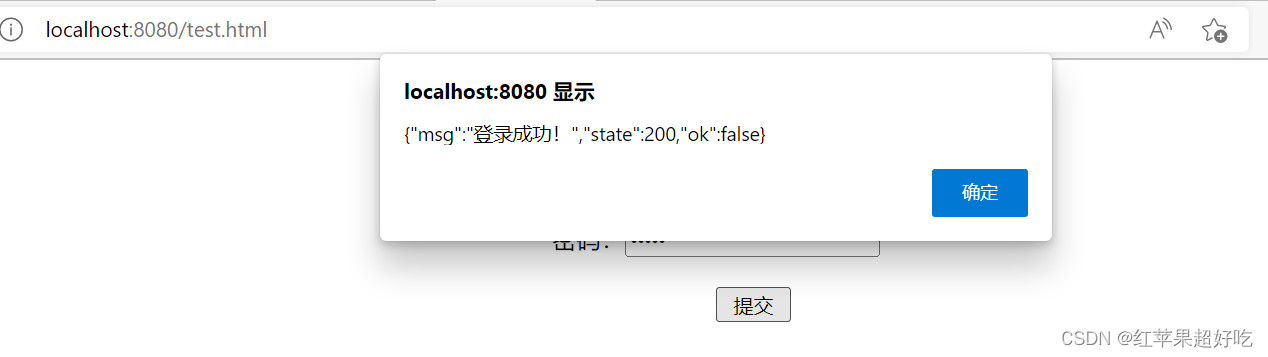
package com.example.demo.test; import org.apache.catalina.User; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.util.StringUtils; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*; import java.util.HashMap; @ResponseBody @Controller public class UserController1 { @RequestMapping("/test") public HashMap<String, Object> login(@RequestParam(value = "username", required = false) String name, String password) { HashMap<String, Object> res = new HashMap<>(); //假设用户只有admin,密码也是admin //状态码 int state = 200; //是否登录成功 boolean ok = false; //原因 String msg = "登录成功!"; //对密码进行验证 if (StringUtils.hasLength(name) && StringUtils.hasLength(password)) { //账号与密码均不为空 if (name.equals("admin") && password.equals("admin")) { //验证通过 ok = true; msg = "登录成功!"; } else { //账号或密码错误 msg = "账号或密码错误!"; } } res.put("state", state); res.put("ok", ok); res.put("msg", msg); //spring中返回map会自动转换成json格式 return res; } }输出结果:
?
2.3实现请求转发和重定向
在介绍请求转发和请求重定向之前,我们先举一个实例来区别一下这两个:
张三向李四借钱,李四说他没有钱了,让他找王五借钱,这种当前丢了,负责人就是张三的行为就是类似于请求重定向。而当张三向李四借钱,李四说自己没钱,然后李四去找王五借钱,最后把钱给张三,而要是这个时候,钱丢了,责任人就是李四,这种行为就是类似于请求转发。
①请求转发:
(1) 第一种方式:此时的forward:/是可以省略的:
@RequestMapping("/fw") public String fw(){ return "forward:/hello.html"; }输出结果:
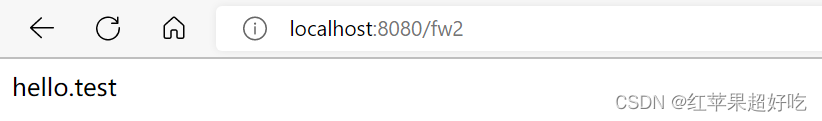
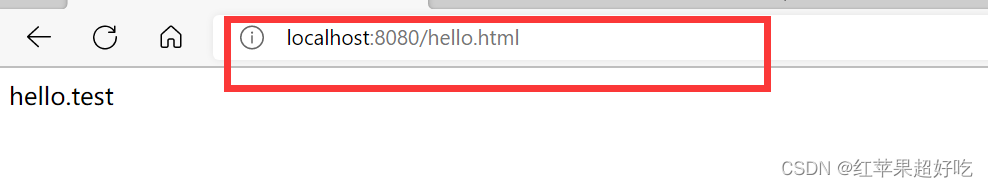
(2)第二种方式:使用request对象来进行跳转
@RequestMapping("/fw2") public void myForward2(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException, ServletException, IOException { req.getRequestDispatcher("hello.html").forward(req, resp); }输出结果:
②请求重定向:
(1) 将请求转发中的forward改为redirect:
代码如下:
@RequestMapping("/rd") public String rd(){ return "redirect:/hello.html"; }输出结果:(注意是跳转到了这个页面)
?(2)通过使用response对象来进行跳转:
代码如下:
@RequestMapping("/rd2") public void rd2(HttpServletResponse res) throws IOException { res.sendRedirect("hello.html"); }输出结果:
关于请求转发和重定向的五大不同可以参考下面这篇博客: