一、Spring Cache介绍
Spring Cache 是Spring - context-xxx.jar中提供的功能,可以结合EHCache,Redis等缓存工具使用。给用户提供非常方便的缓存处理,缓存基本判断等操作,可以直接使用注解实现。 ? 在包含了Spring - context-xxx.jar的Spring Boot项目中,在启动类中添加@EnableCaching注解,即可开启缓存功能。默认Spring Cache是不开启。
二、Spring Cache加载缓存工具顺序
只要检测到项目中配置了下面缓存工具(导入了依赖,在Spring容器中发现对应工具的内容),无论导入多少个缓存工具依赖,只用优先级最高的一个。 ? 默认寻找缓存工具的顺序:(为什么Redis配置上就可以用的原因)
-
Generic
-
JCache (JSR-107) (EhCache 3, Hazelcast, Infinispan, and others)
-
EhCache 2.x
-
Hazelcast
-
Infinispan
-
Couchbase
-
Redis
-
Caffeine
-
Simple
三、基于Spring Cache完成缓存管理
(1)导入依赖
<parent>
? ? <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
? ? <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
? ? <version>2.3.12.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<dependencies>
? ? <dependency>
? ? ? ? <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
? ? ? ? <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
? ? </dependency>
? ? <dependency>
? ? ? ? <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
? ? ? ? <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
? ? </dependency>
</dependencies>
(2)编写配置文件
spring:
? redis:
? ? host: 192.168.8.128
? ? port: 6379 # 默认值,可省略
(3)编写启动类
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableCaching
public class SpringCacheApplication {
? ? public static void main(String[] args) {
? ? ? ? SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class,args);
? ? }
}
四、使用
(1)Cacheable:查询缓存的注解
@Service
public class SpringCacheServiceImpl implements SpringCacheService {
/**
* 查询数据
* Cacheable - 查询缓存的注解。
* 固定流程:
* 1. 根据key访问缓存服务器,查询缓存数据。
* 2. 判断缓存查询结果
* 2.1 缓存查询有结果,直接返回。当前方法不执行
* 2.2 缓存查询无结果,进入后续流程。
* 3. 执行当前方法代码逻辑。
* 4. 代码返回值作为value,保存到缓存服务器中。
* 5. 返回方法的返回结果。
* 属性:
* 完整的缓存key是: cacheNames + "::" + key
* cacheNames - 缓存key的前缀,字符串类型。只能使用字符串字面值赋值。
* key - 缓存key的后缀。字符串类型。可以使用字符串字面值和SpringEL表达式赋值。
* 赋值的时候,如果是字符串的字面值,必须使用 '' 标记。
* @return
*/
@Override
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "test", key = "'getAll'")
public List<String> getAll() {
// 模拟数据库访问
System.out.println("开始访问数据库。。。。");
List<String> result = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++){
result.add("user-" + i);
}
System.out.println("数据库查询结束,查询结果是:" + result);
return result;
}
}/**
* 主键查询
* 缓存的key必须和方法参数的值相关。
*
* 使用SpringEL,访问方法的参数表。
* 访问方式有:
* #root.method.args[下标]
* #方法参数变量名
*
* 常见的key属性赋值方式是: 方法名称(参数值)
*/
@Override
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "test", key = "#root.methodName + '(' + #id + ')'")
public String getById(Long id) {
System.out.println("开始访问数据库....");
String result = "getById - " + id;
System.out.println("访问数据库结束,查询结果是:" + result);
return result;
}(2)CachePut:?保存数据到缓存服务器。
/**
* 新增
* 希望保存数据成功后,同时缓存到Redis中。
* 后续主键查询的时候,可以减少数据库查询次数。
*
* CachePut - 保存数据到缓存服务器。是针对新增和更新使用的缓存注解。
* 固定流程:
* 1. 执行当前方法。
* 2. 根据注解拼接key,把方法的返回值作为value,保存的缓存服务器。
* 3. 方法返回
* @return
*/
@Override
@CachePut(cacheNames = "test", key = "'getById(' + #id + ')'")
public String add(Long id, String name) {
// 完整的数据
String data = name + " - " + id;
// 保存到数据库
System.out.println("保存数据 【" + data + "】 到数据库");
?
return data;
}(3)CacheEvict:缓存淘汰。
/**
* 根据主键删除数据
* 当删除数据库数据成功后,也要删除缓存中的数据。避免查询的时候,基于缓存,
* 查询到脏数据。
*
* CacheEvict - 缓存淘汰。
* 固定流程:
* 1. 执行方法
* 2. 根据注解中的key,访问缓存服务器,删除键值对
* 3. 方法返回。
*
* 属性:
* allEntries - 布尔类型。是否删除cacheNames作为前缀的所有键值对。默认false。
* 谨慎使用。
*/
@Override
@CacheEvict(cacheNames = "test", key = "'getById(' + #id + ')'")
public String removeById(Long id) {
System.out.println("删除数据,主键是:" + id);
return "删除主键是" + id + "数据";
}(4)CachConfig:公共前缀,使用在类上
@CachConfig(cacheNames = "test")
五、condition和unless属性
(1) condition
condition是普通条件。如果条件成立则进行缓存。此判断为进入到方法体之前的判断,所以#result不允许用在这里。如果在condition中出现#result会导致条件恒不成立,不进行缓存。
@Override
@Cacheable(/*cacheNames = "test", */key = "#root.methodName + '(' + #id + ')'",
condition = "#id >= 10"
)
public String getById(Long id) {
System.out.println("开始访问数据库....");
String result = "getById - " + id;
System.out.println("访问数据库结束,查询结果是:" + result);
return result;
}(2)unless
unless是方法执行完成后的条件,当符合条件不被缓存。注意:#result只能写在这个属性中。多用在返回结果为null时不缓存效果。
@Override
@Cacheable(/*cacheNames = "test", */key = "#root.methodName + '(' + #id + ')'",
unless = "#id >= 10"
)
public String getById(Long id) {
System.out.println("开始访问数据库....");
String result = "getById - " + id;
System.out.println("访问数据库结束,查询结果是:" + result);
return result;
}(3)SpringEL中的常见变量
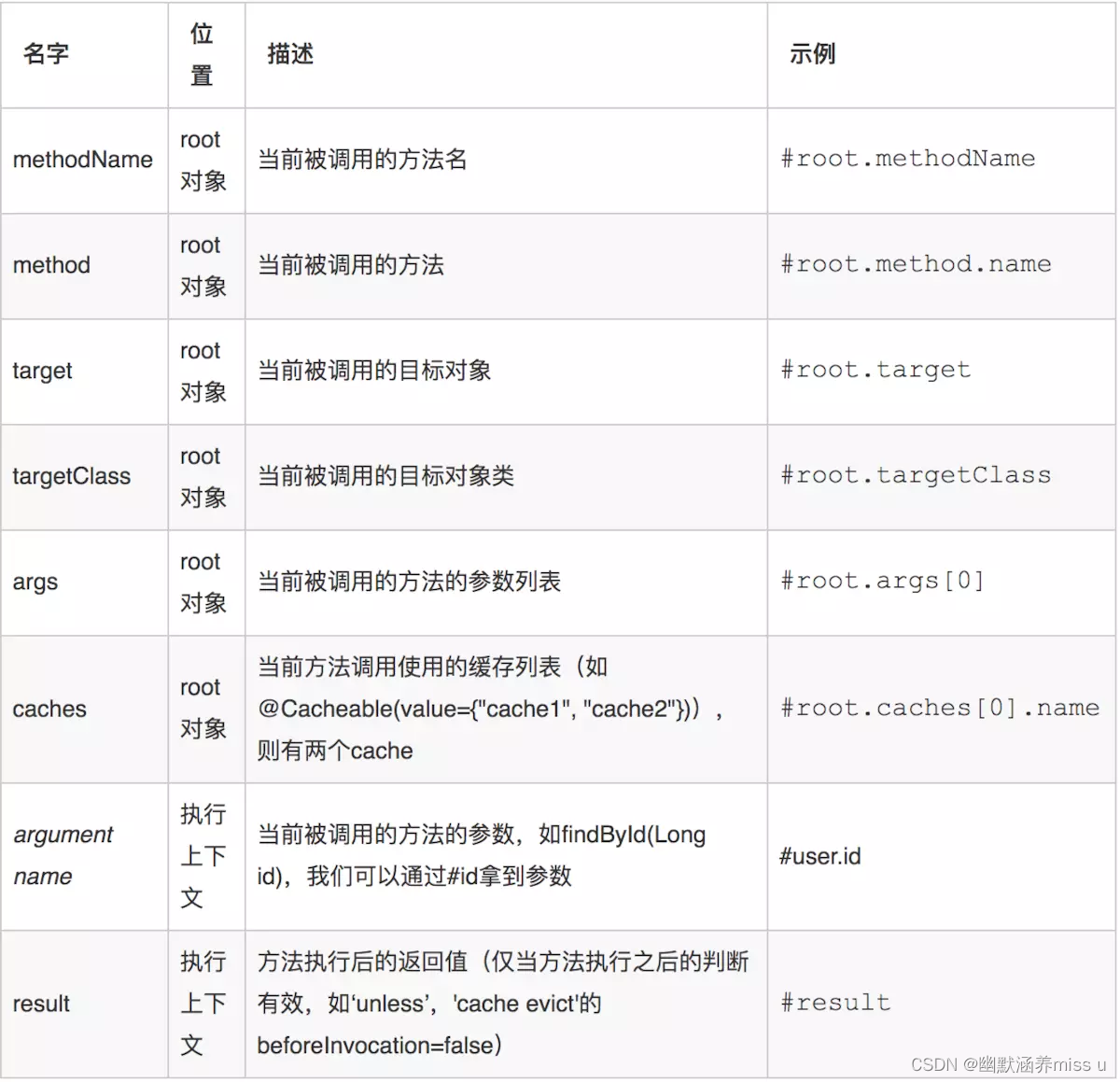
?六、Spring Cache缓存管理器配置
@Configuration
public class MySpringCacheConfiguration {
/**
* 创建一个CacheManager,缓存管理器。
* 实现缓存的访问配置管理。
* 如:缓存有效期。键值对的序列化方式等。
* 在SpringCache技术中,要求,一个Spring容器上下文只有唯一的CacheManager对象。
*
* RedisCacheManager - Redis缓存服务器的管理工具。
*/
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory factory){
// 创建默认的缓存配置管理。
RedisCacheConfiguration configuration =
RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig();
// 配置,可以提供缓存有效期和键值对序列化器等。
// RedisCacheConfiguration设计比较特殊。每个配置的修改,都会创建一个新的RedisCacheConfiguration对象并返回。
configuration =
configuration
.serializeKeysWith(
RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(
new StringRedisSerializer()
)
) // 设置key的序列化工具
.serializeValuesWith(
RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(
new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer()
)
) // 设置value的序列化工具
.entryTtl(Duration.ofMinutes(30L)) // 设置所有键值对的有效期
.disableCachingNullValues() ; // 是否忽略value为null的数据缓存保存过程。
// 使用构建器,默认构建的管理器,是默认配置逻辑。
// 永久保存数据,key是字符串序列化工具。value是JDKSerializable序列化工具
// 可以提供自定义的配置逻辑。 RedisCacheConfiguration
RedisCacheManager redisCacheManager =
RedisCacheManager
.builder() // 构建器。用于构建RedisCacheManager的工具。必须提供连接工厂
.cacheWriter( // 提供连接工厂
RedisCacheWriter.lockingRedisCacheWriter(factory)
)
.cacheDefaults(configuration) // 基于提供的配置,创建管理器。
.build();
return redisCacheManager;
}
}