前言
- 此文章接前面笔记内容,主要内容是vue-cli、vue-router
- 前面笔记
七?、Vue CLI详解
(一)、Vue CLI
1.什么是Vue CLI
- 如果你只是简单写几个Vue的Demo程序, 那么你不需要Vue CLI.
- 如果你在开发大型项目, 那么你需要, 并且必然需要使用Vue CLI
- 使用Vue.js开发大型应用时,我们需要考虑代码目录结构、项目结构和部署、热加载、代码单元测试等事情。
- 如果每个项目都要手动完成这些工作,那无疑效率比较低效,所以通常我们会使用一些脚手架工具来帮助完成这些事情。
- CLI是什么意思?
- CLI是Command-Line Interface, 翻译为命令行界面, 但是俗称脚手架.
- Vue CLI是一个官方发布 vue.js 项目脚手架
- 使用 vue-cli 可以快速搭建Vue开发环境以及对应的webpack配置.?
- 脚手架长什么样子?

2.Vue CLI使用前提 - Node
-
安装NodeJS
-
可以直接在官方网站中下载安装.
-
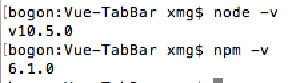
- 检测安装的版本
- 默认情况下自动安装Node和NPM
- Node环境要求8.9以上或者更高版本
- 什么是NPM呢?
- NPM的全称是Node Package Manager
- 是一个NodeJS包管理和分发工具,已经成为了非官方的发布Node模块(包)的标准。
- 后续我们会经常使用NPM来安装一些开发过程中依赖包.?
- cnpm安装
- 由于国内直接使用 npm 的官方镜像是非常慢的,这里推荐使用淘宝 NPM 镜像。
- 你可以使用淘宝定制的 cnpm (gzip 压缩支持) 命令行工具代替默认的 npm:
-
npm install -g cnpm --registry=https://registry.npm.taobao.org -
这样就可以使用 cnpm 命令来安装模块了:
cnpm install [name]
3.Vue CLI使用前提 - Webpack
-
Vue.js官方脚手架工具就使用了webpack模板
-
对所有的资源会压缩等优化操作
-
它在开发过程中提供了一套完整的功能,能够使得我们开发过程中变得高效。
-
- Webpack的全局安装?
npm install webpack -g
4.Vue CLI的使用
-
安装Vue脚手架
-
npm install -g @vue/cli
-
- 注意:上面安装的是Vue CLI3的版本,如果需要想按照Vue CLI2的方式初始化项目时不可以的。
?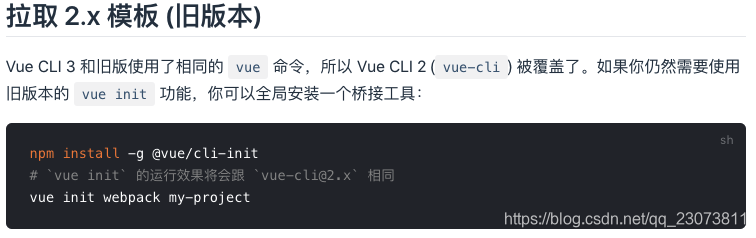
- ?Vue CLI2初始化项目
vue init webpack my-project
- Vue CLI3初始化项目
vue create my-project(二)、Vue CLI2
?1.(掌握)Vue CLI2详解--Vue CLI初始化项目过程

?2.(理解)目录结构详解
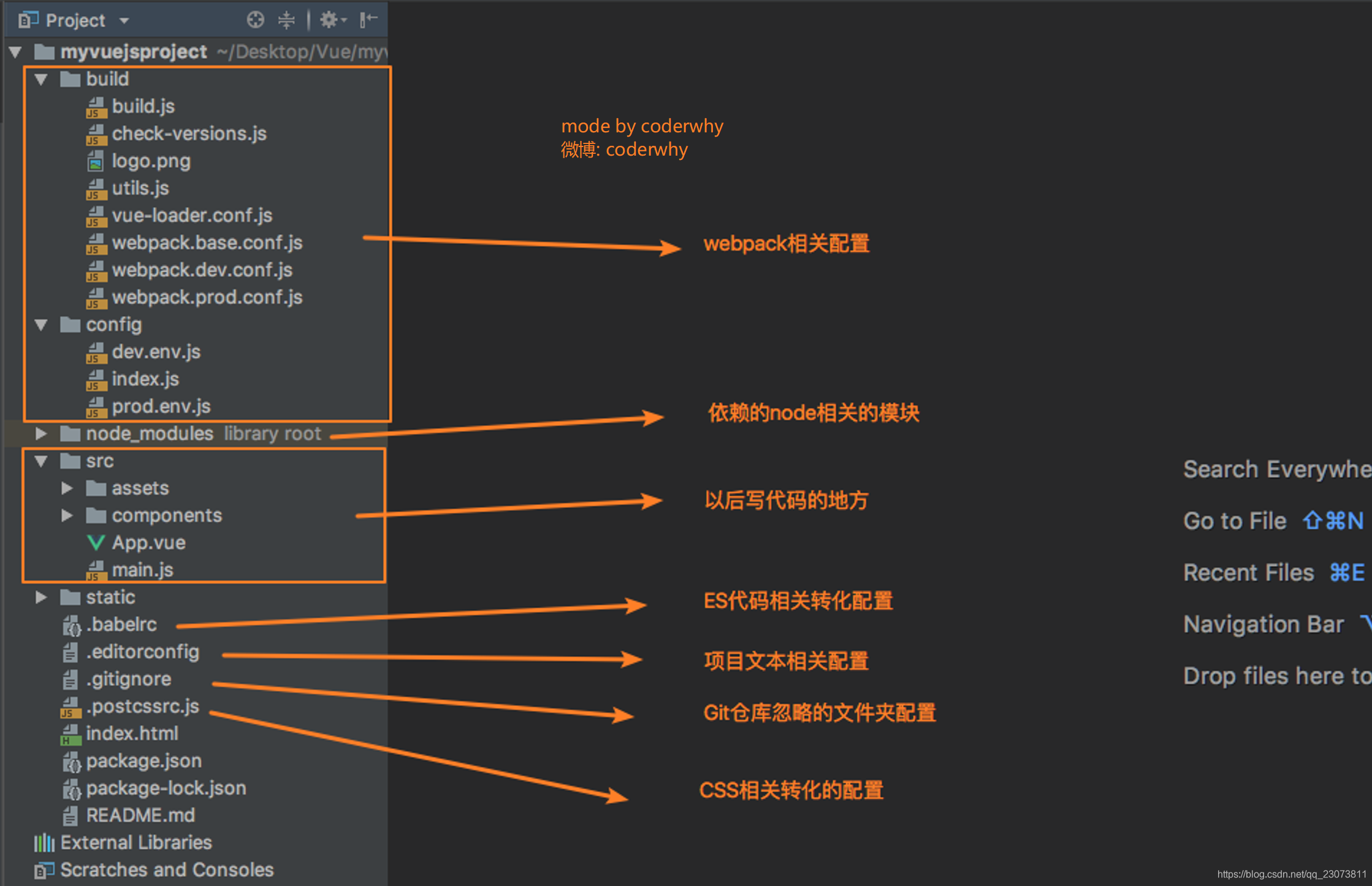
3.(理解)Runtime-Compiler和Runtime-only的区别

- 简单总结
- 如果在之后的开发中,你依然使用template,就需要选择Runtime-Compiler
- 如果你之后的开发中,使用的是.vue文件夹开发,那么可以选择Runtime-only?
4.render和template
- Runtime-Compiler 和 Runtime-only

- 为什么存在这样的差异呢?
- 我们需要先理解Vue应用程序是如何运行起来的。
- Vue中的模板如何最终渲染成真实DOM。
- 我们来看下面的一幅图。?
5.Vue程序运行过程
?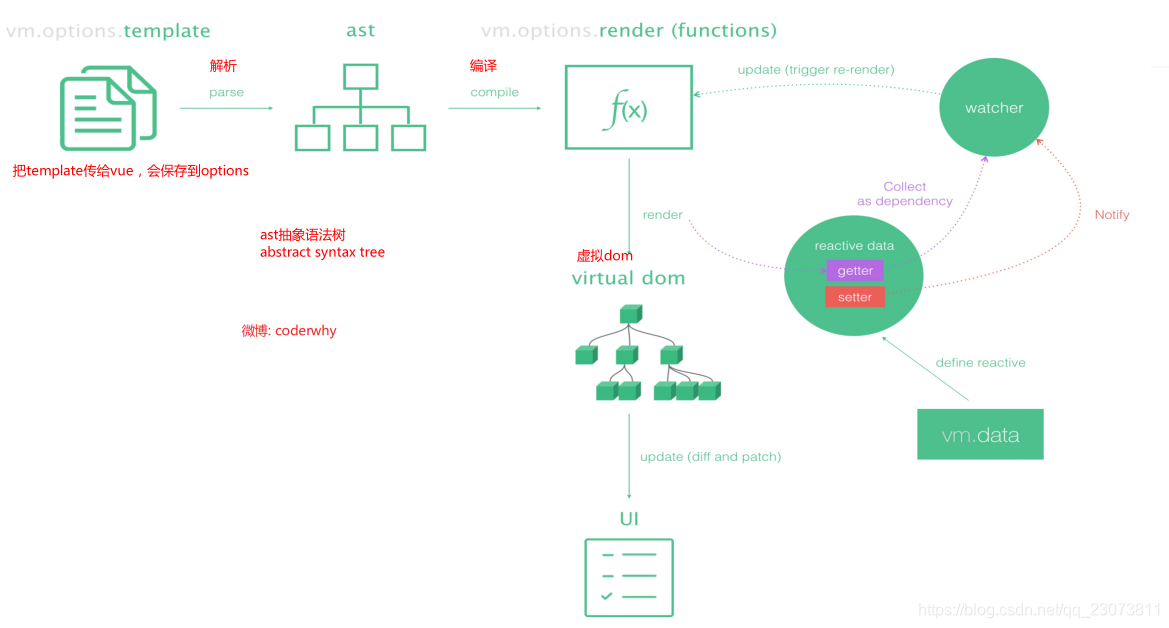
- ?总结
-
Runtime-Compiler:
-
template?->?ast?->?render?->?vdom?->?真实DOM
-
-
Runtime-only:(1.性能更高?2.下面的代码量更少)
-
render?->?vdom?->?UI
-
6.render函数的使用
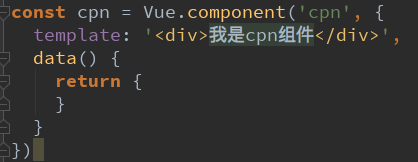

?main.js代码:
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App'
Vue.config.productionTip = false // 消息提示的环境配置,设置为开发环境或者生产环境
/* eslint-disable no-new */
/*
// runtime-compiler
new Vue({
el: '#app',
components: { App },
template: '<App/>',
})
*/
// const cpn = { // 组件
// template: '<div>{{message}}</div>',
// data() {
// return {
// message: '我是组件message'
// }
// }
// }
// 也可以用下面这个方案 runtime-only
new Vue({
el: '#app',
render: function (createElement) { // createElement是一个函数
// 1.使用方式一: createElement('标签', {标签的属性}, ['内容'])
// 1.1 基本使用
// return createElement('h2', {
// class: 'box'
// },
// ['Hello World'])
// 1.2 嵌套render函数
// return createElement('h2', {
// class: 'box'
// },
// ['Hello World', createElement('button', ['按钮'])])
// 2.传入组件对象:
// return createElement(cpn)
return createElement(App)
}
})
// runtime-compiler(v1)
// template -> ast -> render -> vdom -> UI
// runtime-only(v2)(1.性能更高 2.下面的代码量更少)
// render -> vdom -> UI
-
那么.vue文件中的template是由谁处理的了?
-
是由vue-template-compiler
-
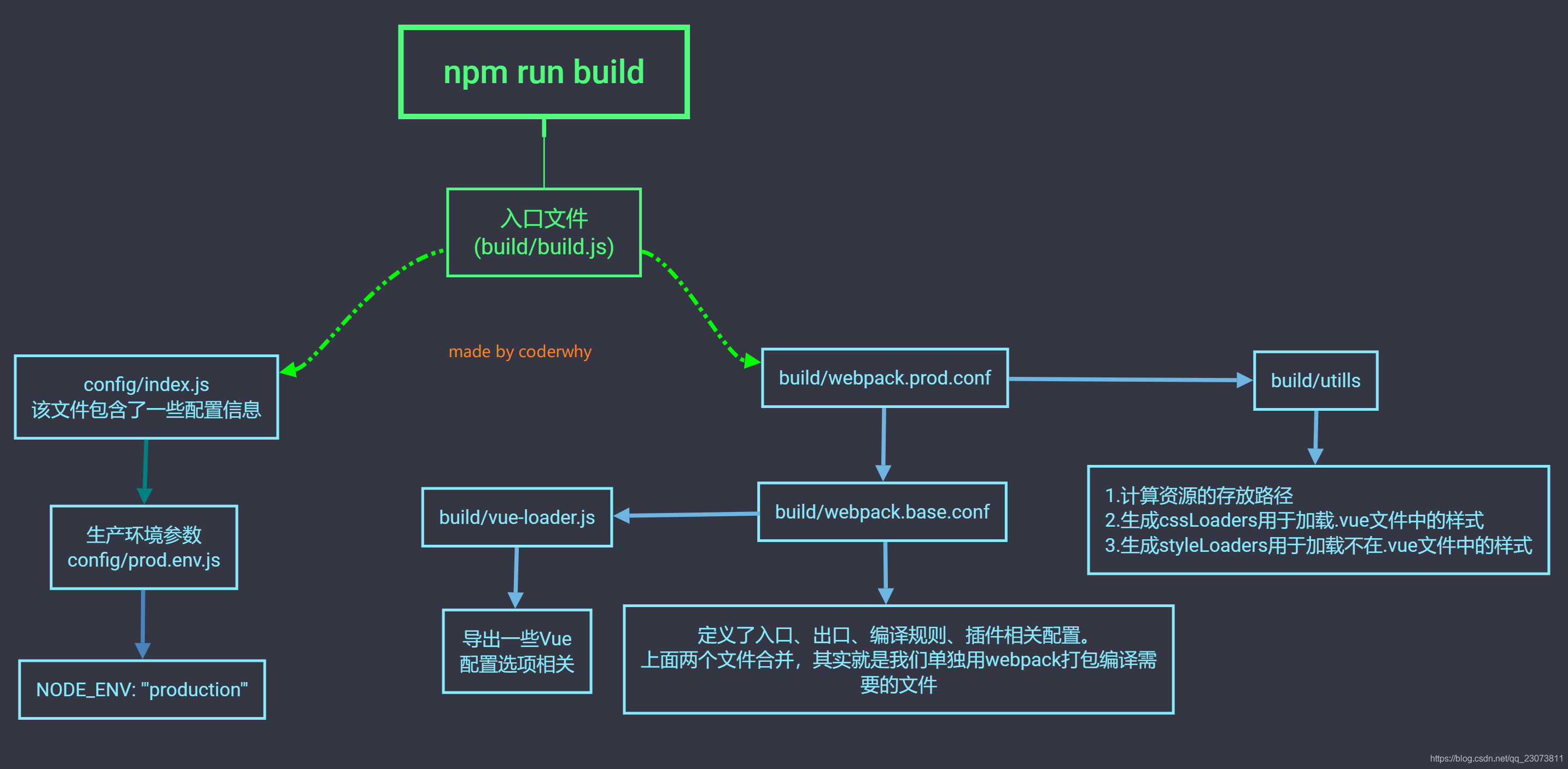
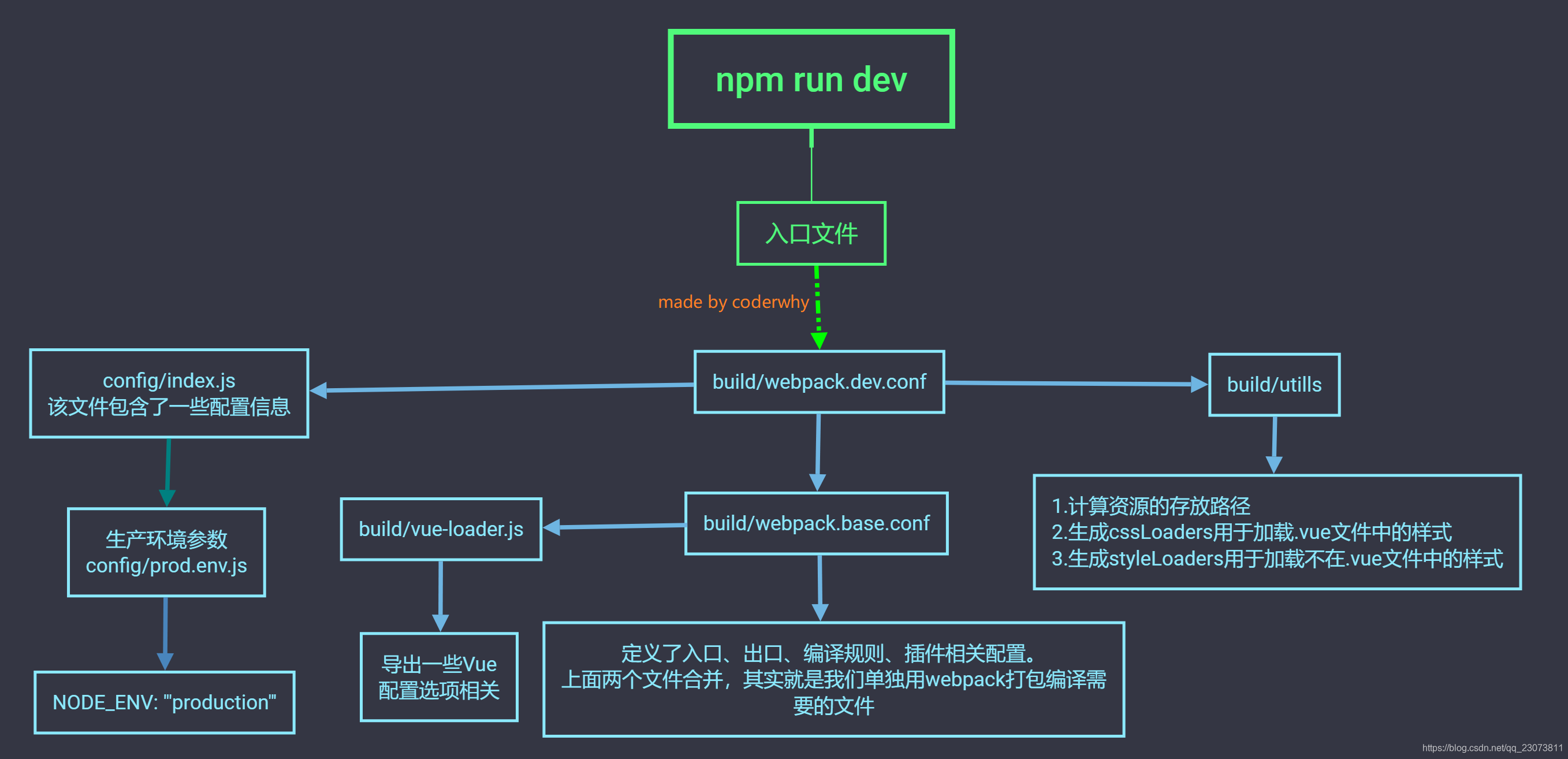
7.npm run build
8.npm run dev?
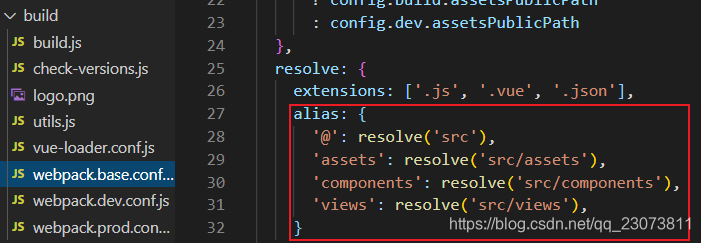
?9.修改配置:webpack.base.conf.js起别名

(三)、Vue CLI3
1.认识Vue CLI3
-
vue-cli 3 与 2 版本有很大区别
-
vue-cli 3 是基于 webpack 4 打造,vue-cli 2 还是 webapck 3
-
vue-cli 3 的设计原则是“0配置”,移除的配置文件根目录下的,build和config等目录
-
vue-cli 3 提供了 vue ui 命令,提供了可视化配置,更加人性化
-
移除了static文件夹,新增了public文件夹,并且index.html移动到public中?
-
?2.Vue CLI3

3.目录结构详解
?4.配置去哪里了?
- UI方面的配置
- 启动配置服务器:vue ui
- 一大堆配置文件去哪里了?
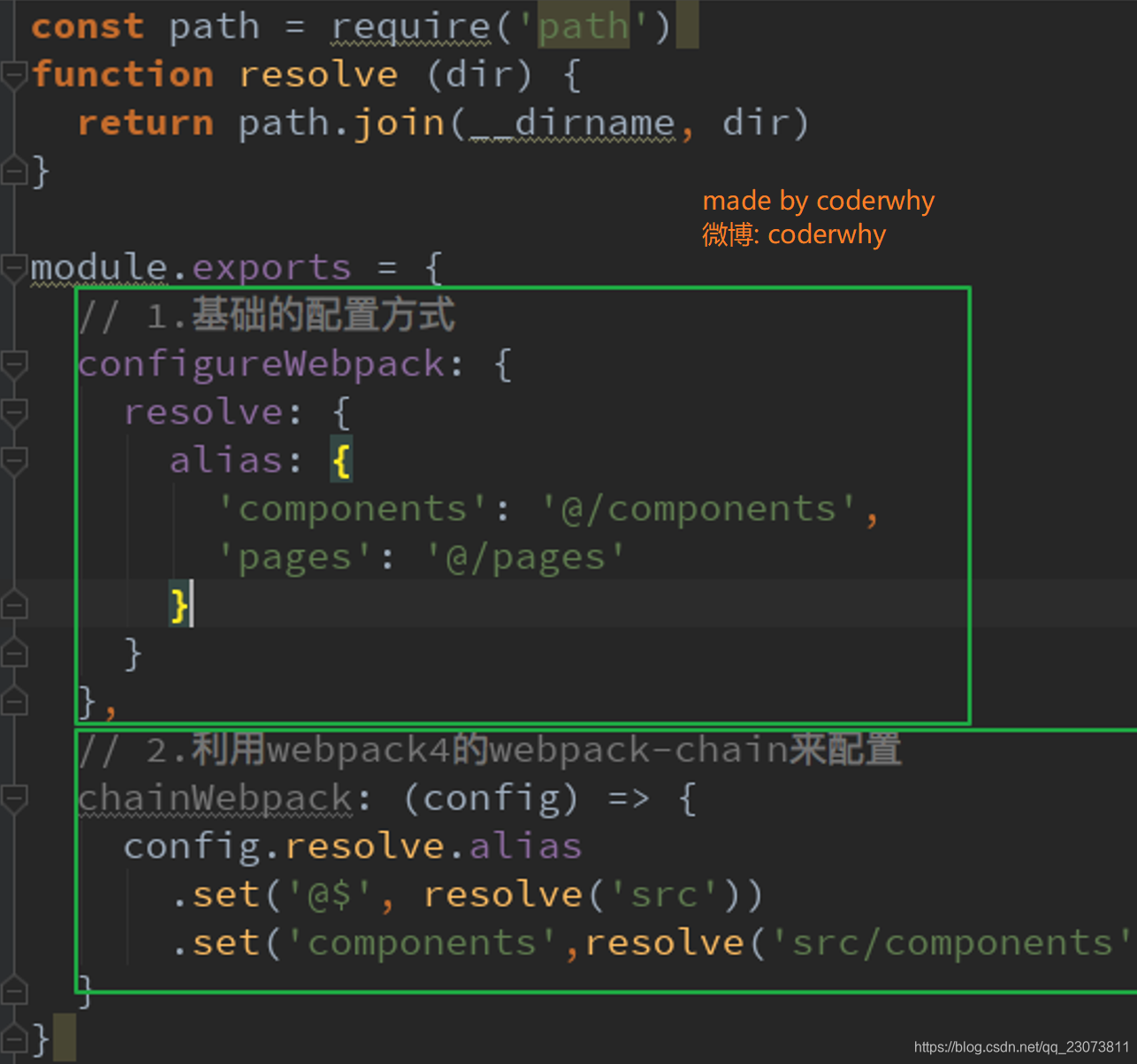
?5.自定义配置:起别名
?(四)、(掌握)箭头函数
1.箭头函数的基本使用
-
箭头函数:?也是一种定义函数的方式
-
定义函数的方式
function
const aaa = function () {
}
// 2.对象字面量中定义函数
const obj = {
bbb() {
}
}
// 3.ES6中的箭头函数
// const ccc = (参数列表) => {
//
// }
const ccc = () => {
}
?2.箭头函数参数和返回值
// 1.参数问题:
// 1.1.放入两个参数
const sum = (num1, num2) => {
return num1 + num2
}
// 1.2.放入一个参数
const power = num => {
return num * num
}
// 2.函数中
// 2.1.函数代码块中有多行代码时
const test = () => {
// 1.打印Hello World
console.log('Hello World');
// 2.打印Hello Vuejs
console.log('Hello Vuejs');
}
// 2.2.函数代码块中只有一行代码
// const mul = (num1, num2) => {
// return num1 + num2
// }
const mul = (num1, num2) => num1 * num2
console.log(mul(20, 30));
// const demo = () => {
// console.log('Hello Demo');
// }
const demo = () => console.log('Hello Demo')
console.log(demo());
?3.箭头函数中this的使用
- 什么时候使用箭头函数?
-
当把一个函数作为参数传到另外一个函数
-
setTimeout(function () {
console.log(this);
}, 1000)
setTimeout(() => {
console.log(this);
}, 1000)-
问题:?箭头函数中的this是如何查找的了?
-
答案:?向外层作用域中,?一层层查找this,?直到有this的定义.
?const obj = { aaa() { setTimeout(function () { console.log(this); // window }) setTimeout(() => { console.log(this); // obj对象 }) } } obj.aaa()const obj = { aaa() { setTimeout(function () { setTimeout(function () { console.log(this); // window }) setTimeout(() => { console.log(this); // window }) }) setTimeout(() => { setTimeout(function () { console.log(this); // window }) setTimeout(() => { console.log(this); // obj }) }) } } obj.aaa()
八、vue-router详解
(一)、内容概述
- 认识路由
- vue-router基本使用
- vue-router嵌套路由
- vue-router参数传递
- vue-router导航守卫
- keep-alive
(二)、(理解)认识路由
?1.什么是路由?
- 说起路由你想起了什么?
- 路由是一个网络工程里面的术语。
- 路由(routing)就是通过互联的网络把信息从源地址传输到目的地址的活动. --- 维基百科
- 额, 啥玩意? 没听懂
- 在生活中, 我们有没有听说过路由的概念呢? 当然了, 路由器嘛.
- 路由器是做什么的? 你有想过吗?
- 路由器提供了两种机制: 路由和转送.
- 路由是决定数据包从来源到目的地的路径.
- 转送将输入端的数据转移到合适的输出端.
- 路由中有一个非常重要的概念叫路由表.
- 路由表本质上就是一个映射表, 决定了数据包的指向.

2.后端路由阶段
-
早期的网站开发整个HTML页面是由服务器来渲染的.
-
服务器直接生产渲染好对应的HTML页面, 返回给客户端进行展示.?
-
- 但是, 一个网站, 这么多页面服务器如何处理呢?
- 一个页面有自己对应的网址, 也就是URL.
- URL会发送到服务器, 服务器会通过正则对该URL进行匹配, 并且最后交给一个Controller进行处理.
- Controller进行各种处理, 最终生成HTML或者数据, 返回给前端.
- 这就完成了一个IO操作.?
- 上面的这种操作, 就是后端路由.
- 当我们页面中需要请求不同的路径内容时, 交给服务器来进行处理, 服务器渲染好整个页面, 并且将页面返回给客户顿.
- 这种情况下渲染好的页面, 不需要单独加载任何的js和css, 可以直接交给浏览器展示, 这样也有利于SEO的优化.?
- 后端路由的缺点:
- 一种情况是整个页面的模块由后端人员来编写和维护的.
- 另一种情况是前端开发人员如果要开发页面, 需要通过PHP和Java等语言来编写页面代码.
- 而且通常情况下HTML代码和数据以及对应的逻辑会混在一起, 编写和维护都是非常糟糕的事情.
3.前端路由阶段
-
前后端分离阶段:
-
随着Ajax的出现, 有了前后端分离的开发模式.
-
后端只提供API来返回数据, 前端通过Ajax获取数据, 并且可以通过JavaScript将数据渲染到页面中.
-
这样做最大的优点就是前后端责任的清晰, 后端专注于数据上, 前端专注于交互和可视化上.
-
并且当移动端(iOS/Android)出现后, 后端不需要进行任何处理, 依然使用之前的一套API即可.
-
目前很多的网站依然采用这种模式开发.?
-
- 单页面富应用阶段:
- 其实SPA最主要的特点就是在前后端分离的基础上加了一层前端路由.
- 也就是前端来维护一套路由规则.?
- 前端路由的核心是什么呢?
- 改变URL,但是页面不进行整体的刷新。
- 如何实现呢??
(三)、(掌握)前端路由的规则
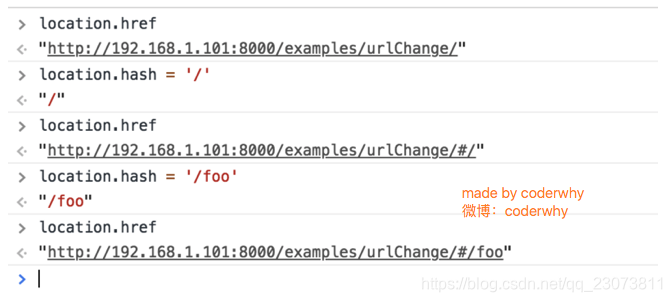
1.URL的hash
-
URL的hash
-
URL的hash也就是锚点(#), 本质上是改变window.location的href属性.
-
我们可以通过直接赋值location.hash来改变href, 但是页面不发生刷新?
-
?
2.HTML5的history模式:pushState
-
history接口是HTML5新增的, 它有五种模式改变URL而不刷新页面.
-
history.pushState()?

3.HTML5的history模式:replaceState?
- ?history.replaceState()

?4.HTML5的history模式:go
- history.go()

5.补充说明
- 上面只演示了三个方法
- 因为 history.back() 等价于 history.go(-1)
- history.forward() 则等价于 history.go(1)
- 这三个接口等同于浏览器界面的前进后退。?
(四)、(掌握)vue-router基础
1.认识vue-router
- 目前前端流行的三大框架, 都有自己的路由实现:
- Angular的ngRouter
- React的ReactRouter
- Vue的vue-router
- 当然, 我们的重点是vue-router
- ?vue-router是Vue.js官方的路由插件,它和vue.js是深度集成的,适合用于构建单页面应用。
- 我们可以访问其官方网站对其进行学习: https://router.vuejs.org/zh/
- vue-router是基于路由和组件的
- 路由用于设定访问路径, 将路径和组件映射起来.
- 在vue-router的单页面应用中, 页面的路径的改变就是组件的切换.
2.安装和使用vue-router
-
因为我们已经学习了webpack, 后续开发中我们主要是通过工程化的方式进行开发的.
-
所以在后续, 我们直接使用npm来安装路由即可.
-
步骤一: 安装vue-router?
npm install vue-router --save -
步骤二: 在模块化工程中使用它(因为是一个插件, 所以可以通过Vue.use()来安装路由功能)?
-
第一步:导入路由对象,并且调用 Vue.use(VueRouter)
import Vue from 'vue' import VueRouter from 'vue-router' Vue.use(VueRouter) -
第二步:创建路由实例,并且传入路由映射配置
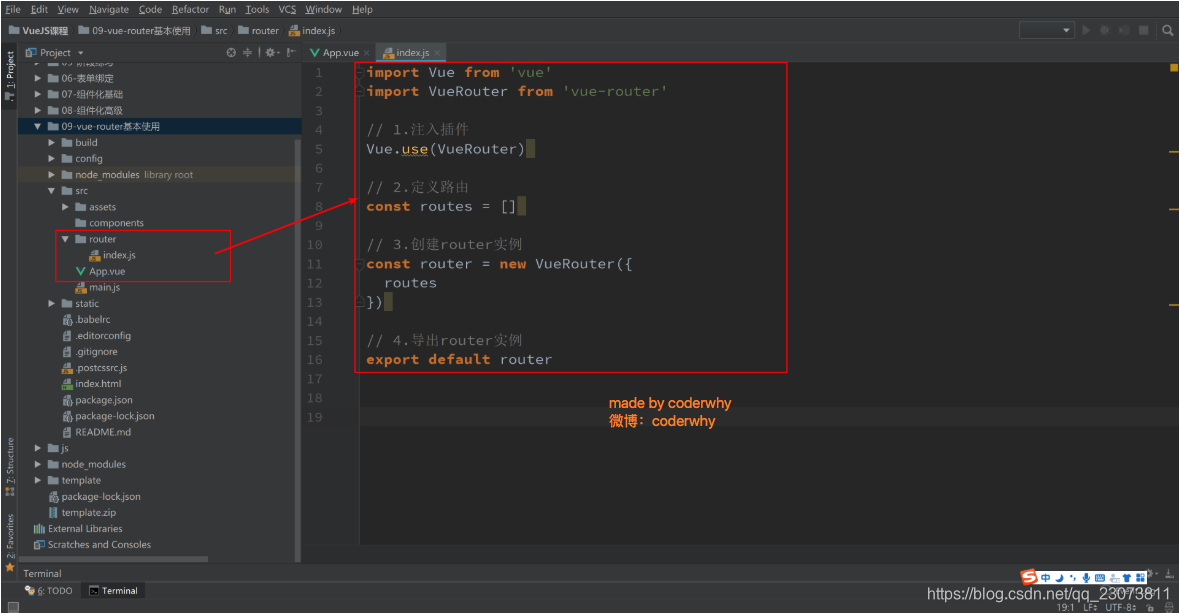
-
第三步:在Vue实例中挂载创建的路由实例
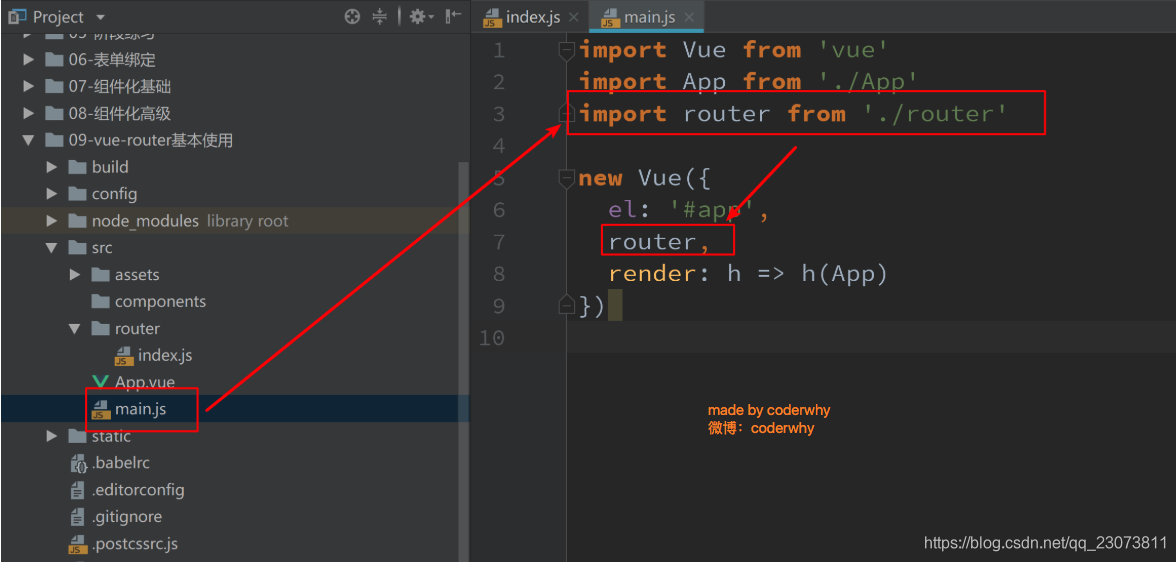
-
-
- ?使用vue-router的步骤:
- 第一步: 创建路由组件
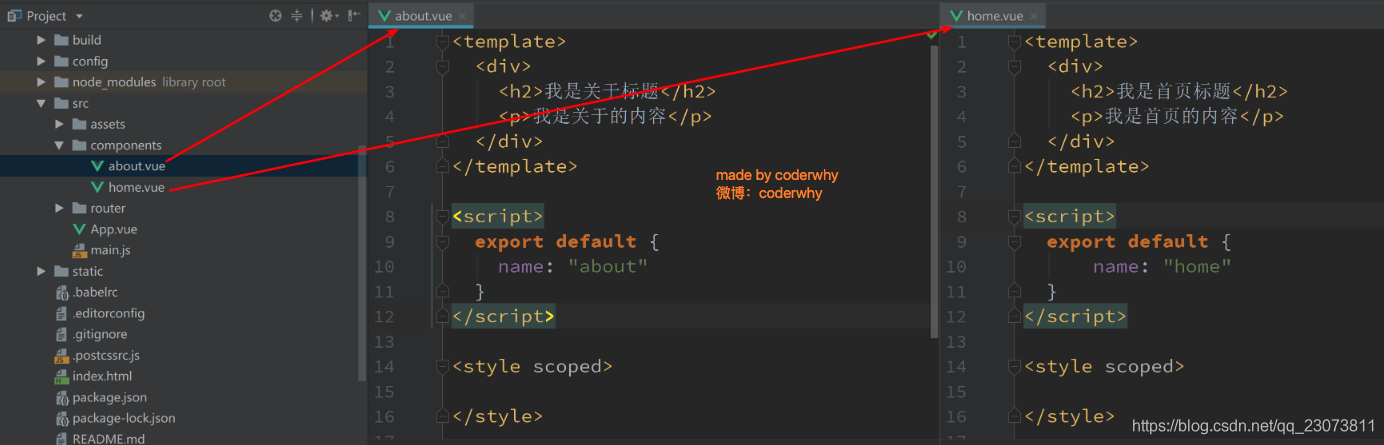
- 第二步: 配置路由映射: 组件和路径映射关系
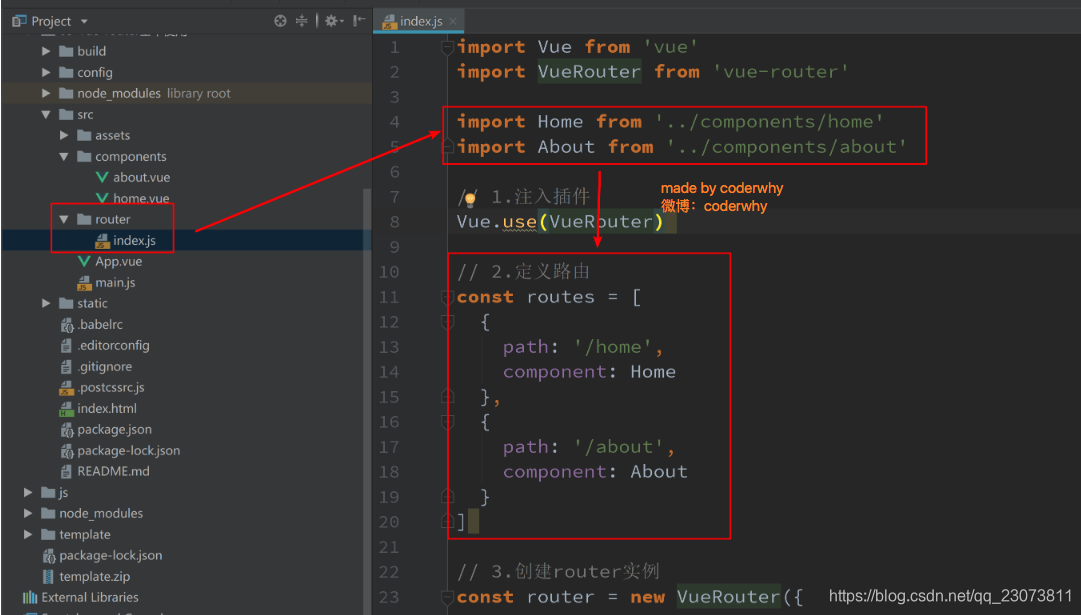
- 第三步: 使用路由: 通过<router-link>和<router-view>
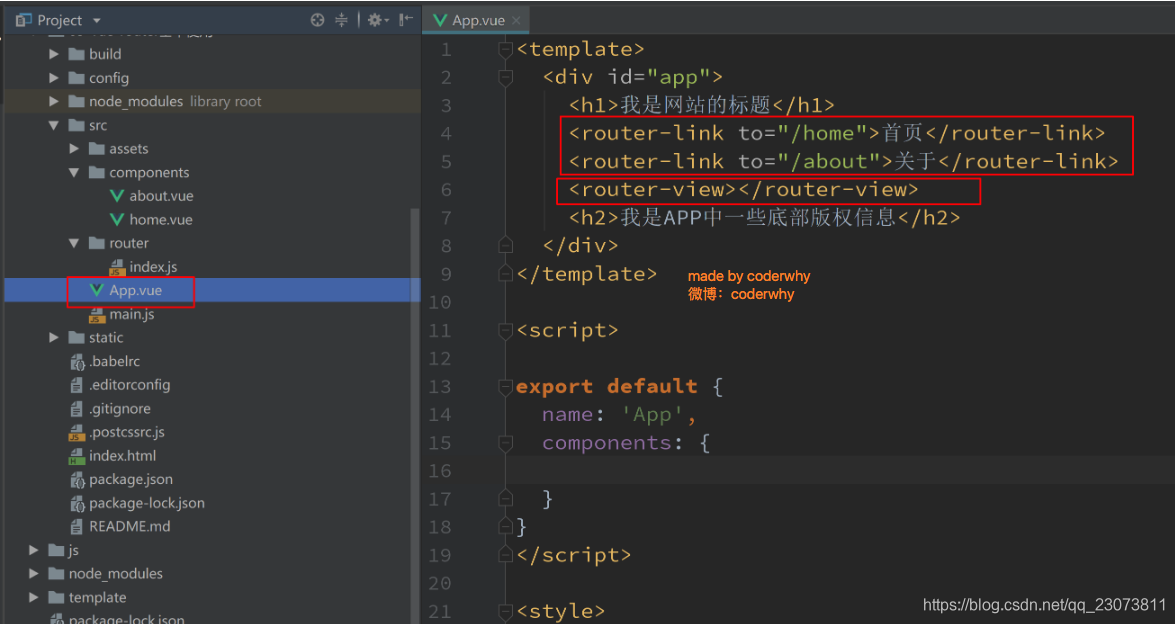
- 第一步: 创建路由组件
- <router-link>: 该标签是一个vue-router中已经内置的组件, 它会被渲染成一个<a>标签.
- <router-view>: 该标签会根据当前的路径, 动态渲染出不同的组件.?
- 网页的其他内容, 比如顶部的标题/导航, 或者底部的一些版权信息等会和<router-view>处于同一个等级.
- 在路由切换时, 切换的是<router-view>挂载的组件, 其他内容不会发生改变.
- 最终效果如下
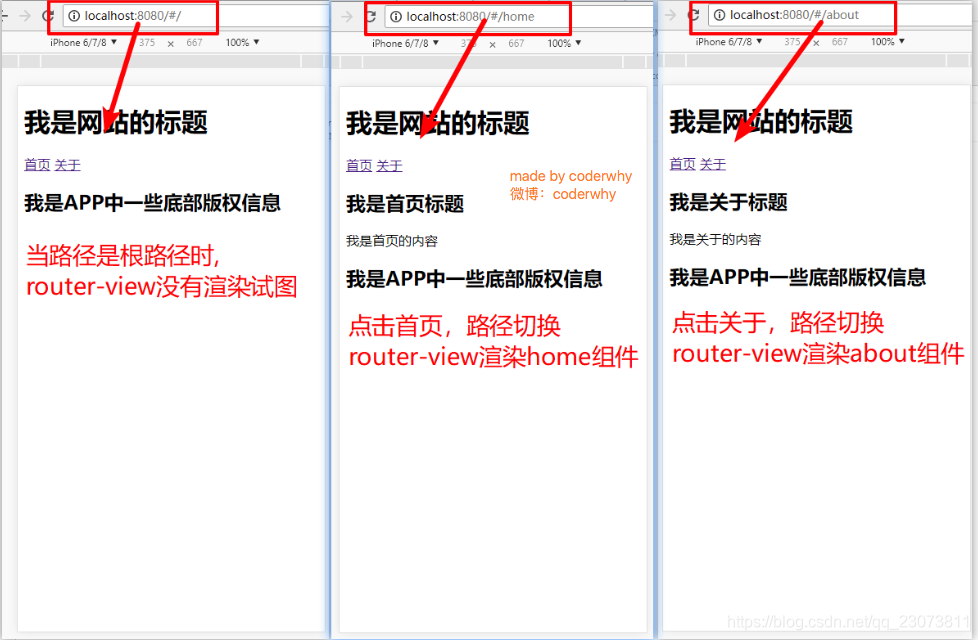
(五)、(掌握)细节处理
1.路由的默认路径
-
我们这里还有一个不太好的实现:
-
默认情况下, 进入网站的首页, 我们希望<router-view>渲染首页的内容.
-
但是我们的实现中, 默认没有显示首页组件, 必须让用户点击才可以.?
-
- 如何可以让路径默认跳到到首页, 并且<router-view>渲染首页组件呢?
- 非常简单, 我们只需要配置多配置一个映射就可以了.?
?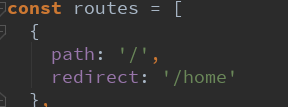
- 配置解析:
- 我们在routes中又配置了一个映射.
- path配置的是根路径: /
- redirect是重定向, 也就是我们将根路径重定向到/home的路径下, 这样就可以得到我们想要的结果了.?
2.HTML5的History模式
-
我们前面说过改变路径的方式有两种:
-
URL的hash
-
HTML5的history
-
默认情况下, 路径的改变使用的URL的hash.
-
- 如果希望使用HTML5的history模式, 非常简单, 进行如下配置即可:?
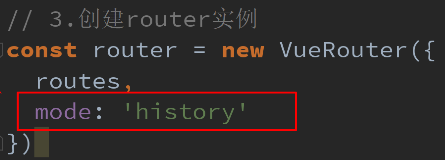
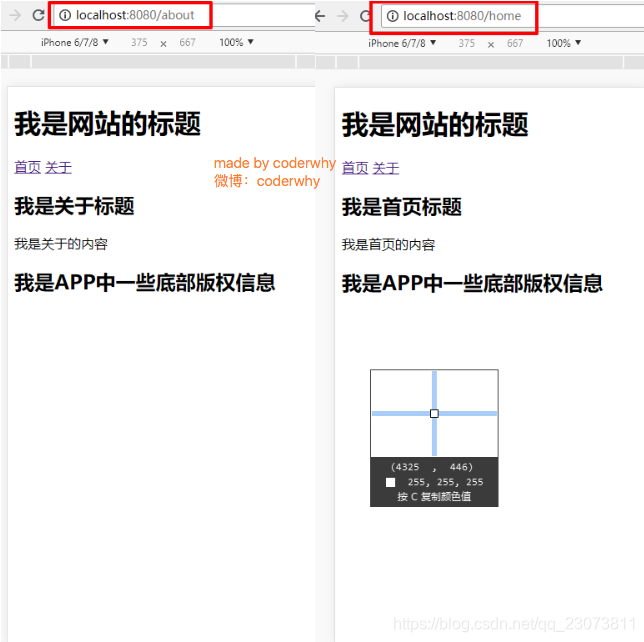
- 补充:history模式的url不会有#符号?
3.router-link补充
-
在前面的<router-link>中, 我们只是使用了一个属性: to, 用于指定跳转的路径.?
- <router-link>还有一些其他属性:
?<router-link to='/home' tag='li' replace>- tag: tag可以指定<router-link>之后渲染成什么组件, 比如上面的代码会被渲染成一个<li>元素, 而不是<a>
- replace: replace不会留下history记录, 所以指定replace的情况下, 后退键返回不能返回到上一个页面中
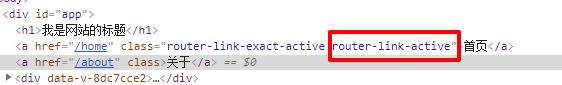
- active-class: 当<router-link>对应的路由匹配成功时, 会自动给当前元素设置一个router-link-active的class, 设置active-class可以修改默认的名称.
- 在进行高亮显示的导航菜单或者底部tabbar时, 会使用到该类.
- 但是通常不会修改类的属性, 会直接使用默认的router-link-active即可.
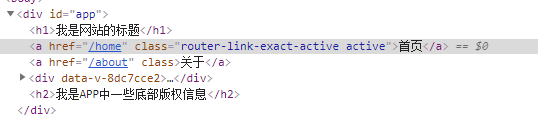
?4.修改linkActiveClass
- 该class具体的名称也可以通过router实例的属性进行修改

- exact-active-class 类似于active-class,
- 只是在精准匹配下才会出现的class.
- 后面看到嵌套路由时, 我们再看下这个属性.?
?
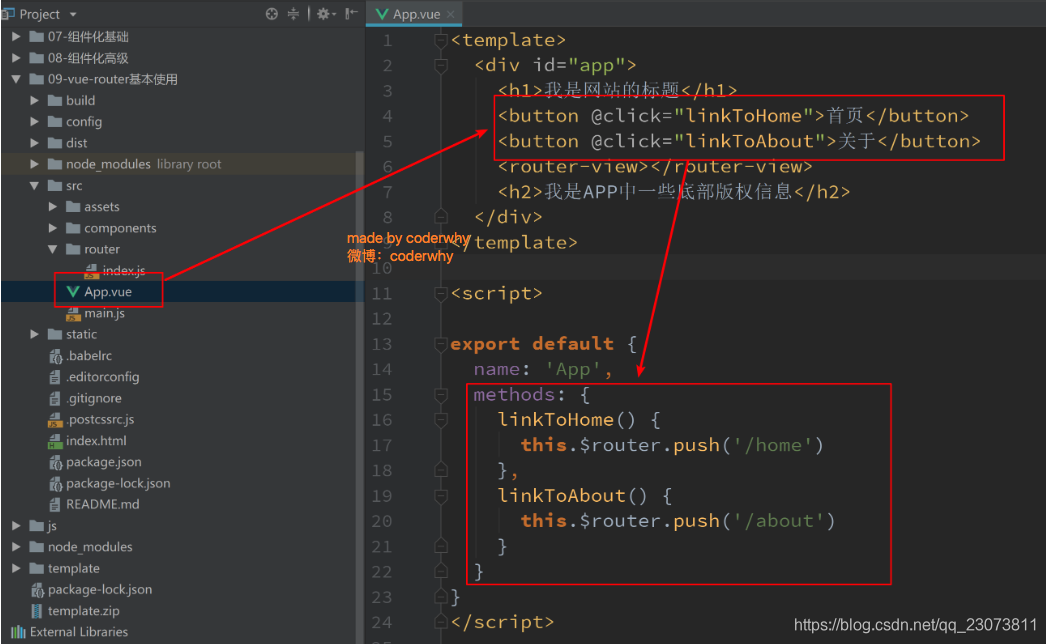
5.路由代码跳转
-
?有时候, 页面的跳转可能需要执行对应的JavaScript代码,
-
这个时候, 就可以使用第二种跳转方式了 比如, 我们将代码修改如下:
?阶段代码
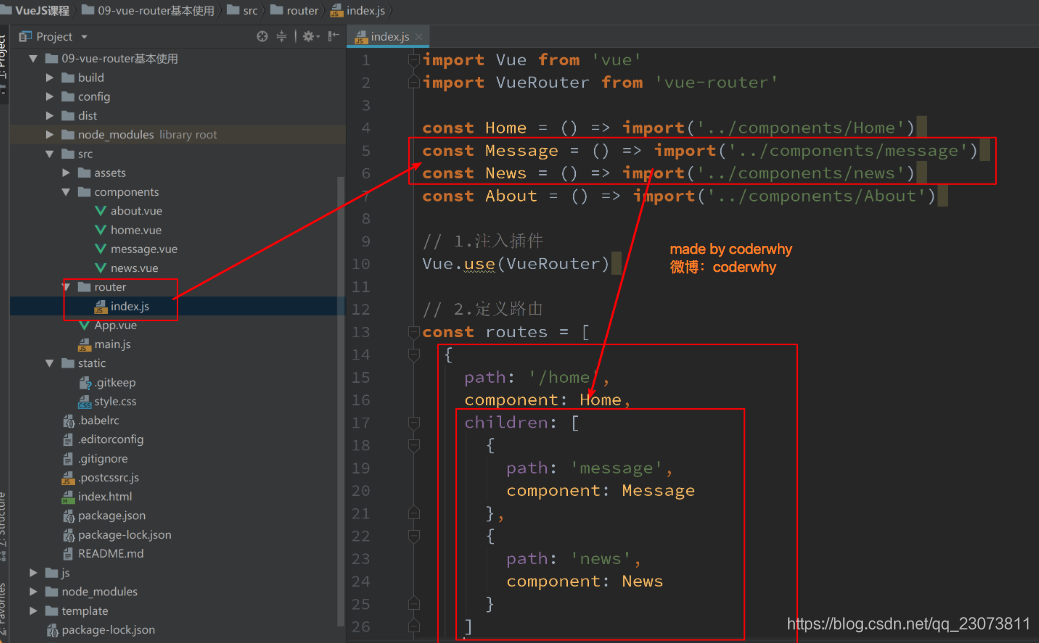
-
router里的index.js?
// 配置路由相关的信息
// 导入路由对象
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
import Vue from 'vue'
import Home from '../components/Home'
import About from '../components/About'
// 1.通过Vue.use(插件), 安装插件
Vue.use(VueRouter)
// 2.创建VueRouter对象
const routes = [
{
path: '',
// redirect重定向
redirect: '/home'
},
{
path: '/home',
component: Home
},
{
path: '/about',
component: About
}
]
// 创建路由实例,并且传入路由映射配置
const router = new VueRouter({
// 配置路由和组件之间的应用关系
routes,
mode: 'history',
linkActiveClass: 'active'
})
// 3.将router对象传入到Vue实例
export default router
?App.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<h2>我是APP组件</h2>
<!-- 使用路由 -->
<!--<router-link to="/home" tag="button" replace active-class="active">首页</router-link>-->
<!--<router-link to="/about" tag="button" replace active-class="active">关于</router-link>-->
<router-link to="/home" tag="button" replace>首页</router-link>
<router-link to="/about" tag="button" replace>关于</router-link>
<!-- // 通过代码的方式修改路由 vue-router -->
<!-- <button @click="homeClick">首页</button>
<button @click="aboutClick">关于</button> -->
<router-view></router-view>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'App',
methods: {
homeClick() {
// 通过代码的方式修改路由 vue-router
// push => pushState
// this.$router.push('/home')
this.$router.replace('/home')
console.log('homeClick');
},
aboutClick() {
// this.$router.push('/about')
this.$router.replace('/about')
console.log('aboutClick');
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
/*.router-link-active {*/
/*color: #f00;*/
/*}*/
.active {
color: #f00;
}
</style>
main.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App'
import router from './router'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
el: '#app',
// 在Vue实例中挂载创建的路由实例
router,
render: h => h(App)
})
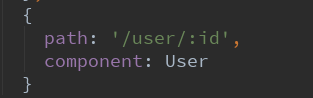
6.动态路由
-
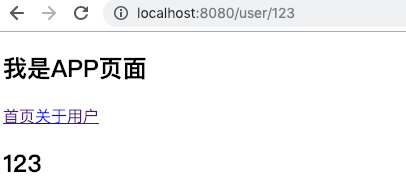
在某些情况下,一个页面的path路径可能是不确定的,比如我们进入用户界面时,希望是如下的路径:
-
/user/aaaa或/user/bbbb
-
除了有前面的/user之外,后面还跟上了用户的ID
-
这种path和Component的匹配关系,我们称之为动态路由(也是路由传递数据的一种方式)。?
-
![]()
?代码:
- ?创建一个User.vue组件
<template>
<div>
<h2>我是用户界面</h2>
<p>我是用户的相关信息, 嘿嘿嘿</p>
<h2>计算属性userId:{{userId}}</h2>
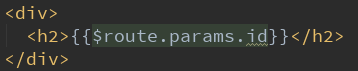
<h2>$route.params.id:{{$route.params.id}}</h2>
<button @click="btnClick">按钮</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "User",
computed: {
userId() {
return this.$route.params.id
}
},
created() {
console.log('User created');
},
destroyed() {
console.log('User destroyed');
},
methods: {
btnClick() {
// 所有的组件都继承自Vue类的原型
console.log(this.$router); // 是我们index.js创建的那个大的路由对象router
console.log(this.$route); // 当前哪个路由处于活跃状态,获取到的就是哪个路由
console.log(this.name);
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
- router文件夹下index.js
...
const routes = [
...
{
path:'/user/:id',
component:User
}
]
const router = new VueRouter({
routes,
mode:'history',
linkActiveClass:'active'
})
export default router- App.vue?
<template>
<div id="app">
<h2>我是APP组件</h2>
<router-link to="/home">首页</router-link>
<router-link to="/about">关于</router-link>
<!-- 动态路由 -->
<!--<router-link :to="/user/yyy">用户</router-link>-->
<!-- 动态拼接 使用v-bind -->
<router-link :to="'/user/'+userId">用户</router-link>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "App",
components: {},
data() {
return {
userId: "zhangsan"
};
},
};
</script>
(六)、(掌握)路由懒加载
1.认识路由的懒加载
- 官方给出了解释:
- 当打包构建应用时,Javascript 包会变得非常大,影响页面加载。
- 如果我们能把不同路由对应的组件分割成不同的代码块,然后当路由被访问的时候才加载对应组件,这样就更加高效了
- 官方在说什么呢?
- 首先, 我们知道路由中通常会定义很多不同的页面.
- 这个页面最后被打包在哪里呢? 一般情况下, 是放在一个js文件中.
- 但是, 页面这么多放在一个js文件中, 必然会造成这个页面非常的大.
- 如果我们一次性从服务器请求下来这个页面, 可能需要花费一定的时间, 甚至用户的电脑上还出现了短暂空白的情况.
- 如何避免这种情况呢? 使用路由懒加载就可以了.
- 路由懒加载做了什么?
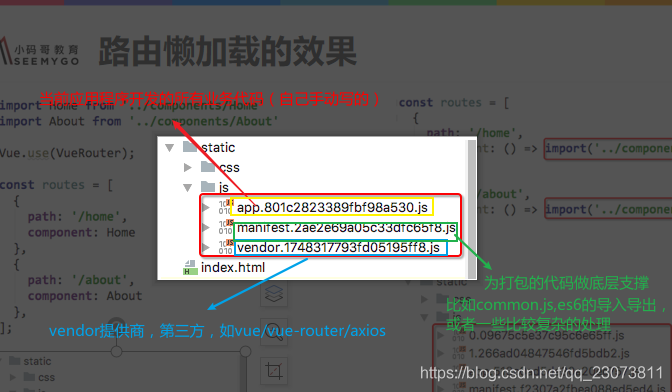
- 路由懒加载的主要作用就是将路由对应的组件打包成一个个的js代码块.
- 只有在这个路由被访问到的时候, 才加载对应的组件
2.路由懒加载的效果
?懒加载打包
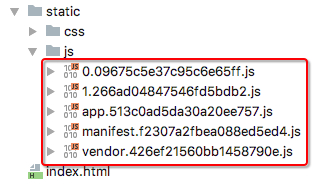
3.懒加载的方式
-
方式一: 结合Vue的异步组件和Webpack的代码分析.?
const Home = resolve => {
require.ensure(['../components/Home.vue'], () => {
resolve(require('../components/Home.vue'))
})
};
- ?方式二: AMD写法
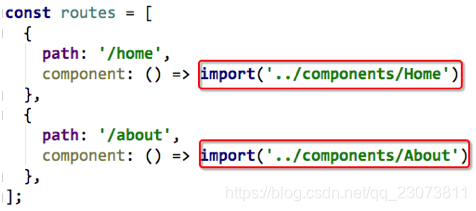
const About = resolve => require(['../components/About.vue'], resolve);- 方式三: 在ES6中, 我们可以有更加简单的写法来组织Vue异步组件和Webpack的代码分割.
const Home = () => import('../components/Home.vue')
(七)、(掌握)路由嵌套
1.认识嵌套路由
- 嵌套路由是一个很常见的功能
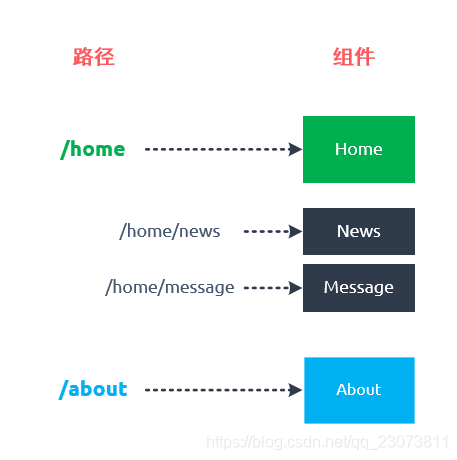
- 比如在home页面中, 我们希望通过/home/news和/home/message访问一些内容.
- 一个路径映射一个组件, 访问这两个路径也会分别渲染两个组件.
- 路径和组件的关系如下:
- 实现嵌套路由有两个步骤:
- 创建对应的子组件, 并且在路由映射中配置对应的子路由.
- 在组件内部使用<router-view>标签.?
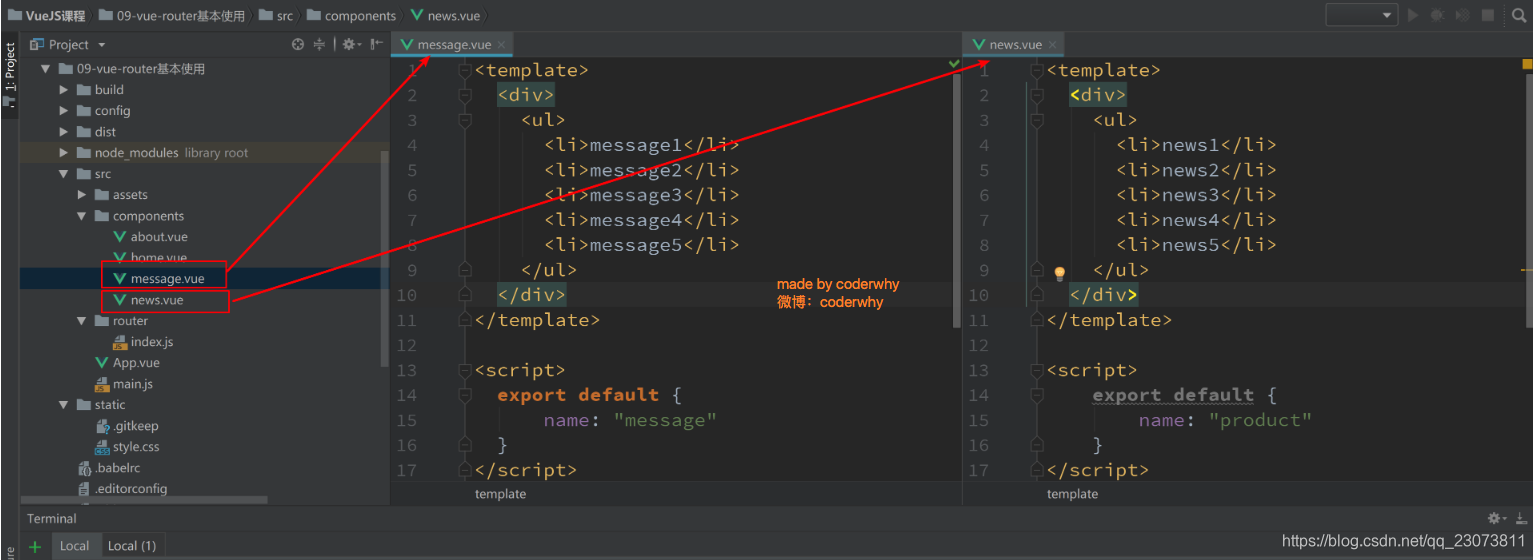
2.嵌套路由实现
-
定义两个组件:?
?

3.嵌套默认路径
-
嵌套路由也可以配置默认的路径, 配置方式如下:?
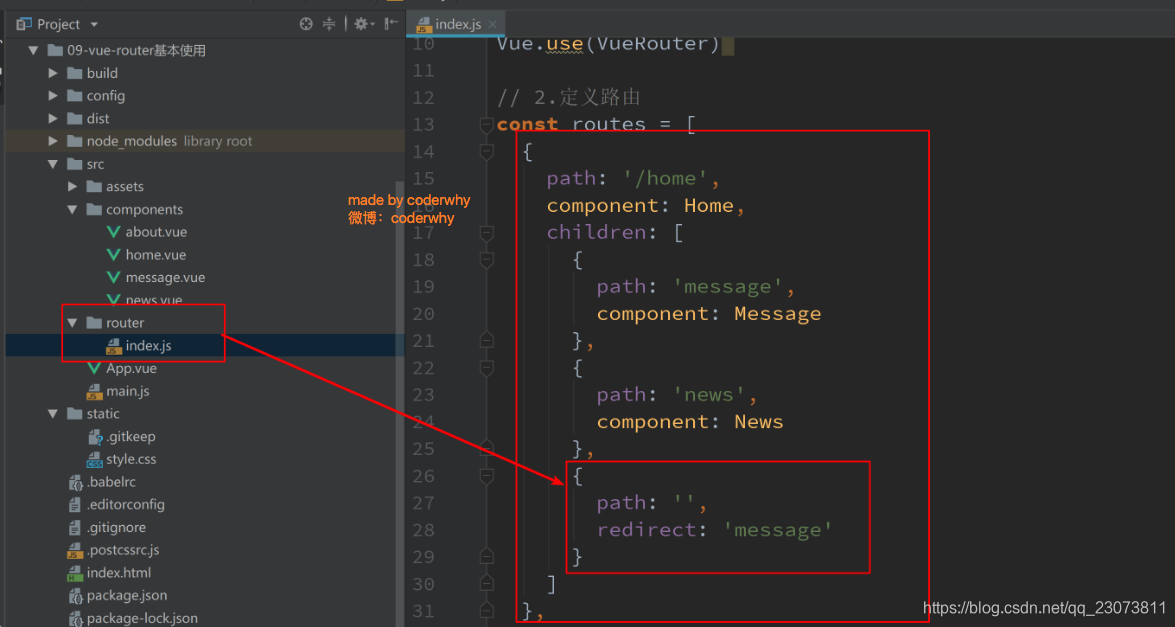
(八)、(掌握)传递参数
?1.准备工作
- 为了演示传递参数, 我们这里再创建一个组件, 并且将其配置好
- 第一步: 创建新的组件Profile.vue
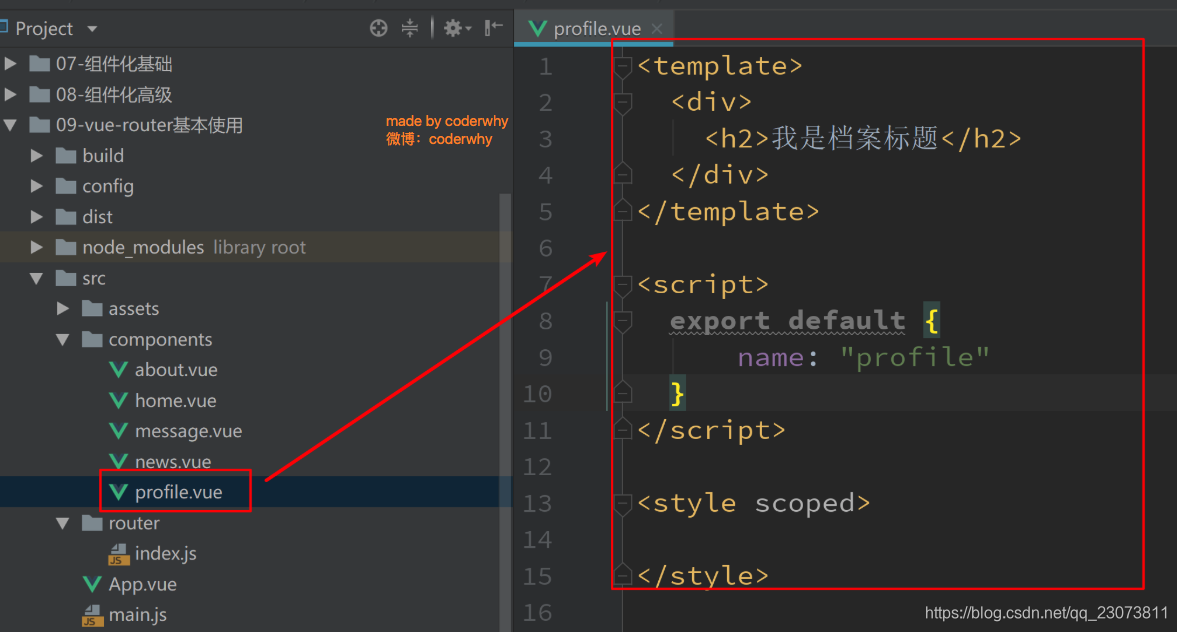
- 第二步: 配置路由映射
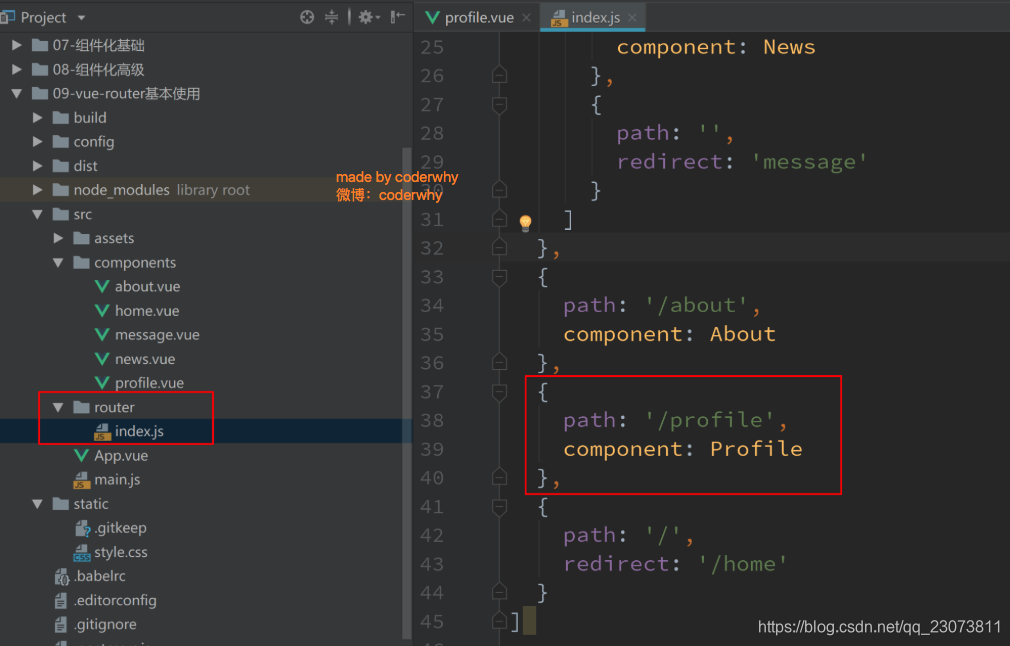
- 第三步: 添加跳转的<router-link>
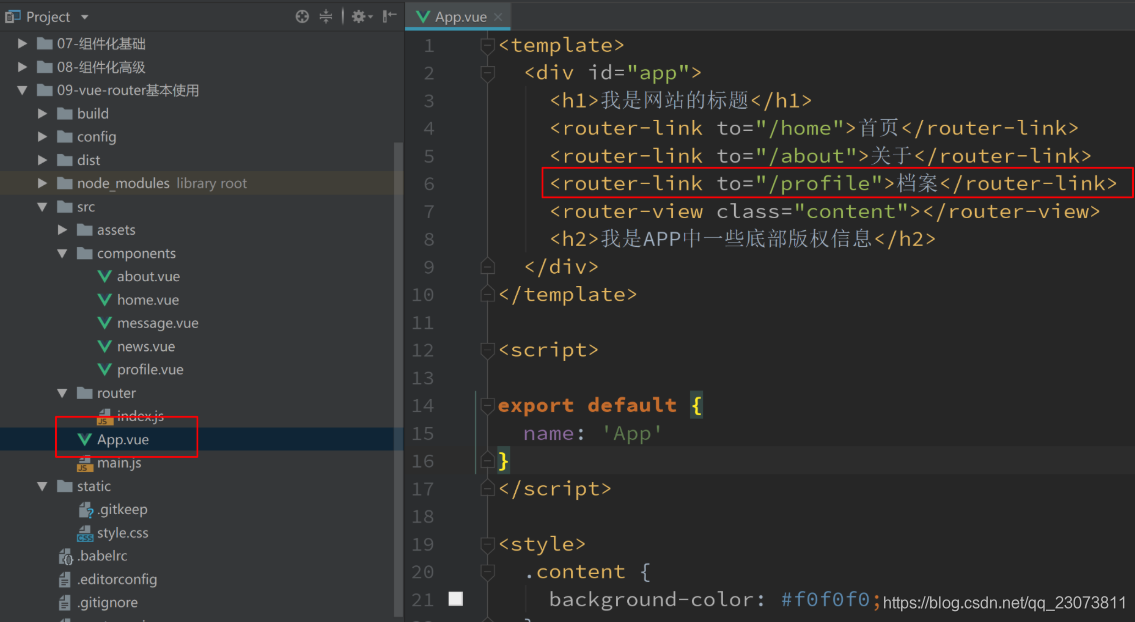
- 第一步: 创建新的组件Profile.vue
2.传递参数的方式
-
?传递参数主要有两种类型:
-
params和query
-
- params的类型:
- 配置路由格式: /router/:id
- 传递的方式: 在path后面跟上对应的值
- 传递后形成的路径: /router/123, /router/abc
- ?query的类型:
- 配置路由格式: /router, 也就是普通配置
- 传递的方式: 对象中使用query的key作为传递方式
- 传递后形成的路径: /router?id=123, /router?id=abc
- 如何使用它们呢? 也有两种方式: <router-link>的方式和JavaScript代码方式?
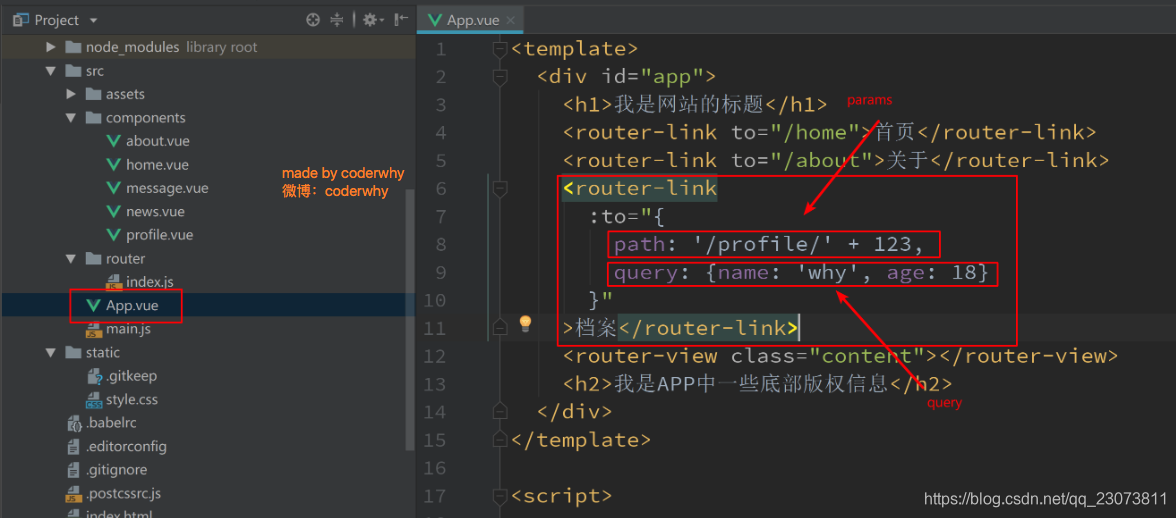
3.传递参数方式一: <router-link>
?4.传递参数方式二: JavaScript代码
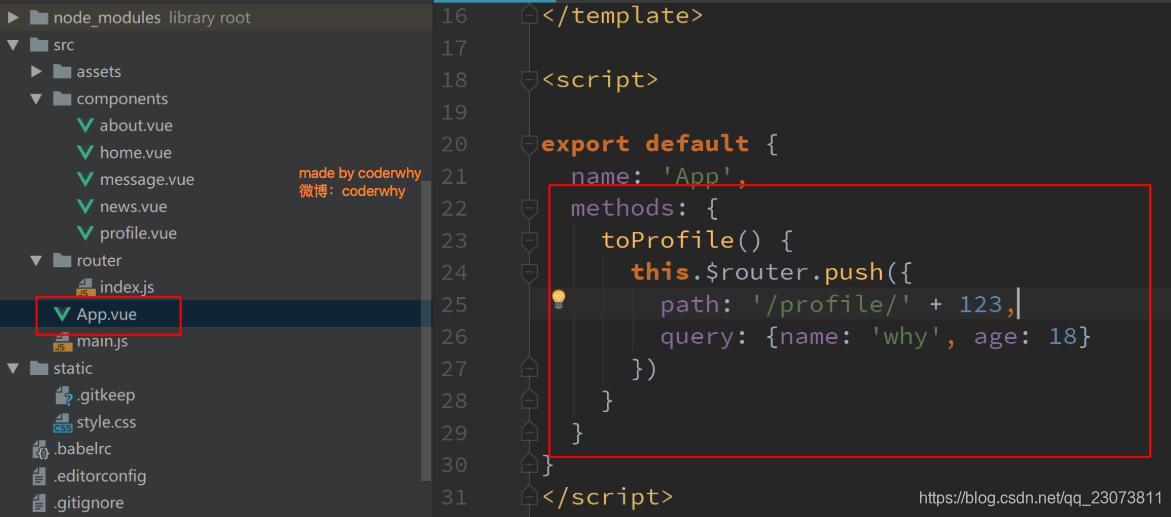
5.获取参数?
- 获取参数通过$route对象获取的.
- 在使用了 vue-router 的应用中,路由对象会被注入每个组件中,赋值为 this.$route ,并且当路由切换时,路由对象会被更新。?
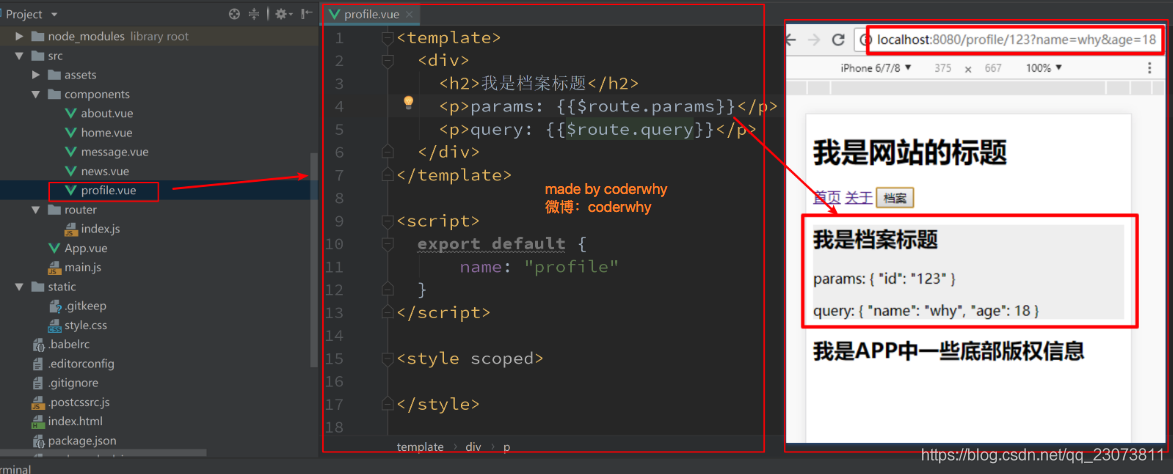
- 通过$route获取传递的信息如下:?
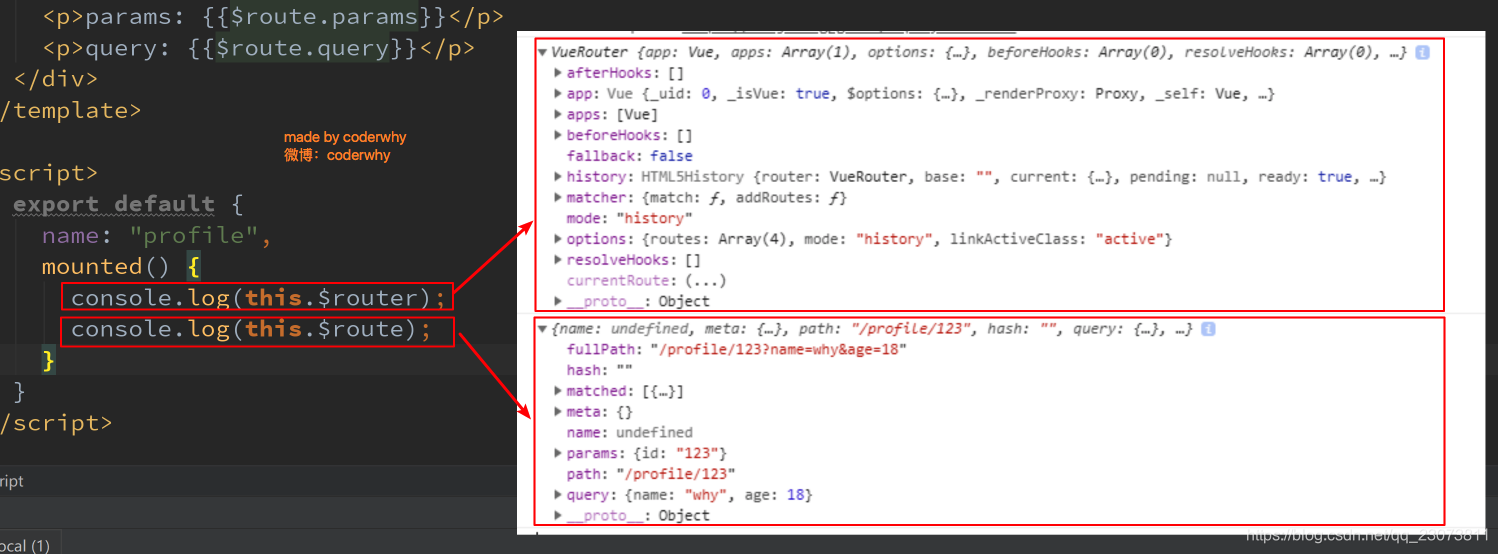
6.(理解)$route和$router是有区别的
-
$route和$router是有区别的
-
$router为VueRouter实例,想要导航到不同URL,则使用$router.push方法
-
$route为当前router跳转对象里面可以获取name、path、query、params等?
-
?7.代码
- profile.vue
<template>
<div>
<h2>我是Profile组件</h2>
<h2>{{$route.query.name}}</h2>
<h2>{{$route.query.age}}</h2>
<h2>{{$route.query.height}}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Profile",
created() {
console.log('Profile created');
},
destroyed() {
console.log('Profile destroyed');
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
- App.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<!-- 导航守卫 keep-alive -->
<h2>我是APP组件</h2>
<router-link to="/home">首页</router-link>
<router-link to="/about">关于</router-link>
<!-- 动态路由 -->
<!--<router-link :to="/user/yyy">用户</router-link>-->
<!-- 动态拼接 使用v-bind -->
<!--<router-link :to="'/user/'+userId">用户</router-link>-->
<!--<!–<router-link to="/profile">档案</router-link>–>-->
<!-- 传递参数类型:1.params(通过path) 2.query -->
<!-- 参数传递方式:1.router-link的to -->
<router-link :to="{path: '/profile', query: {name: 'why', age: 18, height: 1.88}}">
档案</router-link>
<!-- 参数传递方式 2.js:this.$router.push -->
<!--
<button @click="userClick">用户</button>
<button @click="profileClick">档案</button> -->
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "App",
components: { Home, HomeNews },
data() {
return {
userId: "zhangsan"
};
},
methods: {
homeClick() {
// 通过代码的方式修改路由 vue-router
// push => pushState
// this.$router.push('/home')
this.$router.replace("/home");
console.log("homeClick");
},
aboutClick() {
// this.$router.push('/about')
this.$router.replace("/about");
console.log("aboutClick");
},
userClick() {
this.$router.push("/user/" + this.userId);
},
profileClick() {
this.$router.push({
path: "/profile",
query: {
name: "kobe",
age: 19,
height: 1.87,
},
});
},
},
};
</script>
<style>
/*.router-link-active {*/
/*color: #f00;*/
/*}*/
.active {
color: #f00;
}
</style>
(九)、导航守卫
“导航”表示路由正在发生改变。
正如其名,
vue-router?提供的导航守卫主要用来通过跳转或取消的方式守卫导航。有多种机会植入路由导航过程中:全局的, 单个路由独享的, 或者组件级的。
?1.为什么使用导航守卫?
- 我们来考虑一个需求: 在一个SPA应用中, 如何改变网页的标题呢?
- 网页标题是通过<title>来显示的, 但是SPA只有一个固定的HTML, 切换不同的页面时, 标题并不会改变.
- 但是我们可以通过JavaScript来修改<title>的内容.window.document.title = '新的标题'.
- 那么在Vue项目中, 在哪里修改? 什么时候修改比较合适呢?
- 普通的修改方式:
- 我们比较容易想到的修改标题的位置是每一个路由对应的组件.vue文件中.
- 通过mounted声明周期函数, 执行对应的代码进行修改即可.
// Home.vue mounted() { console.log('home mounted'); document.title='首页' }, // About.vue mounted() { console.log('home mounted'); document.title='关于' }, // ... // 其他页面也是这样写 - 但是当页面比较多时, 这种方式不容易维护(因为需要在多个页面执行类似的代码).?
- 有没有更好的办法呢? 使用导航守卫即可.
- 什么是导航守卫?
- vue-router提供的导航守卫主要用来监听监听路由的进入和离开的.
- vue-router提供了beforeEach和afterEach的钩子函数, 它们会在路由即将改变前和改变后触发.?
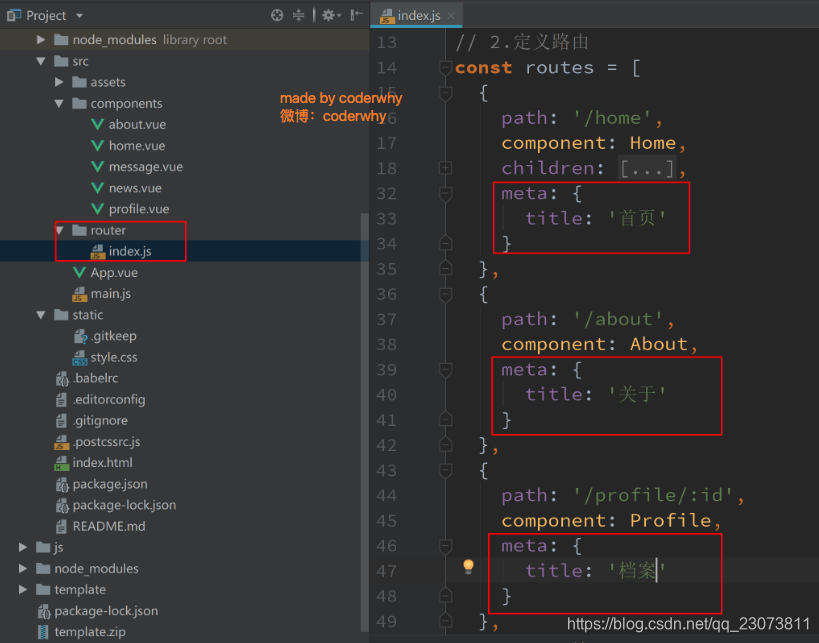
2.(掌握)导航守卫使用
-
我们可以利用beforeEach来完成标题的修改.
-
首先, 我们可以在钩子当中定义一些标题, 可以利用meta来定义
-
其次, 利用导航守卫,修改我们的标题.?
-
?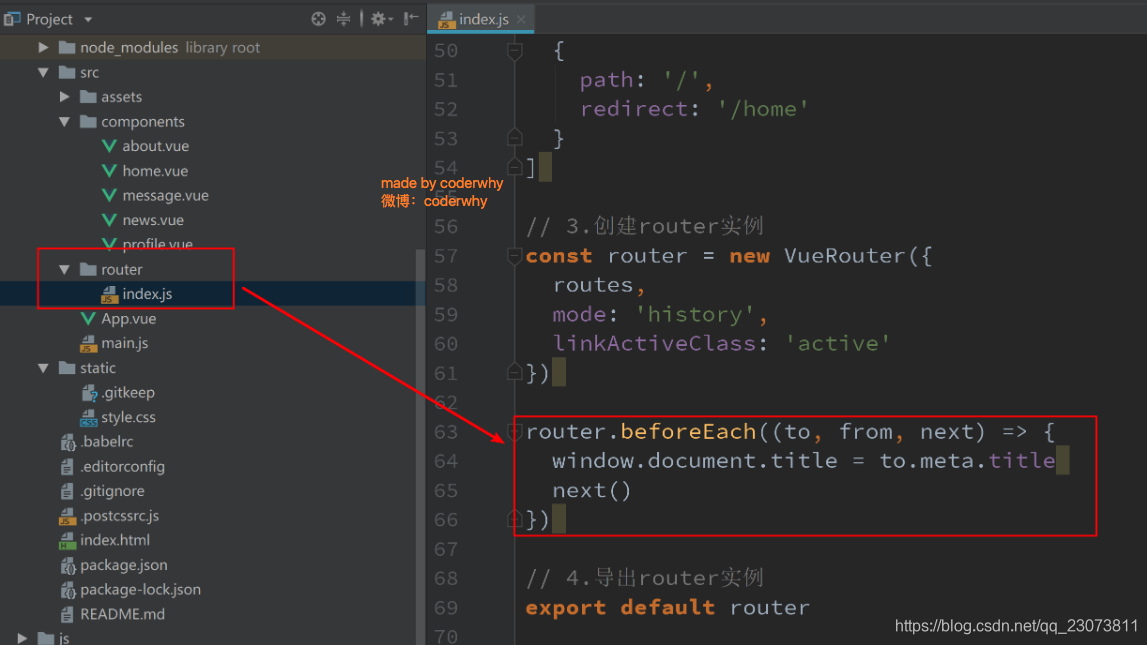
- 导航钩子的三个参数解析:
- to: 即将要进入的目标的路由对象.
- from: 当前导航即将要离开的路由对象.
- next: 调用该方法后, 才能进入下一个钩子.?
- ?router下的index.js
// ...
const routes = [
{
path: '',
// redirect重定向
redirect: '/home'
},
{
path: '/home',
component: Home,
// meta元数据(描述数据的数据)
meta: {
title: '首页'
},
// 嵌套路由
children: [
// {
// path: '',
// redirect: 'news'
// },
{
path: 'news',// 没有斜杠 /
component: HomeNews
},
{
path: 'message',
component: HomeMessage
}
]
},
{
path: '/about',
component: About,
meta: {
title: '关于'
},
},
{
path: '/user/:id',
component: User,
meta: {
title: '用户'
},
},
{
path: '/profile',
component: Profile,
meta: {
title: '档案'
},
}
]
const router = new VueRouter({
// ...
})
// 1. 全局导航守卫
// 1.1 前置守卫(guard) 路由跳转之前
// beforeEach()注册一个全局前置守卫,本身是一个函数,又传入一个函数guard,有三个参数
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
// 从from跳转到to
// // to 和 from都是route对象
// document.title = to.meta.title
// 上面这样写的话如果有嵌套路由的话是undefined,要使用matched(匹配)获取
document.title = to.matched[0].meta.title
console.log(to);// 到哪个页面去?
console.log(from);// 从哪个页面来?
// 调用该方法后,才能进入下一个钩子
// 如果是后置钩子,也就是afterEach,不需要主动调用next()函数
// 这里其实可以判断用户登陆权限之类的,拦截访问 ,权限不符调用next(false)拦截
next()
})
// 1.2 后置钩子(hook) 不需要主动调用next()函数
router.afterEach((to, from) => {
console.log('----');
})
// 钩子->回调
export default router
3.(理解)导航守卫补充
- 补充一:如果是后置钩子, 也就是afterEach, 不需要主动调用next()函数.
- 补充二: 上面我们使用的导航守卫, 被称之为全局守卫(beforeEach、afterEach).
- 路由独享的守卫(beforeEnter).
- 组件内的守卫(beforeRouterEnter、beforeRouterUpdate、beforeRouterLeave).?
- 更多内容, 可以查看官网进行学习:
- 路由独享的守卫(beforeEnter)
const routes = [
// ...
{
path: '/about',
component: About,
meta: {
title: '关于'
},
// 2.路由独享的守卫
beforeEnter: (to, from, next) => {
console.log('about beforeEnter');
next()
}
},
// ...
]
const router = new VueRouter({
//...
})- 组件内的守卫(beforeRouterEnter、beforeRouterUpdate、beforeRouterLeave)
// Home.vue
<template>
<div>
<h2>我是首页</h2>
<p>我是首页内容, 哈哈哈</p>
<router-link to="/home/news">新闻</router-link>
<router-link to="/home/message">消息</router-link>
<router-view></router-view>
<h2>{{message}}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Home",
data() {
return {
name: "yyy",
};
},
beforeRouteEnter(to, from, next) {
// 在渲染该组件的对应路由被 confirm 前调用
// 不!能!获取组件实例 `this`
// 因为当守卫执行前,组件实例还没被创建
// console.log(to);
// console.log(from);
console.log(this); // undefined
next((vm) => { // 通过传一个回调给 next来访问组件实例
console.log(vm.name);
});
},
beforeRouteUpdate(to, from, next) {
// 在当前路由改变,但是该组件被复用时调用
// 举例来说,对于一个带有动态参数的路径 /foo/:id,在 /foo/1 和 /foo/2 之间跳转的时候,
// 由于会渲染同样的 Foo 组件,因此组件实例会被复用。而这个钩子就会在这个情况下被调用。
// 可以访问组件实例 `this`
console.log("beforeRouteUpdate");
next();
},
beforeRouteLeave(to, from, next) {
// 导航离开该组件的对应路由时调用
// 可以访问组件实例 `this`
console.log(this.$route.path);
next();
},
};
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
(十)、(掌握)keep-alive
keep-alive遇见vue-router
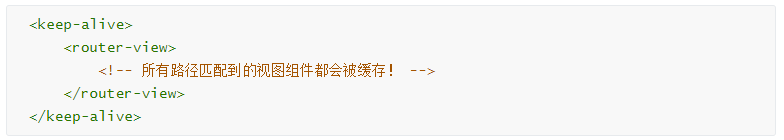
- keep-alive 是 Vue 内置的一个组件,可以使被包含的组件保留状态,或避免重新渲染。
- 它们有两个非常重要的属性:
- include - 字符串或正则表达,只有匹配的组件会被缓存
- exclude - 字符串或正则表达式,任何匹配的组件都不会被缓存?
- router-view 也是一个组件,如果直接被包在 keep-alive 里面,所有路径匹配到的视图组件都会被缓存:?
- ?通过create声明周期函数来验证
?App.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<!-- 导航守卫 keep-alive -->
<router-link to="/home">首页</router-link>
<router-link to="/about">关于</router-link>
<!-- 在vue中我们可以使用keepalive来进行组件缓存 -->
<keep-alive exclude="Profile,User">
<router-view />
</keep-alive>
</div>
</template>
?Home.vue
<template>
<div>
<h2>我是首页</h2>
<p>我是首页内容, 哈哈哈</p>
<router-link to="/home/news">新闻</router-link>
<router-link to="/home/message">消息</router-link>
<router-view></router-view>
<h2>{{ message }}</h2>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "Home",
data() {
return {
message: "你好啊",
path: "/home/news",
};
},
created() {
console.log("home created");
},
mounted() {
console.log("home mounted");
// document.title='首页'
},
destroyed() {
console.log("home destroyed");
},
// 这两个函数, 只有该组件被保持了状态使用了keep-alive时, 才是有效的
activated() {
// 活跃状态
this.$router.push(this.path);
console.log("activated");
},
deactivated() {
console.log("deactivated");
},
// 离开当前路由页面时调用
beforeRouteLeave(to, from, next) {
// 首页中使用path属性记录离开时的路径,在beforeRouteLeave中记录
console.log(this.$route.path);
this.path = this.$route.path;
next();
},
};
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
??Profile.vue
<script>
export default {
name: "Profile",
created() {
console.log('Profile created');
},
destroyed() {
console.log('Profile destroyed');
}
}
</script>User.vue
<script>
export default {
name: "User",
created() {
console.log('User created');
},
destroyed() {
console.log('User destroyed');
},
}
</script>
(十一)、(掌握)TabBar练习
1.TabBar实现思路

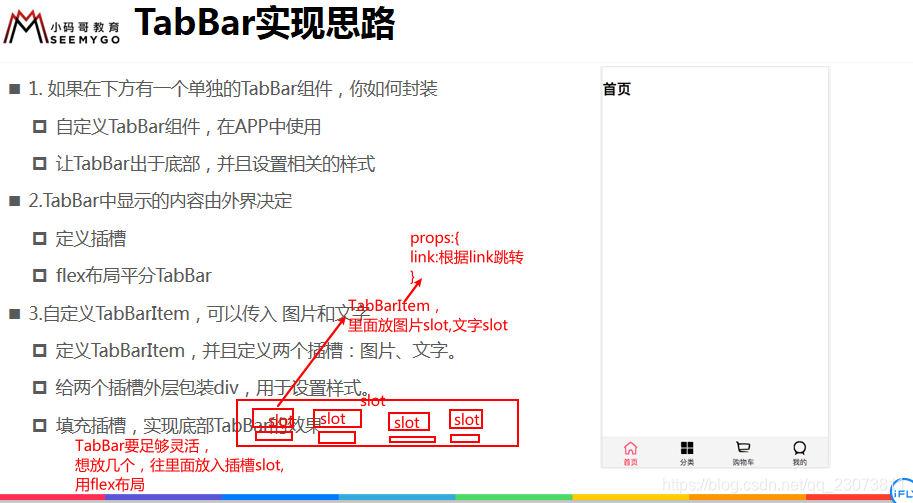
- 1. 如果在下方有一个单独的TabBar组件,你如何封装
- 自定义TabBar组件,在APP中使用
- 让TabBar出于底部,并且设置相关的样式
- 2.TabBar中显示的内容由外界决定
- 定义插槽
- flex布局平分TabBar
- 3.自定义TabBarItem,可以传入 图片和文字
- 定义TabBarItem,并且定义两个插槽:图片、文字。
- 给两个插槽外层包装div,用于设置样式。
- 填充插槽,实现底部TabBar的效果?
- 4.传入 高亮图片
- 定义另外一个插槽,插入active-icon的数据
- 定义一个变量isActive,通过v-show来决定是否显示对应的icon
- 5.TabBarItem绑定路由数据
- 安装路由:npm install vue-router —save
- 完成router/index.js的内容,以及创建对应的组件
- main.js中注册router
- APP中加入<router-view>组件
- 6.点击item跳转到对应路由,并且动态决定isActive
- 监听item的点击,通过this.$router.replace()替换路由路径
- 通过this.$route.path.indexOf(this.link) !== -1来判断是否是active
- 7.动态计算active样式 封装新的计算属性:this.isActive ? {'color': 'red'} : {}?
2.代码实现?

?
分析:
?3.步骤代码详解
(1)基本结构的搭建(无封装组件)
- ?assets / css / base.css
body{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}- App.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<div id="tab-bar">
<div class="tab-bar-item">首页</div>
<div class="tab-bar-item">分类</div>
<div class="tab-bar-item">购物车</div>
<div class="tab-bar-item">我的</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "App",
components: {},
};
</script>
<style>
@import "../src/assets/css/base.css";
#tab-bar {
/* 本身的样式 */
background-color: #f6f6f6;
box-shadow: 0 -1px 1px rgba(100, 100, 100, 0.2);
/* 利用flex进行布局 */
display: flex;
/* 定位相关 */
position: fixed;
left: 0;
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
}
.tab-bar-item {
flex: 1;
text-align: center;
height: 49px;
}
</style>
- 效果图,基本结构搭建完成?
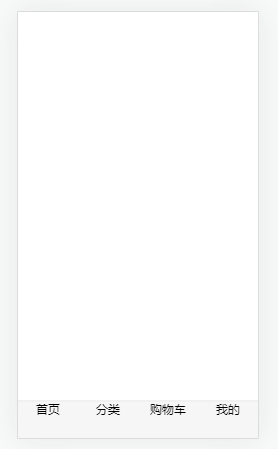
?(2) TabBar和TabBarItem组件封装
复习知识点:(十一)插槽?
- ?App.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<tab-bar>
<!--TabBar的 slot 有几个就填几个item -->
<tab-bar-item>
<!-- TabBarItem的slot 传入不同图片 -->
<img slot="item-icon" src="./assets/img/tabbar/home.svg" alt="">
<div slot="item-text">首页</div>
</tab-bar-item>
<tab-bar-item>
<img slot="item-icon" src="./assets/img/tabbar/category.svg" alt="">
<div slot="item-text">分类</div>
</tab-bar-item>
<tab-bar-item>
<img slot="item-icon" src="./assets/img/tabbar/shopcart.svg" alt="">
<div slot="item-text">购物车</div>
</tab-bar-item>
<tab-bar-item>
<img slot="item-icon" src="./assets/img/tabbar/profile.svg" alt="">
<div slot="item-text">我的</div>
</tab-bar-item>
</tab-bar>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import TabBar from './components/tabbar/TabBar'
import TabBarItem from './components/tabbar/TabBarItem'
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
TabBar,
TabBarItem
}
}
</script>
<style>
/* 在css里面引用需要用@import; */
@import "./assets/css/base.css";
</style>
- TabBar.vue
<template>
<div id="tab-bar">
<!-- 使用插槽,以便能往里面动态传入TabBarItem -->
<slot></slot>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "TabBar",
};
</script>
<style scoped>
#tab-bar {
/* 利用flex进行布局 */
display: flex;
/* 本身的样式 */
background-color: #f6f6f6;
box-shadow: 0 -1px 1px rgba(100, 100, 100, 0.2);
/* 定位相关 */
position: fixed;
left: 0;
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
}
</style>
- ?TabBarItem.vue
<template>
<div class="tab-bar-item">
<!--所有的item都展示同一个图片, 同一个文字,-->
<!--<img src="../../assets/img/tabbar/home.svg" alt="">-->
<!--<div>首页</div>-->
<!-- 使用插槽动态传入图片文字 -->
<slot name="item-icon"></slot>
<slot name="item-text"></slot>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "TabBarItem",
};
</script>
<style scoped>
.tab-bar-item {
flex: 1;
text-align: center;
height: 49px;
font-size: 14px;
}
.tab-bar-item img {
width: 24px;
height: 24px;
margin-top: 3px;
/* 去掉图片与文字默认的间隔3px */
vertical-align: middle;
margin-bottom: 2px;
}
</style>
- ?效果图,目前基本样式已完成

?(3)给TabBarItem传入active图片?
- ??App.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<tab-bar>
<tab-bar-item>
<img slot="item-icon" src="../src/assets/img/tabbar/home.svg" alt="">
<img slot="item-icon-active" src="../src/assets/img/tabbar/home_active.svg" alt="">
<div slot="item-text">首页</div>
</tab-bar-item>
<tab-bar-item>
<img slot="item-icon" src="../src/assets/img/tabbar/category.svg" alt="">
<img slot="item-icon-active" src="../src/assets/img/tabbar/category_active.svg" alt="">
<div slot="item-text">分类</div>
</tab-bar-item>
<tab-bar-item>
<img slot="item-icon" src="../src/assets/img/tabbar/shopcart.svg" alt="">
<img slot="item-icon-active" src="../src/assets/img/tabbar/shopcart_active.svg" alt="">
<div slot="item-text">购物车</div>
</tab-bar-item>
<tab-bar-item>
<img slot="item-icon" src="../src/assets/img/tabbar/profile.svg" alt="">
<img slot="item-icon-active" src="../src/assets/img/tabbar/profile_active.svg" alt="">
<div slot="item-text">我的</div>
</tab-bar-item>
</tab-bar>
</div>
</template>
- TabBarItem.vue
<template>
<div class="tab-bar-item">
<slot v-if="!isActive" name="item-icon"></slot>
<!-- 图片active插槽 -->
<slot v-else name="item-icon-active"></slot>
<slot :class="{ active: isActive }" name="item-text"></slot>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "TabBarItem",
data() {
return {
isActive: true,
};
},
};
</script>
<style>
/* ... */
.active {
color: red;
}
</style>- 但是上面的TabBarItem.vue这样写会有问题,文字样式不起效果
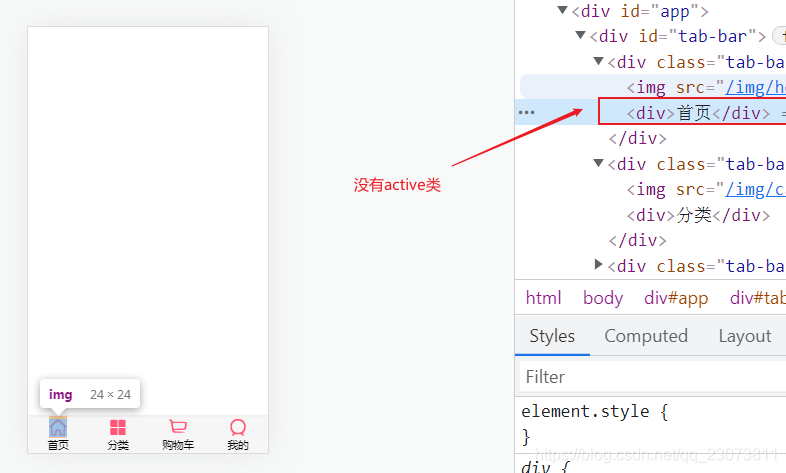
- ?把TabBarItem.vue的HTML改成下面
<template>
<div class="tab-bar-item">
<div v-if="!isActive">
<slot name="item-icon"></slot>
</div>
<!-- 图片active插槽 -->
<div v-else>
<slot name="item-icon-active"></slot>
</div>
<!-- 这样写样式不起效果 -->
<!-- <slot :class="{ active: isActive }" name="item-text"></slot> -->
<!-- 渲染的时候会直接把它这个替换成 <div slot="item-text">首页</div> -->
<!-- 一般不会直接在插槽上绑定动态属性,因为渲染时会把它替换掉
外面套一个div这样不会把原来的替换掉,上面两个最好也这样写 -->
<div :class="{ active: isActive }">
<slot name="item-text"></slot>
</div>
</div>
</template>
- 效果图?
?
?(4)TabBarItem与路由结合效果
复习知识点:(七)父传子--props
- 创建如下文件夹以及文件
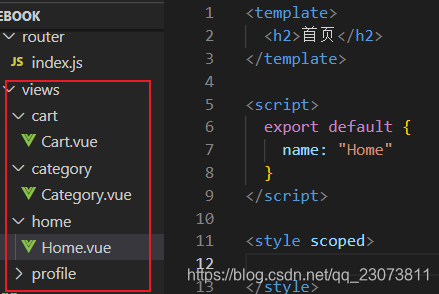
- 安装路由,并配置,route下index.js代码?
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
const Home = () => import('../views/home/Home')
const Category = () => import('../views/category/Category')
const Cart = () => import('../views/cart/Cart')
const Profile = () => import('../views/profile/Profile')
// 1.安装插件
Vue.use(VueRouter)
// 2.创建路由对象
const routes = [
{
path: '',
redirect: '/home'
},
{
path: '/home',
component: Home
},
{
path: '/category',
component: Category
},
{
path: '/cart',
component: Cart
},
{
path: '/profile',
component: Profile
}
]
const router = new VueRouter({
routes,
mode: 'history'
})
// 3.导出router
export default router
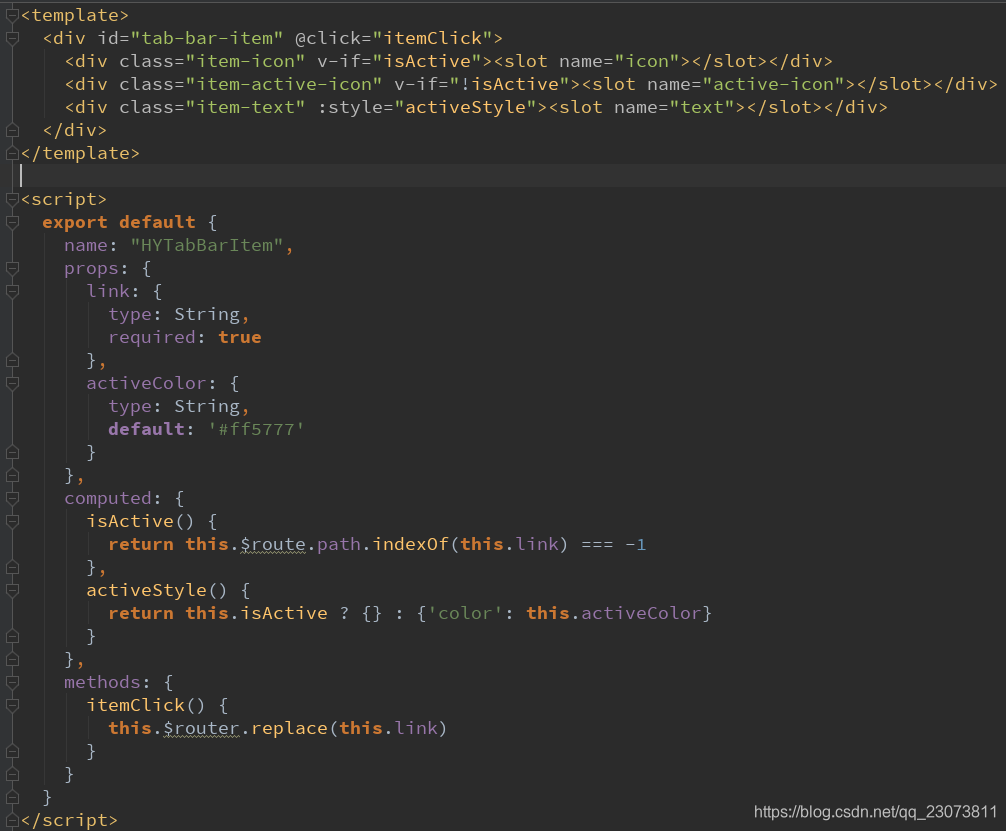
- ?用props传入动态的路径path,用itemClick监听点击,跳转到不同页面
- TabBarItem.vue
<template>
<div class="tab-bar-item" @click="itemClick">
<div v-if="!isActive">
<slot name="item-icon"></slot>
</div>
<div v-else>
<slot name="item-icon-active"></slot>
</div>
<div :class="{ active: isActive }">
<slot name="item-text"></slot>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "TabBarItem",
data() {
return {
isActive: true,
};
},
props:{
path:String
},
methods: {
itemClick(){
this.$router.replace(this.path)
}
},
};
</script>
// ...- ?App.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<router-view></router-view>
<tab-bar>
<!-- 因为这里是字符串,所以不需要加冒号: ,直接使用path传递 -->
<tab-bar-item path='/home'>
<img slot="item-icon" src="../src/assets/img/tabbar/home.svg" alt="">
<img slot="item-icon-active" src="../src/assets/img/tabbar/home_active.svg" alt="">
<div slot="item-text">首页</div>
</tab-bar-item>
<tab-bar-item path='/category'>
<img slot="item-icon" src="../src/assets/img/tabbar/category.svg" alt="">
<img slot="item-icon-active" src="../src/assets/img/tabbar/category_active.svg" alt="">
<div slot="item-text">分类</div>
</tab-bar-item>
<tab-bar-item path='/cart'>
<img slot="item-icon" src="../src/assets/img/tabbar/shopcart.svg" alt="">
<img slot="item-icon-active" src="../src/assets/img/tabbar/shopcart_active.svg" alt="">
<div slot="item-text">购物车</div>
</tab-bar-item>
<tab-bar-item path='/profile'>
<img slot="item-icon" src="../src/assets/img/tabbar/profile.svg" alt="">
<img slot="item-icon-active" src="../src/assets/img/tabbar/profile_active.svg" alt="">
<div slot="item-text">我的</div>
</tab-bar-item>
</tab-bar>
</div>
</template>- ?效果,点击哪个item就跳转到对应页面

(5)TabBarItem的动态颜色控制?
- ?App.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<router-view></router-view>
<tab-bar>
<tab-bar-item path='/home' activeColor='deepPink'>
<img slot="item-icon" src="../src/assets/img/tabbar/home.svg" alt="">
<img slot="item-icon-active" src="../src/assets/img/tabbar/home_active.svg" alt="">
<div slot="item-text">首页</div>
</tab-bar-item>
<tab-bar-item path='/category' activeColor='deepPink'>
<img slot="item-icon" src="../src/assets/img/tabbar/category.svg" alt="">
<img slot="item-icon-active" src="../src/assets/img/tabbar/category_active.svg" alt="">
<div slot="item-text">分类</div>
</tab-bar-item>
<tab-bar-item path='/cart' activeColor='deepPink'>
<img slot="item-icon" src="../src/assets/img/tabbar/shopcart.svg" alt="">
<img slot="item-icon-active" src="../src/assets/img/tabbar/shopcart_active.svg" alt="">
<div slot="item-text">购物车</div>
</tab-bar-item>
<tab-bar-item path='/profile' activeColor='deepPink'>
<img slot="item-icon" src="../src/assets/img/tabbar/profile.svg" alt="">
<img slot="item-icon-active" src="../src/assets/img/tabbar/profile_active.svg" alt="">
<div slot="item-text">我的</div>
</tab-bar-item>
</tab-bar>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import TabBar from "../src/components/tabbar/TabBar.vue";
import TabBarItem from "../src/components/tabbar/TabBarItem.vue";
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
TabBar,
TabBarItem,
},
};
</script>
<style>
@import "../src/assets/css/base.css";
</style>
- TabBarItem.vue
<template>
<!-- 在这里监听点击 不要去App.vue里面的,在那写要监听四个 -->
<div class="tab-bar-item" @click="itemClick">
<div v-if="!isActive">
<slot name="item-icon"></slot>
</div>
<!-- 图片active插槽 -->
<div v-else>
<slot name="item-icon-active"></slot>
</div>
<!-- 这样写样式不起效果 -->
<!-- <slot :class="{ active: isActive }" name="item-text"></slot> -->
<!-- 渲染的时候会直接把它这个替换成 <div slot="item-text">首页</div> -->
<!-- 一般不会直接在插槽上绑定动态属性,因为渲染时会把它替换掉
外面套一个div这样不会把原来的替换掉,上面两个最好也这样写 -->
<div :style="activeStyle">
<slot name="item-text"></slot>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: "TabBarItem",
props: {
path: String,
activeColor: {
type: String,
default: "red",
},
},
data() {
return {
// isActive: true
};
},
computed: {
// 动态决定isActive
isActive() {
// /home -> item1(/home) = true
// /home -> item1(/category) = false
// /home -> item1(/cart) = false
// /home -> item1(/profile) = false
// indexOf()返回某个指定的字符串值在字符串中首次出现的位置。 == -1 说明不存在
return this.$route.path.indexOf(this.path) !== -1;
// 或者用这个也行
// return this.$route.path === this.path;
},
// 根据传进来的值activeColor 给文字动态绑定style
activeStyle() {
return this.isActive ? { color: this.activeColor } : {};
},
},
methods: {
itemClick() {
// 路由跳转 动态路径props里面的path
this.$router.replace(this.path);
},
},
};
</script>
<style scoped>
.tab-bar-item {
flex: 1;
text-align: center;
height: 49px;
font-size: 14px;
}
.tab-bar-item img {
width: 24px;
height: 24px;
margin-top: 3px;
vertical-align: middle;
margin-bottom: 2px;
}
</style>
- 效果图,点击哪个,文字颜色就改变

可以再做一层封装?,封装成MainTabBar.vue
<template>
<tab-bar>
<!-- 因为这里是字符串,所以不需要加冒号: ,直接使用path传递 -->
<tab-bar-item path="/home" activeColor="pink">
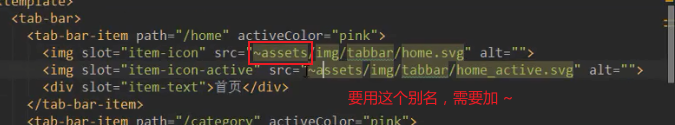
<img slot="item-icon" src="~assets/img/tabbar/home.svg" alt="">
<img slot="item-icon-active" src="~assets/img/tabbar/home_active.svg" alt="">
<div slot="item-text">首页</div>
</tab-bar-item>
<tab-bar-item path="/category" activeColor="pink">
<img slot="item-icon" src="../../assets/img/tabbar/category.svg" alt="">
<img slot="item-icon-active" src="../../assets/img/tabbar/category_active.svg" alt="">
<div slot="item-text">分类</div>
</tab-bar-item>
<tab-bar-item path="/cart" activeColor="pink">
<img slot="item-icon" src="../../assets/img/tabbar/shopcart.svg" alt="">
<img slot="item-icon-active" src="../../assets/img/tabbar/shopcart_active.svg" alt="">
<div slot="item-text">购物车</div>
</tab-bar-item>
<tab-bar-item path="/profile" activeColor="deepPink">
<img slot="item-icon" src="../../assets/img/tabbar/profile.svg" alt="">
<img slot="item-icon-active" src="../../assets/img/tabbar/profile_active.svg" alt="">
<div slot="item-text">我的</div>
</tab-bar-item>
</tab-bar>
</template>
<script>
import TabBar from 'components/tabbar/TabBar'
import TabBarItem from 'components/tabbar/TabBarItem'
export default {
name: "MainTabBar",
components: {
TabBar,
TabBarItem
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
App.vue?
<template>
<div id="app">
<router-view></router-view>
<main-tab-bar/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import MainTabBar from './components/mainTabbar/MainTabBar'
export default {
name: 'App',
components: {
MainTabBar
}
}
</script>
<style>
@import "./assets/css/base.css";
</style>
?4.tabbar文件路径问题
可以起别名
?